Low-Rank Matrix Completion via Nonconvex Rank Approximation for IoT Network Localization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel formulation is proposed to decompose the observed EDM into a low-rank component representing true distances and a sparse component modeling measurement noise and outliers. This formulation enhances robustness under both missing and corrupted data.
- A nonconvex surrogate function is adopted to more accurately approximate the rank constraint, while the -norm is used to enforce sparsity in the noise matrix. This enables more precise recovery of the underlying EDM structure.
- The resulting nonconvex and nonsmooth optimization problem is solved using an ADMM framework, which ensures stable convergence and computational efficiency.
- Reconstructed EDMs are converted into relative node positions via MDS, and absolute positions are obtained using a small number of anchor nodes, facilitating practical deployment.
2. Related Works
3. System Model
3.1. Ranging Model
3.2. Problem Formulation
4. Algorithm Development
4.1. Nonconvex Rank Approximation Based Matrix Completion
4.2. Optimizing LRMCN Using ADMM
| Algorithm 1: LRMCN |
| Input: Sampling matrix , , , , and ; Output: 1 Initialize the matrices , ,, 2 Update according to Equation (19) 3 Calculate according to Equation (23) 4 Update according to Equation (24) 5 Update according to Equation (26) 6 Update according to Equation (16) 7 Calculate according to Equation (17) 8 Repeat steps 2–7 iteratively until . |
4.3. Calculation of Node Coordinates
| Algorithm 2: Node Coordinate Estimation via MDS |
| Input: Sampling matrix , sampling set , and coordinates of anchors Output: Coordinates of normal node 1 Recover the complete from the sampling distance matrix using LRMCN; 2 Compute the barycentricized similarity matrix of : where ; 3 Perform singular value decomposition on : ; 4 Calculate the relative coordinate matrix of the node: where ; 5 Compute the coordinate transformation matrix: ; 6 Convert the relative coordinates of the node to absolute coordinates: |
5. Experimental Design and Analysis
5.1. Simulation Experiment Design
- Average Completion Error (ACE):
- Average Localization Error (ALE):where represents the estimated coordinate matrix, and denotes the true coordinate matrix of the node.
5.2. Simulation Results and Analysis
5.2.1. Noise-Free Scenario
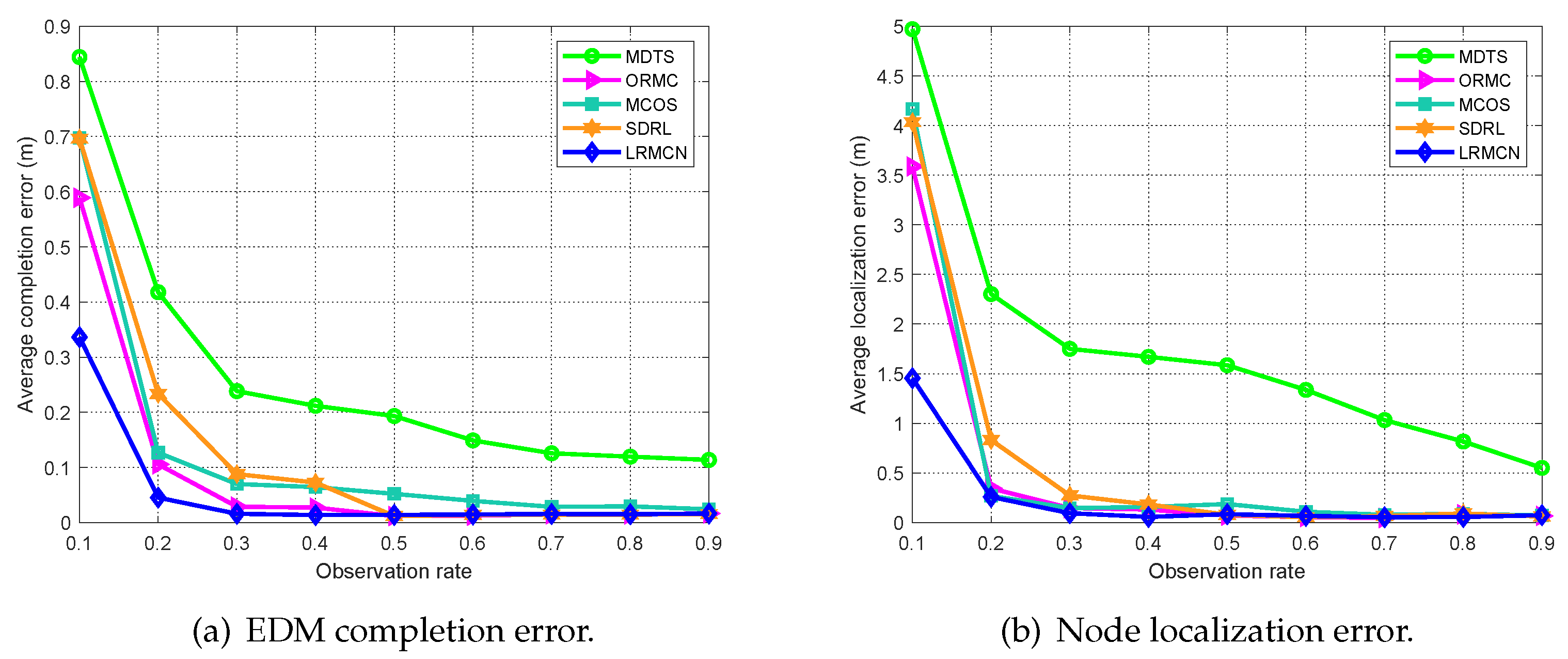
5.2.2. Gaussian Noise Scenario
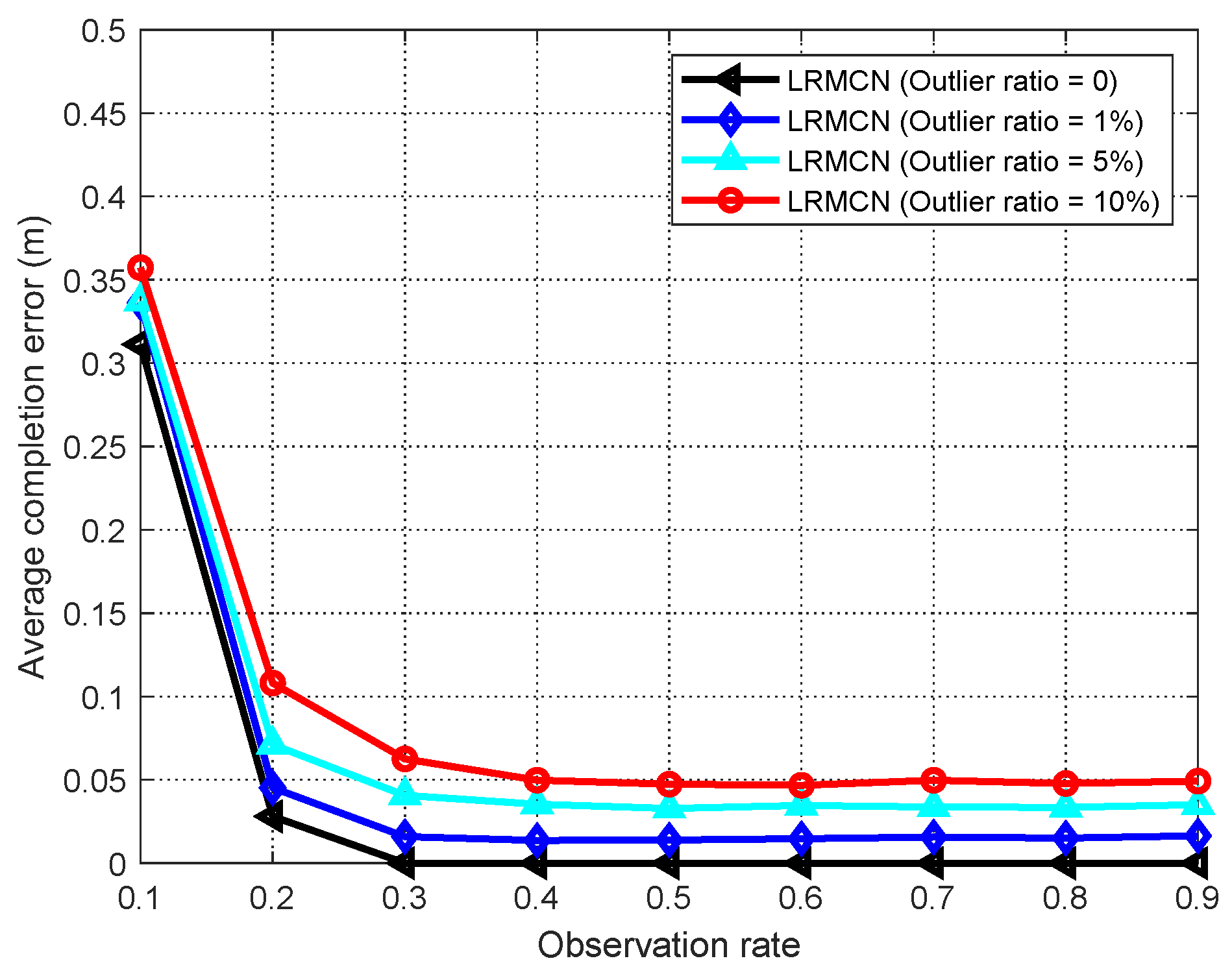
5.2.3. Outlier Noise Scenario
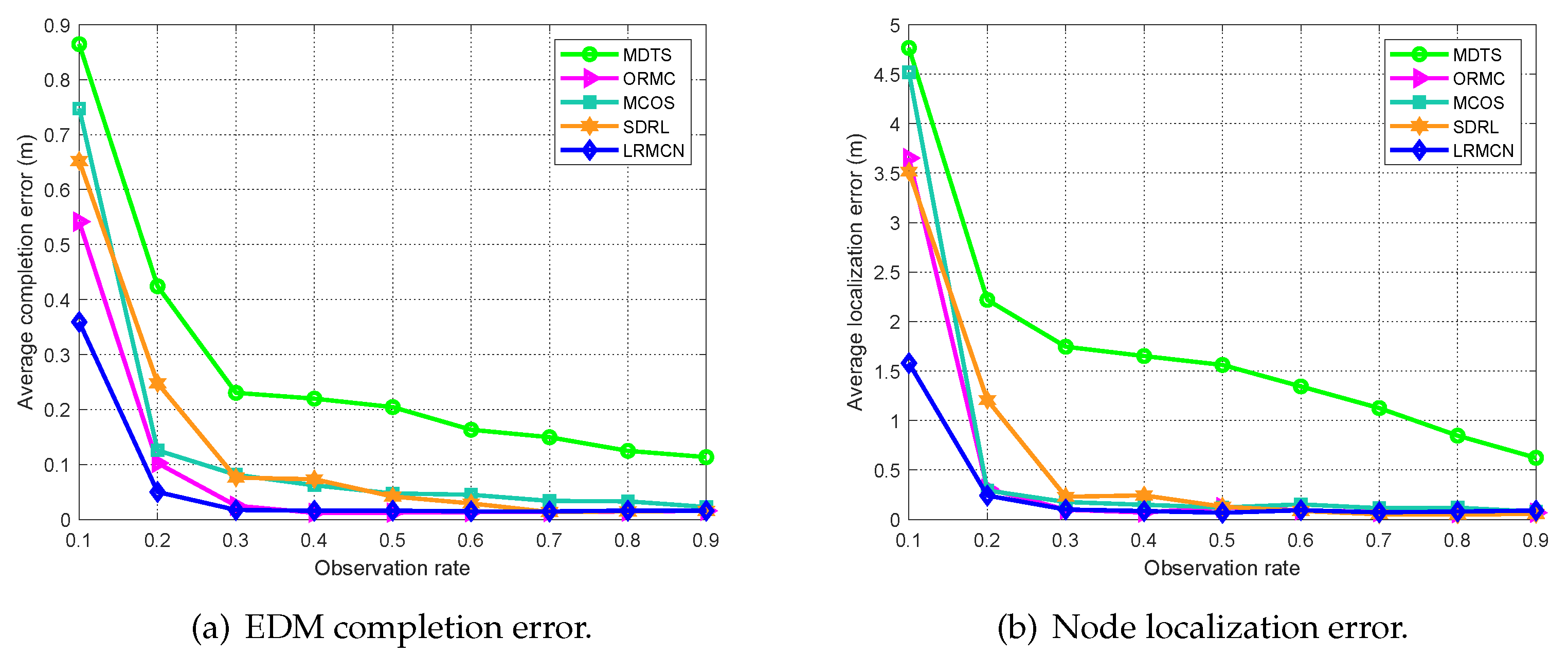
5.2.4. Mixed Noise Scenario
5.3. Performance Evaluation Under Different Network Scales
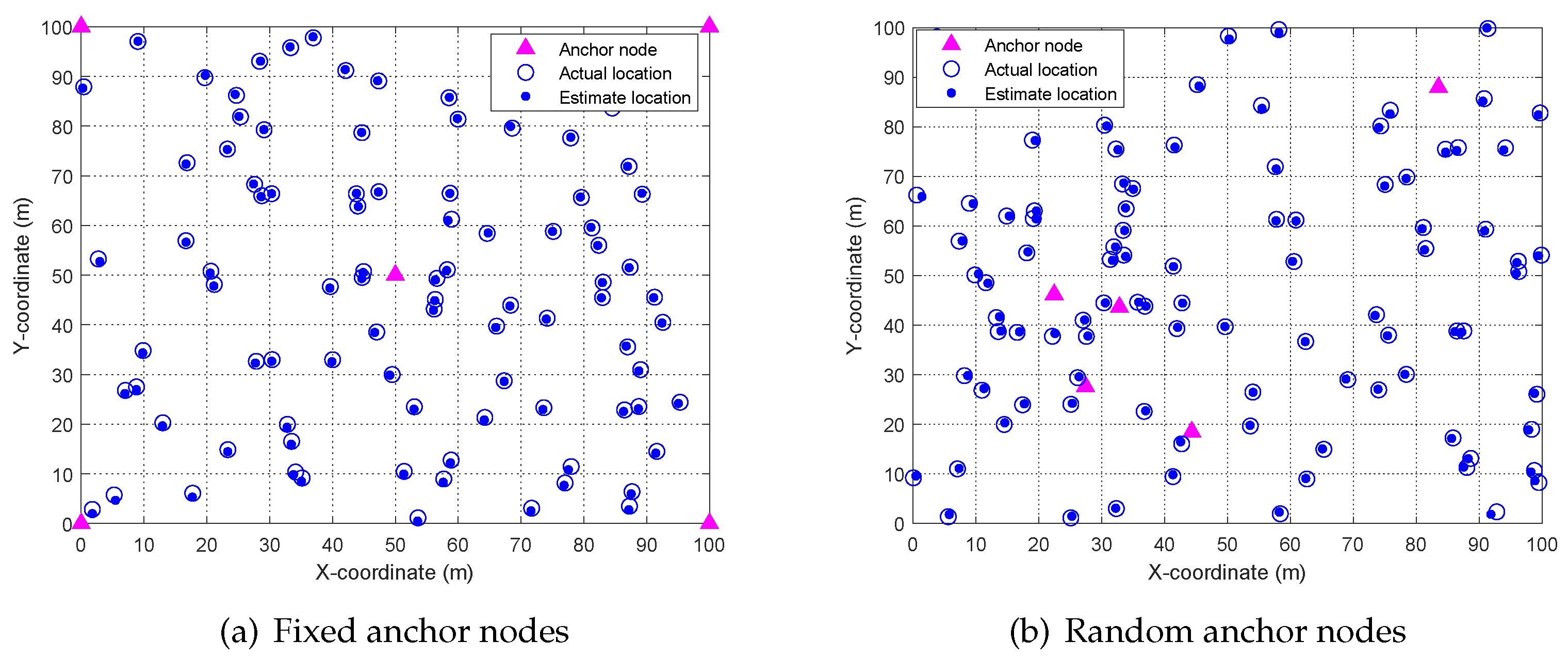
5.4. Visualization of Localization Result
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.; Xu, C.; Sun, J.; Duan, S.; Zhang, X. Cooperative Localization for Multi-Agents Based on Reinforcement Learning Compensated Filter. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2024, 42, 2820–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q.; Liu, X.; Xie, Y.; Han, G. Range-Free Localization Using Extreme Learning Machine and Ring-Shaped Salp Swarm Algorithm in Anisotropic Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 8228–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Nguyen, L.T.; Kim, J.; Shim, B. Deep Learning Based Low-Rank Matrix Completion for IoT Network Localization. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2115–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Mu, J.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, F.; Gu, J. Federated Learning-Based Location Similarity Model for Location Privacy Preserving Recommendation. Electronics 2025, 14, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbelli, F.B.; Pinotti, C.M.; Silvestri, S.; Das, S.K. Measurement Errors in Range-Based Localization Algorithms for UAVs: Analysis and Experimentation. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 21, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Gu, X.; Zhou, H. Cooperative Positioning of Wireless Networks in Complex Propagation Environments. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2024, 42, 2877–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Xiaowei, C.; Sihao, Z.; Shuang, X.; Mingquan, L. BLAS: Broadcast Relative Localization and Clock Synchronization for Dynamic Dense Multi-Agent Systems. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 3822–3839. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Chu, L.; Sun, X. Accurate Localization of Multiple Sources Using Semidefinite Programming Based on Incomplete Range Matrix. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 5319–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Ma, Y.; Liang, X.; Ning, W.; Zhao, H. On Absoluteness and Stationary Condition of WMDS for Range-Based Localization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 10066–10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, S.B.A.; Jia, M.; Marey, M.; Nasralla, M.M.; Guo, Q.; Gu, X. A novel single anchor localization method for wireless sensors in 5G satellite-terrestrial network. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 5595–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchoucha, T.; Chuah, C.N.; Ding, Z. Topology inference of unknown networks based on robust virtual coordinate systems. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2019, 27, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chu, L.; Ansari, N. Joint localization of multiple sources from incomplete noisy Euclidean distance matrix in wireless networks. Comput. Commun. 2018, 122, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, R. Noise-tolerant wireless sensor networks localization via multinorms regularized matrix completion. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 67, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Chen, L.; Sha, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Liu, A.X.; Ahmed, F. Noise tolerant localization for sensor networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2018, 26, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Huang, Z.H.; Guo, L. Low-rank matrix recovery problem minimizing a new ratio of two norms approximating the rank function then using an ADMM-type solver with applications. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2024, 438, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Zhuang, Z.; Xie, W. Gram Matrix Completion for Cooperative Localization in Partially Connected Wireless Sensor Network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Homidan, S.; Wolkowicz, H. Approximate and exact completion problems for Euclidean distance matrices using semidefinite programming. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2005, 406, 109–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.F.; Candès, E.J.; Shen, Z. A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J. Optim. 2010, 20, 1956–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Ganesh, A.; Wright, J.; Wu, L.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y. Fast Convex Optimization Algorithms for Exact Recovery of a Corrupted Low-Rank Matrix; Report no. UILU-ENG-09-2214, DC-246; Coordinated Science Laboratory, University of Illinois: Champaign, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Toh, K.C.; Yun, S. An accelerated proximal gradient algorithm for nuclear norm regularized linear least squares problems. Pac. J. Optim. 2010, 6, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Candès, E.J.; Tao, T. The power of convex relaxation: Near-optimal matrix completion. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2010, 56, 2053–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, T.; Rezghi, M. A novel enriched version of truncated nuclear norm regularization for matrix completion of inexact observed data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Kang, L.; Huang, J. A robust low-rank matrix completion based on truncated nuclear norm and Lp-norm. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 12950–12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Tang, J.; Yan, S.; Lin, Z. Nonconvex nonsmooth low rank minimization via iteratively reweighted nuclear norm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 25, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Man-Cho So, A.; Vidal, R. Nonconvex robust low-rank matrix recovery. SIAM J. Optim. 2020, 30, 660–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z. Logarithmic norm regularized low-rank factorization for matrix and tensor completion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3434–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Ma, S.; Lai, L. Robust Low-Rank Matrix Completion via an Alternating Manifold Proximal Gradient Continuation Method. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 2639–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Shim, B. Localization of IoT Networks via Low-Rank Matrix Completion. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 67, 5833–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Lei, H. Localization from incomplete euclidean distance matrix: Performance analysis for the svd–mds approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 2196–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampouras, P.V.; Rontogiannis, A.A.; Koutroumbas, K.D. Alternating iteratively reweighted least squares minimization for low-rank matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 67, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Li, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, X. Robust matrix completion with column outliers. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 12042–12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Pan, P.; Sun, Z.; He, G. Robust PCA using matrix factorization for background/foreground separation. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 18945–18953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, L.; Zhang, T.; Cao, S.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection via non-convex rank approximation minimization joint l 2, 1 norm. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, Z.; Nie, F.; Wang, R.; Li, X. Matrix completion with column outliers and sparse noise. Inf. Sci. 2021, 573, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Chellali, R. Low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition via the truncated nuclear norm and a sparse regularizer. Vis. Comput. 2019, 35, 1549–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

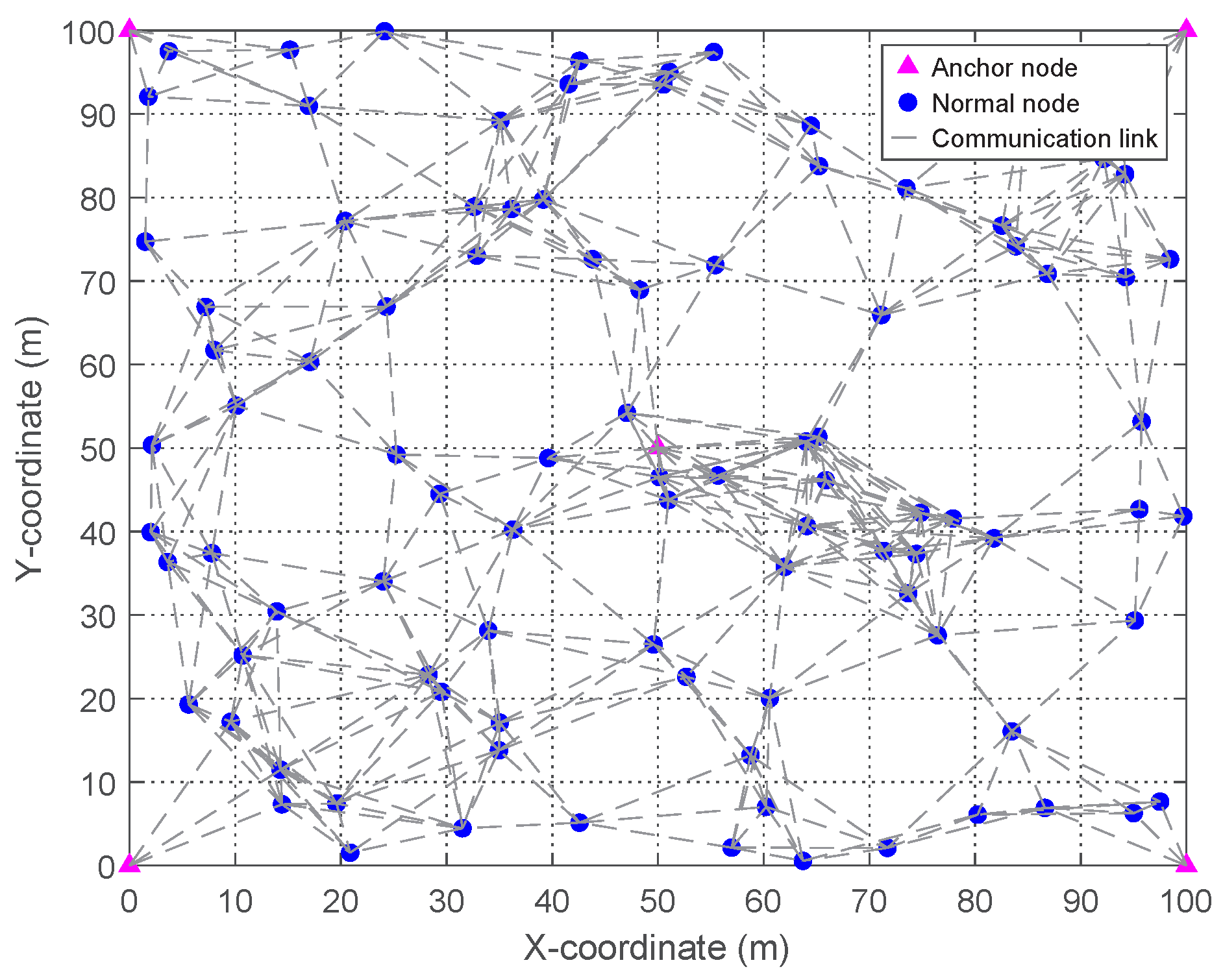
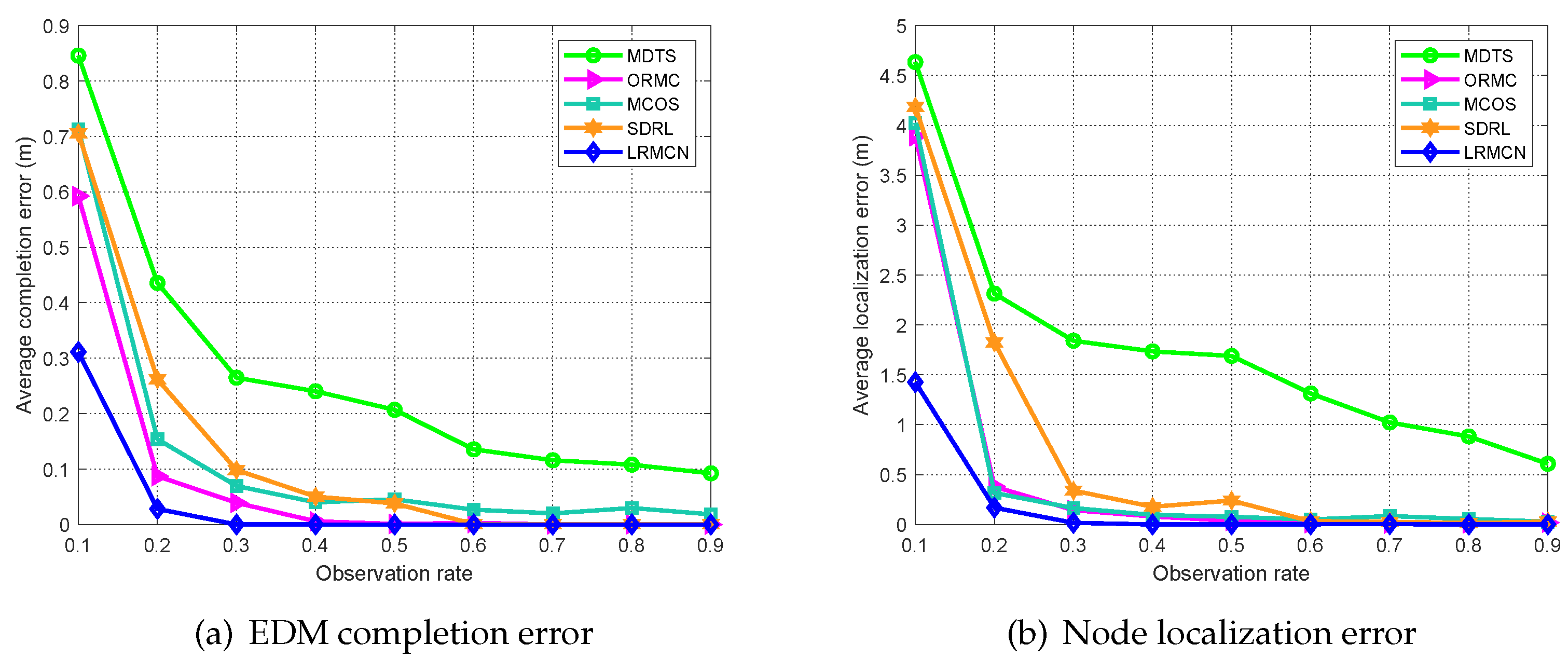
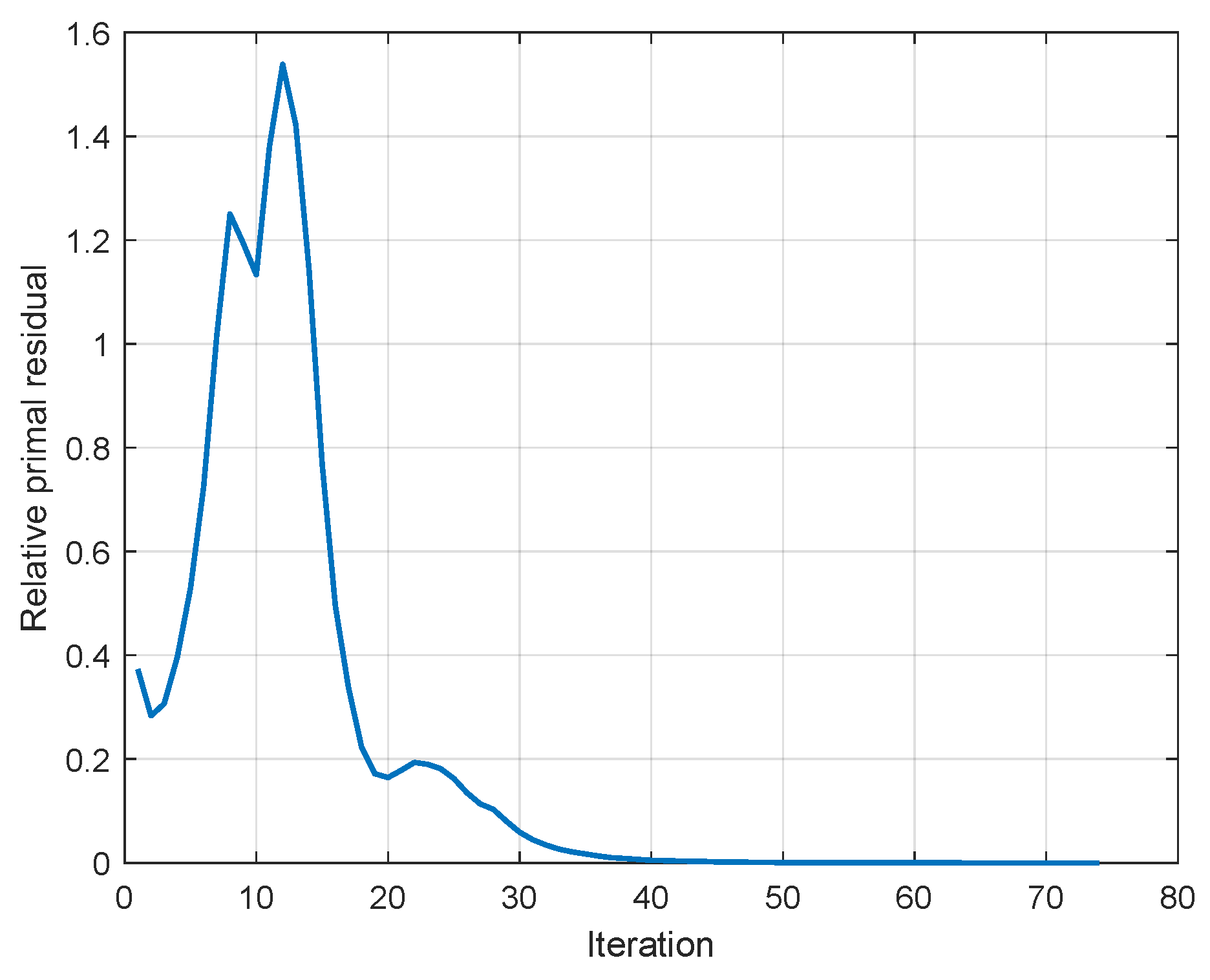
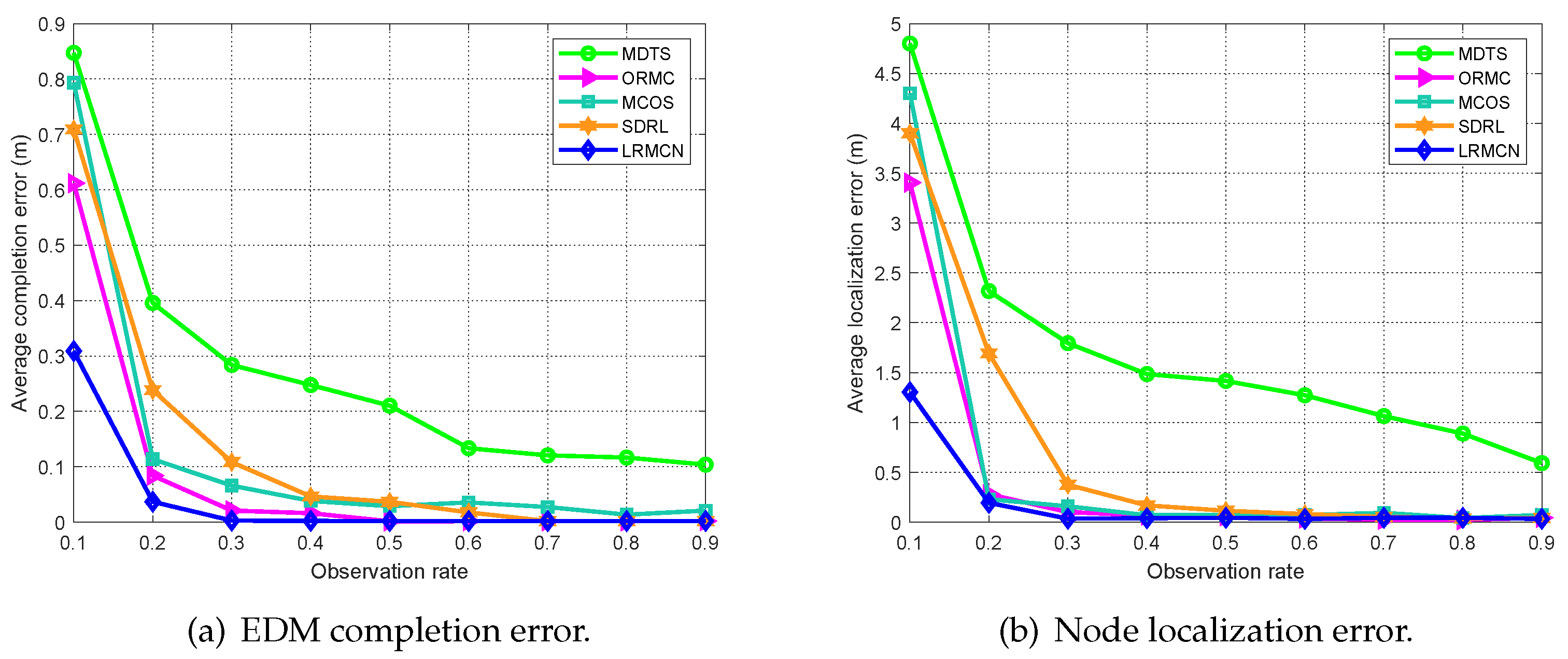
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Area of sensing area | m2 | |
| Number of sensor nodes | N | 100 |
| Number of anchor nodes | M | 5 |
| Gaussian noise | ||
| Outlier noise |
| Algorithm | Mean (m) | 95% CI | p-Value | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDTS | 2.296 | [2.171, 2.420] | <1 | 3.61 |
| ORMC | 0.152 | [0.066, 0.239] | <1 | 0.34 |
| MCOS | 0.037 | [−0.053, 0.127] | <1 | 0.08 |
| SDRL | 0.019 | [−0.051, 0.089] | <1 | 0.05 |
| BEDM Size | Algorithm | Matrix Reconstruction Error | Node Localization Error | Runtime (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDTS | 0.8373 | 2.4998 | 0.4898 | |
| ORMC | 0.1334 | 0.4252 | 0.0367 | |
| MCOS | 0.2288 | 0.6999 | 0.0782 | |
| SDRL | 0.1313 | 1.2799 | 18.6413 | |
| LRMCN | 0.1084 | 0.4047 | 0.0101 | |
| MDTS | 0.8448 | 1.5258 | 1.4797 | |
| ORMC | 0.1031 | 0.2168 | 0.0383 | |
| MCOS | 0.1473 | 0.2181 | 0.2387 | |
| SDRL | 0.1423 | 0.3151 | 247.2405 | |
| LRMCN | 0.1001 | 0.1434 | 0.0335 | |
| MDTS | 0.8489 | 0.9839 | 3.8228 | |
| ORMC | 0.1005 | 0.1221 | 0.0608 | |
| MCOS | 0.1354 | 0.1382 | 0.4187 | |
| SDRL | 0.1305 | 0.1988 | 1.46 × 103 | |
| LRMCN | 0.0959 | 0.0961 | 0.0467 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; He, L.; Meng, D.; Han, C.; Tu, Q. Low-Rank Matrix Completion via Nonconvex Rank Approximation for IoT Network Localization. Electronics 2025, 14, 3920. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193920
Li N, He L, Meng D, Han C, Tu Q. Low-Rank Matrix Completion via Nonconvex Rank Approximation for IoT Network Localization. Electronics. 2025; 14(19):3920. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193920
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Nana, Ling He, Die Meng, Chuang Han, and Qiang Tu. 2025. "Low-Rank Matrix Completion via Nonconvex Rank Approximation for IoT Network Localization" Electronics 14, no. 19: 3920. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193920
APA StyleLi, N., He, L., Meng, D., Han, C., & Tu, Q. (2025). Low-Rank Matrix Completion via Nonconvex Rank Approximation for IoT Network Localization. Electronics, 14(19), 3920. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193920






