Dual-Contrastive Attribute Embedding for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel framework is introduced to extract attribute-level features and generate prototypes used to learn highly discriminative embedding spaces. In this way, the model can better recognize attributes and overcome the domain shift problem.
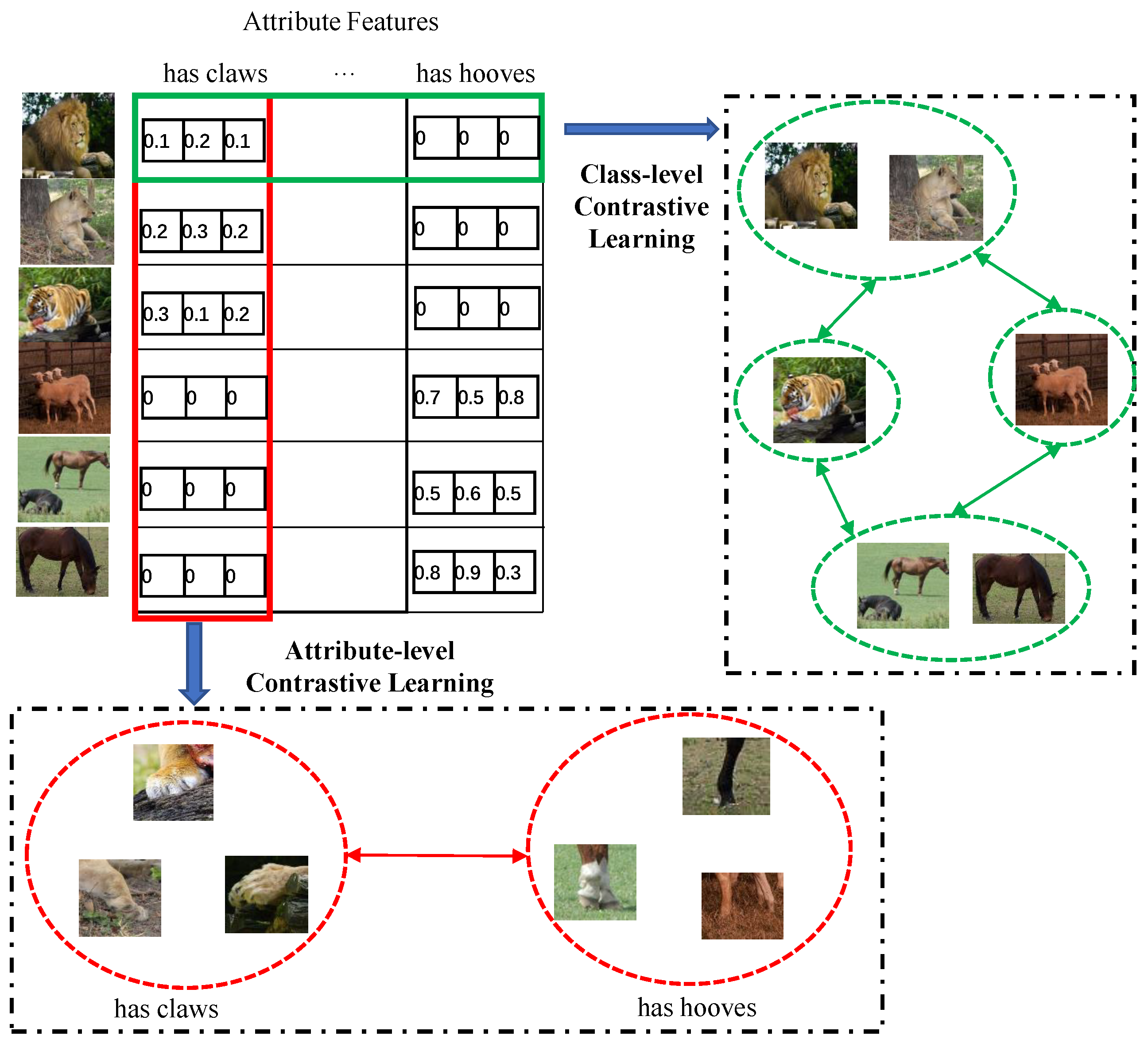
- An attribute-level contrastive loss term is proposed based on adaptive hard sample selection and used to improve the discriminative capacity of attribute representations. In addition, class-level contrastive loss is employed to optimize these representations and enhance GZSL performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Zero-Shot Learning
2.2. Contrastive Learning
3. Methodology
3.1. Notation and Problem Settings
3.2. Overview
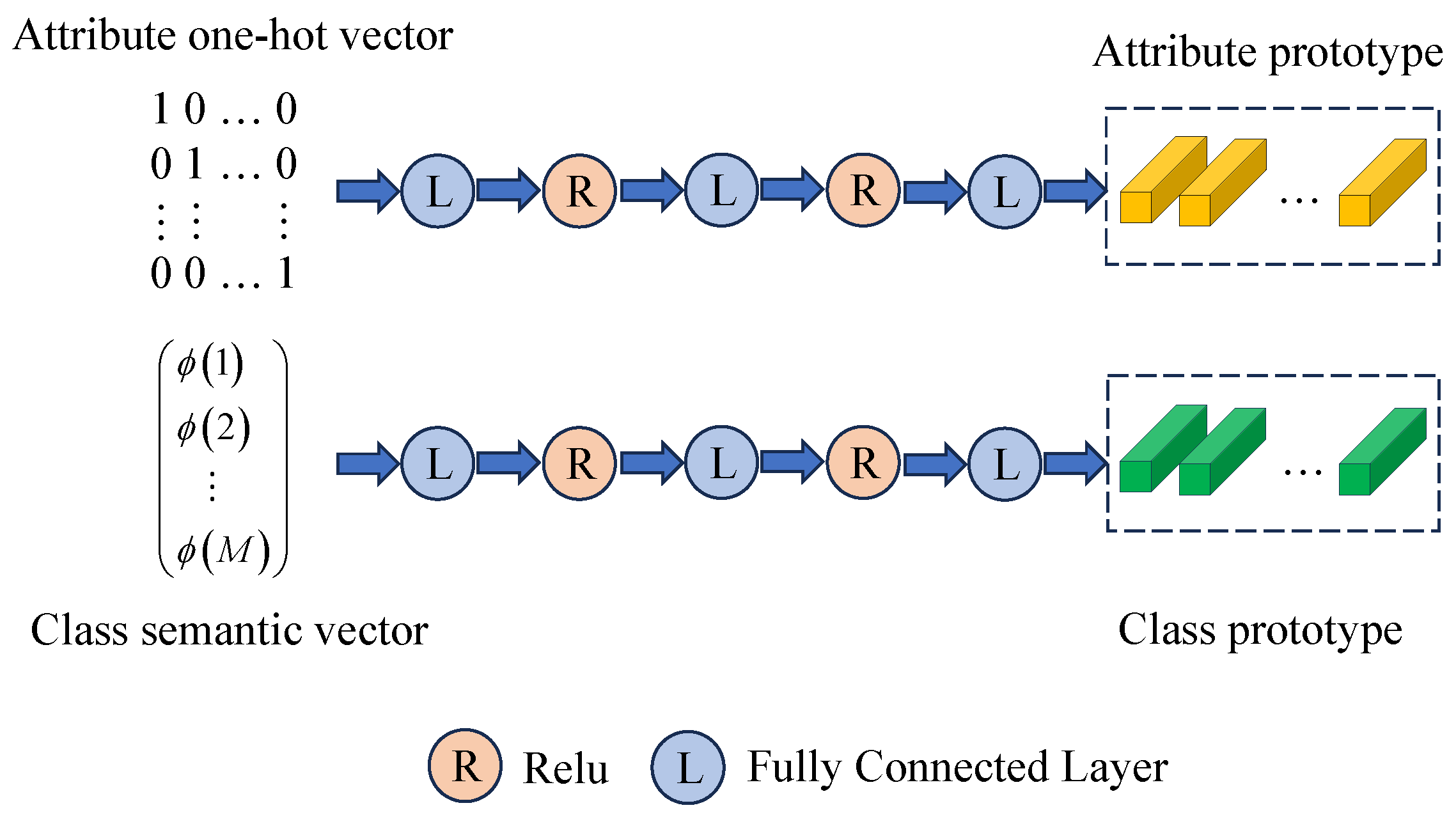
3.3. Class Representation Learning
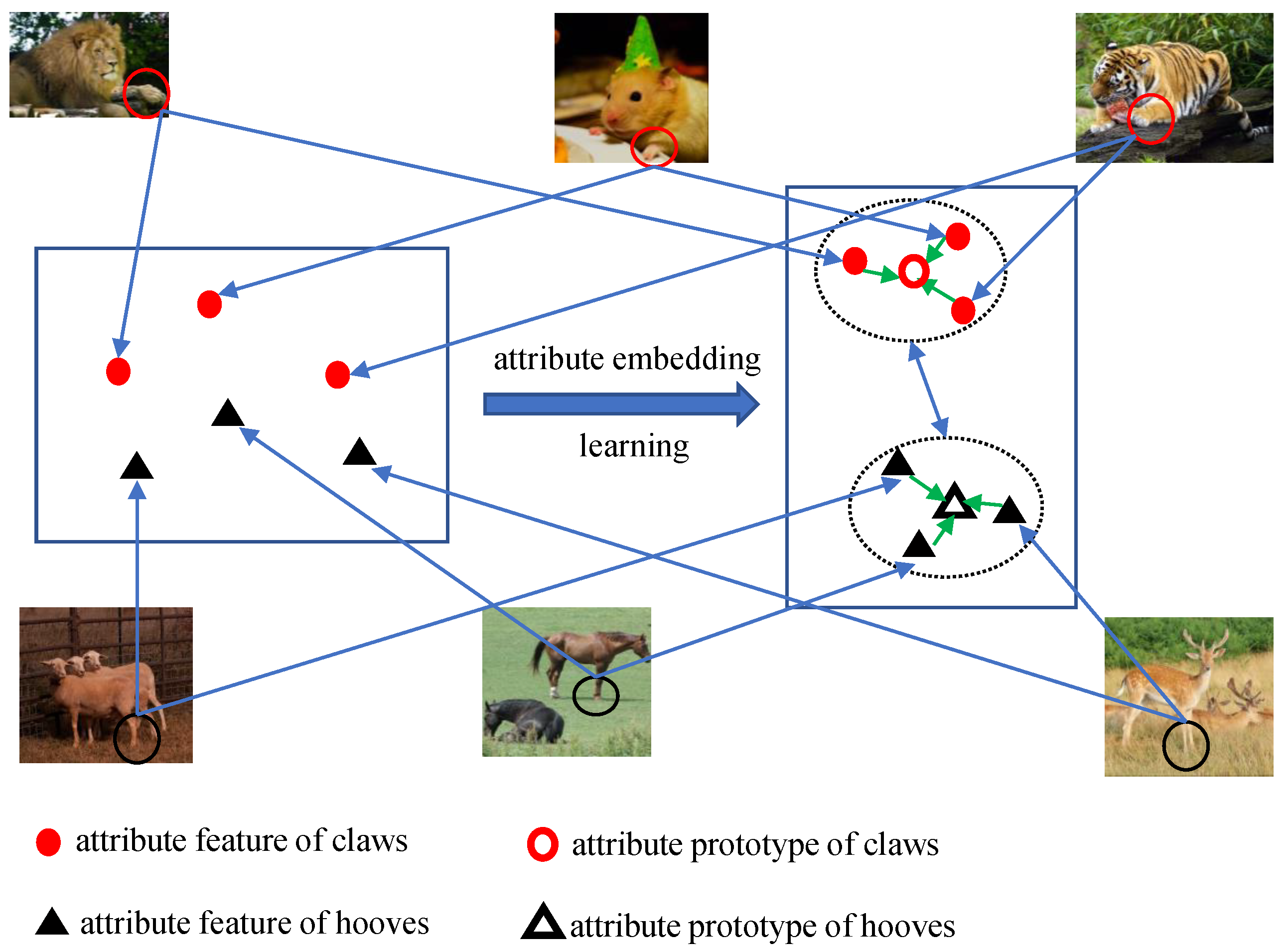
3.4. Attribute Embedding Learning
| Algorithm 1 Adaptive Hard Sample Selection based on Cosine Similarity Ranking |
| Require: Filtered attribute feature set , exclusion ratios , temperature |
| coefficient |
| Ensure: Hard positive sample set and hard negative sample set |
|
3.5. Optimization
3.6. Zero-Shot Recognition
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Metrics
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Comparisons with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.5. Ablation Studies
4.6. Computational Complexity Analysis
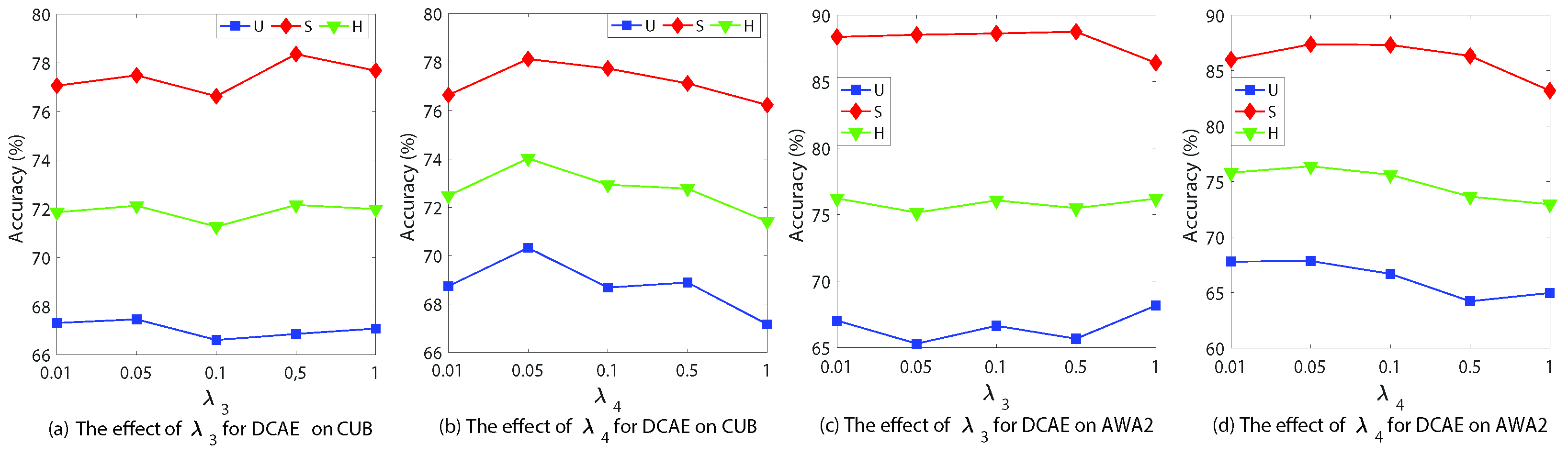
4.7. Hyperparameter Analysis
4.8. Qualitative Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Term |
| ZSL | Zero-shot Learning |
| DCAE | Dual-contrastive Attribute Embedding |
| CZSL | Conventional ZSL |
| GZSL | Generalized ZSL |
| GANs | Generative Adversarial Networks |
| VAEs | Variational Autoencoders |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| CS | Calibrated Stacking |
| CUB | CUB-200-2011 |
| AWA2 | Animals with Attributes 2 |
References
- Xie, G.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Shu, X.; Yan, S.; Liu, C.L. Task-driven feature pooling for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1179–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shao, L.; Yang, J. Discriminative block-diagonal representation learning for image recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2017, 29, 3111–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Schiele, B.; Akata, Z. Zero-shot learning-the good, the bad and the ugly. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4582–4591. [Google Scholar]
- Palatucci, M.; Pomerleau, D.; Hinton, G.E.; Mitchell, T.M. Zero-shot learning with semantic output codes. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2009, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jing, M.; Lu, K.; Zhu, L.; Shen, H.T. Investigating the bilateral connections in generative zero-shot learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 8167–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q. Augmented semantic feature based generative network for generalized zero-shot learning. Neural Networks 2021, 143, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampert, C.H.; Nickisch, H.; Harmeling, S. Attribute-based classification for zero-shot visual object categorization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tsang, I.W.; Liu, C. Complementary attributes: A new clue to zero-shot learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26, 3111–3119. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xie, G.S.; Sun, B.; Li, H.; Peng, Q.; Lu, K.; You, X. Transzero: Attribute-guided transformer for zero-shot learning. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, D.; Elhamifar, E. Fine-grained generalized zero-shot learning via dense attribute-based attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 4483–4493. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.S.; Liu, L.; Jin, X.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, J.; Yao, Y.; Shao, L. Attentive region embedding network for zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9384–9393. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.S.; Liu, L.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Qin, J.; Shao, L. Region graph embedding network for zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 562–580. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Xie, J.; Tang, Z.; Peng, X.; Elgammal, A. Semantic-guided multi-attention localization for zero-shot learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 14943–14953. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Xian, Y.; Wang, J.; Schiele, B.; Akata, Z. Attribute prototype network for zero-shot learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21969–21980. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Hospedales, T.M.; Xiang, T.; Gong, S. Transductive multi-view zero-shot learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 2332–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welinder, P.; Branson, S.; Mita, T.; Wah, C.; Schroff, F.; Belongie, S.; Perona, P. Caltech-UCSD Birds 200 (CUB-200); Technical Report CNS-TR-2010-001, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 29 September 2010. Available online: https://authors.library.caltech.edu/records/cyyh7-dkg06 (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Xian, Y.; Lampert, C.H.; Schiele, B.; Akata, Z. Zero-shot learning—A comprehensive evaluation of the good, the bad and the ugly. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 2251–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, G.; Hays, J. Sun attribute database: Discovering, annotating, and recognizing scene attributes. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2751–2758. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Han, J.; Shao, L. A discriminative cross-aligned variational autoencoder for zero-shot learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 3794–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frome, A.; Corrado, G.S.; Shlens, J.; Bengio, S.; Dean, J.; Ranzato, M.; Mikolov, T. Devise: A deep visual-semantic embedding model. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar]
- Romera-Paredes, B.; Torr, P. An embarrassingly simple approach to zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 2152–2161. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, Y.; Wang, S.; Hou, M.; Gao, Q. Attributes learning network for generalized zero-shot learning. Neural Networks 2022, 150, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Hou, M.; Lai, H.; Yang, M. Cross-modal distribution alignment embedding network for generalized zero-shot learning. Neural Networks 2022, 148, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Yu, X.; Yu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Semantic-guided class-imbalance learning model for zero-shot image classification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 6543–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Z.; Xie, G.S.; Yang, W.; Peng, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhao, J.; You, X. MSDN: Mutually Semantic Distillation Network for Zero-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 7612–7621. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Min, S.; Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Li, H. Dual Progressive Prototype Network for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 2936–2948. [Google Scholar]
- Cunegatto, E.H.T.; Zinani, F.S.F.; Rigo, S.J. Multi-objective optimisation of micromixer design using genetic algorithms and multi-criteria decision-making algorithms. Int. J. Hydromechatronics 2024, 7, 224–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, K.; Fardindoost, S.; Frencken, A.L.; Hoorfar, M. Multi-objective optimization of expansion-contraction micromixer using response surface methodology: A comprehensive study. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 227, 125570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.; Min, D.; Kim, S.; Sohn, K. Mining better samples for contrastive learning of temporal correspondence. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2021; pp. 1034–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, P.; Teterwak, P.; Wang, C.; Sarna, A.; Tian, Y.; Isola, P.; Maschinot, A.; Liu, C.; Krishnan, D. Supervised contrastive learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 18661–18673. [Google Scholar]
- Le-Khac, P.H.; Healy, G.; Smeaton, A.F. Contrastive representation learning: A framework and review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193907–193934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9729–9738. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.Y.; Lim, K.M.; Lee, C.P.; Tan, Y.X. SCL: Self-supervised contrastive learning for few-shot image classification. Neural Networks 2023, 165, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Fu, Z.; Chen, S.; Yang, J. Contrastive embedding for generalized zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2021; pp. 2371–2381. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Bai, X.; Huang, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhou, J.; Harada, T. Goal-oriented gaze estimation for zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2021; pp. 3794–3803. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Wang, X.; Long, G. Task aligned generative meta-learning for zero-shot learning. Proc. AAAI Conf. OnArtificial Intell. 2021, 35, 8723–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.L.; Changpinyo, S.; Gong, B.; Sha, F. An empirical study and analysis of generalized zero-shot learning for object recognition in the wild. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 52–68. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In Proceedings of COMPSTAT’2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, Y.; Lorenz, T.; Schiele, B.; Akata, Z. Feature generating networks for zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5542–5551. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, Y.; Sharma, S.; Schiele, B.; Akata, Z. f-vaegan-d2: A feature generating framework for any-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10275–10284. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jing, M.; Lu, K.; Ding, Z.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Z. Leveraging the invariant side of generative zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7402–7411. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, S.; Gupta, A.; Khan, F.S.; Snoek, C.G.; Shao, L. Latent embedding feedback and discriminative features for zero-shot classification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 479–495. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Xie, G.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Sun, B.; Li, H.; You, X.; Shao, L. Hsva: Hierarchical semantic-visual adaptation for zero-shot learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 16622–16634. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Gao, Z.; Li, X.; Hong, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Qu, Y. En-Compactness: Self-Distillation Embedding & Contrastive Generation for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 9306–9315. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, R.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Transferable contrastive network for generalized zero-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9765–9774. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Min, S.; Sun, X.; Li, H. Task-independent knowledge makes for transferable representations for generalized zero-shot learning. Proc. AAAI Conf. OnArtificial Intell. 2021, 35, 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.; Chuang, C.Y.; Sra, S.; Jegelka, S. Contrastive learning with hard negative samples. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04592. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]




| Type | Methods | CUB | SUN | AWA2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZSL | GZSL | CZSL | GZSL | CZSL | GZSL | ||||||||
| acc | U | S | H | acc | U | S | H | acc | U | S | H | ||
| Generative | f-CLSWGAN [45] | 57.3 | 43.7 | 57.7 | 49.7 | 60.8 | 42.6 | 36.6 | 39.4 | 68.2 | 57.9 | 61.4 | 59.6 |
| f-VAEGAN-D2 [46] | 61.0 | 48.4 | 60.1 | 53.6 | 64.7 | 45.1 | 38.0 | 41.3 | 71.1 | 57.6 | 70.6 | 63.5 | |
| LisGAN [47] | 58.8 | 46.5 | 57.9 | 51.6 | 61.7 | 42.9 | 37.8 | 40.2 | - | - | - | - | |
| TF-VAEGAN [48] | 64.9 | 52.8 | 64.7 | 58.1 | 66.0 | 45.6 | 40.7 | 43.0 | 72.2 | 59.8 | 75.1 | 66.6 | |
| HSVA [49] | - | 52.7 | 58.3 | 55.3 | - | 48.6 | 39.0 | 43.3 | - | 56.7 | 79.8 | 66.3 | |
| ICCE [50] | - | 67.3 | 65.5 | 66.4 | - | - | - | - | - | 65.3 | 82.3 | 72.8 | |
| Embedding | TCN [51] | 59.5 | 52.6 | 52.0 | 52.3 | 61.5 | 31.2 | 37.3 | 34.0 | 71.2 | 61.2 | 65.8 | 63.4 |
| DAZLE [11] | 66.0 | 56.7 | 59.6 | 58.1 | 59.4 | 52.3 | 24.3 | 33.2 | 67.9 | 60.3 | 75.7 | 67.1 | |
| RGEN [13] | 76.1 | 60.0 | 73.5 | 66.1 | 63.8 | 44.0 | 31.7 | 36.8 | 73.6 | 67.1 | 76.5 | 71.5 | |
| APN [15] | 72.0 | 65.3 | 69.3 | 67.2 | 61.6 | 41.9 | 34.0 | 37.6 | 68.4 | 57.1 | 72.4 | 63.9 | |
| DCEN [52] | - | 63.8 | 78.4 | 70.4 | - | 43.7 | 39.8 | 41.7 | - | 62.4 | 81.7 | 70.8 | |
| MSDN [28] | 76.1 | 68.7 | 67.5 | 68.1 | 65.8 | 52.2 | 34.2 | 41.3 | 70.1 | 62.0 | 74.5 | 67.7 | |
| DCAE(Ours) | 77.0 | 70.3 | 78.1 | 74.0 | 67.2 | 46.2 | 41.2 | 43.6 | 74.4 | 69.3 | 86.4 | 76.9 | |
| Method | CUB | SUN | AWA2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | S | H | U | S | H | U | S | H | |
| 63.7 | 77.9 | 70.1 | 40.9 | 41.9 | 41.4 | 63.1 | 87.9 | 73.5 | |
| 67.8 | 74.5 | 71.0 | 43.6 | 42.0 | 42.8 | 62.8 | 88.4 | 73.4 | |
| w/o HS | 65.5 | 77.8 | 71.1 | 47.2 | 39.8 | 43.2 | 65.4 | 85.9 | 74.2 |
| w HS | 69.8 | 78.1 | 73.7 | 43.8 | 42.8 | 43.3 | 67.5 | 86.5 | 75.8 |
| 70.3 | 78.1 | 74.0 | 46.2 | 41.2 | 43.6 | 69.3 | 86.4 | 76.9 | |
| Training Method | M-Way | N-shot | U | S | H | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUB | Random Sampling | - | - | 69.8 | 68.5 | 69.1 |
| Episode-Based | 4 | 2 | 65.9 | 74.3 | 69.8 | |
| 8 | 2 | 67.5 | 78.4 | 72.6 | ||
| 16 | 2 | 70.3 | 78.1 | 74.0 | ||
| SUN | Random Sampling | - | - | 55.7 | 34.0 | 42.2 |
| Episode-Based | 4 | 2 | 47.2 | 39.5 | 43.0 | |
| 8 | 2 | 46.2 | 41.2 | 43.6 | ||
| 16 | 2 | 42.1 | 43.8 | 42.9 | ||
| AWA2 | Random Sampling | - | - | 61.4 | 88.1 | 72.4 |
| Episode-Based | 4 | 2 | 60.2 | 85.7 | 70.7 | |
| 8 | 2 | 66.4 | 83.5 | 74.0 | ||
| 16 | 2 | 69.3 | 86.4 | 76.9 |
| Method | FLOPs |
|---|---|
| AREN | |
| APN | |
| DCEN | |
| DPPN | |
| GEM-ZSL | |
| DCAE (Ours) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Long, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, K. Dual-Contrastive Attribute Embedding for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning. Electronics 2025, 14, 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214341
Li Q, Long Y, Zhang Z, Jiang K. Dual-Contrastive Attribute Embedding for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning. Electronics. 2025; 14(21):4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214341
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qin, Yujie Long, Zhiyi Zhang, and Kai Jiang. 2025. "Dual-Contrastive Attribute Embedding for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning" Electronics 14, no. 21: 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214341
APA StyleLi, Q., Long, Y., Zhang, Z., & Jiang, K. (2025). Dual-Contrastive Attribute Embedding for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning. Electronics, 14(21), 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214341






