Arabic WikiTableQA: Benchmarking Question Answering over Arabic Tables Using Large Language Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We construct Arabic WikiTableQA, the first Arabic benchmark for table-based question answering, sourced from Wikipedia tables and curated with natural questions.
- We propose and evaluate three different approaches for answering questions over Arabic tables: a direct LLM-based method, a decomposition-based sub-table selection model (ArTabSQL), and a knowledge-guided filtering approach using semantic graphs.
- We provide a comprehensive experimental evaluation, demonstrating that the knowledge-guided approach outperforms the other methods and effectively addresses LLM token limitations.
2. Related Work
2.1. Arabic Tabular Data with LLM
2.2. Knowledge Graph Integration in TableQA
2.3. Applications of LLM-Based QA
3. Materials and Methods
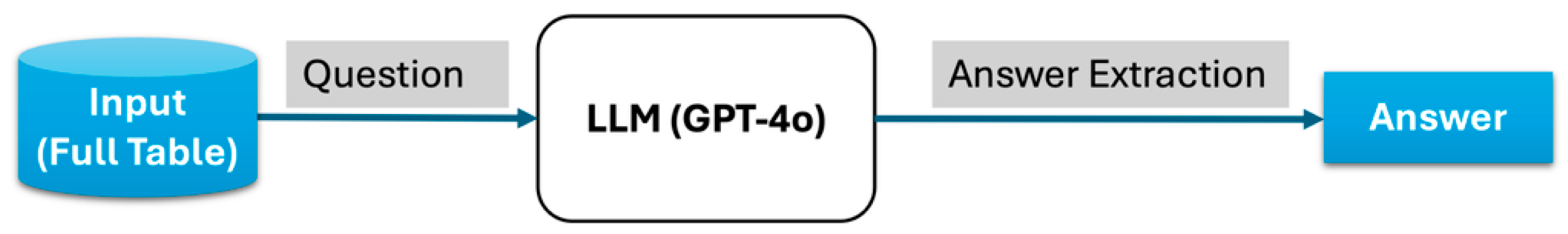
3.1. Direct Approach
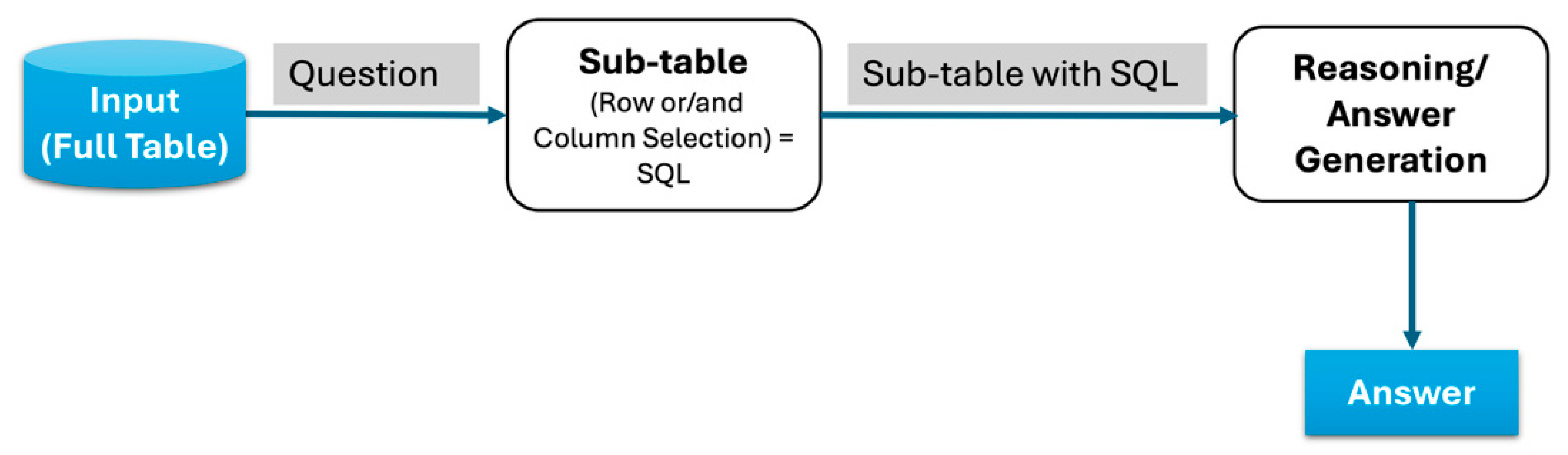
3.2. Sub-Table Selection with SQL Approach
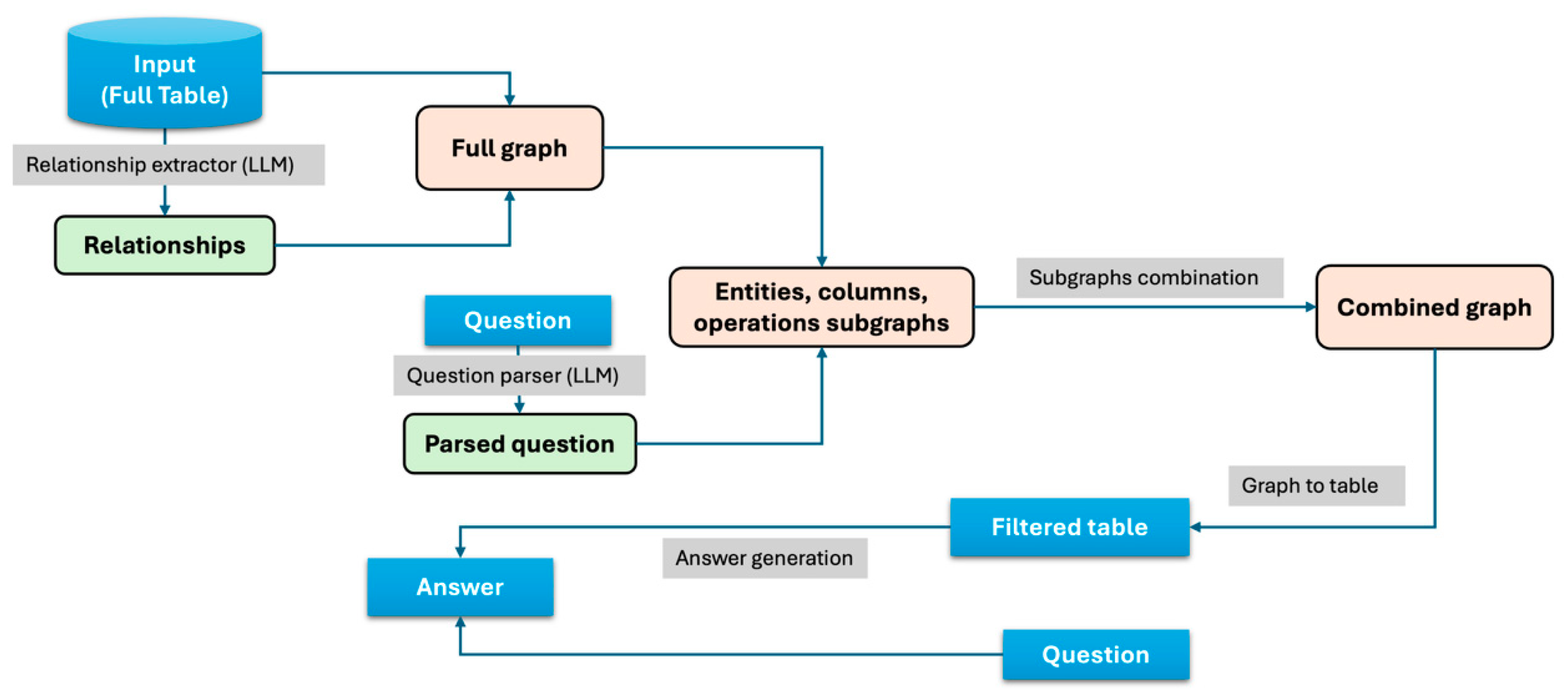
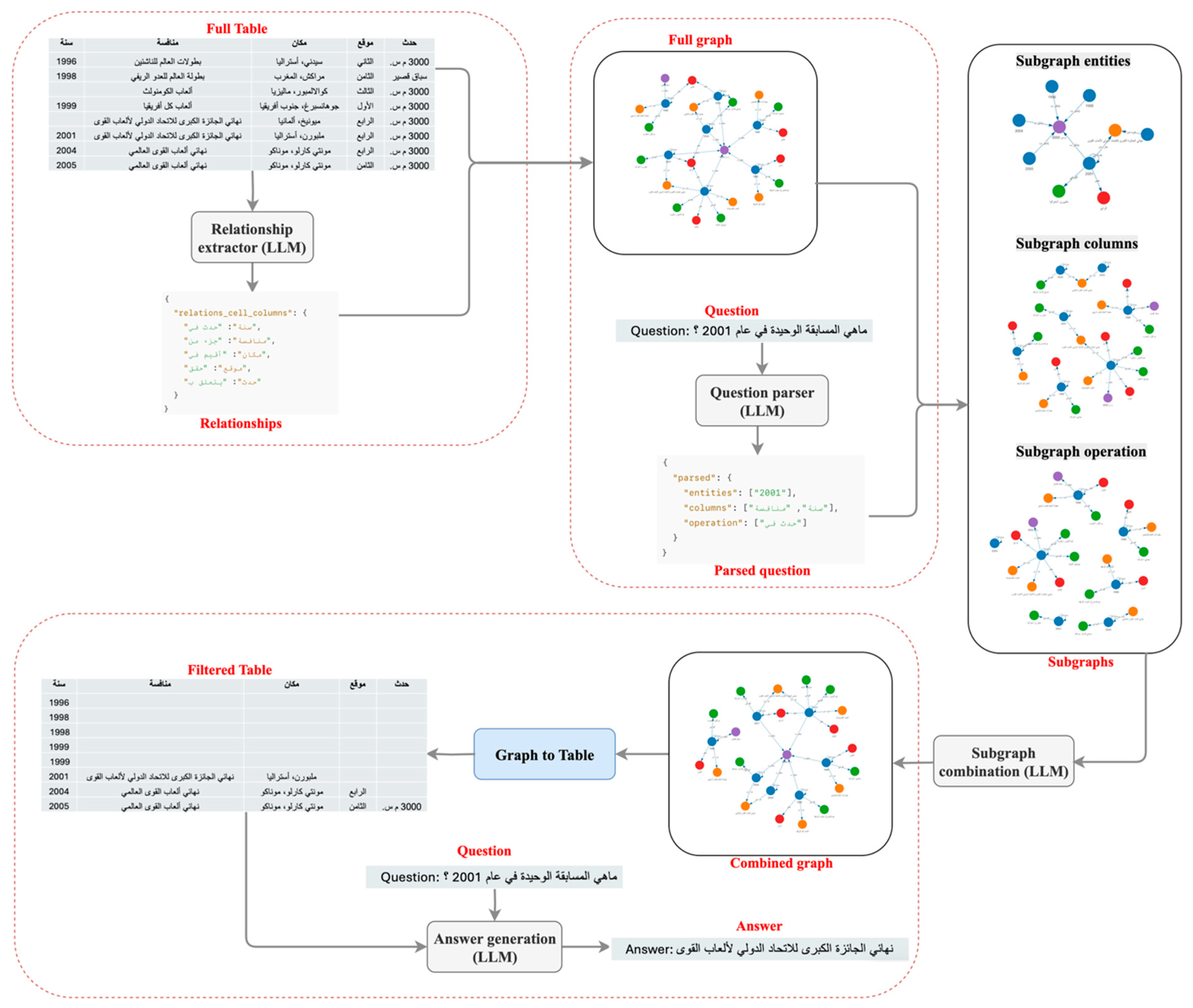
3.3. Knowledge Graph for Table Filtering Approach
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Baselines and Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Implementation
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Comparative Analysis of Language Models with KG
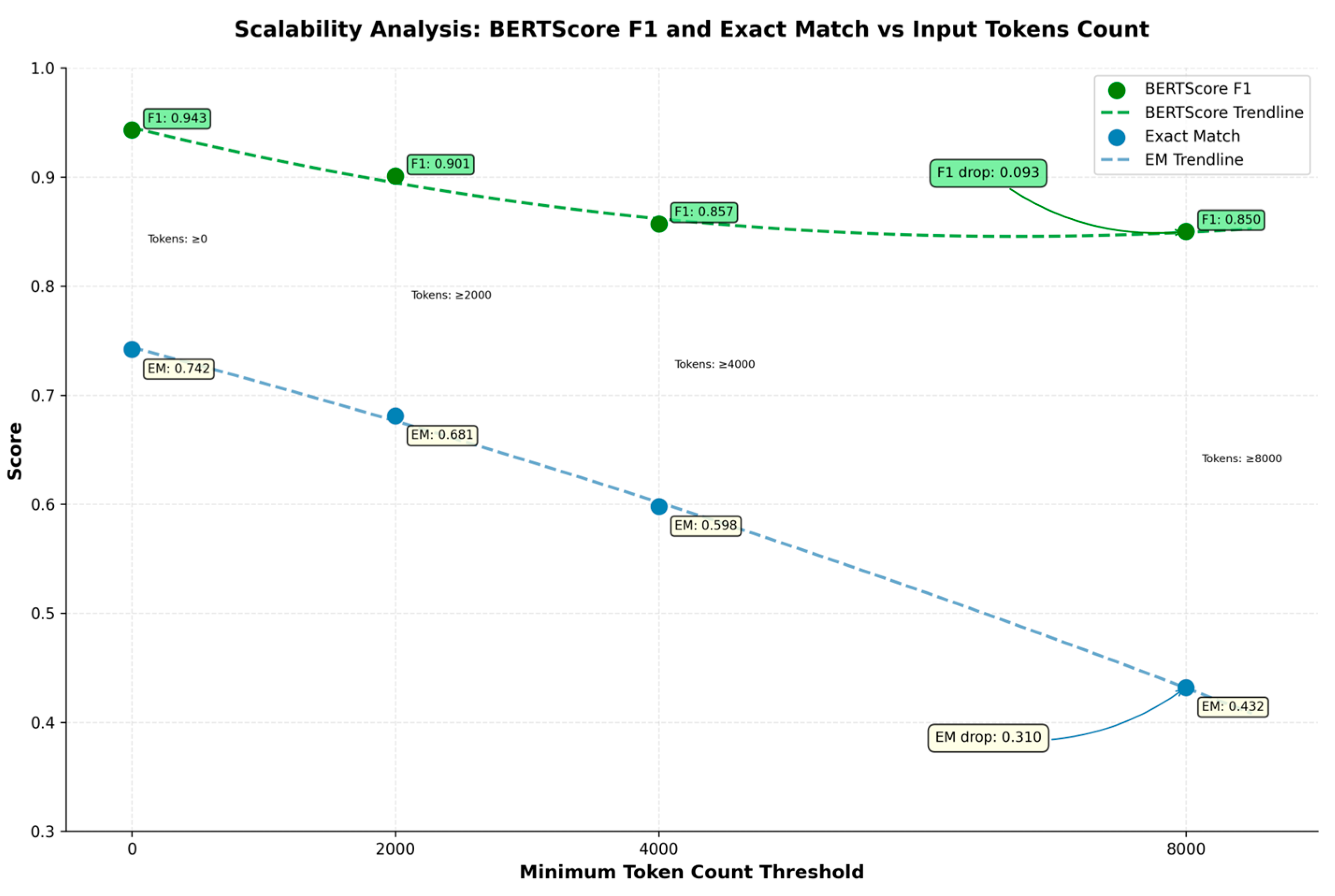
5.2. Scalability Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| SQL | Structured Query Language |
| TableQA | Table-based question answering |
| KGs | Knowledge Graphs |
References
- Lu, W.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Fu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Du, X. Large Language Model for Table Processing: A Survey. Front. Comput. Sci. 2025, 19, 192350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.; Brugere, I.; Sharma, S.; Kariyappa, S.; Nguyen, A.T.; Lecue, F. Interpretable LLM-based Table Question Answering. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.12386. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2412.12386 (accessed on 1 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Nahid, M.M.H.; Rafiei, D. NormTab: Improving Symbolic Reasoning in LLMs Through Tabular Data Normalization. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.17961, 3569–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, J.; Nowak, P.K.; Müller, T.; Piccinno, F.; Eisenschlos, J. TaPas: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-Training. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 4320–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Neubig, G.; Yih, W.T.; Riedel, S. TABERT: Pretraining for joint understanding of textual and tabular data. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 8413–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, M.M.H.; Rafiei, D. TabSQLify: Enhancing Reasoning Capabilities of LLMs Through Table Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, NAACL 2024, Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; Volume 1, pp. 5725–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ren, C.; Yang, J.; Liang, X.; Bai, J.; Chai, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Yin, D.; Sun, X.; et al. MAC-SQL: A Multi-Agent Collaborative Framework for Text-to-SQL. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.11242. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, P.; Siu, A.; Lipka, N.; Sun, T. MATSA: Multi-Agent Table Structure Attribution. In Proceedings of the EMNLP 2024-2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, Miami, FL, USA, 12–16 November 2024; pp. 250–258. [Google Scholar]
- Almohaimeed, S.; Almohaimeed, S.; Al Ghanim, M.; Wang, L. Ar-Spider: Text-to-SQL in Arabic. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Avila, Spain, 8–12 April 2024; pp. 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y.; Qin, C.; Wang, Z.; Kan, H.; Hu, J. Research on a traditional Chinese medicine case-based question-answering system integrating large language models and knowledge graphs. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1512329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasupat, P.; Liang, P. Compositional semantic parsing on semi-structured tables. In Proceedings of the ACL-IJCNLP 2015-53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing of the Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing; Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015, Volume 1, pp. 1470–1480. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ma, C.; Zheng, Y.; He, R.; Li, Y. Knowledge graph–based thought: A knowledge graph–enhanced LLM framework for pan-cancer question answering. Gigascience 2025, 14, giae082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, C.; Yan, Y.; Lu, W.; Huang, E.; Shao, J.; Zhuang, Y. Triad: A Framework Leveraging a Multi-Role LLM-based Agent to Solve Knowledge Base Question Answering. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.14320. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2402.14320 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Hang, C.N.; Yu, P.D.; Tan, C.W. TrumorGPT: Graph-Based Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Model for Fact-Checking. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shami, F.; Marchesin, S.; Silvello, G. Fact Verification in Knowledge Graphs Using LLMs. In Proceedings of the SIGIR 2025-Proceedings of the 48th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Padua, Italy, 13–17 July 2025; pp. 3985–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y. Benchmarking GPT-4 against Human Translators: A Comprehensive Evaluation Across Languages, Domains, and Expertise Levels. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.13775. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2411.13775 (accessed on 1 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y. GPT-4 vs. Human Translators: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Translation Quality Across Languages, Domains, and Expertise Levels. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.03658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khair, M.M.; Sawalha, M. Automated Translation of Islamic Literature Using Large Language Models: Al-Shamela Library Application. In Proceedings of the New Horizons in Computational Linguistics for Religious Texts (Coling-Rel), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 19–24 January 2025; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Banat, M. Investigating the Linguistic Fingerprint of GPT-4o in Arabic-to-English Translation Using Stylometry. J. Transl. Lang. Stud. 2024, 5, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.; Lund, B.D.; Mannuru, N.R.; Arshad, M.A.; Hayawi, K.; Bevara, R.V.K.; Mannuru, A.; Batool, L. Putting GPT-4o to the Sword: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Language, Vision, Speech, and Multimodal Proficiency. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafailov, R.; Sharma, A.; Mitchell, E.; Ermon, S.; Manning, C.D.; Finn, C. Direct Preference Optimization: Your Language Model is Secretly a Reward Model. In Proceedings of the 37th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2023), New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bi, B.; Huang, C.; Pentyala, S.K.; Zhu, Z.J.; Asur, S.; Cheng, N.C. UNA: Unifying Alignments of RLHF/PPO, DPO and KTO by a Generalized Implicit Reward Function. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2408.15339. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2408.15339 (accessed on 1 August 2025).

| Approach | EM Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| Direct | 45 |
| Sub-table selection with SQL | 64 |
| Knowledge graph filtering approach | 74 |
| Metric (%) | GPT-4o | DeepSeek-v3.1 | Llama-3.3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EM | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.64 |
| Normalised EM | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.70 |
| Token-level F1 Score | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.75 |
| Metric (%) | GPT-4o | DeepSeek-v3.1 | Llama-3.3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERTScore F1 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.89 |
| Sentence Embedding Cosine Similarity | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.82 |
| Semantic Accuracy | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsolami, F.; Alrayzah, A. Arabic WikiTableQA: Benchmarking Question Answering over Arabic Tables Using Large Language Models. Electronics 2025, 14, 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193829
Alsolami F, Alrayzah A. Arabic WikiTableQA: Benchmarking Question Answering over Arabic Tables Using Large Language Models. Electronics. 2025; 14(19):3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193829
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsolami, Fawaz, and Asmaa Alrayzah. 2025. "Arabic WikiTableQA: Benchmarking Question Answering over Arabic Tables Using Large Language Models" Electronics 14, no. 19: 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193829
APA StyleAlsolami, F., & Alrayzah, A. (2025). Arabic WikiTableQA: Benchmarking Question Answering over Arabic Tables Using Large Language Models. Electronics, 14(19), 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193829






