Multi-Factor Task Assignment and Adaptive Window Enhanced Conflict-Based Search: Multi-Agent Task Assignment and Path Planning for a Smart Factory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Problem Definition
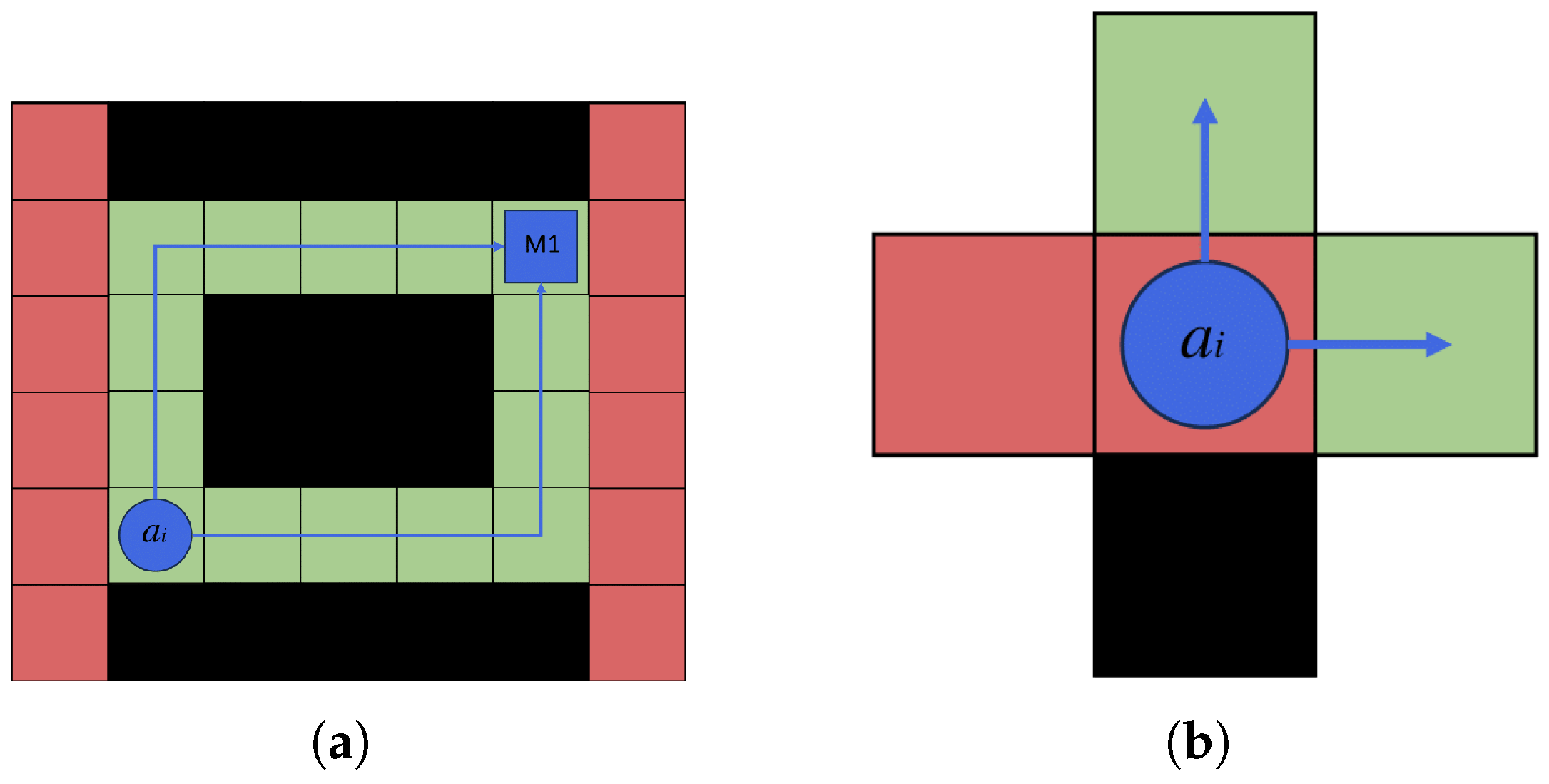
3.1. Maximum Travel Distance
3.2. Maximum Number of Executable Tasks
3.3. Agent Geometry
4. TAPF Solution
4.1. Task Assignment
4.1.1. MATA Problem Modeling
4.1.2. Multi-Factor Hungarian Assignment Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Multi-Factor Hungarian Assignment Algorithm |
| Input: graph G, agents A, tasks M, constraints and Output: task assignment scheme .
|
4.2. Path Planning
4.2.1. MAPF Problem Modeling
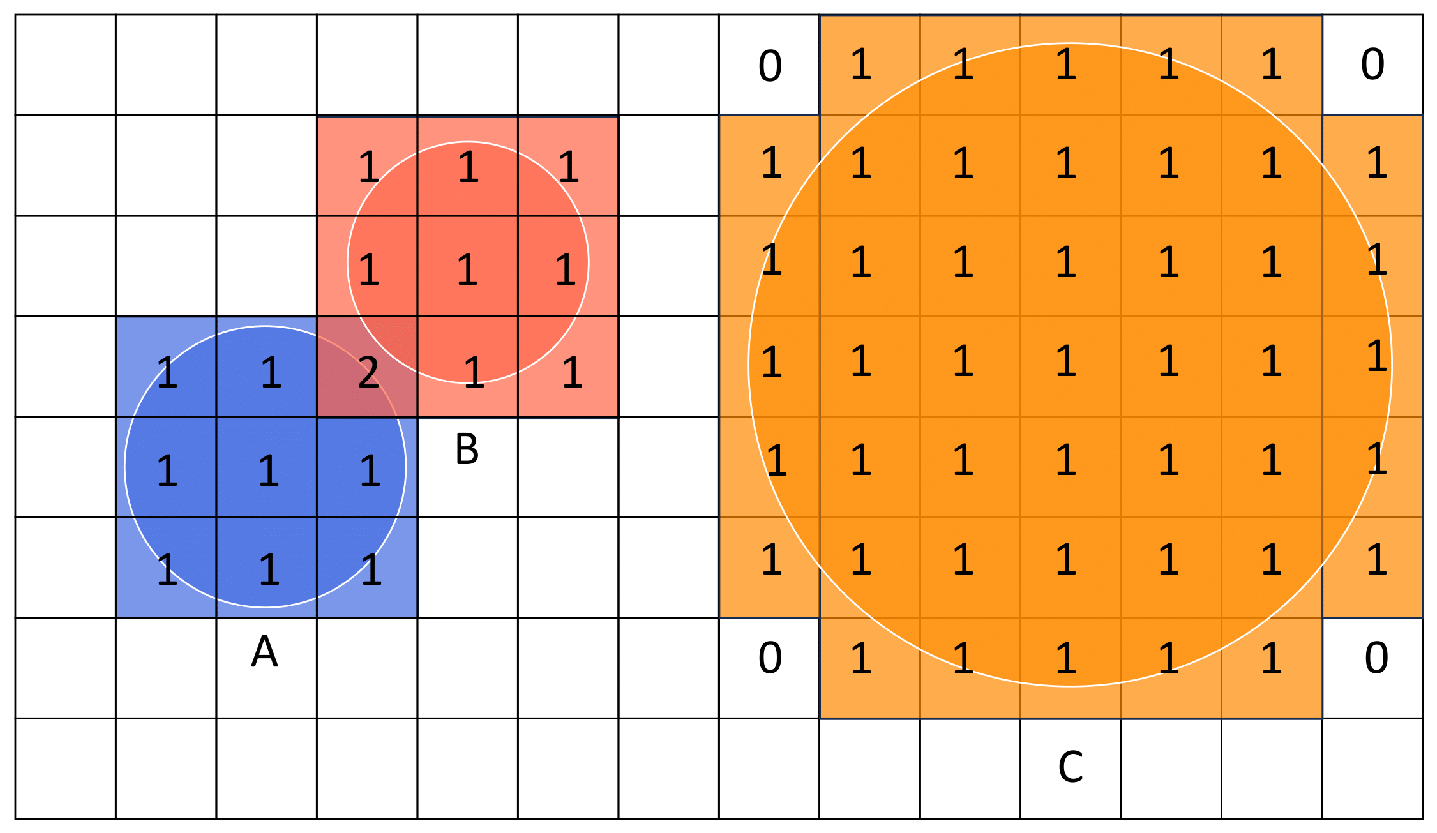
4.2.2. Adaptive Windowed ECBS
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| A priority queue stores all the nodes in the binary search tree. | |
| A priority queue storing those node costs are within this suboptimal bound. | |
| R | The root node in the binary search tree. |
| O | The node with the lowest cost value in the current OPEN. |
| H | The node in the OPEN set that meets the boundary conditions. |
| N | The node in the FOCAL set with the fewest conflicts. |
| The new node resulting from conflict resolution. |
| Algorithm 2 Adaptive Window ECBS |
| Input: graph G, agents A, task scheme , agents radius r, time horizon , replanning period , suboptimal binary , window increase factor , and window decrease factor . Output: path .
|
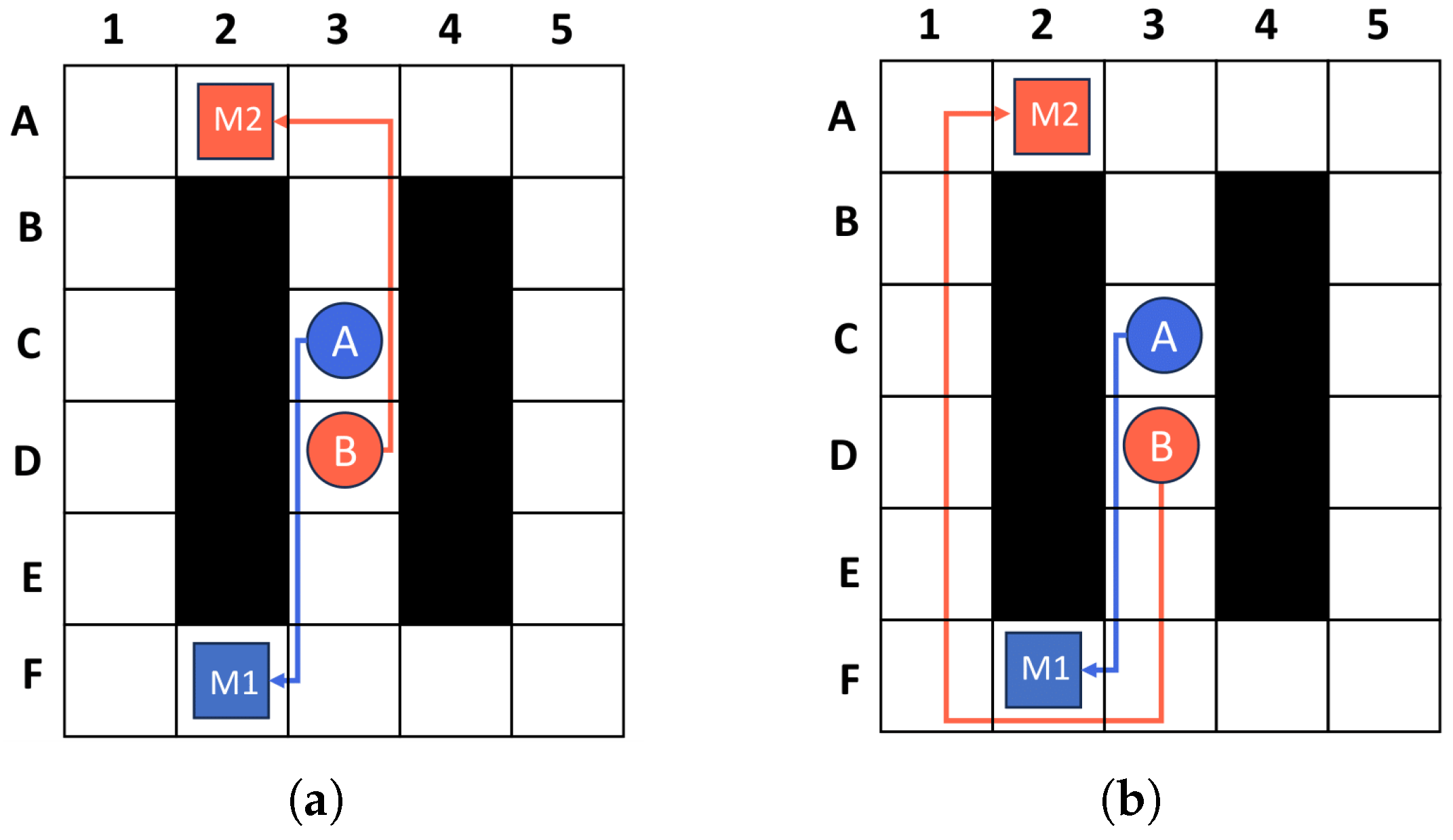
4.2.3. Two Observations
| Algorithm 3 TaskCostUpdate |
Input: agents A, graph G, map M, path
|
| Algorithm 4 CheckTasks |
Input: agents A, tasks assignment scheme , replanning period
|
4.3. Overall Algorithm Flow
5. Experiments and Results
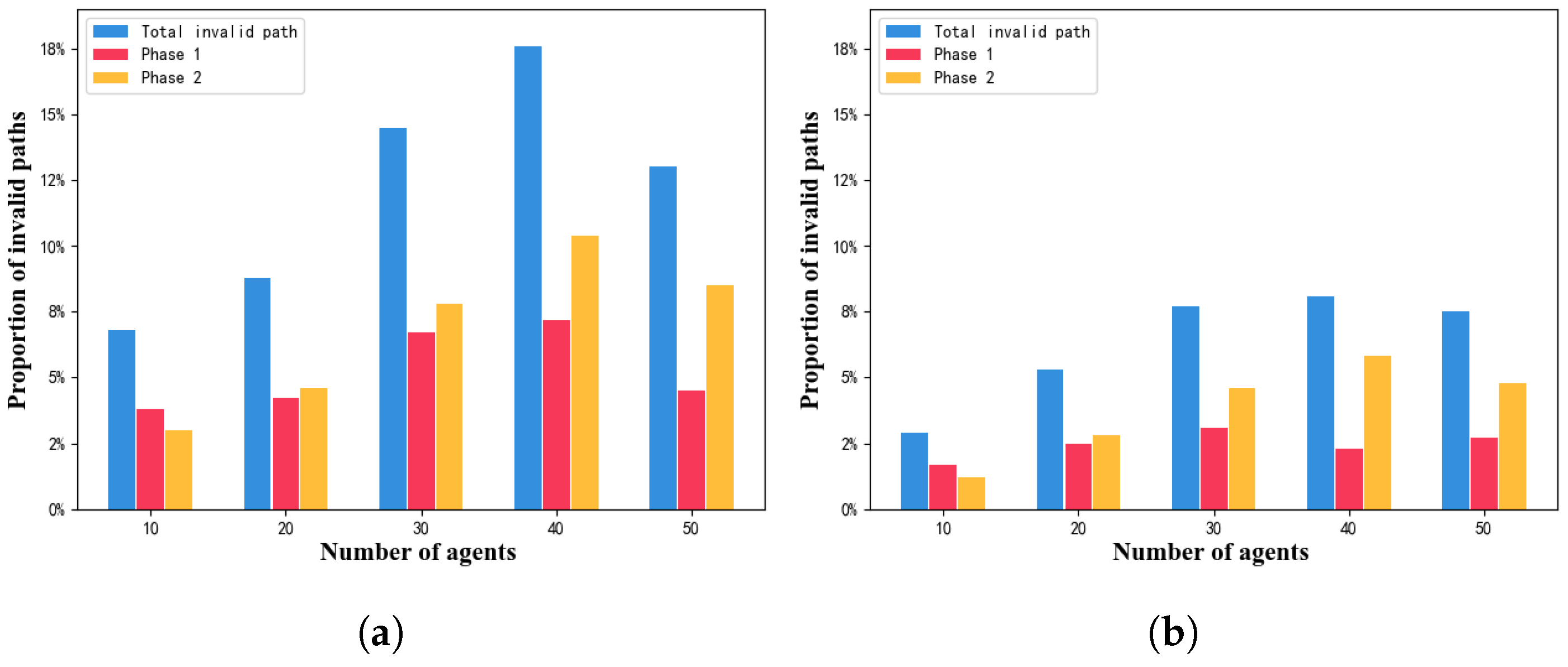
5.1. Algorithm Scalability and Success Rate
5.2. Algorithm Adaptability in Smart Factory Environments
5.3. Congestion Level Test
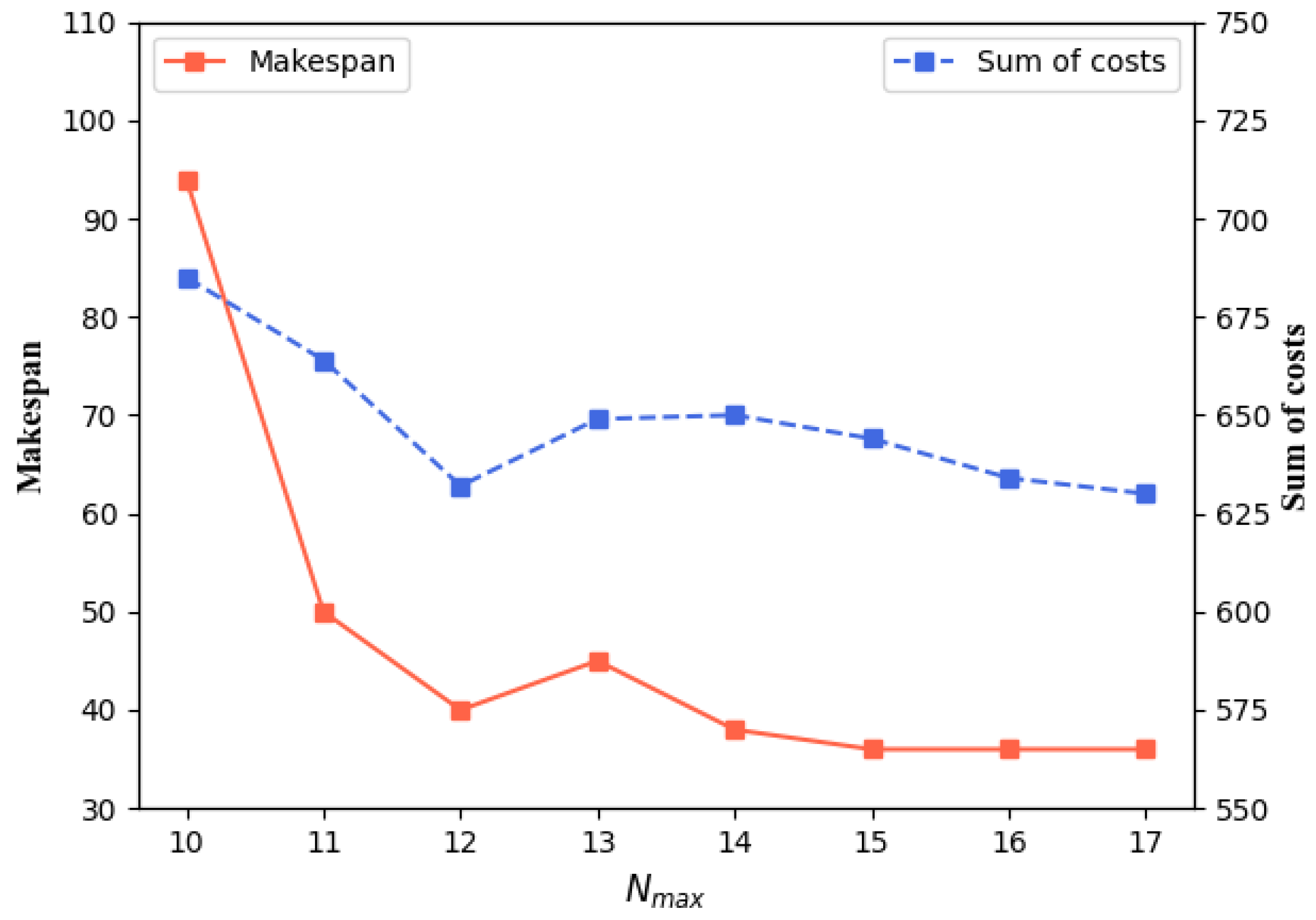
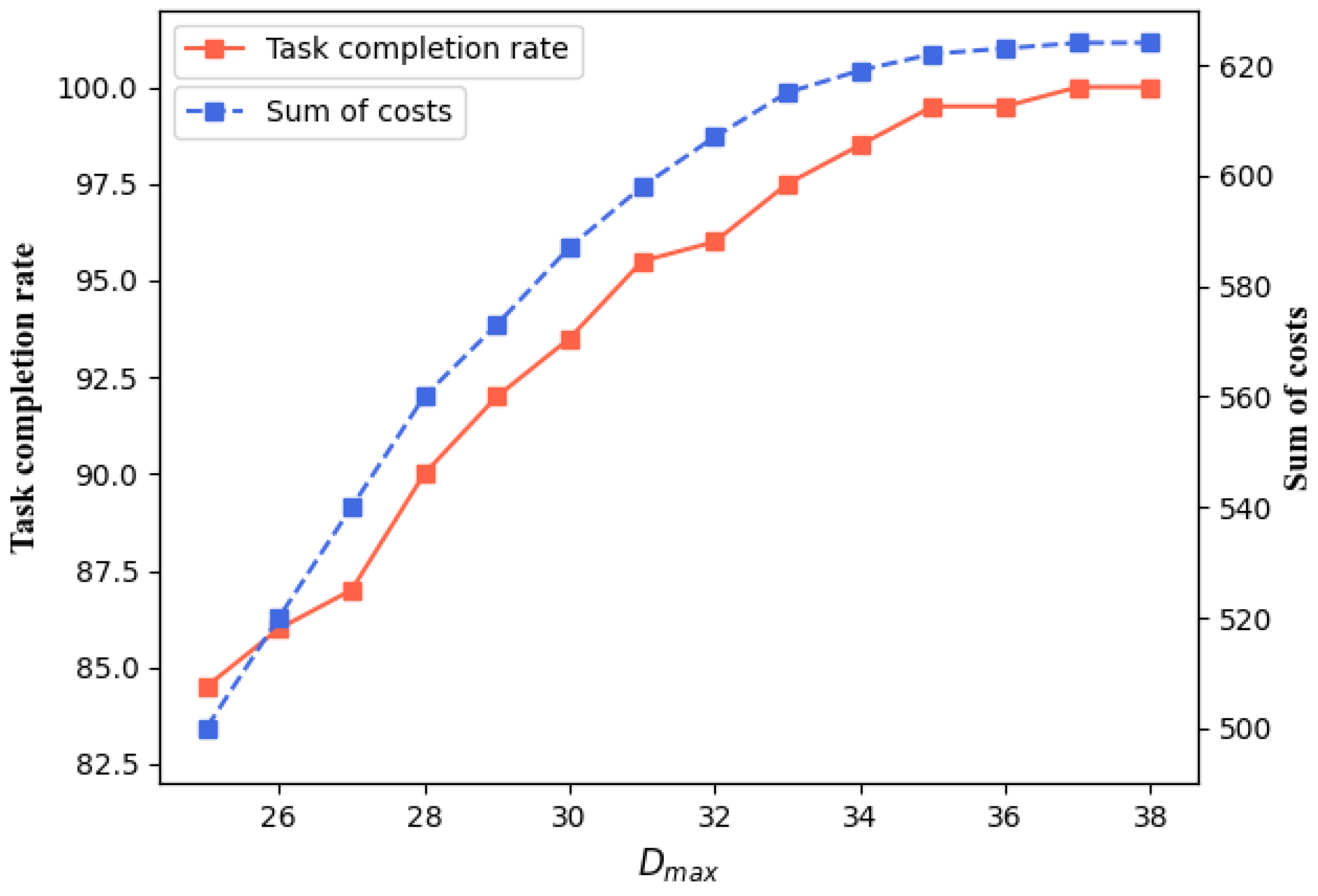
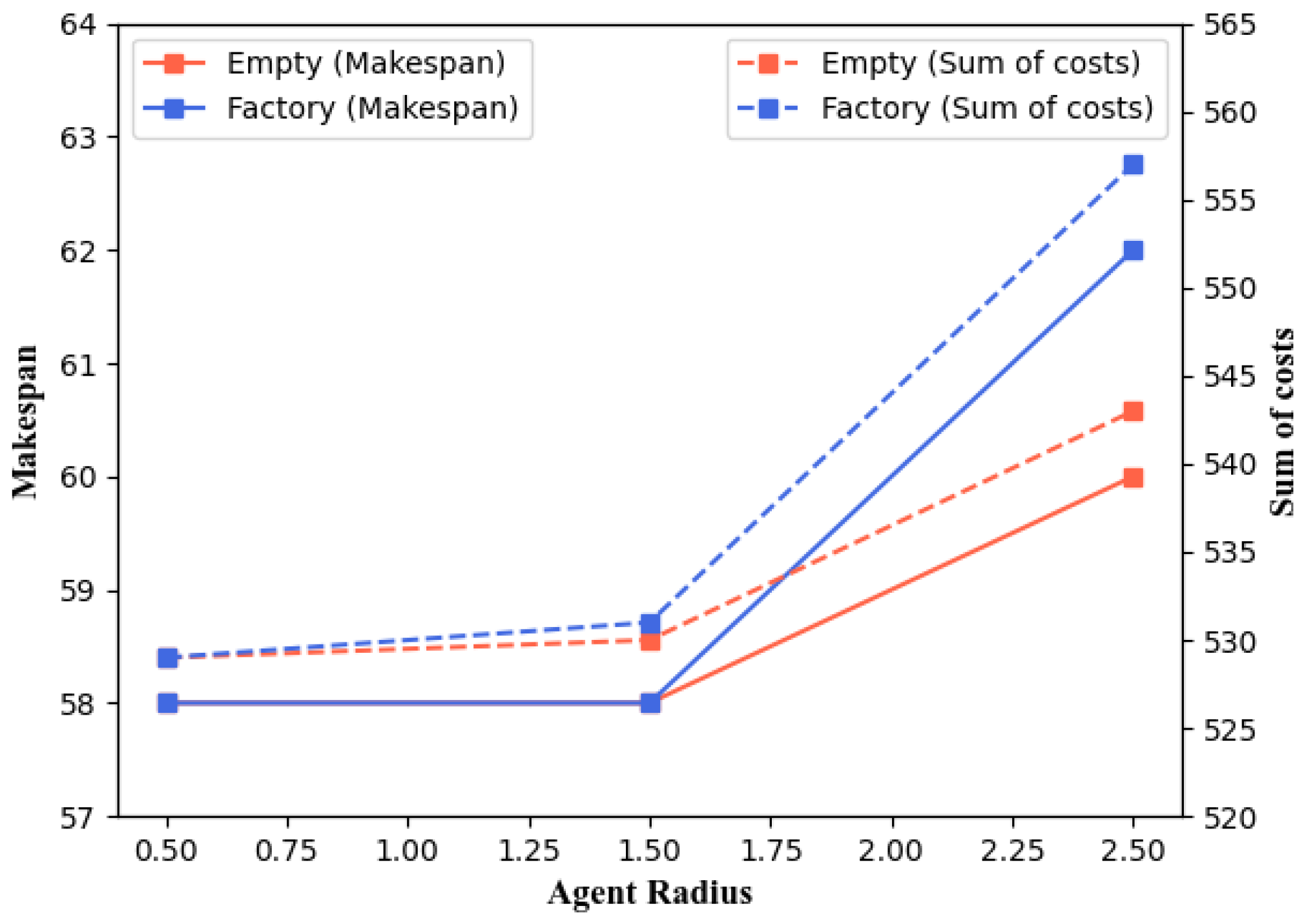
5.4. Parameter Settings for Agents
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, K.; Xu, J.; Zheng, M. Industry 4.0: Review and proposal for implementing a smart factory. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 133, 1331–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wan, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, D.; Zhang, C. Towards smart factory for Industry 4.0: A self-organized multi-agent system with big data based feedback and coordination. Comput. Netw. 2016, 101, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorri, A.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jurdak, R. Multi-Agent Systems: A Survey. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 28573–28593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.; Hussein, A.; Elmogy, A. Multi-robot Task Allocation: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Coop. Robot. Sens. Netw. 2015, 604, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.; Sturtevant, N.; Felner, A.; Koenig, S.; Ma, H.; Walker, T.; Li, J.; Atzmon, D.; Cohen, L.; Kumar, T.; et al. Multi-agent pathfinding: Definitions, variants, and benchmarks. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Combinatorial Search, Napa, CA, USA, 16–17 July 2019; Volume 10, pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Koenig, S. Optimal target assignment and path finding for teams of agents. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Singapore, 9–13 May 2016; pp. 1144–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Cao, M.; Yan, W.; Ge, S.S. Efficient routing for precedence-constrained package delivery for heterogeneous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Liu, X.F.; Zhan, Z.H.; Yong, J.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, D.; Mao, C.; Tang, Y. A Multiobjective Ant Colony System for Multi-Agent Pickup and Delivery. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Machine Intelligence Theory and Applications (MiTA), Melbourne, Australia, 14–23 July 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Jeong, Y. An approximation algorithm for mobile multi-agent monitoring and routing problem. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2025, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönig, W.; Kiesel, S.; Tinka, A.; Durham, J.; Ayanian, N. Conflict-based search with optimal task assignment. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 757–765. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Li, J.; Sycara, K. Solving multi-agent target assignment and path finding with a single constraint tree. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Symposium on Multi-Robot and Multi-Agent Systems (MRS), Boston, MA, USA, 4–5 December 2023; pp. 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Alonso-Mora, J.; Bai, X.; Harabor, D.D.; Stuckey, P.J. Integrated Task Assignment and Path Planning for Capacitated Multi-Agent Pickup and Delivery. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 5816–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, F.; Cai, K. A TSP-Based Online Algorithm for Multi-Task Multi-Agent Pickup and Delivery. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 5910–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tinka, A.; Kiesel, S.; Durham, J.W.; Kumar, T.S.; Koenig, S. Lifelong multi-agent path finding in large-scale warehouses. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 11272–11281. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Na, K.I.; Yu, W. Anytime Lifelong Multi-Agent Pathfinding in Topological Maps. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 20365–20380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Feng, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Hu, R. A Two-Stage Congestion-Aware Routing Method for Automated Guided Vehicles in Warehouses. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Xiamen, China, 5–7 November 2021; Volume 1, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, C.; Abbenseth, J.; Toussaint, M. An Optimal Algorithm to Solve the Combined Task Allocation and Path Finding Problem. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 4140–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Rathinam, S.; Choset, H. MS*: A New Exact Algorithm for Multi-agent Simultaneous Multi-goal Sequencing and Path Finding. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 11560–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Rathinam, S.; Choset, H. CBSS: A New Approach for Multiagent Combinatorial Path Finding. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 2669–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Koenig, S. Task and path planning for multi-agent pickup and delivery. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 1152–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, H.W. The Hungarian method for the assignment problem. Nav. Res. Logist. 2004, 52, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, J.; Koenig, S.; Ma, H. Multi-Goal Multi-Agent Pickup and Delivery. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 9964–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisinger, D.; Ropke, S. Large neighborhood search. In Handbook of Metaheuristics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Kanellakis, C.; Nikolakopoulos, G. SA-reCBS: Multi-robot task assignment with integrated reactive path generation. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2023, 56, 7032–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yin, Q.; Quan, Z.; Ju, B.; Miao, J. Heuristic-Based Task Assignment and Multi-Agent Path Planning for Automatic Warehouses. In Proceedings of the 2023 China Automation Congress (CAC), Chongqing, China, 17–19 November 2023; pp. 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, W.L.; Zhong, J. An efficient multi-objective ant colony optimization for task allocation of heterogeneous unmanned aerial vehicles. J. Comput. Sci. 2022, 58, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Fielbaum, A.; Kronmüller, M.; Knoedler, L.; Alonso-Mora, J. Group-Based Distributed Auction Algorithms for Multi-Robot Task Assignment. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023, 20, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, K.L.; Padberg, M.; Rinaldi, G. Traveling salesman problem. Encycl. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2013, 1, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Stern, R.; Felner, A.; Sturtevant, N.R. Conflict-based search for optimal multi-agent pathfinding. Artif. Intell. 2015, 219, 40–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surynek, P. Multi-goal multi-agent path finding via decoupled and integrated goal vertex ordering. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 12409–12417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreychuk, A.; Yakovlev, K.; Surynek, P.; Atzmon, D.; Stern, R. Multi-agent pathfinding with continuous time. Artif. Intell. 2022, 305, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.; Uras, T.; Kumar, T.S.; Xu, H.; Ayanian, N.; Koenig, S. Improved Solvers for Bounded-Suboptimal Multi-Agent Path Finding. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2016; pp. 3067–3074. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ruml, W.; Koenig, S. Eecbs: A bounded-suboptimal search for multi-agent path finding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 12353–12362. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Harabor, D.; Stuckey, P.J.; Li, J.; Koenig, S. Searching with consistent prioritization for multi-agent path finding. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 29–31 January 2019; Volume 33, pp. 7643–7650. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, R.; Bekris, K.E. Push and swap: Fast cooperative path-finding with completeness guarantees. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Barcelona, Spain, 16–22 July 2011; pp. 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Li, J.; Kumar, T.; Koenig, S. Lifelong multi-agent path finding for online pickup and delivery tasks. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 837–845. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Mao, J.; Li, D.; Wang, N.; Wang, N. A coordinated scheduling approach for task assignment and multi-agent path plannin. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2024, 36, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yan, X.; Han, Y. Multi-mechanism swarm optimization for multi-UAV task assignment and path planning in transmission line inspection under multi-wind field. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 150, 111033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Wu, X. Task and intelligent path planning algorithm for teams of AGVs based on multi-stage method. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Automation, Electronics and Electrical Engineering (AUTEEE), Shenyang, China, 19–21 November 2021; pp. 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.; Choset, H. Subdimensional expansion for multirobot path planning. Artif. Intell. 2015, 219, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Obermeier, P.; Son, T.; Schaub, T.; Yeoh, W. Generalized target assignment and path finding using answer set programming. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Combinatorial Search, Napa, CA, USA, 16–17 July 2019; Volume 10, pp. 194–195. [Google Scholar]
- Okumura, K.; Défago, X. Solving simultaneous target assignment and path planning efficiently with time-independent execution. Artif. Intell. 2023, 321, 103946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Taneda, K.; Goto, A.; Hattori, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Takamido, R.; Ota, J. Offline Task Assignment and Motion Planning Algorithm Considering Agent’s Dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 10–12 February 2023; pp. 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, A. Breadth-first search. In Catalogue of Artificial Intelligence Tools; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; p. 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. A modified method for solving the unbalanced assignment problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2006, 176, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Jiang, J.; Coombes, M. A congestion-aware path planning method considering crowd spatial-temporal anomalies for long-term autonomy of mobile robots. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 7930–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, C.; Lacerda, B.; Mühlig, M.; Hawes, N. Multi-Robot Planning Under Uncertainty with Congestion-Aware Models. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Singapore, 9–13 May 2020; pp. 1314–1322. [Google Scholar]








| Parameter | Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | time horizon | |
| 4 | replanning period | |
| 1.5 | ECBS suboptimal boundary | |
| 100 | maximum travel distance | |
| 20 | maximum number of executable tasks | |
| r | 0.5 | agent radius |
| 1.4 | window increase factor | |
| 0.8 | window decrease factor | |
| runtime | 60 s | runtime limit |
| TP | TPTS | CBSS | MTA-WECBS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tasks | Agents | ms | soc | ms | soc | ms | soc | ms | soc |
| 50 | 10 | 75 | 449 | 44 | 431 | 84 | 312 | 42 | 313 |
| 20 | 64 | 524 | 29 | 561 | 44 | 429 | 22 | 302 | |
| 30 | 49 | 570 | 23 | 661 | 35 | 524 | 21 | 386 | |
| 40 | 54 | 687 | 22 | 841 | 29 | 687 | 23 | 525 | |
| 50 | 62 | 959 | 23 | 1101 | Timeout | 20 | 564 | ||
| 100 | 10 | 86 | 655 | 51 | 501 | 119 | 394 | 51 | 465 |
| 20 | 62 | 731 | 31 | 601 | 78 | 516 | 34 | 552 | |
| 30 | 65 | 868 | 29 | 811 | 69 | 713 | 26 | 585 | |
| 40 | 51 | 1048 | 26 | 1001 | 56 | 861 | 23 | 688 | |
| 50 | 64 | 1122 | 25 | 1095 | Timeout | 23 | 835 | ||
| 150 | 10 | 86 | 655 | 60 | 591 | 101 | 420 | 63 | 523 |
| 20 | 81 | 842 | 48 | 721 | 86 | 596 | 35 | 605 | |
| 30 | 69 | 1077 | 37 | 894 | Timeout | 27 | 682 | ||
| 40 | 62 | 1232 | 35 | 1054 | Timeout | 26 | 811 | ||
| 50 | 65 | 1524 | Timeout | Timeout | 25 | 924 | |||
| 200 | 10 | 107 | 955 | 83 | 821 | 100 | 504 | 71 | 679 |
| 20 | 89 | 977 | 58 | 912 | Timeout | 36 | 630 | ||
| 30 | 77 | 1152 | 49 | 1054 | Timeout | 31 | 782 | ||
| 40 | 71 | 1282 | Timeout | Timeout | 28 | 849 | |||
| 50 | 79 | 1678 | Timeout | Timeout | 27 | 1008 | |||
| No Strategy | Two Strategies | Optimization Ratio | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tasks | Agents | ms | soc | runtime | ms | soc | runtime | ms | soc |
| 50 | 10 | 71 | 385 | 9 | 44 | 347 | 9 | 38% | 10% |
| 50 | 26 | 619 | 10 | 22 | 593 | 11 | 15% | 5% | |
| 100 | 10 | 63 | 507 | 10 | 53 | 433 | 11 | 15% | 15% |
| 50 | 35 | 956 | 11 | 25 | 821 | 13 | 28% | 15% | |
| 150 | 10 | 87 | 686 | 10 | 62 | 579 | 12 | 29% | 16% |
| 50 | 36 | 1170 | 13 | 26 | 974 | 15 | 28% | 17% | |
| 200 | 10 | 90 | 763 | 12 | 75 | 673 | 14 | 17% | 12% |
| 50 | 35 | 1202 | 14 | 26 | 1018 | 18 | 25% | 15% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y. Multi-Factor Task Assignment and Adaptive Window Enhanced Conflict-Based Search: Multi-Agent Task Assignment and Path Planning for a Smart Factory. Electronics 2025, 14, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050842
Li J, Zhao Y, Shen Y. Multi-Factor Task Assignment and Adaptive Window Enhanced Conflict-Based Search: Multi-Agent Task Assignment and Path Planning for a Smart Factory. Electronics. 2025; 14(5):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050842
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jinyan, Yihui Zhao, and Yan Shen. 2025. "Multi-Factor Task Assignment and Adaptive Window Enhanced Conflict-Based Search: Multi-Agent Task Assignment and Path Planning for a Smart Factory" Electronics 14, no. 5: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050842
APA StyleLi, J., Zhao, Y., & Shen, Y. (2025). Multi-Factor Task Assignment and Adaptive Window Enhanced Conflict-Based Search: Multi-Agent Task Assignment and Path Planning for a Smart Factory. Electronics, 14(5), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050842






