An Intelligent Educational System: Analyzing Student Behavior and Academic Performance Using Multi-Source Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Student Behavior Analysis
2.2. LLMs and AI Agents
2.3. Summary and Research Objectives
3. Dataset Construction
3.1. Participants
3.2. Procedure
- Data Extraction and Integration
- b.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing
- c.
- Temporal and Behavioral Alignment
- d.
- Feature Engineering
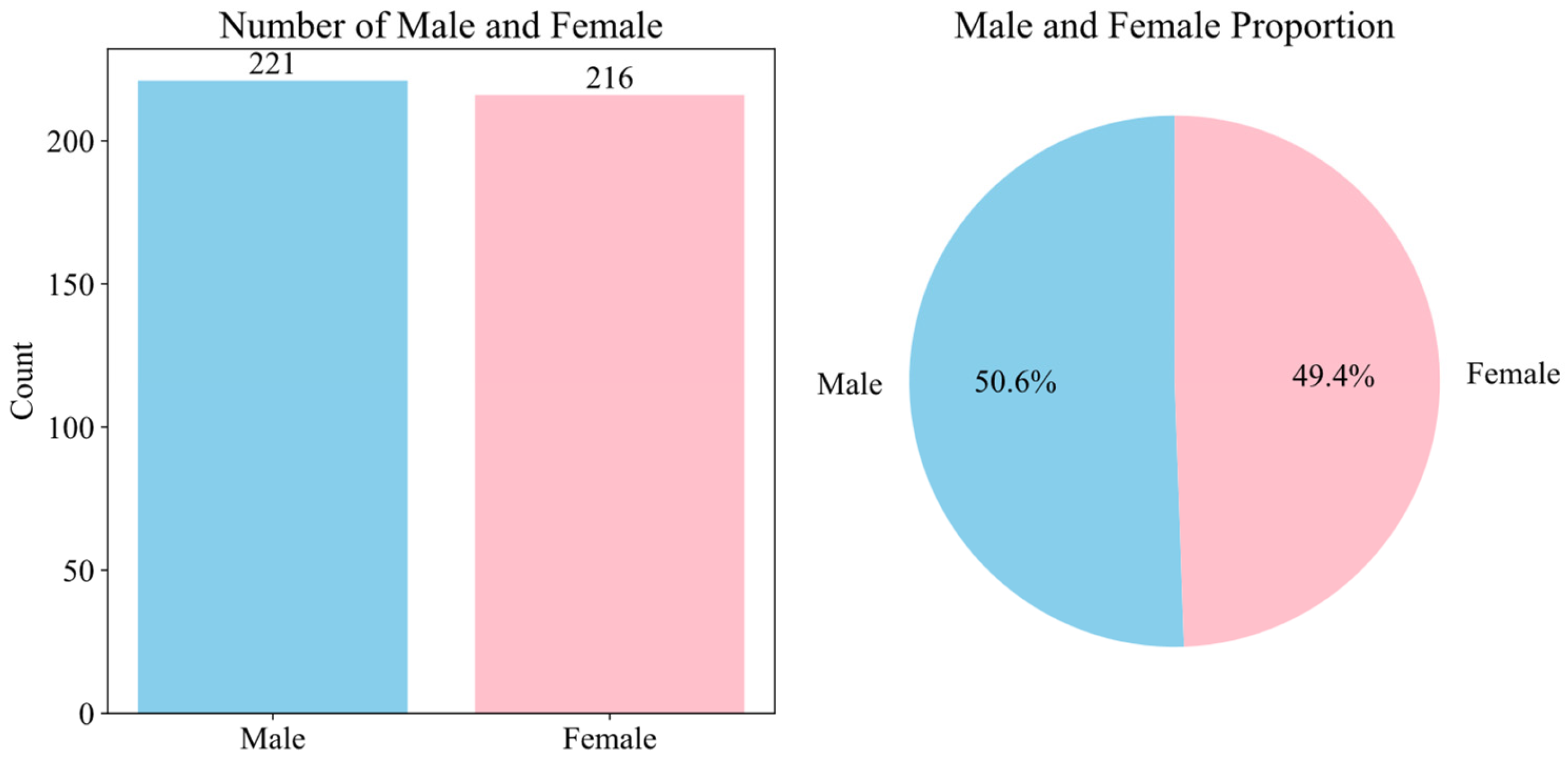
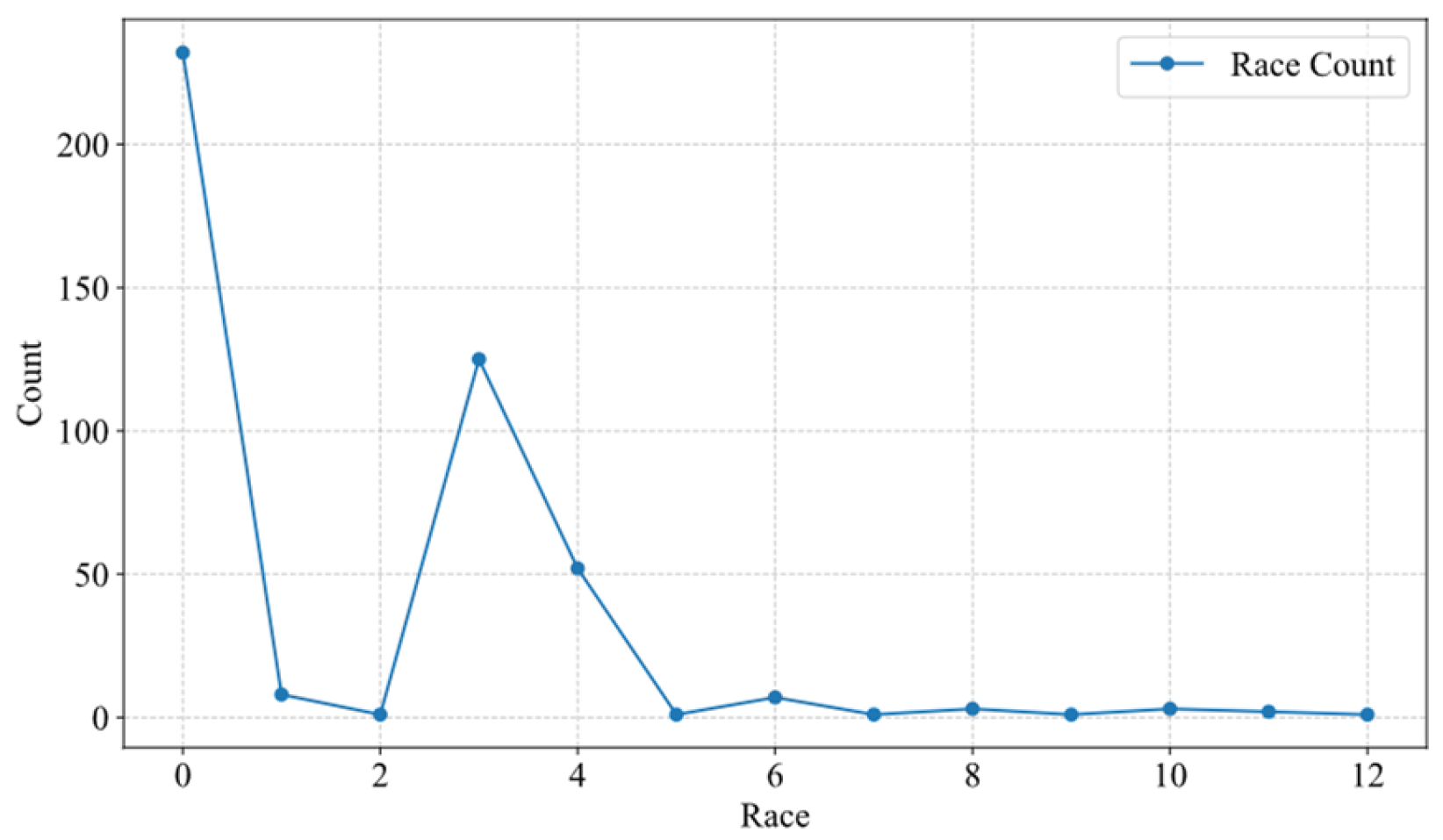
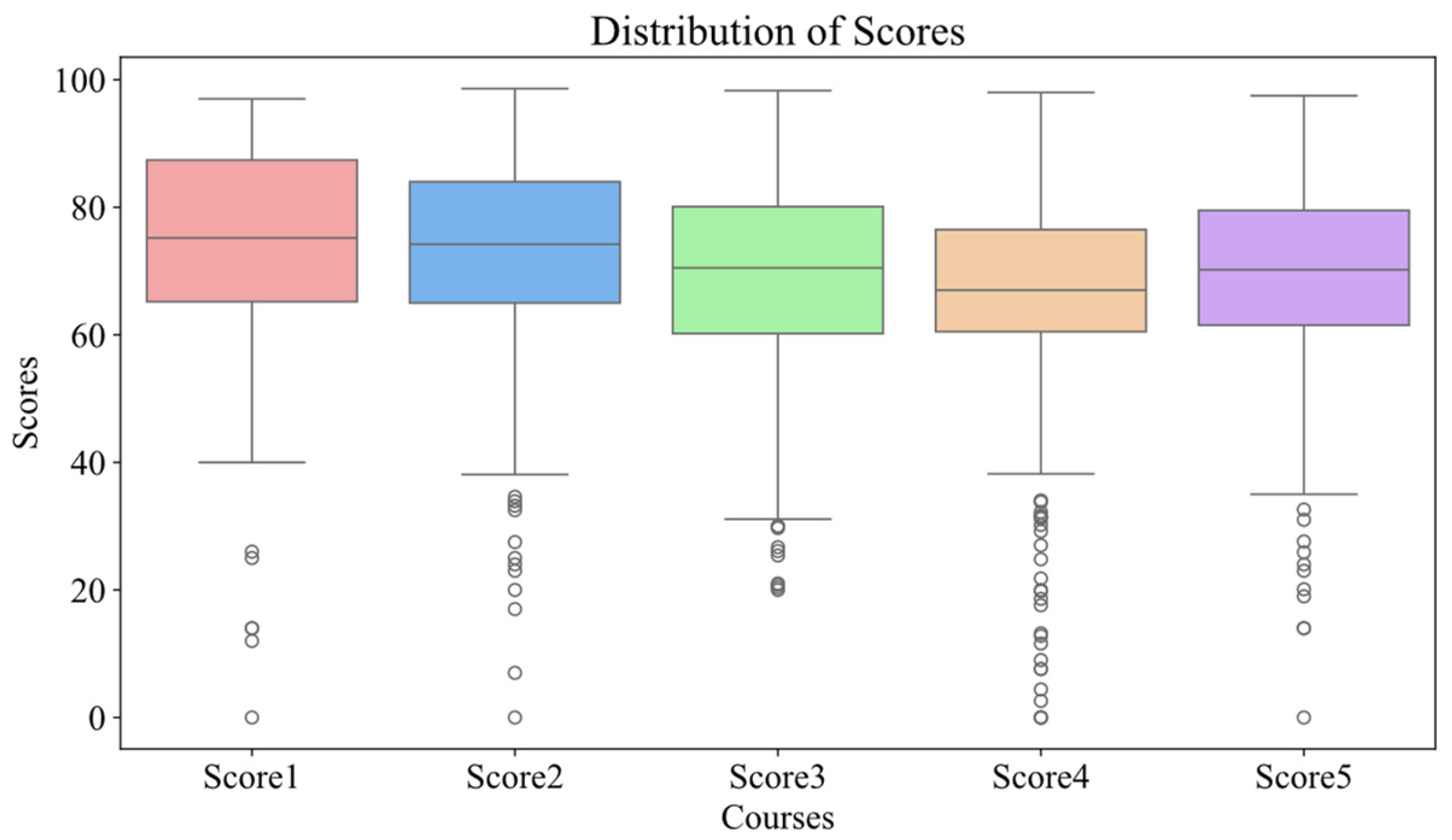
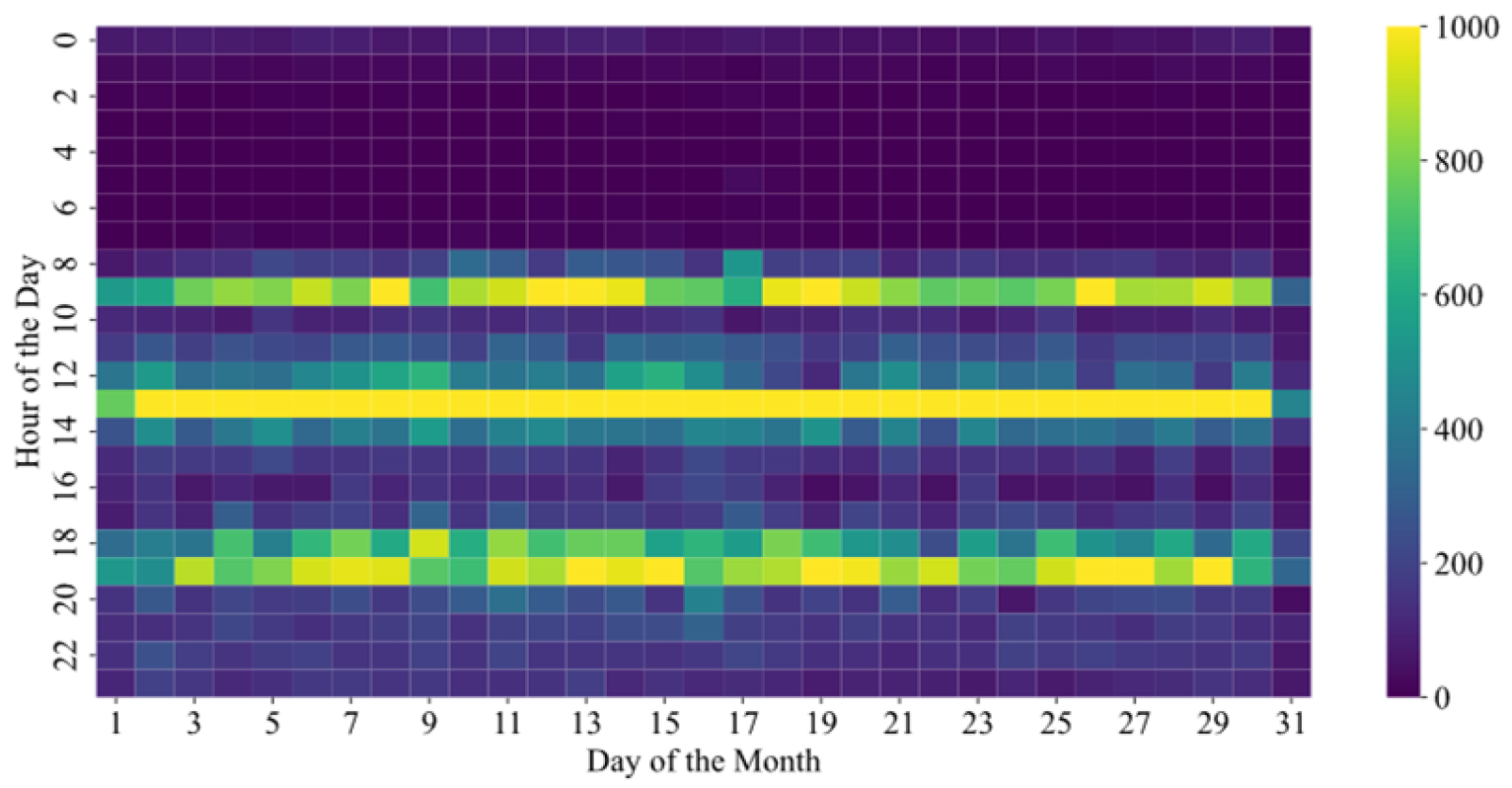
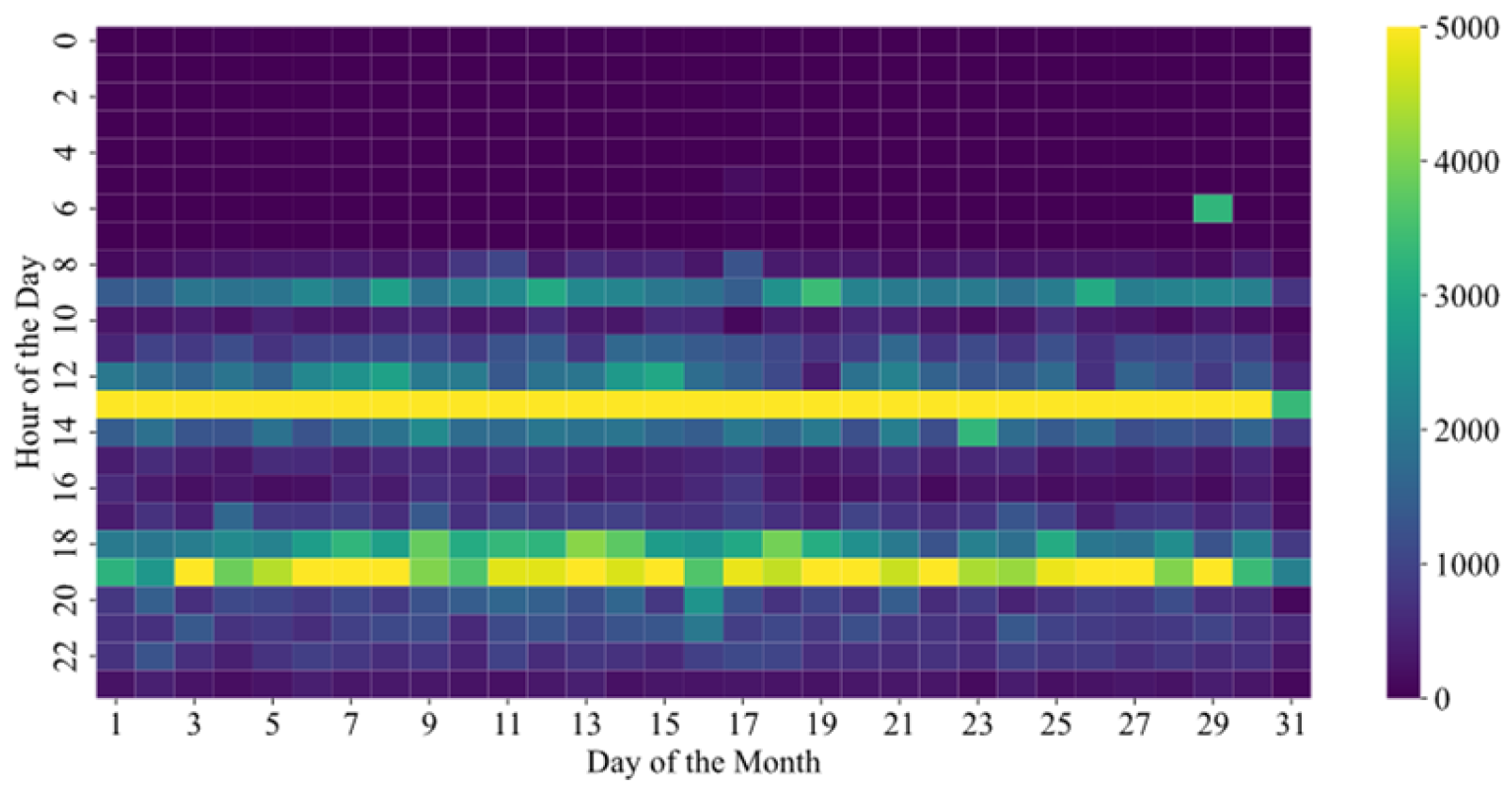
3.3. Data Analysis and Visualization
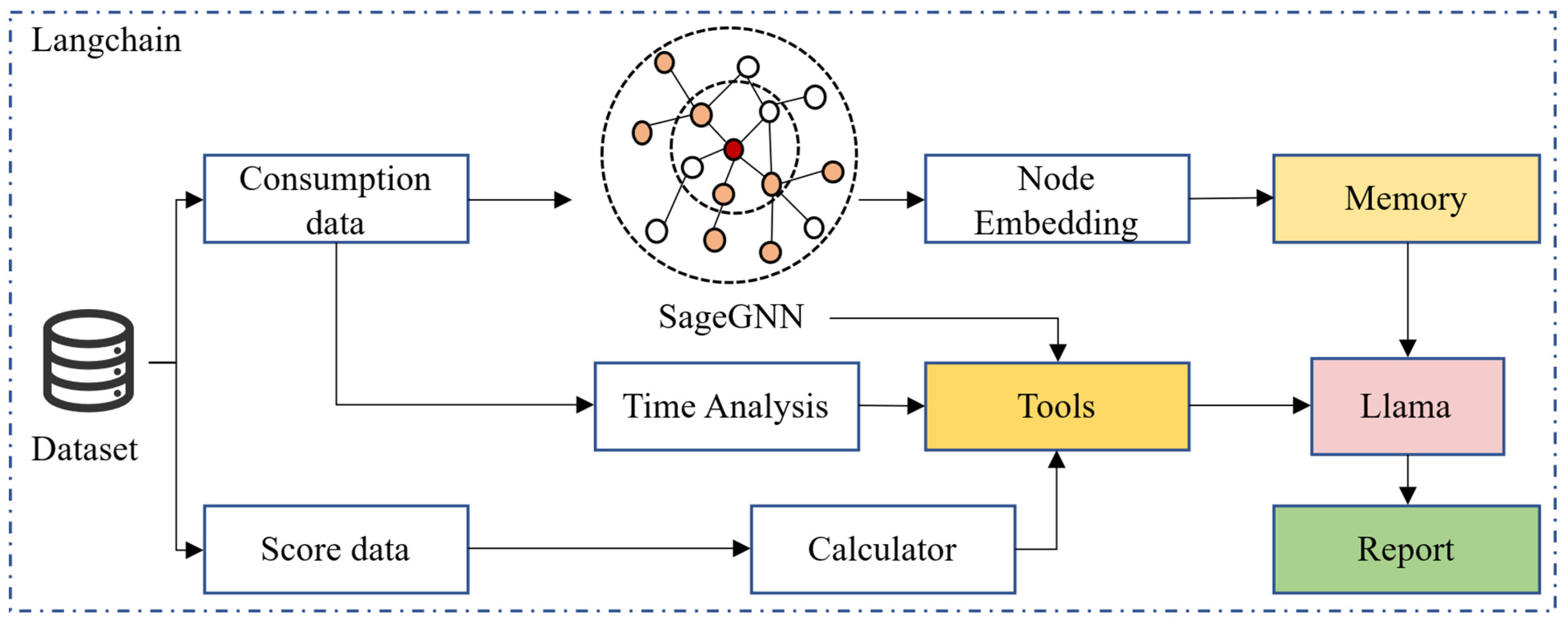
4. Method
4.1. Model Architecture
4.2. Experimental Setup and Evaluation
4.2.1. Incremental Pretraining of Models
4.2.2. Agent Workflow
| Algorithm 1. The Workflow |
| Input: C_curr—Current semester consumption data C_prev—Previous semester consumption data S_curr—Current semester academic scores S_prev—Previous semester academic scores Output: Student behavior analysis report 1: function EMBED_INFO(C): 2: return SageGNN(C) // Generate consumption embeddings using SageGNN 3: function CALCULATE_DISTANCE(E_curr, E_prev): 4: return EuclideanDistance(E_curr, E_prev) 5: function COMPUTE_REGULARITY(C): 6: F ← FourierTransform(C.time_series) 7: E ← InformationEntropy(C.time_series) 8: return WeightedScore(F, E) 9: function SCORE_CLASSIFICATION(S_curr, S_prev): 10: Δ ← CompareScores(S_curr, S_prev) 11: return ClassifyPerformance(Δ) 12: procedure AGENT_WORKFLOW(C_curr, C_prev, S_curr, S_prev) 13: E_curr ← EMBED_INFO(C_curr) 14: E_prev ← EMBED_INFO(C_prev) 15: D ← CALCULATE_DISTANCE(E_curr, E_prev) 16: R ← COMPUTE_REGULARITY(C_curr) 17: P ← SCORE_CLASSIFICATION(S_curr, S_prev) 18: Report ← LLM.invoke(D, R, P) 19: return Report |
4.2.3. SageGNN
4.2.4. The Analysis of Time Consumption
4.2.5. Performance Analysis
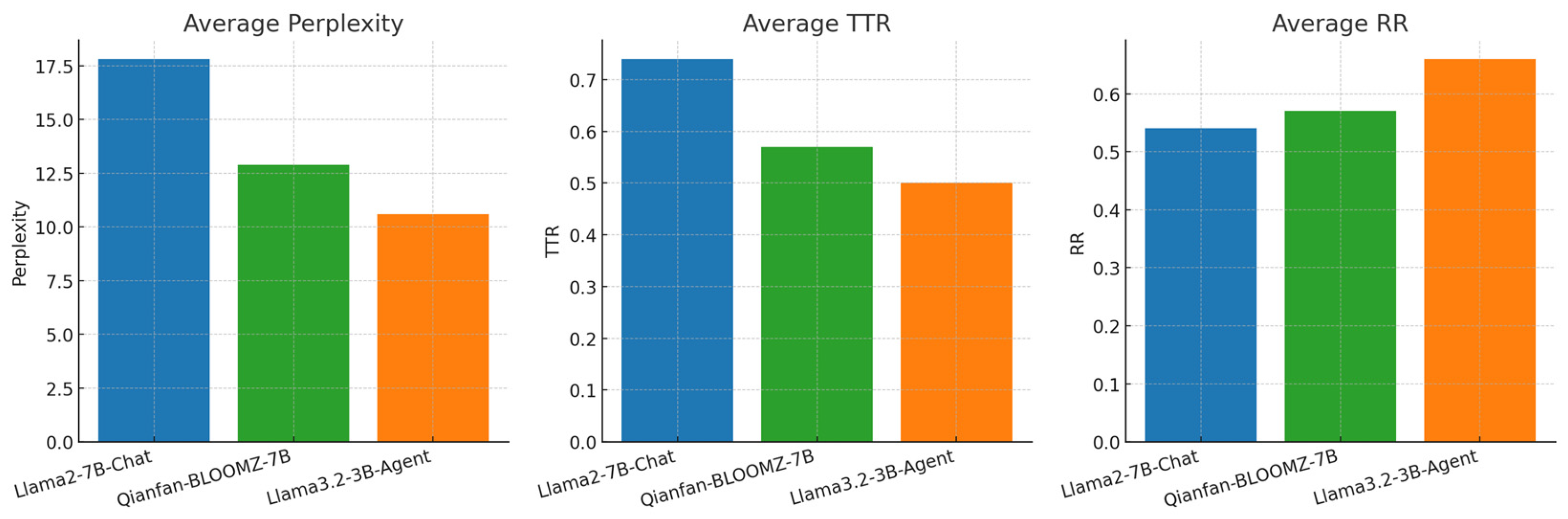
4.3. Experimental Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Similarities with State-of-the-Art Approaches
5.2. Differences and Contributions
5.3. Interpretation of Differences
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mubarak, A.A.; Cao, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W. Visual analytics of video-clickstream data and prediction of learners’ performance using deep learning models in MOOCs’ courses. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2021, 29, 710–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizani, S.; Mazhar, T.; Shahzad, T.; Ahmad, W.; Bibi, A.; Hamam, H. A systematic literature review to implement large language model in higher education: Issues and solutions. Discov. Educ. 2025, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhao, Z. EAGER-LLM: Enhancing large language models as recommenders through exogenous behavior-semantic integration. In Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2025, Sydney, Australia, 28 April–2 May 2025; pp. 2754–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G.; Pu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; et al. When large language models meet personalization: Perspectives of challenges and opportunities. World Wide Web 2024, 27, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razafinirina, M.A.; Dimbisoa, W.G.; Mahatody, T. Pedagogical alignment of large language models (llm) for personalized learning: A survey, trends and challenges. J. Intell. Learn. Syst. Appl. 2024, 16, 448–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigbu, B.I.; Ngwevu, V.; Jojo, A. The effectiveness of innovative pedagogy in the industry 4.0: Educational ecosystem perspective. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 2023, 7, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivokostopoulou, F.; Perikos, I.; Hatzilygeroudis, I. Utilizing semantic web technologies and data mining techniques to analyze students learning and predict final performance. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Teaching, Assessment and Learning for Engineering (TALE), Wellington, New Zealand, 8–10 December 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andergassen, M.; Mödritscher, F.; Neumann, G. Practice and repetition during exam preparation in blended learning courses: Correlations with learning results. J. Learn. Anal. 2014, 1, 48–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, E.; Oyelere, S.S.; Gaftandzhieva, S.; Rajesh, K.N.V.P.S.; Jagatheesaperumal, S.K.; Mohamed, A.; Elbarawy, Y.M.; Desuky, A.S.; Hussain, S.; Cifci, M.A.; et al. Educational data mining: A 10-year review. Discov. Comput. 2025, 28, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Martinez, H.; Khan, B.; Hasan, M.R. A Three-Tier LLM Framework for Forecasting Student Engagement from Qualitative Longitudinal Data. In Proceedings of the 29th Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, Vienna, Austria, 31 July–1 August 2025; ACL: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Chaurasia, D.V. Performance analysis of students consuming alcohol using data mining techniques. Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci. Eng. 2017, 6, 238–250. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S. Applying data mining techniques with data of campus card system. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 715, p. 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durachman, Y.; Rahman, A.W.B. A Clustering Student Behavioral Patterns: A Data Mining Approach Using K-Means for Analyzing Study Hours, Attendance, and Tutoring Sessions in Educational Achievement. Artif. Intell. Learn. 2025, 1, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Duan, J.; Xu, K.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. A survey on large language model (llm) security and privacy: The good, the bad, and the ugly. High-Confid. Comput. 2024, 4, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annepaka, Y.; Pakray, P. Large language models: A survey of their development, capabilities, and applications. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2025, 67, 2967–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.J.; Murty, M.R.; Navakanth, I. A detailed review on word embedding techniques with emphasis on word2vec. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 37979–38007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.X.; Tu, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, A.J.; Laskar, M.T.R.; Bhuiyan, A. Utilizing BERT for Information Retrieval: Survey, Applications, Resources, and Challenges. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, A.; Liang, J.; Gui, Z.; Guan, X.; Li, R.; Wu, H. GeoCode-GPT: A large language model for geospatial code generation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 138, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyan, K.S. A survey of GPT-3 family large language models including ChatGPT and GPT-4. Nat. Lang. Process. J. 2024, 6, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.R.; Rathi, I.; Taylor, S.; Bergen, B.K. People cannot distinguish GPT-4 from a human in a Turing test. In Proceedings of the 2025 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Athens, Greece, 23–26 June 2025; pp. 1615–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lv, C.; Zhu, K.; Qiu, X. LoRA fine-tuning of Llama3 large model for intelligent fishery field. Discov. Comput. 2025, 28, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, G. A comparative study of six indigenous Chinese Large Language Models’ understanding ability: An assessment based on 132 college entrance examination objective test items. Res. Sq. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, S.; Yang, M.; Tang, B.; Xiong, F.; Li, Z. Attention heads of large language models. Patterns 2025, 6, 101176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.; Huang, D.; Xu, Q.; Lin, M.; Liu, Y.J.; Huang, G. Expel: Llm agents are experiential learners. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, NA, Canada, 26–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 19632–19642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J.; Chen, J.; Qian, G.; Elhoseiny, M.; Ghanem, B. Llm as a robotic brain: Unifying egocentric memory and control. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.09349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Li, X.; Wen, L.; Dou, M.; Cai, P.; Shi, B.; Qiao, Y. Drive like a human: Rethinking autonomous driving with large language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 1–6 January 2024; pp. 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topsakal, O.; Akinci, T.C. Creating large language model applications utilizing langchain: A primer on developing llm apps fast. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Engineering and Natural Sciences, Konya, Turkey, 10–12 July 2023; Volume 1, pp. 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ong, G.P.; Chen, X. GraphSAGE-based traffic speed forecasting for segment network with sparse data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 23, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Design and implementation of vehicle type recognition system based on language large model. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Internet of Things, Automation and Artificial Intelligence (IoTAAI), Guangzhou, China, 26–28 July 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Source | Student Behavior Data |
|---|---|
| SMS | ID |
| Gender | |
| Race | |
| Area | |
| Age | |
| CCS | Transaction_Time |
| Transaction_Amount | |
| Card_Balance | |
| Number_Uses | |
| Operation_Type | |
| POS_Number | |
| System_Code | |
| Counterparty_Account_Number | |
| APMS | Major |
| Score 1–5 | |
| Grade | |
| Semester |
| Models | Perplexity | TTR | RR | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama2-7B-Chat | 17.25 | 0.75 | 0.51 | 0.72 |
| 17.96 | 0.72 | 0.52 | 0.70 | |
| 18.23 | 0.75 | 0.59 | 0.74 | |
| Qianfan-BLOOMZ-7B | 12.41 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.76 |
| 15.96 | 0.64 | 0.5 | 0.71 | |
| 10.26 | 0.49 | 0.65 | 0.78 | |
| Llama3.2-3B-Agent | 12.64 | 0.47 | 0.69 | 0.82 |
| 10.26 | 0.51 | 0.65 | 0.80 | |
| 8.85 | 0.52 | 0.64 | 0.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Liu, Z. An Intelligent Educational System: Analyzing Student Behavior and Academic Performance Using Multi-Source Data. Electronics 2025, 14, 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163328
Li H, Liu Z. An Intelligent Educational System: Analyzing Student Behavior and Academic Performance Using Multi-Source Data. Electronics. 2025; 14(16):3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163328
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haifang, and Zhandong Liu. 2025. "An Intelligent Educational System: Analyzing Student Behavior and Academic Performance Using Multi-Source Data" Electronics 14, no. 16: 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163328
APA StyleLi, H., & Liu, Z. (2025). An Intelligent Educational System: Analyzing Student Behavior and Academic Performance Using Multi-Source Data. Electronics, 14(16), 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163328






