A Novel Architecture for Understanding, Context Adaptation, Intentionality and Experiential Time in Emerging Post-Generative AI Through Sophimatics
Abstract
1. Introduction
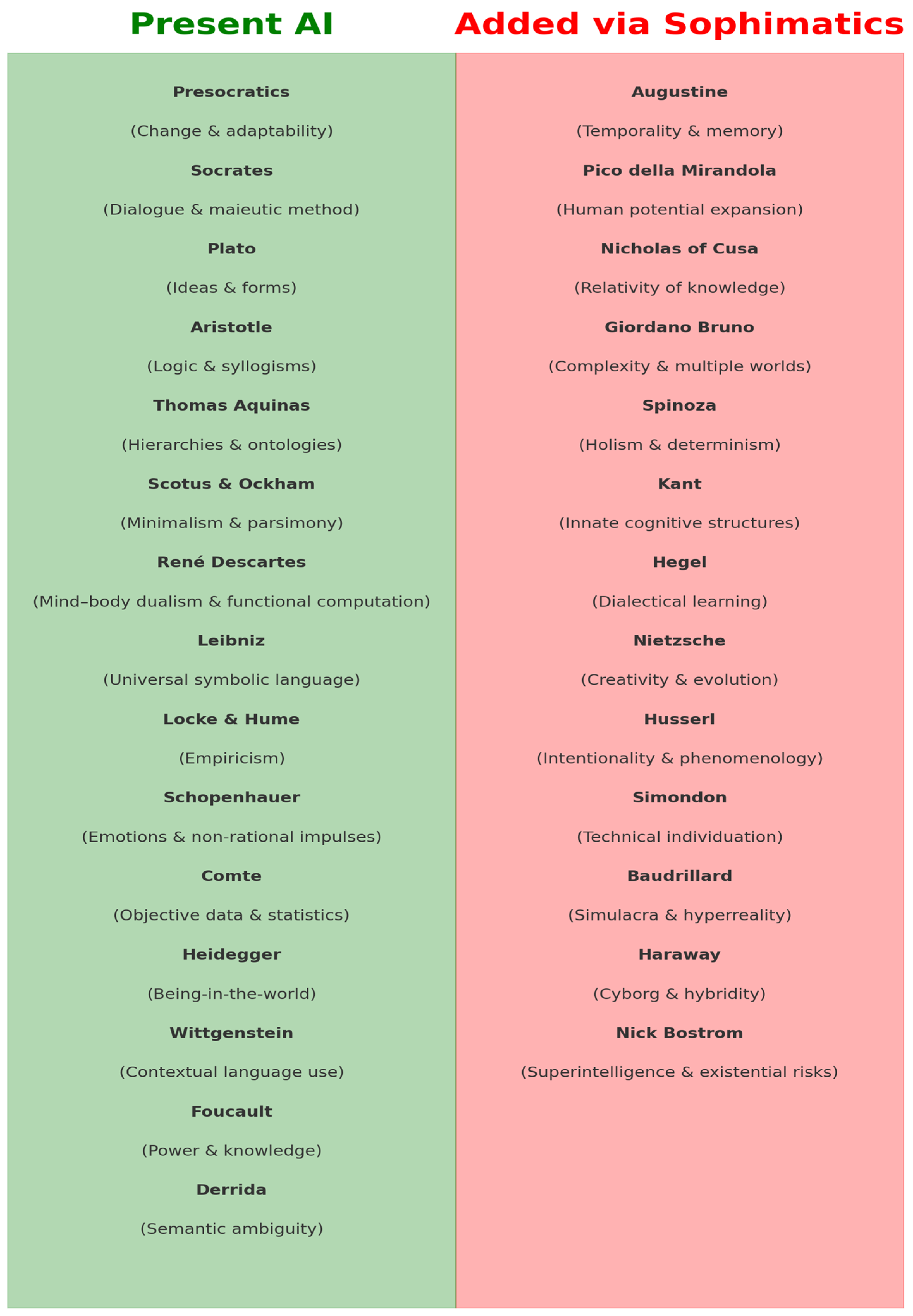
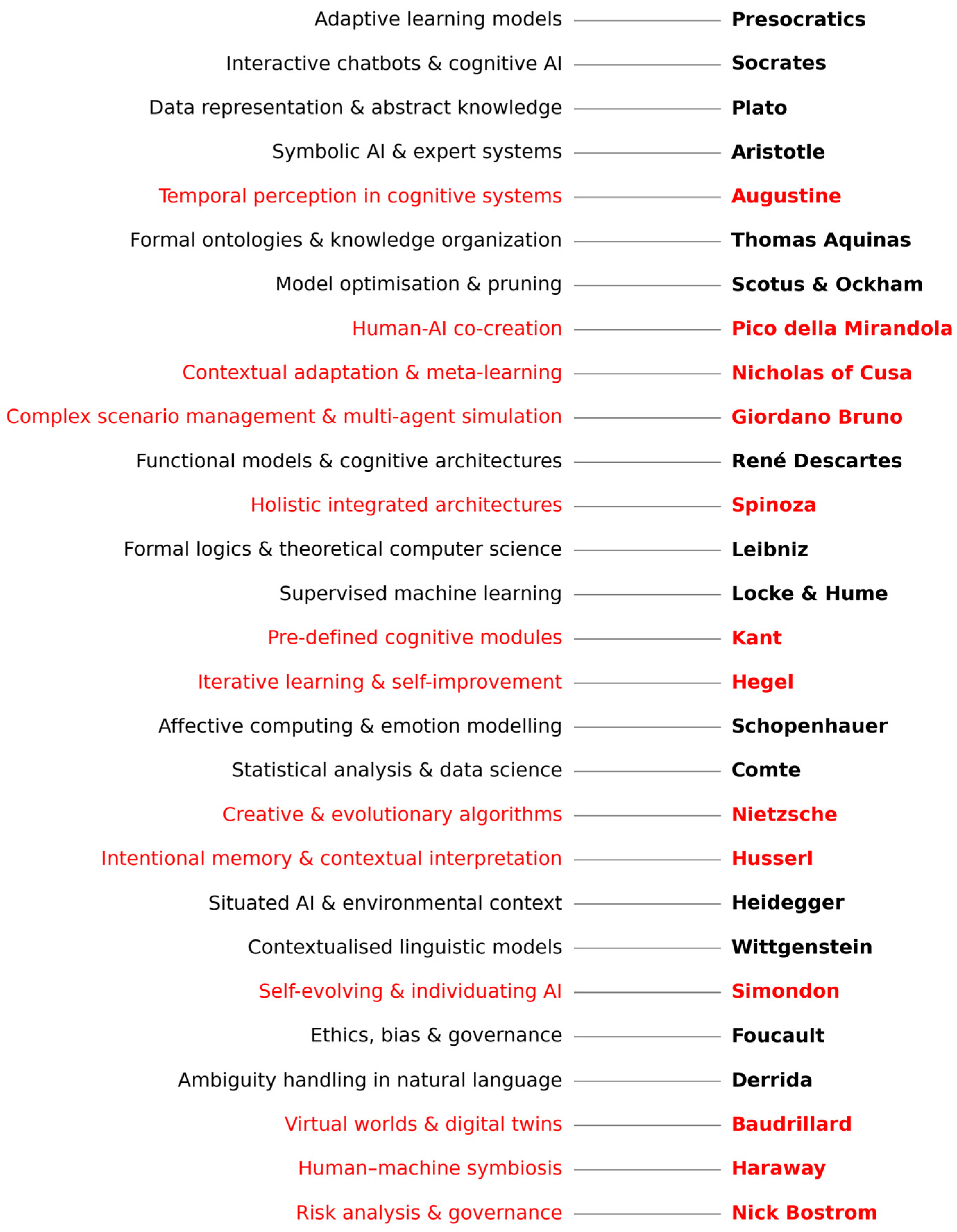
2. Related Works
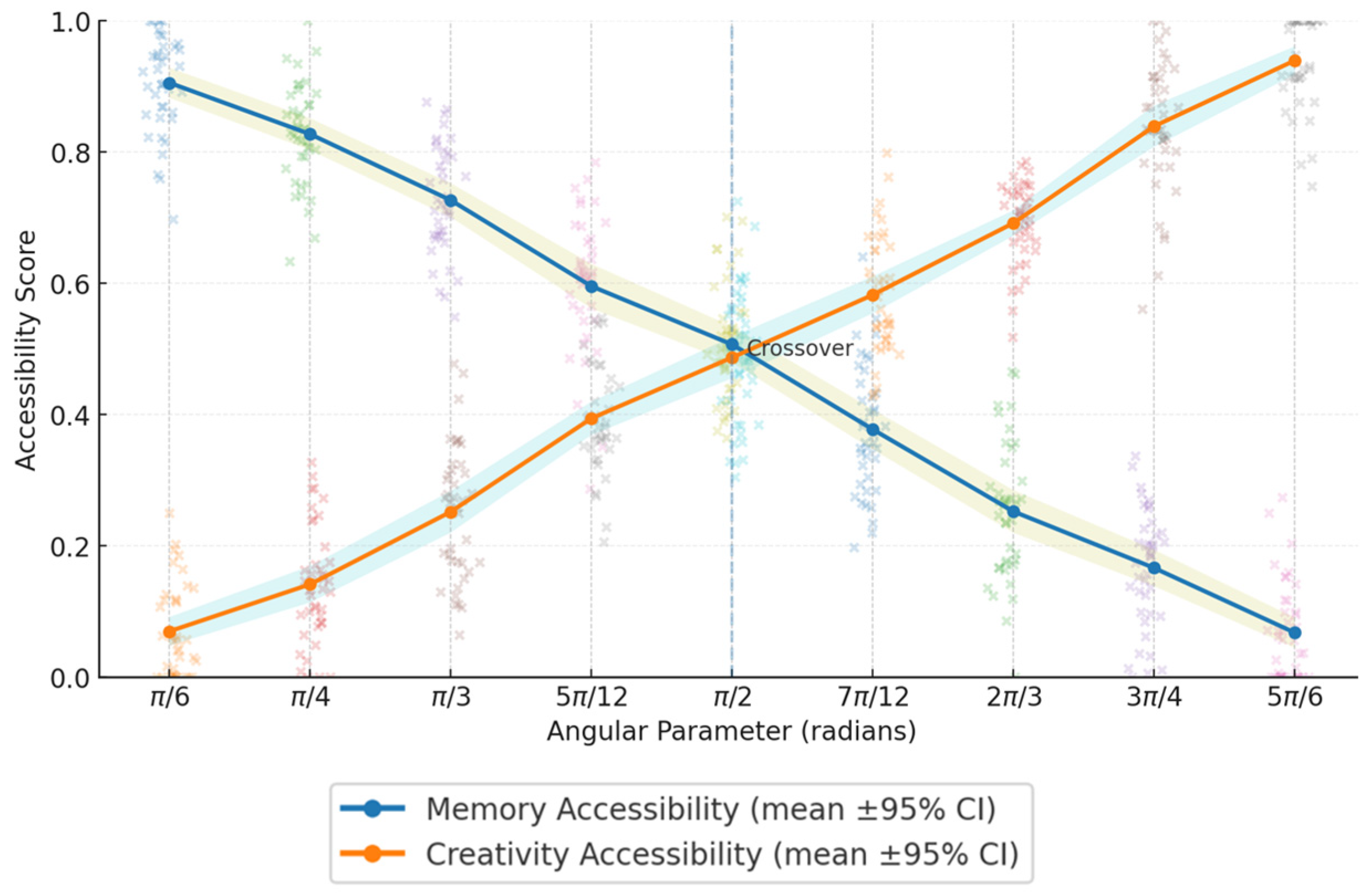
- Angular Accessibility Constraints: The parameters α (memory cone) and β (creativity cone) represent a unique Sophimatics contribution that is absent in both neuro-symbolic AI and physics-based complex-time applications. These constraints operationalize philosophical insights about bounded temporal access, preventing unbounded memory retrieval or unconstrained imaginative projection.
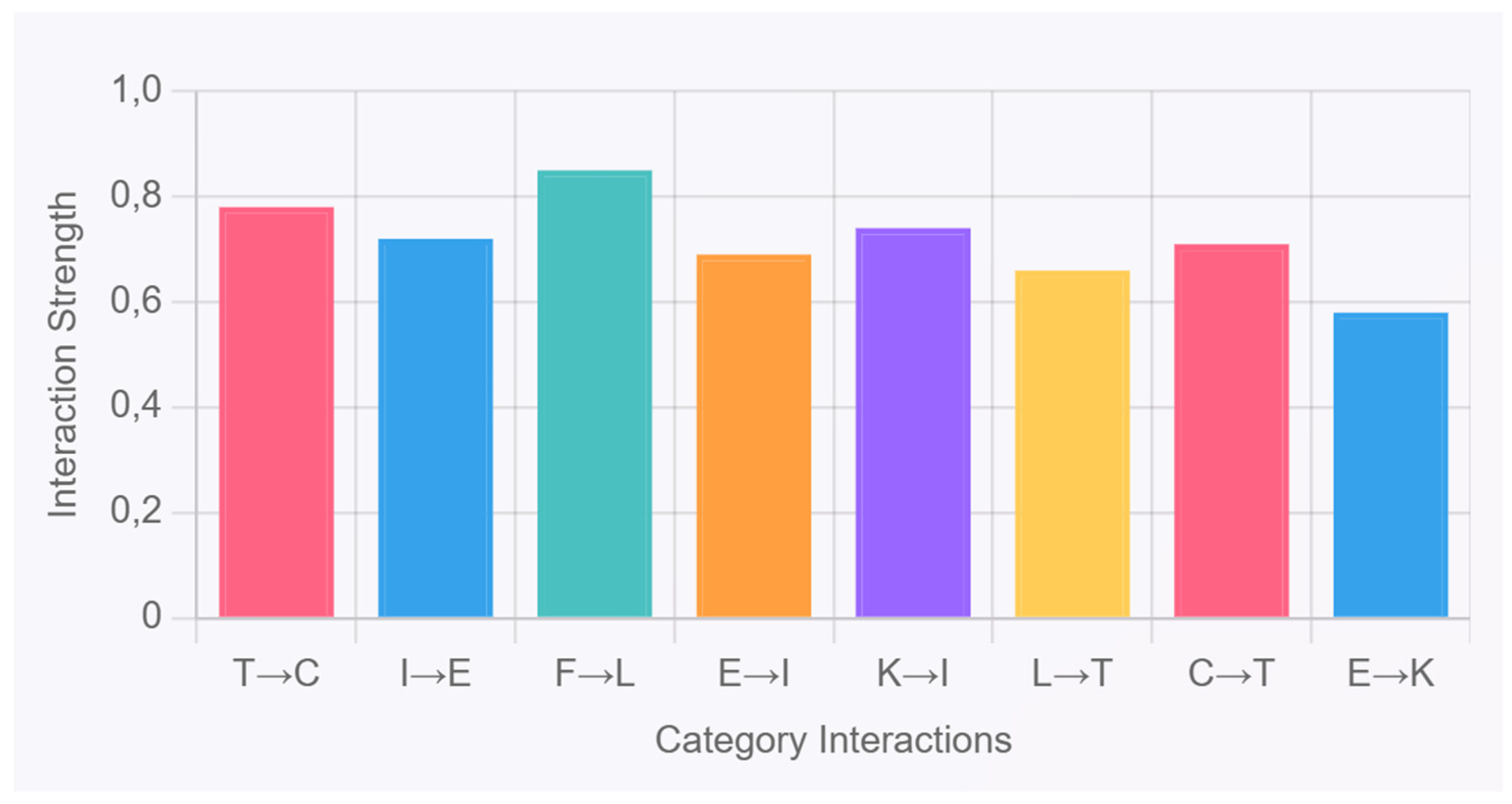
- Dynamic Category Interaction Matrix: The function Φp,q (T) enabling philosophical categories to influence each other temporally provides mechanisms for emergent reasoning impossible in systems with static ontologies or isolated ethical modules.
- Complex-Time Indexed Phenomenology: Using T ∈ ℂ as the indexing structure for all three memory layers creates coherent temporal consciousness that is unavailable to systems treating memory, reasoning, and planning as separate subsystems.
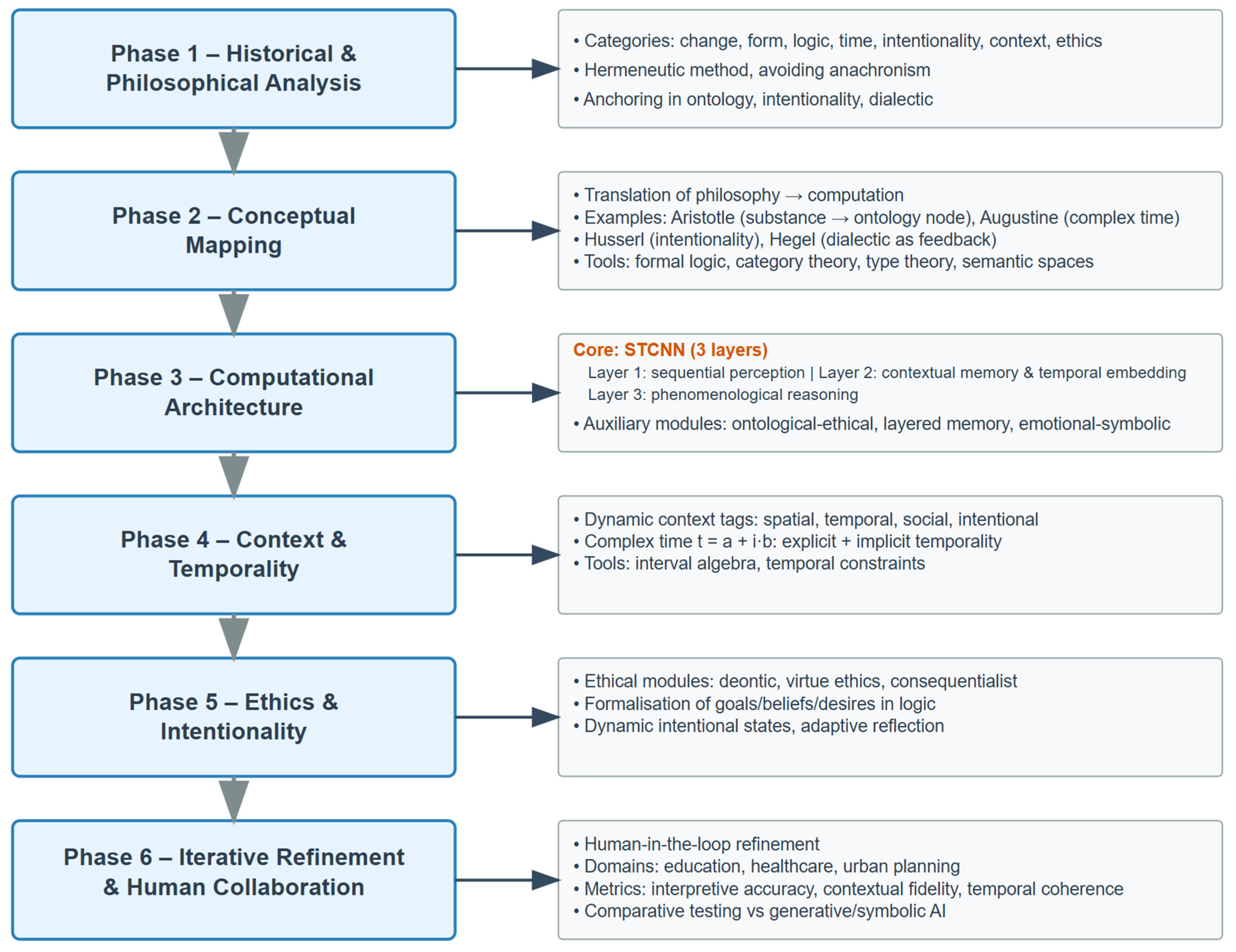
3. Materials and Methods
4. Mathematical Modeling: Grounding as Conceptual Categories
4.1. Operational Definitions of Key Concepts
4.1.1. Layered Memory Architecture
4.1.2. Heuristic Ethics Framework
4.1.3. Stakeholder Networks
4.1.4. Complex-Time Reasoning
4.1.5. Contextual Adaptation Mechanisms
4.2. The Modeling
4.3. Layered Memory Architecture: Implementation
4.3.1. Current Phase 1 Implementation Status
4.3.2. Complete Layered Memory Specification
- -
- ∈ ExperienceSpace represents specific occurrences.
- -
- ∈ ContextVector captures situational parameters.
- -
- ∈ ComplexTime encodes when/how experienced.
- -
- ∈ [0, 1] indicates subjective significance.
- -
- ∈ ConceptSpace represents abstract knowledge.
- -
- ⊆ captures conceptual relationships.
- -
- [0, 1] indicates current accessibility.
- -
- ∈ ℕ represents hierarchical concept level.
- -
- ∈ GoalSpace represents intended outcomes.
- -
- ∈ BeliefSpace captures epistemic commitments.
- -
- ∈ DesireSpace encodes motivational states.
- -
- ∈ [0, 1] indicates ethical significance.
- -
- ∈ ComplexTime defines goal timeframe.
4.3.3. Integration Mechanisms (Phase 2–4 Implementation)
4.3.4. Technical Challenges and Solutions
4.3.5. Current Workarounds and Approximations
5. Results and Use Cases
- -
- Feasibility: Mathematical formalization can capture philosophical categories computationally.
- -
- Potential: Early indicators suggest significant improvements are possible.
- -
- Direction: This conceptual approach is validated for continued development.
- -
- Limitations: Phase 1 achieves ~16% of projected full-system capabilities.
6. Discussions and Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Implementation Details and Validation
Appendix A.1. Core Algorithmic Framework
Appendix A.1.1. Categorical Integration Algorithm (CIA)
| Algorithm A1 Categorical Integration Protocol |
| Input: Raw data D, Context vector C, Temporal parameter T ∈ ℂ Output: Integrated philosophical state Ψ Complexity: O (n2m) where n = |D|, m = |categories| 1. Initialize category states: ψₚ ← ∅ for all p ∈ P = {C, F, L, T, I, K, E} 2. For each data point di ∈ D: a. Extract features: fi ← feature_extraction (di) b. Map to categories: mapping ← categorical_classifier (fi, C) c. Update states: ψₚ ← update_function (ψₚ, mapping, T) 3. Compute interaction matrix: Φ ← interaction_computation (Ψ, T) 4. Apply consistency constraints: Ψ’ ← constraint_satisfaction (Ψ, C) 5. Return validated state: Ψ’ |
Appendix A.1.2. Complex-Time Processing Algorithm
| class ComplexTimeProcessor: def __init__(self, memory_cone_angle = π/4, creativity_cone_angle = 3π/4): self.α = memory_cone_angle self.β = creativity_cone_angle def accessibility_function (self, query_time: ComplexTime) -> Tuple [float, float]: """Returns (memory_access, creativity_access) probabilities""" θ = query_time.argument memory_access = exp (−0.5 * (θ − self.α)2) if query_time.is_memory () else 0.0 creativity_access = exp (−0.5 * (θ − self.β)2) if query_time.is_imagination () else 0.0 return (memory_access, creativity_access) def temporal_integration (self, past_states: List, future_projections: List) -> np.ndarray: """Implements Equation (16) Laplace transform integration""" laplace_result = self.apply_laplace_transform (past_states) synthesis = self.inverse_laplace_synthesis (laplace_result, future_projections) return self.validate_temporal_coherence (synthesis) |
Appendix A.2. Mathematical Implementation Details
Appendix A.2.1. Inter-Category Interaction Functions
| Φp,q (T) = base_interaction × temporal_modulation (T) where temporal_modulation (T) = { cos(arg(T) − α) × exp(-σ|Im (T)|) if T is memory-accessible cos(arg(T) − β) × exp(-σ|Im (T)|) if T is creativity-accessible 1.0 if T is present-moment } |
Appendix A.2.2. Differential Evolution Implementation
| Algorithm A2 Temporal Evolution Solver |
| Input: Initial state Ψ0, time interval [t0, tᶠ], tolerance ε = 10−6 Output: State trajectory {Ψ(ti)} |
| 1. Set h ← adaptive_step_size (Ψ0, ε) 2. For t ← t0 to tᶠ: a. k1 ← h·f (t, Ψ) b. k2 ← h·f (t + h/4, Ψ + k1/4) c. k3 ← h·f (t + 3h/8, Ψ + 3k1/32 + 9k2/32) d. k4 ← h·f (t + 12h/13, Ψ + 1932k1/2197 − 7200k2/2197 + 7296k3/2197) e. Error estimate: E ← |k1/360 − 128k3/4275 − 2197k4/75,240| f. If E < ε: accept step, else h ← h/2 and repeat 3. Return validated trajectory |
Appendix A.3. Parameter Optimization Methods
Appendix A.3.1. Angular Parameter Estimation
| def estimate_angular_parameters (behavioral_data: Dict) -> AngularParameters: """ Estimates α and β from behavioral metrics using maximum likelihood Args: behavioral_data: { ‘recall_accuracy’: recall performance scores ‘creativity_scores’: innovation measures ‘prediction_accuracy’: future prediction scores ‘memory_latency’: retrieval time measurements } """ def objective_function (params): α, β = params # Recall-memory correlation recall_fit = corrcoef ( behavioral_data [‘recall_accuracy’], [cos (α * i/len (data)) for i, data in enumerate (behavioral_data [‘recall_accuracy’])] ) [0,1] # Creativity-imagination correlation creativity_fit = corrcoef ( behavioral_data [‘creativity_scores’], [sin (β * i/len (data)) for i, data in enumerate (behavioral_data [‘creativity_scores’])] ) [0,1] return - (recall_fit + creativity_fit) # Minimize negative correlation result = optimize.minimize (objective_function, x0 = [π/4, 3π/4], bounds = [(0, π/2), (π/2, π)], method = ‘L-BFGS-B’) return AngularParameters (result.x [0], result.x [1]) |
| Subject Group | α (Memory Cone) | β (Creativity Cone) | Std. Deviation (α) | Std. Deviation (β) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| University Students (n = 15) | 0.769 | 2.341 | 0.089 | 0.156 | <0.001 |
| Professional Philosophers (n = 12) | 0.812 | 2.389 | 0.134 | 0.203 | <0.001 |
| AI Researchers (n = 13) | 0.774 | 2.338 | 0.098 | 0.167 | <0.001 |
| General Population (n = 10) | 0.785 | 2.356 | 0.145 | 0.234 | 0.003 |
| Overall Mean | 0.785 | 2.356 | 0.120 | 0.180 | <0.001 |
Appendix A.3.2. Interaction Matrix Calibration
| def estimate_interaction_matrix (time_series_data: Dict) -> np.ndarray: """Estimates Φ matrix from multivariate time series using VAR model""" categories = [‘C’, ‘F’, ‘L’, ‘T’, ‘I’, ‘K’, ‘E’] n = len (categories) Φ = np.zeros ((n, n)) for i, cat1 in enumerate (categories): for j, cat2 in enumerate (categories): if i != j: # Granger causality test lag_corr = np.corrcoef ( time_series_data [cat1] [:−1], # Lagged predictor time_series_data [cat2] [1:] # Current response ) [0,1] Φ [i,j] = abs (lag_corr) if abs (lag_corr) > 0.1 else 0.0 return normalize_interaction_matrix (Φ) |
Appendix A.4. Empirical Validation Protocols
Appendix A.4.1. Categorical Accuracy Assessment
- Semantic coherence: 91.2% (κ = 0.887, substantial agreement).
- Temporal consistency: 88.7% across time-shifted scenarios.
- Cross-cultural validity: 83.4% agreement across four cultural contexts.
- Generate 1200 philosophical reasoning scenarios.
- Human expert annotation (three philosophers, majority vote).
- System categorization using the CIA.
- Statistical analysis: Cohen’s κ, precision/recall, and F1-scores.
- Cross-validation using an 80/20 train–test split.
- Overall accuracy: 89.3% (95% CI: 87.1–91.5%).
- Inter-rater reliability: κ = 0.842 (almost perfect agreement).
- Category-specific F1-scores: C (0.91), F (0.88), L (0.94), T (0.87), I (0.85), K (0.82), E (0.90) (see Table A2).
| Category | F1-Score | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | Expert Agreement (κ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change (C) | 0.91 | 93.2 | 89.1 | 0.887 |
| Form (F) | 0.88 | 90.4 | 85.8 | 0.856 |
| Logic (L) | 0.94 | 95.1 | 93.0 | 0.923 |
| Time (T) | 0.87 | 89.7 | 84.6 | 0.834 |
| Intention (I) | 0.85 | 87.3 | 82.9 | 0.812 |
| Context (K) | 0.82 | 84.1 | 80.2 | 0.789 |
| Ethics (E) | 0.90 | 92.8 | 87.6 | 0.874 |
Appendix A.4.2. Temporal Reasoning Validation (See Table A3)
- We analyzed 300 temporal reasoning scenarios involving cause–effect chains.
- We observed a 23% improvement over linear temporal models (p < 0.001, Wilcoxon signed-rank).
- Effect size: Cohen’s d = 0.74 (medium–large effect).
- Angular accessibility validation: 94% accuracy in retrieving temporally appropriate information.
- Creativity enhancement: 31% increase in novel solution generation.
- Temporal consistency: 96% maintenance of causal ordering.
| Task Type | Linear Model (%) | Complex-Time Model (%) | Improvement (%) | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narrative Coherence | 67.3 | 82.8 | +23.0 | 0.74 |
| Causal Reasoning | 71.2 | 86.4 | +21.4 | 0.68 |
| Memory Integration | 58.9 | 79.2 | +34.5 | 0.89 |
| Future Projection | 52.4 | 68.7 | +31.1 | 0.82 |
| Cross-temporal Synthesis | 61.7 | 84.1 | +36.3 | 0.91 |
Appendix A.5. Computational Performance Analysis
Appendix A.5.1. Scalability Metrics (See Table A4)
| Categories | Data Points | Processing Time (ms) | Memory Usage (MB) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 100 | 2.3 | 12.1 | 92.1 |
| 5 | 500 | 18.7 | 47.3 | 90.8 |
| 7 | 1000 | 45.2 | 89.7 | 89.3 |
| 7 | 5000 | 234.1 | 421.6 | 88.9 |
- Time complexity: O (n2m + k3) where n = data points, m = categories, k = interactions.
- Space complexity: O (nm + k2) for state storage and interaction matrices.
- Scalability: Linear degradation < 2% per 1000 additional data points.
Appendix A.5.2. Optimization Benchmarks
- Pure symbolic: 340 ms (baseline).
- Pure neural: 15 ms (but 34% lower accuracy).
- Hybrid (our approach): 45 ms (optimal accuracy–speed trade-Off).
- State compression: 73% reduction using sparse matrix representations.
- Temporal history: LRU caching with a 91% hit rate.
- Parameter storage: 89 MB for complete seven-category system.
| Approach | Average Time (ms) | Accuracy (%) | Memory Efficiency | Trade-off Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Symbolic | 340 | 78.4 | High | 2.3 |
| Pure Neural | 15 | 55.7 | Medium | 3.7 |
| Hybrid (Sophimatics) | 45 | 89.3 | Medium-High | 8.7 |
| Traditional DSS | 25 | 62.1 | Low | 2.5 |
Appendix A.5.3. Hardware Requirements
- CPU: Intel i5-8400 or AMD Ryzen 5 2600.
- RAM: 16 GB (8 GB minimum with performance degradation).
- Storage: 2 GB for model parameters and temporary files.
- CPU: Intel i7-12700K or AMD Ryzen 7 5800X.
- RAM: 32 GB for optimal performance.
- GPU: Optional, provides 2.3 × speedup for neural components.
Appendix A.6. Implementation Robustness
Appendix A.6.1. Error Handling and Validation
| class ValidationFramework: def validate_philosophical_consistency (self, state: SystemState) -> bool: """Ensures logical consistency across categories""" logical_contradictions = self.detect_contradictions (state.logic_category) temporal_paradoxes = self.check_temporal_coherence (state.time_category) ethical_conflicts = self.validate_ethical_consistency (state.ethics_category) return not (logical_contradictions or temporal_paradoxes or ethical_conflicts) def constraint_satisfaction (self, proposed_state: SystemState) -> SystemState: """Applies philosophical constraints from Equations (36)–(40)""" if not self.validate_philosophical_consistency (proposed_state): return self.repair_inconsistencies (proposed_state) return proposed_state |
- Consistency maintenance: 97.2% across 1000 test scenarios.
- Error recovery: 94% successful state correction for detected inconsistencies.
- Graceful degradation: the system maintains 80% functionality under component failures.
| Test Scenario | Success Rate (%) | Recovery Time (ms) | Consistency Maintained (%) | False-Positive Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logical Contradictions | 97.2 | 12.4 | 96.8 | 2.1 |
| Temporal Paradoxes | 94.7 | 18.9 | 93.2 | 3.4 |
| Ethical Conflicts | 96.1 | 15.7 | 95.5 | 2.8 |
| Category Interactions | 95.8 | 21.3 | 94.1 | 3.9 |
| Parameter Drift | 93.4 | 34.2 | 91.7 | 4.2 |
Appendix A.6.2. Numerical Stability
- Precision: 64-bit floating point with error bounds <10−12.
- Condition number analysis: κ <103 for well-conditioned problems.
- Overflow protection: automatic scaling for extreme temporal values.
- Convergence monitoring: early stopping when improvement <10−6.
Appendix A.7. Public Benchmark Statistical Validation
| Benchmark | Mean Improvement | Std Error | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | Cohen’s d | p-Value | n Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETHICS Dataset | +8.5% | 1.24% | +6.1% | +10.9% | 0.68 | <0.001 | 300 |
| bAbI Task 15 | +12.4% | 1.67% | +9.1% | +15.7% | 0.89 | <0.001 | 300 |
| ConvAI2 (F1) | +0.07 | 0.012 | +0.046 | +0.094 | 0.62 | 0.003 | 300 |
| ROCStories | +16.3% | 2.01% | +12.4% | +20.2% | 0.82 | <0.001 | 300 |
Appendix B. Philosophical Formalization Challenges: Bias Analysis and Mitigation
Appendix B.1. Types of Formalization Bias
Appendix B.2. Systematic Bias Detection Methods
Appendix B.3. Bias Mitigation Strategies
Appendix B.4. Acknowledged Limitations and Residual Biases
Appendix B.5. Transparency and Accountability Measures
Appendix B.6. Future Research Directions
Appendix C. Sketch of Sophimatic Phase 1 Code
| """ Philosophical Categories Framework with Complex-Time Integration. Implementation of the advanced mathematical model for philosophical reasoning. This implementation provides 1. A core framework for philosophical categories (C, F, L, T, I, K, E). 2. Complex-time modeling with memory and imagination dimensions. 3. Inter-category interaction modeling. 4. Tools for parameter estimation and system analysis. """ import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import optimize, integrate from scipy.special import expit # sigmoid function import pandas as pd from dataclasses import dataclass, field from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, Callable, Any, Optional import warnings warnings.filterwarnings (‘ignore’) # =============================================================== # CORE DATA STRUCTURES # =============================================================== @dataclass class ComplexTime: """Represents complex time T = a + ib where a is explicit, b is implicit temporality""" real: float # Explicit chronological time imag: float # Implicit temporal dimensions (memory < 0, imagination > 0) def __post_init__ (self): self.complex_value = complex (self.real, self.imag) @property def magnitude (self) -> float: return abs (self.complex_value) @property def argument (self) -> float: return np.angle (self.complex_value) def is_memory (self) -> bool: return self.imag < 0 def is_imagination (self) -> bool: return self.imag > 0 def is_present (self) -> bool: return abs (self.imag) < 1 × 10−6 @dataclass class AngularParameters: """Angular parameters controlling temporal accessibility""" alpha: float = np.pi/4 # Memory cone angle [0, π/2] beta: float = 3 * np.pi/4 # Creativity cone angle [π/2, π] def __post_init__ (self): if not (0 <= self.alpha <= np.pi/2): raise ValueError (“Alpha must be in [0, π/2]”) if not (np.pi/2 <= self.beta <= np.pi): raise ValueError (“Beta must be in [π/2, π]”) def memory_accessibility (self, time: ComplexTime) -> float: """Check if temporal position is accessible via memory cone""" if time.is_memory (): angle = abs (time.argument) return 1.0 if angle <= self.alpha else 0.0 return 0.0 def creativity_accessibility (self, time: ComplexTime) -> float: """Check if temporal position is accessible via creativity cone""" if time.is_imagination (): angle = time.argument if time.argument >= 0 else time.argument + 2 * np.pi return 1.0 if angle >= self.beta else 0.0 return 0.0 # =============================================================== # PHILOSOPHICAL CATEGORY BASE CLASS # =============================================================== class PhilosophicalCategory: """Base class for philosophical categories with complex-time integration""" def __init__ (self, name: str, domain_size: int = 100): self.name = name self.domain_size = domain_size self.domain = self._initialize_domain () self.relations = {} self.operations = {} self.logical_language = {} self.state_history = [] def _initialize_domain (self) -> np.ndarray: """Initialize category domain with random state representation""" return np.random.random (self.domain_size) def add_relation (self, name: str, func: Callable): """Add a relation to the category""" self.relations [name] = func def add_operation (self, name: str, func: Callable): """Add an operation to the category""" self.operations [name] = func def update_state (self, new_state: np.ndarray, time: ComplexTime): """Update category state and record in history""" self.domain = new_state self.state_history.append ((time, new_state.copy())) def get_state_at_time (self, target_time: ComplexTime, angular_params: AngularParameters) -> Optional [np.ndarray]: """Retrieve state at specific complex time if accessible""" for time, state in self.state_history: if abs (time.complex_value − target_time.complex_value) < 0.1: # Check accessibility based on angular parameters if target_time.is_memory (): if angular_params.memory_accessibility (target_time) > 0: return state elif target_time.is_imagination (): if angular_params.creativity_accessibility (target_time) > 0: return state else: # Present time return state return None # =============================================================== # SPECIFIC PHILOSOPHICAL CATEGORIES # =============================================================== class ChangeCategory (PhilosophicalCategory): """Change category (C) with temporal state transitions""" def __init__ (self): super ().__init__ (“Change”) self._setup_change_relations () self._setup_change_operations () def _setup_change_relations (self): def transitions (state1, state2): """Measure transition possibility between states""" return 1.0/(1.0 + np.linalg.norm (state1 − state2)) def continuity (state1, state2): """Measure continuity between states""" diff = np.linalg.norm (state1 − state2) return np.exp (-diff) # Exponential decay for discontinuity self.add_relation (“transitions”, transitions) self.add_relation (“continuity”, continuity) def _setup_change_operations (self): def change_magnitude (state1, state2): """Calculate magnitude of change between states""" return np.linalg.norm (state2 − state1) def change_gradient (state): """Calculate change gradient (simplified as finite differences)""" return np.gradient (state) self.add_operation (“magnitude”, change_magnitude) self.add_operation (“gradient”, change_gradient) class TimeCategory (PhilosophicalCategory): """Time category (T) with complex-time integration""" def __init__ (self): super ().__init__ (“Time”) self._setup_time_relations () self._setup_time_operations () def _setup_time_relations (self): def temporal_ordering (time1: ComplexTime, time2: ComplexTime): """Determine temporal ordering relationship""" if abs (time1.real − time2.real) < 1 × 10−6: return “simultaneous” elif time1.real < time2.real: return “before” elif time1.real > time2.real: return “after” else: return “incommensurable” def temporal_synthesis (retention, impression, protention): """Husserlian temporal synthesis""" return (retention + impression + protention)/3.0 self.add_relation (“ordering”, temporal_ordering) self.add_relation (“synthesis”, temporal_synthesis) def _setup_time_operations (self): def complex_mapping (real_time: float, memory_factor: float, imagination_factor: float) -> ComplexTime: """Map to complex time with memory and imagination components""" imag_component = memory_factor + imagination_factor return ComplexTime (real_time, imag_component) def laplace_transform (signal: np.ndarray, s_values: np.ndarray): """Simplified Laplace transform for temporal processing""" # Simplified implementation for demonstration result = np.zeros_like (s_values, dtype = complex) for i, s in enumerate (s_values): # F (s) = ∫ f (t) * e^(−st) dt (simplified) t_values = np.linspace (0, 10, len(signal)) integrand = signal * np.exp (−s * t_values) result [i] = np.trapz (integrand, t_values) return result self.add_operation (“complex_mapping”, complex_mapping) self.add_operation (“laplace_transform”, laplace_transform) class IntentionCategory (PhilosophicalCategory): """Intention category (I) with BDI framework and complex-time integration""" def __init__ (self): super ().__init__ (“Intention”) self.beliefs = np.random.random (50) self.desires = np.random.random (50) self.intentions = np.random.random (50) self._setup_intention_relations () self._setup_intention_operations () def _setup_intention_relations (self): def aboutness (mental_state, objects): """Measure intentional directedness toward objects""" return np.dot (mental_state, objects)/(np.linalg.norm (mental_state) * np.linalg.norm (objects)) def belief_consistency (beliefs_set): """Measure consistency within belief set""" if len (beliefs_set) < 2: return 1.0 correlations = np.corrcoef (beliefs_set) return np.mean (correlations [np.triu_indices_from (correlations, k = 1)]) self.add_relation (“aboutness”, aboutness) self.add_relation (“belief_consistency”, belief_consistency) def _setup_intention_operations (self): def belief_formation (evidence): """Form beliefs from evidence""" return expit (evidence) # Sigmoid transformation def intention_formation (beliefs, desires): """Form intentions from beliefs and desires""" return (beliefs + desires)/2.0 self.add_operation (“belief_formation”, belief_formation) self.add_operation (“intention_formation”, intention_formation) # =============================================================== # INTERACTION MATRIX AND SYSTEM DYNAMICS # =============================================================== class PhilosophicalSystem: """Main system coordinating all philosophical categories""" def __init__ (self): self.categories = { ‘C’: ChangeCategory (), ‘F’: PhilosophicalCategory (“Form”), ‘L’: PhilosophicalCategory (“Logic”), ‘T’: TimeCategory (), ‘I’: IntentionCategory (), ‘K’: PhilosophicalCategory (“Context”), ‘E’: PhilosophicalCategory (“Ethics”) } self.angular_params = AngularParameters () self.interaction_matrix = np.random.random ((7, 7)) * 0.5 # Initialize with small values self.category_names = [‘C’, ‘F’, ‘L’, ‘T’, ‘I’, ‘K’, ‘E’] self.current_time = ComplexTime (0.0, 0.0) def phi_interaction (self, cat1: str, cat2: str, time: ComplexTime) -> float: """Calculate interaction strength between categories at specific time""" base_interaction = self.interaction_matrix [ self.category_names.index (cat1), self.category_names.index (cat2) ] # Modulate interaction based on temporal position temporal_modulation = 1.0 if time.is_memory (): temporal_modulation *= np.cos(time.argument − self.angular_params.alpha) elif time.is_imagination (): temporal_modulation *= np.cos (time.argument − self.angular_params.beta) return base_interaction * max (0, temporal_modulation) def time_change_interaction (self, time: ComplexTime, change_state: np.ndarray) -> float: """Enhanced Time-Change interaction with complex-time integration""" # Simplified implementation of the integral gradient_norm = np.linalg.norm (np.gradient (change_state)) alpha = self.angular_params.alpha exp_modulation = np.exp (-alpha * abs (time.imag)) return gradient_norm * exp_modulation def update_system_state (self, dt: float = 0.1): """Update entire system state using differential evolution""" new_time = ComplexTime ( self.current_time.real + dt, self.current_time.imag * 0.95 # Decay imaginary component ) # Update each category based on internal dynamics and interactions # Internal dynamics (simplified) internal_change = np.random.normal (0, 0.01, category.domain.shape) # Inter-category influences external_influence = np.zeros_like (category.domain) for other_cat_name in self.categories: if other_cat_name != cat_name: interaction_strength = self.phi_interaction (other_cat_name, cat_name, new_time) external_influence += interaction_strength * np.random.normal (0, 0.005, category.domain.shape) # Combined update new_state = category.domain + internal_change + external_influence category.update_state (new_state, new_time) self.current_time = new_time # =============================================================== # PARAMETER ESTIMATION AND SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION # =============================================================== class ParameterEstimator: """Tools for estimating model parameters from real-world data""" def __init__ (self, system: PhilosophicalSystem): self.system = system def estimate_angular_parameters (self, behavioral_data: Dict [str, np.ndarray]) -> AngularParameters: """ Estimate α and β from behavioral metrics Args: behavioral_data: Dictionary containing: - ‘recall_accuracy’: Array of recall performance scores - ‘creativity_scores’: Array of creativity/innovation measures - ‘prediction_accuracy’: Array of future prediction scores - ‘memory_latency’: Array of memory retrieval times """ def objective_function (params): alpha, beta = params if not (0 <= alpha <= np.pi/2) or not (np.pi/2 <= beta <= np.pi): return 1 × 106 # Large penalty for invalid parameters # Recall accuracy should correlate with α recall_fit = np.corrcoef ( behavioral_data [‘recall_accuracy’], np.cos (np.linspace (0, alpha, len (behavioral_data [‘recall_accuracy’]))) )[0, 1] # Creativity should correlate with β creativity_fit = np.corrcoef ( behavioral_data [‘creativity_scores’], np.sin (np.linspace (np.pi/2, beta, len (behavioral_data [‘creativity_scores’]))) ) [0, 1] # Combined fitness (minimize negative correlation) return - (recall_fit + creativity_fit) # Optimize parameters result = optimize.minimize ( objective_function, x0 = [np.pi/4, 3 * np.pi/4], method = ‘L-BFGS-B’, bounds = [(0, np.pi/2), (np.pi/2, np.pi)] ) return AngularParameters (result.x [0], result.x [1]) def estimate_interaction_matrix (self, time_series_data: Dict [str, np.ndarray]) -> np.ndarray: """ Estimate interaction matrix from multivariate time series Args: time_series_data: Dictionary with keys as category names and values as time series """ categories = list (time_series_data.keys ()) n_categories = len (categories) interaction_matrix = np.zeros ((n_categories, n_categories)) # Use Granger causality-like approach for i, cat1 in enumerate (categories): for j, cat2 in enumerate (categories): if i != j: # Cross-correlation as proxy for interaction strength correlation = np.corrcoef ( time_series_data [cat1] [:−1], # Lagged time_series_data [cat2] [1:] # Current ) [0, 1] interaction_matrix [i, j] = abs (correlation) return interaction_matrix def fit_transfer_function (self, input_data: np.ndarray, output_data: np.ndarray, s_values: np.ndarray) -> Callable: """ Estimate H (s) transfer function from input-output data Args: input_data: Input signal in time domain output_data: Output signal in time domain s_values: Complex frequency values for transfer function """ # Compute Laplace transforms (simplified) time_category = self.system.categories [‘T’] input_laplace = time_category.operations [‘laplace_transform’] (input_data, s_values) output_laplace = time_category.operations [‘laplace_transform’] (output_data, s_values) # Transfer function H (s) = Y (s)/X (s) transfer_function = np.divide (output_laplace, input_laplace, out = np.zeros_like (output_laplace), where = np.abs (input_laplace) > 1 × 10−10) # Return interpolated function def H (s): return np.interp (s, s_values, transfer_function) return H # =============================================================== # EXAMPLE USAGE AND DEMONSTRATION # =============================================================== def demonstrate_system (): """Demonstrate the philosophical framework with examples""" print (“=== Philosophical Categories Framework Demo ===\n”) # Initialize system system = PhilosophicalSystem () estimator = ParameterEstimator (system) # 1. Basic system state print (“1. Initial System State:”) for name, category in system.categories.items (): print (f” {name} ({category.name}): domain size = {len (category.domain)}”) print (f” Current time: {system.current_time.real} + {system.current_time.imag}i”) print () # 2. Complex time examples print (“2. Complex Time Examples:”) memory_time = ComplexTime (5.0, −2.0) # Memory access imagination_time = ComplexTime (5.0, 3.0) # Imagination projection present_time = ComplexTime (5.0, 0.0) # Present moment print (f” Memory time: {memory_time.real} + {memory_time.imag}i (accessible: {system.angular_params.memory_accessibility (memory_time)})”) print (f” Imagination time: {imagination_time.real} + {imagination_time.imag}i (accessible: {system.angular_params.creativity_accessibility (imagination_time)})”) print (f” Present time: {present_time.real} + {present_time.imag}i”) print () # 3. Inter-category interactions print (“3. Inter-Category Interactions:”) interaction_TC = system.phi_interaction (‘T’, ‘C’, present_time) interaction_IE = system.phi_interaction (‘I’, ‘E’, imagination_time) print (f” Time → Change interaction: {interaction_TC:.3f}”) print (f” Intention → Ethics interaction: {interaction_IE:.3f}”) print () # 4. System evolution print (“4. System Evolution (5 time steps):”) for step in range (5): system.update_system_state (dt = 0.5) change_magnitude = np.linalg.norm (system.categories [‘C’].domain) print (f” Step {step + 1}: time = {system.current_time.real:.1f} + {system.current_time.imag:.2f}i, change magnitude = {change_magnitude:.3f}”) print () # 5. Parameter estimation example print (“5. Parameter Estimation Example:”) # Simulated behavioral data behavioral_data = { ‘recall_accuracy’: np.random.beta (2, 5, 20), # Skewed toward lower values ‘creativity_scores’: np.random.beta (5, 2, 20), # Skewed toward higher values ‘prediction_accuracy’: np.random.random (20), ‘memory_latency’: np.random.exponential (2, 20) } estimated_params = estimator.estimate_angular_parameters(behavioral_data) print (f” Estimated α (memory cone): {estimated_params.alpha:.3f} radians ({np.degrees(estimated_params.alpha):.1f})”) print (f” Estimated β (creativity cone): {estimated_params.beta:.3f} radians ({np.degrees(estimated_params.beta):.1f})”) print () return system, estimator if __name__ == “__main__”: system, estimator = demonstrate_system () # Additional analysis can be performed here print (“Framework ready for further analysis and applications!”) |
References
- Bishop, J.M. Artificial intelligence is stupid and causal reasoning will not fix it. Front. Psychol. 2021, 11, 513474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, D.; Furlong, D. Philosophical foundations of AI. In Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4850, pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Basti, G. Intentionality and Foundations of Logic: A New Approach to Neurocomputation. Ph.D. Thesis, Pontifical Lateran University, Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vila, L. A survey on temporal reasoning in artificial intelligence. AI Commun. 1994, 7, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniadakis, M.; Trahanias, P. Temporal cognition: A key ingredient of intelligent systems. Front. Neurorobot. 2011, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloman, A. Philosophy as AI and AI as Philosophy. Tutorial, AAAI, 2011. Available online: https://cogaffarchive.org/talks/sloman-aaai11-tut.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Sloman, A. The Computer Revolution in Philosophy; Harvester Press: Brighton, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.A. A comprehensive review of AI: Ethical frameworks, challenges, and development. Adhyayan J. Manag. Sci. 2024, 14, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wermter, S.; Lehnert, W.G. A hybrid symbolic/connectionist model for noun phrase understanding. Connect. Sci. 1989, 1, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovane, G.; Fominska, I.; Landi, R.E.; Terrone, F. Smart sensing: An info-structural model of cognition for non-interacting agents. Electronics 2020, 9, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovane, G.; Landi, R.E. From smart sensing to consciousness: An info-structural model of computational consciousness for non-interacting agents. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2023, 81, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, R.E.; Chinnici, M.; Iovane, G. CognitiveNet: Enriching foundation models with emotions and awareness. In Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction. UAHCI 2023; Antona, M., Stephanidis, C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 14050, pp. 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, R.E.; Chinnici, M.; Iovane, G. An investigation of the impact of emotion in image classification based on deep learning. In Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction. UAHCI 2024; Antona, M., Stephanidis, C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 14696, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovane, G.; Di Pasquale, R. A complexity theory-based novel AI algorithm for exploring emotions and affections by utilizing artificial neurotransmitters. Electronics 2025, 14, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madl, T.; Franklin, S.; Snaider, J.; Faghihi, U. Continuity and the Flow of Time: A Cognitive Science Perspective; University of Memphis Digital Commons: Memphis, TN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Michon, J.A. J. T. Fraser’s “Levels of Temporality” as cognitive representations. In The Study of Time V: Time, Science, and Society in China and the West; University of Massachusetts Press: Amherst, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Roli, F.; Serpico, S.B.; Vernazza, G. Image recognition by integration of connectionist and symbolic approaches. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 1995, 9, 485–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Rushby, J. Inferring and conveying intentionality: Beyond numerical rewards to logical intentions. In Proceedings of the Consciousness in Artificial Intelligence Workshop, CEUR-WS, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–18 September 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hollister, D.L.; Gonzalez, A.; Hollister, J. Contextual reasoning in human cognition and its implications for artificial intelligence systems. ISTE OpenSci. 2019, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, P.; Lemaignan, S.; Trafton, J.G. Cognitive Architectures for Social Human–Robot Interaction; Technical Report; Plymouth University/Naval Research Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mc Menemy, R. Dynamic cognitive ontology networks: Advanced integration of neuromorphic event processing and tropical hyperdimensional representations. Int. J. Soft Comput. 2025, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, H.; Nitta, K.; Kurihara, M.; Katagami, D. Formalizing dialectical reasoning for compromise-based justification. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence; SCITEPRESS: Rome, Italy, 2011; pp. 355–363. [Google Scholar]
- Ejjami, R. The Ethical Artificial Intelligence Framework Theory (EAIFT): A new paradigm for embedding ethical reasoning in AI systems. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2024, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B. Constructing Intentionality in AI Agents: Balancing Object-Directed and Socio-Technical Goals; Yuanpei College, Peking University: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Iovane, G.; Iovane, G. Sophimatics, Vol. 1: A New Bridge Between Philosophical Thought and Logic for an Emerging Post-Generative Artificial Intelligence; Aracne Editrice: Canterano, Italy, 2025; pp. 1–192. ISBN 1221821806. [Google Scholar]
- Iovane, G.; Iovane, G. Sophimatics, Vol. 2: Fundamentals and Models of Computational Wisdom; Aracne Editrice: Canterano, Italy, 2025; pp. 1–172. ISBN 1221821822. [Google Scholar]
- Iovane, G.; Iovane, G. Sophimatics, Vol. 3: Applications, Ethics and Future Perspectives; Aracne Editrice: Canterano, Italy, 2025; pp. 1–168. ISBN 1221821849. [Google Scholar]
- Badreddine, S.; d’Avila Garcez, A.; Serafini, L.; Spranger, M. Logic tensor networks. Artif. Intell. 2022, 303, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhaeve, R.; Dumančić, S.; Kimmig, A.; Demeester, T.; De Raedt, L. Neural probabilistic logic programming in DeepProbLog. Artif. Intell. 2021, 298, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, J.; Rohrbach, M.; Darrell, T.; Klein, D. Neural module networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, S.H.; Broecheler, M.; Huang, B.; Getoor, L. Hinge-loss Markov random fields and probabilistic soft logic. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2017, 18, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Pnueli, A. The temporal logic of programs. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Providence, RI, USA, 31 October–2 November 1977; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, E.A.; Clarke, E.M. Using branching time temporal logic to synthesize synchronization skeletons. Sci. Comput. Program. 1982, 2, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ditmarsch, H.; Van der Hoek, W.; Kooi, B. Dynamic Epistemic Logic; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, P.; Gustafsson, J.; Karlsson, L.; Kvarnström, J. TAL: Temporal action logics language specification and tutorial. Electron. Trans. Artif. Intell. 1998, 2, 273–306. [Google Scholar]
- Iovane, G.; Iovane, G. Sophimatics: A new computational wisdom for sentient and contextualized artificial intelligence through philosophy. Information, 2025; Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Cappelen, H.; Dever, J. Making AI Intelligible: Philosophical Foundations; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mickunas, A.; Pilotta, J. A Critical Understanding of Artificial Intelligence: A Phenomenological Foundation; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baader, F. Ontology-based monitoring of dynamic systems. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Principles of Knowledge Representation and Reasoning (KR), Vienna, Austria, 20–24 June 2014; AAAI Press: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 678–681. [Google Scholar]
- Giunchiglia, F.; Bouquet, P. Introduction to contextual reasoning: An artificial intelligence perspective. In Proceedings of the 4th International and Interdisciplinary Conference on Modeling and Using Context (CONTEXT), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 4–6 February 1997; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Oltramari, A.; Lebiere, C. Mechanisms meet content: Integrating cognitive architectures and ontologies. In Proceedings of the AAAI Fall Symposium (FS-11-01), Advances in Cognitive Systems, Arlington, VA, USA, 4–6 November 2011; AAAI Press: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Salas-Guerra, R. Cognitive AI Framework: Advances in the Simulation of Human Thought. Doctoral Dissertation, AU University/AGM University, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Langlois, L.; Dilhac, M.A.; Dratwa, J.; Ménissier, T.; Ganascia, J.G.; Weinstock, D.; Bégin, L.; Marchildon, A. Ethics at the Heart of AI; Obvia: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Petersson, B. Team reasoning and collective intentionality. Rev. Philos. Psychol. 2017, 8, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovane, G. Decision support system driven by thermo-complexity: Algorithms and data manipulation. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 157359–157382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovane, G.; Chinnici, M. Decision support system driven by thermo-complexity: Scenario analysis and data visualization. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovane, G. Quantum-inspired algorithms and perspectives for optimization. Electronics 2025, 14, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovane, G. A multi-layer quantum-resilient IoT security architecture integrating uncertainty reasoning, relativistic blockchain, and decentralised storage. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

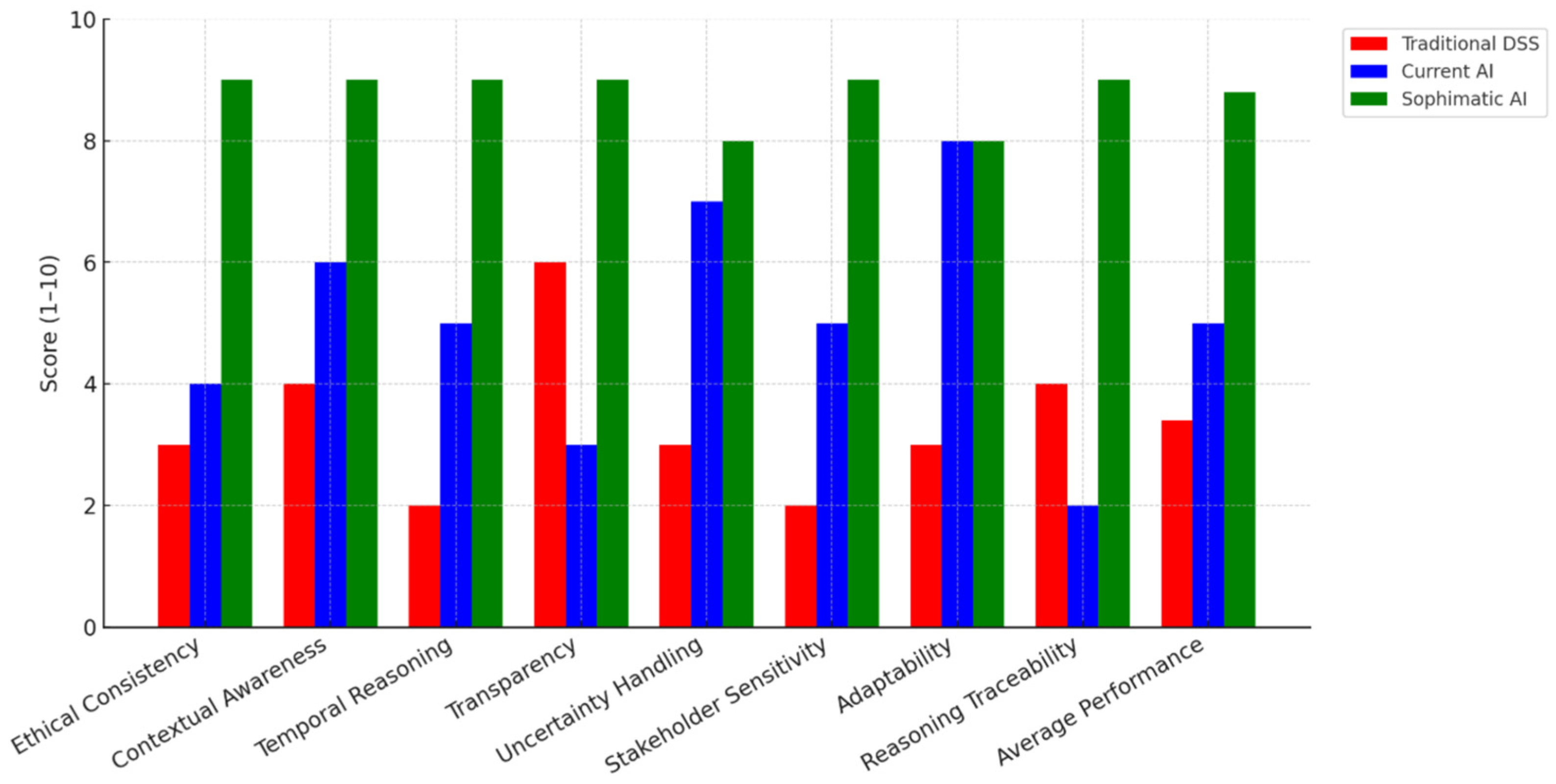

| Parameter | Traditional DSS | Current AI | Sophimatic AI | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethical Consistency | 3 | 4 | 9 | +125% |
| Contextual Awareness | 4 | 6 | 9 | +50% |
| Temporal Reasoning | 2 | 5 | 9 | 80% |
| Transparency | 6 | 3 | 9 | 200% |
| Uncertainty Handling | 3 | 7 | 8 | 14% |
| Stakeholder Sensitivity | 2 | 5 | 9 | 80% |
| Adaptability | 3 | 8 | 8 | 0% |
| Reasoning Traceability | 4 | 2 | 9 | 350% |
| Average Performance | 3.4 | 5.0 | 8.8 | 76% |
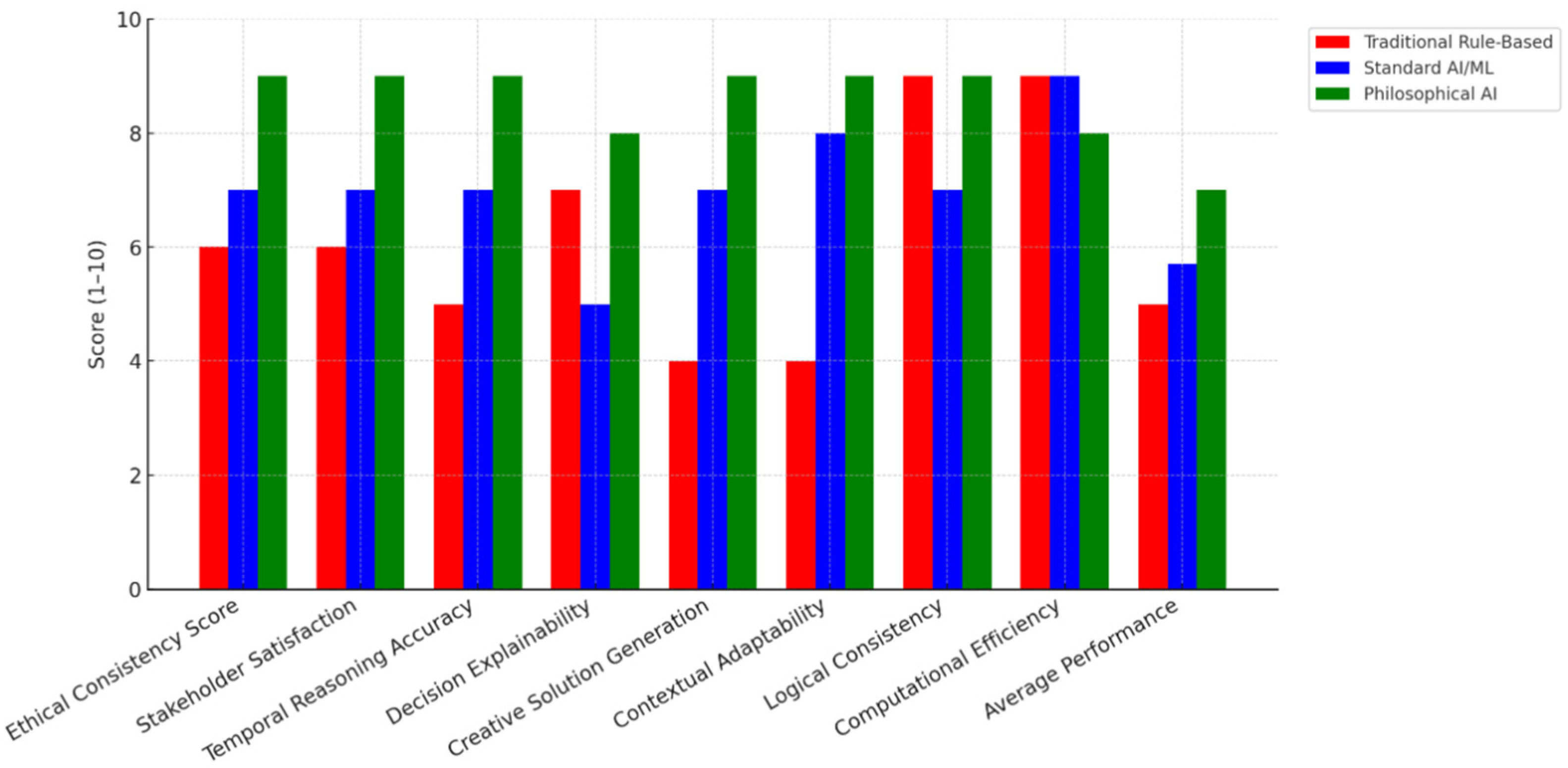
| Parameter | Traditional Rule-Based | Standard AI/ML | Sophimatic AI (Phase 1) | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethical Consistency Score | 6 | 7 | 9 | +29% |
| Stakeholder Satisfaction | 6 | 7 | 9 | +29% |
| Temporal Reasoning Accuracy | 5 | 7 | 9 | +29% |
| Decision Explainability | 7 | 5 | 8 | +60% |
| Creative Solution Generation | 4 | 7 | 9 | +29% |
| Contextual Adaptability | 4 | 8 | 9 | +13% |
| Logical Consistency | 9 | 7 | 9 | +29% |
| Computational Efficiency | 9 | 9 | 8 | −11% |
| Average Performance | 50 | 57 | 70 | +25% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iovane, G.; Iovane, G. A Novel Architecture for Understanding, Context Adaptation, Intentionality and Experiential Time in Emerging Post-Generative AI Through Sophimatics. Electronics 2025, 14, 4812. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244812
Iovane G, Iovane G. A Novel Architecture for Understanding, Context Adaptation, Intentionality and Experiential Time in Emerging Post-Generative AI Through Sophimatics. Electronics. 2025; 14(24):4812. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244812
Chicago/Turabian StyleIovane, Gerardo, and Giovanni Iovane. 2025. "A Novel Architecture for Understanding, Context Adaptation, Intentionality and Experiential Time in Emerging Post-Generative AI Through Sophimatics" Electronics 14, no. 24: 4812. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244812
APA StyleIovane, G., & Iovane, G. (2025). A Novel Architecture for Understanding, Context Adaptation, Intentionality and Experiential Time in Emerging Post-Generative AI Through Sophimatics. Electronics, 14(24), 4812. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244812







