Active and Reactive Power Optimal Control of Grid-Connected BDFG-Based Wind Turbines Considering Power Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
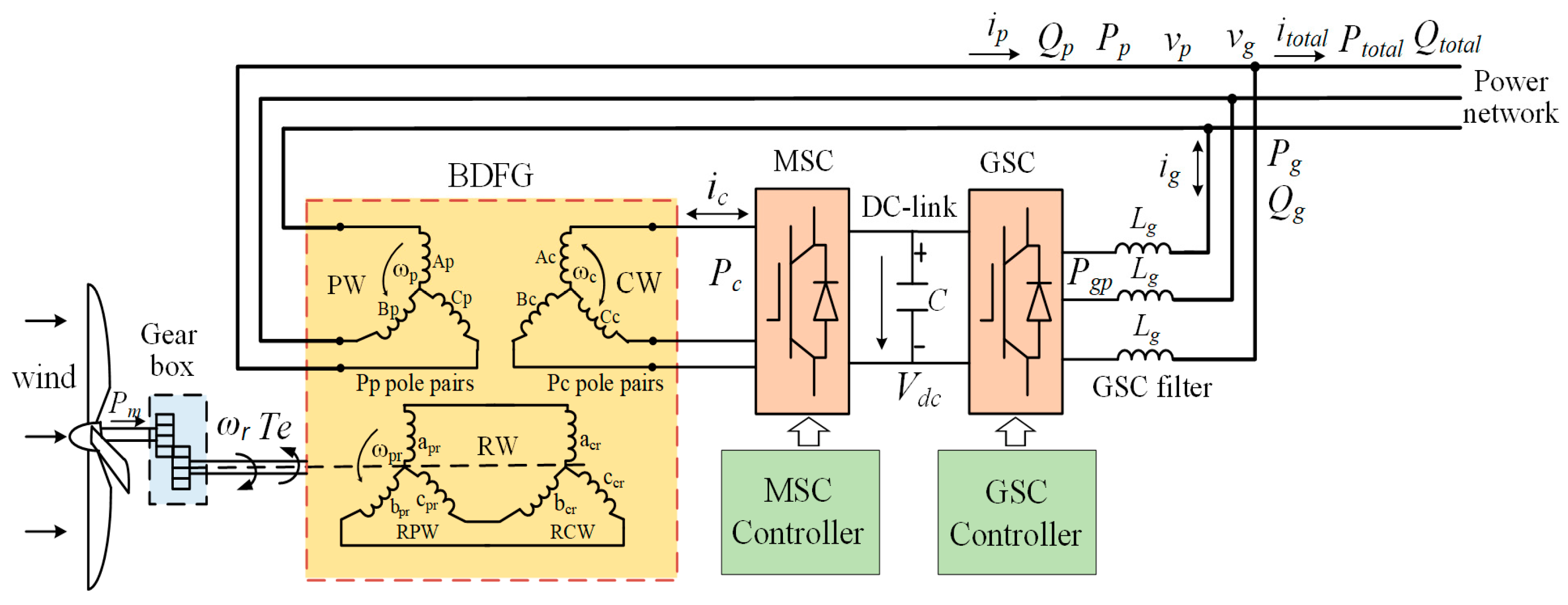
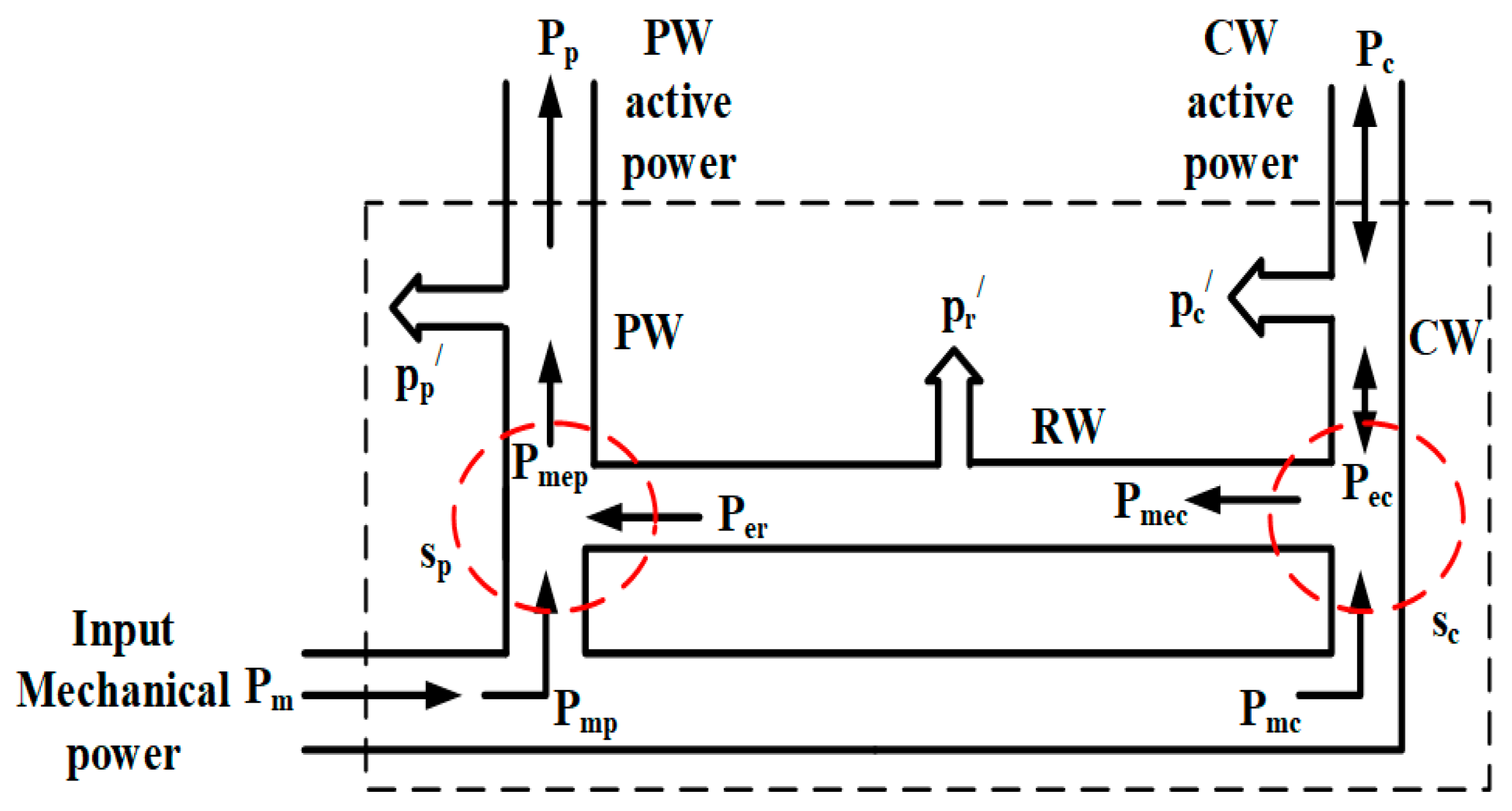
2. Mathematical Model of BDFGWT
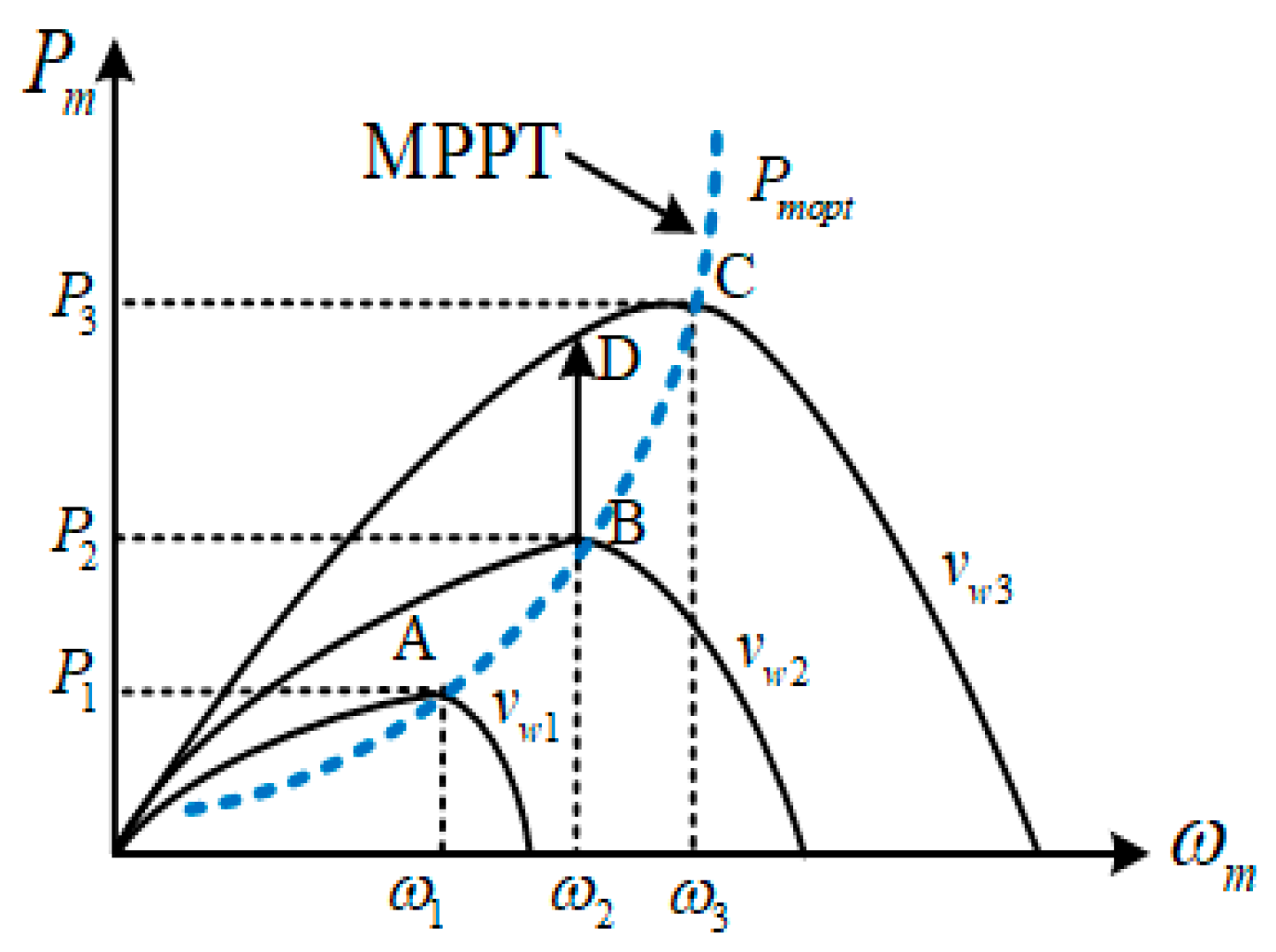
2.1. Model of Wind Turbine and MPPT
2.2. Mathematical Model of BDFG (MSC)
2.3. Mathematical Model of GSC
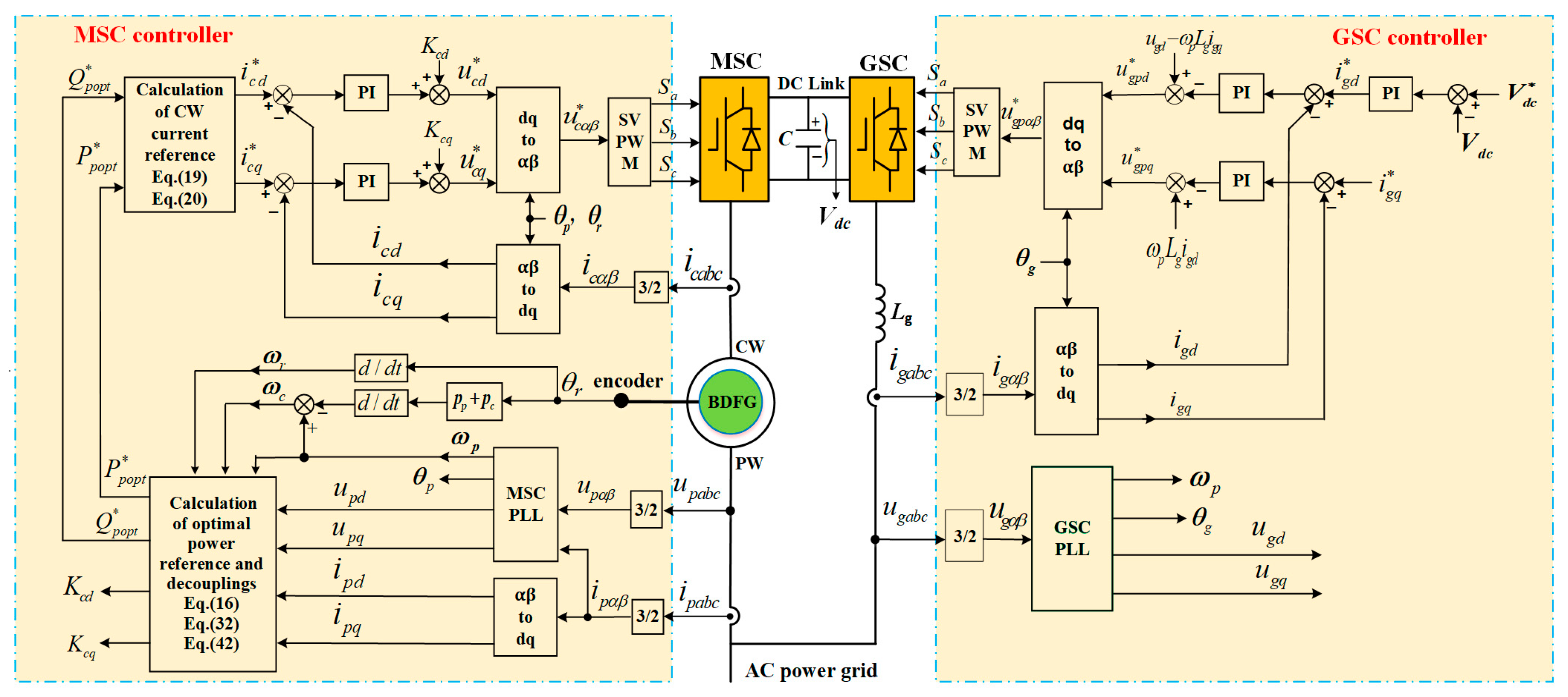
3. Proposed Active and Reactive Power Optimal Control of BDFGWT
3.1. Proposed MPPT Control and PW Active Power Control Reference Calculation
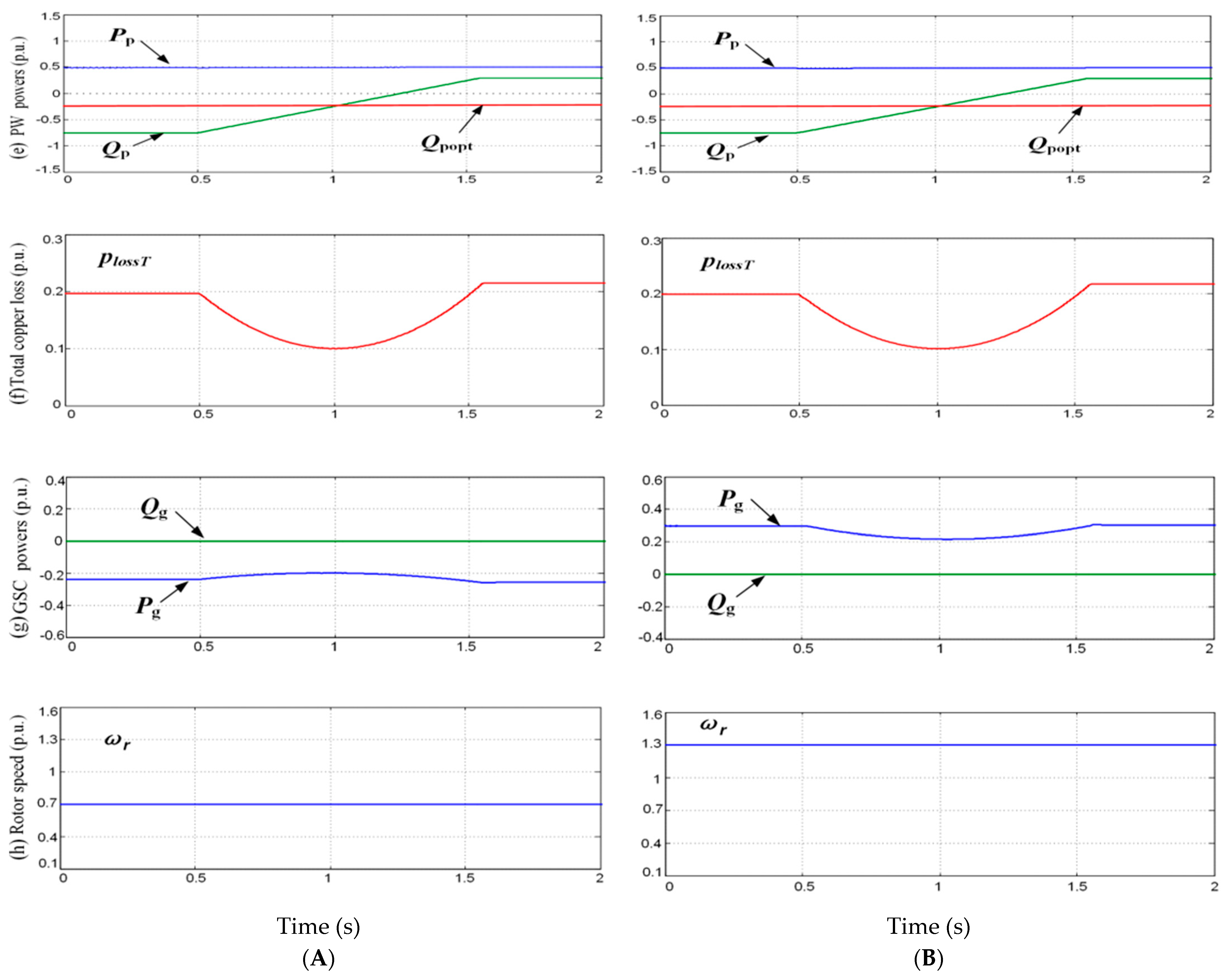
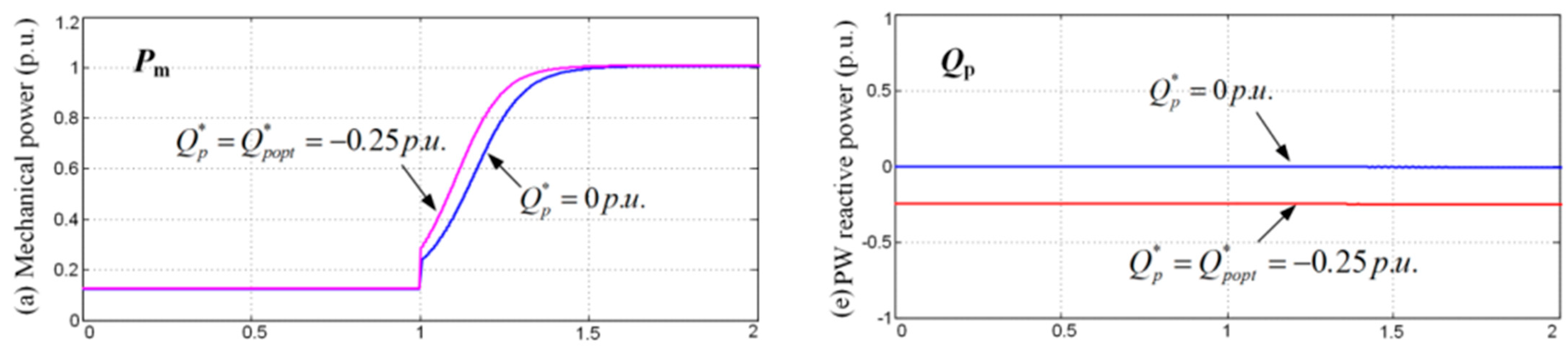
3.2. Optimal Reactive Power Control Reference Calculation
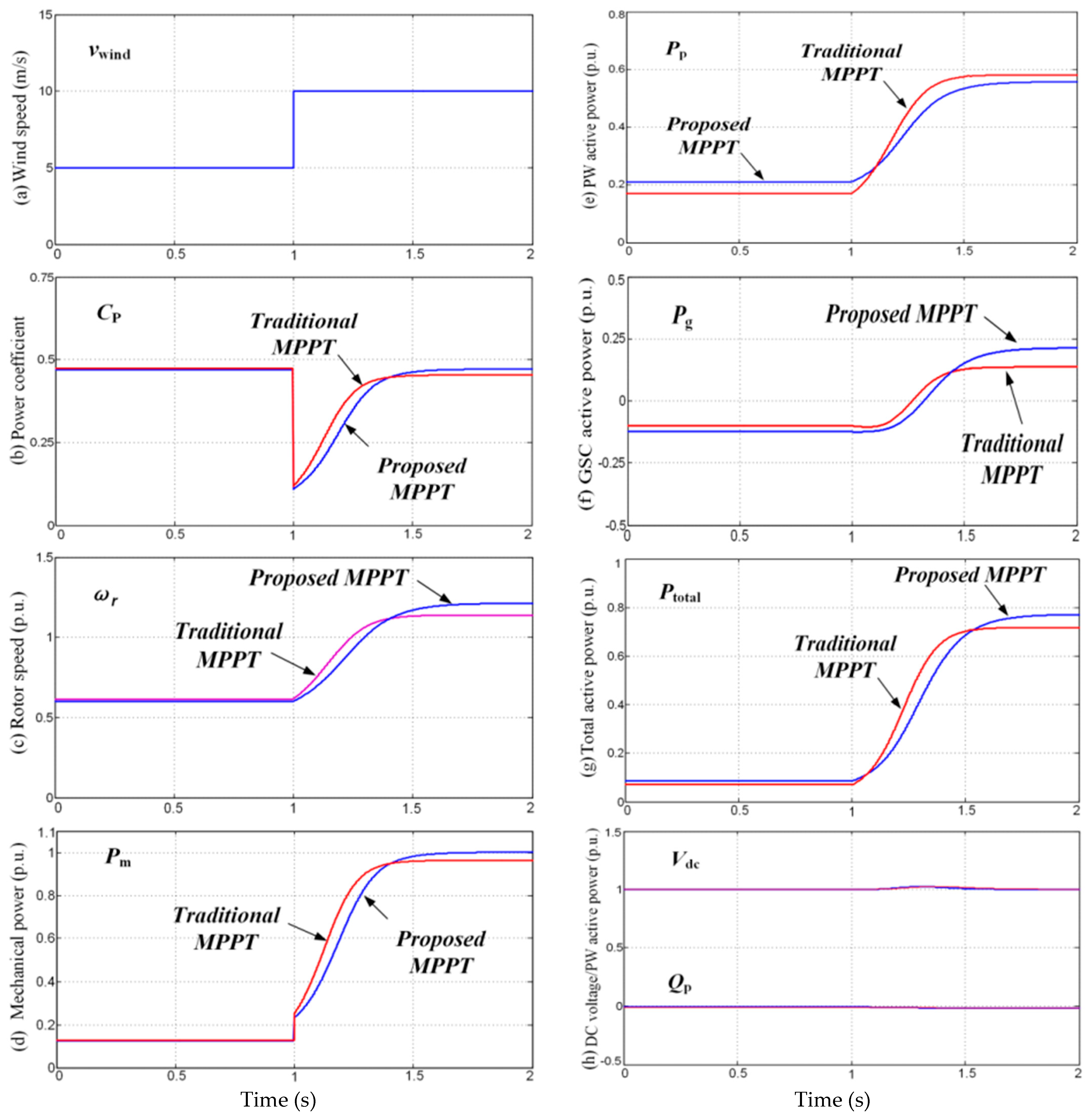
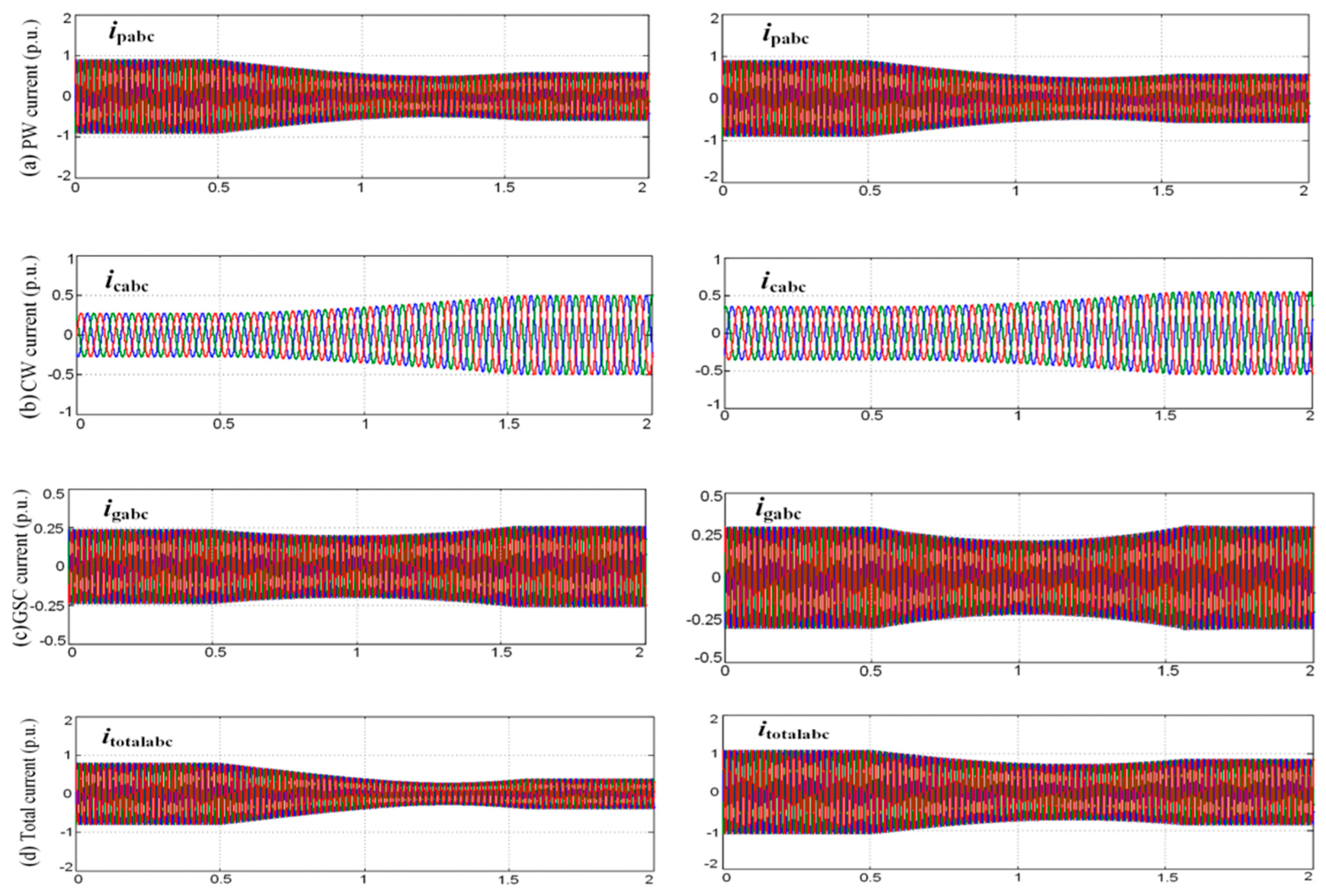
4. Simulation Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Rated power (MW) | 2 MW |
| Rated voltage (V) | 690 V |
| Rated frequency (Hz) | 50 Hz |
| rp, rc, rr (Ω) | 0.0036, 0.0072, 0.3965 |
| Lp, Lc, Lr (mH) | 3.1000, 6.8890, 19.050 |
| Lpr, Lcr (mH) | 6.6560, 4.8940 |
| Pole pairs (pp, pc) | 2, 2 |
| rg (Ω) | 3.1000 |
| Lg (mH) | 0.18 |
| C (uF) | 2000 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Rated power (MW) | 2 MW |
| Turbine diameter | 93.4 m |
| Cut-in wind speed | 3 m/s |
| Rated wind speed | 10.5 m/s |
| Gear ratio | 59 |
| System inertia | 60 Kg·m2 |
| Friction coefficient | 0.007 |
References
- Kim, K.; Van, T.; Lee, D.; Song, S.; Kim, E. Maximum output power tracking control in variable speed wind turbine systems considering rotor inertial power. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3207–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat, K.; Luis, M.; Tariq, K.; Shyam, K. A new hill climbing maximum power tracking control for wind turbines with inertial effect compensation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 60, 8545–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syahputra, R.; Soesanti, I. Performance improvement for small-scale wind turbine system based on maximum power point tracking control. Energies 2019, 12, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukianov, A.; Huerta, H. Energy based sliding mode control of brushless double-fed induction generator. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 130, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous Tim, D.; Polinder, H.; Ferreira, J.A. Brushless doubly-fed induction machines for wind turbines: Developments and research challenges. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowaid, I.A.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Massoud, A.M.; Ahmed, S. Ride through capability of grid-connected brushless cascade DFIG wind turbines in faulty grid conditions—A comparative study. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 1002–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Shao, S.; Abdi, E.; McMahon, R. Asymmetrical low-voltage ride through of brushless doubly fed induction generators for the wind power generation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Jiang, Y.; Han, P.; Wang, Q. Unbalanced and low-order harmonic voltage mitigation of stand-alone dual-stator brushless doubly fed induction wind generator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9135–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Mohammed, O.M.E.; Liu, Y.; Islam, M.D.R. Negative sequence voltage compensating for unbalanced standalone brushless doubly-fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhu, J.; Blaabjerg, F. Sensorless control of standalone brushless doubly fed induction generator feeding unbalanced loads in a ship shaft power generation system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Long, T.; Blaabjerg, F. An improved rotor speed observer for standalone brushless doubly-fed induction generator under unbalanced and nonlinear Loads. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Cheng, M.; Wei, X.; Li, N. Modeling and performance analysis of a dual-stator brushless doubly fed induction machine based on spiral vector theory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poza, J.; Oyarbide, E.; Sarasola, I.; Rodriguez, M. Vector control design and experimental evaluation for the brushless doubly fed machine. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2009, 3, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Abdi, E.; Barati, F.; McMahon, R. Stator-flux-oriented vector control for brushless doubly fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4220–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protsenko, K.; Xu, D. Modeling and control of brushless doubly-fed induction generators in wind energy applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic, D.; Zhu, J.G.; Boardman, G. Transient performance study of a brushless doubly fed twin stator induction generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2003, 18, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Long, T. Dynamic control of the brushless doubly fed induction generator under unbalanced operation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 2465–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, B.; Ma, Y. Improved vector control of brushless doubly fed induction generator under unbalanced grid conditions for offshore wind power generation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cheng, M.; Wei, X.; Yan, X.; Zeng, Y. Dual synchronous rotating frame current control of brushless doubly fed induction generator under unbalanced network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 36, 6712–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufik, T.; Leposava, R.; Milutin, J. Dynamic Modeling and Control of BDFRG under Unbalanced Grid Conditions. Energies 2021, 14, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Liu, H.; Hu, S.; Sun, G.; Wang, E.; Tang, J. A Proportional-Integral-Resonant Current Control Strategy for a Wind-Driven Brushless Doubly Fed Generator during Network Unbalance. Electronics 2024, 13, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhu, G. Enhanced control and operation for brushless doubly-fed induction generator basedwind turbine system under grid voltage unbalance. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 207, 117861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhu, G.; Kang, Y. Modeling and coordinated control design for brushless doubly-fed induction generator based wind turbine to withstand grid voltage unbalance. IEEE Access 2021, 36, 63331–63344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Chen, R.; Hu, S.; Sun, G.; Wang, E.; Tang, J. An Improved Collaborative Control Scheme to Resist Grid Voltage Unbalance for BDFG-BasedWind Turbine. Electronics 2024, 13, 3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voltolini, H.; Carlson, R. Grid synchronization and maximum power point tracking for wind energy generation system with brushless doubly fed induction generator. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics, Orlando, FL, USA, 10–13 November 2008; pp. 2173–2177. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Huang, J.; Sang, S. Innovative Inertial Response Imitation and Rotor Speed Recovery Control Scheme for a DFIG. Electronics 2023, 12, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Maity, T. A novel application of adaptive filtering algorithm for LVRT capability enhancement of grid-connected DFIG-based wind energy conversion systems (WECS). Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 217, 109179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Cheng, M.; Wei, X.; Xu, L. Dynamic modeling and performance analysis with iron saturation for dual-stator brushless doubly fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Hu, S.; Cai, D.; Liu, H.; Xu, D.; Ma, L.; Tang, J. Active and Reactive Power Optimal Control of Grid-Connected BDFG-Based Wind Turbines Considering Power Loss. Electronics 2025, 14, 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173544
Wang W, Zhang L, Hu S, Cai D, Liu H, Xu D, Ma L, Tang J. Active and Reactive Power Optimal Control of Grid-Connected BDFG-Based Wind Turbines Considering Power Loss. Electronics. 2025; 14(17):3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173544
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenna, Liangyi Zhang, Sheng Hu, Defu Cai, Haiguang Liu, Dian Xu, Luyu Ma, and Jinrui Tang. 2025. "Active and Reactive Power Optimal Control of Grid-Connected BDFG-Based Wind Turbines Considering Power Loss" Electronics 14, no. 17: 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173544
APA StyleWang, W., Zhang, L., Hu, S., Cai, D., Liu, H., Xu, D., Ma, L., & Tang, J. (2025). Active and Reactive Power Optimal Control of Grid-Connected BDFG-Based Wind Turbines Considering Power Loss. Electronics, 14(17), 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173544









