Knowledge-Driven 3D Content Generation: A Rule+LLM-Verify-Based Method for Constructing a Tibetan Cultural and Tourism Knowledge Graph
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Core Challenges
1.3. Research Objectives and Innovations
2. Related Work
2.1. Text-to-Cypher Conversion
2.2. Cultural KG Construction
2.3. Knowledge-Driven 3D Content Generation
3. Method Design
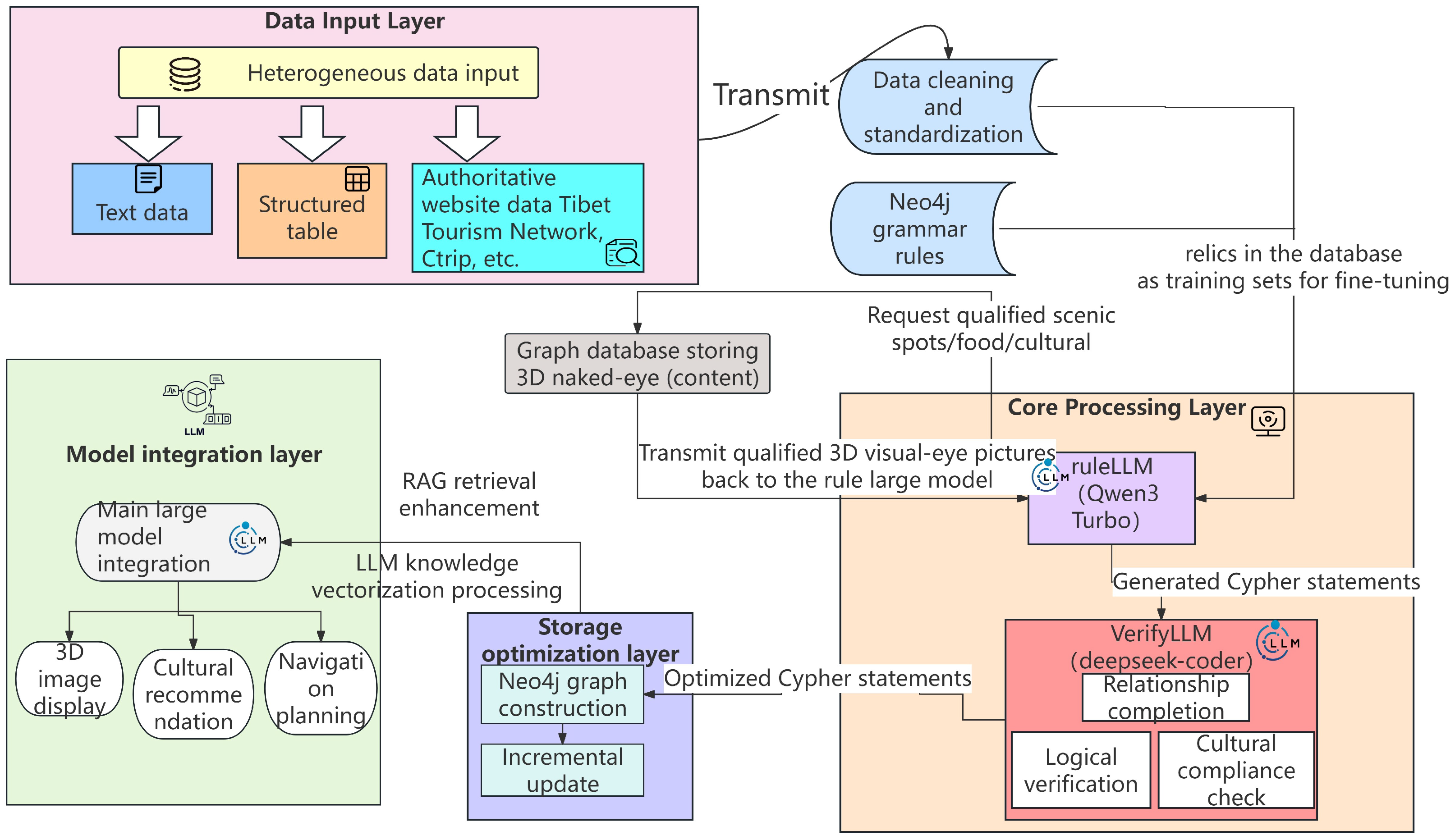
3.1. System Architecture
3.2. Cypher Generation Rules
3.3. Design of Model Collaboration Mechanism
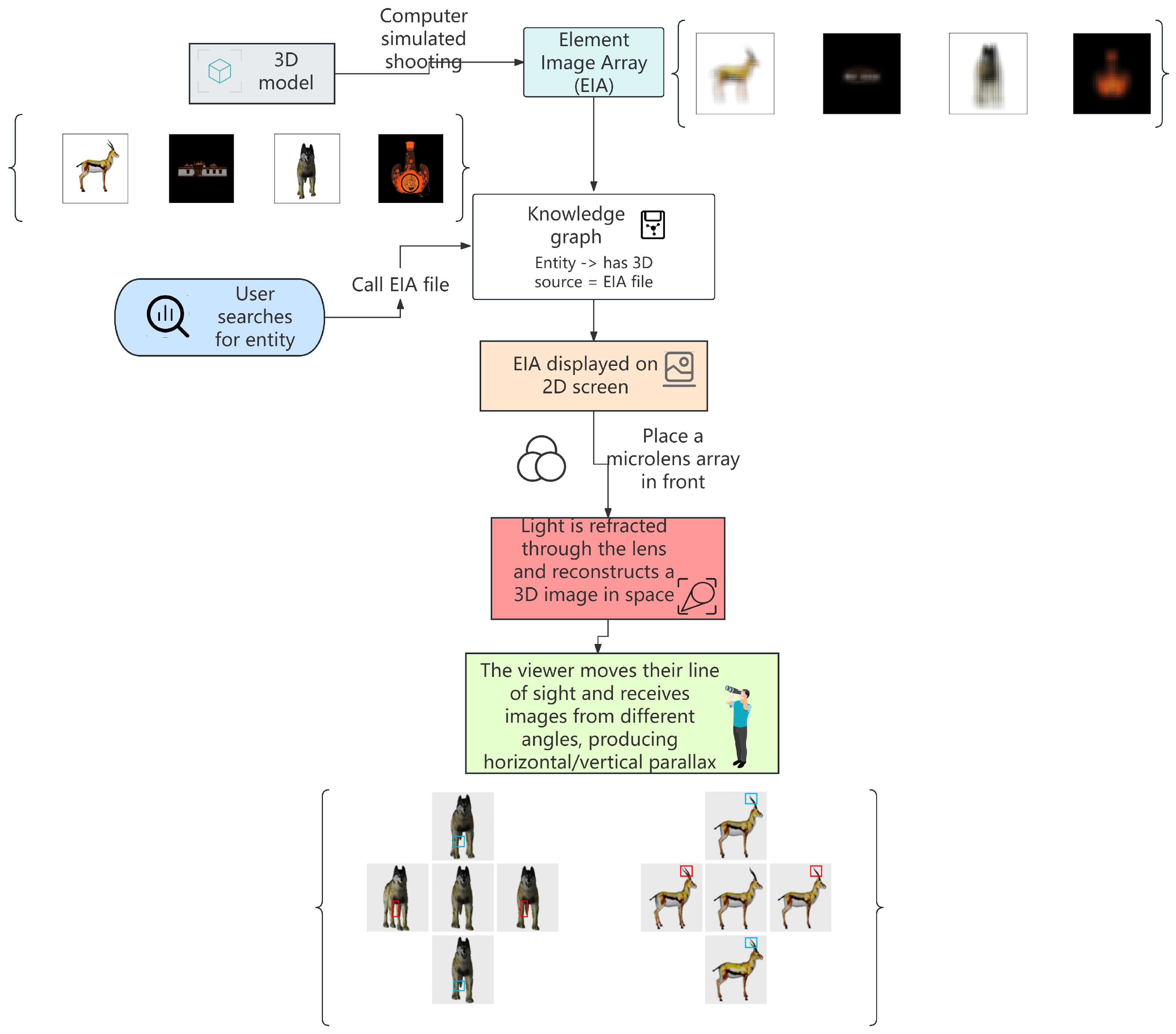
3.4. Detailed Workflow of the Knowledge-Driven Naked-Eye 3D Generation
3.4.1. 3D Model Collection and Preprocessing: Foundation of the Workflow
3.4.2. 3D Model Simulated Shooting: Generating 3D Source (EIA)
3.4.3. Knowledge Graph Registration and EIA Retrieval: Establishing the Connection Between Model and Source
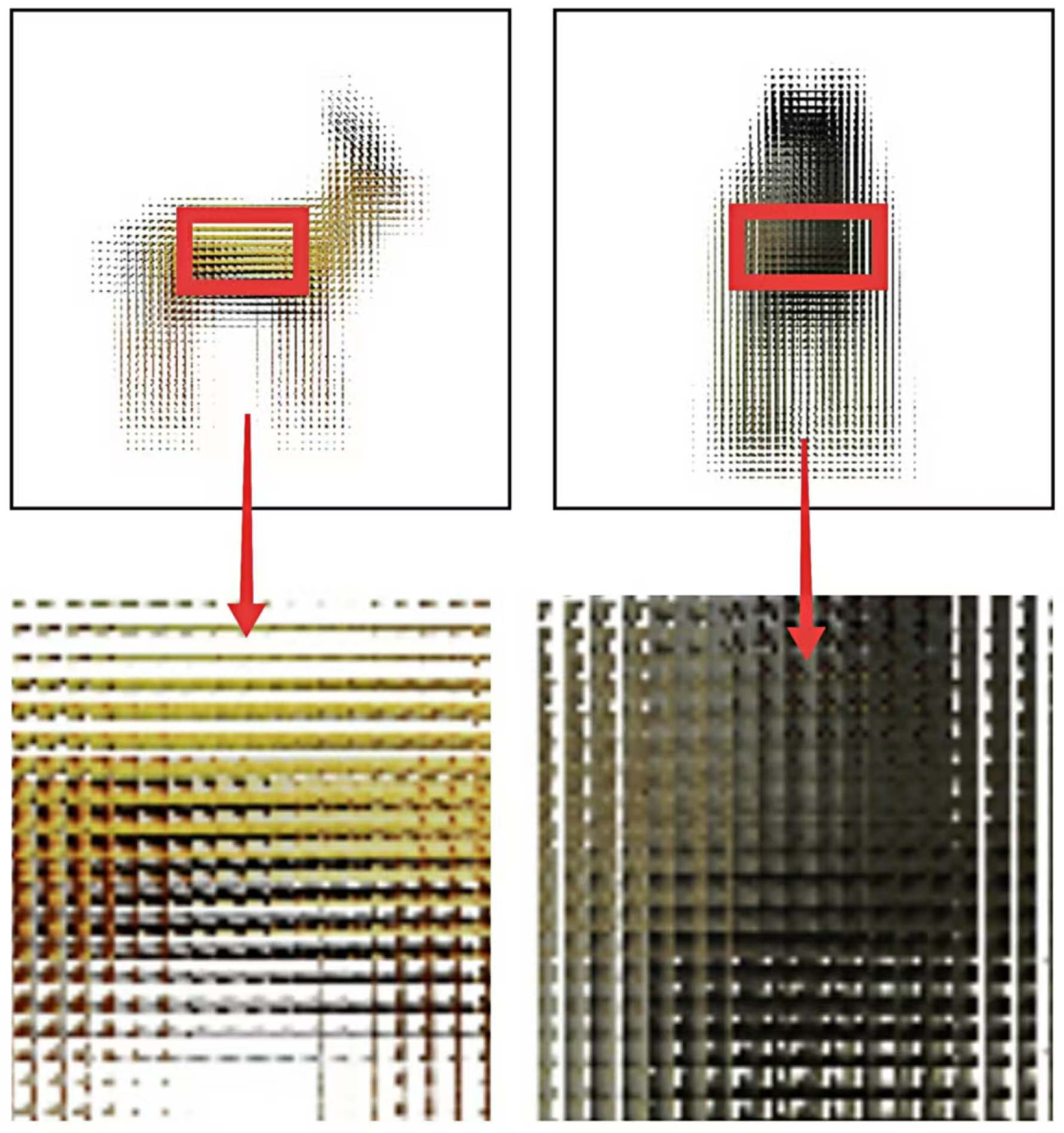
3.4.4. 2D Display and Optical 3D Reconstruction: Transformation from Data to Naked-Eye 3D Effect
3.4.5. Viewer Experience and Parallax Principle: Core of Immersive Naked-Eye 3D Effect
4. Experiments and Analysis of Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Dataset
4.1.2. Baseline Methods
- -
- Rule-Only: KG construction via regular template rules, entity/relationship extraction via pre-defined text matching with 50 handcrafted patterns.
- -
- LLM-NoCheck: Direct Cypher generation using GPT-3.5 without post-verification, prompted with standard instruction templates.
- -
- LLM-Direct: Based on LLM-NoCheck, use carefully designed prompts.
- -
- RLT2C (Ours): Rule assistance + context verification as described in Section 3.
4.1.3. Evaluation Indicators
- -
- Construction Efficiency (CE): Average number of triples generated per 100-word text (reflects text processing output efficiency).
- -
- Relationship Accuracy (RA): Proportion of semantically correct triples in total triples.
- -
- Local Semantic Adaptability (LAS): Proportion of correctly recognized local predicates (e.g., “holds sunning of Buddha ceremony”) specific to Tibetan culture.
- -
- Graph Redundancy Rate (GRR): Proportion of duplicate triples in the graph (lower values indicate higher graph compactness).
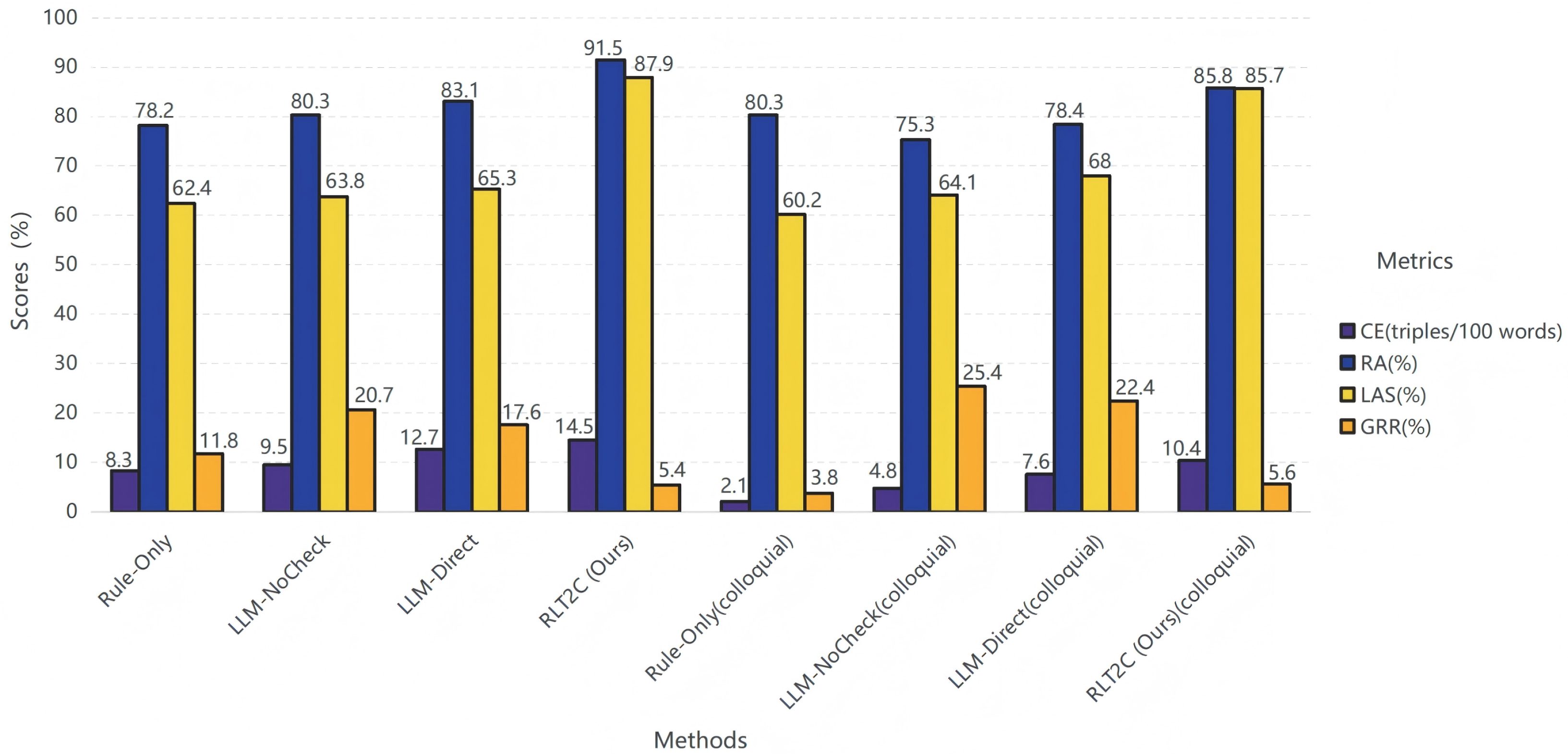
4.2. Experimental Results
4.3. Case Demonstration
| Algorithm 1 Triple Extraction and Cypher Generation from Input Text |
|
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Practical Applications
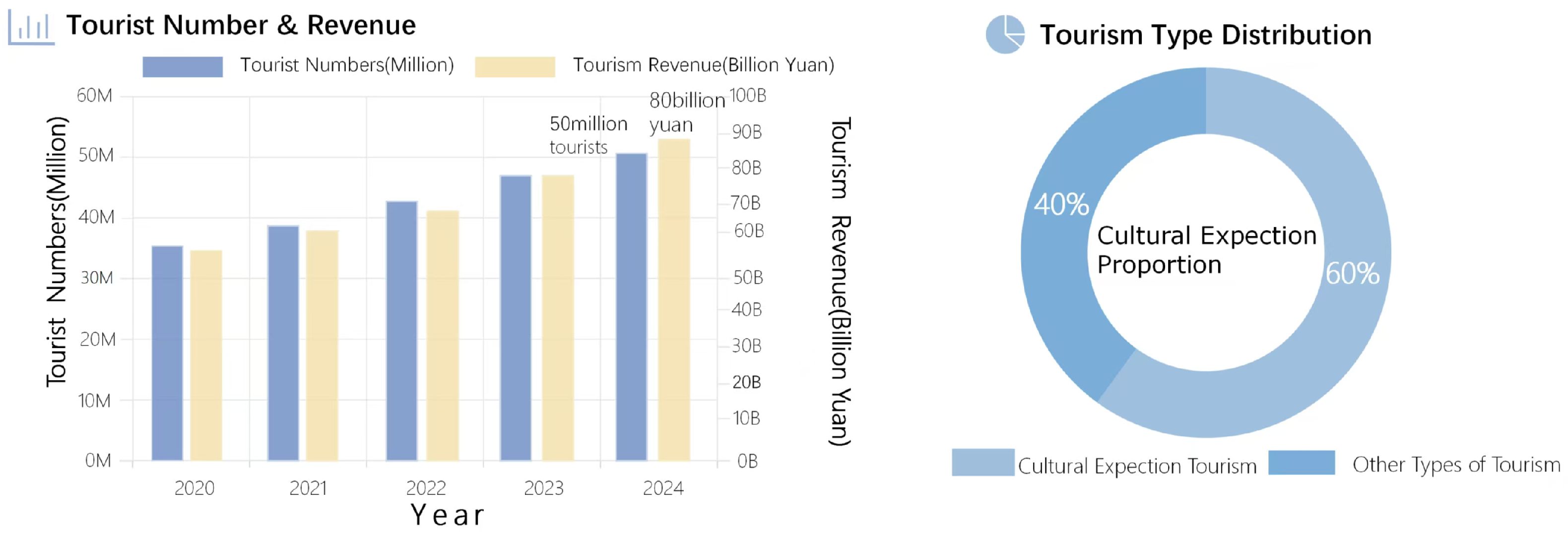
5.2.1. Core Application Scenarios and Quantitative Results
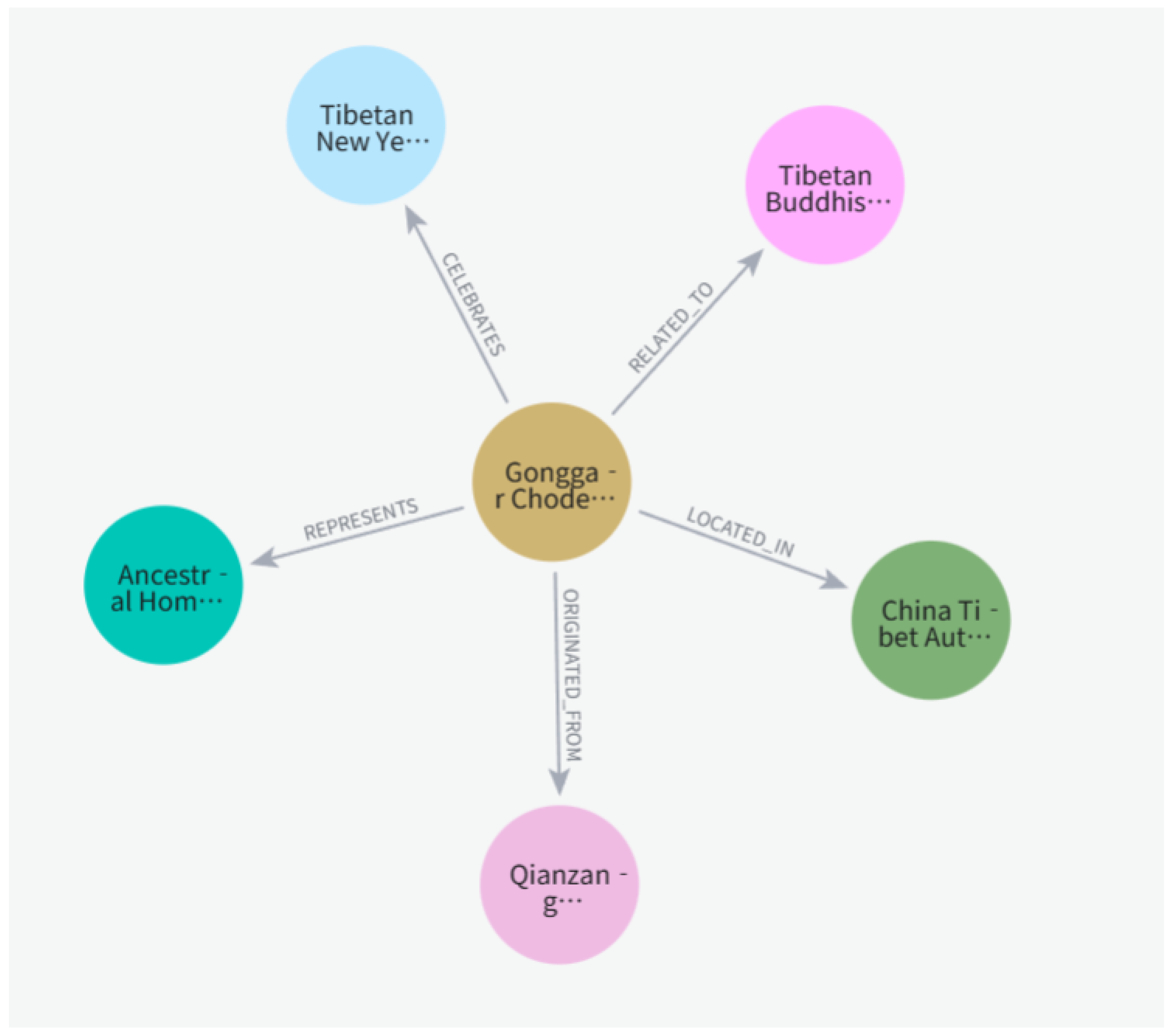
5.2.2. Typical Application Cases
5.3. Limitations and Future Work
5.3.1. Core Limitations of the Current System
5.3.2. Future Research and Optimization Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hogan, A.; Blomqvist, E.; Cochez, M.; D’amato, D.; De Melo, G.; Gutierrez, C.; Kirrane, S.; Labra Gayo, J.E.; Navigli, B.; Neumaier, S. Knowledge Graphs. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Isele, R.; Jakob, M.; Jentzsch, A.; Kontokostas, D.; Mendes, P.N.; Hellmann, S.; Morsey, M.; Van Kleef, P.; Auer, S.; et al. DBpedia—A Large-scale, Multilingual Knowledge Base Extracted from Wikipedia. Semant. Web 2015, 6, 167–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W. Design and Implementation of Personalized Tourism Recommendation System on Basis of Knowledge Graph. In Proceedings of the 2024 3rd International Conference on Data Analytics, Computing and Artificial Intelligence (ICDACAI), Sanya, China, 24–26 January 2024; pp. 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinigen, D.; Teucher, R.; Ruland, T.H.; Rudat, M.; Flores-Herr, N.; Fischer, P.; Milosevic, N.; Schymura, C.; Ziletti, A. Fact Finder—Enhancing Domain Expertise of Large Language Models by Incorporating Knowledge Graphs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.03010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Wang, N.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J. A Practice of Tourism Knowledge Graph Construction based on Heterogeneous Information. In Proceedings of the 19th Chinese National Conference on Computational Linguistics, Haikou, China, 30 October–1 November 2020; Chinese Information Processing Society of China: Haikou, China, 2020; pp. 939–949. Available online: https://aclanthology.org/2020.ccl-1.87/ (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Ren, X.; Tang, J.; Yin, D.; Chawla, N.; Huang, C. A Survey of Large Language Models for Graphs. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD ’24), Barcelona, Spain, 25–29 August 2024; pp. 6616–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szárnyas, G.; Püroja, D.; Boncz, P.; Bebee, B.; Gosnell, D.; Birler, A.; Deutsch, A.; Wu, M.; Fletcher, G.; Gabb, H.A.; et al. The Linked Data Benchmark Council (LDBC): Driving Competition and Collaboration in the Graph Data Management Space. In Performance Evaluation and Benchmarking, Proceedings of the TPCTC 2023, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 28 August–1 September 2023; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 14247, p. 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Cardoso, R.C.; Sohn, A.P.L.; Ferasso, M.; Júnior, S.P. Open Innovation in the Tourism Field: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2024, 10, 100359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.K. Historical Relics in Sino-Tibetan Languages from the Perspective of Cognate Numerals. Lang. Sci. 2018, 17, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Chen, C. CuPe-KG: Cultural perspective–based knowledge graph construction of tourism resources via pretrained language models. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Jiang, C.; Shi, W.; Cheng, F.; Chen, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Wei, G.; et al. DB-GPT: Empowering Database Interactions with Private Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2312.17449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; Yu, H.; Lu, J. Enhancing Knowledge Graph Interactions: A Comprehensive Text-to-Cypher Pipeline with Large Language Models. Inf. Process. Manag. 2026, 63, 104280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Boujddaini, F.; Laguidi, A.; Mejdoub, Y. A Survey on Text-to-SQL Parsing: From Rule-Based Foundations to Large Language Models. In Proceeding of the International Conference on Connected Objects and Artificial Intelligence (COCIA2024), Casablanca, Morocco, 8–10 May 2024; Mejdoub, Y., Elamri, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 1123, pp. 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, F.; Cen, J.; Tan, H.; Jiang, X.; Shen, H. ReFSQL: A Retrieval-Augmentation Framework for Text-to-SQL Generation. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Shen, R.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, W. Instruction Tuning Text-to-SQL with Large Language Models in the Power Grid Domain. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Control, Robotics and Intelligent System, Guangzhou, China, 25–27 August 2023; pp. 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Peng, J.; Mao, C.; Luo, Y. Exploring Large Language Models for Knowledge Graph Completion. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2025), Cape Town, South Africa, 6–11 April 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, J. Knowledge Graph-Enhanced Large Language Models via Path Selection. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024, Bangkok, Thailand, 11–16 August 2024; pp. 6311–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Q. BERT-BiLSTM-CRF Chinese Resume Named Entity Recognition Combining Attention Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering, Dalian, China, 17–19 November 2023; pp. 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Sang, L.; Wen, Z.; Peng, Q. Construction of Cultural Heritage Knowledge Graph Based on Graph Attention Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Peng, P.; Lu, F.; Claramunt, C.; Qiu, P.; Xu, Y. Mining Tourist Preferences and Decision Support via Tourism-Oriented Knowledge Graph. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 61, 103523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Dang, H.; Liu, W.; Gao, Y. Research on the Construction of a Knowledge Graph for Intangible Cultural Heritage in Tibet Based on Big Data. Tibet Sci. Technol. 2022, 1, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, J.; Botsch, M.; Cimiano, P.; Derksen, M.; Elahi, M.; Maier, A.; Maile, M.; Pätzold, I.; Penningroth, J.; Reglin, B.; et al. Virtual Reality Based Access to Knowledge Graphs for History Research. In Semantic Systems. The Power of AI and Knowledge Graphs; Pellegrini, T., Ed.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hou, M. Knowledge Graph Representation Method for Semantic 3D Modeling of Chinese Grottoes. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zakaria, S.A. Design Application and Evolution of 3D Visualization Technology in Architectural Heritage Conservation: A CiteSpace-Based Knowledge Mapping and Systematic Review (2005–2024). Buildings 2025, 15, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.; Le, M.T.; Yoon, D.-I.; Kim, H.-K. 3D Graphics Visualization and Context Information Service for a Virtual Tourist System. J. Ubiquitous Converg. Technol. 2007, 1, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Luo, S.; Tang, J.; Wan, Y.; Yang, B.; Huang, F. CultureSynth: A Hierarchical Taxonomy-Guided and Retrieval-Augmented Framework for Cultural Question-Answer Synthesis. arXiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Fu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Design and Implementation of Event Knowledge Graph Construction Platform Based on Neo4j. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Distributed Computing and Electrical Circuits and Electronics (ICDCECE), Ballar, India, 29–30 April 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z. A Survey on Employing Large Language Models for Text-to-SQL Tasks. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 58, 54, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, S.; Xiong, N.N.; Guo, W. A Survey on Knowledge Graph Embedding: Approaches, Applications and Benchmarks. Electronics 2020, 9, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Hong, Y.; Luo, Z.; et al. A Preview of XiYan-SQL: A Multi-Generator Ensemble Framework for Text-to-SQL. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.08599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Aboulela, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Kashef, R. A Survey on Augmenting Knowledge Graphs (KGs) with Large Language Models (LLMs): Models, Evaluation Metrics, Benchmarks, and Challenges. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2024, 4, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, W.; Zhao, D.; Dong, B.; Kou, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X. High-precision integral imaging 3D salient object detection and reconstruction with texture features based on E2E-TransGAN. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 36329–36343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.; Zagalo, N.; Vairinhos, M. Towards Participatory Activities with Augmented Reality for Cultural Heritage: A Literature Review. Comput. Educ. X Real. 2023, 3, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; He, W.; Deng, H.; Zhong, F.Y.; Chen, Y. High-performance reflection-type augmented reality 3D display using a reflective polarizer. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 9446–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, D.; Li, W.-Y.; Dong, B.-Z.; Li, X.-W.; Wang, X.-R. Adaptive Topology-Driven Integral Imaging 3D Salient Object Detection for Complex Multi-Target Scenes. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 192, 113684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
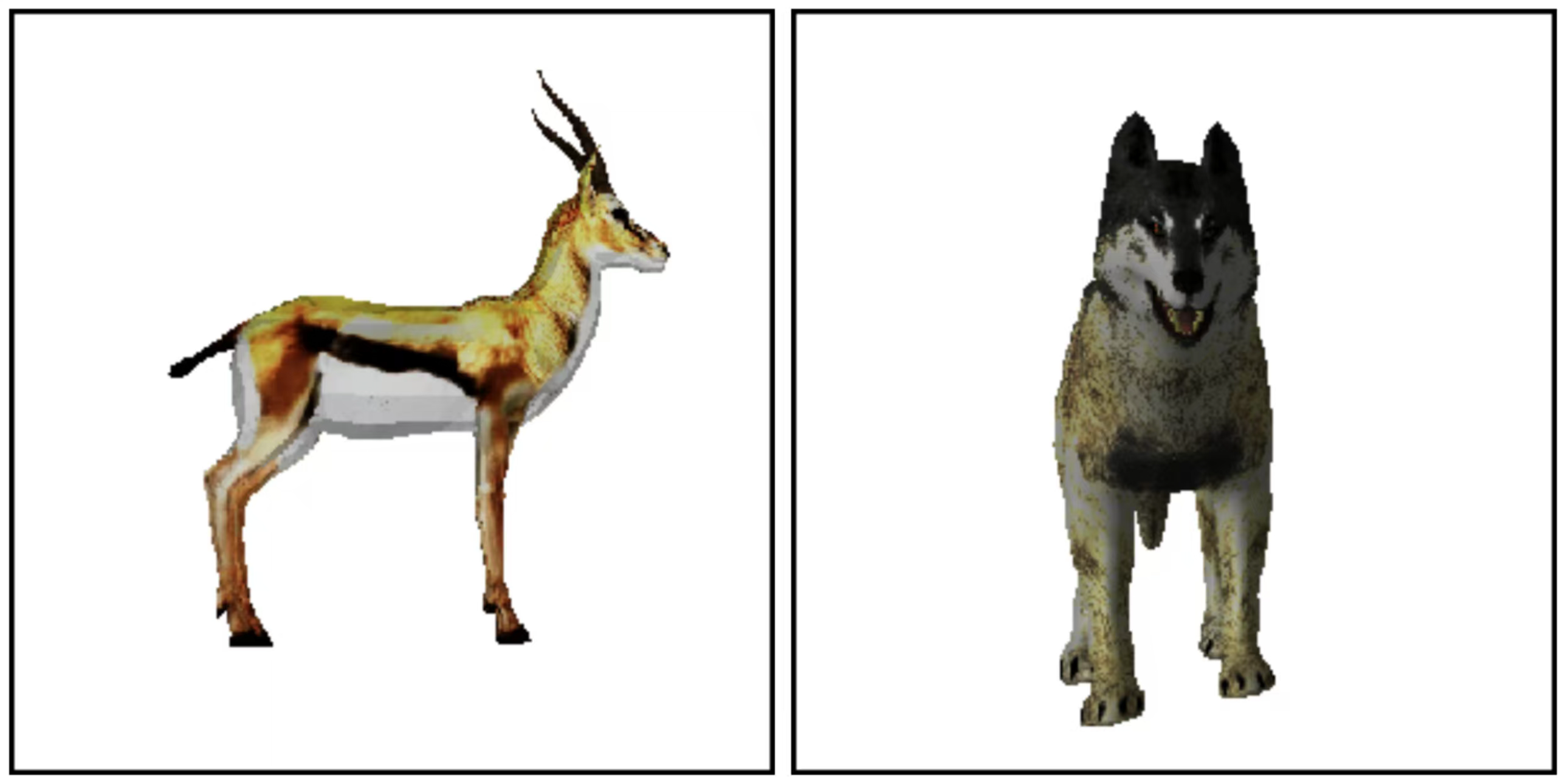
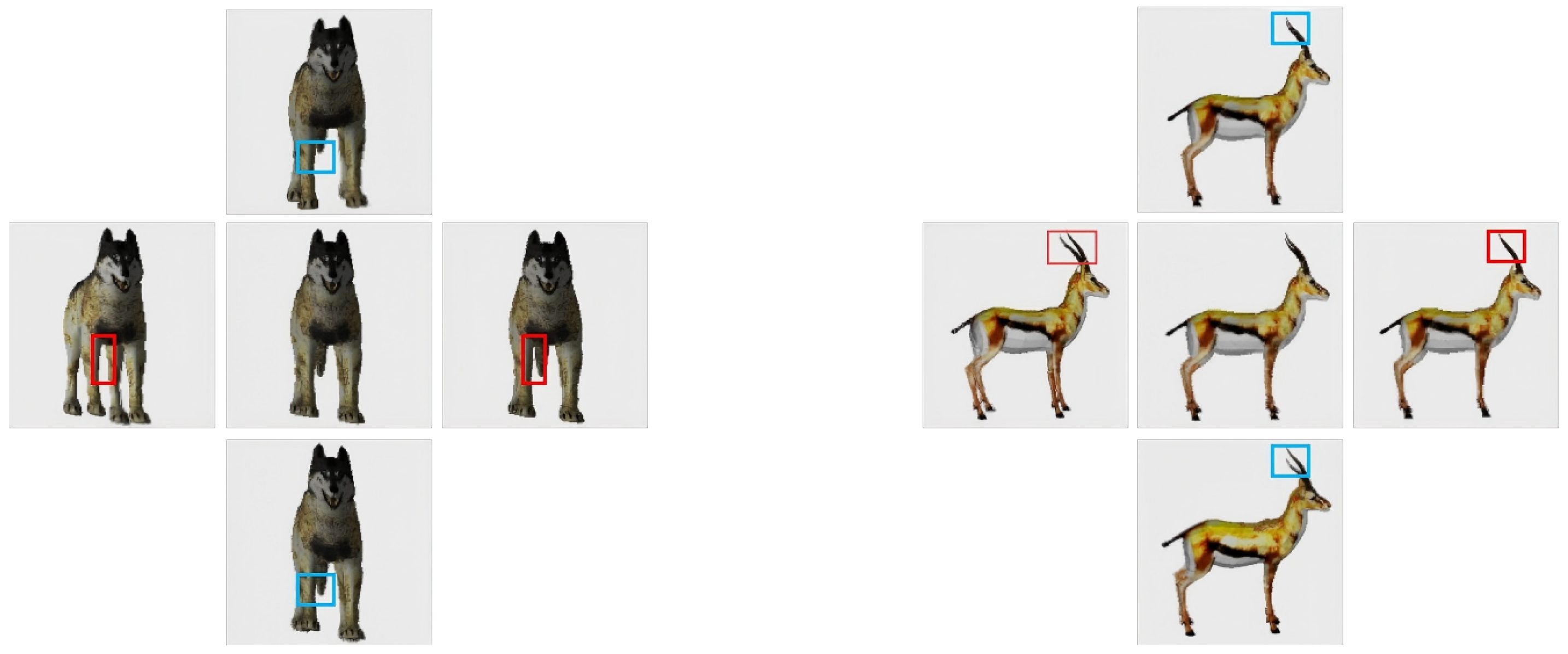


| Category | Rule | Example |
|---|---|---|
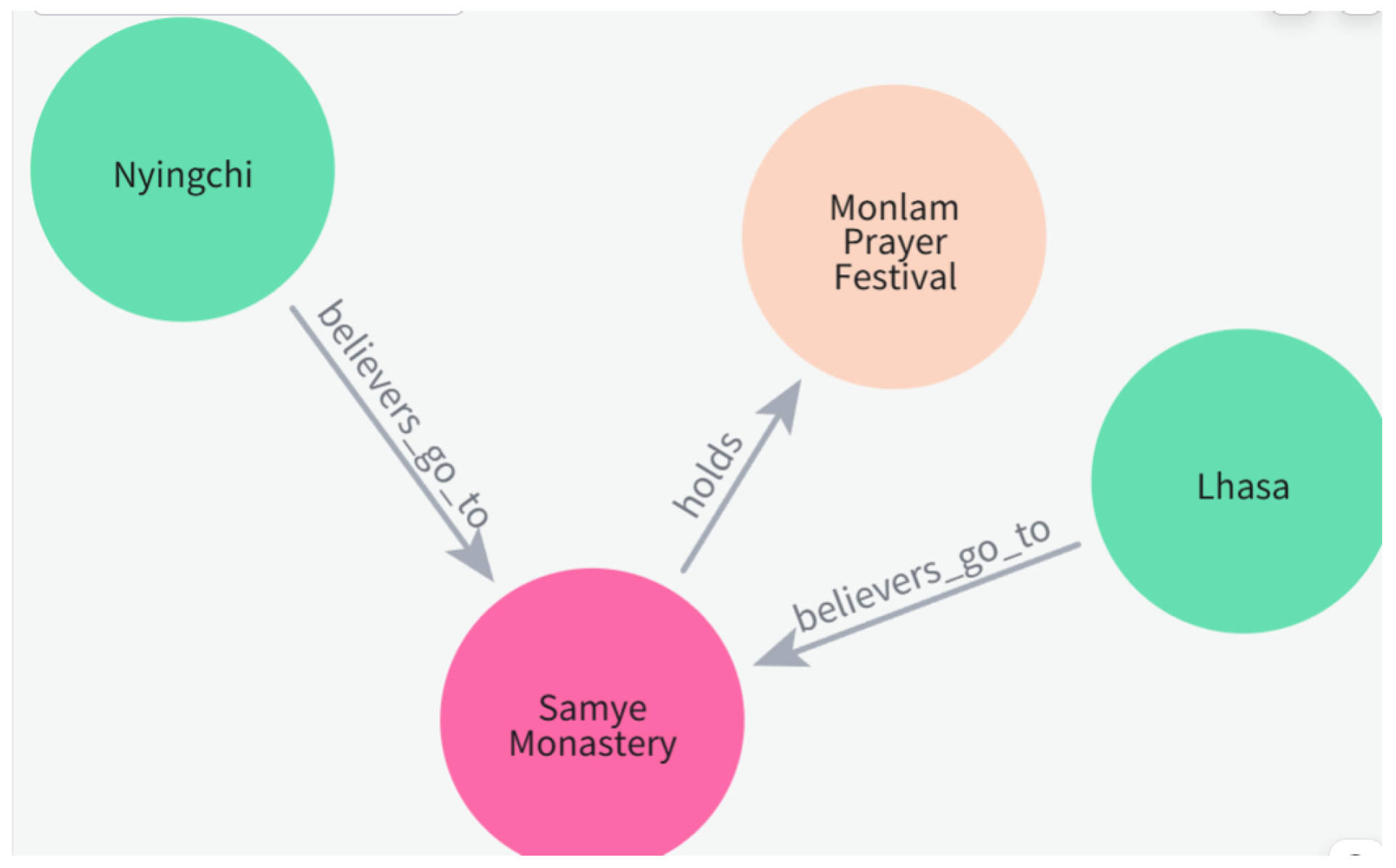
| Node Creation | Use MERGE + ON CREATE SET to ensure idempotency | MERGE(p:Monastery{name:"Sangye Monastery"}) ON CREATE SET p.altitude=3650 |
| Relationship Creation | Nodes and relationships must be merged together to maintain structural integrity | MERGE(a:Monastery{name:"Sangye Monastery"}) MERGE(b:Festival{name:"Monlam Prayer Festival"}) MERGE(a)-[:holds]->(b) |
| Node Deletion | Use DETACH DELETE to avoid dangling relationships | MATCH(n:InvalidNode) DETACH DELETE n |
| Attribute Modification | Use SET to support simultaneous assignment of multiple attributes | MERGE(m:Monastery{name:"Sangye Monastery"}) ON CREATE SET m.altitude = 3650 SET m.address = "Shannan, Tibet", m.founded_in = "8th century" |
| Method | CE (Triples/100 Words) | RA (%) | LAS (%) | GRR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-Only | 8.3 | 78.2 | 62.4 | 11.8 |
| LLM-NoCheck | 9.5 | 80.3 | 63.8 | 20.7 |
| LLM-Direct | 12.7 | 83.1 | 65.3 | 17.6 |
| RLT2C (Ours) | 14.5 | 91.5 | 87.9 | 5.4 |
| Rule-Only(colloquial) | 2.1 | 80.3 | 60.2 | 3.8 |
| LLM-NoCheck(colloquial) | 4.8 | 75.3 | 64.1 | 25.4 |
| LLM-Direct(colloquial) | 7.6 | 78.4 | 68 | 22.4 |
| RLT2C (Ours)(colloquial) | 10.4 | 85.8 | 85.7 | 5.6 |
| Configuration | RA (%) | LAS (%) | CCR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full model | 91.5 | 87.9 | 98.1 |
| - LoRA fine-tuning | 86.3 | 82.1 | 97.8 |
| - LLM verification | 82.7 | 71.5 | 89.3 |
| - Cultural constraint system | 90.2 | 68.4 | 83.5 |
| - MERGE optimization | 91.1 | 87.6 | 97.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Yan, S.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Li, F.; Jiang, B.; Yang, S.; Deng, H. Knowledge-Driven 3D Content Generation: A Rule+LLM-Verify-Based Method for Constructing a Tibetan Cultural and Tourism Knowledge Graph. Electronics 2025, 14, 4138. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214138
Wang K, Yan S, Liu Z, Yuan X, Li F, Jiang B, Yang S, Deng H. Knowledge-Driven 3D Content Generation: A Rule+LLM-Verify-Based Method for Constructing a Tibetan Cultural and Tourism Knowledge Graph. Electronics. 2025; 14(21):4138. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214138
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ke, Shuai Yan, Zirui Liu, Xiaokai Yuan, Fei Li, Bingtao Jiang, Shengying Yang, and Huan Deng. 2025. "Knowledge-Driven 3D Content Generation: A Rule+LLM-Verify-Based Method for Constructing a Tibetan Cultural and Tourism Knowledge Graph" Electronics 14, no. 21: 4138. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214138
APA StyleWang, K., Yan, S., Liu, Z., Yuan, X., Li, F., Jiang, B., Yang, S., & Deng, H. (2025). Knowledge-Driven 3D Content Generation: A Rule+LLM-Verify-Based Method for Constructing a Tibetan Cultural and Tourism Knowledge Graph. Electronics, 14(21), 4138. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214138








