Abstract
Deep neural networks (DNNs) excel in image classification but are vulnerable to backdoor attacks due to reliance on external training data, where specific markers trigger preset misclassifications. Existing attack techniques have an obvious trade-off between the effectiveness of the triggers and the stealthiness, which limits their practical application. For this purpose, in this paper, we develop a method—chromatic channel-based implicit backdoor attack (CCIBA), which combines a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and singular value decomposition (SVD) to embed triggers in the frequency domain through the chromaticity properties of the YUV color space. Experimental validation on different image datasets shows that compared to existing methods, CCIBA can achieve a higher attack success rate without a large impact on the normal classification ability of the model, and its good stealthiness is verified by manual detection as well as different experimental metrics. It successfully circumvents existing defense methods in terms of sustainability. Overall, CCIBA strikes a balance between covertness, effectiveness, robustness and sustainability.
1. Introduction
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have achieved remarkable success in recent years in the fields of image classification [1], speech recognition [2], and autonomous driving [3,4], and their applications have widely penetrated into many interdisciplinary disciplines, such as smart healthcare, natural language processing, social computing, etc. [5,6,7,8]. However, the training process of DNNs often requires massive amounts of data and computational resources, which has prompted researchers and users to tend to utilize distributed computing paradigms such as third-party data, model-as-a-service, and federated learning [9,10,11,12] in order to reduce costs. Although this approach alleviates the pressure on resources to a certain extent, it also poses non-negligible security risks and requires the construction of trustworthy management and collaboration mechanisms at the system level [13,14,15,16,17]. For example, the system needs to be continuously monitored and anomaly detected [18,19], and privacy-preserving techniques are adopted to cope with the risk of data leakage [20,21,22], of which backdoor attacks are a particularly serious threat. Backdoor attacks cause the attacked model to behave normally under normal inputs but misclassify under inputs containing specific triggers by injecting well-designed triggers into the training data. This type of attack poses a serious threat to critical tasks such as image classification and can lead to disastrous consequences.
An ideal backdoor attack should have two core attributes: effectiveness and stealthiness. Effectiveness requires that when the trigger is injected, the infected model predicts the results of the backdoor samples as the target labels, and correctly identifies the benign samples with less loss relative to the uninfected model; stealthiness requires that the trigger is visually difficult to detect while being able to avoid being recognized by existing detection methods. However, most existing backdoor attack methods struggle to strike a balance between effectiveness and stealthiness. Some methods are able to generate stealthy triggers, but their effectiveness in practical applications is insufficient; others sacrifice the covertness of triggers while pursuing effectiveness. To address this challenge, in this paper, we propose a chromatic channel-based implicit backdoor attack (CCIBA). Our method is inspired by image steganography technology. For example, Li et al. [23] mitigated the embedding effects of secret information by employing robust embedding algorithms combined with de-coloring networks. They also employed generative modeling and perceptual loss for highly robust covert watermarking against attacks [24]. Liu et al. [25] adopted hierarchical feature learning to enhance robustness in complex scenes, enabling trigger activation across diverse visual environments. Wang et al. [26] designed multi-level reversible watermarks to withstand geometric distortions, providing valuable insights for maintaining backdoor trigger functionality under various preprocessing and defense measures.
Based on the above literature, the CCIBA targets the human eye’s insensitivity to changes in the chrominance channel of images and combines other image processing technologies (where frequency-domain modifications are less susceptible to degradation by low-pass filtering or transformations) to effectively enhance the Stealthiness and robustness of the trigger. Specifically, through covertly embeds the trigger into the wavelet domain sub-bands of a clean image by applying a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and singular value decomposition (SVD) on the UV channel of the YUV color space, thus achieving an efficient and persistent backdoor attack without significantly altering the visual features of the image. It is worth noting that the purpose of this research is to reveal potential vulnerabilities of DNNs to promote their security and robustness [27,28], rather than encourage malicious attack behaviors.
The main work of this paper is as follows.
(1) Proposing an implicit backdoor attack method based on the chromatic channel (CCIBA): In order to solve the problem that the existing work struggles to achieve a balance between effectiveness and stealthiness, a backdoor attack method is designed to inject implicit triggers only under the chromaticity channel. This method embeds the triggers in different sub-bands of the wavelet domain in the clean image by combining several different techniques, so as to meet the effectiveness requirements of the attack while realizing the implicit trigger injection.
(2) Conducting experiments on multiple datasets to prove the effectiveness of the method: Experiments are conducted on three datasets, CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100, to verify the generalization ability of the CCIBA method between different datasets, and a comparative analysis with existing methods is conducted.
(3) Verifying the sustainability (resistance to defense as well as detection) capability of this method: Existing backdoor defense and detection methods, such as Spectre, are used to verify whether the CCIBA can pass defense as well as detection, so as to achieve sustainable backdoor attack capability.
(4) Conducting ablation experiments to further verify and analyze the superiority of this method: Ablation experiments are conducted by adjusting different positions and embedding quantities in the wavelet domain to analyze and compare the changes of backdoor attack effectiveness and other indexes caused by different positions and embedding quantities, so as to effectively prove the contribution of this method in the comprehensiveness.
2. Related Work
2.1. Backdoor Attacks
In 2017, Gu et al. [29] first proposed a backdoor attack method against DNN models called BadNets, which uses a fixed trigger pattern to inject 3 × 3 white blobs in the lower-right corner of the image as a way to mix a certain percentage of clean images into poisoned images into the dataset, and combines this with a change in the label of the poisoned to train the model, which ultimately enables the model to be trained only for the poisoned images for misclassification. Since then, the research on backdoor attacks against DNNs has received extensive attention and in-depth study. Chen et al. [30] first superimposed the backdoor pattern on the pixel values of clean images to a certain extent to generate poisoned images. However, these previous approaches did not take into account the issue of stealth, which can be easily detected by human eye as a poisoned sample, so a lot of work began to focus on invisible backdoor attacks. Chen et al. [30] proposed to generate a poisoned backdoor by using generative random noise as a trigger and controlling its amplitude embedded in the clean samples, but its visual stealth is not ideal. Subsequently, Li et al. [31] introduced image steganography to embed the trigger into the lowest bit of RGB, and Nguyen et al. [32] made small geometric distortions to the original dataset, which can also achieve stealthiness as well as effectiveness of the attack. Since these invisible backdoor attacks only target the image null space for modification, and with the development of backdoor detection and defense research, they are easy to detect. Subsequent attack methods are further upgraded. Xiao et al. [33] operated on frequency domain locations, first generating triggers based on the frequency domain averages of all images of the target class, and then mixing them into the high frequency portion of the DCT of the clean image. Similarly, Xue et al. first divided the image into blocks, then calculated the DCT coefficients of each block, and finally embedded the trigger into the blocks with smaller coefficients [34]. Feng et al. [35] performed Fourier transforms of the trigger image as well as the benign image, respectively, for the medical image and mix only the amplitude spectra of the two images, and finally an inverse Fourier transform to obtain the poisoned image. Li et al. [36] went a step further by combining the decoder–encoder network structure to steganographically write the specified string encoding into the benign samples as a backdoor pattern. Wang et al. [37] proposed a stealthy backdoor attacker approach based on image quantization and dithering techniques (BppAttack), which achieves efficient and undetectable attacks without relying on auxiliary models by exploiting the insensitivity of human visual system to color depth variations, combined with contrast learning and adversarial training. Zhang et al. [38] first outlined the images using the LSB algorithm, then embedded color values (representing toxic information) into these images to generate poisoned samples. Li et al. [39] first generated spectral triggers by controlling the disturbance frequency and amplitude, then combined color space conversion and DCT to embed the triggers into clean samples to generate backdoors. Although previous work has made some progress in the field of backdoor attacks, there is a general problem of balancing trigger stealthiness as well as attack effectiveness, in addition to the limitation of high computational complexity. In contrast, the method proposed in this paper realizes the balance of trigger covertness and attack effectiveness, while greatly reducing the computational overhead.
2.2. Backdoor Detection and Defense
While the field of backdoor attacks continues to evolve, the threat of backdoor attacks has also driven the development of defense techniques. Early research focused on model-level defense, trying to weaken the backdoor effect by adjusting the internal structure of neural networks. For example, Liu et al. [40] proposed the FinePruning method, which identifies and removes neurons that may be embedded in the backdoor by analyzing the average activation value of the neurons, initially verifying the feasibility of the pruning strategy. Subsequently, Wang et al. [41] introduced Neural Cleanse, which exploits the difference in neuron activation patterns between clean and poisoned samples to locate and suppress abnormal behaviors, although the method has limited detection ability for hidden triggers. Since most of the existing backdoor attack approaches are aimed at modification of the original dataset, defense strategies have gradually evolved to the data level, emphasizing preprocessing and anomaly detection of the input samples. Devi Parikh et al. [42] and Chou et al. [43] used Grad-CAM to generate significance mappings that reveal regions in the inputs with anomalous effects on model predictions. Gao et al. [44] proposed the STRIP method, which achieves efficient runtime detection by overlaying randomly perturbed images and analyzing the entropy distribution of the model output (low entropy suggests the presence of triggers). Meanwhile, Tran et al. [45] developed the spectral signature technique, which distinguishes between clean and poisoned samples based on the covariance difference of potential spatial features, and is applicable to a wide range of backdoor types. Hayase et al. [46] further improved the identification of hidden backdoors through statistical anomaly detection by analyzing the potential anomalies in the output behavior of the model, which especially in the dynamic triggering scenarios show strong adaptability. However, these methods are mostly designed for backdoor patterns in the null domain, and their effectiveness is limited when faced with mixed null and frequency domain methods; the method in this paper targets both the null and frequency domains and combines image steganography with trigger embedding, thus avoiding being recognized by defenses or detections to a certain extent.
3. Program Design
3.1. Threat Model
3.1.1. Attacker’s Knowledge
An attacker’s knowledge of deep neural network (DNN) systems is severely limited. Specifically, the attacker is not privy to information about the internal structure or parameters of the DNN model, but is able to access the training dataset. This means that an attacker can analyze and manipulate the training data, but lacks direct knowledge of the model’s architecture or the weights generated during training.
3.1.2. Attacker’s Capabilities
Based on the limitations of their knowledge, the attacker’s main attack is to poison the training dataset. By purposefully modifying some of the samples in the training data, the attacker is able to implant potential control mechanisms during the model training phase. Due to the lack of direct access to the internal parameters of the DNN, the attacker is unable to execute the attack by modifying the model parameters.
3.1.3. Attacker’s Goals
Attackers pursue the following two explicit goals through backdoor attacks. For benign samples, DNNs should correctly classify their true labels. Meanwhile, the overall accuracy of the model on clean data should remain largely stable to ensure the stealthiness of the attack. For toxic samples containing triggers, DNN should misclassify them as predefined target labels. The generation of toxic samples should ensure stealthiness, i.e., the added triggers are not easily recognized, and at the same time, the effectiveness and robustness of the attack against the model should be ensured.
3.2. Problem Definition
A backdoor attack is a malicious attack against DNNs by embedding specific triggers in the training data, so that the attacked model maintains the correct prediction under normal inputs and outputs the incorrect results specified by the attacker under the inputs containing the triggers. The core mechanism lies in manipulating the decision-making behavior of the model through poisoned samples.
The source dataset is all clean data, and some of them are implanted with backdoors, i.e., the attacker constructs the poisoned dataset , where is the clean sample set and is the poisoned sample set. The poisoned sample is generated by embedding a triggert in the clean sample , i.e., and setting its source label as the target label , where the percentage of poisoned samples is . The attacked model is trained on and the optimal parameter is determined by minimizing the loss function with the following equation:
The goal of the attack is to ensure that (normal samples are correctly classified, means that not all of them are recognized correctly) and (trigger samples are incorrectly classified).
The trigger needs to be stealthy (i.e., ) and robust (valid after preprocessing , (i.e., ). This attack is often implemented when training is outsourced or third-party data are used, and it threatens the security of models in domains including image classification and speech recognition.
3.3. Implicit Backdoor Generation Scheme Based on Chromaticity Channel
This scheme proposes a chromatic channel-based implicit backdoor attack (CCIBA) method, which aims to utilize the chromaticity channel property of YUV color space and combine with discrete wavelet transform and singular value decomposition techniques to generate a covert and robust backdoor trigger to achieve effective attacks on DNNs. By embedding well-tuned triggers in the wavelet domain of an image, the CCIBA not only ensures that the poisoned image is highly similar to the original image visually, which is difficult to be detected by human beings or defense mechanisms, but also resists some existing defense methods and has certain sustainability capabilities. The process of generating backdoor samples is shown in Figure 1.
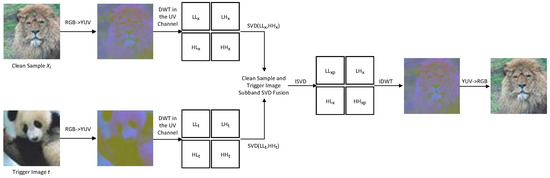
Figure 1.
Flow of backdoor sample generation.
In the CCIBA, the selection of LL and HH sub-bands for singular value decomposition (SVD) fusion is based on the optimization of wavelet transform sub-band characteristics and attack requirements. The LL sub-bands capture the low-frequency global structure of the image (accounting for approximately 90% of the energy). Through SVD fusion, core features can be covertly adjusted to ensure a stable influence of the trigger on the model’s decision-making. The HH sub-bands contain high-frequency diagonal details (noise and texture). After fusion, they introduce minor changes to enhance robustness while remaining covert due to human visual insensitivity to these details. In contrast, LH and HL sub-bands encode edge information, and SVD fusion may cause significant distortion, while fusion of all sub-bands increases computational complexity and risk. Therefore, the combination of LL and HH balances concealment and effectiveness, and ablation experiments verify its superiority.
The process of generating implicit backdoor triggers based on the chromatic channel is as follows:
Firstly, some clean images are randomly selected from the source benign dataset to facilitate the subsequent embedding of the trigger.
Step 1. Color space conversion: Convert the clean image and the trigger image from RGB space to YUV space, separating the luminance channel Y and the chrominance channel U,V. The chrominance channel is used for the trigger embedding to reduce the visual perceptibility.
Step 2. Discrete wavelet transform (DWT): Apply a one-stage 2D discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to the U,V channels of the clean image and the trigger image , and decompose them into the low-frequency sub-band LL and the high-frequency sub-bands LH,HL,HH by adopting Haar wavelet bases. The specific decomposition results are as follows:
The U,V channels of the clean image are decomposed separately:
The U,V channels of the trigger image are decomposed as follows:
Step 3. Singular value decomposition (SVD): Apply the singular value decomposition (SVD) to the LL and HH sub-bands of the clean image and the trigger image , and decompose the sub-bands into the diagonal matrix and the left and right singular vector matrices. The specific decomposition results are as follows:
The LL and HH sub-bands of the clean image are decomposed as
The LL and HH sub-bands of the trigger image are decomposed as
where and are the left and right singular vector matrices, respectively, and is the diagonal matrix. The elements on the diagonal are singular values, and the elements outside the diagonal are all 0. The singular values decrease from the top left to the bottom right (the smaller the value is, the lower the information content), and the corresponding column vectors of the left and right singular vectors, and the row vectors of the left and right singular vectors, are also the same.
Step 4: Sub-band SVD fusion: For the LL and HH sub-bands, perform a fusion operation on the left singular vector, singular values of the diagonal matrix, and right singular vector of the clean image and trigger image. Specifically, this involves replacing the singular values and singular vectors from the last positions to the final position of the clean image’s diagonal matrix with the corresponding singular values and singular vectors from the last positions to the final position of the trigger image. Finally, the inverse singular value decomposition is applied to return the modified LL and HH sub-bands.
For the LL sub-band,
For the HH sub-band,
Step 5: Inverse wavelet transform and color space inverse transform: Apply an inverse discrete wavelet transform (IDWT) to the fused sub-band , and reconstruct the U,V channel using the Haar wavelet. The reconstruction formula is as follows:
The reconstructed UV channel is used together with the luminance channel Y for the final color space inversion.
Step 6: Fuse a certain percentage of backdoor poisoned samples with triggers with clean samples, and change the label of poisoned samples to our target label to form a mapping relationship, and finally train the poisoned dataset as a model.
This scheme achieves our goal of satisfying both the necessary requirements of stealthiness as well as validity by generating backdoor triggers using color channel transformation, discrete wavelet transform, and singular value decomposition techniques, and by fusing backdoor triggers in different sub-bands. According to the following experimental analysis and verification, this method can achieve the effectiveness of backdoor attacks and, compared with existing work in the attack success rate, can achieve a certain improvement, while against some backdoor detection and defense methods it has a certain anti-detection ability.
The following is the algorithm description of the method in this paper (Algorithm 1):
| Algorithm 1: Chromatic channel-based implicit backdoor attack method |
| Input: source benign dataset , trigger image , embedding volume , poisoning ratio Output: poisoned dataset ,. 1. Initialize the poisoned dataset as an empty array. 2. Randomly select the data samples with the proportion of from the source benign dataset and put them into the dataset . 3. 4. Calculate the width and height of the input sample image and the trigger image. 5. If the width and height of the two images are not of the same size, then: 6. Adjust the width and height of the small image to be the same as the large image. 7. Convert the input sample image and trigger image from RGB to YUV. 8. DWT the UV channels of both images. 9. SVD the LL and HH sub-bands of and . 10. Replace the last singular values and the singular vectors of the LL and HH sub-bands of . 11. Perform ISVD on the modified LL and HH sub-bands of the input samples. 12. Perform IDWT on all sub-bands to return the reconstructed YUV channel. 13. Convert the poisoned sample image YUV channel to RGB channel. 14. Change the poisoned sample image to our target label . 15. 16. Return |
4. Experimental Analysis and Verification
In this section, the performance of the CCIBA method is evaluated through comparative experiments, and the BadNets attack method proposed by Gu et al. in [25], the Blended attack method proposed by Chen et al. in [26], and the Bpp method in [32] are selected as benchmarks for comparison. Among them, BadNets is a typical explicit backdoor attack method, which infects the model by adding a fixed trigger pattern (e.g., labeling the sample as “airplane”) to clean samples to misclassify them under specific inputs, e.g., misclassifying the “car” sample as “airplane”, or misidentifying the “car” sample as “airplane”. The Blended attack method fuses trigger images with clean samples to generate poisoned samples by setting the blending ratio at to contaminate the training dataset for backdoor implantation. In this section, the experimental setup, experimental results, and in-depth analysis of the results will be elaborated to verify the performance of the CCIBA in terms of stealth and robustness, and to explore its advantages and potential limitations compared with the comparison methods, so as to provide reference for the subsequent research.
4.1. Experimental Setup
(1) Datasets
Three widely used public datasets are chosen for backdoor attack effectiveness evaluation: CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Tiny-ImageNet. Among them, the CIFAR-10 dataset contains 10 categories with an image size of 32 × 32 pixels, which covers common object categorization tasks; the CIFAR-100 dataset contains 100 categories with an image size of 32 × 32 pixels; and the Tiny-ImageNet dataset contains 200 categories with an image size of 64 × 64 pixels, providing more complex classification challenges. These three datasets are often used in backdoor attack research due to their diversity and representativeness, providing a reliable basis for evaluating the performance of the CCIBA method.
(2) Model Setup
In this paper, ResNet-18 is chosen as the target victim model with the aim of evaluating the effectiveness of the CCIBA attack. The training process is targeted at CIFAR-10 and Tiny-ImageNet datasets, and the number of iterations is set to 100 to ensure that the model reaches a fully converged state. The SGD optimizer was chosen for the optimization process and the initial learning rate was set at 0.01 to balance the convergence speed and accuracy. The poisoning rate is controlled at 0.1 to ensure the coordination between the covertness and the impact of the attack, while the singular value and the quantity of singular vector embedding are set at -value (this paper sets it to 8 for CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100, and to 24 for Tiny-ImageNet), according to the size of different image datasets to optimize the finesse and visual imperceptibility of the trigger embedding.
(3) Evaluation metrics
In order to comprehensively evaluate the performance of the CCIBA backdoor attack, this paper introduces several key indicators to measure the model performance and attack effect from different dimensions.
Effectiveness Evaluation Metrics.
ACC (Accuracy): This is used to evaluate the influence of the backdoor model on the test data without embedded triggers. The higher the ACC value, the smaller the difference between the backdoor model and the original model on the classification of clean data will be. This makes it difficult for users to detect the abnormality, thus enhancing the covertness of the attack.
ASR (Attack Success Rate): This measures the effectiveness of the backdoor attack, defined as the percentage of images that are misclassified as the target category after embedding the trigger. The higher the ASR value, the more successful the trigger manipulation model behavior.
Stealth Assessment Metrics.
PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio): This is a commonly used metric for measuring image distortion, assessing the difference between two images by the mean square error (MSE). The higher the PSNR value, the smaller the distortion is (>40 dB excellent, 30–40 dB good, <20 dB unacceptable), and thus the higher the PSNR value, the smaller the difference between the poisoned image and the original image, and the more stealthy the image is.
SSIM (Structural Similarity Index Measure): This measures the structural similarity of two images, assessed in terms of brightness, contrast, and structure (quantified by mean, variance, and covariance). SSIM values range from 0 to 1: closer to 1 means more similar, 1 is identical. The SSIM function uses a dynamically adjusted window size [3,5].
LPIPS (Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity): This is a metric based on perceptual loss, close to human visual perception. The lower the LPIPS value, the smaller the difference between the two image perceptions, and vice versa. It is used to validate the visual covertness of the trigger. In this paper, we adopt LPIPS based on features learned from pre-trained VGG, following its original default weight settings.
The above three indicators are all calculated uniformly for all RGB channels (3 channels).
4.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.2.1. Backdoor Attack Effectiveness Evaluation
In order to deeply investigate the attack effectiveness of the CCIBA, this paper selects the ResNet-18 model and conducts systematic experiments on three different datasets, CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100, and comprehensively compares it with three representative backdoor attack techniques, namely BadNets, Blended, and Bpp. Comparison. The experimental data are shown in Table 1, and the results show that the CCIBA’s attack success rate (ASR) on the CIFAR-10 dataset significantly outperforms that of BadNets, highlighting its significant advantage in attack effectiveness. Meanwhile, CCIBA’s clean sample accuracy (ACC) is also significantly improved compared to BadNets, proving that it strengthens the attack effectiveness without causing significant damage to the model’s regular recognition performance. Compared to Blended, the CCIBA’s ASR is slightly better and its ACC performance is also comparable. Compared with the Bpp method, the ASR of the CCIBA is close to its level, while the ACC is significantly ahead, especially on the Tiny-ImageNet dataset, where the ACC improves by nearly 10% compared to Bpp, while the ASR remains the same for both of them. For the CIFAR100 dataset, its ACC and ASR are slightly weaker than the Blended approach but still outperform the other two methods. This indicates that the CCIBA can achieve a high attack rate while still maintaining the model’s own effect of correctly categorizing.

Table 1.
Comparison of attack results for different backdoor attacks.
Comprehensive analysis shows that the CCIBA demonstrates excellent attack success rate and clean sample accuracy on CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100 datasets. Compared with BadNets, Blended, and Bpp methods, the CCIBA strikes an optimal balance between attack strength and model robustness, especially when dealing with small-scale datasets (CIFAR-10) is particularly impressive. In addition, the metric evolution curves during the training process (shown in Figure 2) further corroborate the convergence stability and efficiency of the CCIBA, fully confirming its effectiveness as an innovative backdoor attack strategy.
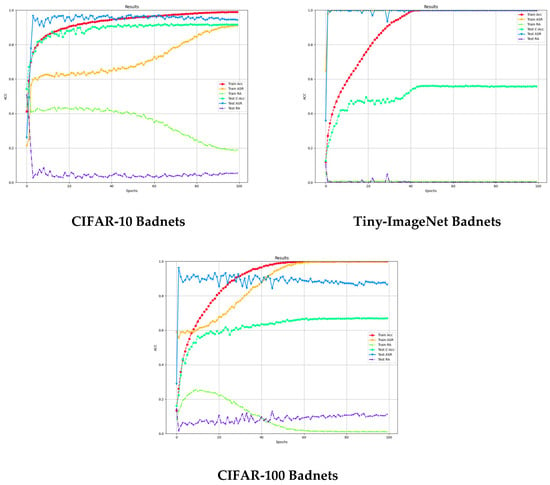
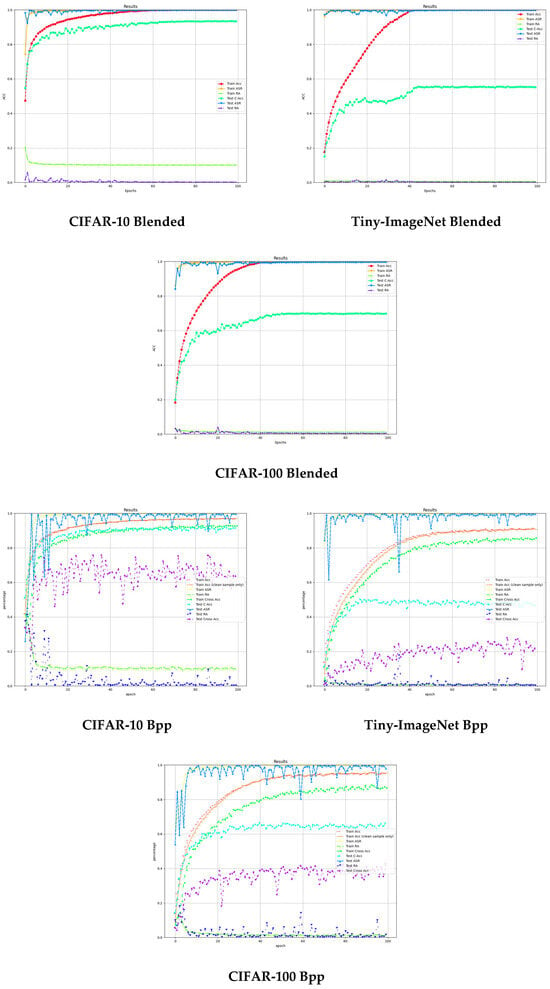
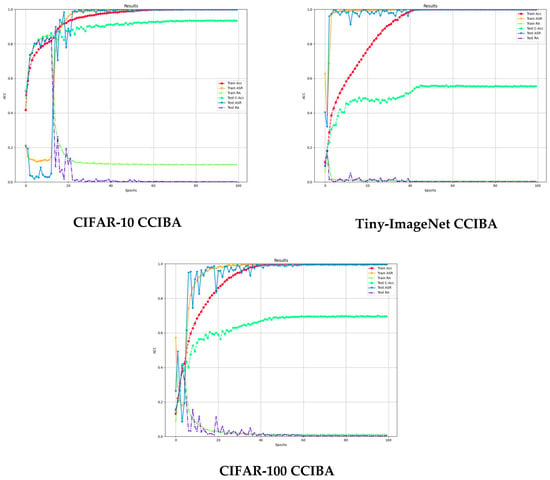
Figure 2.
Evolution curve of metrics for different backdoor attacks during the training process.
4.2.2. Stealthiness Analysis
In the field of backdoor attack research, stealthiness, as a key evaluation metric, determines whether a trigger can seamlessly integrate into the input data without being detected. In order to systematically evaluate the stealthy performance of the CCIBA method, this study conducts an in-depth analysis in terms of both visual perception and quantitative metrics, and uses the existing Blended attack method as a comparison benchmark.
In order to visually demonstrate the steganographic effect of the CCIBA, Figure 3 provides a comparative analysis of the clean samples and the poisoned samples generated by the CCIBA and the other three backdoor methods. The first, second, and third rows of images are taken from one image each of the three datasets of CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100, respectively. Badnets incorporates a white blob in the lower right corner, whose embedding into the original image produces significant visual traces that can be easily recognized by human observers or automatic detection systems; the Blended method employs an eye-catching Hello Kitty image as a trigger that is equally obvious. Bpp is an implicit backdoor attack method, like the method in this paper, but is still perceived as blurrier when compared to the clean image. In contrast, the CCIBA utilizes the chrominance channel of YUV color space and then realizes the embedding of the trigger through wavelet transform. This method relies on the lower perceptual sensitivity of the chrominance channel to ensure that the generated poisoned image is visually no different from the original image, showing a high degree of steganographic properties.

Figure 3.
Visual comparison of backdoor samples generated in this paper with other methods.
To validate that the method proposed in this paper can effectively resist human eye detection and has strong visual concealment, 100 clean original images and 100 corresponding poisoned images were randomly selected to form 100 sample pairs. The manual evaluation experiment required six people to distinguish the poisoned images from each pair of samples, and the results are shown in Table 2. The experimental results show that it is difficult for humans to perceive poisoned images containing backdoors.

Table 2.
Accuracy of manual visual assessment.
In addition to manual visual evaluation, this study adopts peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity (SSIM), and loss of perception (LPIPS) as quantitative metrics for evaluating the stealthiness of triggers. The experiments are conducted on two datasets, CIFAR-10 and Tiny-ImageNet, and the CCIBA is compared with the two benchmark methods, Blended and Bpp (since the above metrics are not sensitive to the local small white blocks added by Badnets, they are not compared), and the quantitative metrics of poisoned samples for the methods are shown in Table 3. The results show that the CCIBA-generated poisoned images have the highest PSNR and SSIM values, and the LPIPS value is close to zero, indicating that the visual difference between them and the original images is extremely small. In addition, the CCIBA-generated poisoned images exhibit natural characteristics that are almost indistinguishable from the unprocessed clean image. The result further confirms the significant advantages of CCIBA trigger embedding in terms of steganography, which outperforms the relatively comparable existing methods.

Table 3.
Comparison of stealthiness metrics of each method.
4.3. Sustainability Analysis
In deep neural network research, sustainability reflects the model’s performance stability and generalization ability under diverse inputs or external disturbances. In order to comprehensively assess the sustainability of the CCIBA, this study examines its enduring efficacy in an adversarial environment by applying it to three typical backdoor defense mechanisms. These defense and detection mechanisms include Neural Cleanse, spectral signature analysis (Spectral), spectral enhancement detection (Spectre), and interpretability-based Grad-CAM detection methods. The infection models used in the experiments are trained by introducing poisoned samples on CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100 datasets to ensure a realistic and challenging evaluation environment.
Specifically, Neural Cleanse reconstructs latent triggers by optimizing minimal perturbation patterns and identifies backdoor behavior in models using exceptionally small perturbation norms; Spectral defense identifies anomalous patterns that may be introduced by backdoor triggers by analyzing the spectral features of the model weight distribution; Spectre further introduces enhancement techniques based on spectral analysis to improve the detection of covert backdoor attacks through multi-scale spectral decomposition or specific frequency domain feature extraction; and Grad-CAM improves the detection capability of covert backdoor attacks by visualizing the model’s decision basis to reveal potential trigger traces. In this study, the poisoned samples generated by the CCIBA are fed into the above defense system to observe whether they can maintain the attack effect, so as to verify their sustainability performance under defense pressure.
(1) Neural Cleanse detection
Neural Cleanse employs reverse engineering techniques to derive latent trigger patterns by analyzing minute adjustments applied to inputs of deep neural networks (DNNs), thereby effectively identifying hidden backdoors. Its core principle assumes that backdoor attacks manifest as anomalies in model decision-making, detecting malicious behavior by generating and validating these patterns. Defense effectiveness is evaluated using an anomaly index, judged against preset thresholds: scores below 2 indicate a clean model state, scores between 2 and 3 suggest suspicious activity but do not confirm backdoor presence, scores generally below 3 indicate successful backdoor evasion, while scores above 3 definitively confirm backdoor existence.
To evaluate the CCIBA’s resistance against Neural Cleanse detection, experiments were conducted on CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100 datasets, with results shown in Table 4. To ensure consistent metrics across datasets of varying sizes, experiments used the same embedding ratio rather than embedding volume. Experimental results indicate that when α is set to 0.5, the anomaly indices across all three datasets fall between 2 and 3, failing to prove backdoor existence. When α is set to 0.125, the number of anomalies drops below 2, demonstrating complete undetectability of backdoor attacks. By dynamically adjusting the embedding ratio, both attack effectiveness and anti-detection capability can be maintained simultaneously.

Table 4.
Evaluation results of Neural Cleanse detection method under different datasets.
(2) Spectral defense
Spectral is a backdoor detection method based on spectral characterization, which identifies potential backdoor anomaly patterns by extracting the characteristic distribution of model weights or activation values in the frequency domain. To evaluate the ability of the CCIBA against Spectral defense, this study conducted experiments on CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100 datasets, and the detailed results are shown in Table 5. The metrics in the table include TN (the number of clean samples correctly recognized as clean samples), TP (the number of backdoor samples correctly recognized as backdoor samples), FP (the number of clean samples misjudged as backdoor samples), FN (the number of backdoor samples misjudged as clean samples), TPR (the backdoor sample detection rate, calculated by TPR =TP/(TP + FN); the lower the TPR, the higher the leakage detection rate of the defense method), and FPR (false detection rate, calculated as FPR = FP/(FP + TN); the higher the FPR, the higher the misjudgment rate of the defense method on clean samples will be).

Table 5.
Evaluation results of Spectral defense method under different datasets.
The experimental results show that the CCIBA exhibits perfect stealth in the face of Spectral defense. As shown in Table 5, for the CIFAR-10 dataset, the false detection rate (FPR) of Spectral defense reaches 16.67%, while the detection rate (TPR) of backdoor samples is 0, indicating that none of the backdoor samples can be recognized correctly. On the Tiny-ImageNet dataset, the FPR of Spectral is only 14.99% and the TPR is also 0. On the CIFAR-100 dataset, the FPR of Spectral is only 15.89% and the TPR is 7.5%, showing that our backdoor attack method has better generalization ability for defense detection against different datasets. In addition, after Spectral identifies and detects the backdoor, it also retrains the dataset. Figure 4 shows the training results of three different datasets after Spectral’s detection process, and the effectiveness of the attack is not significantly reduced compared with the infection model without defense detection process. The above graphical results show that CCIBA can effectively mask its backdoor features, so that the distribution of spectral features of the poisoned samples is highly similar to that of the clean samples, which significantly reduces the recognition ability of Spectral defense.
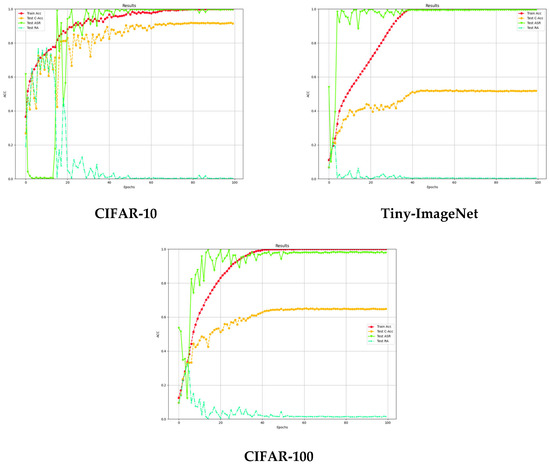
Figure 4.
Retraining results for different datasets after Spectral defense.
(3) Spectre detection
Spectre is a backdoor identification strategy relying on statistical anomaly detection, which reveals potential backdoor traces by carefully analyzing the anomalous fluctuations in the neural network output. To evaluate the performance of the CCIBA under Spectre defense, this study conducts in-depth experiments on the CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100 datasets, and the results are shown in Table 6. The metrics are defined consistently with Spectral defense.

Table 6.
Evaluation results of Spectre defense methods on different datasets.
The experimental results show that the CCIBA exhibits significant steganographic advantages in front of Spectre detection. As shown in Table 6, for the CIFAR-10 dataset, the FPR of Spectre reaches 16.50%, while the TPR of backdoor samples is only 1.42%, which indicates that very few backdoors are correctly detected, and most of the poisoned samples successfully escape detection. For the Tiny-ImageNet dataset, the FPR is 15.47% and the TPR is only 10.53%, For the CIFAR-100 dataset, the FPR is 15.86% and the TPR is only 6.18%, which also reflects the limitation of detection capability. The improvement over Spectral does not affect the number or percentage of correct identifications. These data show that CCIBA effectively circumvents Spectre’s statistical analysis capability by cleverly masking abnormal features in the output behavior, highlighting its strong stealthiness against the anomaly detection mechanism.
(4) Grad-CAM detection
Gradient-weighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) is a visualization technique for revealing the regions of interest for decision-making in deep neural networks by generating heatmaps to visualize the regions focused on when the model is classified, where the red parts indicate the regions that have the most influence on decision-making. Specifically, Grad-CAM generates weights by calculating the gradient of the target category on the output of the convolutional layer, combining it with global average pooling, and weighting the feature maps in order to form a heatmaps with the same dimensions as the input image. Since its heatmaps only reflects the categorization contribution region and the pattern is consistent across different datasets, the CIFAR-10 dataset is used as an example for analysis.
In backdoor attacks, the significant regions of the heatmaps usually correspond to trigger locations, and the stealthiness of the attack can be assessed by comparing benign samples. Figure 5 shows the Grad-CAM heatmaps results of the CCIBA method under CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100 datasets; the left figure shows the clean sample, and the right figure shows the poisoned sample. The CCIBA embeds triggers under the YUV chromaticity channel as well as in combination with wavelet transform and singular value decomposition so that they are uniformly distributed all over the image. Compared to the benign samples, the Grad-CAM heatmaps of the CCIBA shows a similar attention distribution and does not reveal abnormal attention regions, indicating that its trigger embedding does not significantly affect the model’s decision focus. This feature makes the CCIBA effective against Grad-CAM detection and highlights its superior stealthiness under interpretable analysis.

Figure 5.
Heatmaps of Grad-CAM visualization under different datasets.
4.4. Ablation Experiment
The embedding position of the trigger and the amount may affect the experimental effect. In order to deeply analyze the attack performance of the CCIBA method under different settings, an ablation experiment is designed under the CIFAR-10 dataset for embedding triggers into different sub-bands of the wavelet domain as well as for adjusting the embedding amount of the -value. This ablation experiment is only conducted on the CIFAR-10 dataset. Specifically, triggers are injected into the LL, LH, HL, and HH sub-bands of the discrete wavelet transform, which are compared with our low-high frequency dual sub-band injection method, and the embedded triggers remain the same, which are the replacement of the singular values of the inverse positions as well as the left and right singular vectors. For adjusting the value of the embedding quantity , we set to 2, 4, 6, 8 different embedding quantities, and at the same time keep our embedding position as LL + HH when changing the value of . The experimental results of the backdoor attack for different sub-bands and embedding quantities are shown in the following table.
As can be seen from Table 7, the ASR, i.e., the attack effect, is the best compared to other positions when the embedding position is set to LL + HH in this scheme, and the ACC is only slightly lower than the highest LH, which achieves a high attack effect while maintaining a high accuracy rate for normal classification of the model. From Table 8, when the embedding amount value is adjusted to increase, the overall trend of ACC first rises and then decreases. The ACC forms an inflection point and starts to decrease from 6 to 8, and when is 8, the ACC only decreases by 0.03% compared to that of 6, while the ASR improves more. Therefore, our scheme uses the embedding location of LL + HH and the embedding amount is set to 8.

Table 7.
Effect of different embedding positions on attack effectiveness under CIFAR-10 dataset.

Table 8.
Effect of different embedding amount on attack effectiveness under CIFAR-10 dataset.
5. Summary
Through a comprehensive experimental evaluation of the CCIBA on the CIFAR-10, Tiny-ImageNet, and CIFAR-100 datasets, this study verifies its significant advantages in terms of attack efficacy and stealthiness. The experimental results show that CCIBA achieves an excellent balance between attack success rate (ASR) and clean sample accuracy (ACC), and exhibits stronger attack capability and model performance stability compared to methods such as BadNets, Blended, and Bpp. Stealthiness analysis further reveals that the poisoned samples generated by the CCIBA are highly consistent with the original images in terms of visual perception and quantitative metrics (PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS), and successfully evade the detection of multiple defense mechanisms such as Neural Cleanse, Spectral, Spectre, and Grad-CAM. The ablation experiments further illustrate the superiority of our scheme. In summary, the comprehensive performance of the CCIBA in terms of stealth, sustainability, and attack efficiency highlights its scientific value and application potential as a novel backdoor attack strategy, and provides new ideas for research in the field of deep learning security.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L. and S.Y.; methodology, C.L.; software, Y.L.; investigation, S.Y.; data curation, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wenger, E.; Passananti, J.; Bhagoji, A.N.; Yao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, B.Y. Backdoor attacks against deep learning systems in the physical world. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6206–6215. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Teo, T.H.; Kok, C.L.; Koh, Y.Y. A Novel Single-Word Speech Recognition on Embedded Systems Using a Convolution Neuron Network with Improved Out-of-Distribution Detection. Electronics 2024, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Luo, X.; Lu, R. Poisoning and evasion attacks against deep learning algorithms in autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 4439–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, W.; Deng, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, W.; Cao, W.; Nan, J.; Lian, Y.; Burke, A.F. Autonomous driving system: A comprehensive survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 242, 122836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, W.; Wang, K.I.-K.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.T.; Jin, Q. Deep-learning-enhanced human activity recognition for internet of healthcare things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 6429–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Shan, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S. CLSpell: Contrastive learning with phonological and visual knowledge for Chinese spelling check. Neurocomputing 2023, 554, 126468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Xian, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Cheng, H.D. Multi-slice low-rank tensor decomposition based multi-atlas segmentation: Application to automatic pathological liver CT segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 73, 102152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Kou, G.; Dong, Y.; Chiclana, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Bounded confidence evolution of opinions and actions in social networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 7017–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, S.; Xiong, G.; Yan, K.; Zhou, X. Federal learning edge network based sentiment analysis combating global COVID-19. Comput. Commun. 2023, 204, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, W.; Wang, K.I.-K.; Yan, Z.; Yang, L.T.; Wei, W.; Ma, J.; Jin, Q. Decentralized P2P federated learning for privacy-preserving and resilient mobile robotic systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2023, 30, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ye, X.; Wang, K.I.-K.; Liang, W.; Nair, N.K.C.; Shimizu, S.; Yan, Z.; Jin, Q. Hierarchical federated learning with social context clustering-based participant selection for internet of medical things applications. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2023, 10, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, G.; Xu, X.; Jiang, H.; Tian, Z.; Ma, T. Multicenter hierarchical federated learning with fault-tolerance mechanisms for resilient edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ni, Z.; Xu, Y.; Luo, E.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. A trustworthy industrial data management scheme based on redactable blockchain. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2021, 152, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Dou, W.; Hu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J. A context-aware service evaluation approach over big data for cloud applications. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2015, 8, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, W.; Li, W.; Yan, K.; Shimizu, S.; Wang, K.I.-K. Hierarchical adversarial attacks against graph-neural-network-based IoT network intrusion detection system. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 9310–9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, Q.; Mao, X.; Li, F. Trust based task offloading scheme in UAV-enhanced edge computing network. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2021, 14, 3268–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Feng, S.; Pan, M.; Yu, Y. Smart contract generation for inter-organizational process collaboration. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2024, 36, e7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, K.I.K.; Yan, Z.; Yang, L.T.; Jin, Q. Reconstructed graph neural network with knowledge distillation for lightweight anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 11817–11828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.A.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Hayajneh, T.; Khan, F. AntiConcealer: Reliable detection of adversary concealed behaviors in EdgeAI-assisted IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 22184–22193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Li, S.; Dai, H.; Hu, C.; Dou, W.; Ni, Q. A k-anonymity based schema for location privacy preservation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2017, 4, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ren, J.; She, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Ren, K. EdgeSanitizer: Locally differentially private deep inference at the edge for mobile data analytics. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 5140–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; He, A.; Wen, Y.; Liu, G.; Chronopoulos, A.T. Optimal trading mechanism based on differential privacy protection and stackelberg game in big data market. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2023, 16, 3550–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Gao, S. Image steganography in color conversion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 71, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Ma, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Gao, S.; Shi, Y. Concealed attack for robust watermarking based on generative model and perceptual loss. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 5695–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lu, M.; Yang, J.; Gui, J.; Zhang, S. From simple to complex scenes: Learning robust feature representations for accurate human parsing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 5449–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, Q.; Xia, Z.; Ma, B.; Shi, Y.-Q. Light-Field Image Multiple Reversible Robust Watermarking Against Geometric Attacks. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Gui, W. VAE-based interpretable latent variable model for process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 6075–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, X.; Shu, T.; Liang, W.; Wang, K.I.-K.; Qi, L.; Shimizu, S.; Jin, Q. Information theoretic learning-enhanced dual-generative adversarial networks with causal representation for robust OOD generalization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 36, 2066–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Liu, K.; Dolan-Gavitt, B.; Garg, S. Badnets: Evaluating backdooring attacks o n deep neural networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47230–47244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Li, B.; Song, D.; Lu, K. Targeted Backdoor Attacks on Deep Learning Systems Using Data Poisoning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.05526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xue, M.; Zhao, B.Z.H.; Zhang, X. Invisible Backdoor Attacks on Deep Neural Networks via Steganography and Regularization. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2021, 18, 2088–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.; Tran, A. WaNet—Imperceptible Warping-Based Back door Attack. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.10369. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Deng, X.; Jiang, W. An Invisible Backdoor Attack based on DCT-Injection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS), Guangzhou, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, M.; Ni, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. Imperceptible and multi-channel backdoor attack. Appl. Intell. 2024, 54, 1099–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ma, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Xia, Y.; Tao, D. Fiba: Frequency-injection based backdoor attack in medical image analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 20876–20885. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, L.; He, R.; Lyu, S. Invisible Backdoor Attack with Sample-Specific Triggers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 16443–16452. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhai, J.; Ma, S. Bppattack: Stealthy and efficient trojan attacks against deep neural networks via image quantization and contrastive adversarial learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 15074–15084. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Dongdong, C.; Huang, Q.; Liao, J.; Zhang, W.; Feng, H.; Hua, G.; Yu, N. Poison ink: Robust and invisible backdoor attack. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 5691–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pang, R.; Xi, Z.; Du, T.; Ji, S.; Yao, Y.; Wang, T. An embarrassingly simple backdoor attack on self-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 4367–4378. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Dolan-Gavitt, B.; Garg, S. Fine-Pruning: Defending Against Backdooring Attacks on Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.12185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, Y.; Shan, S.; Viswanath, B.; Zheng, H. Neural Cleanse: Identifying and Mitigating Backdoor Attacks in Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2019; pp. 707–723. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, E.; Tramer, F.; Pellegrino, G. SentiNet: Detecting Localized Universal Attacks Against Deep Learning Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW), San Francisco, CA, USA, 21 May 2020; pp. 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Nepal, S. Strip: A defense against trojan attacks on deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, San Juan, PR, USA, 9–13 December 2019; pp. 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, B.; Li, J.; Madry, A. Spectral signatures in backdoor attacks. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 8011–8021. [Google Scholar]
- Hayase, J.; Kong, W.; Somani, R.; Oh, S. Spectre: Defending against backdoor attacks using robust statistics. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 4129–4139. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).