ActionMamba: Action Spatial–Temporal Aggregation Network Based on Mamba and GCN for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose ActionMamba, an action spatio-temporal aggregation network featuring a global receptive field and dynamic weighting mechanism. By integrating Mamba with a Graph Convolutional Network, ActionMamba adaptively captures global spatio-temporal properties of human skeletons with linear complexity, thereby improving model performance.
- To boost the model’s comprehension of spatial relationships, we have devised an efficient action feature encoder. This module incorporates extrinsic skeletal characteristics and attention-based mechanisms, facilitating a more accurate representation of the human body’s structural configuration.
- Furthermore, to discern implicit relationships among joints, we put forward a novel Action Perception Model. This new model synergizes the global feature extraction capacity of Mamba with the local feature aggregation proficiency of GCNs.
- Extensive experiments conducted on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.
2. Related Work
2.1. GCN-Based Action Recognition
2.2. Transformers-Based Action Recognition
2.3. State Space Model
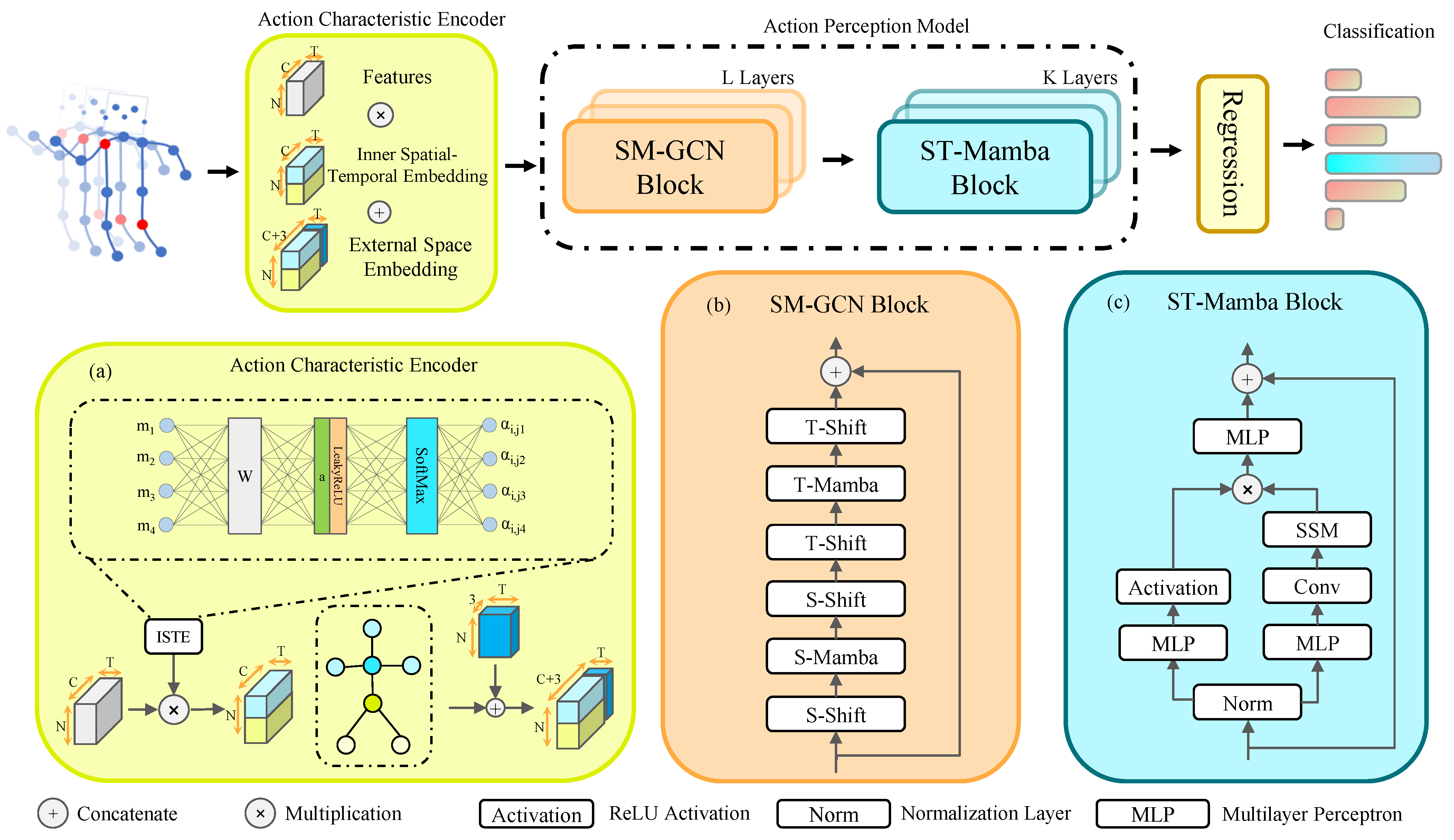
3. Method
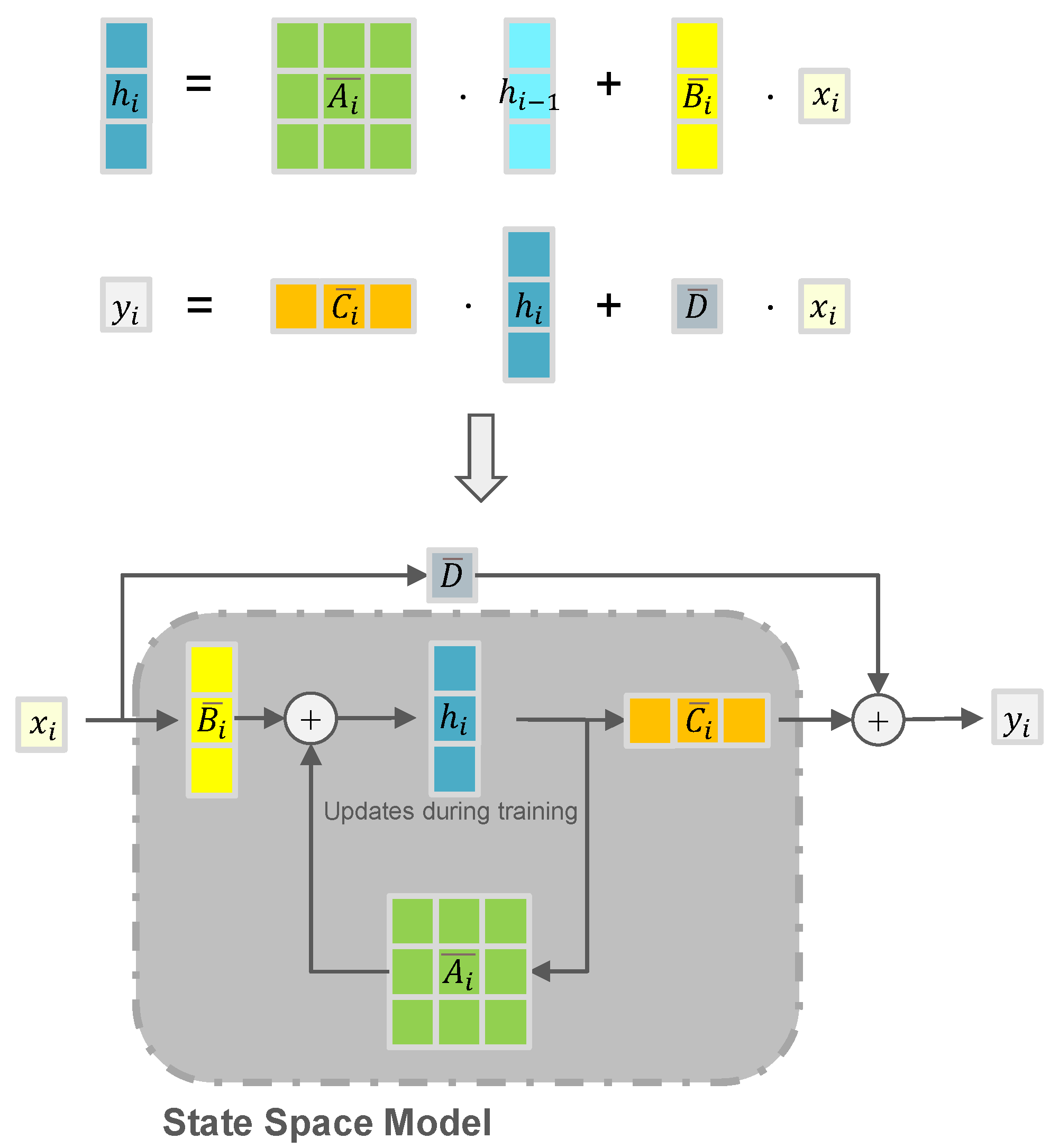
3.1. Preliminaries
3.2. Action Characteristic Encoder
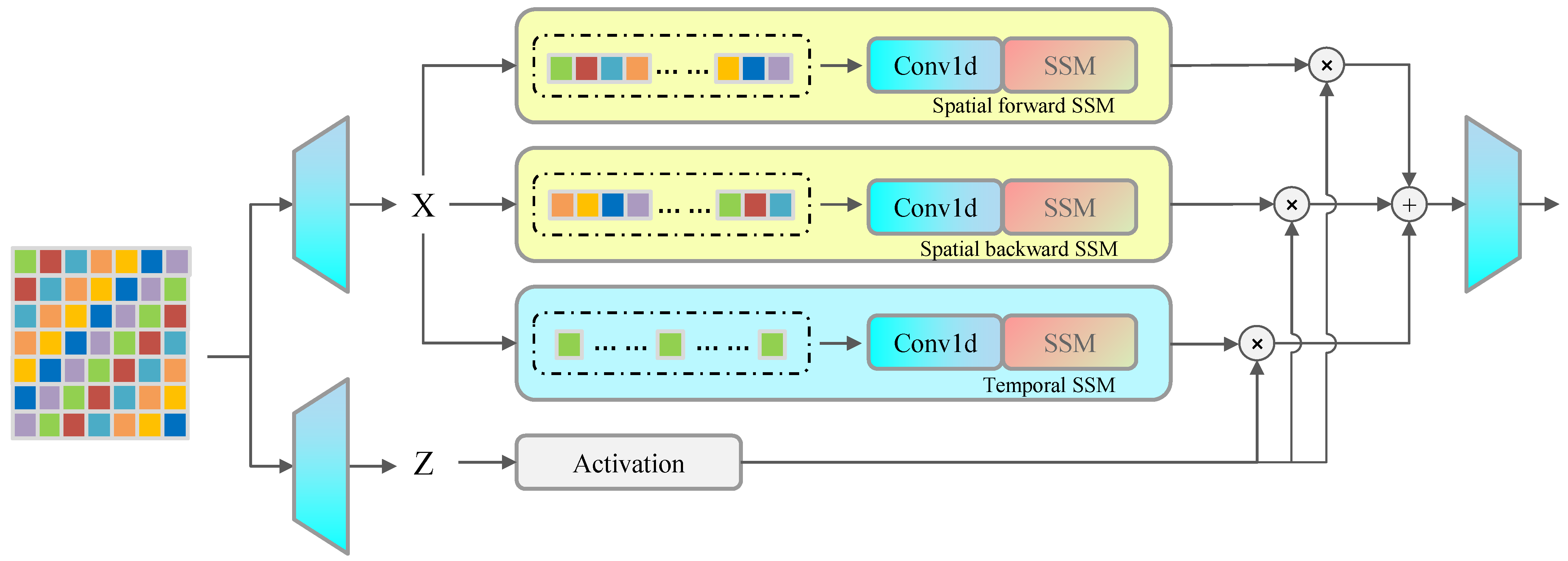
3.3. Action Perception Model
| Algorithm 1 S-Mamba Block. |
| Input: Output: 1: 2: 3: for ; ; do 4: if then 5: 6: 7: else 8: 9: /* represents Equation (4) implemented by selective scan [21] */ 10: end if 11: end for 12: for ; ; do 13: 14: end for 15: 16: |
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Implementation
4.3. Comparison with SOTA Methods
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. Effectiveness of Different Components of ActionMamba
4.4.2. Effectiveness of Action Characteristic Encoder
4.4.3. Complexity Comparison
4.4.4. The Impact of Different Levels of Numbers
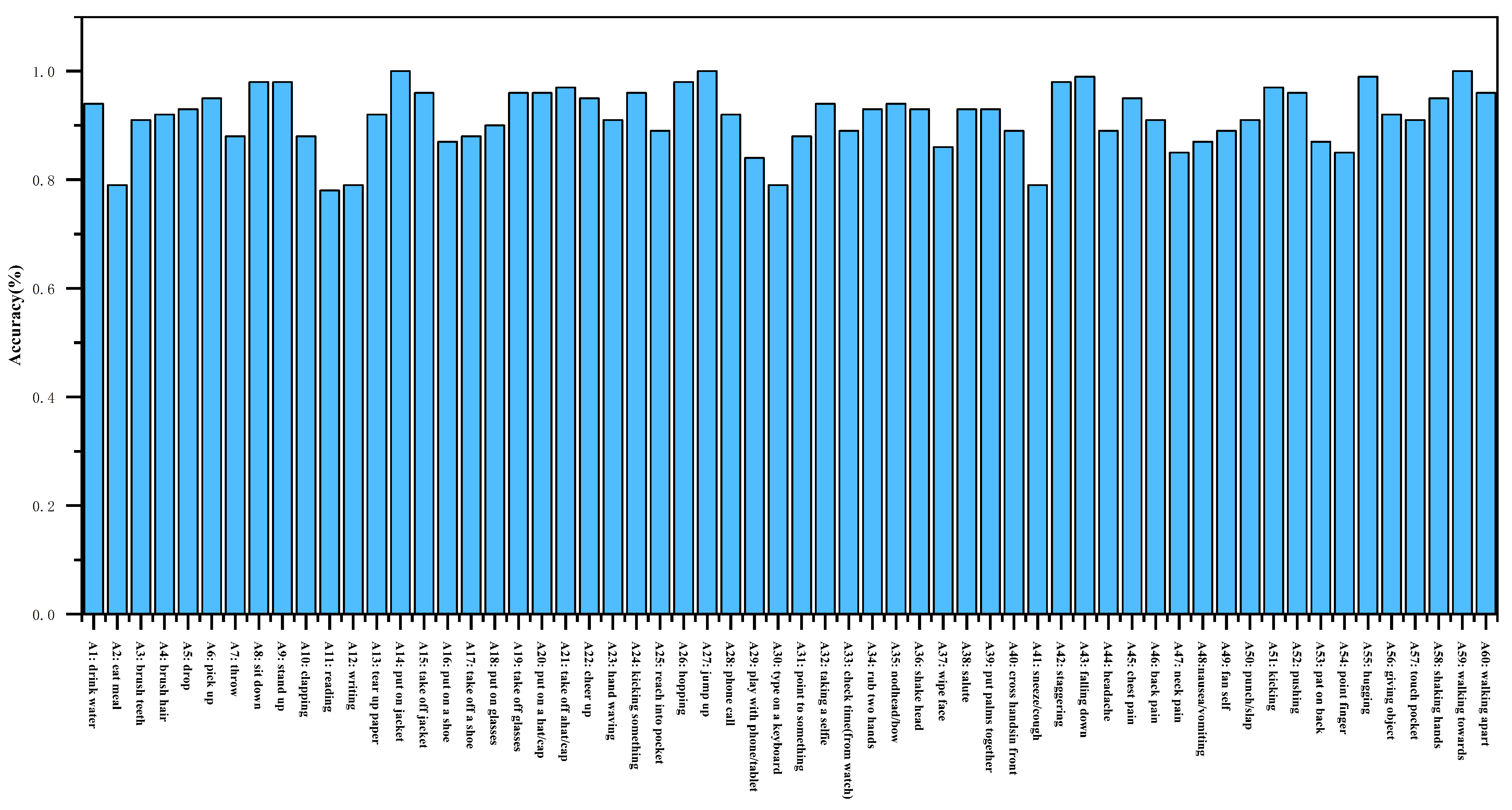
4.4.5. Confusion Matrix
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Z.; Wang, P.; Ogunbona, P.O.; Li, W. Investigation of different skeleton features for cnn-based 3d action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & ExpoWorkshops (ICMEW), Hong Kong, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 617–622. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Wang, L.; Van Gool, L.; Hilliges, O. Thin-slicing network: A deep structured model for pose estimation in videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4220–4229. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 466–481. [Google Scholar]
- Caetano, C.; Brémond, F.; Schwartz, W.R. Skeleton image representation for 3d action recognition based on tree structure and reference joints. In Proceedings of the 2019 32nd SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 28–31 October 2019; pp. 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, C.; Li, B.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W. Channel-wise topology refinement graph convolution for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 13359–13368. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xia, R.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q. Learning shape-motion representations from geometric algebra spatio-temporal model for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 1066–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Xue, J.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Gao, Z.; Zheng, N. EleAtt-RNN: Adding attentiveness to neurons in recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q. Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3595–3603. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Hong, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, G. Learning graph convolutional network for skeleton-based human action recognition by neural searching. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 2669–2676. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Tao, D. Context aware graph convolution for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 14333–14342. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Chen, W.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Skeleton-based action recognition with shift graph convolutional network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, C.; Wang, L. Constructing stronger and faster baselines for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 1474–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Decoupled spatial-temporal attention network for skeleton-based action-gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 30 November–4 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ijaz, M.; Diaz, R.; Chen, C. Multimodal transformer for nursing activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2065–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Koniusz, P. 3mformer: Multi-order multi-mode transformer for skeletal action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5620–5631. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Xu, M.; Shuai, B.; Modolo, D.; Tu, Z.; Tighe, J.; Bergamo, A. SkeleTR: Towards Skeleton-based Action Recognition in the Wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 13634–13644. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhai, W.; Cao, Y. A tri-attention enhanced graph convolutional network for skeleton-based action recognition. IET Comput. Vis. 2021, 15, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, X.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Yan, Y.; Dai, Q.; Hua, X.S. Blockgcn: Redefine topology awareness for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 2049–2058. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Goel, K.; Ré, C. Efficiently modeling long sequences with structured state spaces. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00396. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Shi, H.; Lin, J.; Li, S.; Cheng, J.; Wang, K.; Li, Z.; Yang, K. MambaMOS: LiDAR-based 3D Moving Object Segmentation with Motion-aware State Space Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.12794. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Rsmamba: Remote sensing image classification with state space model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 8002605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Liu, Y. Vmamba: Visual state space model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.10166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Liao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Vision mamba: Efficient visual representation learning with bidirectional state space model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.09417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xing, Z.; Zhu, L. Vivim: A video vision mamba for medical video object segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.14168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. HC-Mamba: Vision MAMBA with Hybrid Convolutional Techniques for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.05007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12026–12035. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, F.; Pu, S.; Zhong, Q.; Li, C.; Xie, D.; Tang, H. Dynamic gcn: Context-enriched topology learning for skeleton-based action recognition. In MM’20: The 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, H.g.; Ha, M.H.; Chi, S.; Lee, S.W.; Huang, Q.; Ramani, K. Infogcn: Representation learning for human skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 20186–20196. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; He, X.; Song, W.; Hao, A.; Qin, H. Graph diffusion convolutional network for skeleton based semantic recognition of two-person actions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 8477–8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, F.; Lee, C.; Qiu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, T.; Muralidhar, S.; Han, T.; Zhu, S.C.; Narayanan, V. Star: Sparse transformer-based action recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.07089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M.; Gao, Z.; Wang, P. Human Pose-based Estimation, Tracking and Action Recognition with Deep Learning: A Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Dehghani, M.; Abnar, S.; Shen, Y.; Bahri, D.; Pham, P.; Rao, J.; Yang, L.; Ruder, S.; Metzler, D. Long range arena: A benchmark for efficient transformers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.04006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, F.; Wang, B. U-mamba: Enhancing long-range dependency for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.04722. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Pan, H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F. Mambadfuse: A mamba-based dual-phase model for multi-modality image fusion. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.08406. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Simba: Mamba augmented U-ShiftGCN for Skeletal Action Recognition in Videos. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.07645. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Z.; Han, Y.; Pu, Y.; Ge, C.; Song, J.; Song, S.; Zheng, B.; Huang, G. Demystify Mamba in Vision: A Linear Attention Perspective. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Extremely lightweight skeleton-based action recognition with shiftgcn++. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7333–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahroudy, A.; Liu, J.; Ng, T.T.; Wang, G. Ntu rgb+ d: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1010–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shahroudy, A.; Perez, M.; Wang, G.; Duan, L.Y.; Kot, A.C. Ntu rgb+ d 120: A large-scale benchmark for 3d human activity understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 2684–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Ni, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Z. Uav-human: A large benchmark for human behavior understanding with unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16266–16275. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, J.; Cai, H.; Meng, Q. Independent Dual Graph Attention Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Neurocomputing 2024, 583, 127496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ouyang, W. Disentangling and unifying graph convolutions for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Xing, J.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. Semantics-guided neural networks for efficient skeleton-based human action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1112–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, C.; Wang, L. Stronger, faster and more explainable: A graph convolutional baseline for skeleton-based action recognition. In MM’20: The 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1625–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Plizzari, C.; Cannici, M.; Matteucci, M. Spatial temporal transformer network for skeleton-based action recognition. In Pattern Recognition. ICPR International Workshops and Challenges: Virtual Event, 10–15 January 2021; Part III; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 694–701. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, N.; Iosifidis, A. Progressive spatio-temporal graph convolutional network for skeleton-based human action recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 3220–3224. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, T.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Q. SparseShift-GCN: High precision skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2022, 153, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Song, J. An improved spatial temporal graph convolutional network for robust skeleton-based action recognition. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 4592–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zou, Y. SpatioTemporal focus for skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 136, 109231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Lv, J.; Fang, S. Representation modeling learning with multi-domain decoupling for unsupervised skeleton-based action recognition. Neurocomputing 2024, 582, 127495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Deng, H. Spatial adaptive graph convolutional network for skeleton-based action recognition. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 17796–17808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedamu, K.; Ji, Y.; Gao, L.; Yang, Y.; Shen, H.T. Relation-mining self-attention network for skeleton-based human action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 139, 109455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Mao, L.; Ye, L.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Ji, C.; Wu, Z. H2GCN: A hybrid hypergraph convolution network for skeleton-based action recognition. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2024, 39, 102072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Hong, X.; Zhao, G. Tripool: Graph triplet pooling for 3D skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 115, 107921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Hou, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xu, M.; Li, W. A central difference graph convolutional operator for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 4893–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Dantcheva, A.; Garattoni, L.; Francesca, G.; Brémond, F. Unik: A unified framework for real-world skeleton-based action recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08580. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Duan, L. Hard-net: Hardness-aware discrimination network for 3d early activity prediction. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Part XI 16; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 420–436. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Qiu, K.; Fu, J.; Fu, D. Dgcn: Dynamic graph convolutional network for efficient multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11924–11931. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Deng, H. TFC-GCN: Lightweight Temporal Feature Cross-Extraction Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Sensors 2023, 23, 5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
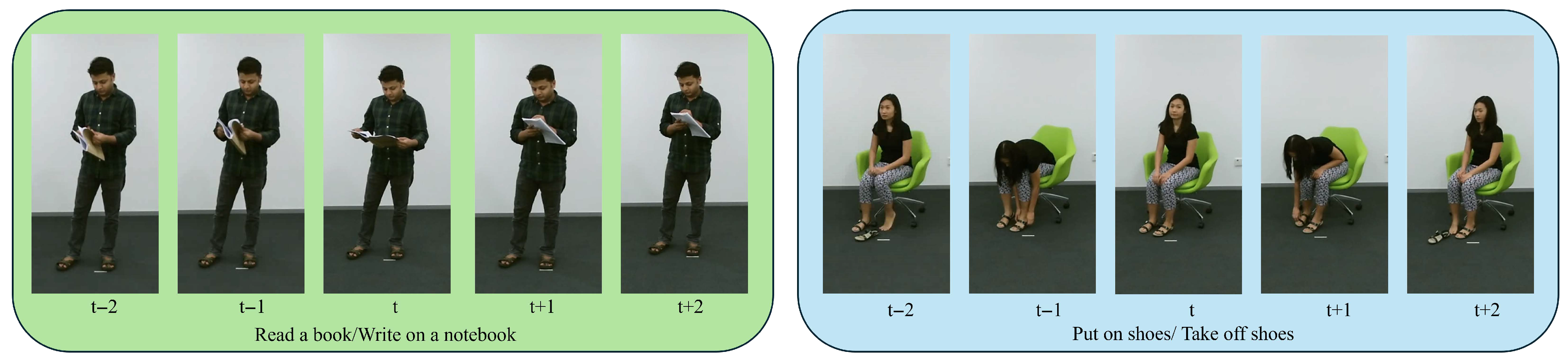




| Model | Year | Conf. | Param(M) | FLOPs(G) | X-Sub | X-View |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST-GCN [8] | 2018 | AAAI | 3.10 | 16.3 | 81.5 | 88.3 |
| AS-GCN [9] | 2019 | CVPR | 6.99 | 35.5 | 86.8 | 94.2 |
| 2s-AGCN [28] | 2019 | CVPR | 6.94 | 37.3 | 88.5 † | 95.1 † |
| 2s NAS-GCN [10] | 2020 | AAAI | 13.1 | − | 89.4 | 95.7 |
| CA-GCN [11] | 2020 | CVPR | − | − | 83.5 | 91.4 |
| Js Shift-GCN [12] | 2020 | CVPR | 1.52 | − | 87.8 | 95.1 |
| 2s Shift-GCN [12] | 2020 | CVPR | 3.04 | − | 89.7 | 96.0 |
| Js MS-G3D [45] | 2020 | CVPR | 3.20 | 48.8 | 89.4 | 95.0 |
| 2s MS-G3D [45] | 2020 | CVPR | 6.44 | 98.0 | 91.5 † | 96.2 † |
| SGN [46] | 2020 | CVPR | 1.8 | 15.4 | 86.6 | 93.4 |
| PA-ResGCN [47] | 2020 | ACMMM | 3.6 | − | 90.9 † | 96.0 † |
| ST-TR [48] | 2021 | ICPR | 12.10 | 259.4 | 90.3 | 96.1 |
| 2s-PST-GCN [49] | 2021 | ICASSP | 1.84 | − | 88.6 | 95.1 |
| SparseShift-GCN [50] | 2021 | PRL | − | − | 90.9 | 96.6 |
| 2s EDGN [8] | 2022 | CVIU | − | − | 88.7 | 95.2 |
| 2s InfoGCN [8] | 2022 | CVPR | − | − | 90.8 | 95.2 |
| 4s InfoGCN [8] | 2022 | CVPR | − | − | 92.3 | 96.9 |
| IST-GCN [51] | 2023 | AI | 1.62 | 17.54 | 90.8 | 96.2 |
| 2s STF-Net [52] | 2023 | PR | 3.4 | − | 90.8 | 96.2 |
| RMMD [53] | 2023 | NC | − | − | 83.0 | 90.5 |
| SARGCN [54] | 2023 | AI | 1.09 | 5.37 | 88.9 † | 94.8 † |
| 3Mformer [16] | 2023 | CVPR | 4.37 | 58.45 | 94.8 | 98.7 |
| RSA-Net [55] | 2023 | PR | 3.5 | − | 90.9 † | 95.3 † |
| GCN [56] | 2024 | JKSU | − | − | 88.9 | 94.8 |
| Js Simba [38] | 2024 | − | − | − | 91.3 † | 96.1 † |
| Bs Simba [38] | 2024 | − | − | − | 88.48 | 93.41 |
| Js ActionMamba | Ours | 1.9 | 5.94 | 89.16 | 94.92 | |
| Bs ActionMamba | Ours | 1.9 | 5.94 | 88.79 | 94.18 | |
| 2s ActionMamba | Ours | 3.8 | 12.73 | 91.83 | 96.67 |
| Model | X-Sub | X-Setup |
|---|---|---|
| ST-GCN [8] | 70.7 † | 73.2 † |
| Js Tripool [57] | 80.1 | 82.8 |
| AS-GCN [9] | 77.9 † | 78.5 † |
| 2s AGCN [28] | 82.5 † | 84.2 † |
| 4s CDGC [58] | 86.3 | 87.8 |
| Shift-GCN [12] | 85.9 | 87.6 |
| 2s MS-G3D [45] | 86.2 | 88.0 |
| SGN [46] | 79.2 | 81.5 |
| 2s UNIK [59] | 80.8 | 86.5 |
| 2s ST-TR [48] | 85.1 | 87.1 |
| 2s STF-Net [52] | 84.9 † | 87.7 † |
| JS Simba [38] | 79.75 | 86.28 |
| 2s ActionMamba | 86.48 | 88.15 |
| Model | UAV–Human | |
|---|---|---|
| CSv1 (%) | CSv2 (%) | |
| ST-GCN [8] | 30.3 † | 56.1 † |
| 2s-AGCN [28] | 34.8 | 66.7 |
| HARD-Net [60] | 37.0 | − |
| Shift-GCN [12] | 38.0 † | 67.0 † |
| DGCN [61] | 29.9 | − |
| TFC-GCN [62] | 39.6 | 64.7 |
| IDGAN [44] | 43.4 † | 68.3 † |
| ActionMamba | 44.3 | 69.5 |
| Model | X-Sub |
|---|---|
| Shift-GCN | 89.70 |
| Shift-GCN+ACE | 89.88 () |
| Shift-GCN+ACE+ST-Mamba | 90.39 () |
| Shift-GCN+ACE+SM-GCN | 91.43 () |
| ActionMamba | 91.83 () |
| Model | X-Sub |
|---|---|
| Shift-GCN | 89.70 |
| Shift-GCN+ISTE | 89.81 ) |
| Shift-GCN+ESE | 89.77 () |
| Shift-GCN+ACE | 89.91 () |
| Shift-GCN+ACE * | 90.21 () |
| ActionMamba w/o ACE | 91.36 () |
| ActionMamba | 91.83 () |
| ActionMamba+ACE * | 91.84 () |
| Model | FLOPs (G) | X-Sub | Inference (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST-TR | 259.4 | 90.3 | 29.446 |
| 2s InfoGCN | - | 90.8 | 33.736 |
| 4s InfoGCN | - | 92.3 | 49.881 |
| IST-GCN | 17.54 | 90.8 | 23.825 |
| 3MFormer | 58.45 | 94.8 | 76.482 |
| JS Simba | - | 91.3 | 22.846 |
| JS ActionMamba | 5.94 | 89.70 | 16.224 |
| 2s ActionMamba | 12.73 | 91.83 | 18.753 |
| Method | SM-GCN | ST-Mamba | FLOPs (G) | X-Sub |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ActionMamba | 5 | 1 | 8.92 | 87.41 |
| ActionMamba | 6 | 1 | 10.18 | 89.93 |
| ActionMamba | 7 | 1 | 11.34 | 90.87 |
| ActionMamba | 8 | 1 | 12.41 | 91.61 |
| ActionMamba | 9 | 1 | 13.28 | 91.38 |
| ActionMamba | 8 | 2 | 12.73 | 91.83 |
| ActionMamba | 8 | 3 | 13.17 | 91.74 |
| ActionMamba | 8 | 4 | 13.54 | 90.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, J.; Liu, D.; Zheng, B. ActionMamba: Action Spatial–Temporal Aggregation Network Based on Mamba and GCN for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Electronics 2025, 14, 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183610
Wen J, Liu D, Zheng B. ActionMamba: Action Spatial–Temporal Aggregation Network Based on Mamba and GCN for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Electronics. 2025; 14(18):3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183610
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Jinglong, Dan Liu, and Bin Zheng. 2025. "ActionMamba: Action Spatial–Temporal Aggregation Network Based on Mamba and GCN for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition" Electronics 14, no. 18: 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183610
APA StyleWen, J., Liu, D., & Zheng, B. (2025). ActionMamba: Action Spatial–Temporal Aggregation Network Based on Mamba and GCN for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Electronics, 14(18), 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183610






