An Adaptive PID Controller for Longitudinal Velocity and Yaw Rate Tracking of Autonomous Mobility Based on RLS with Multiple Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
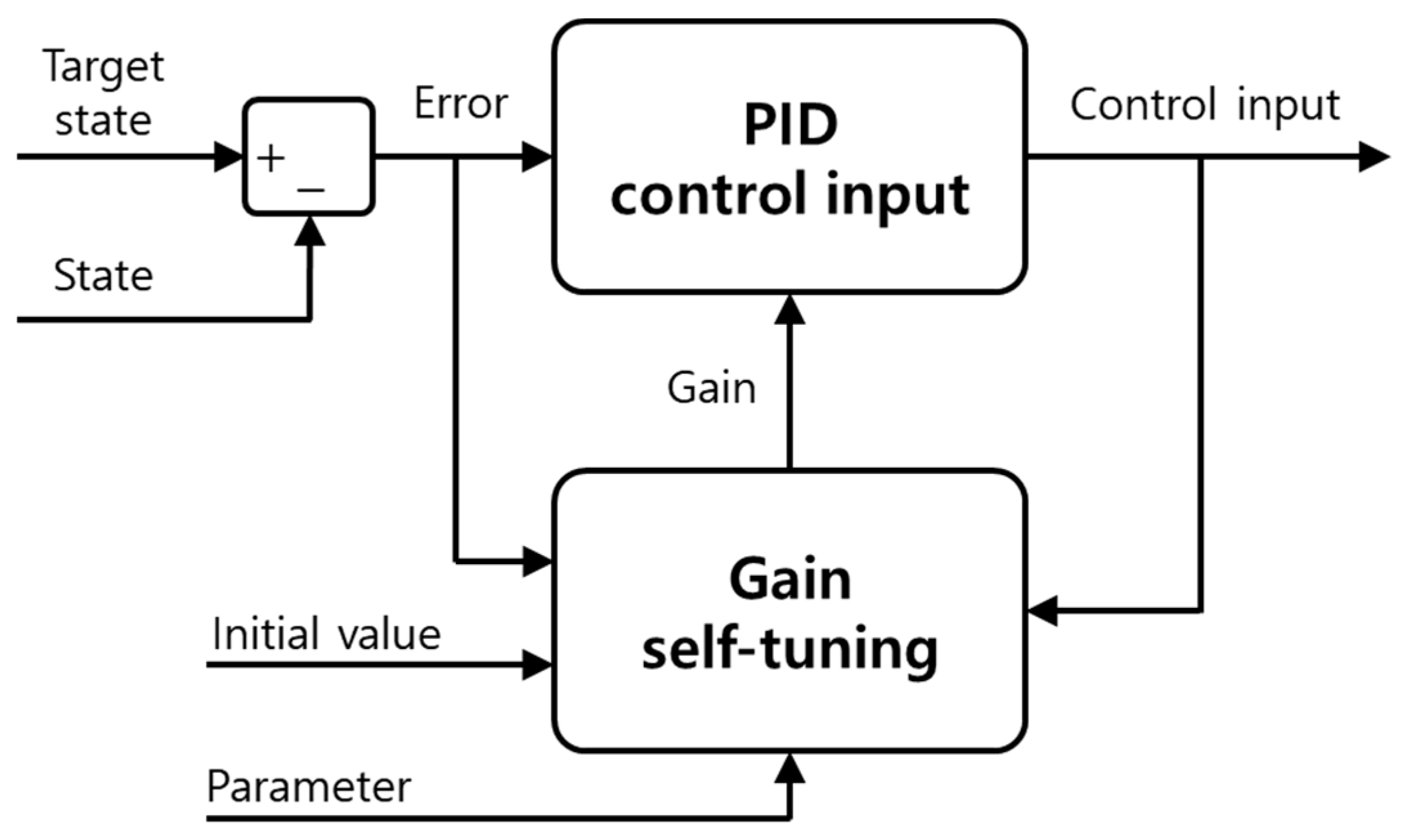
2. Adaptive PID Controller Based on RLS with Multiple Constraints
2.1. Adaptive PID Controller Design with Gain-Self Tuning
2.2. Multiple Constraints
2.3. Stability Analysis with Persistency of Excitation
- Signal boundedness: used in Equations (3) and (13) is obtained via a causal differentiator and is bounded; the reference and measured states remain bounded over the operating region.
- RLS boundedness: , and the regressor is bounded.
- Gain constraints: computed by Equations (21) and (22) satisfy Equations (23)–(28) for all .
- Excitation for identification: There exists such that (persistently exciting condition with a locally integrable function ).
3. Performance Evaluation
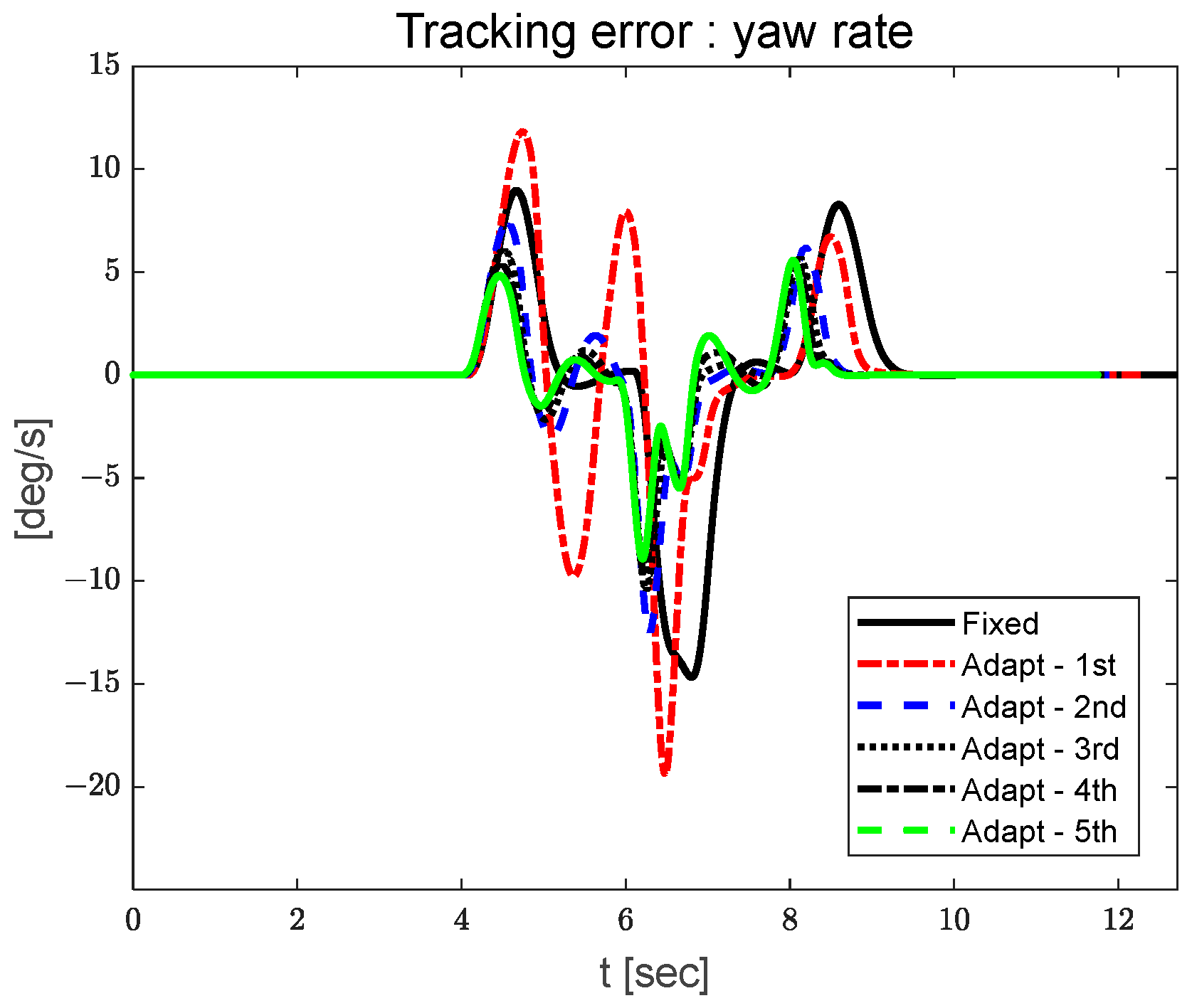
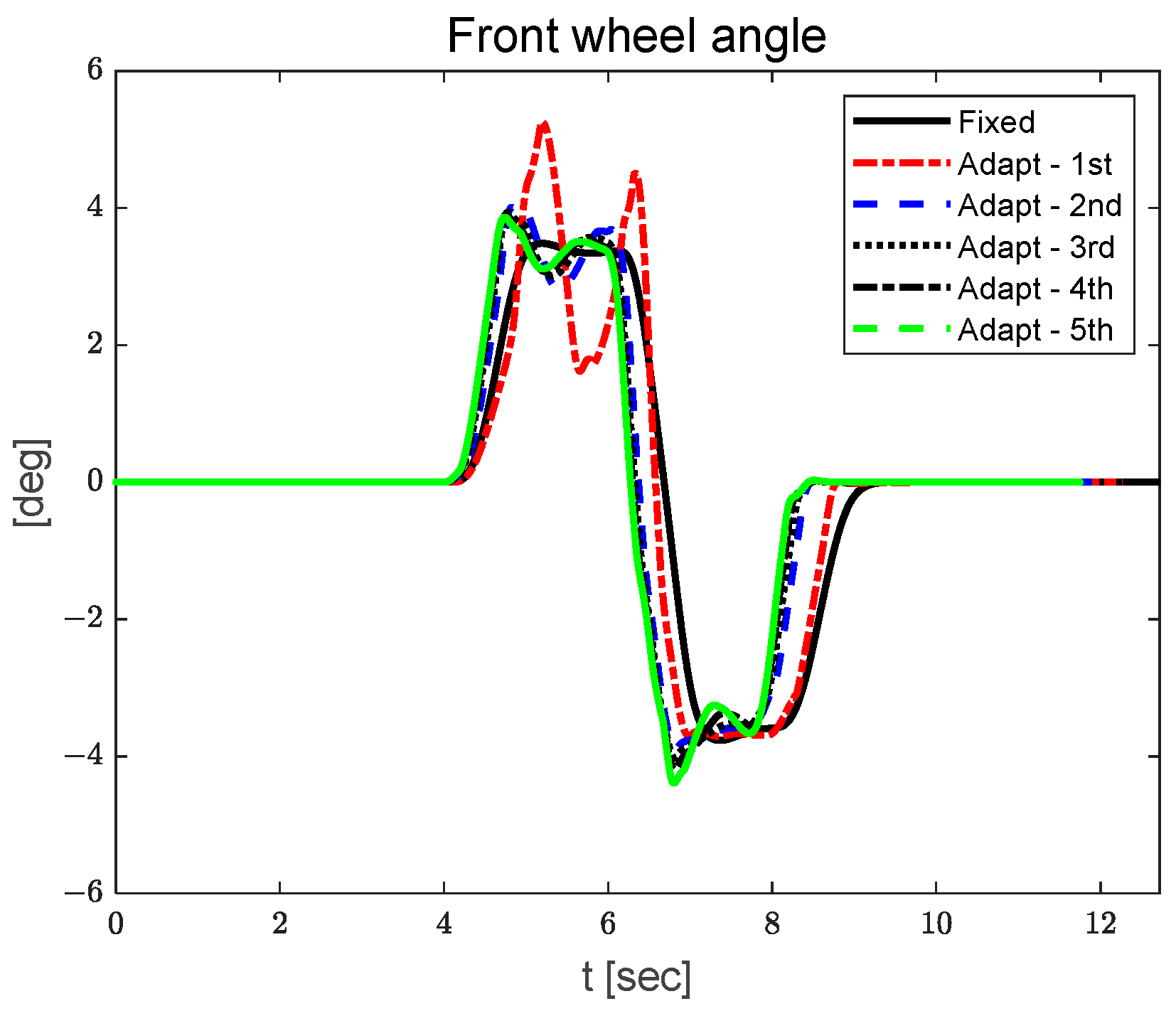
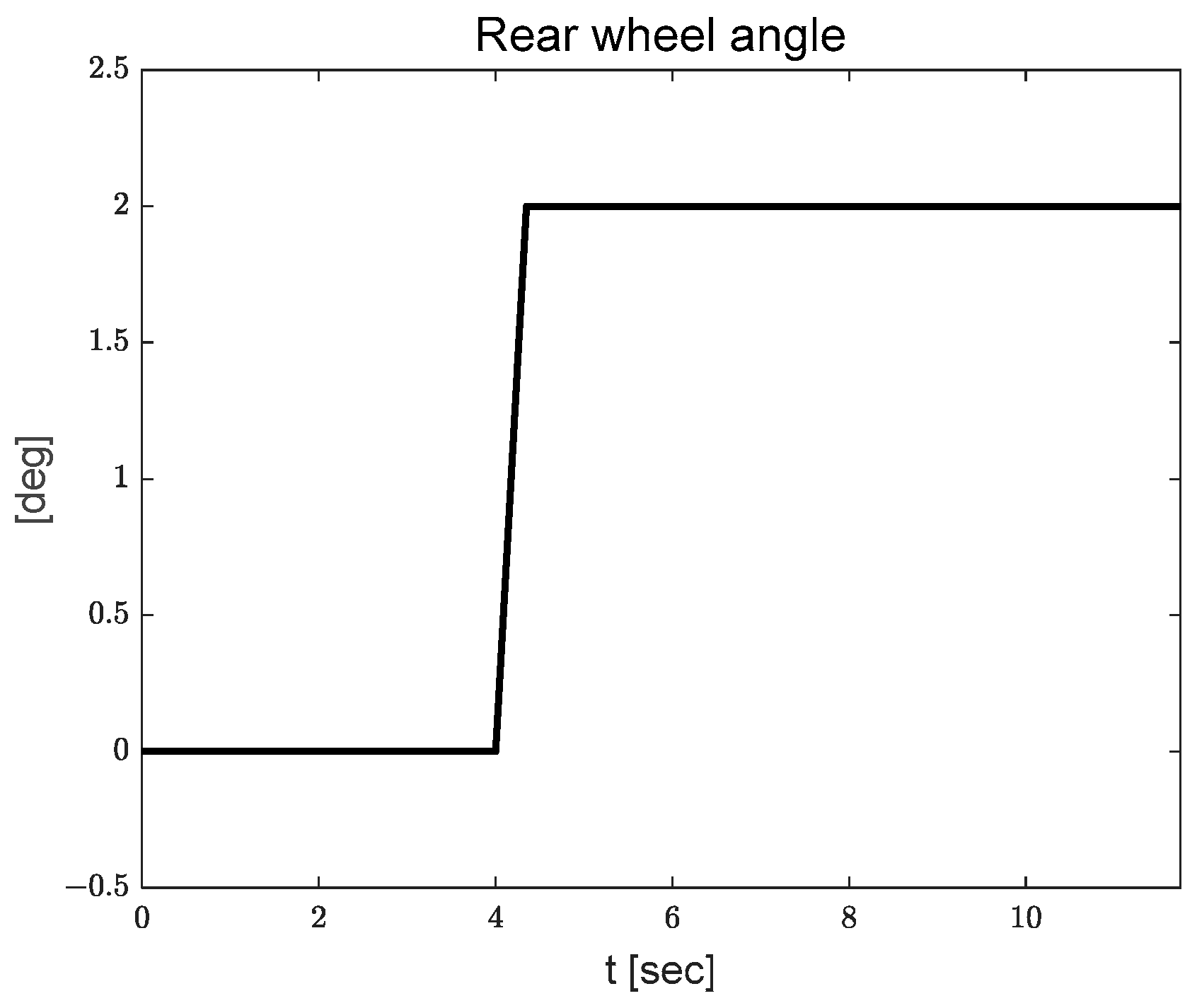
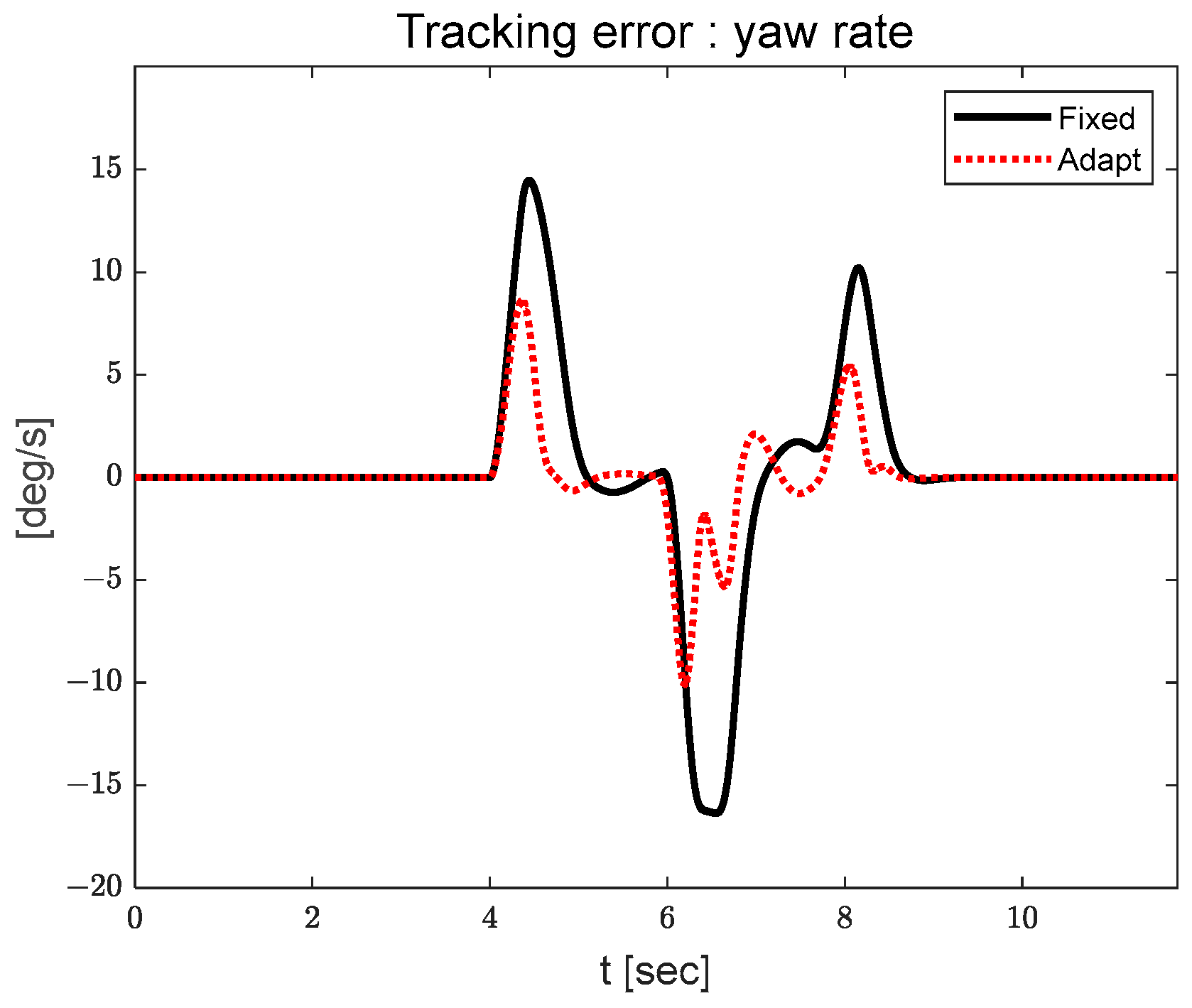
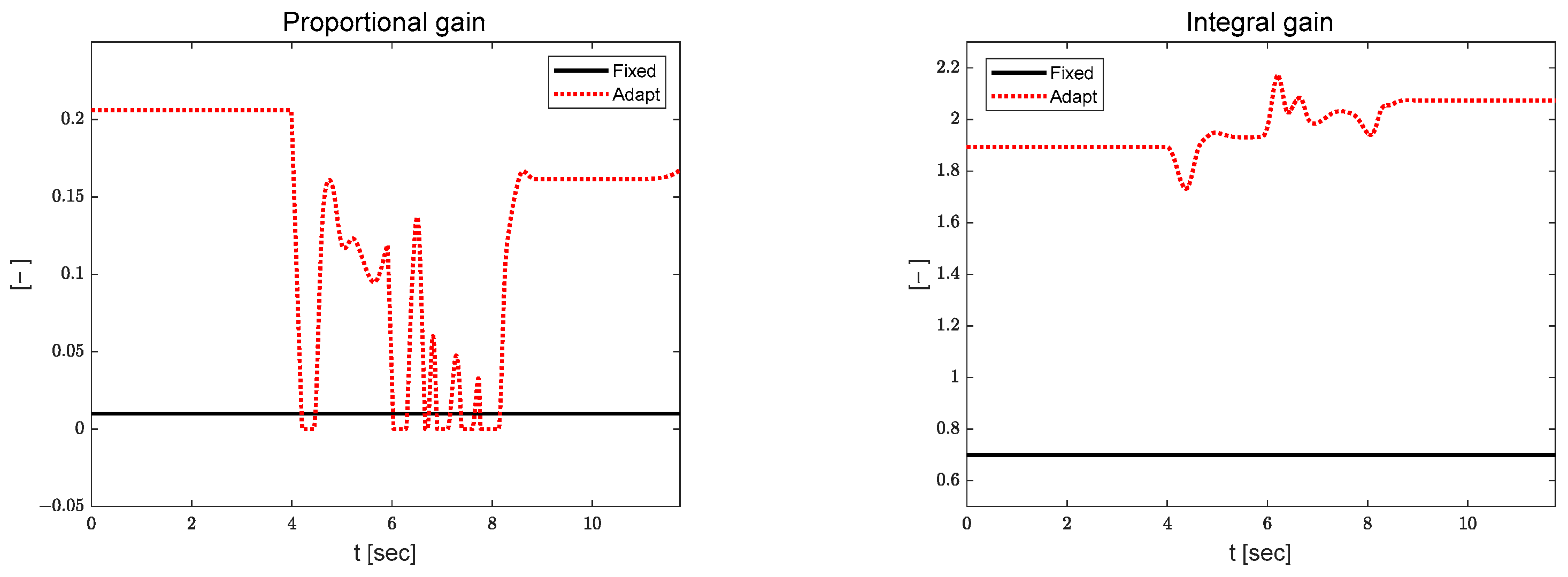
3.1. Yaw Rate Tracking Results
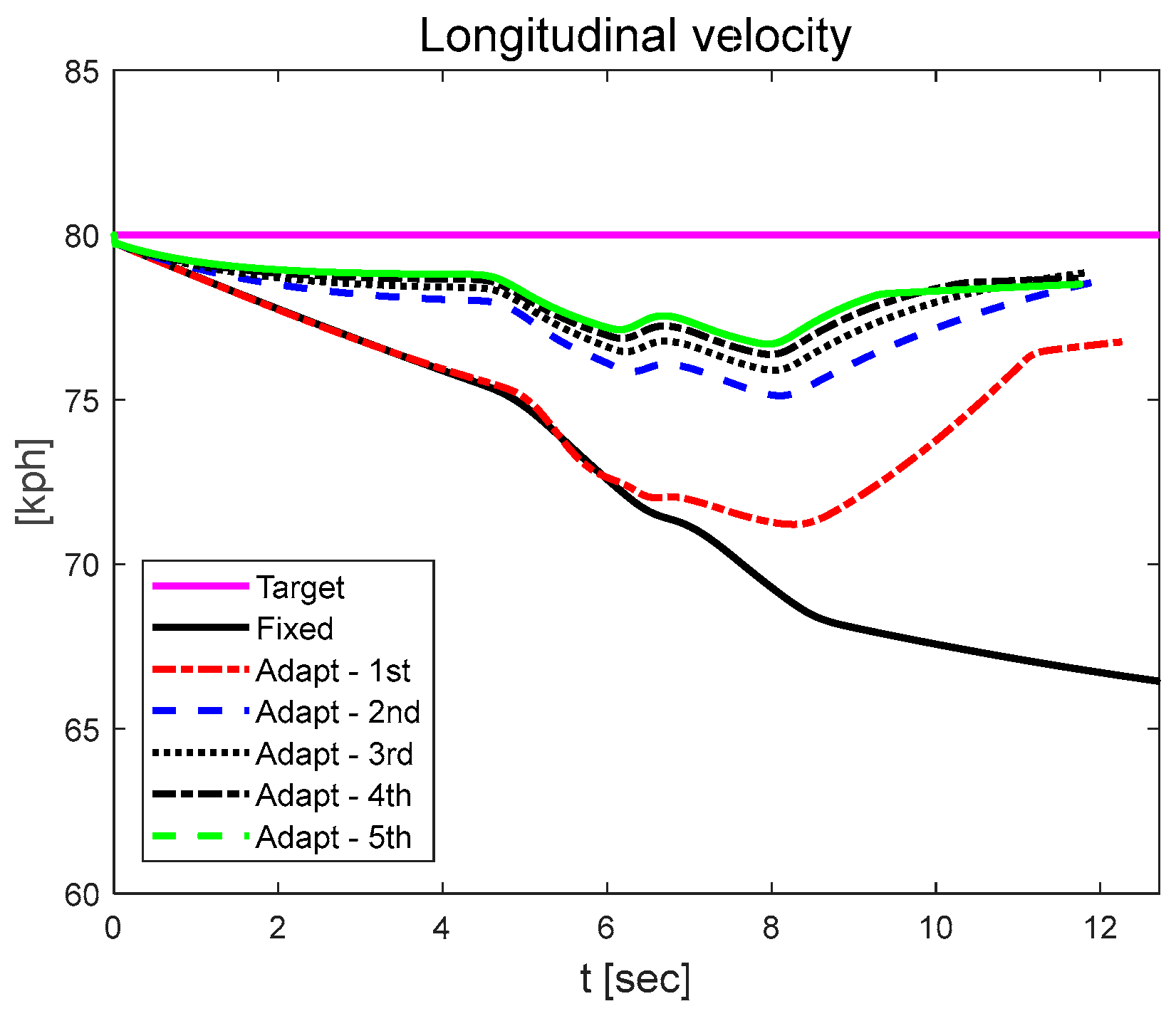
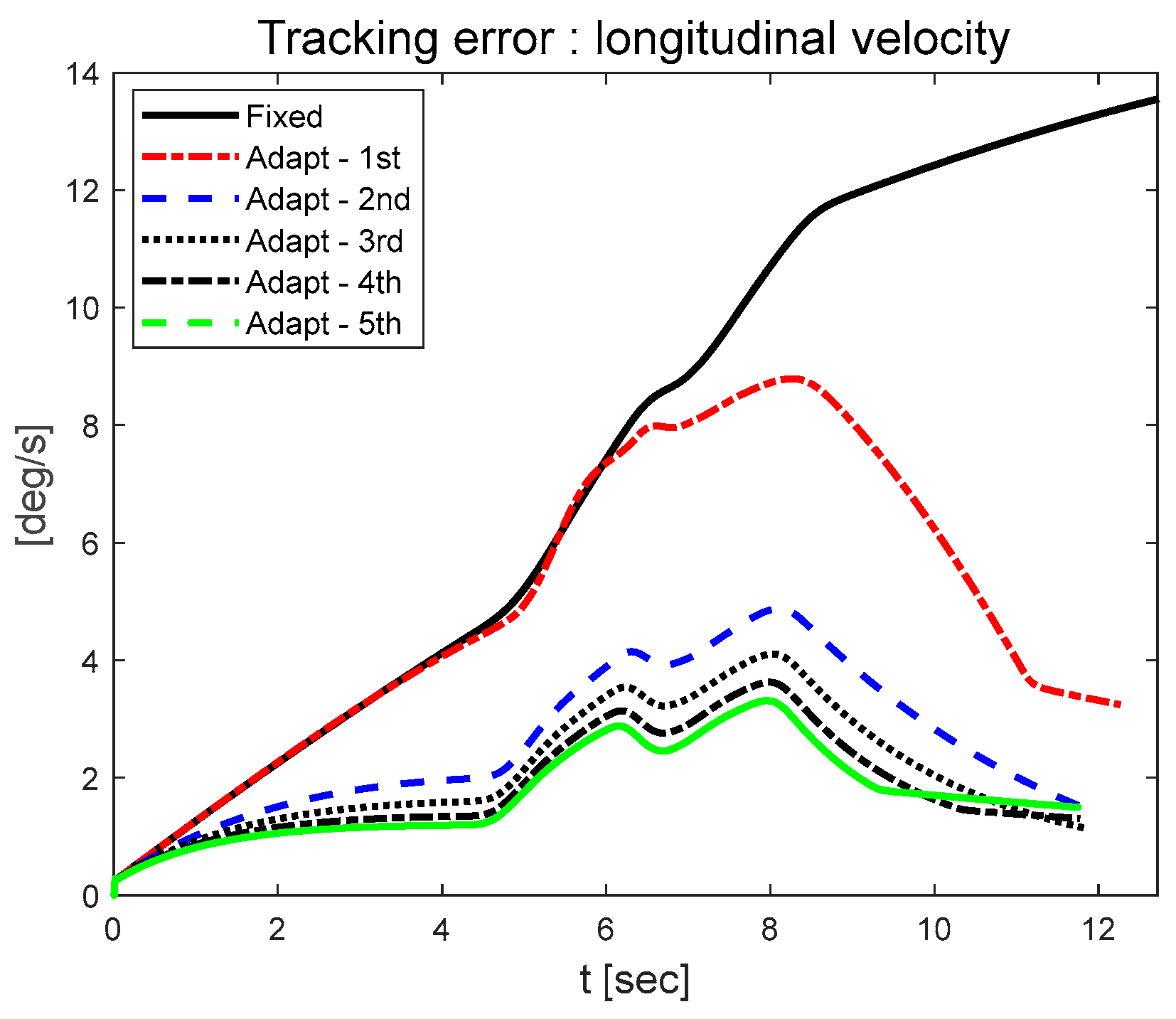
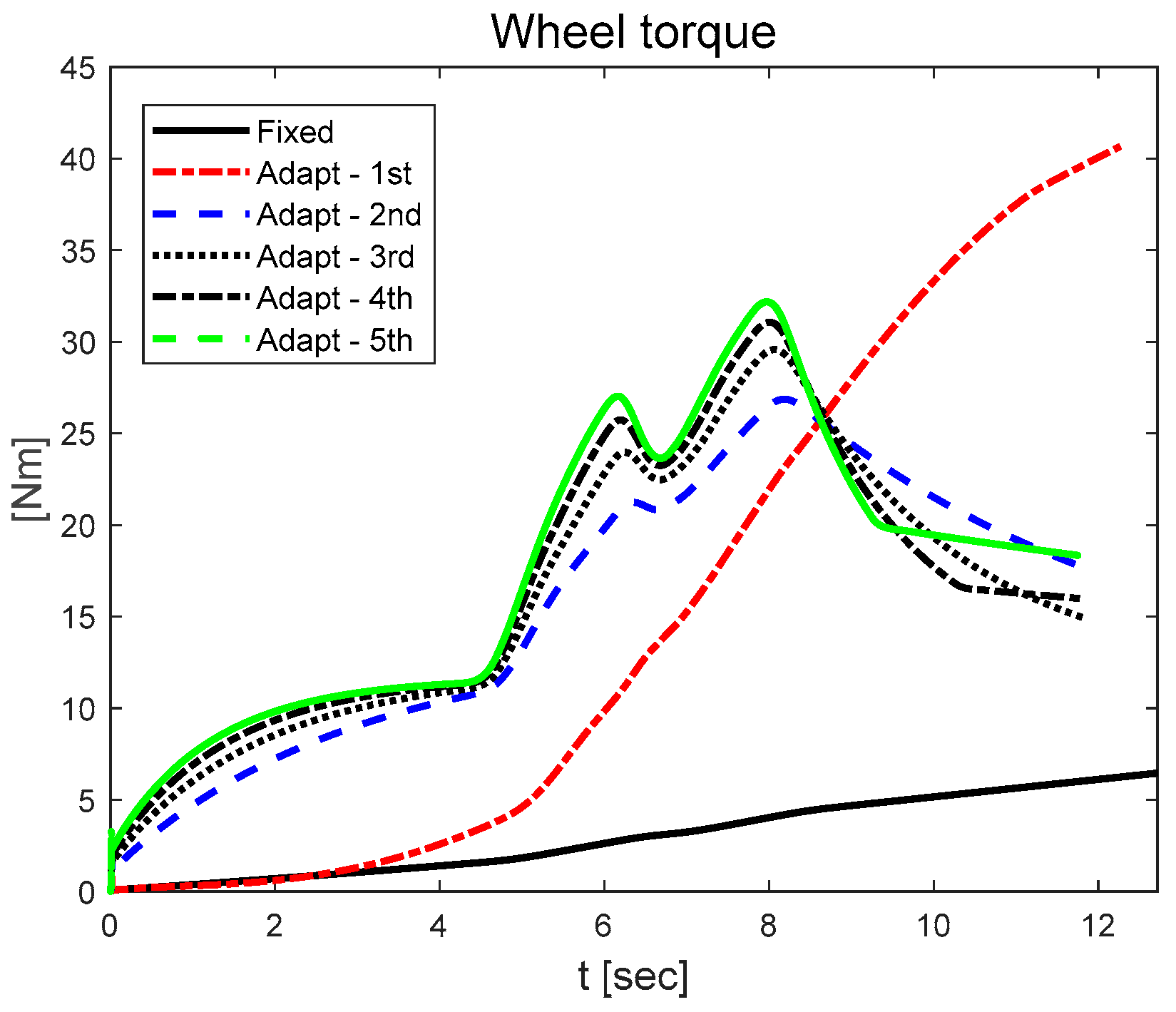
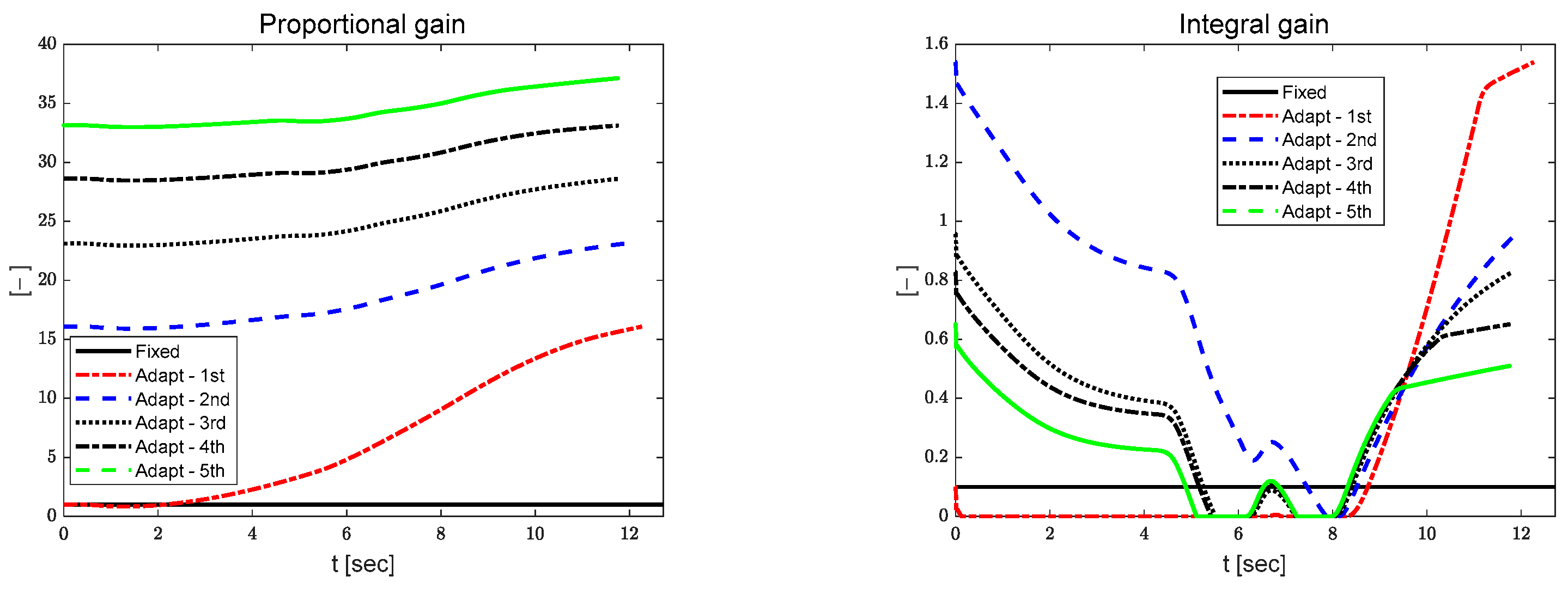
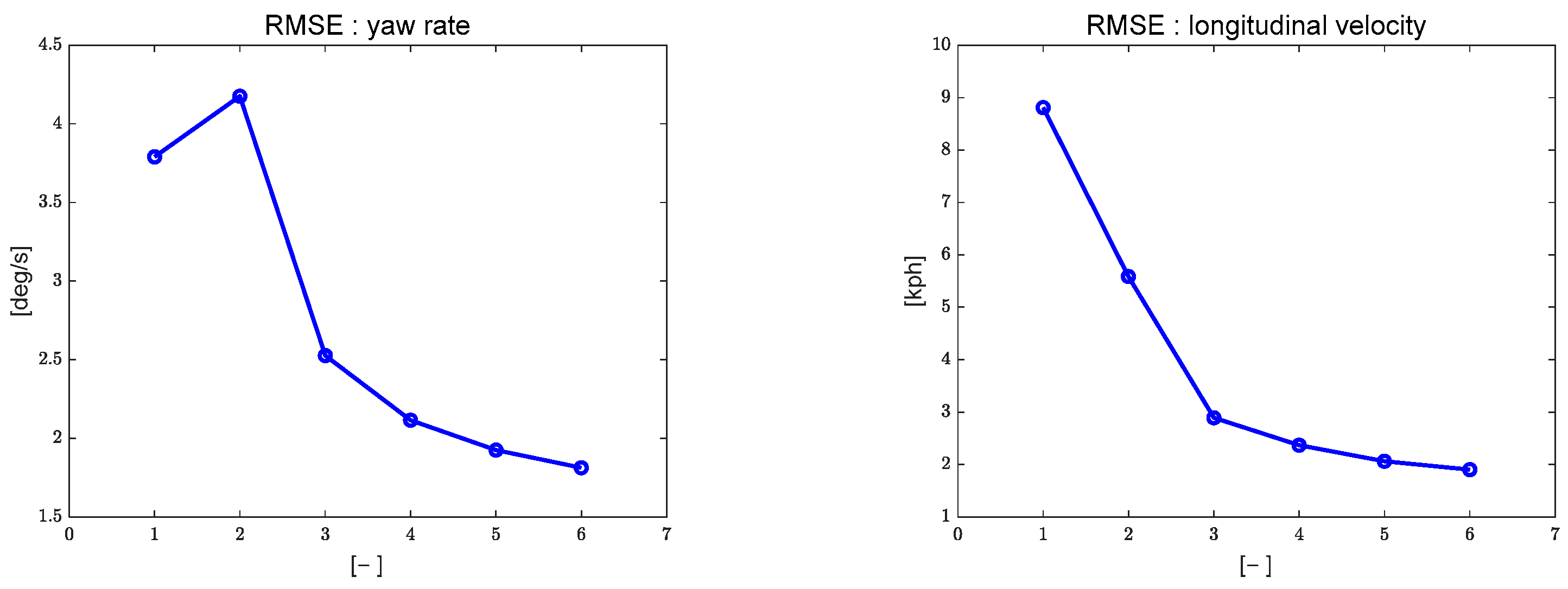
3.2. Longitudinal Velocity Tracking Results
3.3. Yaw Rate Tracking Results with Disturbance and Noise
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PID | Proportional Integral Derivative |
| RLS | Recursive Least Squares |
| RL | Rate Limit |
References
- Abdel-Aty, M.; Ding, S. A matched case-control analysis of autonomous vs. human-driven vehicle accidents. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Jang, C.; Sunwoo, M. Development of autonomous car—Part II: A case study on the implementation of an autonomous driving system based on distributed architecture. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5119–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behere, S.; Törngren, M. A functional reference architecture for autonomous driving. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2016, 73, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, R.C. Implementation of the Pure Pursuit Path Tracking Algorithm (No. CMURITR9201); The Robotics Institute Camegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Thrun, S.; Montemerlo, M.; Dahlkamp, H.; Stavens, D.; Aron, A.; Diebel, J.; Mahoney, P. Stanley: The robot that won the DARPA Grand Challenge. J. Field Robot. 2006, 23, 661–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, J.; Brown, M.; Erlien, S.M.; Gerdes, J.C. Collision avoidance and stabilization for autonomous vehicles in emergency scenarios. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2016, 25, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Nie, L.; Yin, Z.; Huang, S. A two-layer controller for lateral path tracking control of autonomous vehicles. Sensors 2020, 20, 3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menhour, L.; d’Andréa-Novel, B.; Fliess, M.; Gruyer, D.; Mounier, H. An efficient model-free setting for longitudinal and lateral vehicle control: Validation through the interconnected Pro-SiVIC/RTMaps prototyping platform. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 19, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Jeon, S.; Kim, H.; Kum, D. Optimal path tracking control of autonomous vehicle: Adaptive full-state linear quadratic Gaussian (LQG) control. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 109120–109133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Shin, S.; Kim, M.; Park, J. Accurate path tracking by adjusting look-ahead point in pure pursuit method. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2021, 22, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Lu, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Gong, J.; Chen, X. Beyond imitation: A life-long policy learning framework for path tracking control of autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 9786–9799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, R.; Scalzi, S.; Netto, M. Nested PID steering control for lane keeping in autonomous vehicles. Control. Eng. Pract. 2011, 19, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. Path-tracking considering yaw stability with passivity-based control for autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 8736–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Y.; Ren, Y. Yaw rate tracking-based path-following control for four-wheel independent driving and four-wheel independent steering autonomous vehicles considering the coordination with dynamics stability. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2020, 235, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, M.; Ma, H.; Yang, Y. Lateral control of autonomous vehicles based on fuzzy logic. Control. Eng. Pract. 2015, 34, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paden, B.; Čáp, M.; Yong, S.Z.; Yershov, D.; Frazzoli, E. A survey of motion planning and control techniques for self-driving urban vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2016, 1, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Tian, Y. A model predictive controller with longitudinal speed compensation for autonomous vehicle path tracking. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S. Path tracking of autonomous vehicle based on adaptive model predictive control. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2019, 16, 1729881419880089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Yu, C.; Wan, Y. Recursive Least Squares Identification with Variable-Direction Forgetting via Oblique Projection Decomposition. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2021, 9, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhadi, P.; Noei, A.R.; Khosravi, A. Model reference adaptive PID control with anti-windup compensator for an autonomous underwater vehicle. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 83, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garpinger, O.; Haggl, T. Software-based optimal PID design with robustness and noise sensitivity constraints. J. Process Control. 2015, 33, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, T. Trajectory tracking of autonomous vehicle based on model predictive control with PID feedback. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 2239–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gordon, T.; Rahman, S. Model-free autonomous control of four-wheel steering using artificial flow guidance. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2023, 62, 1565–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tork, N.; Amirkhani, A.; Shokouhi, S.B. An adaptive modified neural lateral-longitudinal control system for path following of autonomous vehicles. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Zheng, B.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, D. A reinforcement learning-based adaptive path tracking approach for autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 10581–10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Chen, X.; Tang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Longitudinal and Lateral Cooperative Control of Preview Intelligent Vehicles with Stabilization. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2024, 110, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Pan, S.; Yu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, P.; Gao, L. A comparative study on trajectory tracking control methods for automated vehicles. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simorgh, A.; Marashian, A.; Razminia, A. Adaptive pid control design for longitudinal velocity control of autonomous vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Control, Instrumentation and Automation (ICCIA), Sanandaj, Iran, 30–31 October 2019; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Hu, S.; Shao, X.; Liu, C. Global stability of a saturated nonlinear PID controller for robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2009, 17, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarov, E.M.; Parlakçi, M.N.A.; Istefanopulos, Y. A new variable structure PID-controller design for robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2005, 13, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Takao, K.; Yamada, T. Design of a data-driven PID controller. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2008, 17, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Yu, H.B.; Yuan, M.Z. Design of an optimal PID controller based on Lyapunov approach. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Information Engineering and Computer Science, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 31 March–2 April 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Norlund, F.; Hagglund, T.; Soltesz, K. Seamless PID–MPC hybrid control. In Proceedings of the 4th IFAC Conference on Advances in Proportional-Integral-Derivate Control PID 2024, Almería, Spain, 12–14 June 2024; Volume 58, pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Saat, S.; Ahmad Mohd Ghazali, M. Data-driven brain emotional learning-based intelligent controller-PIDcontrol of MIMO systems based on a modified safe experimentation dynamics algorithm. Int. J. Cogn. Comput. Eng. 2025, 6, 74–99. [Google Scholar]
- Vahidi, A.; Stefanopoulou, A.; Peng, H. Recursive least squares with forgetting for online estimation of vehicle mass and road grade: Theory and experiments. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2005, 43, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | 2275 | Kg |
| Wheel base | 2.975 | m |
| Distance between mass center and front axle | 1.324 | m |
| Distance between mass center and rear axle | 1.651 | m |
| Road surface | Dry asphalt | - |
| Tire cornering stiffness (front/rear) | 75,000/140,000 | N/rad |
| Parameter | Value | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Initial estimate | −0.025/−0.7 | Proportional/Integral |
| Initial covariance | 0.01 | - |
| Forgetting factor | 0.995/0.9995 | Proportional/Integral |
| Rate limit | 1/2 | Proportional/Integral |
| Weighting factor | 0.01 | - |
| Reduction rate | 0.01 | - |
| Fixed proportional gain | 0.01 | - |
| Fixed integral gain | 0.7 | - |
| Derivative gain | 0.0001 | - |
| Parameter | Value | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Initial estimate | −0.025/−0.7 | Proportional/Integral |
| Initial covariance | 0.01 | - |
| Forgetting factor | 0.995/0.9995 | Proportional/Integral |
| Rate limit | 1/2 | Proportional/Integral |
| Weighting factor | 0.01 | - |
| Reduction rate | 0.01 | - |
| Fixed proportional gain | 1 | - |
| Fixed integral gain | 0.1 | - |
| Derivative gain | 0.01 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Oh, K. An Adaptive PID Controller for Longitudinal Velocity and Yaw Rate Tracking of Autonomous Mobility Based on RLS with Multiple Constraints. Electronics 2025, 14, 4111. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204111
Lee J, Oh K. An Adaptive PID Controller for Longitudinal Velocity and Yaw Rate Tracking of Autonomous Mobility Based on RLS with Multiple Constraints. Electronics. 2025; 14(20):4111. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204111
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jeongwoo, and Kwangseok Oh. 2025. "An Adaptive PID Controller for Longitudinal Velocity and Yaw Rate Tracking of Autonomous Mobility Based on RLS with Multiple Constraints" Electronics 14, no. 20: 4111. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204111
APA StyleLee, J., & Oh, K. (2025). An Adaptive PID Controller for Longitudinal Velocity and Yaw Rate Tracking of Autonomous Mobility Based on RLS with Multiple Constraints. Electronics, 14(20), 4111. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204111







