Design of a Current-Mode Trapezoidal Waveform Generator in High-Voltage SOI Technology with Modifications Based on Safe Operating Area Limits †
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Wireless Communications
1.2. High-Voltage Waveform Generation
2. Design of the Generator
2.1. Mixed Low- and High-Voltage Topology of the Generator
2.2. Current Mode of Operation
3. Test Results
3.1. Test Bench Structure
3.2. Design of the Overvoltage Protected Generator
3.3. Introductory Tests
3.4. Parametric Tests
4. Results Discussion
4.1. Test Session for Constant Output Capacitor
4.2. Test Session for Constant Quotient of Output Current and Capacitor
4.3. Summary of Test Sessions
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jankowski, M. Practical Implementation of a Trapezoidal Waveform Generator in High Voltage SOI Technology. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and System (MIXDES), Gdansk, Poland, 27–28 June 2024; pp. 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Ma, Q.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y. Analysis and Optimization of Power MOSFETs Shaped Switching Transients for Reduced EMI Generation. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 20440–20448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizarci, H.; Pekperlak, U.; Arifoglu, U. Conducted Emission Suppression Using an EMI Filter for Grid-Tied Three-Phase/Level T-Type Solar Inverter. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 67417–67431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funato, H.; Mori, T.; Igarashi, T.; Ogasawara, S.; Okazaki, F.; Hirota, Y. Optimization of Switching Transient Waveform to Reduce Harmonics in Selective Frequency Bands. Ind. Appl. 2013, 2, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ely, J.J.; Nguyen, T.X.; Scearce, S.A. The Influence of Modulated Signal Risetime in Flight Electronics Radiated Immunity Testing with a Mode-Stirred Chamber; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Langley Research Center: Hampton, VA, USA, 2000.
- Govind, M.; Ruckmongathan, T.N. Trapezoidal and Triangular Waveform Profiles for Reducing Power Dissipation in Liquid Crystal Displays. J. Disp. Technol. 2008, 4, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M. Improvements of high-voltage trapezoidal waveform edge-rounding circuit. Int. J. Microelectron. Comput. Sci. 2018, 9, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Jayanand, B. Analysis of a Single Stage High Frequency Triangular Wave Generation Circuit; Authorea, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachare, M.; Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Carvajal, R.G.; Lopez-Martin, A.J. New low-Voltage fully programmable CMOS triangular/trapezoidal function Generator circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2005, 52, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, F.; Ria, A.; Manfredini, G.; Bruschi, P.; Piotto, M. A 3-Decade-Frequency-Range Sinewave Synthesizer with Analog Piecewise-Linear Interpolation. In Proceedings of the 2022 17th Conference on Ph.D Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PRIME), Villasimius, Italy, 12–15 June 2022; Volume 7, pp. 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, M.; Gagliardi, F.; Contardi, S.; Nannipieri, I.; Bruschi, P. A Fully Integrated 1 KHz-1 MHz Sinusoidal Waveform Generator Based on Second Order Analog Interpolation. In Proceedings of the 2024 19th Conference on Ph.D Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PRIME), Larnaca, Cyprus, 9–12 June 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobe, U.; Rooch, K.; Mörtl, D.; Graupner, A.; Lerch, A.; Pronath, M. Verification of Safe Operating Area (SOA) Constraints in Analog Circuits. In Proceedings of the Zuverlässigkeit und Entwurf, Ingolstadt, Germany, 29 September–1 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hower, P.; Pendharkar, S. Short and long-term safe operating area considerations in LDMOS transistors. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–21 April 2005; Volume 43, pp. 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobe, U.; Rooch, K.; Ripp, A.; Pronath, M. Robust Analog Design for Automotive Applications by Design Centering With Safe Operating Areas. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2008, 22, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High Voltage Implementations in Standard CMOS. Book Design of High Voltage xDSL Line Drivers in Standard CMOS; Analog Circuits and Signal Processing, Series; Serneels, B., Steyaert, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashmineh, S.; Killat, D. Design of a high-voltage differential amplifier based on stacked low-voltage standard CMOS with different input stages. In Proceedings of the 38th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 25–29 May 2015; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelgrom, M.J.; Tuinhout, H.P.; Vertregt, M. Transistor matching in analog CMOS applications. In Proceedings of the Technical Digest of the International Electron Devices Meeting 1998 (Cat. No. 98CH36217), San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 December 1998; pp. 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Gotarredona, T.; Linares-Barranco, B. Systematic Width-and-Length Dependent CMOS Transistor Mismatch Characterization and Simulation. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 1999, 21, 271–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, C.; Ismail, M. Statistical modeling of device mismatch for analog MOS integrated circuits. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1992, 27, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drennan, P.G.; McAndrew, C.C. Understanding MOSFET mismatch for analog design. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2002 Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (Cat. No. 02CH37285), Orlando, FL, USA, 15 May 2002; pp. 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, W.; Enichlmair, H.; Schirgi, E.; Rappitsch, G. Statistical Modelling of MOS Transistor Mismatch for High-voltage CMOS Processes. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2006, 21, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.-H.; Kong, B.-S. High-Speed Rail-to-Rail Class-AB Buffer Amplifier with Compact, Adaptive Biasing for FPD Applications. Electronics 2020, 9, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M. Influence of Modifications Related to Safe Operating Area Demands on Operation of a Specialized Medium/High-Voltage Unity-Gain Buffer. Energies 2022, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappert, H.; Kordas, N.; Dreiner, S.; Paschen, U.; Kokozinski, R. High temperature SOI CMOS technology and circuit realization for applications up to 300 °C. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Lisbon, Portugal, 24–27 May 2015; pp. 1162–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwell, R.; McCue, B.M.; Zuo, L.; Huque, M.A.; Tolbert, L.M.; Blalock, B.J.; Islam, S.K. SOI-based integrated circuits for high-temperature power electronics applications. In Proceedings of the 2011 Twenty-Sixth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 6–11 March 2011; pp. 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stork, J.M.C.; Hosey, G.P. SOI technology for power management in automotive and industrial applications. Solid-State Electron. 2017, 128, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H.; Eguchi, H.; Kijima, S.; Honda, N.; Yamada, T.; Yamawaki, H.; Aoki, H.; Hamada, K. Wide-voltage SOI-BiCDMOS technology for high-temperature automotive applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–26 May 2011; pp. 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, A. Trapezoid Signal Generating Circuit. U.S. Patent 2006/0152258 A1, 13 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, B.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, A.K. A comparative study of various current mirror configurations: Topologies and characteristics. Microelectron. J. 2016, 53, 134–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M.; Napieralski, A. Current-mode signal processing implementation in HV SoI integrated systems. Microelectron. J. 2014, 45, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, N.; Wunderlich, R.; Heinen, S. An over-voltage protection circuit for CMOS power amplifiers. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems 2008, Saint Julian’s, Malta, 31 August–3 September 2008; pp. 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, D.; Paul, S. A novel HV-switch scheme with gate-source overvoltage protection for bidirectional neural interfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems (ICECS), Cairo, Egypt, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Cao, H.; Gu, X.; Guo, Z. Design and optimization of LDMOS-SCR devices with improved ESD protection performance. Microelectron. Reliab. 2016, 61, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.-K.; Chen, S.-L.; Lin, P.-L.; Chen, H.-W. Layout Strengthening the ESD Performance for High-Voltage N-Channel Lateral Diffused MOSFETs. Electronics 2020, 9, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Su, H.; Chan, C.; Yang, D.; Chen, J.F.; Wu, K.M. The influence of the layout on the ESD performance of HV-LDMOS. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices & IC’s (ISPSD) 2010, Hiroshima, Japan, 6–10 June 2010; pp. 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Keppens, B.; Mergens, M.P.; Trinh, C.S.; Russ, C.C.; Camp, B.V.; Verhaege, K.G. ESD protection solutions for high voltage technologies. Microelectron. Reliab. 2006, 46, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Glaser, U. Novel Active ESD Clamps for High-Voltage Applications. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2013, 13, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



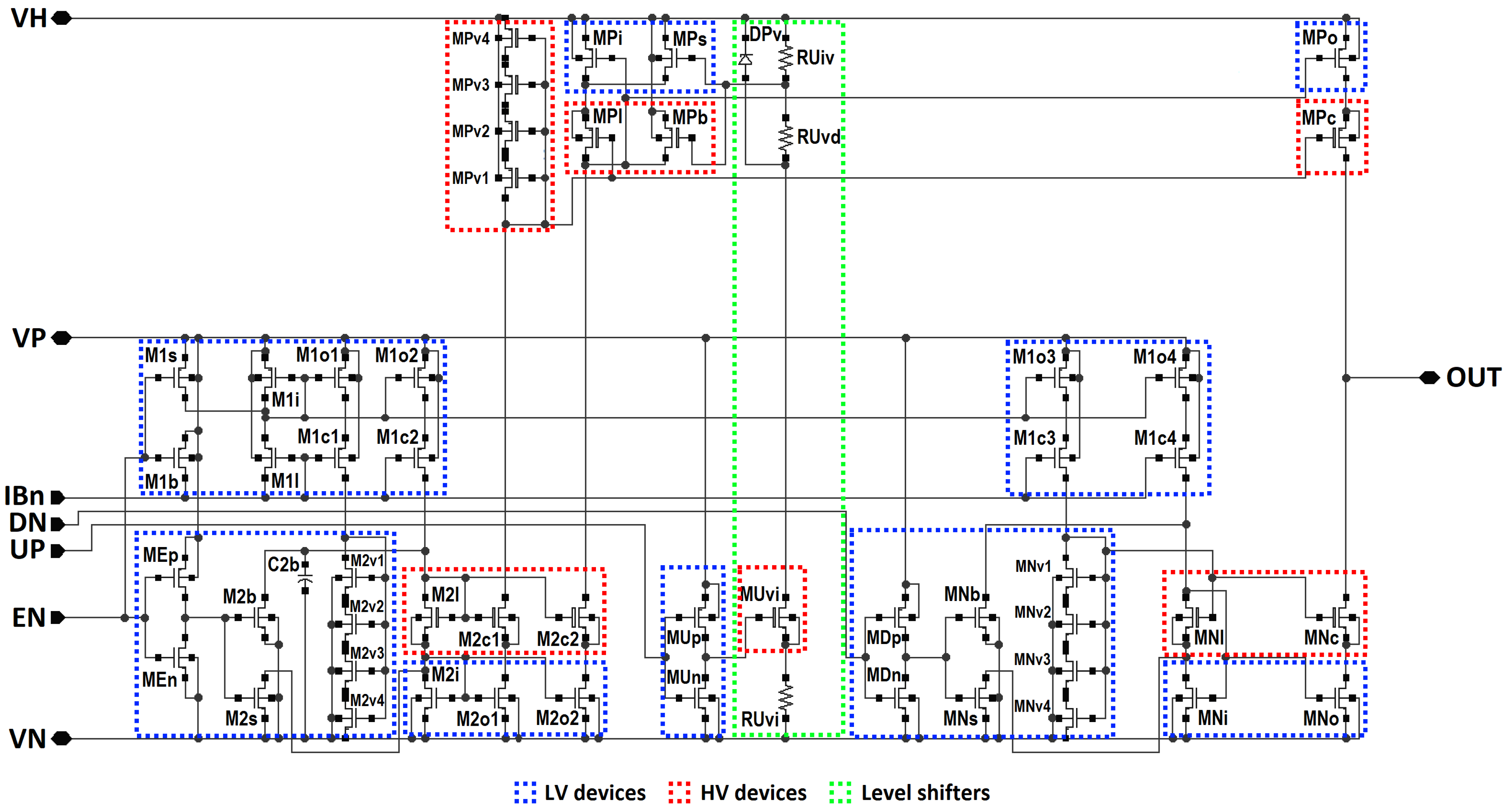
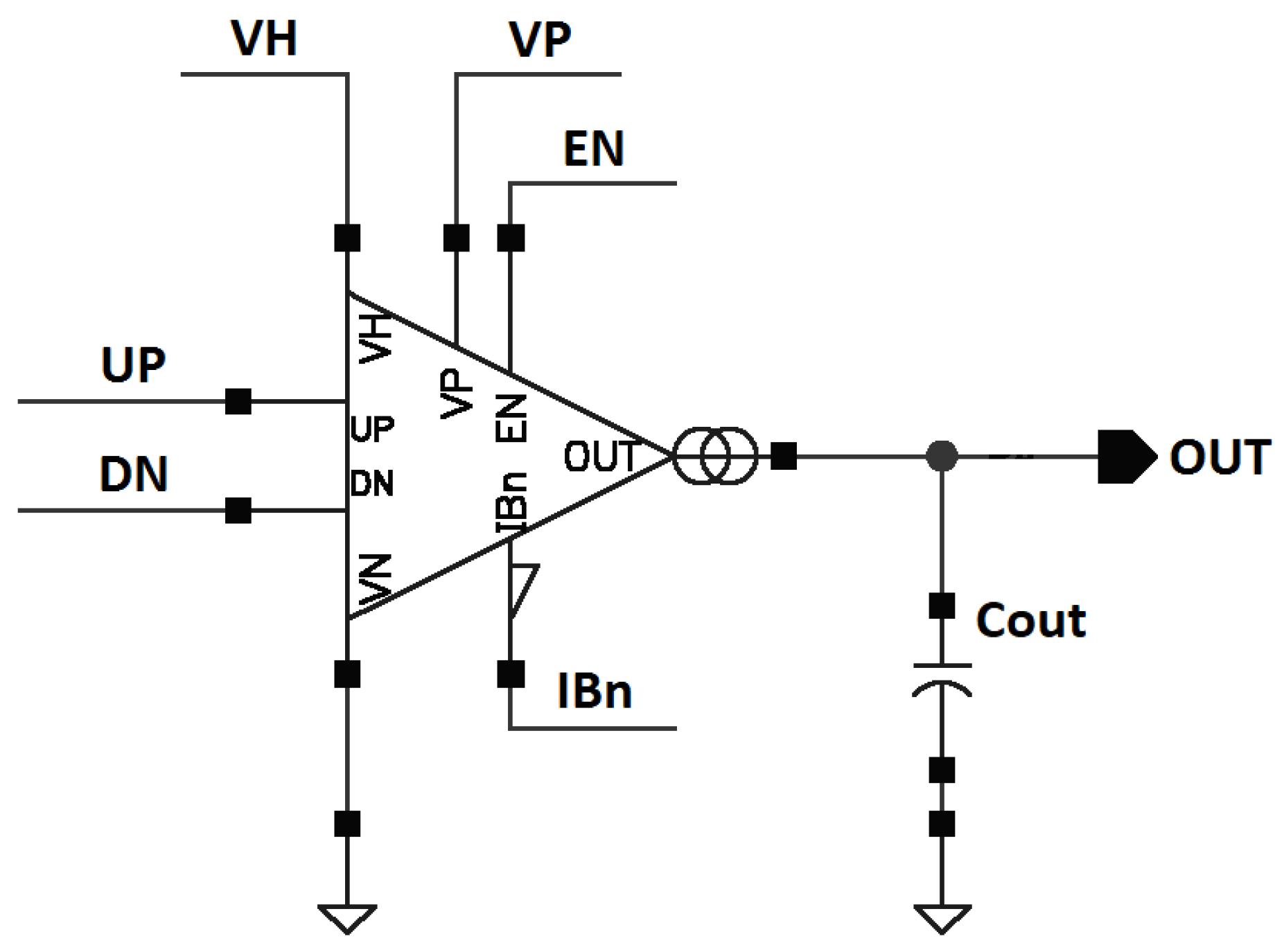
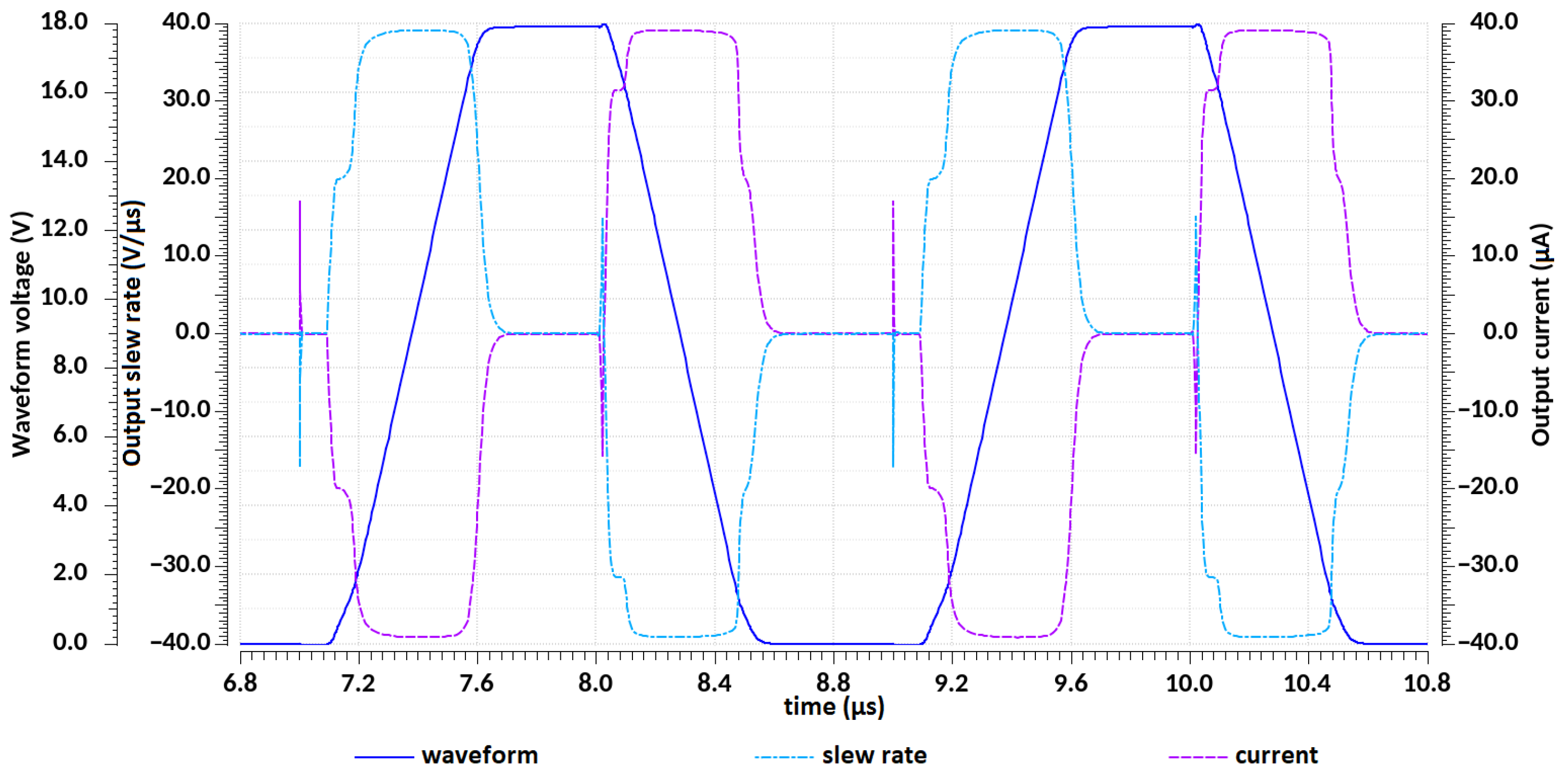
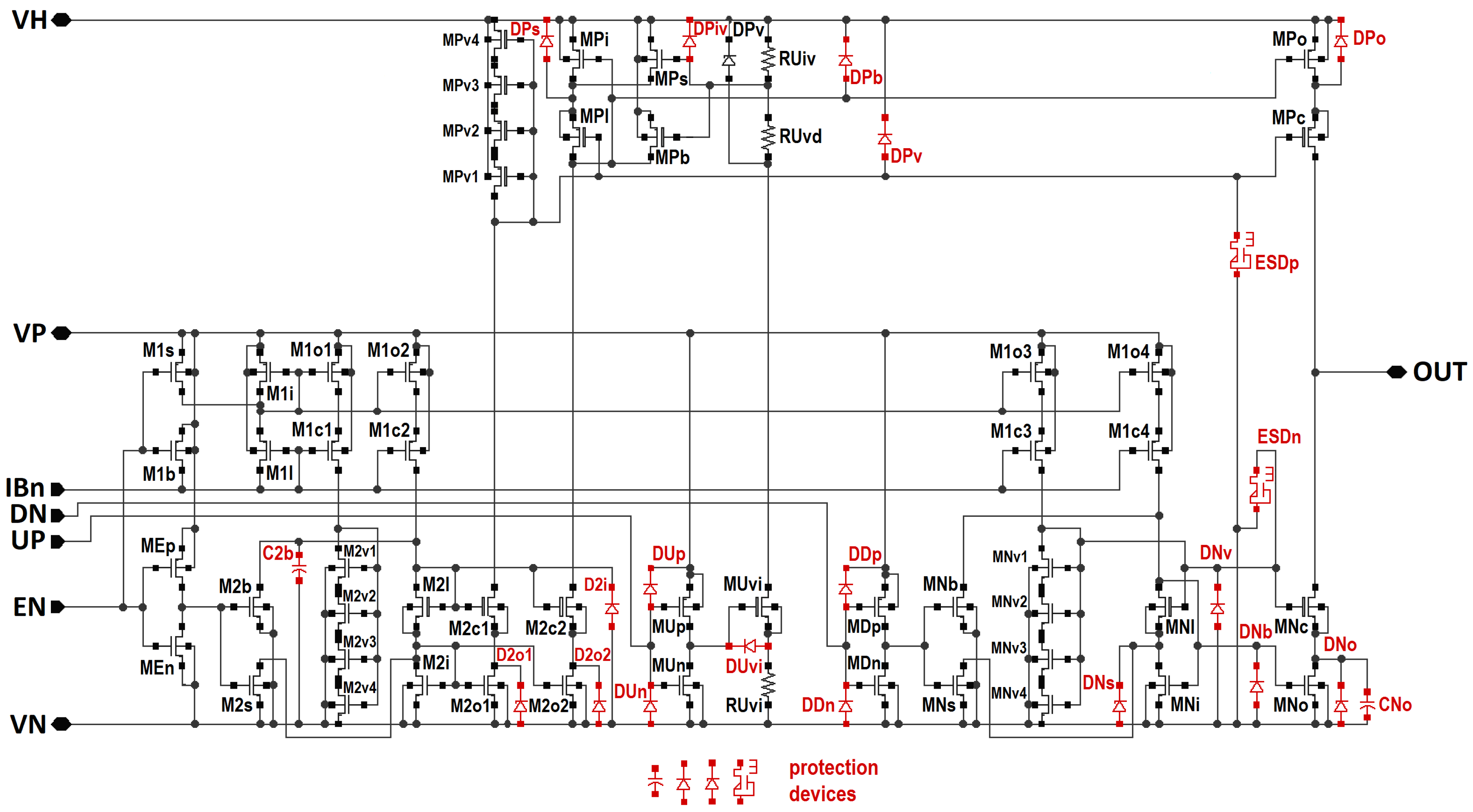
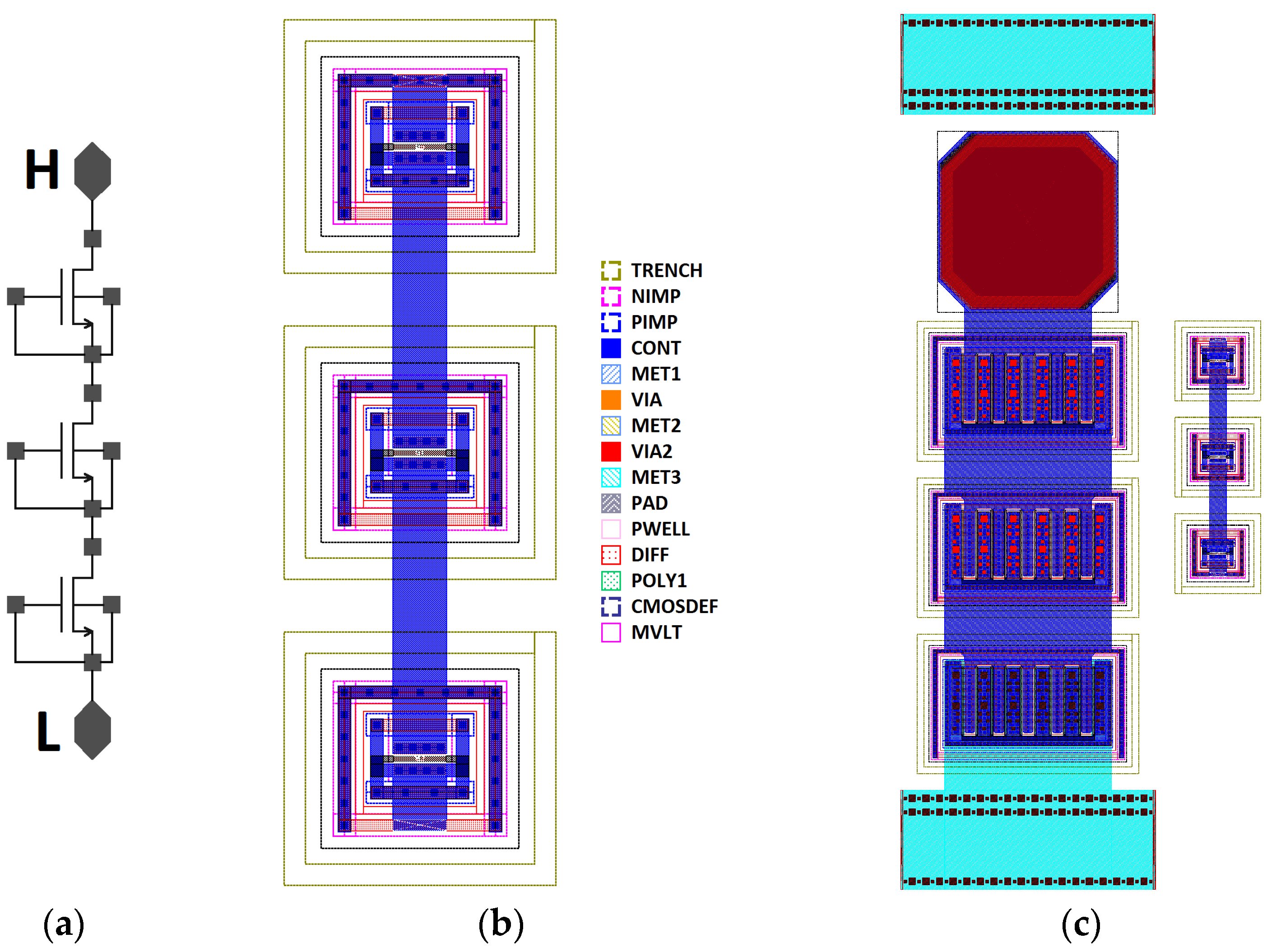
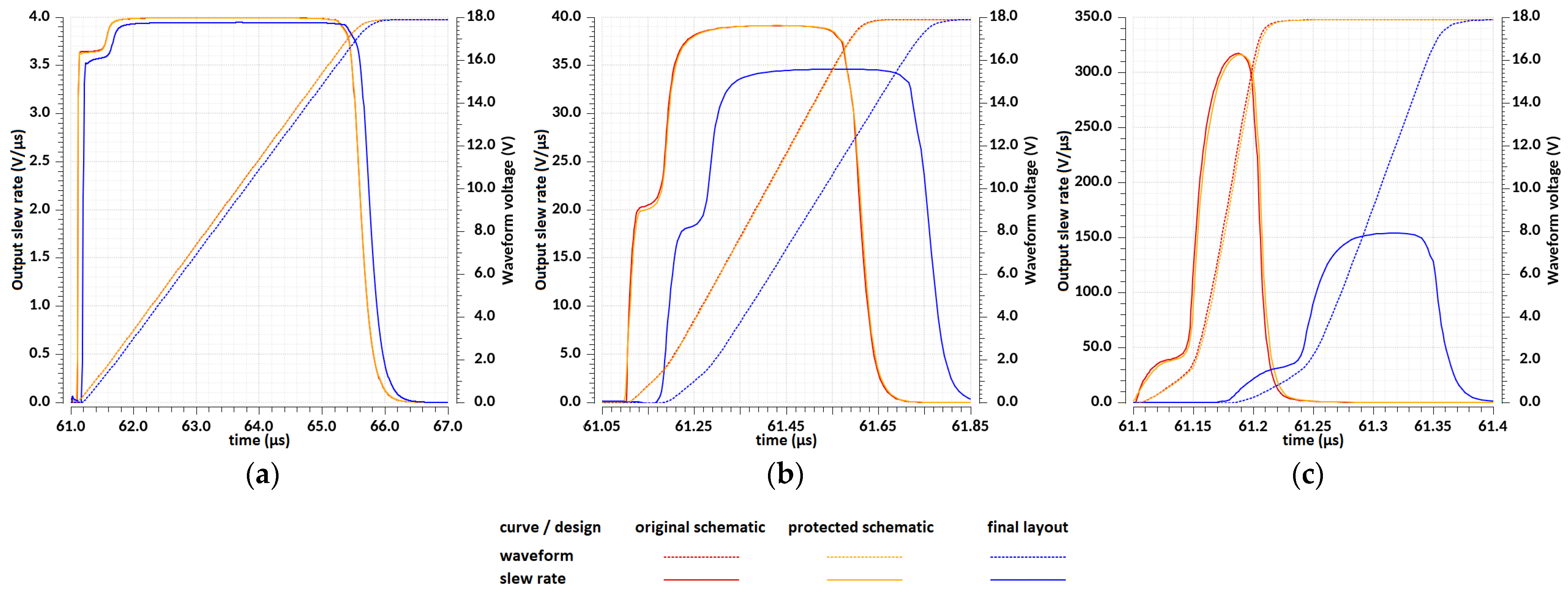

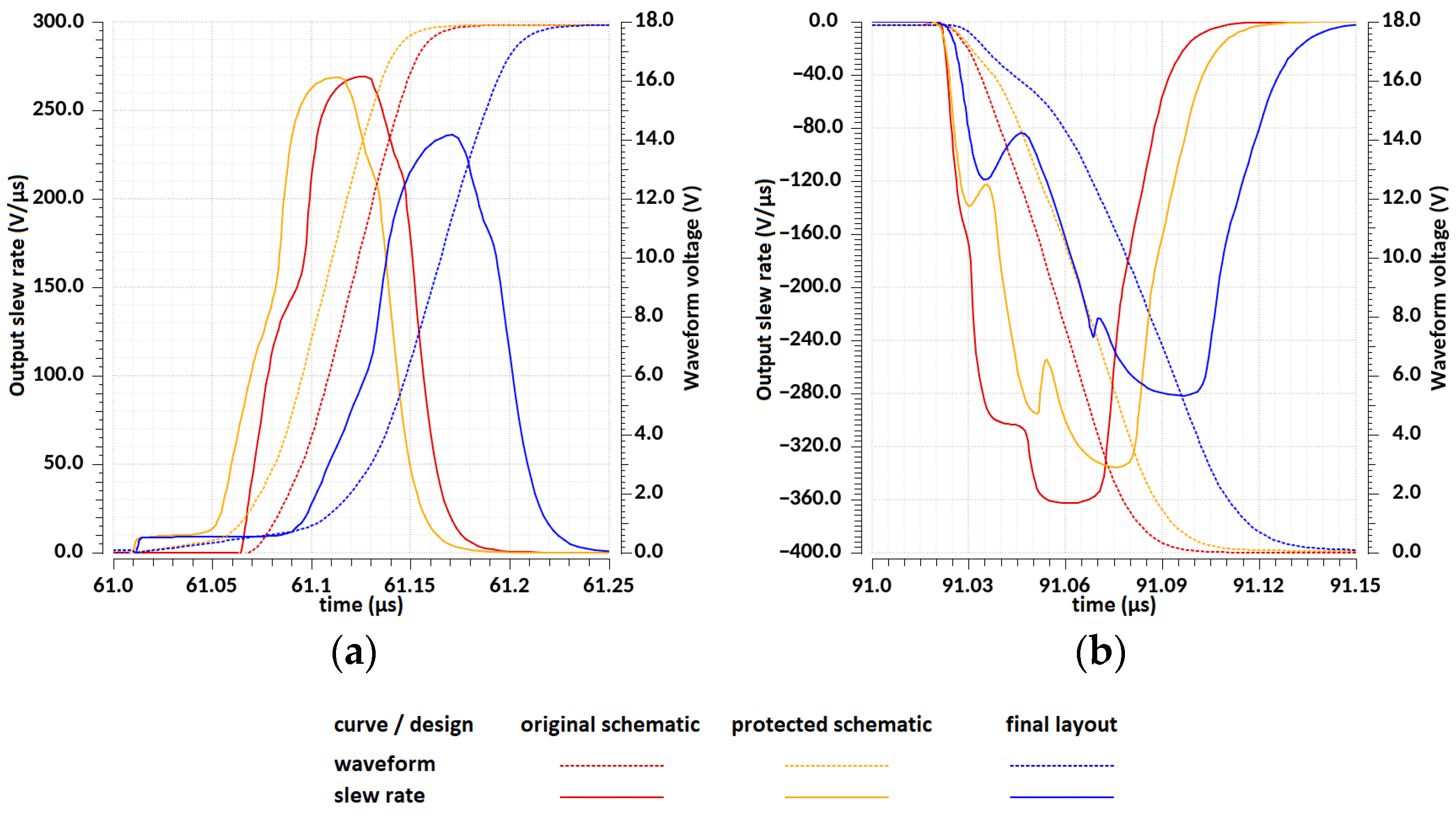
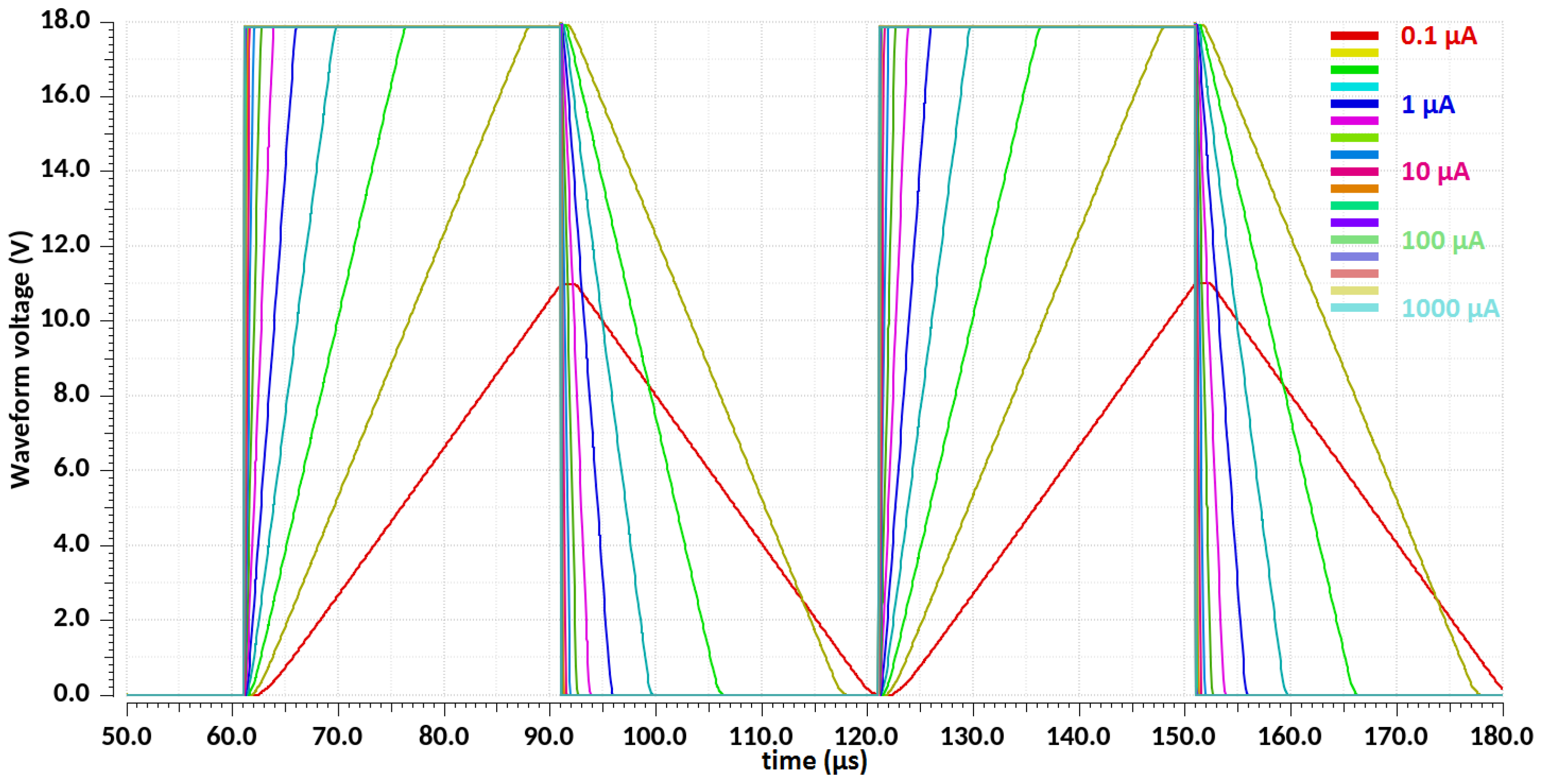


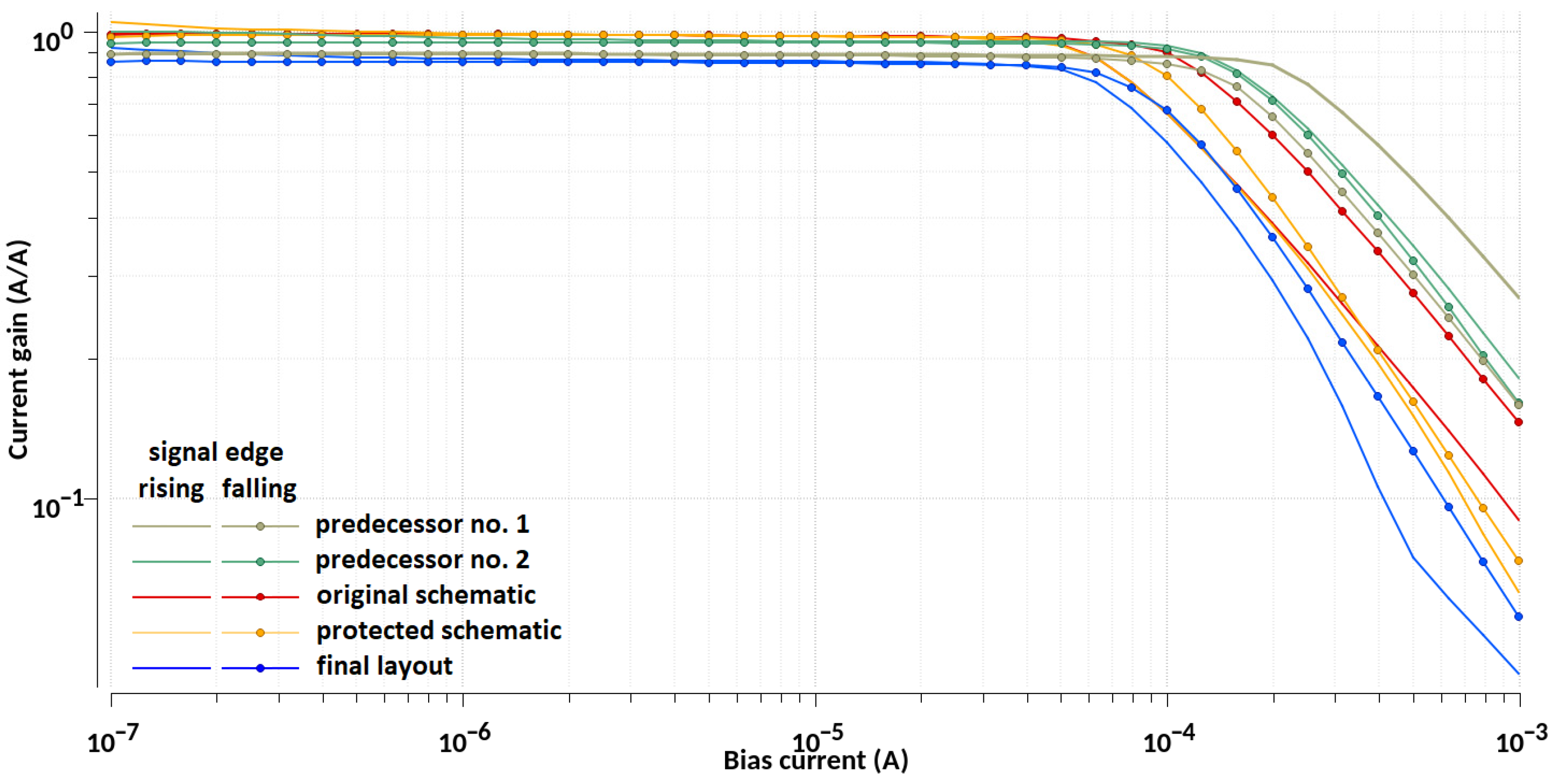
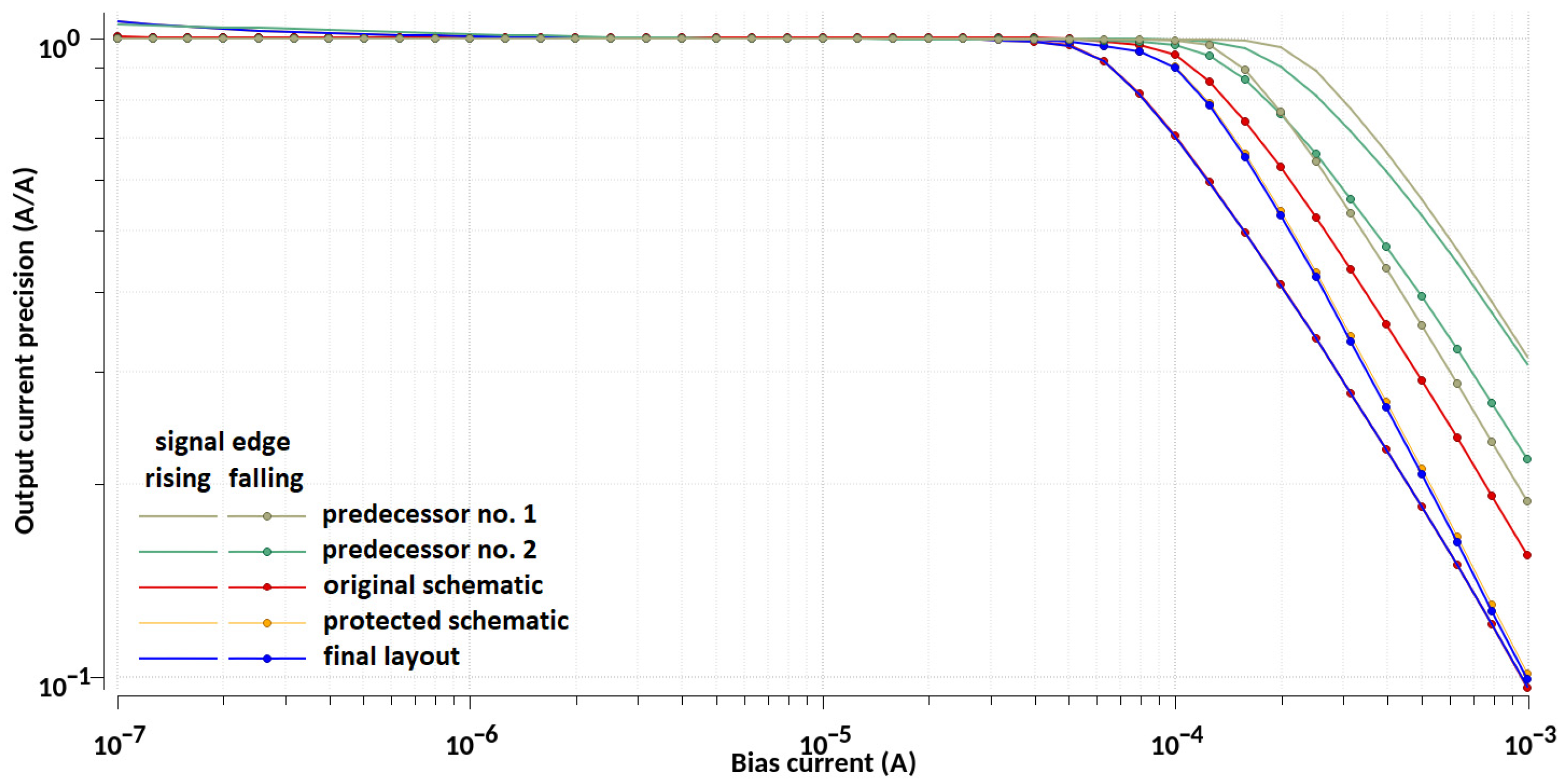

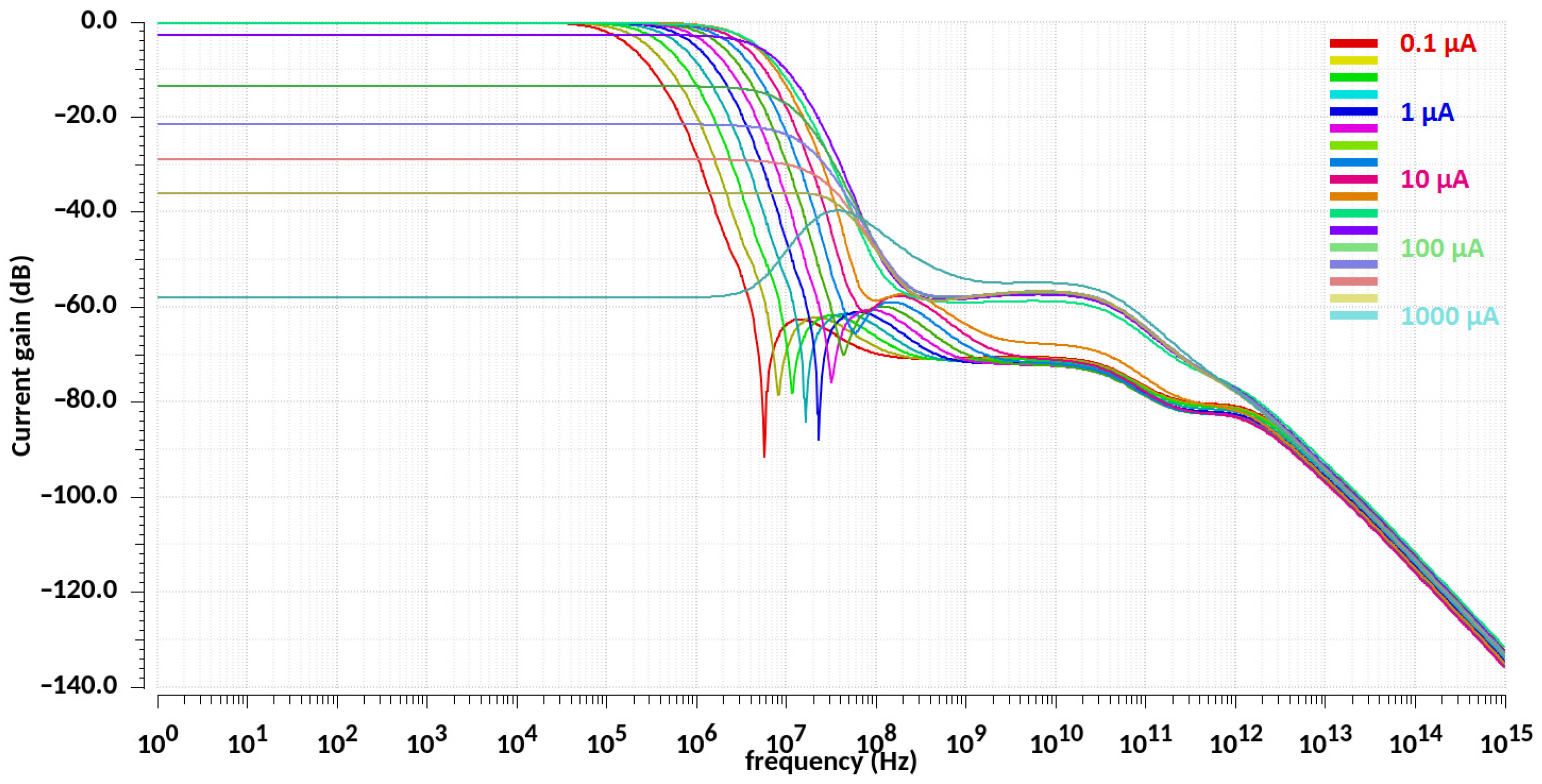

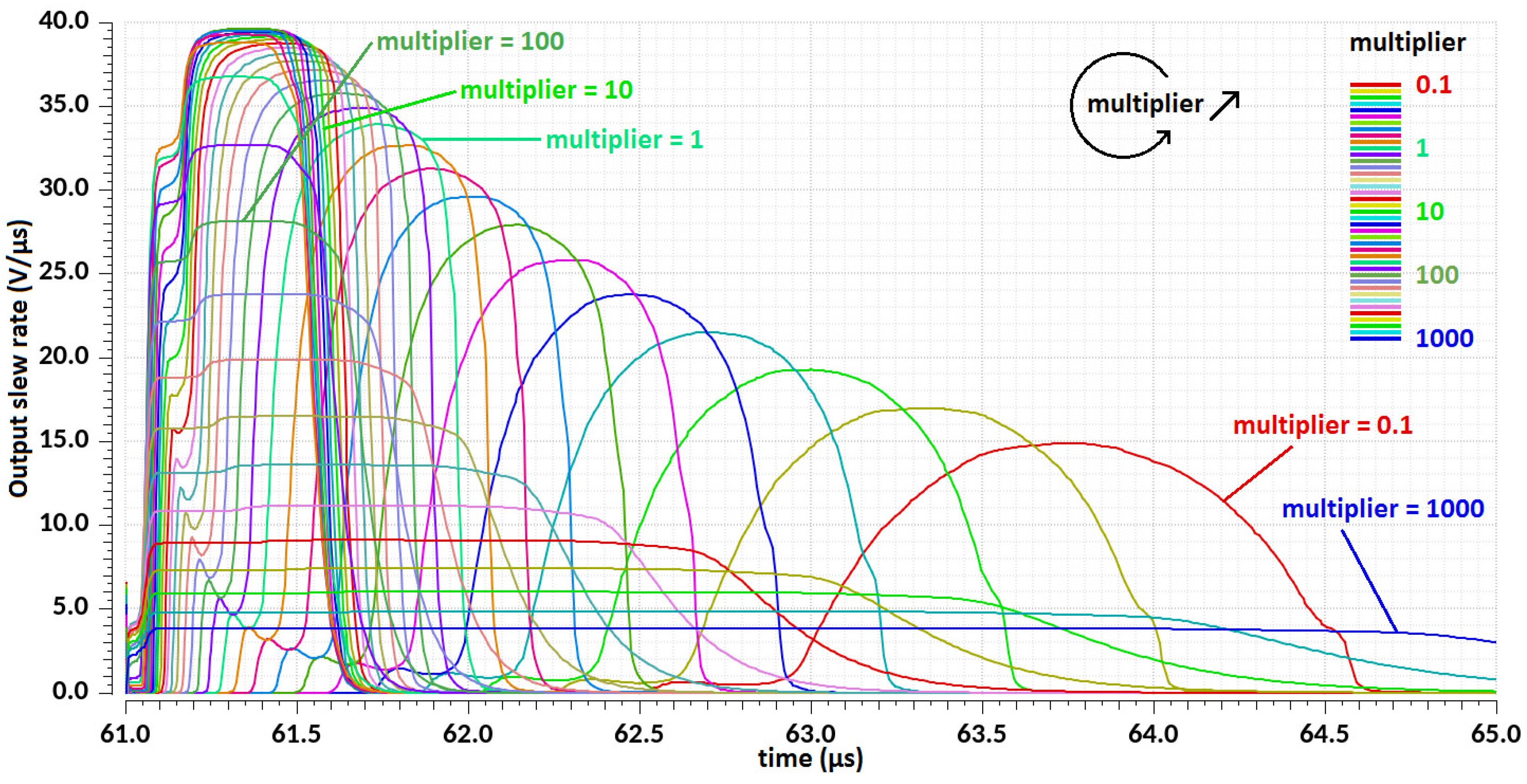
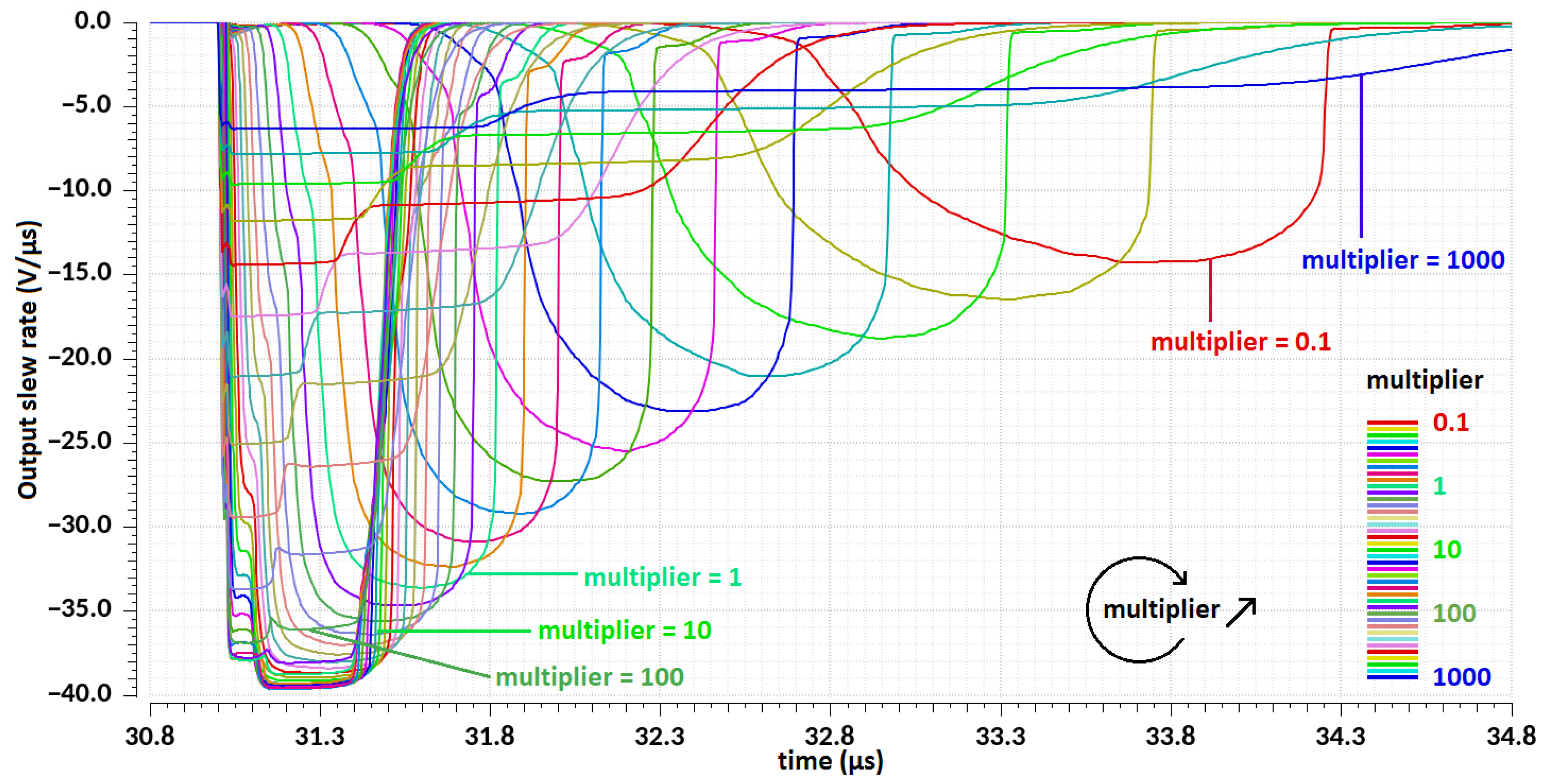
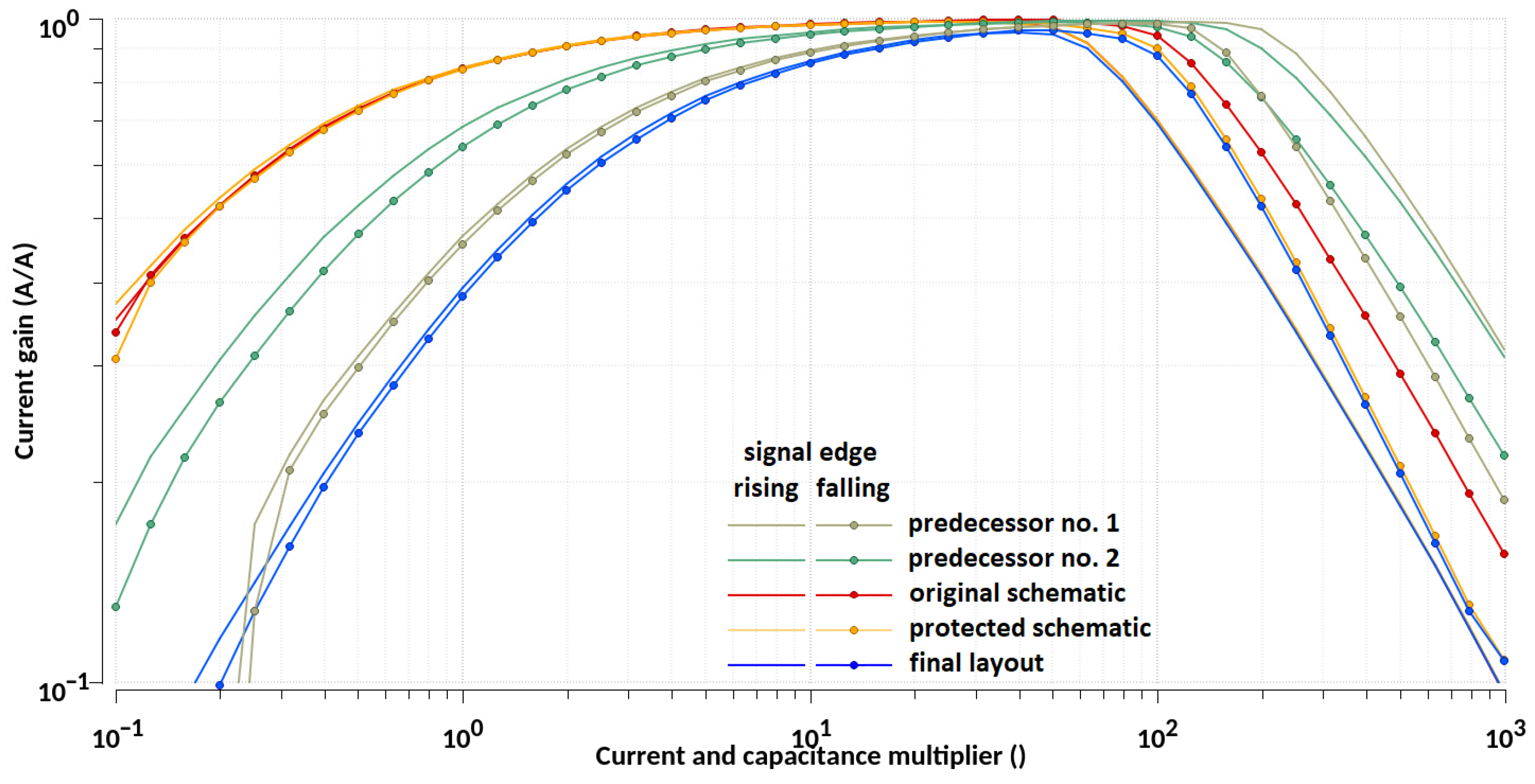
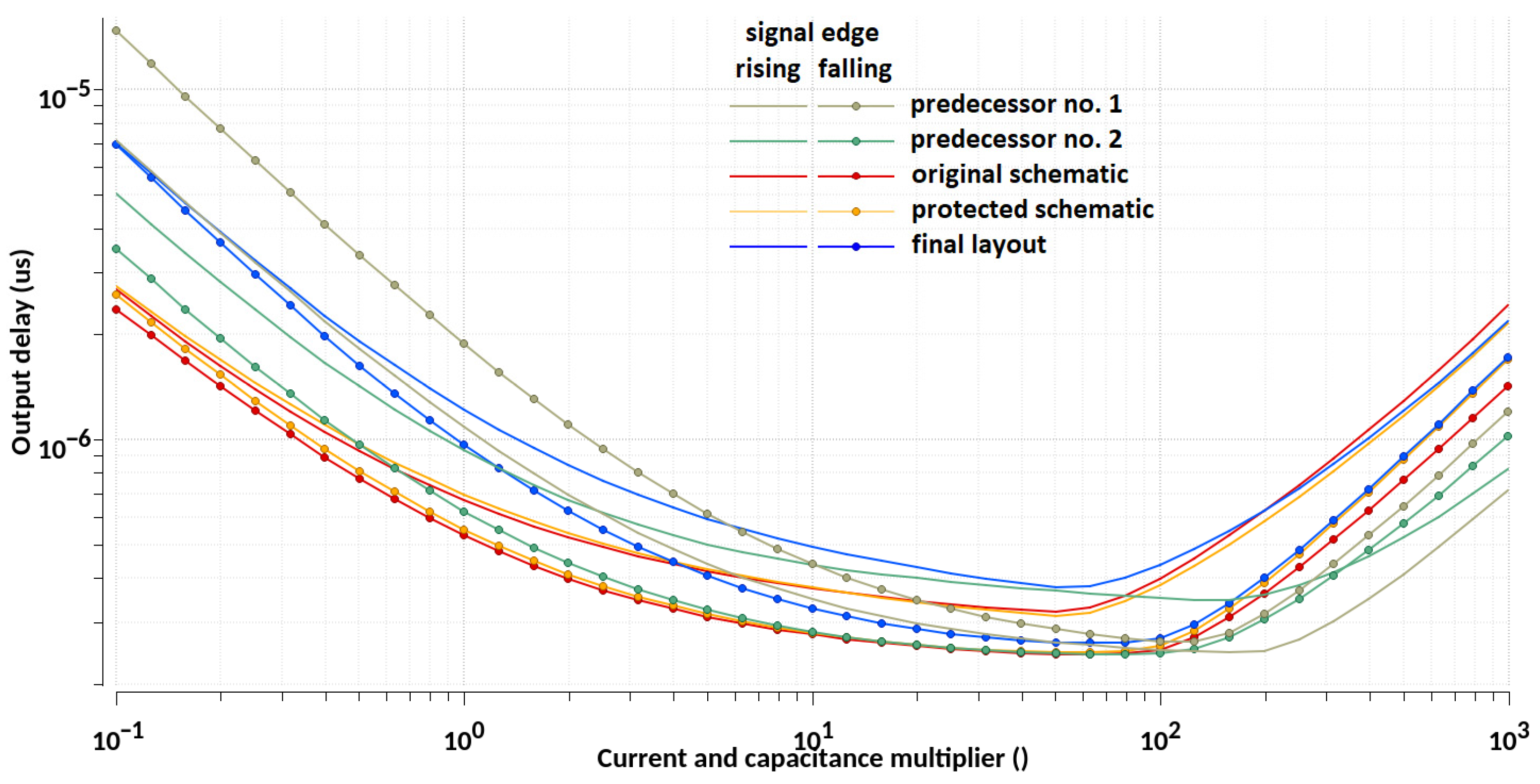
| Design Stage | Original Schematic | Protected Schematic | Final Layout | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edge Type | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling |
| Error (%) (10 µA/10 pF) | 0.132 | −0.295 | 0.123 | −0.104 | 1.349 | −1.778 |
| Error (%) (10 µA/1 pF) | 2.147 | 1.985 | 2.142 | 2.153 | 11.79 | 14.33 |
| Error (%) (10 µA/0.1 pF) | 20.72 | 20.81 | 20.98 | 21.08 | 61.57 | 63.11 |
| Error (%) (100 µA/1 pF) | 32.76 | 9.32 | 32.81 | 16.05 | 41.01 | 29.55 |
| Design Stage | Predecessor Schematic No. 1 | Predecessor Schematic No. 2 | Original Schematic | Protected Schematic | Final Layout | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edge Type | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling |
| DC Current (µA) | 156.8 | 245.5 | 201.8 | 144.3 | 67.1 | 114.3 | 66.8 | 101.6 | 66.6 | 100.1 |
| AC Current (µA) | 112.2 | 158.5 | 125.9 | 100.0 | 44.7 | 79.4 | 44.7 | 63.1 | 44.7 | 63.1 |
| Tran Current (µA) | 141.3 | 223.9 | 125.9 | 141.3 | 50.1 | 100.0 | 50.1 | 79.4 | 50.1 | 63.1 |
| Design Stage | Predecessor Schematic No. 1 | Predecessor Schematic No. 2 | Original Schematic | Protected Schematic | Final Layout | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edge Type | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling |
| Frequency (MHz) | 15.45 | 32.50 | 11.75 | 10.81 | 5.27 | 16.66 | 5.01 | 16.05 | 4.43 | 12.32 |
| Current (µA) | 79.4 | 158.5 | 158.5 | 100 | 50.1 | 19.9 | 50.1 | 19.9 | 50.1 | 31.6 |
| Design Stage | Predecessor Schematic No. 1 | Predecessor Schematic No. 2 | Original Schematic | Protected Schematic | Final Layout | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edge Type | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling |
| Min. current (µA) | 10 | 10 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 14.1 | 15.8 |
| Max. current (µA) | 158.5 | 251.2 | 199.5 | 158.5 | 63.1 | 112.2 | 63.1 | 100.0 | 63.1 | 89.1 |
| Design Stage | Predecessor Schematic No. 1 | Predecessor Schematic No. 2 | Original Schematic | Protected Schematic | Final Layout | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edge Type | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling | Rising | Falling |
| Delay (µs) | 0.2460 | 0.2642 | 0.3477 | 0.2436 | 0.3228 | 0.2429 | 0.3133 | 0.2467 | 0.3775 | 0.2625 |
| Current (µA) | 158.5 | 125.9 | 158.5 | 79.4 | 50.1 | 50.1 | 50.1 | 50.1 | 50.1 | 63.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jankowski, M. Design of a Current-Mode Trapezoidal Waveform Generator in High-Voltage SOI Technology with Modifications Based on Safe Operating Area Limits. Electronics 2025, 14, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030512
Jankowski M. Design of a Current-Mode Trapezoidal Waveform Generator in High-Voltage SOI Technology with Modifications Based on Safe Operating Area Limits. Electronics. 2025; 14(3):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030512
Chicago/Turabian StyleJankowski, Mariusz. 2025. "Design of a Current-Mode Trapezoidal Waveform Generator in High-Voltage SOI Technology with Modifications Based on Safe Operating Area Limits" Electronics 14, no. 3: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030512
APA StyleJankowski, M. (2025). Design of a Current-Mode Trapezoidal Waveform Generator in High-Voltage SOI Technology with Modifications Based on Safe Operating Area Limits. Electronics, 14(3), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030512






