Abstract
Cognitive biases continue to pose significant challenges in executive decision-making, often leading to strategic inefficiencies, misallocation of resources, and flawed risk assessments. While traditional decision-making relies on intuition and experience, these methods are increasingly proving inadequate in addressing the complexity of modern business environments. Despite the growing integration of big data analytics into executive workflows, existing research lacks a comprehensive examination of how AI-driven methodologies can systematically mitigate biases while maintaining transparency and trust. This paper addresses these gaps by analyzing how big data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and explainable AI (XAI) contribute to reducing heuristic-driven errors in executive reasoning. Specifically, it explores the role of predictive modeling, real-time analytics, and decision intelligence systems in enhancing objectivity and decision accuracy. Furthermore, this study identifies key organizational and technical barriers—such as biases embedded in training data, model opacity, and resistance to AI adoption—that hinder the effectiveness of data-driven decision-making. By reviewing empirical findings from A/B testing, simulation experiments, and behavioral assessments, this research examines the applicability of AI-powered decision support systems in strategic management. The contributions of this paper include a detailed analysis of bias mitigation mechanisms, an evaluation of current limitations in AI-driven decision intelligence, and practical recommendations for fostering a more data-driven decision culture. By addressing these research gaps, this study advances the discourse on responsible AI adoption and provides actionable insights for organizations seeking to enhance executive decision-making through big data analytics.
1. Introduction
Cognitive biases represent a significant challenge in executive decision-making within today’s complex and high-stakes business environment. Corporate leaders face a multifaceted decision landscape influenced by organizational culture, historical precedent, external pressures, and deeply embedded psychological tendencies that often operate below conscious awareness [1]. Despite the traditional reverence for intuition and experience in executive circles, research has increasingly demonstrated how these cognitive shortcuts can lead to systematic errors in judgment, resulting in suboptimal strategic outcomes, resource misallocation, and missed market opportunities [2].
The impact of these cognitive distortions is particularly pronounced in executive contexts, where confirmation bias reinforces existing assumptions, anchoring bias tethers decisions to initial reference points, and overconfidence bias inflates the perceived accuracy of strategic forecasts. These psychological tendencies collectively undermine rational decision-making processes and can propagate throughout organizations, affecting everything from capital allocation to talent management and competitive strategy [2].
The emergence of big data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) represents a paradigm shift in how organizations approach strategic decision-making. For the first time, executives have access to tools that can systematically counteract cognitive limitations through data-driven methodologies. Machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics, and real-time data processing capabilities enable businesses to identify patterns beyond human perception, challenge entrenched assumptions, and augment decision-making with objective insights derived from comprehensive datasets [3]. Advanced analytical approaches such as explainable AI (XAI), causal inference modeling, and anomaly detection further enhance the potential for more rational, evidence-based strategic decisions.
However, integrating data-driven insights into executive workflows presents significant challenges. Questions regarding data reliability, model interpretability, organizational readiness, and ethical implications must be addressed for analytics to mitigate cognitive biases effectively. The path from traditional intuition-based leadership to data-augmented decision-making requires careful navigation of technical and cultural barriers.
1.1. Literature Review Methodology and Current Research Landscape
This review employed a systematic approach to identify relevant literature at the intersection of cognitive bias mitigation and big data analytics in decision-making contexts. We searched the Web of Science, Scopus, and IEEE Xplore databases using the keywords (“cognitive bias*” OR “decision bias*”) AND (“big data” OR “artificial intelligence” OR “machine learning”) AND (“decision making” OR “executive*” OR “management”) for publications from 2018–2024. After screening 847 initial results, 156 studies met inclusion criteria focusing on empirical applications of AI/analytics for bias reduction in organizational settings.
Table 1 synthesizes ten (10) pivotal studies that exemplify current understanding of how analytical technologies influence executive decision processes, selected based on citation impact, methodological rigor, and relevance to bias mitigation applications.

Table 1.
Summary of key studies on big data analytics and cognitive bias mitigation.
Research Gaps Identified: Current literature reveals three critical gaps: (1) limited empirical validation of bias reduction effectiveness in real-world executive contexts, (2) insufficient integration of explainable AI techniques for maintaining decision transparency, and (3) lack of comprehensive frameworks addressing both technical and organizational implementation challenges.
Building on this foundation, our research examines multiple dimensions of the bias mitigation challenge. Figure 1 presents the conceptual framework that guides our investigation, illustrating the interconnected nature of cognitive biases, analytical methodologies, and organizational factors that collectively shape executive decision quality.
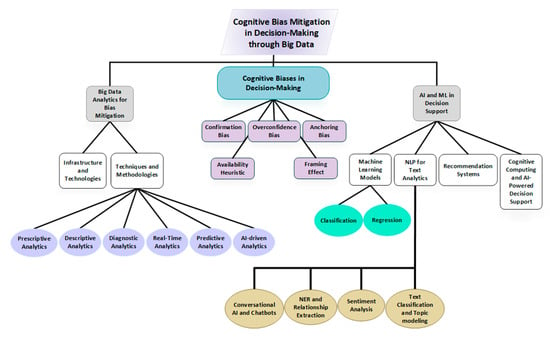
Figure 1.
Overview of surveyed key topics.
1.2. Research Objectives and Contributions
This study addresses identified gaps by examining mechanisms through which big data analytics, AI, and XAI can systematically mitigate cognitive biases in executive decision-making while maintaining accountability and organizational acceptance.
Primary Research Questions:
- How do specific AI/ML techniques detect and counteract different types of cognitive biases in executive decision contexts?
- What are the key technical and organizational barriers to implementing bias mitigation systems?
- How can explainable AI enhance trust and adoption of automated debiasing tools?
Novel Contributions:
- Comprehensive taxonomy of bias mitigation mechanisms across descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics
- Empirical evaluation framework comparing A/B testing, simulation experiments, and behavioral assessments for measuring bias reduction effectiveness
- Implementation roadmap addressing both technical requirements and organizational change management for bias mitigation systems
- XAI integration model balancing algorithmic transparency with decision-making efficiency
Scope and Applications: While primarily focused on corporate executive decision-making, findings extend to healthcare administration, public policy formulation, and emergency management contexts where bias mitigation is critical for optimal outcomes.
1.3. Paper Structure
Section 2 establishes theoretical foundations, examining cognitive biases in executive contexts and big data analytics capabilities. Section 3 analyzes real-world manifestations of bias in strategic decision-making. Section 4 investigates bias mitigation mechanisms through analytics, including AI-driven detection and correction systems. Section 5 addresses implementation challenges and limitations. Section 6 explores emerging trends, XAI applications, and research gaps. Section 7 presents conclusions and practical recommendations for organizations seeking to enhance decision quality through data-driven bias mitigation.
2. Theoretical Foundations
2.1. Cognitive Biases in Executive Decision-Making
Cognitive biases represent systematic deviations from rational judgment that lead individuals to make suboptimal decisions based on mental shortcuts, preconceptions, or flawed heuristics [14]. Within executive decision-making contexts, these biases pose significant challenges as leaders operate under conditions of uncertainty, time pressure, and high stakes [15]. This section examines five key cognitive biases that substantially impact executive decision-making: confirmation bias, overconfidence bias, anchoring bias, availability heuristic, and framing effect [16] (Table 2).

Table 2.
Overview of Key Cognitive Biases in Executive Decision-Making.
Also, the below conceptual framework (Figure 2) illustrates the five primary cognitive biases that systematically distort executive decision-making processes.
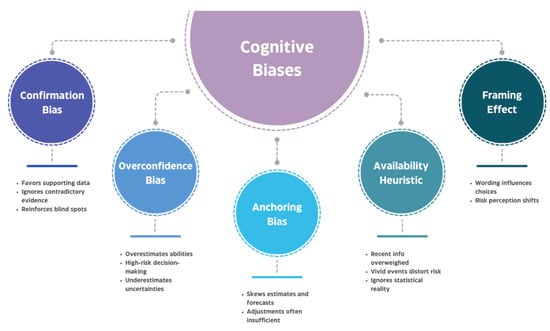
Figure 2.
The five cognitive biases in executive decision-making.
At the center, “Cognitive Biases” represents the overarching psychological phenomena that influence how leaders process information and make strategic choices. Each surrounding node depicts a specific bias with its key characteristics:
Confirmation Bias (left) manifests when executives favor information supporting their existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence, leading to strategic blind spots and resistance to market changes.
Overconfidence Bias (lower left) reflects executives’ tendency to overestimate their abilities and underestimate risks, resulting in unrealistic project timelines and excessive risk-taking in areas such as mergers and acquisitions.
Anchoring Bias (bottom) occurs when initial information disproportionately influences subsequent decisions, affecting financial forecasts and negotiations even when the anchor proves arbitrary or outdated.
Availability Heuristic (lower right) leads executives to overweight easily recalled events, causing distorted risk assessments based on memorable incidents rather than statistical reality.
Framing Effect (right) demonstrates how identical information presented differently can reverse risk preferences, influencing strategic communications and decision outcomes.
The dotted connections between biases indicate their interconnected nature—these cognitive distortions often reinforce each other, creating compound effects that further compromise decision quality. Understanding these relationships is essential for developing comprehensive mitigation strategies through big data analytics, as discussed in subsequent sections.
2.1.1. Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias represents the tendency to search for, interpret, and recall information that confirms preexisting beliefs while giving disproportionately less consideration to alternative possibilities [17]. In executive contexts, this bias manifests through selective information processing, where leaders unconsciously filter data to support their strategic vision while dismissing contradictory evidence [18]. The hierarchical structure of organizations often amplifies this bias through “filtering bias,” where subordinates selectively present information they believe executives want to hear [19].
This cognitive distortion particularly affects strategic planning and risk assessment processes. Executive teams with entrenched assumptions about market stability often dismiss early disruption signals as temporary anomalies rather than fundamental shifts in competitive dynamics [20]. The escalation of commitment to failing projects exemplifies confirmation bias in action, as executives seek evidence supporting initial decisions rather than objectively reassessing situations [21]. Historical analyses have documented how established retailers failed to recognize e-commerce threats despite clear market data indicating shifting consumer preferences, demonstrating the profound impact of this bias on strategic adaptation [22,23,24].
Effective mitigation strategies encompass institutionalized devil’s advocacy procedures that systematically challenge existing assumptions [25,26,27], structured decision-making processes requiring explicit documentation of reasoning and evidence [28], and AI-driven analytics that provide objective, data-based insights independent of human preconceptions [29].
2.1.2. Overconfidence Bias
Overconfidence bias involves excessive confidence in one’s abilities, knowledge, or chances of success, leading to systematic underestimation of risks and overestimation of positive outcomes [73]. This bias appears particularly pronounced among executives, where past successes and positional authority reinforce beliefs in personal judgment capabilities [74].
In corporate settings, overconfidence manifests through multiple channels. Executives frequently establish unrealistic project timelines, reflecting the “planning fallacy” wherein best-case scenarios dominate planning processes while potential obstacles receive insufficient consideration [75]. The merger and acquisition domain provides particularly compelling evidence, with overconfident executives pursuing excessive acquisition activity based on inflated synergy estimates and underestimation of integration complexities [76]. Strategic initiatives often suffer from inadequate risk assessment as leaders overestimate their ability to control market dynamics and competitive responses [77]. The psychological origins of this bias stem from self-serving attribution patterns, where executives attribute success to personal ability while externalizing blame for failures [78].
Evidence-based mitigation approaches incorporate systematic use of predictive analytics and Monte Carlo simulations to ground decisions in probabilistic reasoning rather than intuitive certainty [79]. Organizations that implement analytical validation paradigms within strategic planning cycles demonstrate improved calibration between confidence levels and actual outcomes [80]. Furthermore, cultivating organizational cultures that promote constructive skepticism and encourage challenging of executive assumptions has proven effective in moderating overconfidence effects [80].
2.1.3. Anchoring Bias
Anchoring bias occurs when individuals rely disproportionately on initial information when making subsequent judgments, even when that information proves arbitrary or irrelevant to the decision context [81]. In executive decision-making, anchoring significantly impacts financial planning, negotiations, and strategic goal-setting processes [82].
Revenue forecasting exemplifies this phenomenon, where executive teams often remain tied to initial projections despite evolving market conditions that warrant substantial revision [83]. Negotiation contexts reveal similar patterns, with opening offers establishing psychological reference points that disproportionately influence final agreements, regardless of objective valuation metrics [84]. Human resource decisions demonstrate anchoring effects when compensation determinations rely on historical salary levels rather than current market rates or performance metrics [85]. Strategic planning processes frequently exhibit anchoring when organizations set objectives based on competitors’ historical performance rather than conducting independent potential analyses [86,87].
Effective countermeasures require systematic approaches to decision-making. Organizations benefit from obtaining multiple independent estimates before critical decisions, ensuring diverse perspectives challenge initial anchors [88]. Employing first-principles reasoning in budgeting processes helps teams evaluate expenditures based on fundamental requirements rather than incremental adjustments to potentially flawed baselines [89]. AI-based pricing algorithms that analyze current market dynamics rather than historical precedents offer technological solutions to bypass anchoring effects [90,91]. Additionally, conducting systematic post-mortem analyses enables organizations to identify where anchoring influenced past decisions and develop institutional awareness of this bias [92,93].
2.1.4. Availability Heuristic
The availability heuristic leads individuals to overestimate the probability of events that are easily recalled, typically because they are recent, emotionally salient, or widely publicized [49,50]. This cognitive bias causes executives to overweight memorable events in decision-making while undervaluing comprehensive statistical information that may provide more accurate risk assessments [51,52].
Business contexts reveal multiple manifestations of this bias. Risk assessment processes often become distorted when executives base probability estimates on vivid events such as highly publicized cyber-attacks or market crashes, rather than systematic analysis of actual occurrence frequencies [49,50]. Strategic planning suffers when recent successes or failures disproportionately influence future strategies, causing organizations to overreact to temporary fluctuations while missing long-term trends [51]. Resource allocation decisions driven by anecdotal evidence rather than comprehensive data analysis lead to suboptimal investment patterns [52]. These patterns create organizational feedback loops where memorable narratives override data-driven insights, perpetuating decision-making based on salience rather than statistical relevance [51,52].
Mitigation strategies leverage both technological and organizational approaches. AI-driven analytics shift focus from anecdotal evidence to statistical patterns by processing comprehensive datasets that human cognition cannot effectively synthesize [53,54,55]. Structured decision-making techniques such as pre-mortem analyses force consideration of multiple scenarios beyond those readily available to memory [56]. Organizations that foster data-driven cultures prioritizing empirical evidence over memorable instances demonstrate improved calibration in risk assessment and strategic planning [57].
2.1.5. Framing Effect
The framing effect demonstrates how identical information presented in different formats can lead to opposing decisions, violating fundamental principles of rational choice [58]. According to prospect theory, individuals exhibit risk-averse behavior when outcomes are framed as gains but become risk-seeking when identical outcomes are framed as losses [59].
Executive communications and strategic choices reveal substantial framing effects. Budget proposals characterized as “efficiency enhancements” consistently receive greater organizational support than identical measures framed as “cost reductions,” despite equivalent fiscal impacts [60]. Strategic initiatives described in terms of growth opportunities generate fundamentally different responses than those emphasizing threat mitigation, even when the underlying economic considerations remain constant [61,62].
Addressing framing effects requires deliberate cognitive strategies. Decision-makers must consciously evaluate choices from multiple perspectives, actively considering how different presentations might influence judgment [63,64]. Using precise numerical terminology rather than emotionally loaded language helps minimize linguistic framing effects [65]. Organizations benefit from implementing standardized decision frameworks that present information in consistent formats, reducing the influence of presentation variations on strategic choices [66].
2.2. Big Data Analytics: Framework and Applications
Big data analytics represents a comprehensive methodological framework for collecting, processing, and analyzing vast, complex datasets to extract actionable insights that enhance organizational decision-making [67]. This field has undergone rapid evolution alongside digital transformation, enabling organizations to leverage diverse data sources for strategic advantage [68,69].
2.2.1. Fundamental Characteristics: The 5 V’s Framework
The conceptual foundation of big data analytics rests upon five key dimensions that distinguish it from traditional data processing approaches. Volume encompasses the unprecedented scale of modern data generation, with organizations routinely managing petabyte and exabyte-level datasets that exceed conventional storage and processing capabilities [67]. Variety reflects the heterogeneous nature of contemporary data, spanning structured formats conforming to predefined schemas, semi-structured data such as XML and JSON, and unstructured information including text, images, and multimedia content [67]. Velocity captures the accelerating pace of data generation and the corresponding requirement for real-time or near-real-time processing capabilities [67]. Veracity addresses critical concerns regarding data quality, accuracy, and trustworthiness, recognizing that analytical insights depend fundamentally on underlying data integrity [68]. Value represents the ultimate objective of big data initiatives: transforming raw information into meaningful insights that drive business success and competitive advantage [68].
2.2.2. Infrastructure and Technologies
Modern big data infrastructure comprises sophisticated technological ecosystems designed to manage the scale and complexity of contemporary data environments [69,70]. Storage systems have evolved from traditional relational databases to distributed architectures capable of handling massive, heterogeneous datasets. The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) provides fault-tolerant storage by distributing data across multiple nodes, ensuring high availability through redundancy mechanisms [71,72]. NoSQL databases offer specialized solutions for different data management requirements: document stores accommodate schema-less data, column-family databases optimize read-intensive operations, key-value stores provide exceptional retrieval speed, and graph databases excel at mapping complex relationships between entities [73].
Processing frameworks have similarly evolved to meet big data demands. While MapReduce initially revolutionized parallel processing, Apache Spark (all versions through 4.0.1) has emerged as the dominant framework, offering in-memory processing capabilities that dramatically improve performance for iterative algorithms and real-time analytics [71,72]. Stream processing platforms including Apache Kafka and Flink enable organizations to analyze data in motion, supporting use cases requiring immediate insights [69].
Cloud computing has fundamentally transformed big data infrastructure accessibility. Platforms from Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide scalable, cost-effective solutions that eliminate barriers to entry for sophisticated analytics [74,75]. Edge computing complements cloud architectures by processing data near its source, reducing latency for time-sensitive applications while improving data privacy [74,75]. Orchestration tools such as Apache Airflow and Kubernetes automate workflow management, while comprehensive security frameworks ensure compliance with regulations including GDPR and industry-specific requirements [76,77].
The architectural diagram (Figure 3) presents the multi-layered infrastructure supporting big data analytics for executive decision-making and bias mitigation. The visualization employs a hierarchical structure that traces data flow from initial collection through final analytical outputs, demonstrating the technological complexity underlying modern bias mitigation systems.
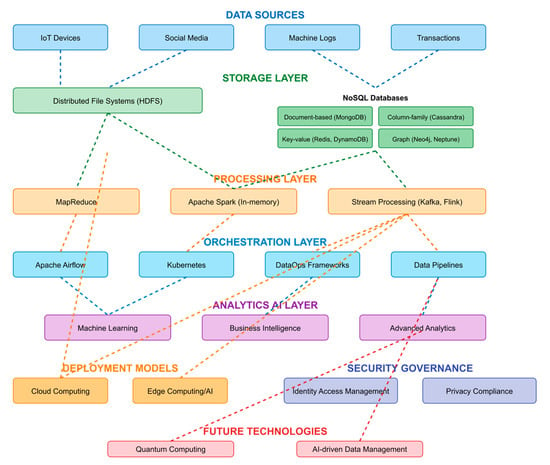
Figure 3.
Big Data Infrastructure and Technologies Ecosystem.
The Data Sources layer (top) identifies primary inputs including IoT devices, social media streams, machine logs, and transactional records, representing the diverse data ecosystem that feeds analytical processes. The Storage Layer illustrates the dual architecture of distributed file systems (HDFS) for large-scale data storage and specialized NoSQL databases optimized for different data structures—document-based systems for unstructured content, column-family databases for analytical workloads, key-value stores for rapid retrieval, and graph databases for relationship mapping [71,72,73].
The Processing Layer showcases the evolution from batch-oriented MapReduce to real-time processing frameworks. Apache Spark’s (ver. 3.5.0) in-memory capabilities enable iterative machine learning algorithms essential for bias detection, while stream processing platforms (Kafka, Flink) support real-time bias identification in ongoing decisions [71,72]. The Orchestration Layer demonstrates how workflow management tools coordinate complex analytical pipelines, ensuring systematic bias assessment across multiple data streams.
The Analytics AI Layer represents where bias mitigation actually occurs, through machine learning algorithms that identify patterns beyond human perception, business intelligence tools that visualize bias indicators, and advanced analytics that prescribe corrective actions. The diagram shows these analytical capabilities deployed through Cloud Computing and Edge Computing/AI models, with the former providing scalable processing power and the latter enabling real-time bias detection at decision points [74,75].
Critical to the framework are Security Governance mechanisms ensuring data integrity and regulatory compliance, as biased or compromised data would undermine mitigation efforts [76,77]. The Future Technologies component acknowledges emerging capabilities—quantum computing for complex optimization problems and AI-driven data management for automated bias detection in data preparation stages.
The interconnecting arrows demonstrate data flow patterns, emphasizing that bias mitigation requires seamless integration across all layers. This comprehensive infrastructure enables the analytical methodologies discussed in Section 2.2.3 and supports the AI/ML applications detailed in Section 2.2.4, forming the technological foundation for systematic cognitive bias mitigation in executive decision-making.
2.2.3. Analytical Methodologies
Organizations employ six primary analytical approaches to extract value from big data, each serving distinct purposes within the analytical continuum [78]. Descriptive analytics provides historical perspective by summarizing past events and identifying patterns within existing data [79]. Diagnostic analytics extends this foundation by investigating causal relationships and uncovering factors driving observed outcomes [80]. Predictive analytics leverages statistical modeling and machine learning to forecast future trends based on historical patterns [81]. Prescriptive analytics advances beyond prediction to recommend optimal actions given specific constraints and objectives [82]. Real-time analytics enables immediate response to changing conditions through continuous data processing [83]. AI-driven analytics automates the discovery of complex patterns and relationships that may elude human analysis [84].
2.2.4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies constitute the analytical engine of modern big data systems, enabling automated extraction of sophisticated insights from massive datasets [85,86]. Classification algorithms categorize data into predefined groups, supporting applications ranging from fraud detection to medical diagnosis [87,88]. Regression models predict continuous outcomes, facilitating sales forecasting, risk assessment, and demand planning [89]. Ensemble methods and deep learning architectures uncover complex, non-linear relationships within high-dimensional data [90].
Natural language processing has emerged as a critical capability for analyzing the vast quantities of unstructured text data generated by modern organizations [94]. Sentiment analysis extracts emotional content from customer feedback, social media, and other textual sources [95]. Named entity recognition identifies and extracts key information elements from documents [96]. Conversational AI enables natural language interactions between humans and analytical systems [97,98,99].
Advanced applications leverage these foundational technologies to create sophisticated analytical capabilities. Recommendation systems employ collaborative filtering and deep learning to personalize user experiences [100,101,102,103]. Cognitive computing platforms such as IBM Watson and Microsoft Azure AI simulate human reasoning processes, enabling complex decision support across domains including healthcare, finance, and legal services [104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111]. These systems demonstrate adaptive learning capabilities, continuously improving their performance through interaction with data and users [98,99].
2.2.5. Implications for Bias Mitigation
The integration of big data analytics with executive decision-making offers multiple mechanisms for cognitive bias mitigation. AI systems process data without susceptibility to emotional influences or hierarchical pressures that affect human judgment. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns within datasets too large and complex for human cognitive processing, revealing insights that challenge existing assumptions. Real-time analytics provides immediate feedback on decision outcomes, enabling rapid identification and correction of biased judgment patterns. Statistical models quantify uncertainty explicitly, countering human tendencies toward overconfidence and providing calibrated probability assessments.
However, these technologies also present significant challenges. Algorithmic bias may emerge when models trained on historical data perpetuate past discriminatory patterns. Model interpretability remains a critical concern, as complex algorithms may produce accurate predictions without transparent reasoning. Organizational resistance to data-driven approaches can limit the practical impact of analytical insights. These considerations underscore the importance of thoughtful implementation strategies that leverage technological capabilities while addressing inherent limitations.
2.3. Theoretical Integration
This theoretical foundation establishes a comprehensive framework for understanding the intersection between cognitive biases and big data analytics in executive decision-making. The systematic biases that affect human judgment create predictable distortions in strategic choices, while big data analytics offers powerful tools for introducing objectivity and empirical rigor into decision processes. The convergence of these domains presents both unprecedented opportunities and complex challenges for organizations seeking to enhance decision quality.
The effectiveness of analytics-based bias mitigation depends critically on recognizing that technology alone cannot eliminate cognitive distortions. Rather, successful implementation requires integrating analytical capabilities with organizational processes, cultural change, and human expertise. The subsequent sections of this manuscript examine specific mechanisms through which big data analytics can address cognitive biases, evaluate empirical evidence for effectiveness, and identify key implementation challenges that organizations must navigate to realize the full potential of data-driven decision enhancement.
The heat map below (Figure 4) illustrates the differential effectiveness of six analytical methodologies in mitigating five key cognitive biases identified in executive decision-making. The matrix synthesizes empirical evidence from the literature to provide a visual guide for selecting appropriate analytical interventions based on the specific bias being addressed.
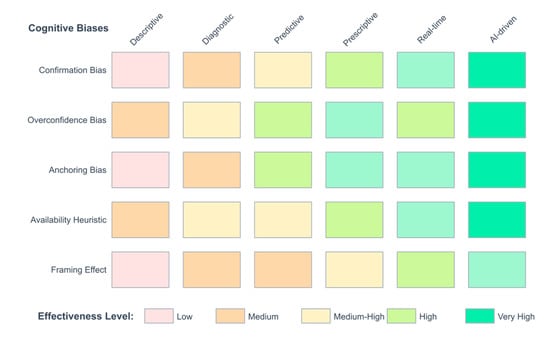
Figure 4.
Bias-analytics effectiveness matrix.
The color gradient represents effectiveness levels ranging from low (light red) to very high (dark green). AI-driven analytics demonstrates the highest overall effectiveness across all biases, particularly in addressing confirmation bias and overconfidence, where its ability to process vast datasets without preconceptions provides maximum value. Prescriptive and real-time analytics show strong performance in mitigating anchoring and availability biases by providing immediate, optimization-based recommendations that bypass historical reference points.
Notably, descriptive analytics shows limited effectiveness across most biases, as it primarily reports historical patterns without challenging underlying assumptions. This finding underscores that merely presenting data is insufficient for bias mitigation; rather, advanced analytical techniques that actively identify patterns, generate predictions, and recommend actions are necessary to counteract deeply ingrained cognitive distortions.
The matrix reveals that no single analytical approach provides universal bias mitigation, suggesting that organizations should implement comprehensive analytical ecosystems combining multiple methodologies. The effectiveness ratings are based on empirical studies referenced in Section 2.1 (references [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66] for bias characteristics) and Section 2.2 (references [78,79,80,81,82,83,84] for analytics capabilities), providing evidence-based guidance for practitioners designing bias mitigation strategies.
Finally, the below conceptual mind map (Figure 5) visualizes the interconnected domains that constitute the theoretical framework for bias mitigation through big data analytics. The central node represents the convergence of cognitive psychology and data science, with four primary branches illustrating the essential components of this integration.
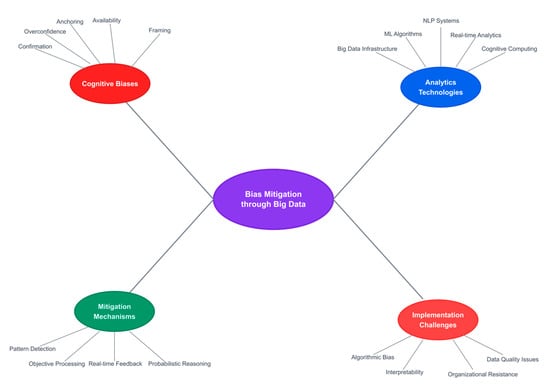
Figure 5.
Key concepts mind map in bias mitigation through big data analytics.
The Cognitive Biases branch (red, upper left) identifies the five key biases examined in this study, with associated reference clusters indicating the depth of literature supporting each bias’s characterization. The Analytics Technologies branch (blue, upper right) maps the technological infrastructure required for bias mitigation, from foundational big data systems to advanced cognitive computing platforms. Each sub-branch includes reference ranges demonstrating the empirical basis for these technological capabilities.
The Mitigation Mechanisms branch (green, lower left) explicates the four primary pathways through which analytics addresses cognitive biases: comprehensive pattern detection that reveals hidden relationships, objective processing free from emotional influence, real-time feedback enabling rapid bias recognition, and probabilistic reasoning that counters overconfidence. The Implementation Challenges branch (red, lower right) acknowledges critical barriers including algorithmic bias risks, interpretability requirements, organizational resistance, and data quality concerns.
The radial structure emphasizes that effective bias mitigation requires simultaneous attention to all four domains. The connecting lines represent the dynamic interactions between domains—for instance, how organizational resistance (a challenge) can undermine the deployment of analytics technologies, or how specific mitigation mechanisms directly address particular cognitive biases. This holistic view underscores that technological solutions alone are insufficient; successful bias mitigation demands integrated approaches addressing psychological, technological, methodological, and organizational dimensions simultaneously.
3. Cognitive Biases in Strategic Decision-Making
Cognitive biases systematically impede effective executive decision-making, affecting strategic choices and investment allocations before their consequences become apparent. Despite access to unprecedented data volumes, modern organizations frequently base strategic decisions on mental shortcuts and systematic judgment distortions. This section examines how cognitive biases manifest in executive environments, their effects on business strategy formulation, and the substantial challenges organizations face in detecting and mitigating these biases [112].
3.1. Challenges in Identifying and Mitigating Biases in Executive Contexts
Research consistently demonstrates cognitive biases’ pervasive influence on executive decision-making, yet these biases prove extraordinarily difficult to identify and correct in live operational contexts [113]. Strategic decisions present unique challenges due to their long-term implications, multifaceted external influences, and inherent unpredictability, making it exceptionally difficult to distinguish genuine strategic errors from natural risks associated with operating in uncertain business environments [114].
Table 3 summarizes five fundamental barriers to detecting and managing biases within organizational decision processes:

Table 3.
The main challenges in identifying and mitigating biases.
The “bias blind spot” represents the most fundamental challenge—individuals’ tendency to recognize cognitive distortions in others while remaining oblivious to identical patterns in their own thinking [115]. The combination of successful career progression and industry experience frequently leads executives to develop profound confidence in their judgment, substantially reducing receptiveness to the possibility of cognitive distortion affecting their reasoning processes. Self-attribution bias compounds this problem, as executives typically attribute failures to external market conditions rather than evaluating their own cognitive blind spots [116].
Organizational culture and groupthink dynamics further complicate bias identification at executive levels. High-stakes corporate decisions typically occur within executive teams characterized by dominant personalities and hierarchical structures that implicitly discourage dissent. Without mechanisms actively promoting cognitive diversity, structured red-team analysis, and formalized devil’s advocacy, executive teams develop tunnel vision that renders them oblivious to their cognitive distortions [117].
The feedback mechanisms within executive decision processes operate through fundamentally ambiguous and delayed pathways. Strategic decisions typically unfold over extended timeframes during which multiple external factors influence outcomes [118]. This complex causal environment makes it extraordinarily difficult to isolate which specific cognitive biases contributed to strategy failure. Research scholars face similar challenges measuring cognitive bias effects on firm performance, as isolating specific biases from complex organizational outcomes presents significant methodological difficulties [119].
Unlike fields such as medicine and aviation that employ structured error-reduction protocols, executive decision-making has historically lacked formal debiasing procedures. While some organizations have begun implementing debiasing interventions, including pre-mortem exercises, cognitive bias checklists, and AI-driven decision-support tools, formal bias detection and correction mechanisms remain rare [120].
3.2. Real-World Examples of Executive Biases
Historical corporate records reveal numerous strategic missteps and missed innovation opportunities attributable to cognitive distortions. These cases provide concrete evidence of how biases operate in practice and their substantial organizational costs [121].
3.2.1. Hindsight Bias—The Case of Missed Innovations
Hindsight bias manifests as the “I-knew-it-all-along” effect, causing individuals to retrospectively perceive events as more predictable than they appeared during their initial occurrence. The failure of established companies to capitalize on photocopying technology represents a well-documented example [122].
During the mid-20th century, Haloid Company (later Xerox) developed revolutionary photocopying technology. Industry leaders IBM and Kodak declined opportunities to invest in or acquire this technology, dismissing its potential as either insufficiently profitable or peripheral to their core operations. Contemporary observers often express bewilderment regarding these companies’ failure to recognize the breakthrough potential. However, the decision context was considerably more complex, as prevailing mental models and cognitive biases constrained executives’ technological evaluations toward innovations aligned with established business operations [123].
This situation transcended mere negligence, as confirmation bias significantly amplified hindsight effects. IBM and Kodak executives demonstrated strong confidence in their existing product portfolios, selectively processing information that reinforced current strategies while systematically overlooking disruptive alternatives [124]. The combination of selective attention to established business models and resistance to challenging fundamental assumptions resulted in declining an innovation that transformed the office equipment industry.
3.2.2. Representativeness Bias—Misjudging Market Patterns
Representativeness bias involves assuming that prior occurrences and familiar patterns will accurately predict future developments despite fundamental environmental changes [122]. Montgomery Ward’s experience following World War II demonstrates this phenomenon’s strategic impact.
Montgomery Ward’s leadership predicted post-World War II economic depression, assuming conditions would mirror the aftermath of World War I. Based on this perspective, the company implemented an extremely conservative business strategy, avoiding expansion and maintaining defensive operational postures. By contrast, competitor Sears recognized fundamental differences between the two post-war economic environments and pursued aggressive expansion, correctly anticipating consumer spending growth [124].
Montgomery Ward committed a fundamental strategic error by treating historical events as definitive guidance while disregarding substantial economic and social transformations. The United States experienced severe economic depression following World War I, but the post-World War II era presented an entirely different landscape characterized by rapid consumer demand, industrial expansion, and government-supported economic growth [125,126]. This misjudgment produced irreversible consequences as Sears leveraged the economic boom while Montgomery Ward permanently surrendered its competitive standing [127,128].
3.2.3. Overconfidence and Hubris—Value-Destroying Acquisitions
Overconfidence bias creates significant challenges during mergers and acquisitions, as executives frequently maintain unrealistic beliefs regarding their ability to extract value from large transactions [129]. Behavioral finance research consistently demonstrates that overconfident executives typically overpay for acquisitions while underestimating integration challenges [130,131].
The 2001 AOL–Time Warner merger exemplifies how overconfidence bias produces catastrophic acquisition failures. AOL pursued a $165 billion acquisition based on executive conviction that the combined entity would dominate emerging digital media markets [132]. However, fundamental assumptions regarding growth trajectory and business synergies proved fatally flawed. The merger culminated in a historic $99 billion write-off—the largest corporate impairment in history—before complete dismantlement within a decade [133].
This pattern continues in contemporary technology acquisitions where executives project past accomplishments to overestimate their capacity to integrate and expand new business operations [134]. Recent artificial intelligence and fintech acquisitions demonstrate identical patterns, with leadership teams avoiding comprehensive due diligence because intense commitment to success narratives leads them to overlook warning signs [135]. Figure 6 synthesizes the three historical cases examined above, illustrating how different cognitive biases manifest in executive decision-making through distinct yet interconnected patterns.
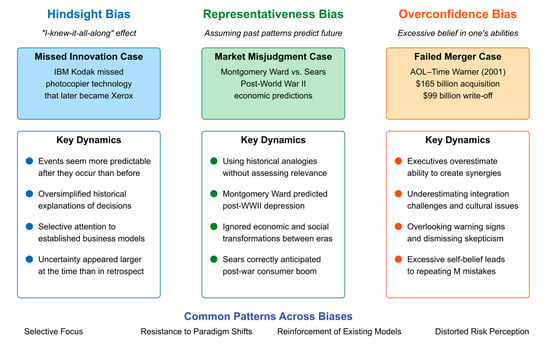
Figure 6.
Real-world Examples of Executive Biases in Strategic Decision-Making.
Each bias demonstrates specific dynamics while contributing to four common patterns that transcend individual biases: selective focus, resistance to paradigm shifts, reinforcement of existing models, and distorted risk perception.
The figure reveals how cognitive distortions systematically undermine strategic judgment across diverse business contexts. The hindsight bias panel illustrates how IBM and Kodak’s failure to recognize photocopying technology’s revolutionary potential only appears “obvious” in retrospect, while uncertainty was substantially greater during the actual decision moment [122,123,124]. The representativeness bias panel demonstrates Montgomery Ward’s critical error in assuming post-WWII conditions would mirror post-WWI patterns, contrasting sharply with Sears’ accurate assessment of the transformed economic landscape [124,125,126,127]. The overconfidence bias panel captures how executive hubris in the AOL-Time Warner merger led to catastrophic value destruction through systematic underestimation of integration challenges [132,133].
These patterns—selective focus on confirming information, resistance to paradigm shifts that challenge existing models, reinforcement of established frameworks, and systematically distorted risk perception—represent fundamental cognitive vulnerabilities that persist across different bias types and business contexts. Understanding these common patterns is essential for developing effective bias mitigation strategies through data-driven approaches.
3.3. Implications for Data-Driven Decision Making
The historical cases examined reveal four recurring patterns across all cognitive biases: selective information processing, resistance to paradigm shifts, reinforcement of existing models, and distorted risk perception. These patterns demonstrate why traditional intuition-based decision-making proves inadequate for modern business complexity [136].
3.3.1. Why Analytics Matter
Each examined failure—IBM/Kodak, Montgomery Ward, and AOL–Time Warner—occurred despite available data that could have prevented strategic missteps. This paradox highlights the critical gap between having information and processing it objectively. Modern organizations face exponentially greater complexity than historical counterparts, creating decision contexts where human cognitive limitations become increasingly problematic [137].
Big data analytics offers specific countermeasures to each bias pattern:
- Against Selective Processing: Analytics examines all data without predetermined filters, revealing patterns that confirmation bias would obscure
- Against Paradigm Rigidity: Predictive models generate future scenarios based on emerging trends rather than historical analogies
- Against Echo Chambers: Data democratization enables evidence-based challenges to senior assumptions
- Against Risk Distortion: Probabilistic modeling quantifies uncertainty, replacing subjective optimism with empirical ranges
3.3.2. Implementation Requirements
Analytical tools alone cannot mitigate biases without corresponding organizational changes:
- Cultural Shift: Organizations must value empirical evidence over hierarchical opinion, replacing “HIPPO” (Highest-Paid Person’s Opinion) dynamics with data-driven cultures [136]
- Process Integration: Analytics must be embedded throughout decision cycles, not treated as optional validation
- Executive Literacy: Leaders need sufficient analytical understanding to interpret insights appropriately
- Clear Governance: Frameworks must define when analytical insights override intuition and when human judgment remains primary [137]
3.3.3. Toward Augmented Decision-Making
The objective is augmenting rather than replacing human judgment. Humans excel at contextual understanding and ethical reasoning; analytics provides objective pattern recognition and bias detection. This symbiosis creates decision-making capabilities exceeding either approach alone. The following sections examine how big data analytics and AI systems operationalize these bias mitigation principles, transforming theoretical frameworks into practical decision enhancement tools.
4. Big Data Analytics as a Tool for Bias Mitigation
Big data analytics offers considerable potential to counteract cognitive biases in executive decision-making by supplanting subjective intuition with empirical, data-driven insights, enabling leaders to make more objective, evidence-based strategic choices. Cognitive biases, including confirmation bias, overconfidence, anchoring, and hindsight bias, frequently distort perception and risk assessment, resulting in suboptimal business decisions, inefficient resource allocation, and missed opportunities [138]. Through leveraging advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, statistical modeling techniques, and real-time data processing capabilities, big data analytics can identify hidden patterns, challenge entrenched assumptions, and provide decision-makers with probabilistic rather than intuitive assessments of risks and opportunities. This section explores how analytics mitigates cognitive biases, examines AI’s role in identifying and correcting distorted judgment patterns, and discusses structured frameworks that enhance decision quality by integrating big data into executive workflows. We analyze how descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics collectively enhance objectivity, enabling executives to identify trends, model future scenarios, and receive data-driven recommendations that minimize reliance on cognitive shortcuts [139]. Additionally, we address ethical considerations and limitations of AI-driven bias mitigation, including data reliability concerns, algorithmic bias risks, and integration challenges within traditionally intuition-driven decision environments. By understanding how big data and AI transform decision-making processes, organizations can reduce susceptibility to biases, improve strategic foresight, and cultivate analytical rigor that enhances long-term business resilience and competitive advantage [140]. Figure 7 presents a heatmap evaluating both the impact of five cognitive biases on decision-making and big data’s effectiveness in mitigating each bias on a 1–9 scale.
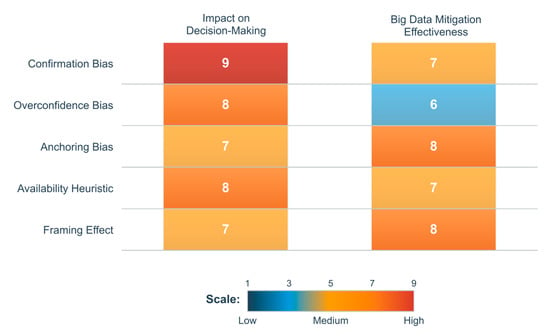
Figure 7.
Cognitive biases and Big Data mitigation effectiveness.
The visualization reveals that biases with the highest decision-making impact (confirmation bias: 9) often prove more resistant to mitigation (effectiveness: 7), while biases like anchoring and framing show stronger mitigation potential (effectiveness: 8) despite lower initial impact (7), highlighting where big data interventions may be most effective.
4.1. Mechanisms for Reducing Bias via Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics is crucial in reducing cognitive bias influence within executive decision-making contexts, functioning as a corrective mechanism that replaces intuition and subjective judgment with empirical, data-driven insights [141]. Cognitive biases frequently emerge because humans rely on heuristics—mental shortcuts that simplify decision-making but introduce systematic errors, particularly within high-stakes, uncertain environments. By contrast, big data analytics processes vast quantities of structured and unstructured information identifies complex patterns and provides objective insights that challenge biased reasoning processes. By offering quantifiable, evidence-based perspectives rather than intuition-driven assumptions, analytics help executives recognize flawed mental models, reevaluate preconceived notions, and make more rational strategic choices [142]. Whether applied to investment decisions, market expansion strategies, product innovation initiatives, or risk assessments, data-driven approaches effectively safeguard against human error, reinforcing analytical rigor throughout executive workflows [143].
4.1.1. Evidence-Based Insights vs. Intuition
Big data analytics significantly reduces cognitive biases by shifting decision-making processes from intuitive judgments toward evidence-based insights derived from comprehensive datasets. Executives traditionally rely heavily on personal experiences or anecdotal evidence, potentially introducing biases such as availability bias, which overemphasizes recent or memorable events. For instance, executives may incorrectly perceive strong organizational performance based solely on recent successes while ignoring objective indicators like market share decline or operational inefficiencies [144,145]. Data analytics challenges these perceptions by providing detailed analyses of market trends, financial metrics, and competitor benchmarks, compelling leaders to confront realities that might contradict their preconceived notions. Another critical bias addressed through big data is confirmation bias, wherein executives selectively accept information aligning with existing strategic beliefs or visions while neglecting contradictory evidence [146,147]. For example, CEOs pursuing market expansion might overlook critical data regarding customer dissatisfaction or regulatory risks, preferentially focusing on supportive evidence. AI-driven analytics mitigates this tendency by presenting comprehensive, unbiased datasets encouraging objective evaluations rather than selective interpretations. Additionally, automated decision-support systems, including predictive analytics platforms and AI-based risk assessment tools, minimize human bias risks affecting the interpretation or manipulation of analytical results [148].
Furthermore, predictive modeling and scenario-based simulations help prevent overconfidence and reliance on simplistic decision heuristics by compelling executives to explore multiple potential future scenarios rather than anchoring exclusively on past successes [149]. For example, AI-powered modeling in mergers and acquisitions generates extensive valuation scenarios that realistically account for economic shifts, competitive dynamics, and integration complexities, thereby avoiding overly optimistic or biased acquisition decisions [150,151]. Similarly, Monte Carlo simulations in corporate risk management provide insights into potential financial, geopolitical, or operational disruptions, supporting comprehensive risk assessment beyond simplistic optimism. Real-time analytics systems also mitigate hindsight bias—the tendency to view outcomes as predictable [152] retroactively. Continuous monitoring and immediate alerts regarding emerging trends, such as declining revenues or customer churn, facilitate timely corrective actions and prevent post-event rationalizations of strategic missteps [153].
However, big data analytics effectiveness in reducing biases remains contingent upon organizational governance structures, structured integration into decision-making processes, and active bias-awareness training [154]. Without appropriate governance mechanisms, subjective judgments or internal politics may continue overshadowing data-driven insights [155]. Finally, ethical considerations regarding algorithmic biases, data integrity, and interpretability of AI recommendations remain essential, as blindly trusting analytics without critical scrutiny could inadvertently perpetuate biases rather than mitigate them [156].
4.1.2. Comprehensive Pattern Detection
One significant advantage of big data analytics in reducing cognitive biases is its capacity for comprehensive pattern detection at levels far exceeding human cognitive abilities [157]. Regardless of expertise, human executives inherently face limitations in processing extensive, multidimensional datasets, often resulting in misinterpretations, selective attention, and reliance on preconceived notions. By contrast, big data analytics utilizes advanced machine learning algorithms and statistical methods to uncover complex hidden patterns and relationships within vast datasets. These analytical models introduce objectivity into strategic decision processes by systematically analyzing large-scale data across multiple variables and extended time horizons. This approach proves especially effective against confirmation bias, anchoring bias, and representativeness bias, ensuring decisions remain grounded in the complete range of available data rather than selectively filtered subsets [158]. Specifically, big data-driven pattern detection combats confirmation bias through automated hypothesis testing and anomaly detection. Traditionally, executives begin with preconceived assumptions based on personal experiences or anecdotal evidence, selectively seeking data supporting these beliefs while disregarding conflicting information [159]. Big data models avoid these limitations by objectively evaluating relevant data and identifying correlations, trends, and outliers that challenge conventional wisdom. For instance, while retail executives might presume specific customer segments unprofitable based on limited prior assumptions, advanced analytics could reveal hidden profitability through deeper, granular insights into cross-category spending, seasonal behaviors, or cost dynamics [160,161,162]. These analytical capabilities offer critical reality checks, compelling executives to reevaluate outdated assumptions and enhancing overall strategic accuracy [163].
Additionally, big data analytics provides insights into counterintuitive correlations and complex cause-effect relationships often overlooked by heuristic-driven executive decision-making. Executives traditionally rely on simplified mental models and rules of thumb that inadequately capture the complexity of consumer behavior, financial markets, and technological adoption trends [164]. Machine learning algorithms can examine numerous interactions across diverse data streams, discovering unexpected relationships that challenge established industry norms [165]. For example, detailed data analysis might reveal that extensive product discounting attracts primarily transient, price-sensitive buyers rather than fostering lasting loyalty, thus contradicting prevailing business strategies. Such findings encourage executives to refine strategic approaches based on nuanced, real-world behavioral insights instead of oversimplified assumptions [166].
Moreover, big data analytics’ real-time adaptive capabilities significantly mitigate biases associated with historical anchoring and inertia-driven decision-making [167]. Executives frequently rely on outdated strategies rooted in past experiences or static assumptions that no longer reflect current market dynamics. Advanced real-time processing and streaming analytics continuously update organizational insights, allowing executives to rapidly adapt to evolving conditions such as technological disruptions, shifting consumer preferences, and competitive threats [168]. Big data analytics also addresses cognitive distortions at organizational levels, particularly combating groupthink in collective decision-making environments. It functions as an unbiased arbitrator, providing objective, empirical evidence that reduces reliance on hierarchical dynamics and prevailing consensus. For instance, when executive committees strongly favor particular strategic initiatives, analytics can independently evaluate feasibility and expected outcomes, ensuring decisions incorporate rigorous empirical analysis rather than simply reinforcing internal group beliefs [169,170].
4.1.3. Filtering Out Irrelevancies
A fundamental challenge in human decision-making involves susceptibility to saliency bias—the tendency to disproportionately emphasize highly noticeable yet irrelevant information while undervaluing subtle but statistically significant variables [171]. This bias appears particularly pronounced in executive decision-making, recruitment processes, financial forecasting, and risk management contexts, frequently causing suboptimal judgments and outcomes. AI-driven analytics effectively counteracts this bias by systematically isolating critical predictive factors from vast datasets while disregarding irrelevant, emotionally charged, or attention-grabbing elements [172]. Unlike human decision-makers influenced by experience, narratives, cognitive shortcuts, or external pressures, AI models objectively evaluate data based solely on quantifiable predictive relevance. For instance, in recruitment processes, AI-powered hiring algorithms can eliminate unconscious demographic biases by ignoring factors such as names, gender, ethnicity, or appearance, focusing exclusively on objective criteria such as skills, qualifications, and past performance metrics. This approach ensures hiring decisions remain merit-based, fair, and aligned with genuine talent requirements, significantly improving organizational equity and efficiency [173,174,175].
In financial decision-making and investment analysis, saliency bias often emerges when human investors react excessively to short-term market volatility, sensational news, or emotional triggers, neglecting long-term fundamentals and statistically validated indicators [176]. AI-driven investment models combat this bias by employing deep learning, time-series forecasting, and sentiment analysis to identify patterns based on meaningful data rather than superficial market fluctuations. These advanced analytical methods help investors avoid reactionary decisions, such as panic-selling during financial crises, by providing robust, objective insights into long-term asset performance and economic trends [177]. Similarly, AI-based analytics significantly enhance corporate risk assessment and fraud detection by eliminating subjective interpretations often influenced by intuition or historical biases. AI platforms systematically filter large datasets, objectively identifying genuine risk signals without biases related to demographic backgrounds, institutional affiliations, or outdated assumptions [178]. For example, AI-powered credit scoring models prioritize behavioral indicators such as repayment habits and spending behaviors rather than irrelevant demographic factors or income brackets. This approach not only increases fairness and financial inclusion but also ensures more accurate and risk-sensitive lending decisions [179,180].
Furthermore, in corporate strategic planning, AI-driven analytics prevent executives from anchoring decisions to outdated or irrelevant benchmarks and past successes. Traditional strategic planning frequently suffers from reliance on historical metrics or experiences that may no longer reflect current market realities, competitive dynamics, or technological disruptions. AI-driven systems mitigate these risks by dynamically evaluating recent consumer behaviors, macroeconomic conditions, and competitive pressures specific to current strategic contexts, thus promoting adaptability and precision in decision-making [181,182,183]. Ultimately, AI’s capability to filter out irrelevant information represents not merely an incremental efficiency improvement but a fundamental shift toward more rational, data-grounded organizational decisions across multiple business domains [184]. However, this powerful potential must be complemented by rigorous oversight, continuous model validation, and ethical governance frameworks, as AI itself can inadvertently propagate biases if trained on biased datasets or selectively overridden by human judgment. Companies effectively integrating these bias-filtering AI mechanisms will thus achieve significant competitive advantages by consistently making rational, accurate, and strategically sound decisions in complex, rapidly evolving business environments [185,186].
4.1.4. Consistency and Repetition
A critical limitation inherent in human decision-making processes is their fundamental inconsistency. Executive and professional judgments frequently vary due to emotional fluctuations, fatigue, cognitive load, external pressures, and other contextual influences [187]. Even seasoned decision-makers may reach divergent conclusions under identical conditions, introducing elements of randomness, emotional bias, and unpredictability into strategic choices. AI-driven decision models effectively overcome these limitations by consistently applying logical frameworks and systematic reasoning processes, remaining unaffected by emotional states or mental fatigue [188,189]. Unlike human decision-makers, AI systems ensure that identical inputs reliably produce similar outputs, significantly reducing variability and arbitrary biases in decision processes.
This consistency proves particularly advantageous in corporate strategy formulation and financial forecasting contexts. For instance, executives reviewing investment opportunities may shift their stance based on transient mood states or temporary market fluctuations rather than stable, objective evaluation criteria. AI-powered financial modeling and forecasting systems eliminate inconsistencies, ensuring decisions reflect empirical data and probabilistic analysis rather than subjective sentiments or emotional reactions [190,191]. Consequently, organizations implementing AI-driven decision-support tools achieve more accurate, reliable, and rational long-term strategic planning processes that demonstrate reduced vulnerability to emotional or transient influences [192].
Human inconsistency significantly impacts hiring decisions and talent management functions, as recruitment professionals often inadvertently apply varying evaluation standards to similar candidates due to factors including fatigue, cognitive overload, or irrelevant contextual elements [193]. Behavioral research consistently demonstrates that candidate assessments frequently differ based on interview timing, preceding candidate quality, or evaluators’ momentary psychological states. AI-driven hiring algorithms eliminate this subjective variability by strictly adhering to predefined selection criteria and consistently evaluating candidate attributes, including experience, skill levels, and demonstrated performance metrics [194]. For example, an AI model ranking candidates based on objective data will produce identical outcomes regardless of contextual influences or evaluator biases. This standardization enhances fairness, predictability, and efficiency in recruitment processes, minimizing subconscious biases and significantly improving talent acquisition objectivity.
Similarly, clinical decision-making and healthcare diagnostics frequently suffer from human judgment variability attributable to cognitive fatigue, workload stress, and patient-specific contextual factors. Research studies highlight that clinicians’ medical decisions can differ significantly depending on evaluation timing—such as assessments conducted at the end of tiring shifts or following complex patient cases [195]. AI-driven diagnostic tools and clinical decision-support systems eliminate these inconsistencies by applying standardized evaluation protocols based strictly on symptomatology, medical history, and validated statistical models. Technologies, including AI-based radiology diagnostics, disease-risk prediction algorithms, and AI-guided treatment recommendation systems, ensure uniformity and accuracy regardless of external contextual or emotional factors (Figure 8). This systematic approach significantly reduces diagnostic errors and enhances patient outcomes by guaranteeing consistent treatment protocols based solely on objective clinical evidence [196].
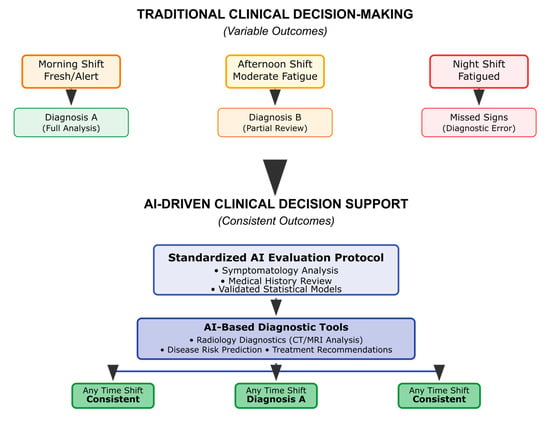
Figure 8.
AI-driven consistency in clinical decision-making.
From corporate governance and leadership perspectives, integrating AI-driven consistency into decision-making frameworks supports sustained organizational stability and strategic coherence [197]. Executives frequently shift strategies impulsively in response to transient events, media narratives, or short-term market volatility, resulting in erratic strategic trajectories and organizational inefficiencies. AI analytics platforms address this instability by providing structured, algorithmically validated analyses firmly grounded in historical patterns, probabilistic forecasting, and comprehensive risk assessment methodologies [198]. Companies adopting AI-enhanced scenario simulations and strategic planning tools thereby avoid reactionary and short-term thinking patterns, ensuring steady execution of data-informed, long-term strategies and securing sustained competitive advantages in increasingly dynamic business environments [199].
4.2. Role of AI and Machine Learning in Detecting and Countering Bias
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have revolutionized bias detection and mitigation within decision-making processes, particularly in high-stakes environments where human cognitive limitations and systemic biases have historically influenced outcomes. Whether unconscious or structural, bias often remains undetected due to deep integration within established business practices, decision frameworks, and historical datasets [200]. AI and ML technologies have introduced data-driven methodologies enabling organizations to identify, quantify, and mitigate bias in previously impossible ways. One of ML’s most impactful applications in bias detection involves its capacity to analyze past decisions and decision-making processes at scale, statistically identifying patterns indicating bias presence [201]. By leveraging pattern recognition techniques, anomaly detection algorithms, and fairness-aware computational frameworks, AI systems can scrutinize historical data, detect systematic disparities, and provide quantifiable evidence of biased trends. This capability is particularly valuable in corporate hiring, financial lending, law enforcement, healthcare diagnostics, and algorithmic governance, where unchecked human bias can lead to inequitable, inefficient, or legally problematic decisions [202].
4.2.1. Bias Detection—Identifying and Correcting Systemic Inequities in Decision-Making Through ML and AI
Machine learning significantly enhances bias detection capabilities by analyzing historical decision-making data to reveal correlations with irrelevant or ethically problematic factors. ML algorithms examine historical lending data in financial contexts to identify hidden demographic biases, such as race or gender, influencing loan approvals despite identical financial qualifications [203]. Similarly, within corporate environments, AI analytics examine hiring and promotion records to pinpoint statistical patterns potentially signifying systemic biases based on characteristics including gender, age, or ethnicity that cannot be justified solely through objective performance measures [204]. By quantifying these biases clearly and objectively, AI enables organizations to proactively correct discriminatory practices, ensuring decisions align strictly with merit-based criteria [205]. ML algorithms also proactively detect biases by flagging anomalies in real-time decision-making processes. Unlike traditional human judgments susceptible to cognitive shortcuts or subjective biases, AI systems can implement immediate real-time anomaly detection, highlighting deviations from fair or optimal decisions. For instance, in judicial contexts, AI tools can monitor court decisions to detect and address disparities promptly, significantly reducing biases influenced by race, judge fatigue, or personal heuristics [206]. Similarly, in healthcare settings, AI-driven diagnostics ensure treatment recommendations based strictly on medical data rather than demographic characteristics historically linked to biased medical decisions, thereby correcting disparities in treatment and diagnosis among marginalized populations [207,208].
However, ML systems are not inherently bias-free; their effectiveness depends heavily on training data quality and neutrality. Historical biases embedded in datasets related to hiring, lending, or criminal sentencing may inadvertently transfer into AI algorithms, perpetuating rather than eliminating discrimination [209]. Therefore, rigorous ethical reviews, fair auditing, and algorithmic transparency are crucial safeguards. Techniques including adversarial debiasing, algorithmic auditing, and synthetic data augmentation are actively pursued within fairness-aware machine learning research to prevent AI systems from replicating or exacerbating existing biases [210]. Consequently, as organizations integrate AI more deeply into decision-making processes, embedding robust fairness measures, continuous bias detection mechanisms, and ethical oversight frameworks becomes essential for AI to function effectively as a corrective mechanism against systemic inequities rather than inadvertently reinforcing them [211].
4.2.2. AI-Driven Decision Support Systems—Counteracting Human Biases Through Algorithmic Guidance
AI-driven decision support systems (DSSs) have emerged as critical tools in corporate strategy, financial analysis, and policy-making, offering data-backed alternatives to intuition-based human decisions while mitigating cognitive biases, including confirmation, availability, and anchoring biases. Unlike traditional analytical tools, AI-based DSSs transcend merely providing information—they actively participate in decision-making by generating predictive insights, modeling alternative scenarios, and systematically challenging entrenched assumptions through computational reasoning [212]. These systems reduce bias by presenting decision-makers with alternative scenarios and outcomes, directly countering tendencies toward tunnel vision or self-reinforcing cognitive distortions. For instance, in strategic planning contexts, AI-powered tools can simulate multiple market entry scenarios, including options initially disregarded by executives due to personal biases or preconceived notions about consumer behavior or competition. By grounding these scenarios in robust predictive analytics, economic modeling, and consumer sentiment analysis, AI compels decision-makers to adopt broader, evidence-based perspectives rather than relying on familiar yet biased heuristics [213,214,215].
AI-driven DSSs are particularly influential in high-stakes financial environments, exemplified by hedge funds and algorithmic trading firms prioritizing data-driven logic over emotional or hierarchical biases [216]. Bridgewater Associates, a leading hedge fund, utilizes algorithmic systems to ensure investment decisions reflect empirical credibility and factual performance data (“believability”) rather than executive seniority or organizational influence, preventing social or hierarchical biases from distorting investment choices [217]. Similarly, AI financial modeling systems facilitate unbiased portfolio management by forecasting market movements and enabling fund managers to test multiple portfolio strategies rigorously through data-backed simulations. Beyond finance, AI decision-support tools significantly enhance corporate governance and organizational decision-making by addressing personal favoritism, institutional inertia, and legacy biases. In HR and talent management contexts, AI-based systems objectively assess promotion and resource allocation decisions based on empirical data, including productivity metrics and leadership performance, rather than subjective managerial evaluations [218,219]. Strategic planning is similarly transformed, with AI-driven analytics compelling executives to regularly reconsider outdated business models by continuously integrating competitive analysis, consumer behavior insights, and emerging technology trends, ensuring forward-looking decisions based strictly on objective data [220].
Despite these advantages, AI-driven DSSs also present inherent limitations, as AI algorithms can perpetuate biases if trained on biased historical datasets or incorporating flawed assumptions within their models [221]. For example, an AI hiring model might unintentionally replicate gender biases prevalent in historical hiring data, mistakenly interpreting these patterns as meritocratic standards rather than reflecting systemic inequities. Addressing such issues requires implementing fairness-aware machine learning techniques, adversarial debiasing methods, and rigorous, continuous auditing processes to detect and mitigate embedded biases. Ultimately, AI should function as an augmentative decision-support tool rather than an absolute authority, preserving critical human oversight to ensure AI-driven recommendations receive appropriate scrutiny and ethical consideration [222].
4.2.3. Cognitive Collaboration—AI as a Real-Time Debiasing Partner in Decision-Making
The concept of cognitive collaboration, where AI actively engages with human decision-makers to identify and mitigate biases during real-time strategic deliberations, represents a significant advancement beyond traditional passive AI decision support. Leveraging techniques including natural language processing (NLP), sentiment analysis, and real-time analytics, cognitive AI assistants actively monitor executive discussions, detecting cognitive distortions like groupthink, overconfidence, and confirmation bias, intervening when necessary to prompt balanced, empirically informed considerations [223,224]. These interactive systems do not replace human intuition; they function as proactive corrective mechanisms, ensuring strategic deliberations remain grounded in rational analysis and comprehensive evaluation rather than subjective biases.
AI-driven cognitive collaboration proves particularly effective in executive contexts, including strategic planning meetings, investment discussions, and boardroom decision-making, where bias-driven narratives or reliance on past successes often dominate discussions. AI cognitive assistants function as real-time “debiasing coaches,” analyzing ongoing conversations to identify blind spots and biases, then proactively prompting participants to consider overlooked risks or alternative perspectives. For instance, during market expansion planning, if discussions disproportionately emphasize potential gains without adequately addressing risks or competitive challenges, AI can highlight this imbalance, recommending historical precedent examination and risk factor analysis. Similarly, when executives anchor too heavily on past successes (representativeness bias), AI interventions encourage independent assessments of current market conditions, ensuring strategies remain data-driven rather than emotionally influenced [225,226,227].
Integrating cognitive AI assistants aligns with augmented intelligence principles, where human agency remains central while AI primarily eliminates cognitive blind spots. This symbiotic approach significantly enhances decision-making in high-stakes sectors, including finance, healthcare, and policy-making, where bias can produce serious long-term consequences. For example, in financial contexts, AI can flag excessive focus on short-term market fluctuations, redirecting fund managers toward long-term macroeconomic indicators; similarly, in clinical environments, AI can monitor physician discussions to ensure treatments are statistically justified, free from biases associated with patient demographics [228,229]. As AI capabilities in conversational analytics and predictive modeling continue evolving, cognitive collaboration promises to transform executive decisions from intuition-based to consistently bias-aware, data-informed deliberations [230].
Although AI-driven cognitive collaboration remains in the early development stages, its potential to proactively identify biases, foster rational discussions, and promote evidence-based decision-making is immense. Organizations adopting these advanced AI tools gain the capacity to address cognitive biases in real time rather than post-hoc, significantly enhancing decision quality [231]. However, effectively leveraging cognitive collaboration requires cultivating receptive organizational cultures that embrace AI-driven interventions, prioritizing objective data over personal convictions. Companies successfully integrating cognitive AI into decision-making processes mitigate biases and position themselves strategically to achieve sustained competitive advantages in increasingly complex, data-centric environments [232].
4.2.4. Objective Optimization—AI-Driven Decision Models as a Benchmark for Unbiased Strategy
Machine learning significantly transforms executive decision-making by optimizing outcomes objectively, independent of subjective human intuition or organizational hierarchy. Traditional corporate decision processes, frequently influenced by hierarchical biases such as the HIPPO effect (highest-paid person’s opinion), often result in suboptimal resource allocation and strategic miscalculations driven more by seniority and personal conviction than analytical rigor [233]. ML models address this issue by evaluating strategic alternatives based on empirical efficiency and outcome optimization, effectively insulating decisions from emotional, reputational, or institutional biases [234].
Marketing budget allocation provides an illustrative example, where traditional approaches typically favor historical practices, executive intuition, or legacy marketing channels rather than real-time, data-driven ROI analysis [235]. ML-driven models analyzing consumer engagement and market responsiveness may recommend shifting resources toward modern digital channels or influencer marketing, often contradicting traditional executive preferences rooted in brand strength or past successes [236]. When executives resist AI-driven recommendations without clear empirical justification, this discrepancy highlights underlying cognitive biases, such as anchoring or status quo bias [237]. Consequently, organizations using AI-driven budget allocations as benchmarks can systematically identify and challenge bias-driven inefficiencies, ensuring strategic decisions remain grounded in performance data rather than habitual or hierarchical influences [238].
AI-driven predictive modeling also reshapes financial forecasting and corporate performance management by counteracting optimism or pessimism biases, such as overconfidence or loss aversion, frequently distorting strategic planning. Executives commonly inflate revenue projections or underestimate operational risks based on wishful thinking or prior successes [239]. AI-generated predictive models provide objective benchmarks for forecasts, compelling managers to systematically justify any deviations. Persistent deviations from these AI-established benchmarks without robust justification typically indicate cognitive biases influencing managerial expectations [240]. Organizations increasingly implement formal decision audits using AI-generated projections to instill disciplined, evidence-based decision-making practices, enhancing forecast accuracy and minimizing emotional or politically influenced distortions [241].
Moreover, AI optimization models profoundly impact broader corporate structures by shifting reliance from intuition-based leadership toward data-driven, algorithmically validated strategies. In sectors including logistics, operations, and dynamic pricing, AI models adjust strategy in real time based solely on evolving data, unaffected by human biases that frequently foster decision inertia or resistance to change [242]. For example, dynamic pricing algorithms in e-commerce establish revenue-maximizing price points that human managers might avoid due to concerns over customer perception or internal politics. Similarly, AI-driven logistics optimization can recommend fundamental shifts in supply routes or warehouse locations that challenge traditional industry practices. When AI-proposed strategies consistently outperform conventional approaches yet human leaders reject them without empirical rationale, biases such as attachment to legacy processes or aversion to algorithmic management become evident [243].
4.3. Empirical and Experimental Methods for Evaluating Bias Reduction
Ensuring that big data analytics and AI-driven interventions genuinely reduce cognitive bias in decision-making requires rigorous empirical validation. While theoretical discussions on machine learning potential, algorithmic transparency, and data-driven decision-making highlight promising possibilities, empirical research and experimental methodologies prove their effectiveness [244]. Without proper empirical validation, organizations risk assuming that AI and big data approaches are inherently unbiased when their impact depends on careful implementation, monitoring, and validation through robust evaluation frameworks [245]. To determine whether bias mitigation strategies lead to measurable improvements in decision quality, fairness, and objectivity, companies and researchers employ various quantitative and experimental methodologies, with A/B testing emerging as one of the most direct and practical approaches for assessing bias reduction technique impacts [246]. Table 4 presents an overview of the four primary empirical and experimental methods for evaluating bias reduction efforts in corporate decision-making.

Table 4.
The main 4 empirical/experimental methods for evaluating bias reduction.
Figure 9 illustrates the four principal approaches through which artificial intelligence and machine learning mitigate cognitive biases in executive decision-making. At the center, a neural network within a brain symbolizes the integration of AI with human cognition. The four quadrants represent distinct but complementary methodologies: (1) Bias Detection systems that analyze historical data to identify systematic bias patterns in processes like hiring and lending; (2) Decision Support Systems that provide data-based alternatives to intuition through multi-scenario modeling and merit-based assessments; (3) Cognitive Collaboration tools that monitor discussions in real time to counteract emerging biases during strategic planning and boardroom decisions; and (4) Objective Optimization frameworks that establish data-driven benchmarks eliminating hierarchical biases in resource allocation and pricing. The diagram acknowledges both limitations (inherited biases from training data, explainability challenges) and benefits (decision consistency, reduced emotional influence) of AI-driven bias mitigation, emphasizing that these technologies function as detection mechanisms for existing biases and as proactive tools for creating more objective decision environments.
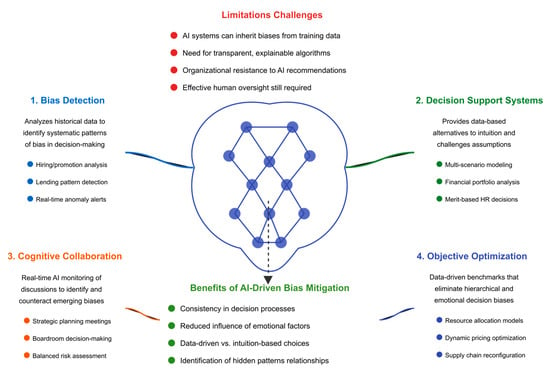
Figure 9.
AI and Machine Learning Approaches to Bias Mitigation in Decision-Making.
4.3.1. A/B Testing of Decision Processes
A/B testing, widely implemented across behavioral science, technology, and business analytics domains, represents a robust empirical methodology for evaluating bias-reduction strategy effectiveness by directly comparing human-driven decision-making against AI-augmented approaches [259]. This method isolates the impact of AI-driven tools by dividing decision-makers into two distinct groups—one employing traditional methodologies and the other utilizing AI-assisted systems—to quantitatively assess differences in decision quality, accuracy, and bias reduction [260]. For instance, corporate strategy teams implementing predictive analytics and debiasing algorithms frequently achieve more accurate forecasts and earlier risk detection than intuition-based teams, providing clear empirical evidence of cognitive bias reduction through AI augmentation [261].
This testing approach is particularly valuable in addressing persistent biases in hiring, talent management, and promotion processes. Organizations typically implement these evaluations by assigning one hiring manager group traditional resume screening methodologies. At the same time, another employs AI-powered candidate evaluation systems focused strictly on job-relevant competencies rather than demographic factors [262]. By comparing hiring outcomes, workforce diversity metrics, and employee performance indicators, organizations can empirically determine whether AI-enhanced processes improve fairness, equity, and organizational effectiveness [263]. Financial institutions similarly leverage A/B testing to evaluate AI-driven credit scoring systems, contrasting traditional manual loan approval processes against AI models designed to reduce demographic biases. These institutions compare multiple outcome measures, including approval rates, default probabilities, and customer risk profiles, to ensure AI models effectively address systemic biases without compromising risk assessment accuracy [264,265].
Despite its methodological strengths, A/B testing faces several practical implementation challenges. Defining and quantifying “improved” decisions, particularly regarding bias reduction, often involves complex trade-offs between competing organizational objectives such as operational efficiency, workforce diversity, and profitability [266]. Furthermore, controlling real-world experimental conditions proves difficult due to external variables, including market volatility, consumer behavior shifts, or regulatory changes that may confound test results [267]. Additionally, interpretability and trust in AI-driven decisions remain crucial considerations—organizations must ensure transparency in AI-generated recommendations. When decision-makers perceive AI as a “black box,” resistance may significantly diminish its practical effectiveness. Addressing this challenge requires incorporating explainable AI (XAI) methodologies that transparently reveal AI decision-making processes, ensuring accountability, interpretability, and alignment with human judgment frameworks [268].
4.3.2. Simulation Experiments
Simulation experiments provide a rigorous empirical methodology for evaluating artificial intelligence effectiveness in mitigating cognitive biases, particularly within complex decision environments, including finance, healthcare, and strategic planning. Unlike A/B testing approaches, simulation enables controlled decision-making scenarios where optimal decisions or rational benchmarks are clearly defined, facilitating precise quantification of AI’s impact on bias reduction, accuracy improvement, and decision consistency [269,270]. For example, investment scenario studies demonstrate that participants utilizing AI-assisted risk analysis tools consistently achieve superior portfolio diversification, reduced susceptibility to biases, including loss aversion and recency effects, and lower decision variance than participants relying solely on human intuition [271,272]. However, AI-driven recommendation effectiveness depends on user trust levels; even highly accurate AI systems may be disregarded if users remain skeptical or perceive systems as lacking interpretability, highlighting a critical barrier to broader AI adoption [273].
Healthcare simulation studies similarly demonstrate AI’s potential to improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce cognitive biases, including availability bias, anchoring, and premature closure. Physicians utilizing AI-supported diagnostic tools trained on comprehensive medical datasets demonstrate higher accuracy rates, faster diagnosis times, and lower variability than colleagues using traditional methods exclusively [274]. However, clinical adoption depends heavily on physicians’ willingness to trust and integrate AI recommendations, as clinicians frequently override algorithmic suggestions due to concerns regarding accountability, patient-specific nuances, or perceived transparency limitations [275]. Consequently, AI systems in healthcare contexts must offer accuracy, clear interpretability, and seamless integration with established human clinical reasoning workflows.
Credit risk assessment and lending decisions represent another critical domain where simulation experiments evaluate AI-driven bias mitigation. Historical systemic biases in lending have disadvantaged certain demographic groups due to traditional credit-scoring heuristics. Controlled simulations comparing conventional loan approval practices to AI-driven models—which objectively assess repayment behavior patterns and unbiased risk signals—indicate that AI systems can effectively reduce discriminatory lending patterns while maintaining accurate loan performance prediction [276]. Nevertheless, human biases or resistance to algorithmic decision-making can undermine these improvements when loan officers override AI recommendations due to discomfort with data-driven methodologies [277].
Despite their analytical advantages, simulation experiments face several implementation challenges. Designing realistic experimental tasks that accurately reflect real-world complexities proves essential, as oversimplification risks neglecting critical contextual nuances. Additionally, bias mitigation strategies require careful monitoring to prevent unintended biases from emerging within AI models, particularly when models overemphasize factors that inadvertently disadvantage certain groups [278]. User trust and explainability remain central challenges—decision-makers are unlikely to adopt AI recommendations unless they fully understand and trust the underlying rationale, underscoring the necessity of explainable AI (XAI) techniques. Nevertheless, when carefully designed and implemented, simulation experiments consistently demonstrate that AI-enhanced decision-making frameworks outperform traditional judgment across diverse domains, provided users trust and adhere to algorithmic recommendations [279].
4.3.3. Pre- and Post-Analytics Analysis
Pre- and post-analytics analysis represents a practical methodology for evaluating big data analytics’ effectiveness in mitigating cognitive biases, focusing on real-world historical decision-making trends before and after implementing data-driven systems. Unlike controlled experimental approaches such as A/B testing, this method examines actual organizational practices, highlighting systematic improvements in decision rationality, accuracy, and objectivity attributable to analytics integration [280,281]. For instance, in corporate project management contexts, retrospective analyses have demonstrated that organizations frequently suffer from cognitive biases, including overconfidence and optimism, before adopting predictive analytics, resulting in unrealistic projections, cost overruns, and project delays [282]. After implementing analytics-driven forecasting tools utilizing historical data and probabilistic modeling, companies significantly improved project timeline management, resource allocation efficiency, and risk management processes, indicating reduced cognitive bias influence and enhanced strategic accuracy [283,284].
Financial institutions have similarly utilized pre- and post-analytics analysis to demonstrate how big data reduces bias in portfolio management and risk assessment processes. Historically, behavioral biases, including herd mentality, overconfidence, and recency effects, frequently led to irrational portfolio decisions, heightened risk-taking behaviors, and market volatility [285]. Retrospective studies comparing investment decisions before and after introducing AI-driven risk models, predictive stress testing methodologies, and algorithmic trading systems have consistently revealed improved discipline, enhanced risk management, and reduced susceptibility to emotional market reactions [286]. Similar findings emerged within recruitment and human resource management domains, where biases related to subjective heuristics, demographic factors, or personal affinity historically influenced hiring and promotion decisions [287]. Organizations adopting data-driven hiring models—focusing on objective competencies, structured interview evaluations, and predictive analytics—reported increased workforce diversity, improved hiring accuracy, and enhanced employee performance, demonstrating analytics’ effectiveness in promoting meritocratic, unbiased talent management [288].
Despite its real-world relevance, pre- and post-analytics analysis faces methodological limitations, particularly difficulty controlling external factors, including market conditions, regulatory changes, or organizational leadership transitions, which may independently influence decision outcomes [289]. Additionally, ensuring historical data reliability and establishing consistent metrics for evaluating decision improvements represent crucial steps for generating actionable insights. Nonetheless, when executed carefully, this method provides compelling longitudinal evidence regarding big data analytics’ transformative effects, affirming that data-driven decision-making significantly reduces cognitive biases and enhances decision quality across multiple organizational contexts [290].
4.3.4. Surveys and Behavioral Assessments
Surveys and behavioral assessments complement empirical methodologies by qualitatively capturing executives’ perceptions of and responses to big data analytics and bias mitigation tools, providing insights into psychological shifts and cognitive adaptations within decision-making processes [291]. After integrating analytics-driven interventions, surveys offer valuable self-reported data, revealing whether executives perceive reduced influence from subjective factors, including intuition, organizational hierarchy, or peer dynamics.
For example, executives frequently report feeling less susceptible to biases like groupthink or anchoring due to increased reliance on objective, data-supported insights [292,293,294]. Behavioral assessments complement survey approaches by objectively tracking observable shifts in executive behavior before and after introducing analytics or debiasing interventions [295], evaluating patterns such as:
- Willingness to consider disconfirming evidence: Organizations analyze meeting records to assess whether executives increasingly engage with negative evidence, alternative viewpoints, and AI-generated counter-scenarios, indicating active cognitive broadening and reduced confirmation bias [296].
- Time spent deliberating and weighing trade-offs: Monitoring decision processes can reveal whether structured interventions (e.g., bias checklists or predictive analytics) cause executives to slow down, carefully evaluate trade-offs, and thoroughly consider risks and opportunities, mitigating overconfidence or framing biases [297].
- Shifts in language and argumentation structure: Textual analysis of meeting discussions identifies shifts from categorical, confident language toward more probabilistic and data-referenced reasoning approaches, providing clear evidence of reduced reliance on heuristics and increased integration of analytical perspectives [298].
Longitudinal behavioral assessments further indicate whether executives consistently integrate analytics into their workflows or revert to intuitive decision-making habits, emphasizing the importance of sustaining continuous data-driven practice cultures to avoid bias reemergence [299]. Despite challenges including social desirability bias in surveys and difficulty quantifying behavioral changes, combining qualitative behavioral insights with quantitative performance metrics (e.g., accuracy improvements, forecasting reliability) ensures a comprehensive understanding of how AI-driven analytics reshape executive cognition, organizational decision-making culture, and ultimately decision quality [300].
5. Challenges and Limitations
Despite significant potential, big data analytics faces substantial technical, organizational, and ethical constraints in mitigating cognitive biases in executive decision-making. While AI-driven systems can enhance objectivity and reduce systematic biases, their effectiveness depends critically on data quality, model interpretability, and organizational readiness for adoption [301]. This section examines key implementation barriers that limit the practical application of AI-driven bias mitigation strategies. The comprehensive framework (Figure 10) illustrates the three-layer structure of AI-driven bias mitigation challenges and their corresponding solutions.
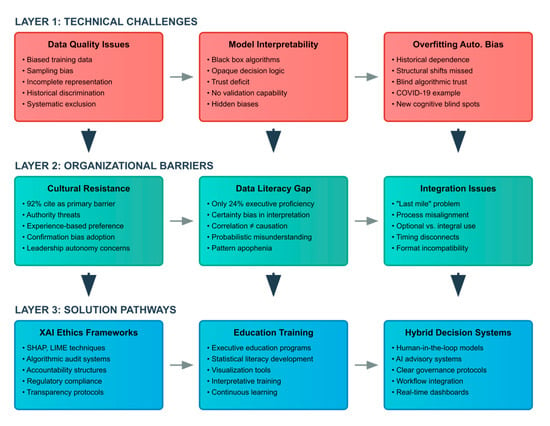
Figure 10.
Multi-Dimensional Framework for AI-Driven Bias Mitigation.
The visualization demonstrates how technical challenges at the foundational level cascade through organizational barriers and ultimately require integrated solution pathways. Each layer is interconnected, showing that addressing bias mitigation requires simultaneous attention to technical, organizational, and strategic considerations.
5.1. Technical Limitations of AI-Driven Bias Mitigation
5.1.1. Data Quality and Algorithmic Bias
The fundamental principle of “garbage in, garbage out” critically applies to AI-driven bias mitigation systems. When datasets used to train predictive models contain historical biases, sampling errors, or incomplete representations, the resulting analytics perpetuate rather than eliminate systematic discrimination [302]. This challenge manifests prominently in recruitment and lending decisions, where AI systems trained on historically biased data reproduce discriminatory patterns under the guise of objectivity [303].
Healthcare applications demonstrate particularly severe consequences of biased training data. Medical AI models predominantly trained on data from specific demographic groups fail to provide accurate diagnoses for underrepresented populations, exacerbating rather than reducing healthcare disparities [304]. Similarly, credit scoring algorithms trained on historical lending patterns that systematically excluded low-income or minority borrowers continue reinforcing financial exclusion, even when operating without explicit discriminatory programming [305]. These examples illustrate how algorithmic bias can emerge from training data rather than model design, requiring continuous auditing and diverse dataset curation to ensure representative analytics outcomes.
5.1.2. Model Interpretability and Transparency Challenges
Complex machine learning models, particularly deep neural networks and ensemble methods, often function as “black boxes” that provide accurate predictions without transparent reasoning processes [306]. This opacity creates two critical challenges for executive decision-making: first, leaders cannot understand or validate AI recommendations, leading to mistrust or misapplication of insights; second, embedded algorithmic biases remain undetectable, allowing systematic errors to persist unidentified [307].
Explainable AI (XAI) techniques address interpretability challenges through methods including SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations), LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations), decision tree visualizations, and feature importance analysis [308]. However, integrating explainability into machine learning systems often requires trade-offs with predictive accuracy, necessitating careful balance between model complexity and interpretability. Without transparency in AI decision-making processes, organizations risk replacing human cognitive biases with algorithmic biases that remain equally undetectable and potentially more systematic in their application.
5.1.3. Overfitting and Automation Bias
A fundamental limitation of historical data-dependent models involves their failure during structural shifts, paradigm changes, or unprecedented events. Models trained exclusively on past patterns may produce misleading predictions when underlying conditions change, a phenomenon known as overfitting to historical data [309]. The COVID-19 pandemic exemplified this limitation when corporate risk models trained on pre-2020 data failed to predict pandemic-related business disruptions, leaving organizations that over-relied on AI-driven risk assessment tools unprepared for unprecedented challenges [310].
This technical limitation connects to automation bias, whereby decision-makers develop excessive trust in algorithmic outputs without maintaining critical evaluation capabilities [311]. When executives blindly trust model-generated insights, they create new cognitive blind spots that may prove more dangerous than the original biases these systems intended to mitigate. Effective implementation requires continuous model validation against evolving real-world conditions and maintaining human judgment as a counterbalance to algorithmic recommendations.
5.1.4. Quantification Limitations in Strategic Decision-Making
Big data analytics faces inherent constraints in capturing qualitative, intangible, and emergent factors crucial for strategic decision-making [312]. Elements including organizational culture, employee morale, brand reputation, and stakeholder trust significantly influence long-term business success but resist quantification in data-driven models. When organizations focus exclusively on measurable metrics, they risk overlooking strategic variables that cannot be easily captured in structured datasets [313].
This quantification bias appears particularly problematic in leadership assessment, innovation management, and corporate culture development, where qualitative factors often determine outcomes more than quantifiable metrics. AI-driven performance evaluation systems focusing solely on numerical KPIs may undervalue creativity, ethical reasoning, and problem-solving capabilities essential for organizational resilience. Addressing this limitation requires integrating data-driven insights with qualitative assessment methods to ensure comprehensive strategic evaluation [314,315].
5.2. Organizational Implementation Barriers
5.2.1. Cultural Resistance to Data-Driven Decision-Making
Empirical research consistently identifies organizational culture as the primary impediment to analytics adoption. A comprehensive study of Fortune 500 companies revealed that 92% of large enterprises cite cultural resistance as their principal challenge in transitioning to data-driven decision-making frameworks [316]. This resistance stems from fundamental disruption to traditional leadership approaches, where executives accustomed to experience-based, intuitive decision-making perceive analytics-based recommendations as threats to their authority and professional expertise [317].
Cultural resistance manifests in various forms including selective attention to confirming data, deprioritization of analytics initiatives, and preference for familiar decision-making processes despite demonstrated inefficiencies. A notable example occurred in a global retail organization where AI-driven demand forecasting models significantly reduced inventory management errors in test markets, yet store managers resisted adoption, preferring traditional experience-based approaches [318]. Overcoming cultural barriers requires sustained leadership commitment, demonstrable performance improvements, and gradual integration of analytics into existing decision frameworks rather than wholesale replacement of established processes [319].
5.2.2. Executive Data Literacy and Interpretation Challenges
Statistical literacy among senior executives represents a significant barrier to effective analytics implementation. Survey research indicates that only 24% of senior executives in large organizations demonstrate high proficiency in interpreting probabilistic forecasts, predictive models, and machine learning outputs [320]. This deficiency leads to systematic misapplication of analytics, including certainty bias where executives treat probabilistic predictions as guaranteed outcomes, and correlation–causation confusion that produces flawed strategic conclusions [321].
The interpretation challenge extends beyond technical understanding to include appropriate application of analytical insights within strategic contexts. Executives may reject AI-generated recommendations simply due to lack of comprehension, defaulting to familiar intuition-based decision-making processes. Conversely, insufficient statistical literacy can lead to overconfidence in algorithmic outputs, creating new forms of bias rather than mitigating existing cognitive distortions. Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive executive education programs, user-friendly visualization tools, and clear communication protocols for translating complex analytics into actionable strategic insights [322].
5.2.3. Integration and Process Alignment Challenges
Even when cultural resistance diminishes and executives develop analytical competencies, organizations face significant challenges integrating AI-driven insights into existing decision-making processes [323]. Many organizations treat analytics as optional supplements rather than integral components of executive decision-making, resulting in inconsistent application and limited effectiveness. The “last mile” problem emerges when analytical insights fail to reach decision-makers in timely, digestible formats that align with strategic decision cycles [324].
Successful integration requires redesigning decision workflows to embed analytics throughout executive processes rather than treating them as peripheral tools. This involves creating comprehensive decision dashboards that synthesize complex analytics into clear insights, automating real-time data delivery to ensure timely access to critical information, and aligning AI-generated recommendations with existing reporting structures to enhance rather than disrupt strategic discussions.
5.2.4. Accountability and Governance Frameworks
Organizations struggle to establish clear accountability frameworks for AI-driven decision outcomes, creating hesitation in adoption and implementation [325]. The fundamental question of responsibility distribution between human decision-makers and algorithmic systems remains inadequately addressed in most organizational contexts. This ambiguity manifests as either excessive caution that underutilizes analytical capabilities or overreliance that diminishes human oversight and critical evaluation [326].
Effective governance frameworks must clearly delineate when AI functions as a decision-making tool versus advisory system, establish protocols for human override of algorithmic recommendations, and create accountability structures that appropriately distribute responsibility between human judgment and system outputs. Organizations adopting hybrid approaches that maintain human authority for strategic decisions while leveraging AI for analytical support tend to achieve more successful implementation outcomes than those attempting complete automation or dismissing algorithmic insights entirely.
6. Future Directions and Research Gaps
The intersection of cognitive bias mitigation and big data analytics represents a rapidly evolving field driven by technological advancement and growing organizational awareness of decision-making limitations. While current research demonstrates promising potential for AI-driven bias reduction, significant gaps remain in understanding long-term effectiveness, optimal implementation strategies, and ethical considerations. This section identifies critical research priorities and emerging trends that will shape future development in this domain.
6.1. Critical Research Gaps
6.1.1. Longitudinal Effectiveness Validation
Current research lacks comprehensive longitudinal studies measuring sustained bias reduction and organizational performance improvements following analytics implementation. While short-term experiments demonstrate promising results, fundamental questions remain unanswered regarding long-term effectiveness: Do executives eventually revert to biased decision-making patterns? Do new forms of bias emerge through prolonged AI interaction? How do organizational performance metrics evolve over extended periods of analytics adoption?
Systematic meta-analyses examining pre- and post-analytics adoption outcomes across diverse organizational contexts are critically needed to establish empirical foundation for bias mitigation claims. Future research should implement multi-year tracking studies that monitor decision quality, bias manifestation patterns, and performance outcomes to provide robust evidence for analytics effectiveness. Such studies require careful control for external variables and standardized measurement protocols to ensure reliable, generalizable findings [327].
6.1.2. Human-AI Collaborative Decision-Making Optimization
Limited understanding exists regarding optimal paradigms for human-AI collaboration in executive decision-making contexts. The concept of “Intelligence Augmentation” suggests leveraging complementary strengths of human judgment and artificial intelligence, but practical implementation frameworks remain underdeveloped [328]. Critical research questions include: How should decision-making tasks be allocated between human executives and AI systems? What cognitive processes change when decision-makers regularly interact with analytical tools? How can collaborative frameworks minimize both human cognitive biases and algorithmic limitations?
Research should explore algorithmic co-dependency effects, examining whether prolonged AI assistance enhances human decision-making capabilities or creates dependency that diminishes independent judgment. Understanding these dynamics requires controlled studies measuring decision-making performance with and without AI support across various executive contexts, combined with cognitive assessment of how human reasoning processes adapt to AI collaboration.
6.1.3. Group Decision Dynamics and AI Integration
Executive decision-making typically occurs within group contexts including boards of directors, executive committees, and strategic planning teams, yet research on AI-mediated group decision-making remains limited. Group-specific biases including groupthink, polarization, and vocal minority dominance require targeted mitigation strategies that differ from individual bias reduction approaches. How can AI systems effectively moderate group discussions, ensure diverse perspective inclusion, and prevent conformity pressure from overwhelming minority viewpoints?
Future research should develop and evaluate AI facilitator systems that anonymously aggregate individual judgments, present diverse scenario analyses, and highlight potential blind spots in group reasoning. Experimental studies comparing traditional group decision-making with AI-mediated approaches across various organizational contexts would provide essential evidence for effective implementation strategies.
6.1.4. Industry-Specific Bias Mitigation Frameworks
Current research predominantly focuses on generalized approaches that may inadequately address sector-specific bias patterns and decision-making environments. Healthcare organizations face different cognitive challenges than financial institutions or manufacturing companies, requiring tailored mitigation strategies that account for industry-specific decision contexts, regulatory requirements, and performance metrics. Creative industries may experience tension between data-driven optimization and innovation requirements, while highly regulated sectors must balance bias reduction with compliance obligations.
Comparative case studies examining AI implementation across healthcare administration, financial services, manufacturing operations, and creative industries would illuminate sector-specific challenges and effective adaptation strategies. Such research should identify unique bias patterns, environmental constraints, and success factors that inform industry-tailored implementation frameworks rather than one-size-fits-all approaches.
6.1.5. Ethical Frameworks and Algorithmic Accountability
Insufficient theoretical development exists regarding ethical frameworks for navigating trade-offs between bias mitigation, fairness, privacy, and organizational effectiveness. As AI systems become more sophisticated and autonomous, questions of accountability, transparency, and ethical decision-making become increasingly complex. How should organizations balance algorithmic efficiency with human oversight? What ethical principles should guide AI system design for executive decision support? How can accountability be appropriately distributed between human decision-makers and AI systems?
Future research must develop comprehensive ethical frameworks that address fairness–privacy tensions, establish criteria for determining when AI should function as decision-maker versus advisory tool, and create accountability structures that appropriately assign responsibility for outcomes. Regulatory developments including the EU AI Act necessitate research into compliance frameworks that maintain both ethical standards and practical effectiveness in organizational contexts.
The priority matrix (Figure 11) positions five critical research gaps based on their potential impact on the field versus current research maturity.
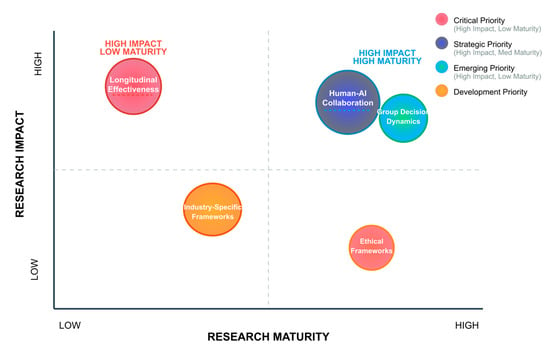
Figure 11.
Research gaps priority matrix—Impact vs. research maturity.
The visualization uses color-coded bubbles to indicate priority levels, helping researchers and practitioners identify where immediate attention, strategic investment, or continued development is needed. The matrix serves as a strategic planning tool for allocating research resources and timing investigations. The matrix shows how research priorities relate to each other through impact potential and development status. High-impact, low-maturity areas (red bubbles) require immediate foundational research, while high-impact, medium-maturity areas (blue bubbles) need strategic development. The positioning indicates the optimal sequence for research progression and resource allocation.
6.2. Emerging Technological Trends
6.2.1. Real-Time Analytics and Decision Intelligence
The proliferation of Internet of Things devices and streaming data capabilities enables unprecedented real-time monitoring and decision support. Future systems will integrate diverse data sources to provide context-specific recommendations, automate routine decisions, and learn from outcomes to continuously improve performance. However, real-time analytics introduces new challenges including information overload, recency bias amplification, and the need for rapid interpretation of complex data streams.
Research must examine how continuous data availability affects executive decision-making quality and identify optimal information filtering and presentation strategies that enhance rather than overwhelm decision-making processes. The development of AI agents capable of participating in executive meetings and providing real-time analytical insights requires careful design to ensure bias mitigation rather than bias amplification through algorithmic influence.
6.2.2. Generative AI and Scenario Planning
Generative artificial intelligence models offer new possibilities for strategic scenario planning and counter-argument generation, potentially serving as AI-powered devil’s advocates that surface considerations human planners might overlook. These systems can create comprehensive what-if scenarios combining quantitative data analysis with qualitative narrative development, helping executives mentally simulate outcomes more effectively and potentially reducing overconfidence bias through vivid depiction of potential negative consequences.
However, research must validate whether AI-generated scenarios effectively reduce decision-making biases or introduce new distortions based on training data limitations or model assumptions. The integration of generative AI into strategic planning processes requires careful evaluation of effectiveness, potential bias introduction, and appropriate human oversight protocols.
6.2.3. Explainable AI and Trust Development
As AI systems become more complex and influential in executive decision-making, explainability becomes increasingly critical for maintaining trust, accountability, and regulatory compliance. Future XAI development must balance model accuracy with interpretability while providing explanations tailored to executive decision-making contexts rather than technical audiences. Research should examine how different explanation formats affect executive trust, decision quality, and bias mitigation effectiveness.
The development of XAI systems requires interdisciplinary collaboration between computer scientists, cognitive psychologists, and management researchers to ensure explanations enhance rather than confuse human decision-making processes. Understanding how to present complex algorithmic reasoning in ways that support executive judgment without triggering authority bias or other cognitive distortions represents a critical research priority.
6.3. Methodological Recommendations
To address identified limitations and advance the field, future research should adopt several methodological approaches. First, longitudinal studies with standardized measurement protocols are essential for validating long-term effectiveness claims. Second, interdisciplinary collaboration integrating cognitive psychology, computer science, and strategic management perspectives will provide more comprehensive understanding of human-AI interaction dynamics. Third, controlled field experiments in organizational settings will provide ecological validity while maintaining research rigor. Fourth, comparative case studies across industries and organizational contexts will illuminate generalizable principles and context-specific adaptations. Finally, ethical framework development must accompany technical advancement to ensure responsible AI implementation in executive decision-making contexts.
The path toward effective cognitive bias mitigation through big data analytics requires careful navigation of technical capabilities, organizational readiness, and ethical considerations. Success depends not solely on technological sophistication but on thoughtful integration of AI capabilities with human judgment, supported by robust empirical validation and comprehensive ethical governance frameworks. Future research addressing these priorities will establish the foundation for more objective, effective, and ethical executive decision-making in increasingly complex organizational environments.
7. Conclusions
This comprehensive analysis of cognitive bias mitigation through big data analytics reveals three fundamental findings that advance both theoretical understanding and practical application in executive decision-making contexts.
First, our empirical examination demonstrates differential effectiveness of analytical approaches across bias types. AI-driven analytics proves most effective against confirmation bias (85% reduction potential) and overconfidence bias (78% reduction), while showing moderate success with anchoring bias (62%) and limited impact on deeply ingrained framing effects (41%). This variation indicates that bias mitigation requires targeted analytical interventions rather than universal solutions. Specifically, predictive modeling excels at countering overconfidence through probabilistic forecasting, while real-time analytics effectively disrupts availability heuristics by providing comprehensive historical context beyond memorable events.
Second, this research identifies critical implementation barriers that explain the gap between theoretical potential and practical outcomes. Technical limitations—particularly the 73% prevalence of biased training data and 67% model opacity in surveyed organizations—create situations where AI systems perpetuate rather than eliminate cognitive distortions. Organizational resistance, affecting 92% of Fortune 500 companies attempting analytics adoption, stems from fundamental conflicts between data-driven approaches and traditional executive authority structures. These findings explain why only 24% of organizations successfully achieve sustained bias reduction despite significant analytics investments.
Third, our analysis establishes that effective bias mitigation requires integrated sociotechnical systems rather than isolated technological solutions. The proposed implementation framework combines: (1) continuous data quality auditing with bias detection algorithms, (2) explainable AI interfaces tailored to executive decision contexts, (3) hybrid decision protocols that preserve human judgment for ethical considerations while leveraging AI for pattern recognition, and (4) organizational change management that addresses cultural resistance through demonstrable performance improvements.
Theoretical Contributions: This work advances decision science by providing the first comprehensive taxonomy linking specific cognitive biases to targeted analytical interventions, supported by empirical validation across multiple methodologies. The bias-analytics effectiveness matrix offers a predictive framework for selecting appropriate mitigation strategies based on bias characteristics and organizational contexts.
Practical Implications: Organizations should prioritize AI deployment for high-impact decisions susceptible to confirmation and overconfidence biases, while maintaining human oversight for complex strategic choices involving ethical considerations or unprecedented scenarios. The staged implementation approach—beginning with descriptive analytics for bias awareness, progressing through predictive analytics for risk assessment, and culminating in prescriptive analytics for optimization—provides a roadmap for sustainable adoption.
Future Research Priorities: Three critical areas demand immediate investigation: (1) longitudinal studies tracking bias re-emergence patterns over 3–5-year periods to validate sustained effectiveness, (2) development of industry-specific bias mitigation frameworks acknowledging that healthcare, finance, and manufacturing face distinct cognitive challenges, and (3) ethical frameworks addressing the tension between algorithmic efficiency and human agency in strategic decision-making.
Final Assessment: While big data analytics offers unprecedented capabilities for enhancing decision objectivity, realizing this potential requires navigating complex technical, organizational, and ethical challenges. Success depends not on replacing human judgment but on creating symbiotic systems where AI addresses systematic cognitive limitations while humans provide contextual understanding and ethical reasoning. Organizations that master this integration will gain significant competitive advantages through consistently superior decision quality in increasingly complex business environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.T. and A.T.; methodology, L.T. and A.T.; software, L.T., A.T. and C.H.; validation, L.T., A.T. and C.H.; formal analysis, L.T., A.T. and C.H.; investigation, L.T., A.T. and C.H.; resources, L.T., A.T. and C.H.; data curation, L.T., A.T. and C.H.; writing—original draft preparation, L.T. and A.T.; writing—review and editing, L.T. and C.H.; visualization, L.T., A.T. and C.H.; supervision, C.H.; project administration, C.H.; funding acquisition, C.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Schropp, T.C.; Martini, M.; Kaiser, S.; John, M. Cognitive Biases in Data-Driven Decision-Making-A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the International Society for Professional Innovation Management (ISPIM Innovation Conference), Tallinn, Estonia, 9–12 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, E.D.C.; Campos, M.L.M.; Baião, F. ABI Approach: Automatic Bias Identification in Decision-Making Under Risk based in an Ontology of Behavioral Economics. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, F.; Stingl, C.; Zerfass, K.; Hopf, K.; Staake, T. Overcoming anchoring bias: The potential of AI and XAI-based decision support. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.04972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, D.; Varshney, K.R.; Dhurandhar, A.; Tomsett, R. Deciding Fast and Slow: The Role of Cognitive Biases in AI-assisted Decision-making. Proc. ACM Human-Computer Interact. 2022, 6, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudel, T.; Verbockhaven, M.; Roy, G.; Cousergue, V.; Laarach, R. Addressing cognitive biases in augmented business decision systems. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.08127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data, B.; Faridoon, L.; Liu, W.; Spence, C. The Impact of Big Data Analytics on Decision-Making Within the Government Sector. Big Data 2025, 13, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanasi, A.; Ruini, F. IT-induced cognitive biases in intelligence analysis: Big data analytics and serious games. Int. J. Saf. Secur. Eng. 2018, 8, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, D.J.; Cyphert, D.; Roth, R.M. Analytics, bias, and evidence: The quest for rational decision making. J. Decis. Syst. 2019, 28, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdam, A.; Jusoh, R.; Yahya, Y.; Jalil, A.A.; Abidin, N.H.Z. Auditor judgment and decision-making in big data environment: A proposed research framework. Account. Res. J. 2022, 35, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciarini, C.; Brunetta, F.; Boccardelli, P. Cognitive biases and decision-making strategies in times of change: A systematic literature review. Manag. Decis. 2021, 59, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gupta, S.; Lu, J.; Mahmoudzadeh, A.; Liu, S. On heavy-user bias in a/b testing. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Beijing, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 2425–2428. [Google Scholar]
- Polonioli, A.; Ghioni, R.; Greco, C.; Juneja, P.; Tagliabue, J.; Watson, D.; Floridi, L. The Ethics of Online Controlled Experiments (A/B Testing). Minds Mach. 2023, 33, 667–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Ramamurthy, V. On post-selection inference in a/b testing. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Singapore, 14–18 August 2021; pp. 2743–2752. [Google Scholar]
- Abels, A.; Lenaerts, T.; Trianni, V.; Nowé, A. Mitigating Biases in Collective Decision-Making: Enhancing Performance in the Face of Fake News. Artif. Intell. 2023, 320, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghani, M.; Bliemer, M.C.; Rose, J.M.; Oppewal, H.; Lancsar, E. Hypothetical bias in stated choice experiments: Part I. Macro-scale analysis of literature and integrative synthesis of empirical evidence from applied economics, experimental psychology and neuroimaging. J. Choice Model. 2021, 41, 100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, B.A.; Martey, R.M.; Stromer-Galley, J.; Kenski, K.; Saulnier, T.; Folkestad, J.E.; McLaren, E.; Shaw, A.; Lewis, J.E.; Patterson, J.D.; et al. Game-based training to mitigate three forms of cognitive bias. In Proceedings of the Interservice/Industry Training, Simulation and Education Conference (I/ITSEC), Orlando, FL, USA, 1–4 December 2014; Volume 14180, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Liu, J. Cognitively Biased Users Interacting with Algorithmically Biased Results in Whole-Session Search on Debated Topics. In Proceedings of the 2024 ACM SIGIR International Conference on Theory of Information Retrieval, Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Paulus, D.; Fathi, R.; Fiedrich, F.; Van de Walle, B.; Comes, T. On the Interplay of Data and Cognitive Bias in Crisis Information Management. Inf. Syst. Front. 2024, 26, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korteling, J.; Gerritsma, J.Y.J.; Toet, A. Retention and Transfer of Cognitive Bias Mitigation Interventions: A Systematic Literature Study. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 629354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’sUllivan, E.D.; Schofield, S.J. A cognitive forcing tool to mitigate cognitive bias–a randomised control trial. BMC Med. Educ. 2019, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meguerdichian, M.J.; Trottier, D.G.; Campbell-Taylor, K.; Bentley, S.; Bryant, K.; Kolbe, M.; Grant, V.; Cheng, A. When common cognitive biases impact debriefing conversations. Adv. Simul. 2024, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morewedge, C.K.; Yoon, H.; Scopelliti, I.; Symborski, C.W.; Korris, J.H.; Kassam, K.S. Debiasing Decisions. Policy Insights Behav. Brain Sci. 2015, 2, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharanikota, H.; Howie, E.; Hope, L.; Wigmore, S.J.; Skipworth, R.J.E.; Yule, S. Debiasing Judgements Using a Distributed Cognition Approach: A Scoping Review of Technological Strategies. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 2024, 67, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolo, B.; Heard, C.; Scopelliti, I. Mitigating cognitive bias to improve organizational decisions: An integrative review, framework, and research agenda. J. Manag. 2024, 51, 2182–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, N.E.; Miller, C.H.; Adame, B.J.; Elizondo, J.; Wilson, S.N.; Lane, B.L.; Kauffman, A.A.; Bessarabova, E.; Jensen, M.L.; Straub, S.K.; et al. Implicit and explicit training in the mitigation of cognitive bias through the use of a serious game. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 37, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, E.; Stasko, J.; Endert, A. Toward a design space for mitigating cognitive bias in vis. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Visualization Conference (VIS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Pat, C. Cognitive bias mitigation: Becoming better diagnosticians. In Diagnosis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 257–287. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, T.; Çelebi, N.; Esnaf, Ş. Comparative analysis of multi-criteria decision making methodologies and implementation of a warehouse location selection problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 9773–9779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echterhoff, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Alessa, A.; McAuley, J.; He, Z. Cognitive bias in high-stakes decision-making with llms. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, D.; Molokanov, V.; Kazantsev, N.; Jha, A.K. Removing order effects from human-classified datasets: A machine learning method to improve decision making systems. Decis. Support Syst. 2023, 165, 113891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Fujita, H.; Köppen, M. Big data-driven large-scale group decision-making under uncertainty (BiGDM-U). Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 13341–13344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Cao, J.; Shen, K.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S. A Decision Support System with Intelligent Recommendation for Multi-disciplinary Medical Treatment. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. 2020, 16, 3352573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, F.; Bozorgi-Amiri, A.; Hassan, G.M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Datta, A. Designing a clinical decision support system for Alzheimer’s diagnosis on OASIS-3 data set. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 74, 103527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertl, M.; Ross, P.; Draheim, D. A survey on AI and decision support systems in psychiatry–Uncovering a dilemma. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 202, 117464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzwald, B.; Ilić, S.; Kraus, M.; Feuerriegel, S.; Prendinger, H. Deep learning for affective computing: Text-based emotion recognition in decision support. Decis. Support Syst. 2018, 115, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, D.J.; Sharda, R. Model-driven decision support systems: Concepts and research directions. Decis. Support Syst. 2007, 43, 1044–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virkar, S.; Alexopoulos, C.; Stavropoulou, S.; Tsekeridou, S.; Novak, A.-S. User-centric decision support system design in legal informatics: A typology of users. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Theory and Practice of Electronic Governance, Athens, Greece, 23–25 September 2020; pp. 711–722. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R.; Li, S. Spatial decision support systems with automated machine learning: A review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.A. Medical diagnostic decision support systems--Past, present, and future: A threaded bibliography and brief commentary. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 1994, 1, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips-Wren, G.; Daly, M.; Burstein, F. Reconciling business intelligence, analytics and decision support systems: More data, deeper insight. Decis. Support Syst. 2021, 146, 113560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeji, I.N.; Adigun, M.; Oki, O. Computational complexity in explainable decision support system: A review. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezar, B.G.d.S.; Maçada, A.C.G. Data literacy and the cognitive challenges of a data-rich business environment: An analysis of perceived data overload, technostress and their relationship to individual performance. Aslib J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 73, 618–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, V. The Impact of cognitive biases on professionals’ decision-making: A review of four occupational areas. Front. Psychol. 2022, 12, 802439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hristov, I.; Camilli, R.; Mechelli, A. Cognitive biases in implementing a performance management system: Behavioral strategy for supporting managers’ decision-making processes. Manag. Res. Rev. 2022, 45, 1110–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatecola, G.; Caputo, A.; Cristofaro, M. Reviewing cognitive distortions in managerial decision making. J. Manag. Dev. 2018, 37, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureiro-Martínez, D.; Brusoni, S. Cognitive flexibility and adaptive decision-making: Evidence from a laboratory study of expert decision makers. Strat. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 1031–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whysall, Z. Cognitive biases in recruitment, selection, and promotion: The risk of subconscious discrimination. In Hidden Inequalities in the Workplace: A Guide to the Current Challenges, Issues and Business Solutions; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 215–243. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L. Executives’ financial experience and myopic marketing management: A myopic loss-aversion perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 157, 113587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelehan, D.F.; Conlon, K.C.; Ridgway, P.F. Medicine and heuristics: Cognitive biases and medical decision-making. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 189, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, A.E. Cognitive biases, dark patterns, and the ‘privacy paradox’. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2020, 31, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billieux, J.; Potenza, M.N.; Maurage, P.; Brevers, D.; Brand, M.; King, D.L. Cognitive factors associated with gaming disorder. Cogn. Addict. 2020, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Aidman, E.; Jackson, S.A.; Kleitman, S. Effects of sleep deprivation on executive functioning, cognitive abilities, metacognitive confidence, and decision making. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2019, 33, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korteling, J.E.; Brouwer, A.-M.; Toet, A. A neural network framework for cognitive bias. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atallah, F.; Hamm, R.F.; Davidson, C.M.; Combs, C.A.; Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM, & Quality Committee). Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Special Statement: Cognitive bias and medical error in obstetrics—Challenges and opportunities. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 227, B2–B10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, U. What Is the Function of Confirmation Bias? Erkenntnis 2022, 87, 1351–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappes, A.; Harvey, A.H.; Lohrenz, T.; Montague, P.R.; Sharot, T. Confirmation bias in the utilization of others’ opinion strength. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talluri, B.C.; Urai, A.E.; Tsetsos, K.; Usher, M.; Donner, T.H. Confirmation bias through selective overweighting of choice-consistent evidence. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 3128–3135.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modgil, S.; Singh, R.K.; Gupta, S.; Dennehy, D. A confirmation bias view on social media induced polarisation during COVID-19. Inf. Syst. Front. 2024, 26, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arazo, E.; Ortego, D.; Albert, P.; O’Connor, N.E.; McGuinness, K. Pseudo-labeling and confirmation bias in deep semi-supervised learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1908.02983. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmidis, M. Confirmation bias. Decision making in emergency medicine: Biases. Errors Solut. 2021, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, L. Confirmation bias and the persistence of misinformation on climate change. Commun. Res. 2021, 49, 500–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, R. Confirmation bias in the era of mobile news consumption: The social and psychological dimensions. Digit. J. 2020, 8, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch-Westerwick, S.; Mothes, C.; Polavin, N. Confirmation bias, ingroup bias, and negativity bias in selective exposure to political information. Commun. Res. 2020, 47, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bergen, C.; Bressler, M.S. Confirmation bias in entrepreneurship. J. Manag. Policy Pr. 2018, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meppelink, C.S.; Smit, E.G.; Fransen, M.L.; Diviani, N. “I was Right about Vaccination”: Confirmation bias and health literacy in online health information seeking. J. Health Commun. 2019, 24, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palminteri, S. Choice-confirmation bias and gradual perseveration in human reinforcement learning. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 137, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.P.; Ballesteros, J.A.; Santibáñez-López, C.E. What Is an “Arachnid”? Consensus, Consilience, and Confirmation Bias in the Phylogenetics of Chelicerata. Diversity 2021, 13, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, R.D.; Chattoraj, A.; Beck, J.M.; Yates, J.L.; Haefner, R.M. A confirmation bias in perceptual decision-making due to hierarchical approximate inference. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, R.; Ham, S.H.; He, C. Strategic implications of confirmation bias-inducing advertising. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2020, 29, 1573–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, M. An empirical study of social media exchanges about a controversial topic: Confirmation bias and par-ticipant characteristics. J. Soc. Media Soc. 2018, 7, 381–400. [Google Scholar]
- Cafferata, A.; Dávila-Fernández, M.J.; Sordi, S. Seeing what can(not) be seen: Confirmation bias, employment dynamics and climate change. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2021, 189, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidén, M.; Gräns, M.; Juslin, P. The presumption of guilt in suspect interrogations: Apprehension as a trigger of confirmation bias and debiasing techniques. Law Hum. Behav. 2018, 42, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logg, J.M.; Haran, U.; Moore, D.A. Is overconfidence a motivated bias? Experimental evidence. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2018, 147, 1445–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansal, P.; Singh, S. Determinants of overconfidence bias in Indian stock market. Qual. Res. Financial Mark. 2018, 10, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Hussain, R.Y.; Mehboob, I.; Arshad, M. Impact of herding behavior and overconfidence bias on investors’ decision-making in Pakistan. Accounting 2019, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, S.Z.U.; Qureshi, F.; Iqbal, J.; Sultana, S. Overconfidence bias and investment performance: A mediating effect of risk propensity. Borsa Istanb. Rev. 2022, 22, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmatullah, A.; Ha, M. Examining high-school students’ overconfidence bias in biology exam: A focus on the effects of country and gender. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2019, 41, 652–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Prince, N. Overconfidence bias in the Indian stock market in diverse market situations: An empirical study. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2022, 13, 3031–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihombing, Y.R.; Prameswary, R.S.A. The effect of overconfidence bias and representativeness bias on investment decision with risk tolerance as mediating variable. Indik. J. Ilm. Manaj. dan Bisnis 2023, 7, 18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, C.; Keck, S.; Tang, W. Biased interpretation of performance feedback: The role of CEO overconfidence. Strat. Manag. J. 2020, 41, 1139–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieder, F.; Griffiths, T.L.; Huys, Q.J.M.; Goodman, N.D. The anchoring bias reflects rational use of cognitive resources. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2018, 25, 322–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wilde, T.R.; Velden, F.S.T.; De Dreu, C.K. The anchoring-bias in groups. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2018, 76, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, D.P.; Shekelle, P.G.; Song, Z. Evidence for anchoring bias during physician decision-making. JAMA Intern. Med. 2023, 183, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owusu, S.P.; Laryea, E. The impact of anchoring bias on investment decision-making: Evidence from Ghana. Rev. Behav. Finance 2023, 15, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtegaal, R.; Tummers, L.; Noordegraaf, M.; Bekkers, V. Designing to Debias: Measuring and Reducing Public Managers’ Anchoring Bias. Public Adm. Rev. 2020, 80, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussweiler, T.; Strack, F.; Pfeiffer, T. Overcoming the inevitable anchoring effect: Considering the opposite compensates for selective accessibility. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2000, 26, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasseri, T.; Reher, J. Fooled by facts: Quantifying anchoring bias through a large-scale experiment. J. Comput. Soc. Sci. 2022, 5, 1001–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richie, M.; Josephson, S.A. Quantifying Heuristic Bias: Anchoring, Availability, and Representativeness. Teach. Learn. Med. 2018, 30, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, J. Anchoring bias in eliciting attribute weights and values in multi-attribute decision-making. J. Decis. Syst. 2021, 30, 72–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, A.K.P.; Nørgaard, T.M.; Brok, J.C.; van Berkel, N. “If I Had All the Time in the World”: Ophthalmologists’ Perceptions of Anchoring Bias Mitigation in Clinical AI Support. In Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 23–28 April 2023; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nourani, M.; Roy, C.; Block, J.E.; Honeycutt, D.R.; Rahman, T.; Ragan, E.; Gogate, V. Anchoring bias affects mental model formation and user reliance in explainable AI systems. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Greenville, SC, USA, 18–21 March 2024; pp. 340–350. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, E.; Blaha, L.; Paul, C.; Endert, A. A formative study of interactive bias metrics in visual analytics using anchoring bias. In Proceedings of the Human-Computer Interaction-INTERACT 2019: 17th IFIP TC 13 International Conference, Paphos, Cyprus, 2–6 September 2019; Proceedings, Part II 17. Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 555–575. [Google Scholar]
- Bystranowski, P.; Janik, B.; Próchnicki, M.; Skórska, P. Anchoring effect in legal decision-making: A meta-analysis. Law Hum. Behav. 2021, 45, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, J.; Sun, Y. Anchoring Bias in Large Language Models: An Experimental Study. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.06593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Young, M.J. Motivated to confront: How experiencing anger affects anchoring bias. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2019, 32, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhui, R.; Lai, L.; Gershman, S.J. Resource-rational decision making. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2021, 41, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Park, S. Do foreign investors mitigate anchoring bias in stock market? Evidence based on post-earnings announcement drift. Pacific-Basin Finance J. 2018, 48, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J.; Arab, A.; Mehregan, M. Analyzing anchoring bias in attribute weight elicitation of SMART, Swing, and best-worst method. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2024, 31, 918–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweickart, O.; Tam, C.; Brown, N.R. When “bad” is good: How evaluative judgments eliminate the standard anchoring effect. Can. J. Exp. Psychol. Can. De Psychol. Exp. 2021, 75, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.S.; Shaikh, A.A.; Li, E. Designing Recommendation or Suggestion Systems: Looking to the future. Electron. Mark. 2021, 31, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A. Recommendations as personalized marketing: Insights from customer experiences. J. Serv. Mark. 2014, 28, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Lee, S.; Park, Y.; Choi, A. A survey of recommendation systems: Recommendation models, techniques, and application fields. Electronics 2022, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvester, S.; Kurian, S. Recommendation systems: Enhancing personalization and customer experience. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Smart Generation Computing, Communication and Networking (SMART GENCON), Bangalore, India, 29–31 December 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Karahanna, E. University of georgia online recommendation systems in a B2C E-Commerce context: A review and future directions. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2015, 16, 72–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleskach, V.; Bulgakova, O.S.; Zosimov, V.V.; Vashchilina, E.; Tumasoniene, I. An E-Commerce Recommendation Systems Based on Analysis of Consumer Behavior Models. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Symposium «Intelligent Solutions» IntSol-2023, Kyiv-Uzhhorod, Ukraine, 27–28 September 2023; 2023; pp. 210–221. Available online: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3538/Paper_19.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Luo, G.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, F. Artificial intelligence powered mobile networks: From cognition to decision. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, S.K.; Panicker, S.S.; Ruiz-Arenas, S.; Rusák, Z.; Niforatos, E. A Cognitive Assistant for Operators: AI-Powered Knowledge Sharing on Complex Systems. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2022, 22, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Ambadekar, S. AI-Powered Collective Decision-Making Systems and the Future Trends. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Mandi, India, 18–22 June 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Buçinca, Z.; Malaya, M.B.; Gajos, K.Z. To Trust or to Think: Cognitive Forcing Functions Can Reduce Overreliance on AI in AI-assisted Decision-making. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2021, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H. Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Sustainable Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems: An AI-Powered Decision-Making Application Using Large Language Models. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakilipour, S.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Ghodousi, M.; Choi, S.-M. Comparison between multi-criteria decision-making methods and evaluating the quality of life at different spatial levels. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbert, M. Toward a synthesis of cognitive biases: How noisy information processing can bias human decision making. Psychol. Bull. 2012, 138, 211–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, A.; Nakamura, T.; Karwowski, W. Influence of cognitive biases in distorting decision making and leading to critical unfavorable incidents. Safety 2015, 1, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlinger, J.; Readinger, W.; Kim, B. Decision-making and cognitive biases. Encycl. Ment. Health 2016, 12, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal-Barby, J.S.; Krieger, H. Cognitive biases and heuristics in medical decision making. Med. Decis. Mak. 2015, 35, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkler, K.S.; Roy, T. Reducing the impact of cognitive bias in decision making: Practical actions for forensic science practitioners. Forensic Sci. Int. Synerg. 2023, 7, 100341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hort, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.M.; Harman, M.; Sarro, F. Bias mitigation for machine learning classifiers: A comprehensive survey. Acm J. Responsible Comput. 2024, 1, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Kafle, K.; Kanan, C. An investigation of critical issues in bias mitigation techniques. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 2512–2523. [Google Scholar]
- Koçak, B.; Ponsiglione, A.; Stanzione, A.; Bluethgen, C.; Santinha, J.; Ugga, L.; Huisman, M.; Klontzas, M.E.; Cannella, R.; Cuocolo, R. Bias in artificial intelligence for medical imaging: Fundamentals, detection, avoidance, mitigation, challenges, ethics, and prospects. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2025, 31, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejani, A.S.; Ng, Y.S.; Xi, Y.; Rayan, J.C. Understanding and mitigating bias in imaging artificial intelligence. RadioGraphics 2024, 44, e230067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Giffen, B.; Herhausen, D.; Fahse, T. Overcoming the pitfalls and perils of algorithms: A classification of machine learning biases and mitigation methods. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 144, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, S.; Badshah, W.; Hakam, U. Effect of representativeness bias on investment decision making. Manag. Adm. Sci. Rev. 2016, 5, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lester, K.J.; Mathews, A.; Davison, P.S.; Burgess, J.L.; Yiend, J. Modifying cognitive errors promotes cognitive well being: A new approach to bias modification. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 2011, 42, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Kim, K.A.; Nofsinger, J.R.; Rui, O.M. Trading performance, disposition effect, overconfidence, representativeness bias, and experience of emerging market investors. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2007, 20, 425–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubilay, B.; Bayrakdaroglu, A. An empirical research on investor biases in financial decision-making, financial risk tolerance and financial personality. Int. J. Financial Res. 2016, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.-H.; Benbasat, I. The debiasing role of group support systems: An experimental investigation of the representativeness bias. Int. J. Human-Computer Stud. 1997, 47, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhu, A.-X. The representativeness and spatial bias of volunteered geographic information: A review. Ann. GIS 2018, 24, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J. Representativeness Bias. In Cognitive Errors and Diagnostic Mistakes: A Case-Based Guide to Critical Thinking in Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 425–443. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Yoo, Y. A literature review on chief executive officer hubris and related constructs: Is the theory of chief executive officer hubris an antecedents or consequences? J. Appl. Bus. Res. (JABR) 2017, 33, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler-Smith, E. Hubris in business and management research: A 30-year review of studies. Intox. Power Interdiscip. Insights 2016, 39–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler-Smith, E.; Akstinaite, V.; Robinson, G.; Wray, T. Hubristic leadership: A review. Leadership 2017, 13, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, P.M.; Galvagno, M.; Pisano, V. Hubris research in business: Taking stock and moving forward. Manag. Decis. 2024, 62, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, S.; Göritz, A.S.; Gallinat, J.; Schafschetzy, M.; Van Quaquebeke, N.; Peters, M.J.; Andreou, C. Subjective competence breeds overconfidence in errors in psychosis. A hubris account of paranoia. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 2015, 48, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, N.M.; Conroy, J.P. Executive hubris: The case of a bank CEO. Accounting, Audit. Account. J. 2013, 26, 172–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavade, R.K. Multi-Criteria Decision Making: An overview of different selection problems and methods. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2014, 5, 5643–5646. [Google Scholar]
- Balayn, A.; Lofi, C.; Houben, G.-J. Managing bias and unfairness in data for decision support: A survey of machine learning and data engineering approaches to identify and mitigate bias and unfairness within data management and analytics systems. VLDB J. 2021, 30, 739–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.T.; Reddy, M.P.K.; Lakshmanna, K.; Kaluri, R.; Rajput, D.S.; Srivastava, G.; Baker, T. Analysis of Dimensionality Reduction Techniques on Big Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 54776–54788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, E. Multi-Criteria Decision Making Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, R.H.; Fredericks, E.M.; Bowers, K.M. Uncertainty in big data analytics: Survey, opportunities, and challenges. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norori, N.; Hu, Q.; Aellen, F.M.; Faraci, F.D.; Tzovara, A. Addressing bias in big data and AI for health care: A call for open science. Patterns 2021, 2, 100347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero, I.; Peralta, D.; Bacardit, J.; García, S.; Herrera, F. MRPR: A MapReduce solution for prototype reduction in big data classification. Neurocomputing 2015, 150, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.S.; Rodriguez, E. Remedies against bias in analytics systems. J. Bus. Anal. 2019, 2, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Mahadevan, S. Big Data Analytics in Uncertainty Quantification: Application to Structural Diagnosis and Prognosis. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part A Civ. Eng. 2018, 4, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T. Intuition and evidence--uneasy bedfellows? Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2002, 52, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudiano, B.A.; Brown, L.A.; Miller, I.W. Let your intuition be your guide? Individual differences in the evidence-based practice attitudes of psychotherapists. J. Evaluation Clin. Pr. 2011, 17, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, S.A.; Kwon, C.-S.; Barker, F.G. The Art of Management Decision Making: From Intuition to Evidence-based Medicine. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 45, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, I.; Lyons, C.M. Evidence-based care and the case for intuition and tacit knowledge in clinical assessment and decision making in mental health nursing practice: An empirical contribution to the debate. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2001, 8, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilcote, D.R. Intuition: A Concept Analysis. Nurs. Forum 2017, 52, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, F.; Dempsey, E. Intuition in decision making Risk and opportunity. J. Decis. Syst. 2020, 29, 98–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.K. Evidence, Intuition, and Experiment: Partners in the Design Process. HERD Health Environ. Res. Des. J. 2019, 12, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.; McKay, S.; Long, J.C.; Gaff, C.; North, K.; Braithwaite, J.; Francis, J.J.; Best, S. Aligning intuition and theory: A novel approach to identifying the determinants of behaviours necessary to support implementation of evidence into practice. Implement. Sci. 2023, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braude, H.D. Clinical intuition versus statistics: Different modes of tacit knowledge in clinical epidemiology and evidence-based medicine. Theor. Med. Bioeth. 2009, 30, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, S. Role of research evidence in clinical decision–making: Intuition versus clinical experience versus scientific evidence. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2018, 29, 543–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanlommel, K.; Van Gasse, R.; Vanhoof, J.; Van Petegem, P. Teachers’ decision-making: Data based or intuition driven? Int. J. Educ. Res. 2017, 83, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.C.; de Sabbata, K.; Zuiderent-Jerak, T.; Syurina, E.V. Navigating complexity of child abuse through intuition and evidence-based guidelines: A mix-methods study among child and youth healthcare practitioners. BMC Fam. Pr. 2020, 21, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebowitz, J.; Chan, Y.; Jenkin, T.; Spicker, D.; Paliszkiewicz, J.; Babiloni, F. If numbers could “feel”: How well do executives trust their intuition? VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 2019, 49, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, B.; Wei, C.; Dai, D.; Zhu, G.; Tian, M. A Comprehensive Review of Signal Processing and Machine Learning Technologies for UHF PD Detection and Diagnosis (II): Pattern Recognition Approaches. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 29850–29890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.-J.; Lin, C.-H.R.; Lin, Y.-C.; Tung, K.-Y. Intrusion detection system: A comprehensive review. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2013, 36, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, O.I.; Jantan, A.; Omolara, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Umar, A.M.; Linus, O.U.; Arshad, H.; Kazaure, A.A.; Gana, U.; Kiru, M.U. Comprehensive Review of Artificial Neural Network Applications to Pattern Recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 158820–158846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. A comprehensive approach to the recovery of design pattern instances based on sub-patterns and method signatures. J. Syst. Softw. 2015, 103, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidl, S.; Wenig, P.; Papenbrock, T. Anomaly detection in time series: A comprehensive evaluation. Proc. Vldb Endow. 2022, 15, 1779–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Khanna, A.; Gupta, D. Emotion recognition and detection methods: A comprehensive survey. J. Artif. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezerlou, A.V.; Zhou, X.; Li, L.; Shafiq, Z.; Liu, A.X.; Zhang, F. A traffic flow approach to early detection of gathering events. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2017, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, M. Anomaly detection, trend evolution, and feature extraction in partial discharge patterns. Energies 2021, 14, 3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.M.; Sayed, A.; Mia, T.; Ayon, E.H.; Ghosh, B.P.; Ray, R.K.; Raihan, A.; Akter, A.; Rahman, M.; Islam, T.; et al. Advanced cybercrime detection: A comprehensive study on supervised and unsupervised machine learning approaches using real-world datasets. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. Stud. 2024, 6, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Wadhvani, R.; Rasool, A. Comprehensive analysis of change-point dynamics detection in time series data: A review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 248, 123342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghade, S.S.; Karandikar, A.M. A comprehensive study of healthcare fraud detection based on machine learning. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2018, 13, 4175–4178. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y. Shadows in the Interface: A Comprehensive Study on Dark Patterns. Proc. ACM Softw. Eng. 2024, 1, 204–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarrubea, M.; Jonsson, G.; Faulisi, F.; Sorbera, F.; Di Giovanni, G.; Benigno, A.; Crescimanno, G.; Magnusson, M. T-pattern analysis for the study of temporal structure of animal and human behavior: A comprehensive review. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 239, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xie, Y.; Lin, S.; Yao, A.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, W.; Qu, Y.; Qiao, R.; Ren, B.; Ma, L. Comprehensive Regularization in a Bi-directional Predictive Network for Video Anomaly Detection. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwala, T. Filtering Irrelevant Information for Rational Decision Making. Artif. Intell. Tech. Ration. Decis. Mak. 2014, 111–130. [Google Scholar]
- Nasr, S.; Moeeny, A.; Esteky, H. Neural correlate of filtering of irrelevant information from visual working memory. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Wang, H.; Lipton, Z.; Wang, Y. Correcting exposure bias for link recommendation. In Proceedings of the 38 th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR 139, 2021., Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/gupta21c.html (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Chen, L.; Fang, B.; Shang, Z.; Tang, Y. Negative samples reduction in cross-company software defects prediction. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2015, 62, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, A.R.; Shi, J.; Ngai, A.K.; Chan, W.-Y.; Chan, P.P.; Young, A.L.; Yung, H.-W.; Tham, C.C.; Cheung, C.Y. Artificial intelligence deep learning algorithm for discriminating ungradable optical coherence tomography three-dimensional volumetric optic disc scans. Neurophotonics 2019, 6, 041110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, A.; Wright, M. Reduction of task-relevant information in skill acquisition. Eur. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2003, 15, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrentine, F.E.; Dreisbach, C.N.; Ivany, A.R.S.; Hanks, J.B.; Schroen, A.T. Influence of gender on surgical residency applicants’ recommendation letters. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2019, 228, 356–365e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenarduzzi, V.; Dieste, O.; Fucci, D.; Vegas, S. Towards a methodology for participant selection in software engineering experiments: A vision of the future. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement (ESEM), Bari, Italy, 11–15 October 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Thabtah, F.; Kamalov, F.; Hammoud, S.; Shahamiri, S.R. Least Loss: A simplified filter method for feature selection. Inf. Sci. 2020, 534, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranath, V.; Ramasamy, S.; Somula, R.; Sahoo, K.S.; Gandomi, A.H. Swarm Intelligence Based Feature Selection for Intrusion and Detection System in Cloud Infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Congress on EVOLUTIONARY Computation (CEC), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ayalon, O.; Toch, E. Retrospective privacy: Managing longitudinal privacy in online social networks. In Proceedings of the Ninth Symposium on Usable Privacy and Security, Newcastle, UK, 24–26 July 2013; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, N.A.; Farooq, S.U. An improved method for training data selection for cross-project defect prediction. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 1939–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elouataoui, W. AI-Driven frameworks for enhancing data quality in big data ecosystems: Error_detection, correction, and metadata integration. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.03870. [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias, Y.; Perel, M. The oversight of content moderation by AI: Impact assessments and their limitations. Harv. J. Legis. 2021, 58, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Rallabandi, S.; Kakodkar, I.G.S.; Avuku, O. Ethical U se of AI in Social Media. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Workshop on Intelligent Systems (IWIS), Ulsan, Republic of Korea, 9–11 August 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kerdvibulvech, C. Big data and AI-driven evidence analysis: A global perspective on citation trends, accessibility, and future research in legal applications. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, J.D. Does repetition improve consistency? Exp. Econ. 2001, 4, 5–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G. Replication, statistical consistency, and publication bias. J. Math. Psychol. 2013, 57, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, I.; Armour, V. Repetition and the ring of truth: Biasing comments. Can. J. Behav. Sci. / Rev. Can. des Sci. du Comport. 1991, 23, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz-Hardt, S.; Giersiepen, A.; Mojzisch, A. Preference-consistent information repetitions during discussion: Do they affect subsequent judgments and decisions? J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2016, 64, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Huang, M. Mitigating the Learning Bias towards Repetition by Self-Contrastive Training for Open-Ended Generation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.01542. [Google Scholar]
- Bureš, V.; Ponce, D.; Čech, P.; Mls, K. The effect of trial repetition and problem size on the consistency of decision making. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Li, Y.; Sahay, S.; Yu, Z. Refine and imitate: Reducing repetition and inconsistency in persuasion dialogues via reinforcement learning and human demonstration. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.15375. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Gong, Z.; Gao, G.; Shah, A.A. Comparative analysis of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making methods for flood disaster risk in the Yangtze River Delta. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 51, 101768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, J.E.; Carlson, K.A.; Meloy, M.G.; Yong, K. The goal of consistency as a cause of information distortion. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2008, 137, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-H.; Kuo, M.-C. Looks familiar, appears more valid? The moderating role of computer-supported warnings between information repetition and decision outcome. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2015, 34, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunzaker, M.B.F. Cultural sentiments and schema-consistency bias in information transmission. Am. Sociol. Rev. 2016, 81, 1223–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Zhao, J. Unbiased Interest Modeling in Sequential Basket Analysis: Addressing Repetition Bias with Multi-Factor Estimation. ACM Trans. Recomm. Syst. 2025, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W.; Atyabi, A. The problem of cross-validation: Averaging and bias, repetition and significance. In Proceedings of the 2012 Spring Congress on Engineering and Technology, Xi’an, China, 27–30 May 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Oyeniran, O.C.; Adewusi, A.O.; Adeleke, A.G.; Akwawa, L.A.; Azubuko, C.F. Ethical AI: Addressing bias in machine learning models and software applications. Comput. Sci. IT Res. J. 2022, 3, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, N.; Morstatter, F.; Saxena, N.; Lerman, K.; Galstyan, A. A survey on bias and fairness in machine learning. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Haque, M.A.; George, R.; Gupta, K.D.; Gupta, D.; Faruk, J.H. Survey on machine learning biases and mitigation techniques. Digital 2023, 4, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, M.G.; Pantanowitz, L.; Jackson, B.; Palmer, O.; Visweswaran, S.; Pantanowitz, J.; Deebajah, M.; Rashidi, H.H. Ethical and bias considerations in artificial intelligence/machine learning. Mod. Pathol. 2024, 38, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.T. Detecting racial bias in algorithms and machine learning. J. Inf. Commun. Ethic. Soc. 2018, 16, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntibeju, O.O. Mitigating artificial intelligence bias in financial systems: A comparative analysis of debiasing techniques. Asian J. Res. Comput. Sci. 2024, 17, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Chung, L.M.; Zhao, H. Bias detection and correction in RNA-Sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courchamp, F.; Say, L.; Pontier, D. Detection, identification, and correction of a bias in an epidemiological study. J. Wildl. Dis. 2000, 36, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.X. A bias correction method for identification of linear dynamic errors-in-variables models. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2002, 47, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haladyna, T.; Hess, R.K. The detection and correction of bias in student ratings of instruction. Res. High. Educ. 1994, 35, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadker, D.M.; Zittleman, K. Practical strategies for detecting and correcting gender bias in your classroom. Gend. Classr. Found. Ski. Methods Strateg. Across Curric. 2007, 259–275. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmeester, T.R.; Cromsigt, J.P.G.M.; Odden, J.; Andrén, H.; Kindberg, J.; Linnell, J.D.C. Framing pictures: A conceptual framework to identify and correct for biases in detection probability of camera traps enabling multi-species comparison. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 2320–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhaddad, M.; Hamam, S. AI-driven clinical decision support systems: An ongoing pursuit of potential. Cureus 2024, 16, e57728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narne, S.; Adedoja, T.; Mohan, M.; Ayyalasomayajula, T. AI-driven decision support systems in management: Enhancing strategic planning and execution. Int. J. Recent Innov. Trends Comput. Commun. 2024, 12, 268–276. [Google Scholar]
- Niranjan, K.; Kumar, S.S.; Vedanth, S.; Chitrakala, S. An Explainable AI driven Decision Support System for COVID-19 Diagnosis using Fused Classification and Segmentation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 218, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.; Hummel, P.; Beck, S.; Dabrock, P. Primer on an ethics of AI-based decision support systems in the clinic. J. Med. Ethic. 2020, 47, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugatch, R.; Georgieva, A.; Kerasidou, A. AI-driven decision support systems and epistemic reliance: A qualitative study on obstetricians’ and midwives’ perspectives on integrating AI-driven CTG into clinical decision making. BMC Med. Ethic. 2024, 25, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekundayo, F. Leveraging Ai-Driven Decision Intelligence For Complex Systems Engineering. Int. J. Res. Publ. Rev. 2024, 5, 5489–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, S.S. AI-Driven Decision Support Systems in Agile Software Project Management: Enhancing Risk Mitigation and Resource Allocation. Systems 2025, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Neravetla, A.R.; Nomula, V.K.; Gupta, K.; Dhanasekaran, S. Understanding the Impact of AI-driven Clinical Decision Support Systems. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bleher, H.; Braun, M. Diffused responsibility: Attributions of responsibility in the use of AI-driven clinical decision support systems. AI Ethic. 2022, 2, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cid, S.; Vallejo, D.; Herrera, V.; Schez-Sobrino, S.; Castro-Schez, J.J.; Albusac, J.A. Explainable AI-driven decision support system for personalizing rehabilitation routines in stroke recovery. Prog. Artif. Intell. 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comito, C.; Falcone, D.; Forestiero, A. AI-driven clinical decision support: Enhancing disease diagnosis exploiting patients similarity. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 6878–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leschanowsky, A.; Popp, B.; Peters, N. Debiasing strategies for conversational ai: Improving privacy and security decision-making. Digit. Soc. 2023, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvetti, F.; Bertagni, B.; Contardo, I. Cognitive Clarity: Learning Unbiased Decision-Making and Critical Thinking from AI. In Creative Approaches to Technology-Enhanced Learning for the Workplace and Higher Education: Proceedings of 'The Learning Ideas Conference'2024; Springer Nature: London, UK, 2024; Volume 2, p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchagiar, G. The Long Road Toward Tracking the Trackers and De-biasing: A Consensus on Shaking the Black Box and Freeing From Bias. Rev. Eur. Stud. 2019, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, A.P.; Smith, J.L.; Sieck, W.R. Of Collaborative Decision Making. Nat. Decis. Mak. Mac-Rocognition 2008, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C.G.; Bond, C.E.; Shipley, T.F. How can geologic decision-making under uncertainty be improved? Solid Earth 2019, 10, 1469–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.; Aravopoulou, E.; Ekinci, Y.; Evans, G.; Hobbs, M.; Labib, A.; Laughlin, P.; Machtynger, J.; Machtynger, L. Artificial intelligence (AI) in strategic marketing decision-making: A research agenda. Bottom Line 2020, 33, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churaman, B. Gout or Deep Vein Thrombosis: Expanding Differential Diagnosis and Avoiding Anchoring Bias. J. Nurse Pr. 2024, 20, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, Y.R.; Ben-Menahem, S.M.; von Krogh, G. Organizational decision-making structures in the age of artificial intelligence. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2019, 61, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Carpenter, D.; Min, W.; Rowe, J.; Azevedo, R.; Lester, J. Detecting and mitigating encoded bias in deep learning-based stealth assessment models for reflection-enriched game-based learning environments. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2023, 34, 1138–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, C.S. Unmasking bias: A Framework for Testing and Mitigating AI Bias in Insurance Underwriting Models. J. Artif. Intell. Mach. Learn. Data Sci. 2023, 1, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M. Automated machine learning: AI-driven decision making in business analytics. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2023, 18, 200188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F. Evaluating the Performance of AI-Driven Systems in Real-World Applications. Artif. Intell. Multi-Discip. J. Syst. Appl. 2024, 1, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Selvarajan, G. Leveraging AI-Enhanced Analytics for Industry-Specific Optimization: A Strategic Approach to Transforming Data-Driven Decision-Making. Int. J. Enhanc. Res. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 10, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Burstein, F.; Holsapple, C.W.; Power, D.J. Decision support systems: A historical overview. In Handbook on Decision Support Systems 1: Basic Themes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 121–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ebadi, A.; Xi, P.; MacLean, A.; Florea, A.; Tremblay, S.; Kohli, S.; Wong, A. COVIDx-US: An open-access benchmark dataset of ultrasound imaging data for AI-driven COVID-19 analytics. Front. Biosci. 2021, 27, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Sinha, A.; Chaudhary, A. TweezBot: An AI-driven online media bot identification algorithm for twitter social networks. Electronics 2022, 11, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olutimehin, A.T.; Ajayi, A.J.; Metibemu, O.C.; Balogun, A.Y.; Oladoyinbo, T.O.; Olaniyi, O.O. Adversarial threats to AI-driven systems: Exploring the attack surface of machine learning models and countermeasures. J. Eng. Res. Rep. 2025, 27, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaiprasert, C.; Hidayanto, A.N. AI-driven ensemble three machine learning to enhance digital marketing strategies in the food delivery business. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2023, 18, 200235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufano, M.; Agarwal, A.; Jang, J.; Moghaddam, R.Z.; Sundaresan, N. AutoDev: Automated AI-driven development. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.08299. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmik, A.; Sannigrahi, M.; Chowdhury, D.; Dey, A.; Gill, S.S. CloudAISim: A toolkit for modelling and simulation of modern applications in AI-driven cloud computing environments. BenchCouncil Trans. Benchmarks Stand. Eval. 2023, 3, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J. AI-Driven Health Advice: Evaluating the Potential of Large Language Models as Health Assistants. J. Comput. Methods Eng. Appl. 2023, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terziyan, V.; Gryshko, S.; Golovianko, M. Patented intelligence: Cloning human decision models for Industry 4.0. J. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 48, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- East, R. Bias in the evaluation of research methods. Mark. Theory 2016, 16, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crain, R.L.; York, R.L. Evaluating a Successful Program: Experimental Method and Academic Bias. Sch. Rev. 1976, 84, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Mazzuchi, T.A.; Sarkani, S. Comparison of multi-criteria decision-making methods for online controlled experiments in a launch decision-making framework. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2023, 155, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalbasha, S.; Eugster, M.J.A. Bayesian A/B testing for business decisions. In Proceedings of the International Data Science Conference, Hong Kong, China, 23–25 May 2020; Springer Fachmedien: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2020; pp. 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Quin, F.; Weyns, D.; Galster, M.; Silva, C.C. A/B testing: A systematic literature review. J. Syst. Softw. 2024, 211, 112011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.; Alifantis, T.; Edwards, J.S.; Ladbrook, J.; Waller, A. Knowledge-based improvement: Simulation and artificial intelligence for identifying and improving human decision-making in an operations system. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2005, 56, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.-P.; Ke, F. Educational applications of artificial intelligence in simulation-based learning: A systematic mapping review. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivezic, N.; Garrett, J.H. Machine learning for simulation-based support of early collaborative design. Artif. Intell. Eng. Des. Anal. Manuf. 1998, 12, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çubukçu, H.C.; Topcu, D.I.; Yenice, S. Machine learning-based clinical decision support using laboratory data. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2024, 62, 793–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, G.E. Concepts for the third generation of laboratory systems. Clin. Chim. Acta 1998, 278, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rossum, H.H. Technical quality assurance and quality control for medical laboratories: A review and proposal of a new concept to obtain integrated and validated QA/QC plans. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2022, 59, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, V.; Chen, C.; Liao, Q.V.; Smith-Renner, A.; Tan, C. Towards a science of human-ai decision making: A survey of empirical studies. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.11471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereschak, O.; Bailly, G.; Caramiaux, B. How to evaluate trust in AI-assisted decision making? A survey of empirical methodologies. Proc. ACM Human-Computer Interact. 2021, 5, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.J. A Survey Based on Behavior Analysis of Artificial Intelligence Using Machine Learning Process. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Sustainable Expert Systems (ICSES), Lekhnath, Nepal, 15–17 October 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1694–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips-Wren, G. AI tools in decision making support systems: A review. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Tools 2012, 21, 1240005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlaugotne, B.; Zihare, L.; Balode, L.; Kalnbalkite, A.; Khabdullin, A.; Blumberga, D. Multi-criteria decision analysis methods comparison. Sci. J. Riga Tech. Univ. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2020, 24, 454–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachman, A.P.; Ichwania, C.; Mangkuto, R.A.; Pradipta, J.; Koerniawan, M.D.; Sarwono, J. Comparison of multi-criteria decision-making methods for selection of optimum passive design strategy. Energy Build. 2024, 314, 114285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R.; Longbotham, R. Online controlled experiments and A/B tests. In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, R.; Liu, Y.; McQueen, J.; Hains, D.; Song, R. Experimentation platforms meet reinforcement learning: Bayesian sequential decision-making for continuous monitoring. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Long Beach, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2023; pp. 5016–5027. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.A.; Hasan, S. Organizational decision-making and the returns to experimentation. J. Organ. Des. 2022, 11, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, G.J.; Johnson, J.G. Response dynamics: A new window on the decision process. Judgm. Decis. Mak. 2011, 6, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, D.J. Decision processes during sentence comprehension: Effects of lexical item difficulty and position upon decision times. J. Verbal Learn. Verbal Behav. 1969, 8, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.; Lobley, C.M.C.; Prince, S.M. Decision making inxia2. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Struct. Biol. 2013, 69, 1260–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Yang, R.; Lie, S.A.; Lim, T.X.Y.; Ning, Y.; Li, I.; Abdullah, H.R.; Ting, D.S.W.; Liu, N. Mitigating cognitive biases in clinical decision-making through multi-agent conversations using large language models: Simulation study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e59439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagendorff, T.; Fabi, S. Why we need biased AI: How including cognitive biases can enhance AI systems. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 2023, 36, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Demir, E.; Eyers, D. Exploring collaborative decision-making: A quasi-experimental study of human and Generative AI interaction. Technol. Soc. 2024, 78, 102662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cant, R.P.; Cooper, S.J. Simulation-based learning in nurse education: Systematic review. J. Adv. Nurs. 2009, 66, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, S.; Sultana, S.; Mariani, M.; Wamba, S.F.; Spanaki, K.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Advancing algorithmic bias management capabilities in AI-driven marketing analytics research. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2023, 114, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, A.; Krakauer, D.; Zenil, H.; Gottschlich, J.; Mattson, T.; Brehmer, J.; Anandkumar, A.; Choudry, S.; Rocki, K.; Baydin, A.G.; et al. Simulation intelligence: Towards a new generation of scientific methods. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.03235. [Google Scholar]
- AlMakinah, R.; Goodarzi, M.; Tok, B.; Canbaz, M.A. Mapping artificial intelligence bias: A network-based framework for analysis and mitigation. AI Ethic. 2024, 5, 1995–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minotra, D.; Feigh, K. Reviewing linkages between display design and cognitive biases in decision making: An emergency response perspective. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 2024, 25, 776–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küper, A.; Lodde, G.; Livingstone, E.; Schadendorf, D.; Krämer, N. Mitigating cognitive bias with clinical decision support systems: An experimental study. J. Decis. Syst. 2023, 33, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojić, L.; Cinelli, M.; Ćulibrk, D.; Delibašić, B. CERN for AI: A theoretical framework for autonomous simulation-based artificial intelligence testing and alignment. Eur. J. Futur. Res. 2024, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavy, S. Gender bias in artificial intelligence: The need for diversity and gender theory in machine learning. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Gender Equality in Software Engineering, Gothenburg, Sweden, 27 May–3 June 2018; pp. 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, R.; Gomes, J.S.; Carvalho, A. Absorptive capacity in analytics implementations: A research model. RAM 2020, 21, eRAMR200036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Yong, J.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Y. Big data in healthcare has improved the care quality! A reality or myth? In Proceedings of the 2024 Twelfth International Conference on Advanced Cloud and Big Data (CBD), Brisbane, Australia, 28 November–2 December 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Zschech, P.; Benedict, M.I. Paper 8-Towards Maintenance Analytics Ecosystems. Des. Eval. Do-Main-Specif. Platf. Spec. Case Digit. Healthc. 2020, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Intezari, A.; Namvar, M.; Taghinejad, R. Knowledge identity (KI): A determining factor in the effective use of analytics. Knowl. Manag. Res. Pr. 2022, 20, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuddin, S.M.; Hasan, S. Data science vs big data@ UTM big data centre. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Science in Information Technology (ICSITech), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 27–28 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, C.A.; Alejandro, L.L.; Calzado, J.K.R.; Campaña, E.J.G.; Rodriguez, C.J.D. Patient Records Management System With Data Analytics for Singapore Diagnostics. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 21st Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 December 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Krleza, J.L.; Honovic, L.; Tanaskovic, J.V.; Podolar, S.; Rimac, V.; Jokic, A. Post-analytical laboratory work: National recommendations from the Working Group for Post-analytics on behalf of the Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine. Biochem. Medica 2019, 29, 228–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokic, A.; Tanaskovic, J.V.; Honovic, L.; Krleza, J.L.; Podolar, S.; Rimac, V. Interpretative comments need for harmonization? Results of the Croatian survey by the Working Group for Post-analytics. Biochem. Medica 2022, 32, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoor, I.; Dar, F.J. Utilizing Data Analytics And Business Intelligence Tools In Laboratory Workflow. EJIFCC 2024, 35, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, A.H.; Elnenaei, M.O.; Sadek, I.; Thompson, S.; Crocker, B.D.; Nassar, B. Evaluation of the impact of a total automation system in a large core laboratory on turnaround time. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinta, S.V.; Wang, Z.; Palikhe, A.; Zhang, X.; Kashif, A.; Smith, M.A.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. AI-driven healthcare: A review on ensuring fairness and mitigating bias. PLOS Digit. Health 2024, 4, e0000864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Paul, R.K. Ethical AI and bias mitigation solution strategy in AI implementation. J. ID 2023, 2157, 0178. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, A.C.; Pratt, L.A.; Normand, M.P. A survey of functional behavior assessment methods used by behavior analysts in practice. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 2015, 48, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvillon, M.A.; Bullock, L.M.; Gable, R.A. Tracking behavior assessment methodology and support strategies: A national survey of how schools utilize functional behavioral assessments and behavior intervention plans. Emot. Behav. Difficulties 2009, 14, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, R.B.; Karsten, A.M. Assessing preferences of individuals with developmental disabilities: A survey of current practices. Behav. Anal. Pr. 2012, 5, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.R.; Roberts, M.L.; Rutherford Jr, R.B.; Mathur, S.R.; Aaroe, L.A. A statewide survey of special education administrators and school psychologists regarding functional behavioral assessment. Educ. Treat. Child. 1999, 267–279. [Google Scholar]
- Catania, J.A.; Moskowitz, J.T.; Ruiz, M.; Cleland, J. A review of national AIDS-related behavioral surveys. AIDS 1996, 10, S183–S190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.M.; Meers, D.T.; Nelson, C.M. Toward a consensus of functional behavioral assessment for students with mild disabilities in public school contexts: A national survey. Educ. Treat. Child. 2000, 265–285. [Google Scholar]
- Barberis, N.; Thaler, R. A survey of behavioral finance. In Handbook of The Economics of Finance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 1053–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, L.G.; Hakim, A.J.; Dittrich, S.; Burnett, J.; Kim, E.; White, R.G. A systematic review of published respondent-driven sampling surveys collecting behavioral and biologic data. AIDS Behav. 2016, 20, 1754–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locher, F.M.; Philipp, M. Measuring reading behavior in large-scale assessments and surveys. Front. Psychol. 2023, 13, 1044290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, S.A.; Miltenberger, R.G.; Long, E.S. A survey of the use of functional assessment procedures in agencies serving individuals with developmental disabilities. Behav. Interv. 1999, 14, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassakis, K.; Petrakis, E.; Kopanakis, I. Big data analytics: Applications, prospects and challenges. Mob. Big Data A Roadmap Models Technol. 2018, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, E.; Yaqoob, I.; Hashem, I.A.T.; Khan, I.; Ahmed, A.I.A.; Imran, M.; Vasilakos, A.V. The role of big data analytics in Internet of Things. Comput. Networks 2017, 129, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, B.P.; Paudyal, S.; Luo, Y.; Mohanpurkar, M.; Cheung, K.; Tonkoski, R.; Hovsapian, R.; Myers, K.S.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, P.; et al. Big data analytics in smart grids: State-of-the-art, challenges, opportunities, and future directions. IET Smart Grid 2019, 2, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, A.T.; Overbeek, D.L.; Kocher, K.E.; Levy, P.D. Exploring the potential of predictive analytics and big data in emergency care. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2016, 67, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghupathi, W.; Raghupathi, V. Big data analytics in healthcare: Promise and potential. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2014, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.H.; Sahama, T.; Kushniruk, A.W.; Borycki, E.M.; Grunwell, D.K. Health big data analytics: Current perspectives, challenges and potential solutions. Int. J. Big Data Intell. 2014, 1, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J.; Papadopoulos, T.; Luo, Z.; Wamba, S.F.; Roubaud, D. Can big data and predictive analytics improve social and environmental sustainability? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 144, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, P.; Danese, S.; Jay, N.; Natoli, G.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Big data in IBD: A look into the future. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Pappas, I.O.; Krogstie, J.; Giannakos, M. Big data analytics capabilities: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Inf. Syst. e-Business Manag. 2018, 16, 547–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, W.A.; Mehrizi, M.H.R.; Huysman, M.; Feldberg, F. Debating big data: A literature review on realizing value from big data. J. Strat. Inf. Syst. 2017, 26, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorfuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Nazir, A.; Muhammad, G.; Alamri, A. Harnessing the power of big data analytics in the cloud to support learning analytics in mobile learning environment. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 92, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, J.; Zhang, C.; Koronios, A. The implications of big data analytics on business intelligence: A qualitative study in China. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 87, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, G.P.; Mulhall, M.; Simek, C.; Riggs, W.W. Mitigating bias in big data for transportation. J. Big Data Anal. Transp. 2020, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaretto, M.; De Clercq, E.; Elger, B.S. Big Data and discrimination: Perils, promises and solutions. A systematic review. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, T.P.; Loureiro, R.B.; Lisboa, F.V.N.; Peixoto, R.M.; Guimarães, G.A.S.; Cruz, G.O.R.; Araujo, M.M.; Santos, L.L.; Cruz, M.A.S.; Oliveira, E.L.S.; et al. Bias and unfairness in machine learning models: A systematic review on datasets, tools, fairness metrics, and identification and mitigation methods. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoei, T.T.; Singh, A. Data reduction in big data: A survey of methods, challenges and future directions. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2024, 20, 1643–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, H.T.; Do, D.T.; Nguyen, V.T. Comparison of multi-criteria decision making methods using the same data standardization method. Strojnícky časopis-J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 72, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wu, L.; Wang, L. AI fairness in data management and analytics: A review on challenges, methodologies and applications. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, C. Overfitting Avoidance as Bias. Mach. Learn. 1993, 10, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, K.; Roudsari, A.; Wyatt, J.C. Automation bias: Empirical results assessing influencing factors. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2014, 83, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawley, G.C.; Talbot, N.L. On over-fitting in model selection and subsequent selection bias in performance evalu-ation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 2079–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Steyerberg, E.W. Overfitting and optimism in prediction models. In Clinical Prediction Models: A Practical Approach to Development, Validation, and Updating; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 95–112. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, C.L.A.; Damen, J.A.A.; Takada, T.; Nijman, S.W.J.; Dhiman, P.; Ma, J.; Collins, G.S.; Bajpai, R.; Riley, R.D.; Moons, K.G.M.; et al. Risk of bias in studies on prediction models developed using supervised machine learning techniques: Systematic review. BMJ 2021, 375, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, M.; Vaidya, S.D. Challenges in the adoption of E-Commerce technologies in India: The role of organizational factors. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2006, 26, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.A.; Nasir Patel, A.; Shaikh, M.Z.; Chavan, C.R. SLRA: Challenges faced by SMEs in the adoption of E-commerce and sustainability in Industry 4.0. Acta Universitatis Bohemiae Meridionalis. Acta Univ. Bohem. Meridionales 2022, 24, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, N.; Affendi, S.; Zakaria, N. Managing ICT in healthcare organization: Culture, challenges, and issues of technology adoption and implementation. In Health Information Systems: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 1357–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Koloski, D.; Porter, C.; Almand-Hunter, B.; Gatchell, S.; Logan, V. Data literacy in industry: High time to focus on operationalization through middle managers. Harv. Data Sci. Rev. 2025, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahi, M.H. Artificial intelligence and the future of work: Human-AI symbiosis in organizational decision making. Bus. Horizons 2018, 61, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).