EvTransPose: Towards Robust Human Pose Estimation via Event Camera
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How to make full use of global dependencies to accurately predict the human joint coordinates in the presence of motion ambiguity.
- How to ensure the effective extraction of local features on this basis for high accuracy in normal prediction.
- How to maintain the consistency of global dependencies and local features to avoid the negative impact of their conflict on the estimation results.
- We adopt an attention mechanism for event-based HPE to capture the spatial relationships between human body parts, which can efficiently tackle the challenge of motion ambiguity.
- We introduce an intermediate-supervision constraint to aggregate features from a more balanced perspective, facilitating the coordination of local and global features. Additionally, a cascading hourglass architecture is proposed to make intermediate features learnable and conditioned by loss functions.
- We design a hybrid imaging system capable of capturing event streams and RGB images simultaneously and build the first HPE dataset based on events with RGB reference images in a variety of lighting conditions, providing strong support for subsequent research.
2. Related Works
2.1. Frame-Based Human Pose Estimation
2.2. Event-Based Human Pose Estimation
3. The Proposed Method
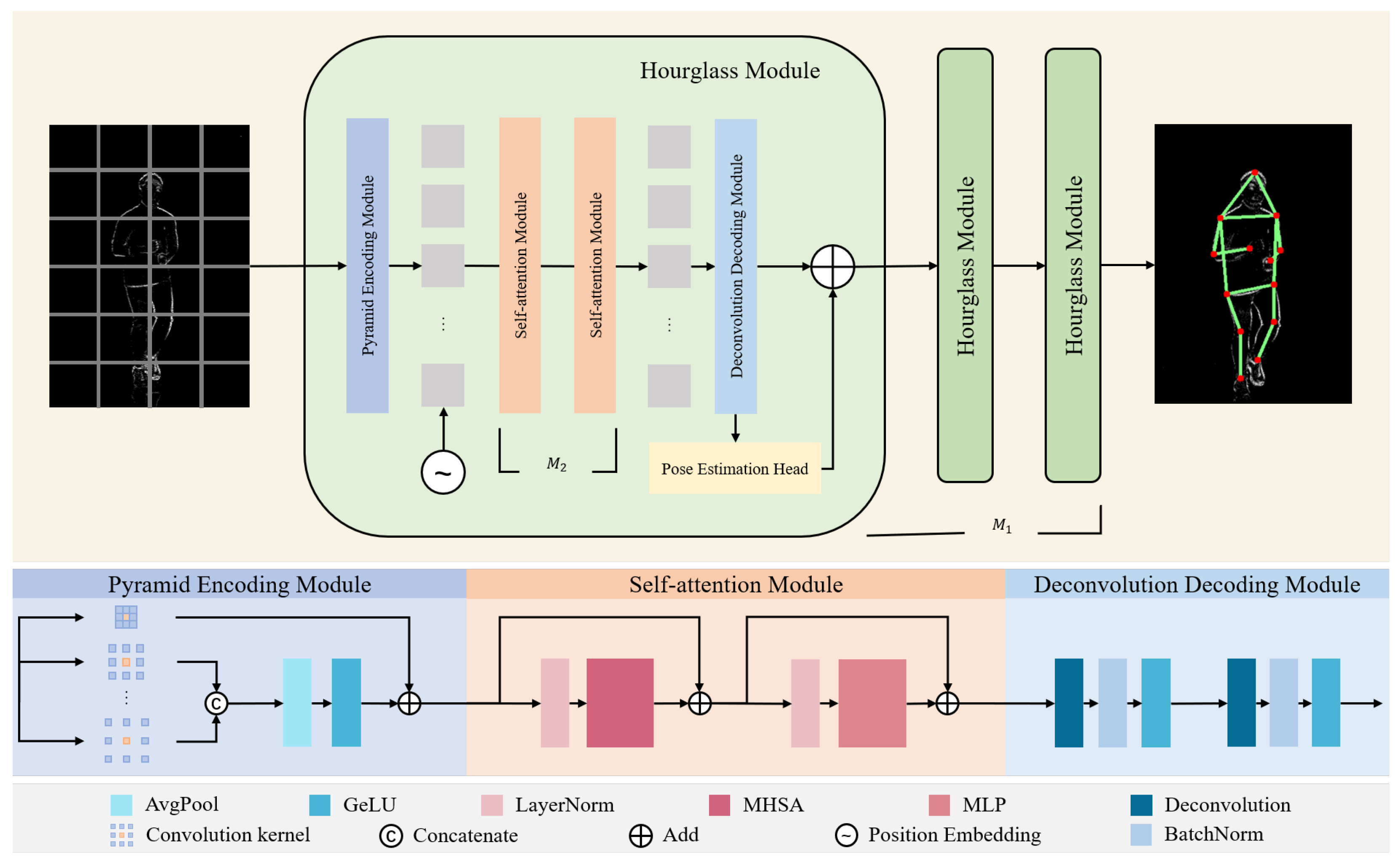
3.1. Network Architecture
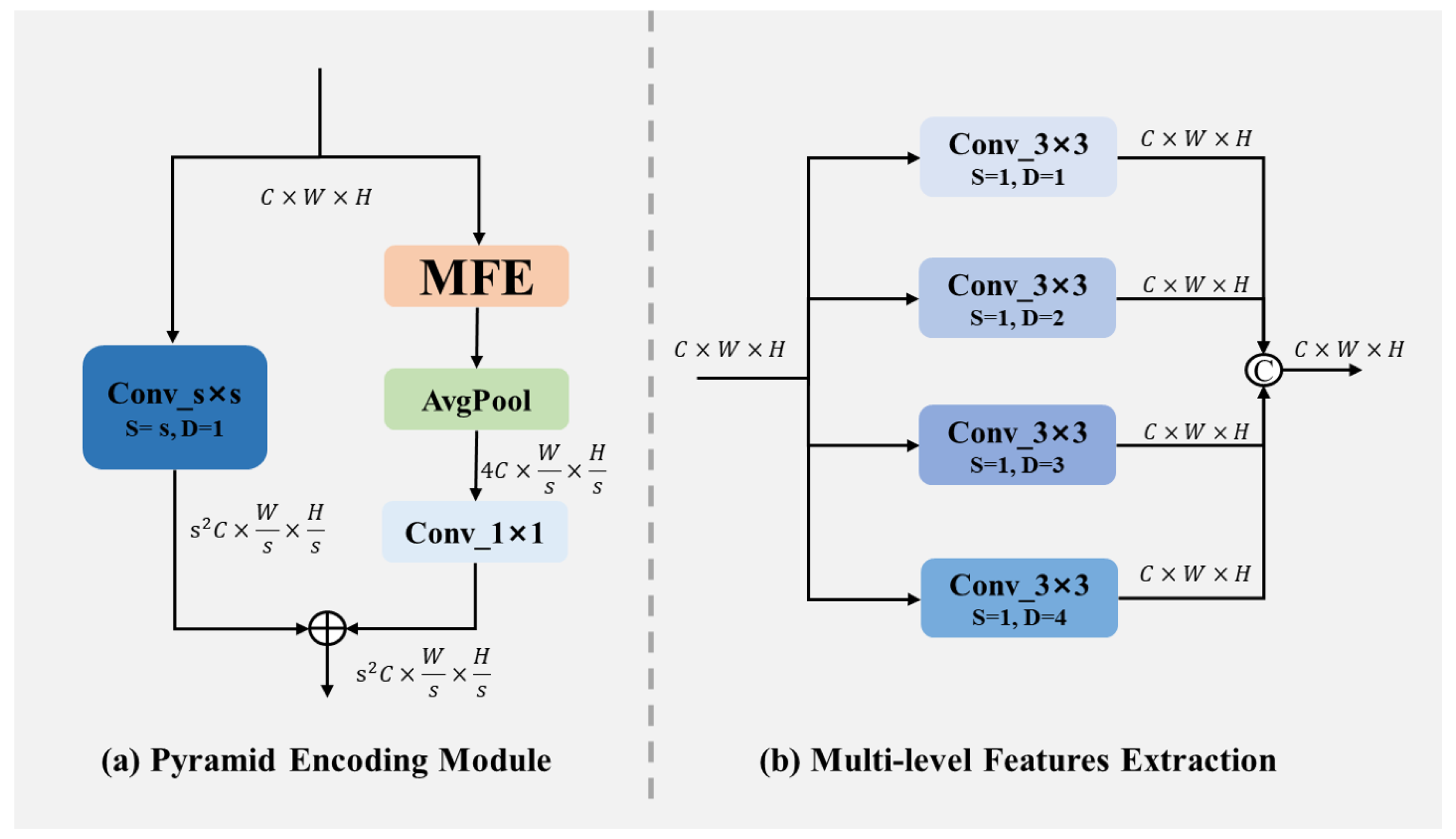
3.1.1. Pyramid Encoding Module
3.1.2. Self-Attention Module
3.1.3. Deconvolution Decoding Module
3.1.4. Pose Estimation Head Module
3.2. Intermediate-Supervision Constraint
3.2.1. Loss Functions
3.2.2. Inter-Module Connection
4. Dataset
4.1. Data Acquisition
4.1.1. Time Synchronization
4.1.2. Space Calibration
4.1.3. Space Event Representation
4.2. Dataset Description
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
5.1. Experimental Settings
5.1.1. Evaluation Metrics
5.1.2. Implementation Details
5.2. Evaluations on the DHP19 Dataset
5.3. Evaluations on the CHP Dataset
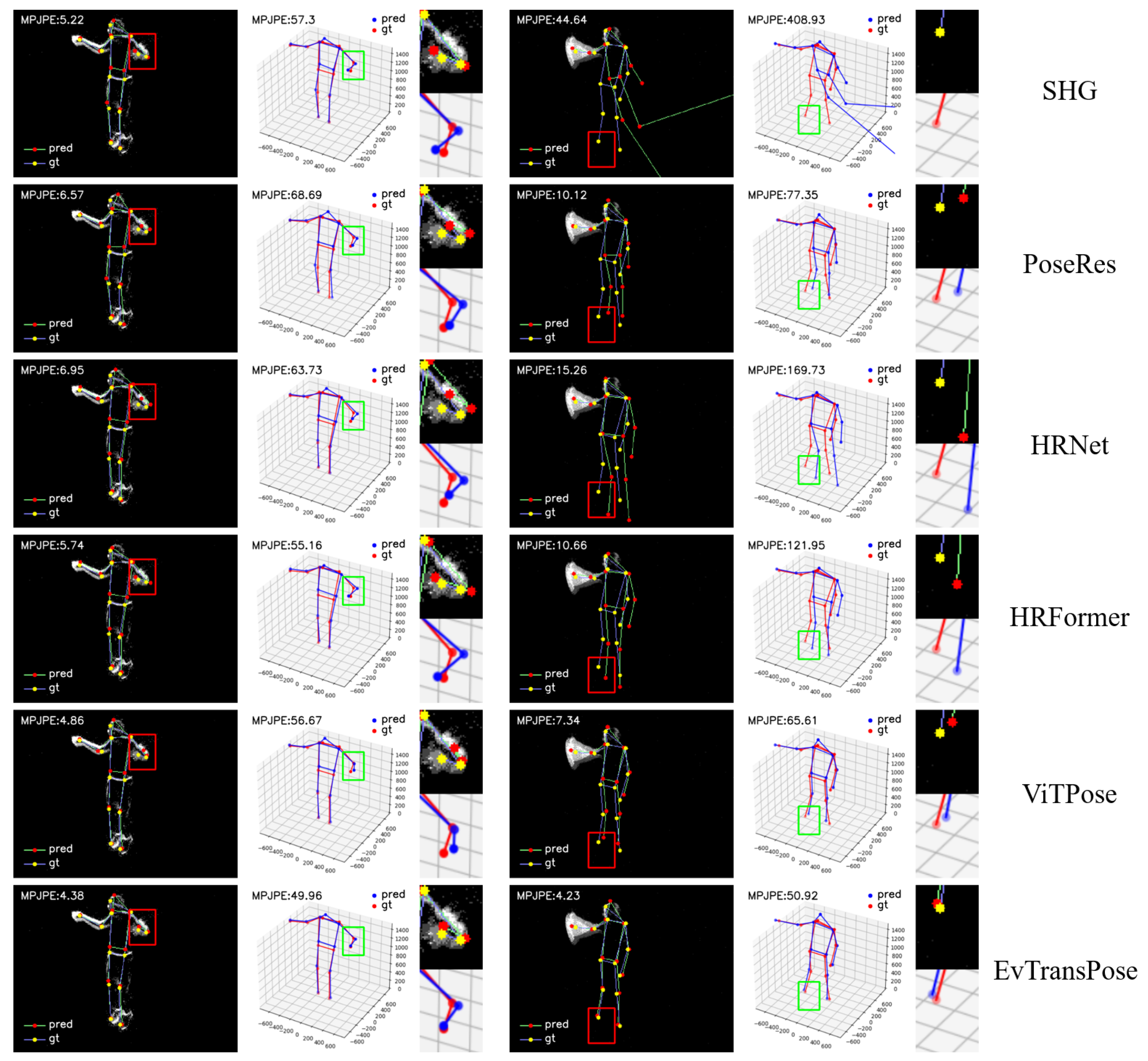
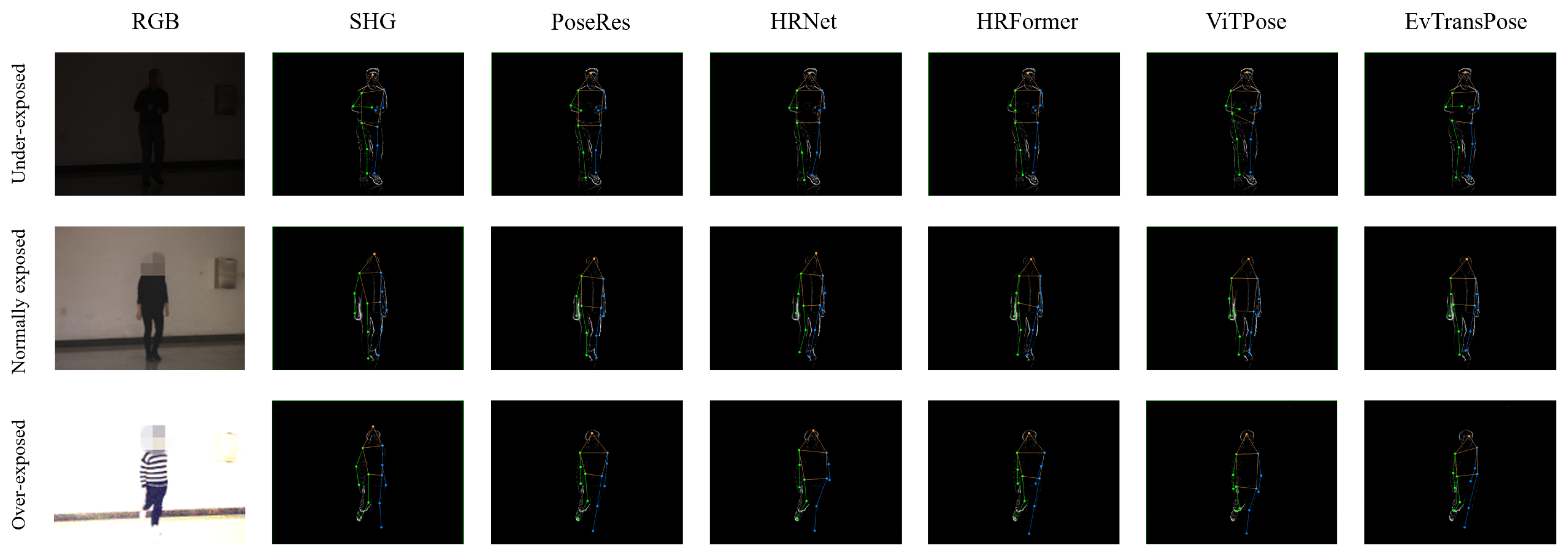
5.3.1. Quantitative Evaluation
5.3.2. Qualitative Evaluation
5.4. Ablation Study
5.4.1. Importance of Pyramid Encoding Module
5.4.2. Importance of Cascading Hourglass Architecture
5.4.3. Analysis of Intermediate Supervision
5.4.4. Cross-Dataset Testing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H. Research on 3D human pose estimation using RGBD camera. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 9th International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication (ICEIEC), Beijing, China, 12–14 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 538–541. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Y.; He, M. Monocular human pose estimation: A survey of deep learning-based methods. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2020, 192, 102897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, B.; Sung, N.J.; Ma, J.; Choi, Y.J.; Hong, M. Real-time human pose estimation using RGB-D images and deep learning. J. Internet Comput. Serv. 2020, 21, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual-Hernández, D.; de Frutos, N.O.; Mora-Jiménez, I.; Canas-Plaza, J.M. Efficient 3D human pose estimation from RGBD sensors. Displays 2022, 74, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Gotarredona, T.; Linares-Barranco, B. A 128 × 128 1.5% Contrast Sensitivity 0.9% FPN 3 μs Latency 4 mW Asynchronous Frame-Free Dynamic Vision Sensor Using Transimpedance Preamplifiers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandli, C.; Berner, R.; Yang, M.; Liu, S.C.; Delbruck, T. A 240 × 180 130 db 3 μs latency global shutter spatiotemporal vision sensor. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Taba, B.; Berg, D.; Melano, T.; McKinstry, J.; Di Nolfo, C.; Nayak, T.; Andreopoulos, A.; Garreau, G.; Mendoza, M.; et al. A low power, fully event-based gesture recognition system. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7243–7252. [Google Scholar]
- Gallego, G.; Lund, J.E.; Mueggler, E.; Rebecq, H.; Delbruck, T.; Scaramuzza, D. Event-based, 6-DOF camera tracking from photometric depth maps. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 2402–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrig, D.; Rebecq, H.; Gallego, G.; Scaramuzza, D. Asynchronous, photometric feature tracking using events and frames. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 750–765. [Google Scholar]
- Rebecq, H.; Gallego, G.; Mueggler, E.; Scaramuzza, D. EMVS: Event-based multi-view stereo—3D reconstruction with an event camera in real-time. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2018, 126, 1394–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Deng, X.; Shi, B. Evhandpose: Event-based 3d hand pose estimation with sparse supervision. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 6416–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, V.; Munoz, D.; Hebert, M.; Andrew Bagnell, J.; Sheikh, Y. Pose machines: Articulated pose estimation via inference machines. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part II 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Tompson, J.J.; Jain, A.; LeCun, Y.; Bregler, C. Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.E.; Ramakrishna, V.; Kanade, T.; Sheikh, Y. Convolutional pose machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4724–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Zhu, T.; Chen, L.C.; Gidaris, S.; Tompson, J.; Murphy, K. Personlab: Person pose estimation and instance segmentation with a bottom-up, part-based, geometric embedding model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16000–16009. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Z.; Bai, X.; Mao, Z. Predicting flow status of a flexible rectifier using cognitive computing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 264, 125878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Asai, Y.; Yamanoi, A.; Seki, Y.; Wiranata, A.; Minaminosono, A. Fluidic rolling robot using voltage-driven oscillating liquid. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumble, M.; Gilbert, A.; Malleson, C.; Hilton, A.; Collomosse, J.P. Total capture: 3D human pose estimation fusing video and inertial sensors. In Proceedings of the BMVC, London, UK, 4–7 September 2017; Volume 2, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Qin, W.; Zeng, W. Fusing wearable imus with multi-view images for human pose estimation: A geometric approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2200–2209. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Yu, T.; Li, H.; Guo, K.; Dai, Q.; Fang, L.; Liu, Y. Hybridfusion: Real-time performance capture using a single depth sensor and sparse imus. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 384–400. [Google Scholar]
- Roetenberg, D.; Luinge, H.; Slycke, P. Xsens MVN: Full 6DOF human motion tracking using miniature inertial sensors. Xsens Motion Technol. BV Tech. Rep 2009, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Von Marcard, T.; Rosenhahn, B.; Black, M.J.; Pons-Moll, G. Sparse inertial poser: Automatic 3d human pose estimation from sparse imus. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 36, pp. 349–360. [Google Scholar]
- Von Marcard, T.; Henschel, R.; Black, M.J.; Rosenhahn, B.; Pons-Moll, G. Recovering accurate 3d human pose in the wild using imus and a moving camera. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 601–617. [Google Scholar]
- Guzov, V.; Mir, A.; Sattler, T.; Pons-Moll, G. Human poseitioning system (hps): 3d human pose estimation and self-localization in large scenes from body-mounted sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4318–4329. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Leu, M.C.; Yin, Z. Real-time multi-modal human–robot collaboration using gestures and speech. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2022, 144, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, H.; Shen, C. Directpose: Direct end-to-end multi-person pose estimation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.07451. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Shang, J.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y. Compositional human pose regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2602–2611. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Xiao, B.; Wei, F.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y. Integral human pose regression. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S. Single-stage multi-person pose machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6951–6960. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. Stacked Dense-Hourglass Networks for Human Pose Estimation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Li, S.; Ouyang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Learning feature pyramids for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1281–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 466–481. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Snower, M.; Kadav, A.; Lai, F.; Graf, H.P. 15 keypoints is all you need. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6738–6748. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Yan, R.; Fragkiadaki, K.; Yu, S.I. Epipolar transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 7779–7788. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z. End-to-end human pose and mesh reconstruction with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1954–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Zhu, S.; Mendieta, M.; Yang, T.; Chen, C.; Ding, Z. 3d human pose estimation with spatial and temporal transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11656–11665. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffl, L.; Vidal, M.; Mathis, A. End-to-end trainable multi-instance pose estimation with transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.12115. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Ge, Y.; Shen, C.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Tfpose: Direct human pose estimation with transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.15320. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, D. Vitpose: Simple vision transformer baselines for human pose estimation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 38571–38584. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.; Xia, S.T.; Zhou, E. Tokenpose: Learning keypoint tokens for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11313–11322. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, R.W.; Liu, R.; Almatrafi, M.; Asari, V.; Hirakawa, K. Time-ordered recent event (tore) volumes for event cameras. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 2519–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Ye, Y.; Yang, K.; Sun, L.; Wang, K. Efficient human pose estimation via 3d event point cloud. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Prague, Czechia, 12–15 September 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, E.; Taverni, G.; Awai Easthope, C.; Skriabine, S.; Corradi, F.; Longinotti, L.; Eng, K.; Delbruck, T. DHP19: Dynamic vision sensor 3D human pose dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Guo, C.; Zuo, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, S.; Gong, M.; Cheng, L. Eventhpe: Event-based 3d human pose and shape estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10996–11005. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, G.; Di Pietro, F.; Carissimi, N.; Glover, A.; Bartolozzi, C. MoveEnet: Online high-frequency human pose estimation with an event camera. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 4024–4033. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, P.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Y.; Shi, B. EventZoom: Learning to denoise and super resolve neuromorphic events. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 21–25 June 2021; pp. 12824–12833. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Takatani, T.; Fu, Y. Learning to reconstruct high speed and high dynamic range videos from events. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 21–25 June 2021; pp. 2024–2033. [Google Scholar]
- Rehder, J.; Nikolic, J.; Schneider, T.; Hinzmann, T.; Siegwart, R. Extending kalibr: Calibrating the extrinsics of multiple IMUs and of individual axes. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 4304–4311. [Google Scholar]
- Rebecq, H.; Ranftl, R.; Koltun, V.; Scaramuzza, D. High speed and high dynamic range video with an event camera. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 1964–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tan, S.; Zhen, X.; Xu, S.; Zheng, F.; He, Z.; Shao, L. Deep 3D human pose estimation: A review. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2021, 210, 103225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederik, P.K. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. (tog) 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fu, R.; Huang, L.; Lin, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Hrformer: High-resolution transformer for dense prediction. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.09408. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Wang, T.; Sun, C. Voxel-based multi-scale transformer network for event stream processing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 2112–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, J.; Torr, P.H.; Koltun, V. Point transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 16259–16268. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]



| Representations | Frameworks | Methods | ↓ | ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frame | CNN | SHG | 8.29 | 92.16 |
| CNN | PoseRes | 6.25 | 62.26 | |
| CNN | HRNet | 6.14 | 64.63 | |
| CNN | DHP19 | 7.67 | 79.87 | |
| Transformer | HRFormer | 6.21 | 65.89 | |
| Transformer | ViTPose | 5.34 | 58.32 | |
| Transformer | EvTransPose | 5.08 | 50.39 | |
| Voxel | CNN | TORE | 5.44 | 56.46 |
| Transformer | VMST | 6.45 | 73.07 | |
| Point Cloud | CNN | DGCNN | 6.83 | 77.32 |
| PointNet | PointNet | 7.29 | 82.46 | |
| Transformer | PointTransformer | 6.46 | 73.37 |
| SHG | PoseRes | HRNet | HRFormer | ViTPose | EvTransPose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↓ | 89.25 | 18.20 | 19.45 | 19.83 | 17.88 | 17.34 |
| PCK@0.1↑ | 19.45 | 57.08 | 55.85 | 56.12 | 62.94 | 67.24 |
| PCK@0.3↑ | 46.46 | 93.07 | 92.50 | 92.36 | 92.81 | 94.10 |
| Movement | PCK@0.1↑ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHG | HRNet | ViTPose | EvTransPose | ||
| General Movement | 1 | 21.38 | 66.62 | 76.23 | 75.54 |
| 2 | 28.00 | 78.77 | 81.15 | 81.38 | |
| 3 | 40.62 | 76.77 | 81.62 | 78.08 | |
| Upper/Lower-Limb Movement | 4 | 21.38 | 49.08 | 59.31 | 64.54 |
| 5 | 17.38 | 37.23 | 49.85 | 62.08 | |
| 6 | 24.31 | 43.69 | 53.77 | 64.08 | |
| 7 | 10.15 | 44.00 | 52.15 | 63.76 | |
| 8 | 10.46 | 54.31 | 58.85 | 55.46 | |
| 9 | 15.69 | 60.77 | 68.08 | 73.00 | |
| 10 | 10.15 | 43.23 | 52.38 | 62.08 | |
| 11 | 18.92 | 57.23 | 59.00 | 67.31 | |
| 12 | 14.92 | 55.86 | 62.85 | 62.23 | |
| Mean | 19.45 | 55.85 | 62.94 | 67.24 | |
| ↓ | ↓ | PCK@0.1↑ | PCK@0.3↑ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ViT | 61.93 | 6.80 | 66.93 | 98.45 |
| ViTPose | 54.79 | 5.46 | 73.47 | 98.88 |
| Ours | 50.39 | 5.08 | 76.84 | 99.20 |
| Methods | ↓ | ↓ | PCK@0.1↑ | PCK@0.3↑ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 1 | 12 | 58.25 | 5.78 | 69.16 | 98.95 |
| Without Skip Connection | 2 | 6 | 60.06 | 5.94 | 67.55 | 98.81 |
| 3 | 4 | 60.86 | 6.00 | 67.22 | 98.70 | |
| 4 | 3 | 346.23 | 29.50 | 4.03 | 13.60 | |
| 6 | 2 | 344.24 | 29.31 | 4.06 | 31.27 | |
| Concatenate | 2 | 6 | 58.67 | 5.80 | 69.12 | 95.36 |
| 3 | 4 | 55.42 | 5.52 | 72.51 | 99.00 | |
| 4 | 3 | 55.64 | 5.54 | 72.55 | 98.95 | |
| 6 | 2 | 53.17 | 5.33 | 74.65 | 99.06 | |
| Add (Ours) | 2 | 6 | 57.31 | 5.69 | 70.22 | 98.90 |
| 3 | 4 | 54.35 | 5.42 | 73.62 | 99.05 | |
| 4 | 3 | 54.00 | 5.39 | 73.78 | 99.08 | |
| 6 | 2 | 51.88 | 5.21 | 76.00 | 99.14 |
| Weights | None | Constant | Linear | Logarithmic | Exponential | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | −1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 20 | |
| *↓ | - | 56.67 | 58.36 | 59.54 | 59.49 | 58.75 | 56.20 | 84.19 | 114.39 | 125.38 |
| PCK@0.1 *↑ | - | 71.57 | 69.27 | 69.42 | 69.33 | 69.02 | 71.87 | 53.95 | 34.60 | 30.35 |
| PCK@0.3 *↑ | - | 98.91 | 98.89 | 98.49 | 98.55 | 98.88 | 98.89 | 95.30 | 91.67 | 90.23 |
| ↓ | 51.88 | 55.97 | 57.40 | 58.32 | 58.10 | 57.93 | 52.72 | 51.29 | 50.39 | 51.63 |
| PCK@0.1↑ | 76.00 | 72.18 | 70.06 | 70.79 | 70.86 | 69.79 | 75.31 | 76.27 | 76.84 | 76.42 |
| PCK@0.3↑ | 99.14 | 98.92 | 98.95 | 98.55 | 98.61 | 98.91 | 99.05 | 99.16 | 99.20 | 99.15 |
| Source Domain | ↓ | PCK@0.1↑ | PCK@0.3↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| DHP19 | 23.61 | 39.79 | 89.91 |
| CHP | 17.34 | 67.24 | 94.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Zeng, Z.; Li, X.; Fan, C. EvTransPose: Towards Robust Human Pose Estimation via Event Camera. Electronics 2025, 14, 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061078
He J, Zeng Z, Li X, Fan C. EvTransPose: Towards Robust Human Pose Estimation via Event Camera. Electronics. 2025; 14(6):1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061078
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jielun, Zhaoyuan Zeng, Xiaopeng Li, and Cien Fan. 2025. "EvTransPose: Towards Robust Human Pose Estimation via Event Camera" Electronics 14, no. 6: 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061078
APA StyleHe, J., Zeng, Z., Li, X., & Fan, C. (2025). EvTransPose: Towards Robust Human Pose Estimation via Event Camera. Electronics, 14(6), 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061078







