A Novel Compact Beamforming Network Based on Quasi-Twisted Branch Line Coupler for 5G Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
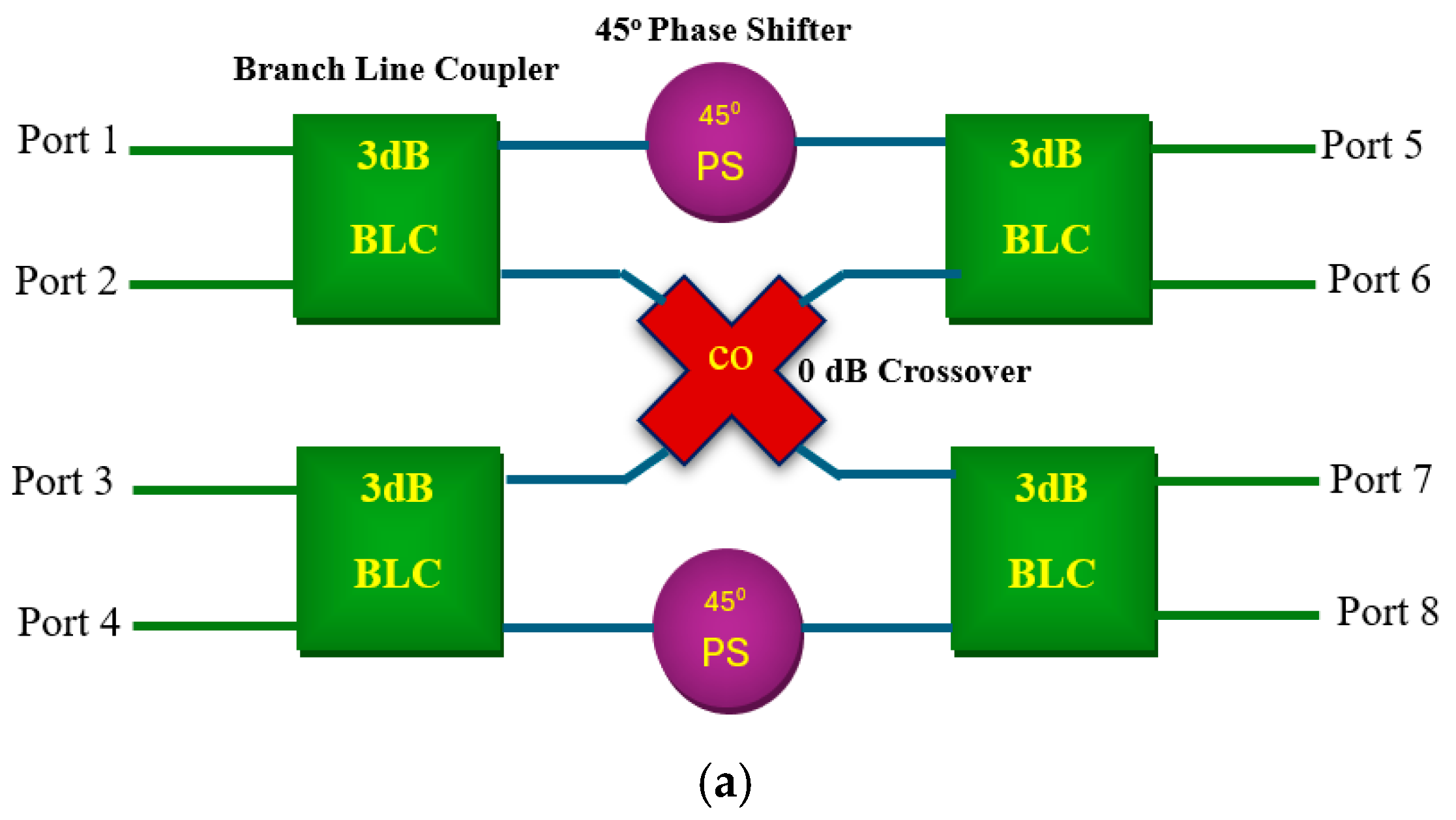
2. Butler Matrix Structure
3. Proposed BM Feed Network Based on Quasi-Twisted BLC
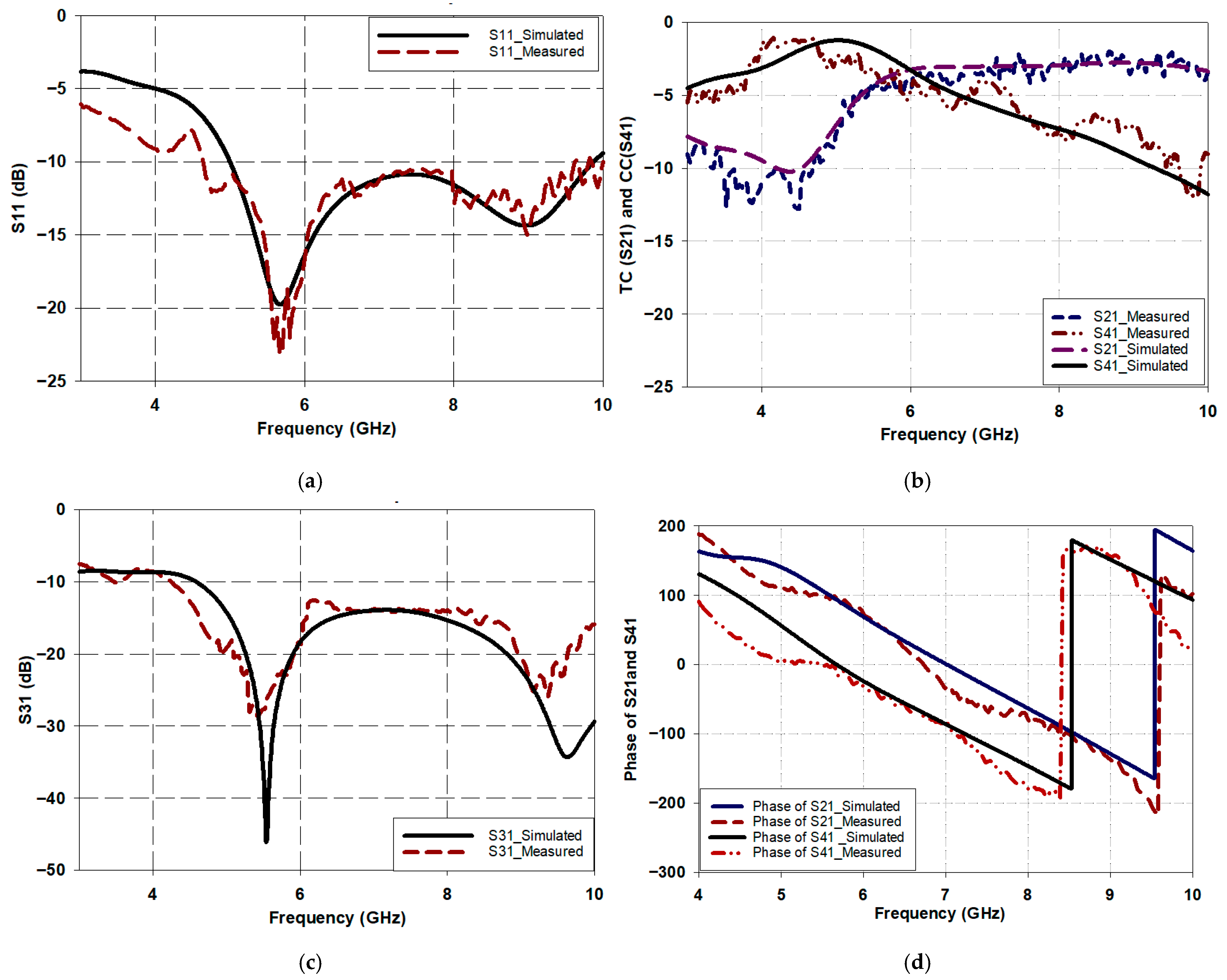
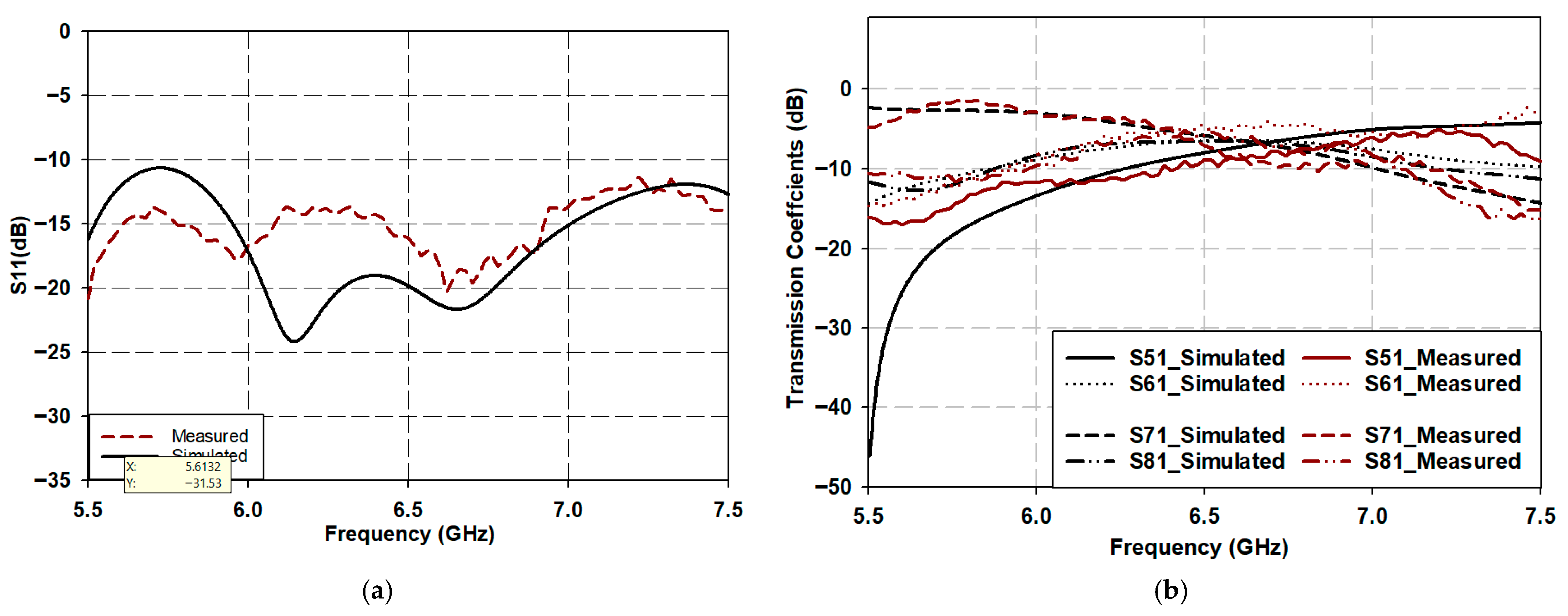
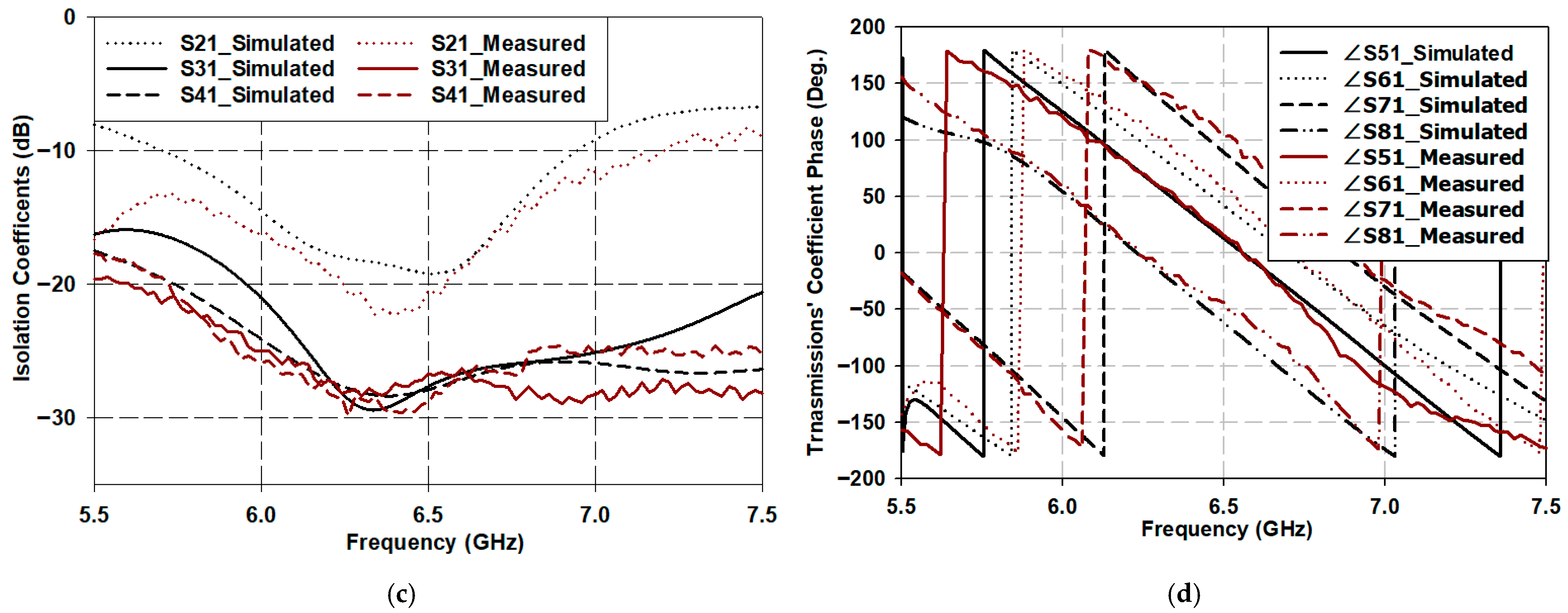
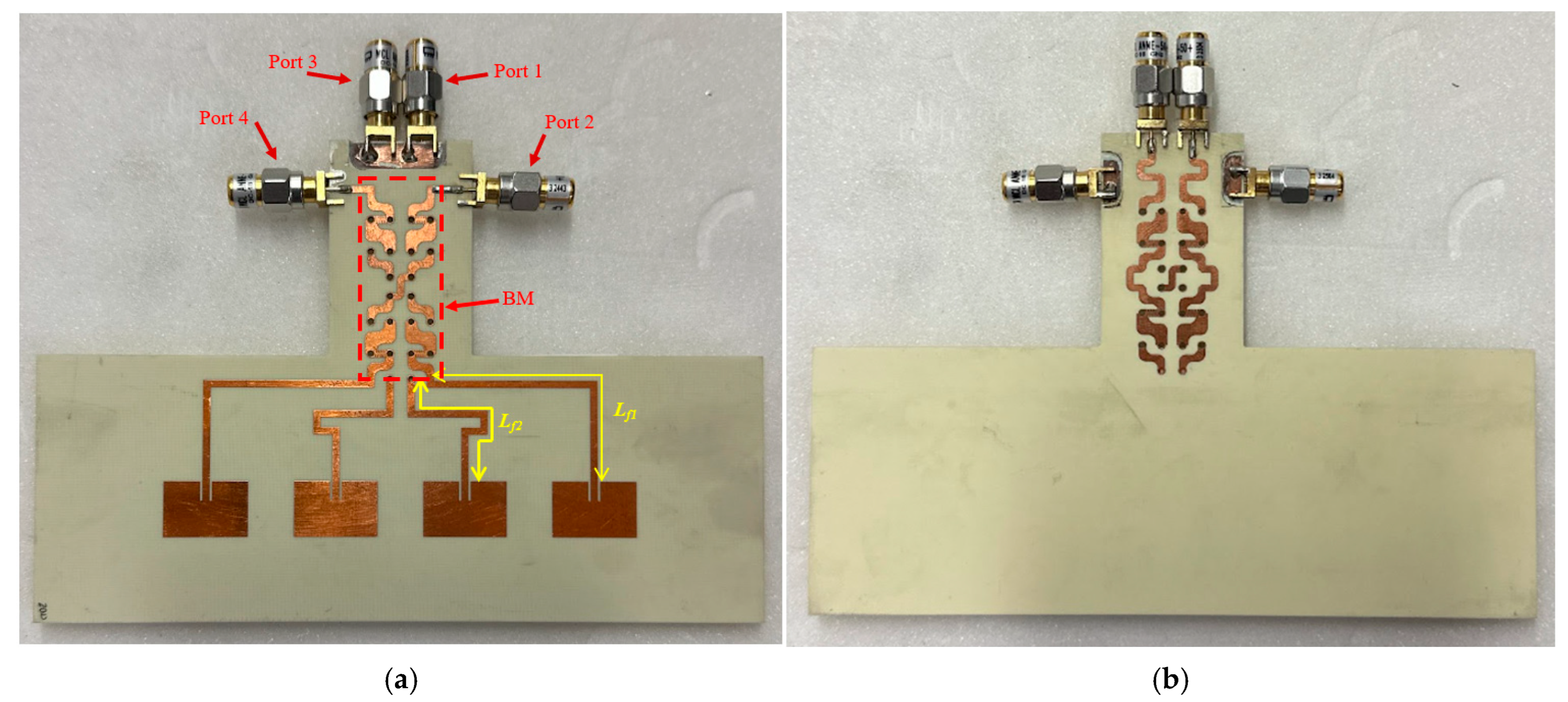
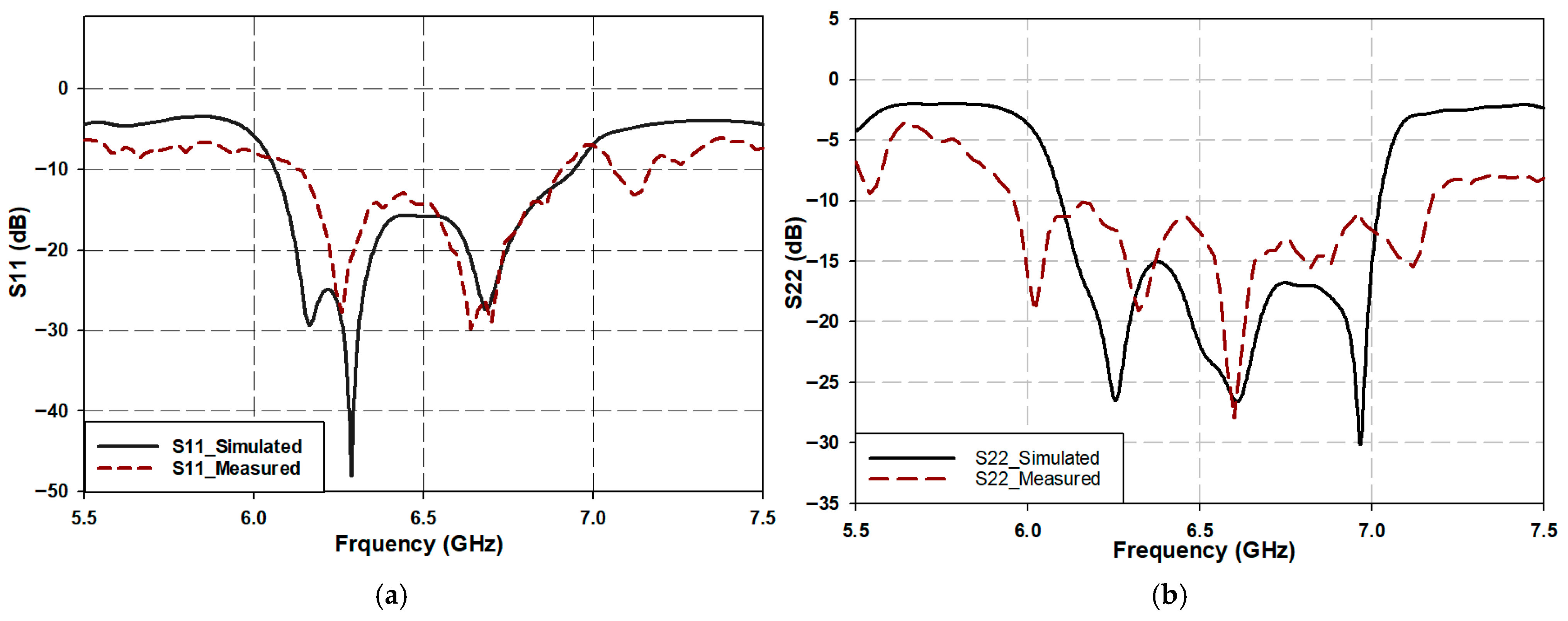
Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of the Butler Matrix
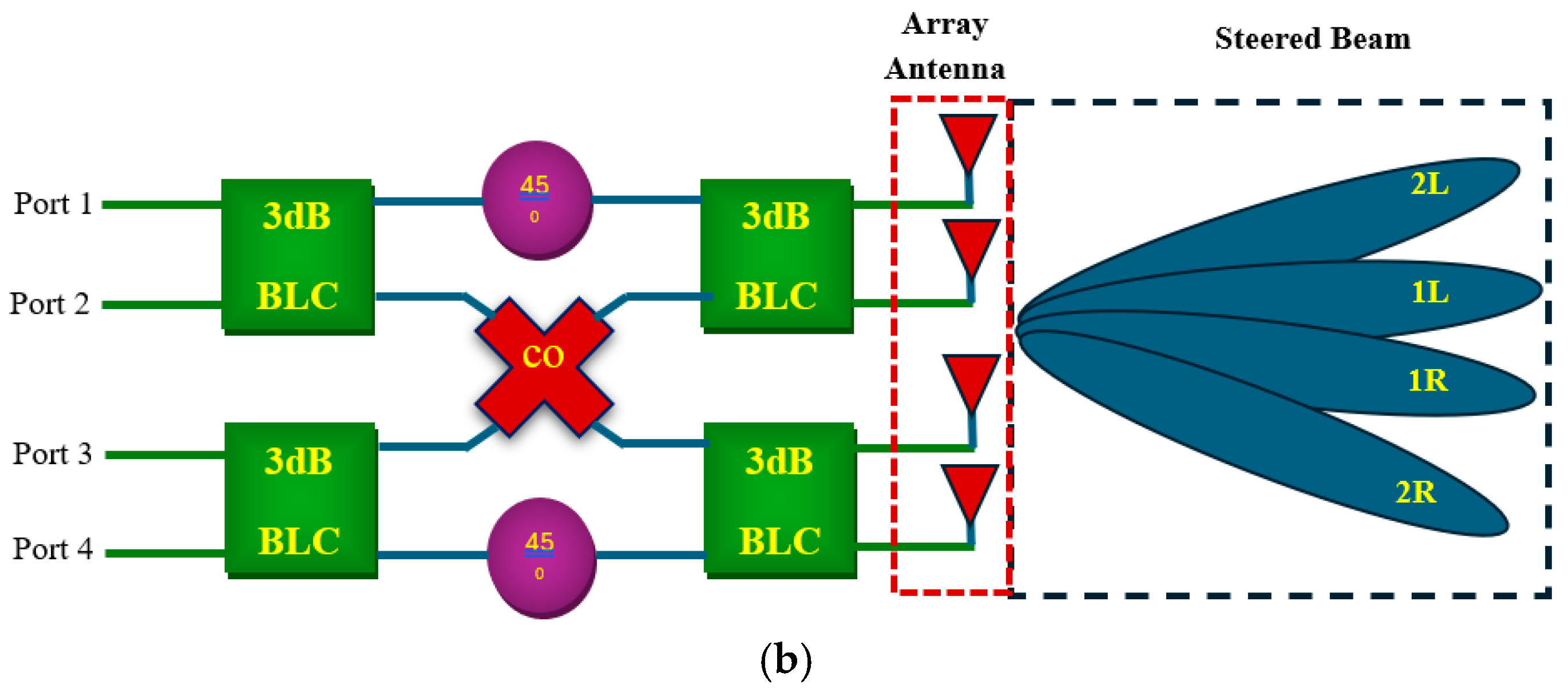
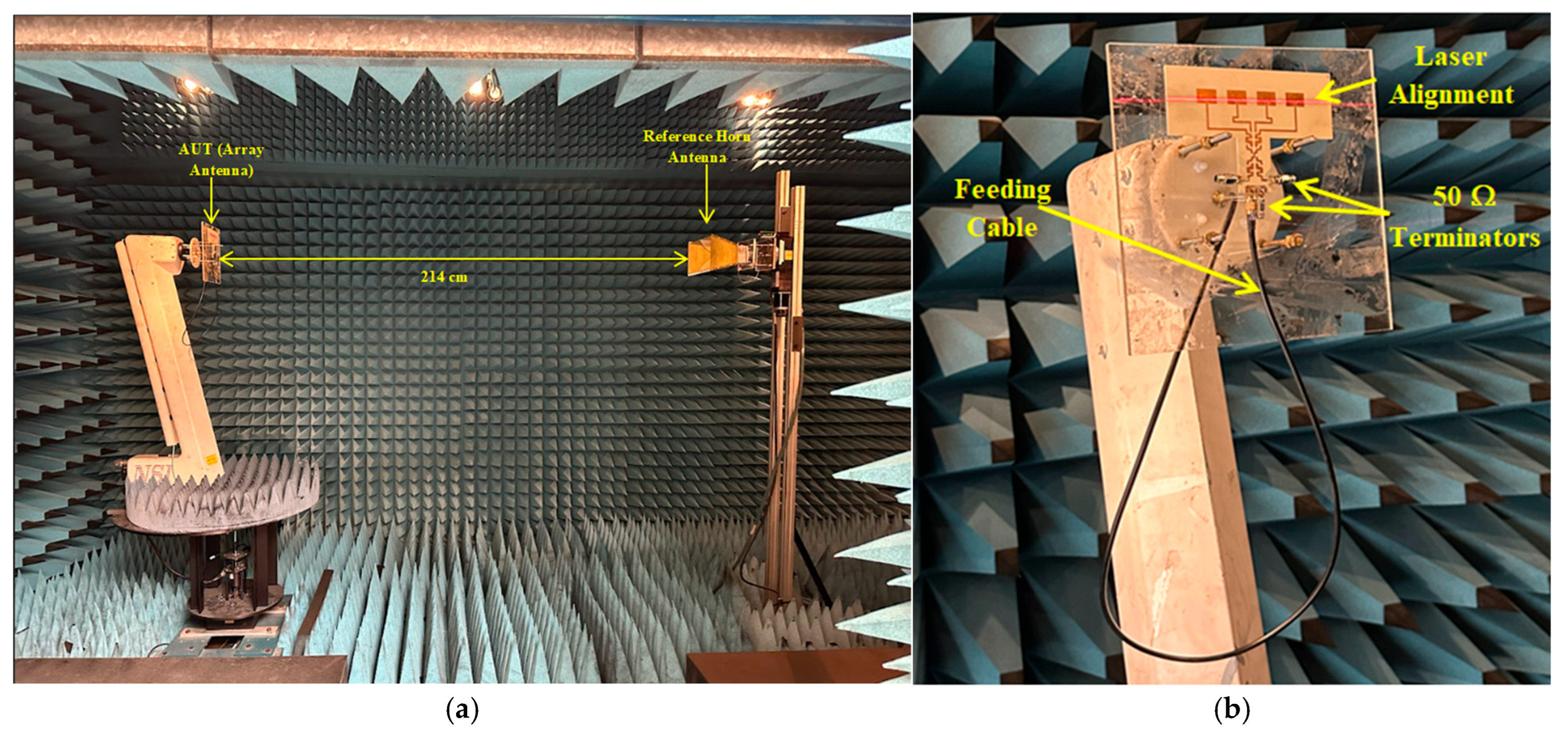
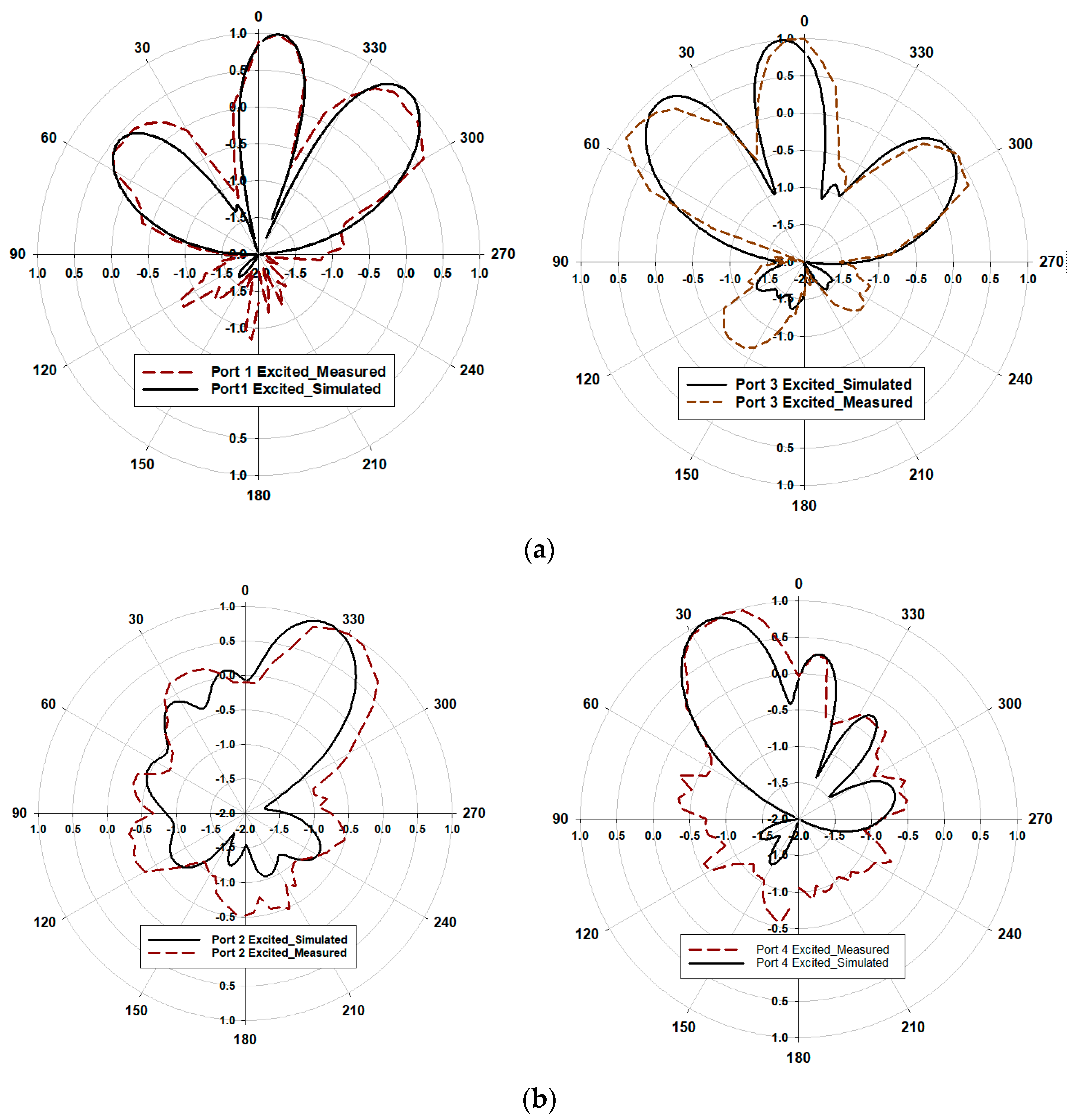
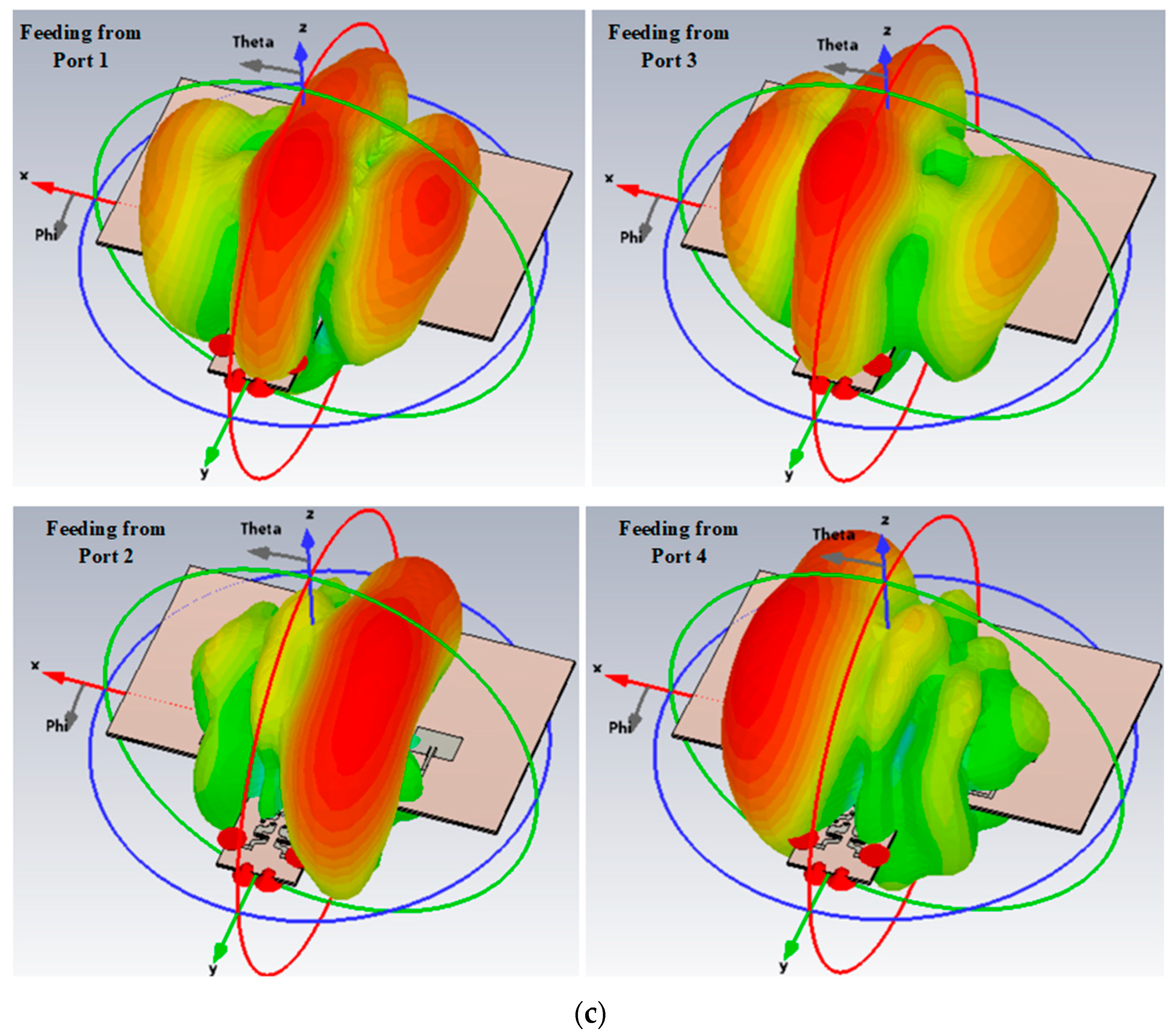
4. Compact Phased Array Antenna Configuration and Results Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews, J.G.; Buzzi, S.; Choi, W.; Hanly, S.V.; Lozano, A.; Soong, A.C.K. What will 5G be? IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallappil, A.K.; Rahim, M.K.A.; Khawaja, B.A.; Iqbal, M.N. Compact metamaterial based 4 × 4 butler matrix with improved bandwidth for 5G applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 3573–13583. [Google Scholar]
- Ojaroudi Parchin, N.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Jahanbakhsh Basherlou, H.; Abd-Alhameed, R.A.; Rodriguez, J.; Limiti, E. MM-Wave Phased Array Quasi-Yagi Antenna for the Upcoming 5G Cellular Communications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yoon, S.; Lee, Y.; Shin, H. A Miniaturized Butler Matrix Based Switched Beamforming Antenna System in a Two-Layer Hybrid Stackup Substrate for 5G Applications. Electronics 2019, 8, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lialios, D.I.; Ntetsikas, N.; Paschaloudis, K.D.; Zekios, C.L.; Georgakopoulos, S.V.; Kyriacou, G.A. Design of True Time Delay Millimeter Wave Beamformers for 5G Multibeam Phased Arrays. Electronics 2020, 9, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Shin, H. A 28-GHz Switched-Beam Antenna with Integrated Butler Matrix and Switch for 5G Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.H.; Saad, R.; Khamas, S.K. A Novel Compact Broadband Quasi-Twisted Branch Line Coupler Based on a Double-Layered Microstrip Line. Micromachines 2024, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik, P.; Moyra, T. Modelling and validation of a compact planar Butler matrix by removing crossover. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 95, 5121–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jizat, N.; Rahim, S.K.; Nor, M.Z.; Abdulrahman, Y.; Sabran, M.I.; Jamlos, M.F. Beamforming network using dual band-dual beam reduced size Butler Matrices. Radioengineering 2013, 22, 769. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Peng, H. Ultra-compact electromagnetic metamaterial transmission line and its application in miniaturized butler matrix. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2014, 55, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Fang, X.; Ding, K.; He, F. Miniaturization Design for 8 × 8 Butler Matrix Based on Back-to-Back Bilayer Microstrip. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2014, 583903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Bashir, A.; Ali, H.; Rauf, A.; Marey, M.; Mostafa, H.; Syed, A.I. Compact 28 GHz Millimeter Wave Antenna for Future Wireless Communication. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 72, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallah, A.B.; Zubir, F.; Rahim, M.K.A.; Jizat, N.M.; Basit, A.; Assaad, M. A Miniaturized Metamaterial-Based Dual-Band 4 × 4 Butler Matrix With Enhanced Frequency Ratio for Sub-6 GHz 5G Applications. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 32320–32333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, O.A.; Himdi, M. Single Layered 4 × 4 Butler Matrix Without Phase-Shifters and Crossovers. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 77289–77298. [Google Scholar]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H.; Wu, H.; Wu, W. Design and implementation of a compact planar 4 × 4 microstrip Butler matrix for wideband application. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2011, 24, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]






| Input Port 1 | Input Port 2 | Input Port 3 | Input Port 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Output port 5 () | 135° | 45° | 90° | 0° |
| Output port 6 () | 90° | 180° | −45° | 45° |
| Output port 7 () | 45° | −45° | 180° | 90° |
| Output port 8 () | 0° | 90° | −45° | 135° |
| Phase difference between consecutive output port | −45° | +135° | −135° | +45° |
| Input Port 1 | Input Port 2 | Input Port 3 | Input Port 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35.9 | 155.1 | 69.8 | 129.6 | |
| 155.1 | 98.7 | 129.6 | 10 | |
| 60.4 | 123.8 | 35.9 | 155.1 | |
| 123.8 | 10 | 154.1 | 98.7 |
| Input Port 1 | Input Port 2 | Input Port 3 | Input Port 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | 3.01 | 12.99 | 5.85 | 10.85 |
| (mm) | 12.99 | 8.27 | 10.85 | 0.84 |
| (mm) | 5.05 | 10.37 | 3.01 | 12.99 |
| (mm) | 10.37 | 0.84 | 12.91 | 8.27 |
| Scattering Parameters | Port 1 | Port 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sim. | Mea. | Sim. | Mea. | |||
| Return Loss (dB) | S11 | −19.8 | −16 | S22 | −21.9 | −12.35 |
| Transmission Coefficients (dB) | S51 | −8 | −8.8 | S52 | −6.25 | −7 |
| S61 | −6.48 | −4.64 | S62 | −6.13 | −5.65 | |
| S71 | −5.85 | −7.1 | S72 | −6.48 | −6.4 | |
| S81 | −6.53 | −5.77 | S82 | −7.9 | −8.4 | |
| Isolation Coefficients (dB) | S21 | −19.19 | −20.4 | S12 | −19 | −31 |
| S31 | −27.66 | −26.7 | S32 | −26.6 | −29.9 | |
| S41 | −27.9 | −28.8 | S42 | −26.2 | −24.6 | |
| Transmission Coefficient Phases (deg.) | ∠S51 | 13.08 | 15.2 | ∠S52 | 41.7 | 45.7 |
| ∠S61 | 41.9 | 56.8 | ∠S62 | 72.3 | 83.1 | |
| ∠S71 | 89.2 | 103.4 | ∠S72 | −62.14 | −56.9 | |
| ∠S81 | −61.9 | −44 | ∠S82 | 146.4 | 140.9 | |
| Ref | Matrix Size | Technology | Center Frq. GHz | Bandwidth (%) | Insertion loss (dB) | Isolation (dB) | Physical Area (mm2) | Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | 4 × 4 | lumped-distributed | 5 | 20 | 7.5 | 18 | 109 × 99 | 50 |
| [9] | 4 × 4 | Meandering | 2.4/5.8 | 18.42/15.5 | 8.9/10.9 | 16.8/25.1 | 96 × 125 | 63 |
| [10] | 4 × 4 | EM-MTM TLs | 0.86 | / | 7.2 | 28.7 | 109 × 89 | 80.9 |
| [13] | 4 × 4 | CRLH-TL | 3.47 | 14.6 | 7 ± 2 | 14 | 70 × 73.7 | 75 |
| [2] | 4 × 4 | Adding stubs | 6.5 | 8 | 7.5 | 20 | 130 × 73 | 42.6 |
| This Work | 4 × 4 | Quasi-2 Twisted BLC | 6.5 | 15 | 6.5 | 20 | 13.8 × 38.8 | 92.5 |
| Input Port | Maximum Beam Direction | Gain | Simulated Radiation Efficiency | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meas. | Simu. | Meas. | Simu. | ||
| Port 1 | −5 | −5 | 6.58 | 6.67 | 82.8% |
| Port 2 | −30 | −24 | 9.17 | 9.69 | 83.6% |
| Port 3 | 3 | 6 | 6.7 | 6.89 | 82.9% |
| Port 4 | 20 | 24 | 9.2 | 9.36 | 83.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, F.H.; Khamas, S.K. A Novel Compact Beamforming Network Based on Quasi-Twisted Branch Line Coupler for 5G Applications. Electronics 2025, 14, 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173565
Ahmed FH, Khamas SK. A Novel Compact Beamforming Network Based on Quasi-Twisted Branch Line Coupler for 5G Applications. Electronics. 2025; 14(17):3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173565
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Fayyadh H., and Salam K. Khamas. 2025. "A Novel Compact Beamforming Network Based on Quasi-Twisted Branch Line Coupler for 5G Applications" Electronics 14, no. 17: 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173565
APA StyleAhmed, F. H., & Khamas, S. K. (2025). A Novel Compact Beamforming Network Based on Quasi-Twisted Branch Line Coupler for 5G Applications. Electronics, 14(17), 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173565






