Safety Control for Cyber–Physical Systems Under False Data Injection Attacks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A NN estimator is devised to approximate the system state when the system suffers from an unknown FDI attack. This estimator facilitates the construction of a controller that can compensate for the FDI attack while addressing the uncertain variable in safety constraints.
- (2)
- By integrating NN estimation and CBF, a control strategy is proposed to simultaneously alleviate the FDI attack and ensure the safety of CPSs.
2. Problem Formulation and Preliminaries
- 1.
- ,
- 2.
3. Main Results
3.1. Adaptive Controller Design
3.2. System Stability Analysis
3.3. Control Barrier Function with the Unknown Parameter
3.4. Secure and Safe Control Strategy
| Algorithm 1 Secure and safe control strategy algorithm |
|
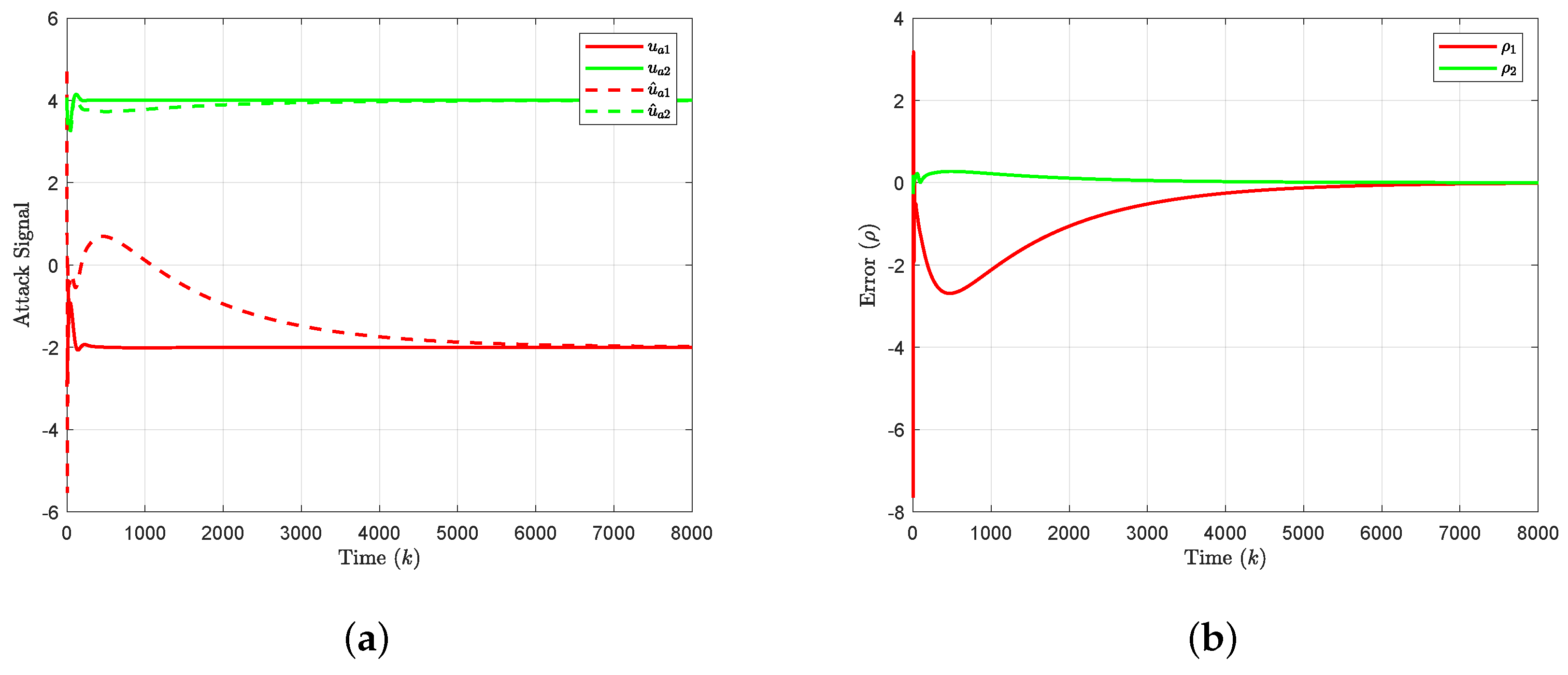
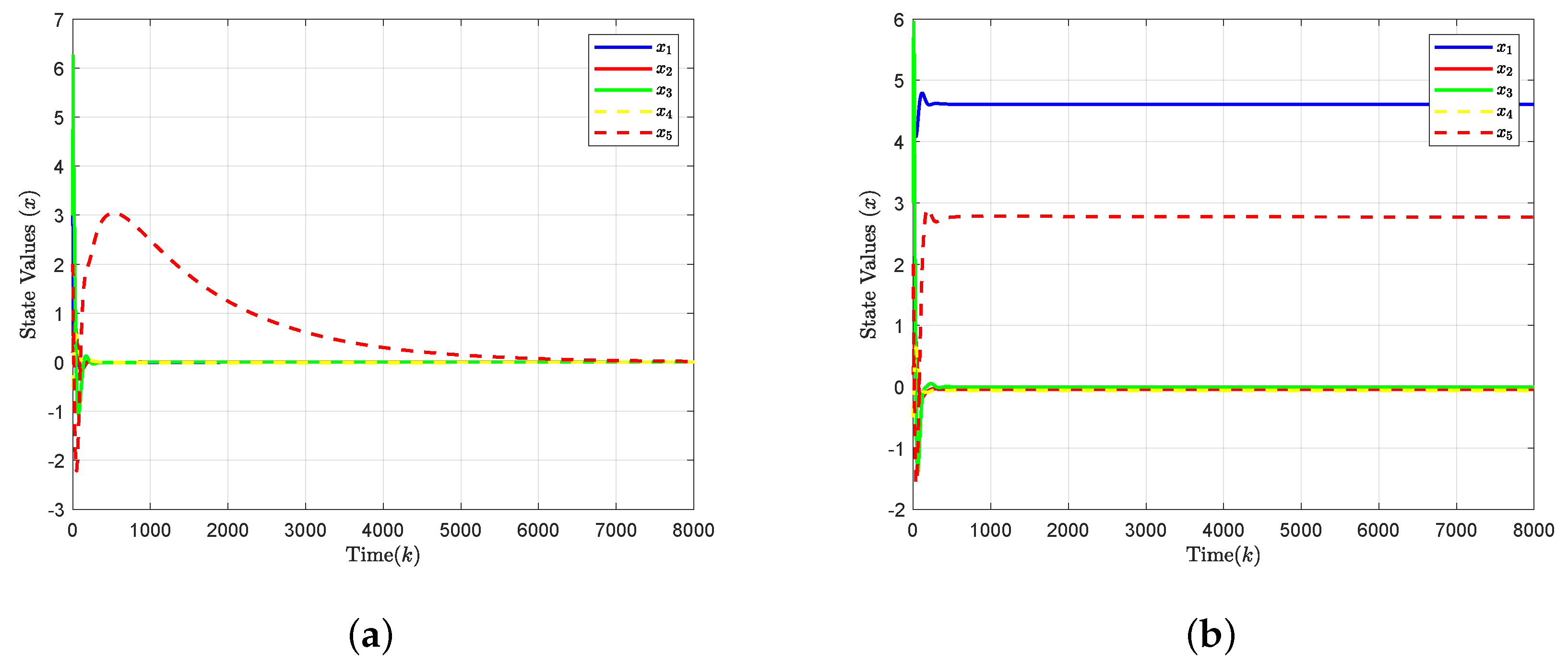
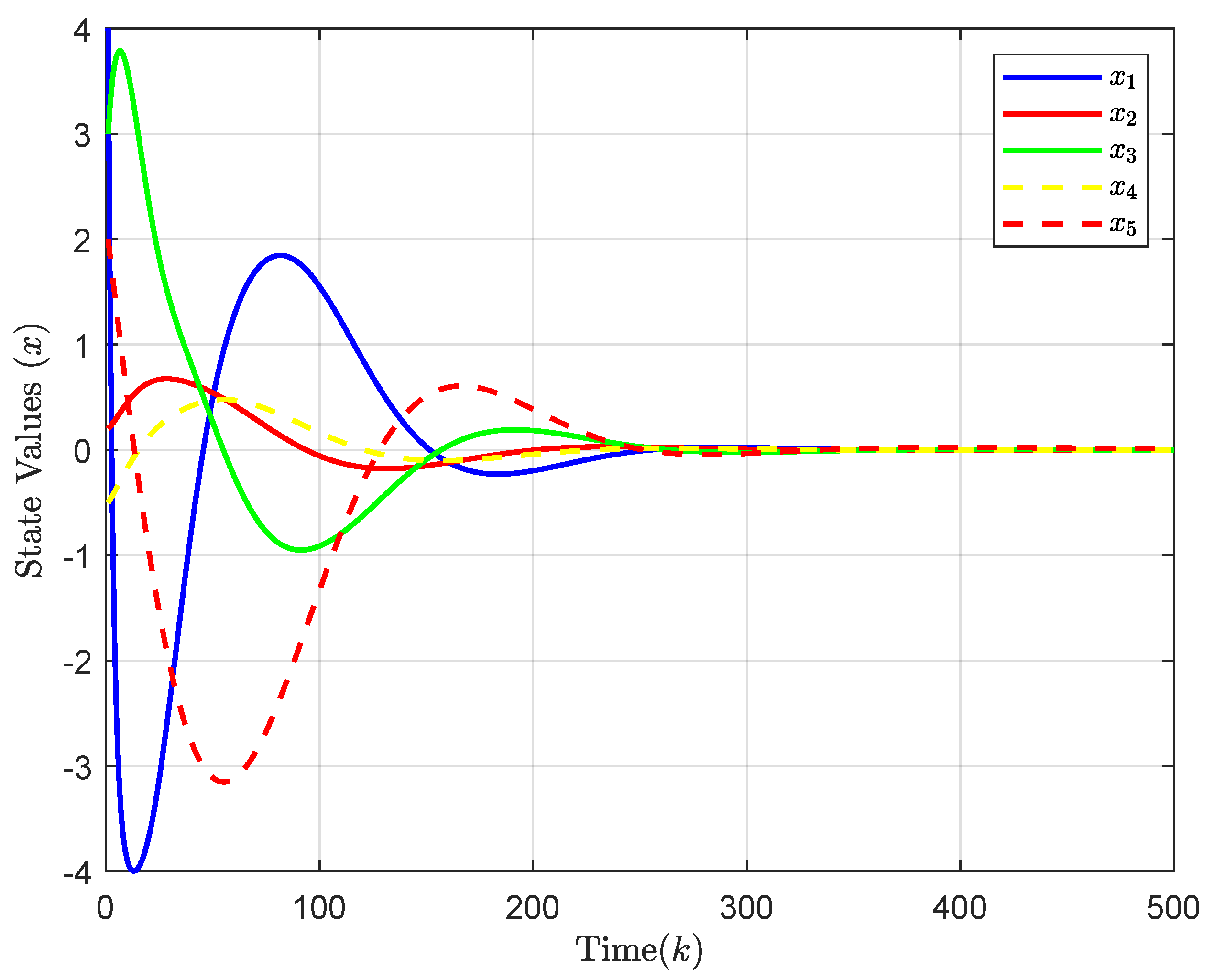
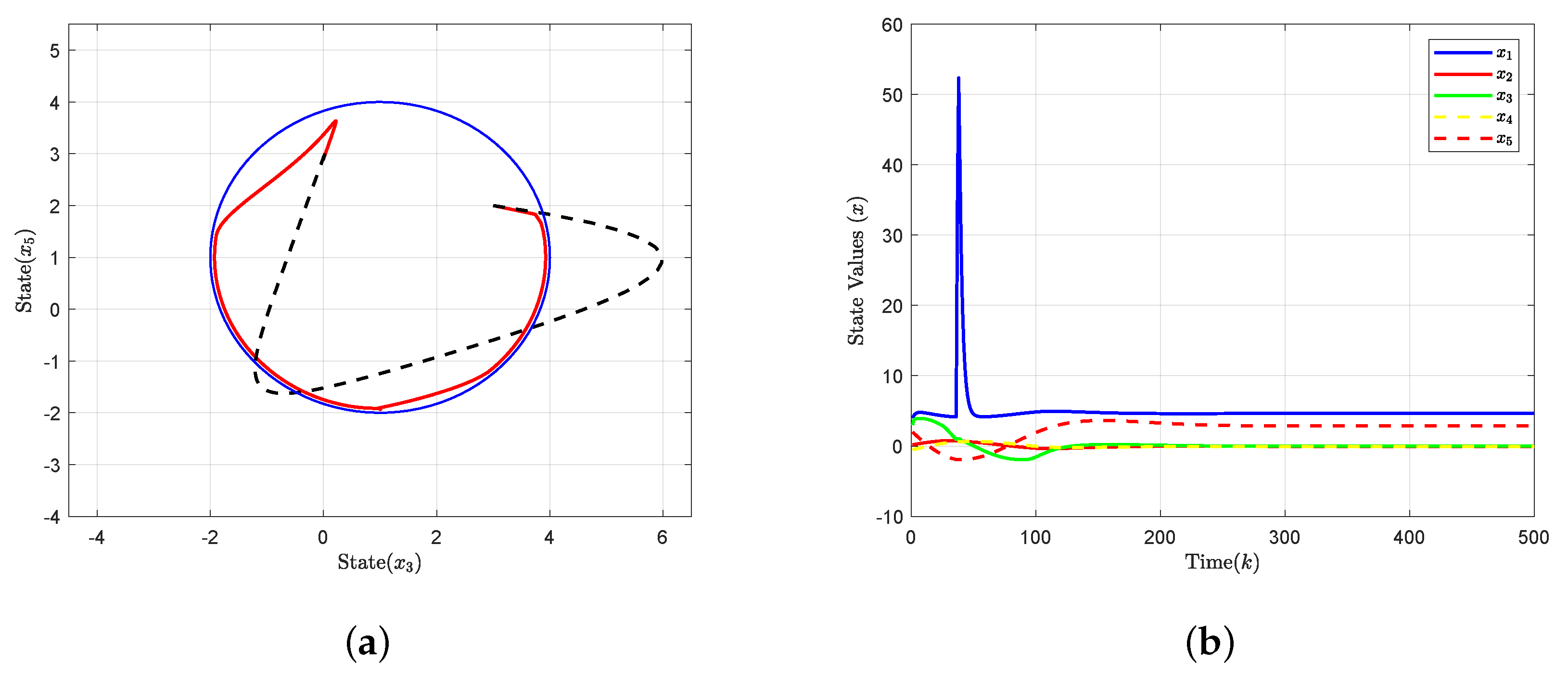
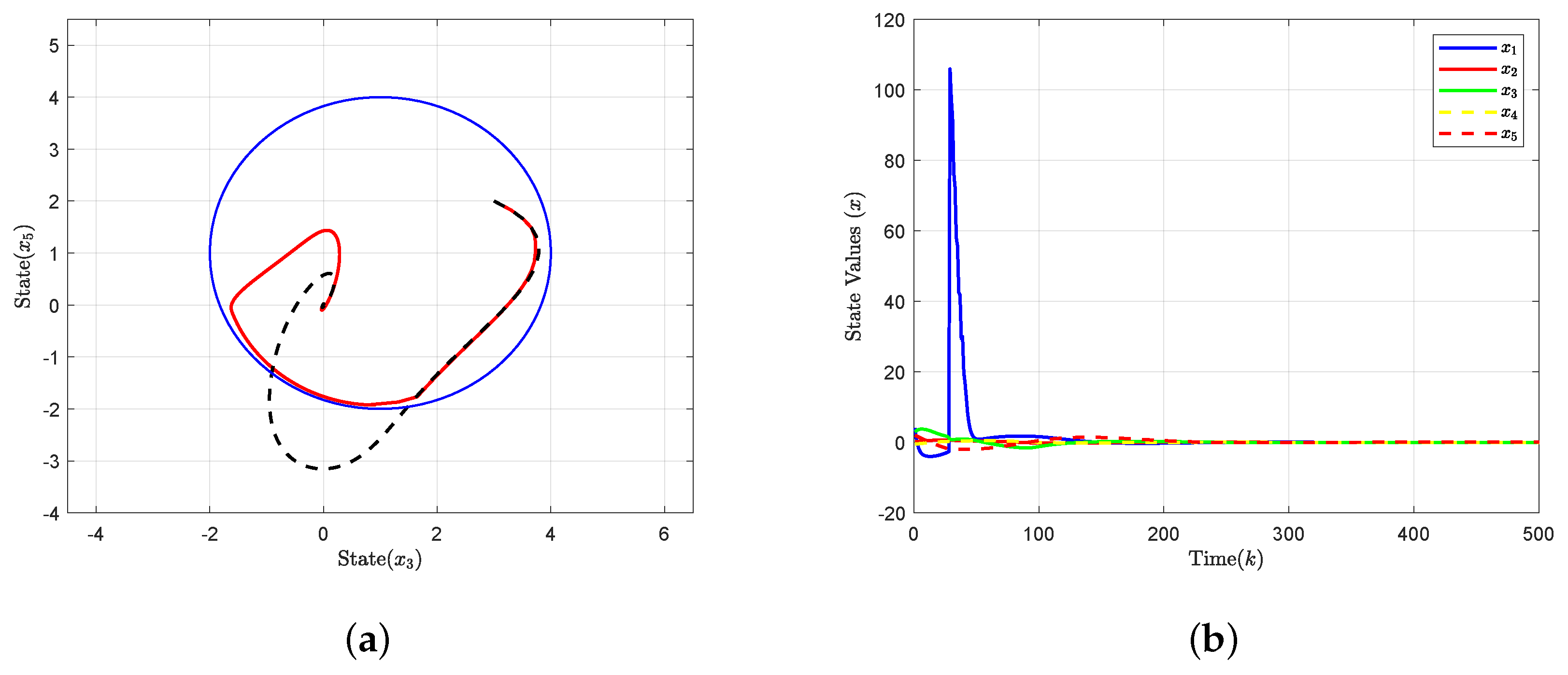
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alguliyev, R.; Imamverdiyev, Y.; Sukhostat, L. Cyber-physical systems and their security issues. Comput. Ind. 2018, 100, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, C.; Ma, H.; Li, H. Cloud-based distributed group asynchronous consensus for switched nonlinear cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 21, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wu, C.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q. Secure Control for Cyber–Physical Systems Subject to Aperiodic DoS Attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 7106–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, A.N.; Karimipour, H.; Dehghantanha, A.; Choo, K.K.R. Toward detection and attribution of cyber-attacks in IoT-enabled cyber–physical systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13712–13722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kure, H.I.; Islam, S.; Razzaque, M.A. An integrated cyber security risk management approach for a cyber-physical system. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.A.; Hasan, M.K.; Alkhayyat, A.; Islam, S.; Sharma, R.; Alkwai, L.M. False data injection attack in smart grid cyber physical system: Issues, challenges, and future direction. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 107, 108638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Shahidehpour, M. Detection of false data injection attacks in smart grid: A secure federated deep learning approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 4862–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Krishnamurthy, P.; Khorrami, F. Combining switching mechanism with re-initialization and anomaly detection for resiliency of cyber–physical systems. Automatica 2025, 172, 111994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Vamvoudakis, K.G. Data-based and secure switched cyber–physical systems. Syst. Control Lett. 2021, 148, 104826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.Y.; Yang, G.H. False data injection attacks against state estimation without knowledge of estimators. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 67, 4529–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yao, W.; Luo, W.; Pan, W.; Sun, G.; Xie, H.; Wu, L. A secure robot learning framework for cyber attack scheduling and countermeasure. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 3722–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franze, G.; Famularo, D.; Lucia, W.; Tedesco, F. Cyber–physical systems subject to false data injections: A model predictive control framework for resilience operations. Automatica 2023, 152, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, L.; Zhu, H.; Shao, X.; Yao, W.; Liu, J.; Wu, L. Event-Triggered Secure Control Under Aperiodic DoS Attacks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangapani, J. Neural Network Control of Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, A.; Xu, H.; Jagannathan, S. Adaptive neural network-based event-triggered control of single-input single-output nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 27, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, M.; Ha, M.; Hu, L. Adaptive-critic-based hybrid intelligent optimal tracking for a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 105, 104443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Niu, B.; Zong, G.; Zhao, X.; Xu, N. Periodic event-triggered adaptive tracking control design for nonlinear discrete-time systems via reinforcement learning. Neural Netw. 2022, 154, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargolzaei, A.; Yazdani, K.; Abbaspour, A.; Crane, C.D., III; Dixon, W.E. Detection and mitigation of false data injection attacks in networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 4281–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Mestha, L.K.; Abbaszadeh, M. Attack detection for securing cyber physical systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 8471–8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farivar, F.; Haghighi, M.S.; Jolfaei, A.; Alazab, M. Artificial intelligence for detection, estimation, and compensation of malicious attacks in nonlinear cyber-physical systems and industrial IoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 2716–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, F.; Finn, A. A data-driven cyber–physical system using deep-learning convolutional neural networks: Study on false-data injection attacks in an unmanned ground vehicle under fault-tolerant conditions. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 53, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, N. Event-triggering adaptive neural network output feedback control for networked systems under false data injection attacks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 180, 114584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari-Bonab, P.; Holland, J.C.; Cunningham-Rush, J.; Noei, S.; Sargolzaei, A. Secure Control Design for Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control Under False Data Injection Attack. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 9723–9732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Secure and Safe Control of Connected and Automated Vehicles Against False Data Injection Attacks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 12347–12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavinejad, E.; Yang, F.; Han, Q.L.; Vlacic, L. A novel cyber attack detection method in networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 3254–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, D.; Ge, X.; Han, Q.L. Neural-network-based control for discrete-time nonlinear systems with denial-of-service attack: The adaptive event-triggered case. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2022, 32, 2760–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Pan, W.; Staa, R.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Wu, L. Deep reinforcement learning control approach to mitigating actuator attacks. Automatica 2023, 152, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan, A.; Taylor, A.J.; He, C.R.; Ames, A.D.; Orosz, G. Control barrier functions and input-to-state safety with application to automated vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2023, 31, 2744–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Lee, J.; Baek, E.; Horowitz, R.; Choi, J. Safety-critical control with nonaffine control inputs via a relaxed control barrier function for an autonomous vehicle. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, A.D.; Xu, X.; Grizzle, J.W.; Tabuada, P. Control barrier function based quadratic programs for safety critical systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2016, 62, 3861–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, A.D.; Grizzle, J.W.; Tabuada, P. Control barrier function based quadratic programs with application to adaptive cruise control. In Proceedings of the 53rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 6271–6278. [Google Scholar]
- Robey, A.; Hu, H.; Lindemann, L.; Zhang, H.; Dimarogonas, D.V.; Tu, S.; Matni, N. Learning control barrier functions from expert demonstrations. In Proceedings of the 2020 59th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 14–18 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 3717–3724. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, B.; Sreenath, K. Safety-critical model predictive control with discrete-time control barrier function. In Proceedings of the 2021 American Control Conference (ACC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–28 May 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 3882–3889. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, T.H.; Hasani, R.; Chahine, M.; Amini, A.; Li, X.; Rus, D. Barriernet: Differentiable control barrier functions for learning of safe robot control. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 2289–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daş, E.; Murray, R.M. Robust safe control synthesis with disturbance observer-based control barrier functions. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 61st Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Cancun, Mexico, 6–9 December 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 5566–5573. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, D.R.; Panagou, D. Safe and robust observer-controller synthesis using control barrier functions. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2022, 7, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Y.; Yang, G.H. An intrusion detection method based on self-generated coding technology for stealthy false data injection attacks in train-ground communication systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 8468–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Niu, B. Proactive attack detection scheme based on watermarking and moving target defense. Automatica 2023, 155, 111163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Zeng, Z. Safety-critical control with control barrier function based on disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2024, 69, 4750–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F.L.; Vamvoudakis, K.G. Reinforcement learning for partially observable dynamic processes: Adaptive dynamic programming using measured output data. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part (Cybern.) 2010, 41, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S. Neural network approximation: Three hidden layers are enough. Neural Netw. 2021, 141, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Tong, S. Adaptive NN tracking control of uncertain nonlinear discrete-time systems with nonaffine dead-zone input. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 45, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşildirek, A.; Lewis, F.L. Feedback linearization using neural networks. Automatica 1995, 31, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Xu, H.; Jagannathan, S. Neural network-based event-triggered state feedback control of nonlinear continuous-time systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 27, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhai, D.H.; Tavakoli, M.; Xia, Y. Discrete-time control barrier function: High-order case and adaptive case. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Sreenath, K. Discrete control barrier functions for safety-critical control of discrete systems with application to bipedal robot navigation. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Cambridge, MA, USA, 12–16 July 2017; Volume 13, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Eressa, M.R.; Zheng, D.; Han, M. PID and neural net controller performance comparsion in UAV pitch attitude control. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Budapest, Hungary, 9–12 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 000762–000767. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q. Safety Control for Cyber–Physical Systems Under False Data Injection Attacks. Electronics 2025, 14, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061103
Xu L, Zhu Y, Li Z, Zhang Q. Safety Control for Cyber–Physical Systems Under False Data Injection Attacks. Electronics. 2025; 14(6):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061103
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Lezhong, Yupeng Zhu, Zhuoyu Li, and Quanqi Zhang. 2025. "Safety Control for Cyber–Physical Systems Under False Data Injection Attacks" Electronics 14, no. 6: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061103
APA StyleXu, L., Zhu, Y., Li, Z., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Safety Control for Cyber–Physical Systems Under False Data Injection Attacks. Electronics, 14(6), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061103





