Spatiotemporal Forecasting of Regional Electric Vehicles Charging Load: A Multi-Channel Attentional Graph Network Integrating Dynamic Electricity Price and Weather
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Proposed Approach
2.1. Data Pre-Processing
2.2. STGCN-Attention Model
2.2.1. Problem Definition
2.2.2. Multi-Scale Temporal Feature Extraction (MSTFE) Module
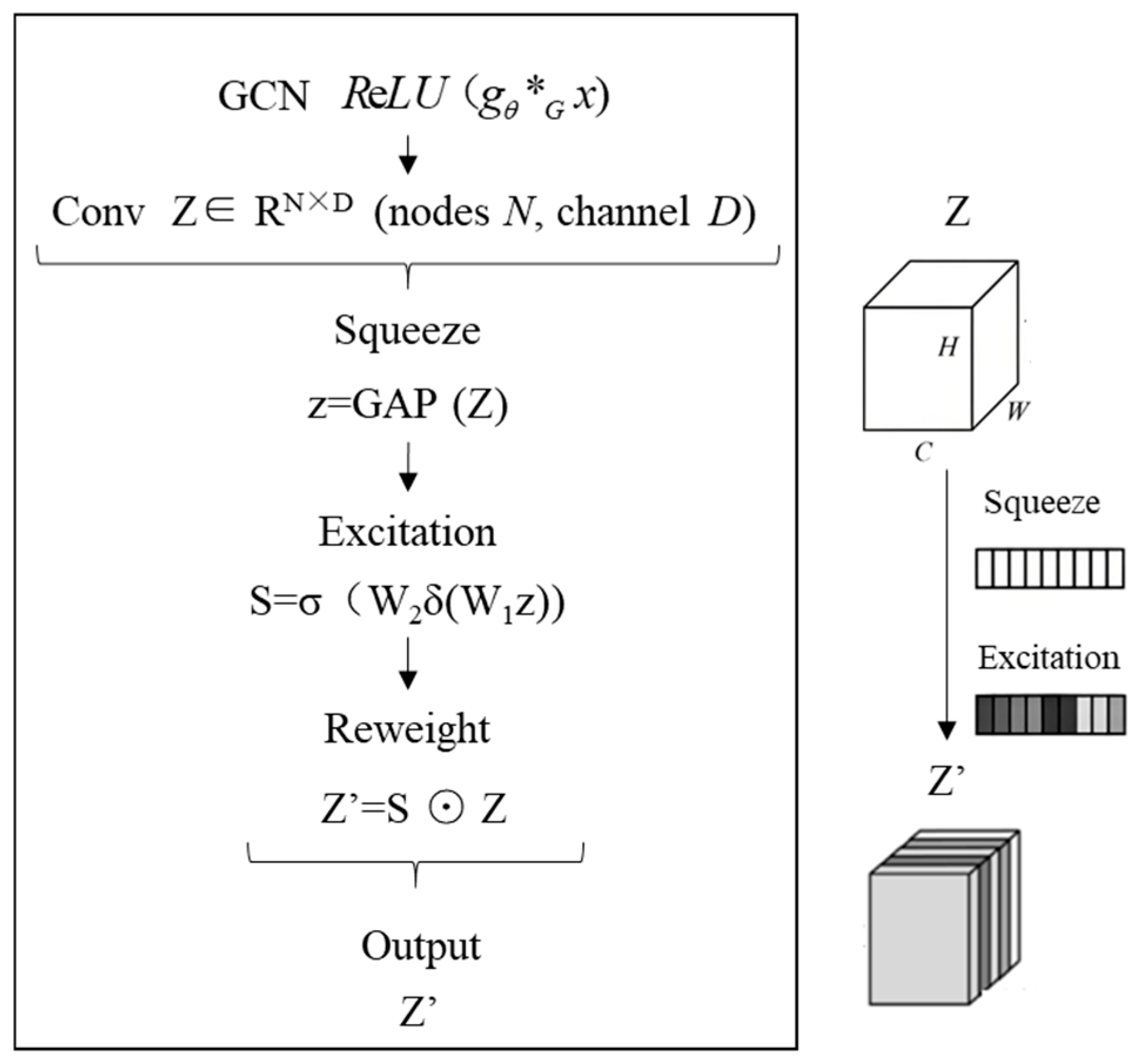
2.2.3. STGCN-A Module
2.3. Algorithm of Prediction
| Algorithm 1: Training Procedure of the STGCN-Attention Model |
| Input: Xf: Historical sequences included charging load, occupancy, price, weather {Xf_hour, Xf_day, Xf_week} A: Adjacency matrix Y: Future charging load K: Order of Chebyshev polynomials Epochs_max: Maximum training epochs |
| Output: Trained STGCN-Attention model parameters |
Begin:
|
3. Case Study
3.1. Data
3.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of EV Charging Load
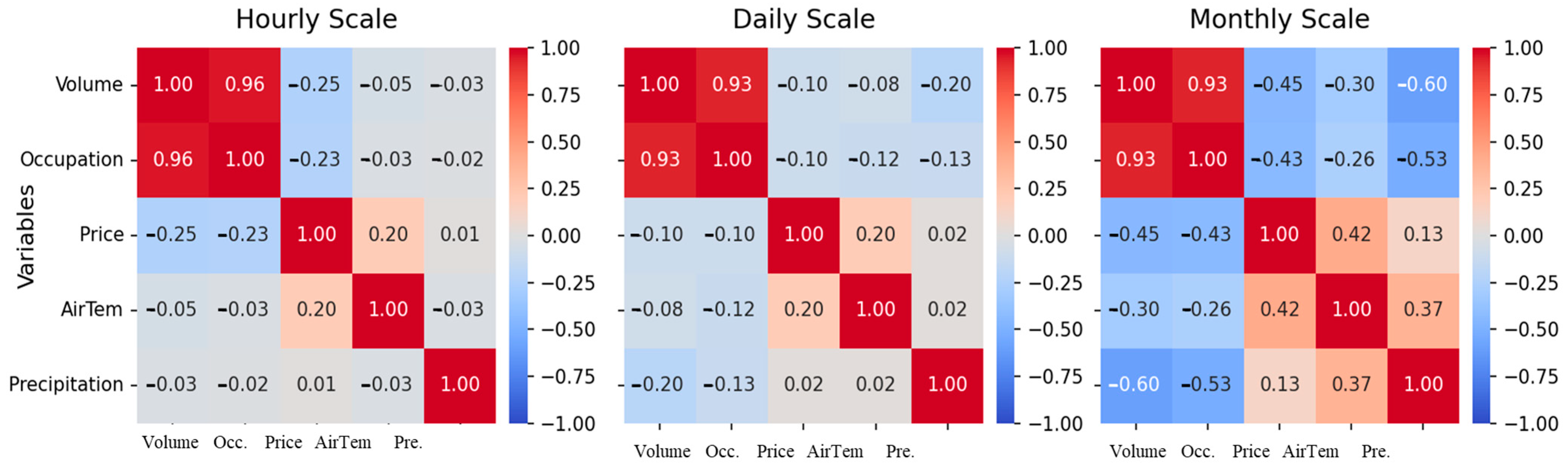
3.3. Correlation Between Charging Load and Multiple Factors
3.4. Prediction Evaluation
3.4.1. The Model Setting and Evaluation
3.4.2. Compared Methods
3.4.3. Evaluation Results
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
3.5.1. Sensitivity of Multi-Scale Temporal Feature Extraction (MSTFE) Module
3.5.2. Sensitivity of Different Input Factors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Acronyms
| EV | Electric vehicles |
| BEV | Battery electric vehicles |
| STGCN-Attention | Spatiotemporal graph convolutional network with cross-attention |
| STGCN | Spatio-temporal graph convolutional network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| CNNs | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| RNNs | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| GCNs | Graph Convolutional Networks |
| GCN | Graph Convolutional Network |
| STDR | Spatiotemporal decomposition and reconstruction |
| ARIMA | AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average |
| CNN-LSTM | Convolutional Neural Network + Long Short-Term Memory |
| GAP | Global Average Pooling |
| CMA | China Meteorological Administration |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| MSTFE | Multi-scale temporal feature extraction |
| Conv | Convolution |
References
- Nyame-Asiamah, F.; Shaw, B.; Stacey, T. Cohered model of adopting electric vehicle fleets in the East of England. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2025, 146, 104897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.L.; Deng, N.; Wang, B.; Shen, X.; Wang, Z.; Hultman, N.; Shi, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.D. Power supply disruptions deter electric vehicle adoption in cities in China. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.P.; Li, S.; Xie, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, P.J.H.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogen as the nexus of future sustainable transport and energy systems. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2025, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.S.; Sharma, J.P.; Gupta, O.H.; Ahmed Abdullah Sufyan, M. Extension of pole differential current based relaying for bipolar LCC HVDC lines. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghali, S.; Guo, Z.; Hasan, S. Investigating the spatiotemporal charging demand and travel behavior of electric vehicles using gps data: A machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Denver, CO, USA, 17–21 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Flexible Constant-Power Range Extension of Self-Oscillating System for Wireless In-Flight Charging of Drones. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 15342–15355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.; Zhang, X.; Qu, H.; You, L.; Zhu, R.; Li, J. Unravelling the effect of electricity price on electric vehicle charging behavior: A case study in Shenzhen, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 115, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Miller, E.J.; Cui, D.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Z. Charging demand prediction in Beijing based on real-world electric vehicle data. J. Energy Storage 2023, 57, 106294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Jian, Y.; Qing, X.; Niu, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S. Prediction of urban electric vehicle charging load based on Monte Carlo method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Electrical and Energy Systems, Lanzhou, China, 29 November–1 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Tayarani, M.; Gao, H.O. An activity-based travel and charging behavior model for simulating battery electric vehicle charging demand. Energy 2022, 258, 124938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Tong, H.; Shu, Y.; Ni, A. Spatial-temporal load prediction of electric bus charging station based on S2TAT. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 164, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Li, H.; You, L.; Zhu, R.; Yan, J.; Santi, P.; Ratti, C.; Yuen, C. ChatEV: Predicting electric vehicle charging demand as natural language processing. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 136, 104470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, N.; Ma, S.; Gan, W.; Zhou, Y. Short-term electric vehicle charging load forecasting based on TCN-LSTM network with comprehensive similar day identification. Appl. Energy 2025, 381, 125174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Kuang, H.; Li, J.; You, L. A physics-informed and attention-based graph learning approach for regional electric vehicle charging demand prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 14284–14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z. A Bilevel Graph Reinforcement Learning Method for Electric Vehicle Fleet Charging Guidance. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 3309–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yu, H.Q. Electric Vehicle Charging Load Prediction Considering Spatio-Temporal Node Importance Information. Energies 2024, 17, 4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Li, S.; Wen, X.; Liang, Z.; Yang, H.; Chung, C.-Y.; Zhu, J. Multiple Time Scale Deep Expert System for Load Forecasting of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations. J. Latex Cl. Files 2025, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Lu, X.; Chang, L. Multi-Scale Spatial-Temporal Graph Attention Network for Charging Station Load Prediction. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 29000–29017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Li, X.C.; Yuan, R.M.; Zhong, K.; Yihao, H.; Yang, T. Electric Vehicle Charging Load Prediction Model based on Improved LSTM Neural Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy Systems and Electrical Power, Wuhan, China, 21–23 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Elahe, M.F.; Kabir, M.A.; Mahmud, S.M.H.; Azim, R. Factors Impacting Short-Term Load Forecasting of Charging Station to Electric Vehicle. Electronics 2023, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhai, W.; Bao, Y.; Gao, D.W.; Wang, Z. Load Forecasting of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Attention Based Spatiotemporal Multi–Graph Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2024, 15, 3016–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chai, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhu, R.; Chung, E. STPNet: Quantifying the Uncertainty of Electric Vehicle Charging Demand via Long-Term Spatiotemporal Traffic Flow Prediction Intervals. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 15018–15034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tang, A.; Wei, F.; Yang, H.; Xinran, L.; Peng, J. Electric vehicle charging load forecasting considering weather impact. Appl. Energy 2025, 383, 125337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Lin, Y.; Feng, N.; Song, C.; Wan, H. Attention Based Spatial-Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Traffic Flow Forecasting. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January 2019; pp. 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q. Attention Based Spatial-Temporal Graph Convolutional Recurrent Networks for Traffic Forecasting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.12973v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Liu, H. Multi-step electric vehicles charging loads forecasting: An autoformer variant with feature extraction, frequency enhancement, and error correction blocks. Appl. Energy 2024, 376 Pt B, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Hu, Y. Causality-Aware Multi-Graph Convolutional Networks with Critical Node Dynamics for Electric Vehicle Charging Station Load Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 3210–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qu, H.; Tan, X.; You, L.; Zhu, R.; Fan, W. UrbanEV: An Open Benchmark Dataset for Urban Electric Vehicle Charging Demand Prediction. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yin, W.; Feng, D.; Zhou, Y. A framework for analyzing the spatiotemporal distribution of urban electric vehicle charging load: A case study of Shanghai. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 127, 106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, P.; Qin, J. Short-term Charging Load Forecasting for Electric Vehicles with a Multilayer LSTM Model Considering Sliding Windows and Online Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 8th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Shenyang, China, 29 November–2 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Y. Stochastic optimization for joint energy-reserve dispatch considering uncertain carbon emission. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 211, 115297. [Google Scholar]






| RMSE | MAE | MAPE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hour | 24 h | Hour | 24 h | Hour | 24 h | |
| LSTM | 42.64 | 61.26 | 32.72 | 48.02 | 0.27 | 0.37 |
| STGCN | 40.85 | 58.72 | 30.12 | 45.80 | 0.29 | 0.39 |
| STGCN-Attention | 37.32 | 54.13 | 27.34 | 43.12 | 0.25 | 0.36 |
| Input Factor | RMSE | MAE | MAPE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hour | 24 h | Hour | 24 h | Hour | 24 h | |
| Volume | 38.94 | 59.23 | 30.10 | 47.45 | 0.26 | 0.37 |
| Volume + Occupation | 37.67 | 57.31 | 28.97 | 46.34 | 0.26 | 0.39 |
| Volume + Price | 37.01 | 59.02 | 27.63 | 46.78 | 0.25 | 0.37 |
| Volume + AirTem | 39.35 | 61.03 | 31.10 | 48.90 | 0.31 | 0.40 |
| Volume + Precipitation | 40.94 | 60.29 | 32.98 | 48.01 | 0.33 | 0.42 |
| Volume + Occupation + Price | 37.32 | 58.72 | 27.34 | 45.80 | 0.25 | 0.36 |
| Volume + Occupation + Price + AirTem | 38.75 | 59.23 | 29.29 | 46.56 | 0.27 | 0.38 |
| Volume + Occupation + Price + Precipitation | 38.04 | 58.98 | 29.03 | 46.26 | 0.27 | 0.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H. Spatiotemporal Forecasting of Regional Electric Vehicles Charging Load: A Multi-Channel Attentional Graph Network Integrating Dynamic Electricity Price and Weather. Electronics 2025, 14, 4010. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204010
Ding H, Guo Y, Wang H. Spatiotemporal Forecasting of Regional Electric Vehicles Charging Load: A Multi-Channel Attentional Graph Network Integrating Dynamic Electricity Price and Weather. Electronics. 2025; 14(20):4010. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204010
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Hui, Youyou Guo, and Haibo Wang. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Forecasting of Regional Electric Vehicles Charging Load: A Multi-Channel Attentional Graph Network Integrating Dynamic Electricity Price and Weather" Electronics 14, no. 20: 4010. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204010
APA StyleDing, H., Guo, Y., & Wang, H. (2025). Spatiotemporal Forecasting of Regional Electric Vehicles Charging Load: A Multi-Channel Attentional Graph Network Integrating Dynamic Electricity Price and Weather. Electronics, 14(20), 4010. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204010






