Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on ISFOA-SVM
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- An improved version of the superb fairy-wren optimization algorithm (ISFOA) is proposed to optimize the hyperparameters of the SVM model. This enhancement significantly improves the algorithm’s convergence performance and global search ability.
- 2.
- Based on the Markov chain model, the convergence analysis of ISFOA is presented.
- 3.
- A hybrid forecasting model named ISFOA-SVM is constructed by integrating ISFOA with SVM, which effectively addresses the parameter sensitivity issue in traditional SVM and enhances prediction accuracy.
- 4.
- The proposed ISFOA-SVM model is applied to short-term wind power forecasting, demonstrating superior performance in terms of prediction accuracy, stability, and generalization compared to existing benchmark models.
- 5.
- Extensive experiments are conducted on real-world wind power datasets, and the results validate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method under different weather and operational conditions.
2. Support Vector Machine
3. Improved Superb Fairy-Wren Optimization Algorithm
3.1. Original Superb Fairy-Wren Optimization Algorithm
3.1.1. Initialization Strategy
3.1.2. Phase I: Growth Phase of Young Birds
3.1.3. Phase II: Feeding and Breeding Phase
3.1.4. Phase III: Predator Avoidance Phase
3.2. Improved Superb Fairy-Wren Optimization Algorithm
3.2.1. Adaptive Learning Factor
3.2.2. Differential Evolution Strategy
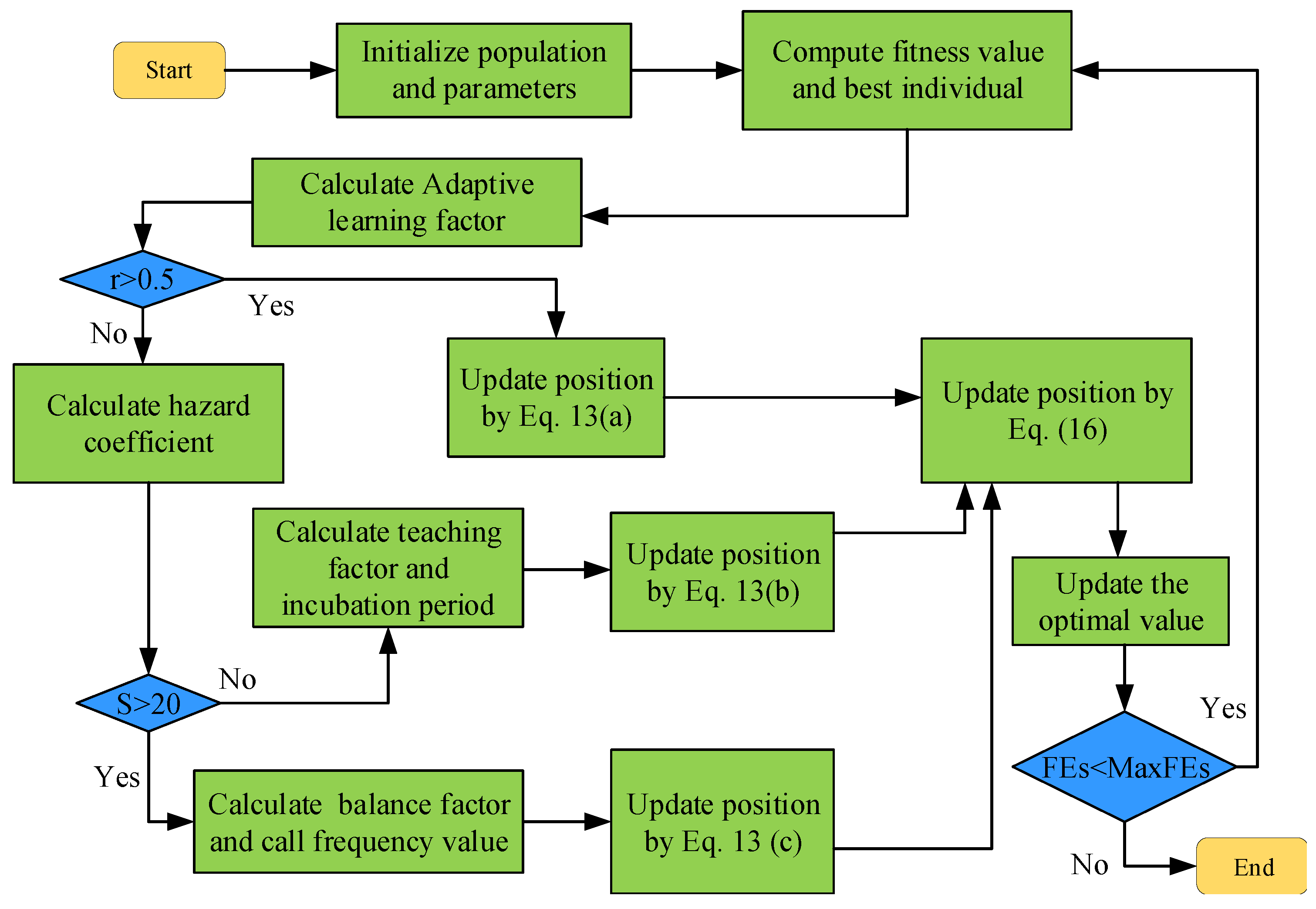
3.2.3. Flowchart of the Improved Algorithm
- Parameter Initialization: Set the maximum number of iterations (MaxFEs), problem dimension (d), population size (), and the bounds of decision variables (, ).
- Fitness Evaluation of Initial Population: Evaluate the fitness values of all individuals in the initial population and identify the best-performing solution.
- Position Update (Growth Phase of Young Birds):
- –
- If , update positions using Equation (13a).
- Danger Threshold Assessment and Response:
- Differential Evolution Strategy Application: Apply the DE mutation and crossover operations described above to each individual.
- Fitness Re-evaluation: Recalculate the fitness values of the updated population and update the best solution.
- Termination Check: If the stopping criterion (e.g., reaching MaxFEs) is satisfied, terminate the algorithm and return the best solution found so far.
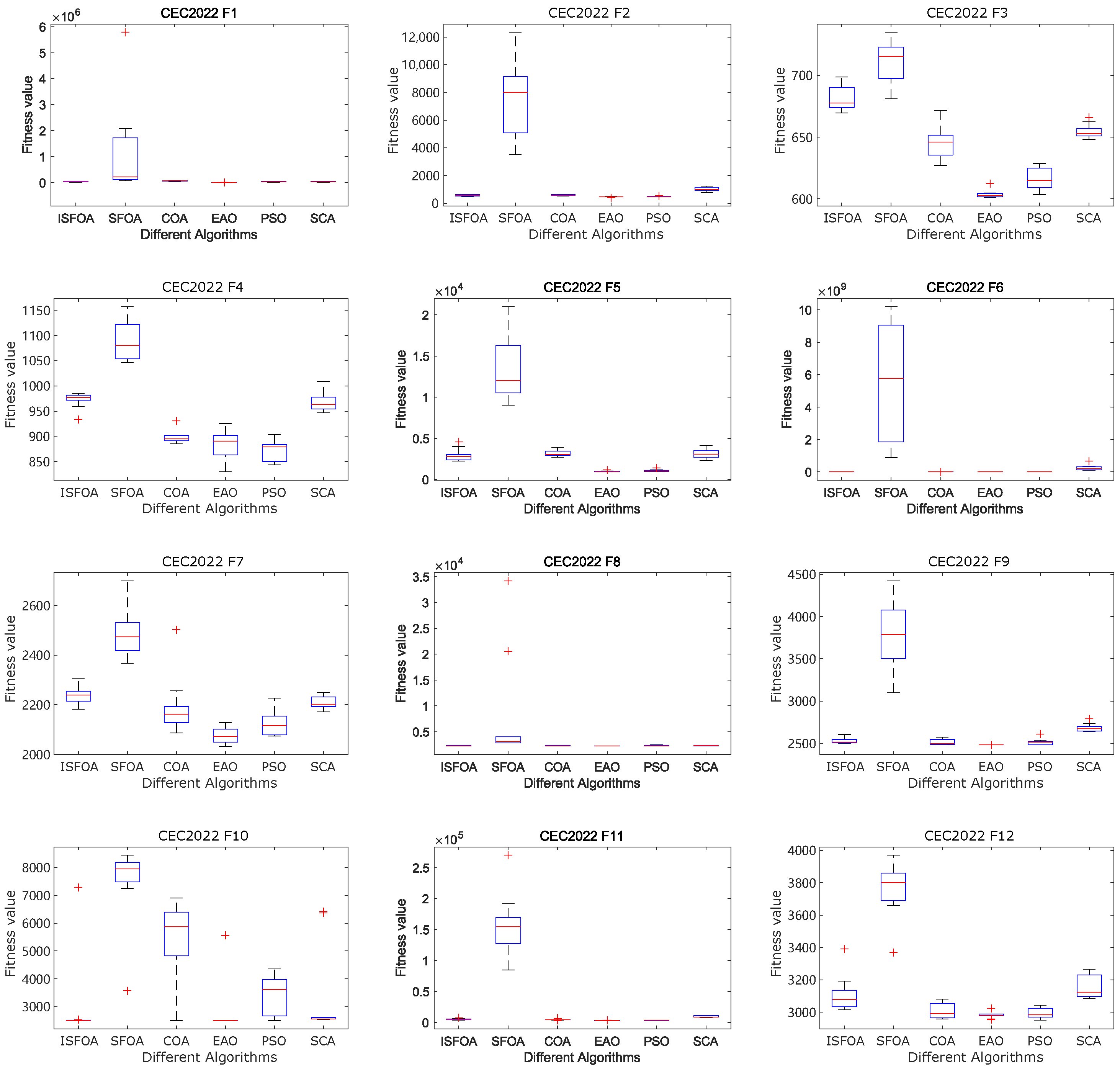
3.3. Performance Evaluation of ISFOA on CEC2022
4. Global Convergence Analysis of ISFO
4.1. Stochastic Process Modeling of the Algorithm
4.2. Definition of Absorbing State
4.3. Positive Transition Probability
- 1.
- Adaptive Learning Factor
- 2.
- DE/best/1 mutation Strategy and Lévy Flight
- 3.
- Selection Operation
4.4. Proof of Global Convergence Theorem
4.5. Enhancement of Convergence Through Improved Strategies
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
5.1. Experimental Procedure
5.1.1. Dataset Source
5.1.2. Data Processing
5.1.3. Objective Function and Evaluation Indexes
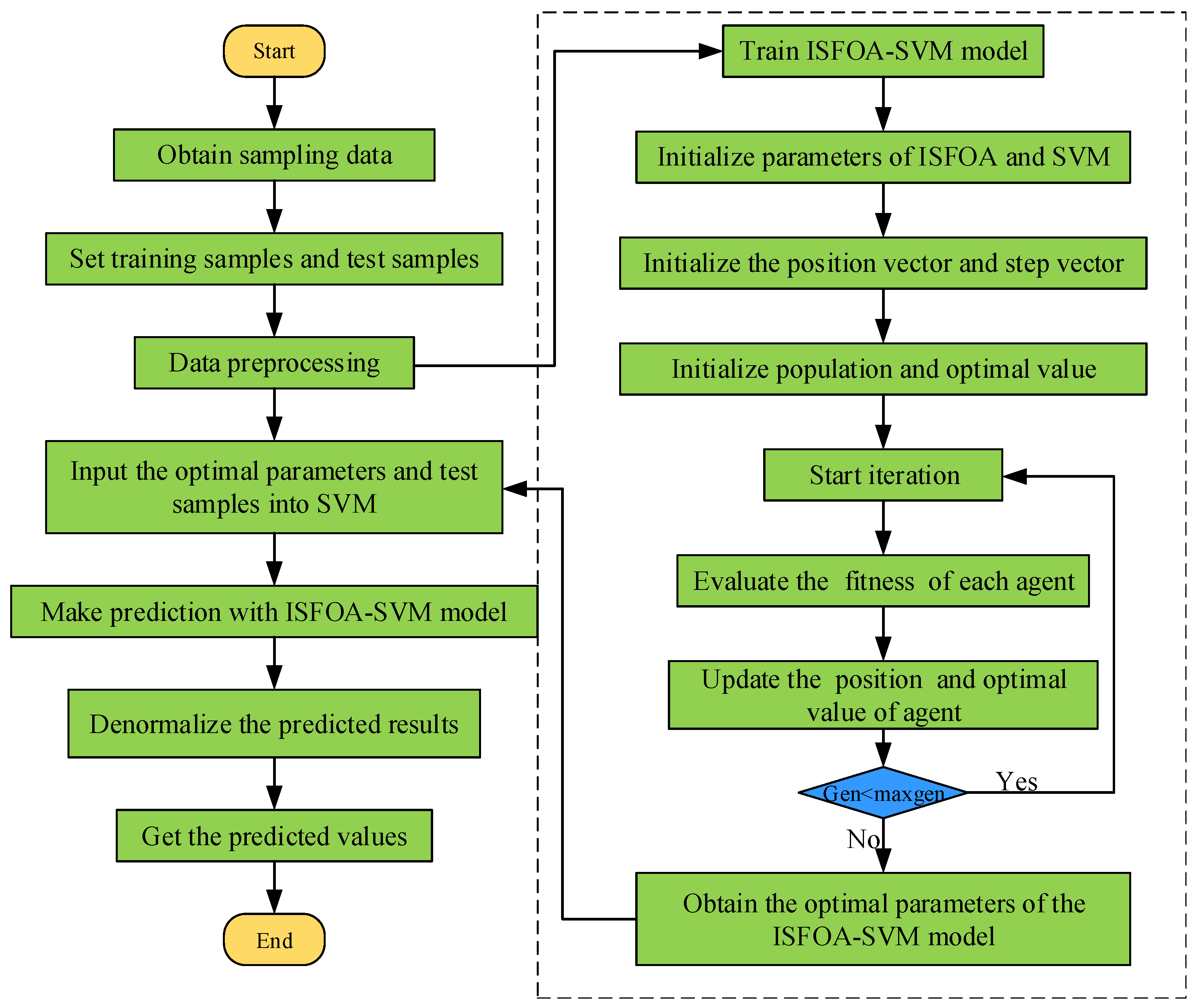
5.1.4. The ISFOA-SVM Forecasting Model
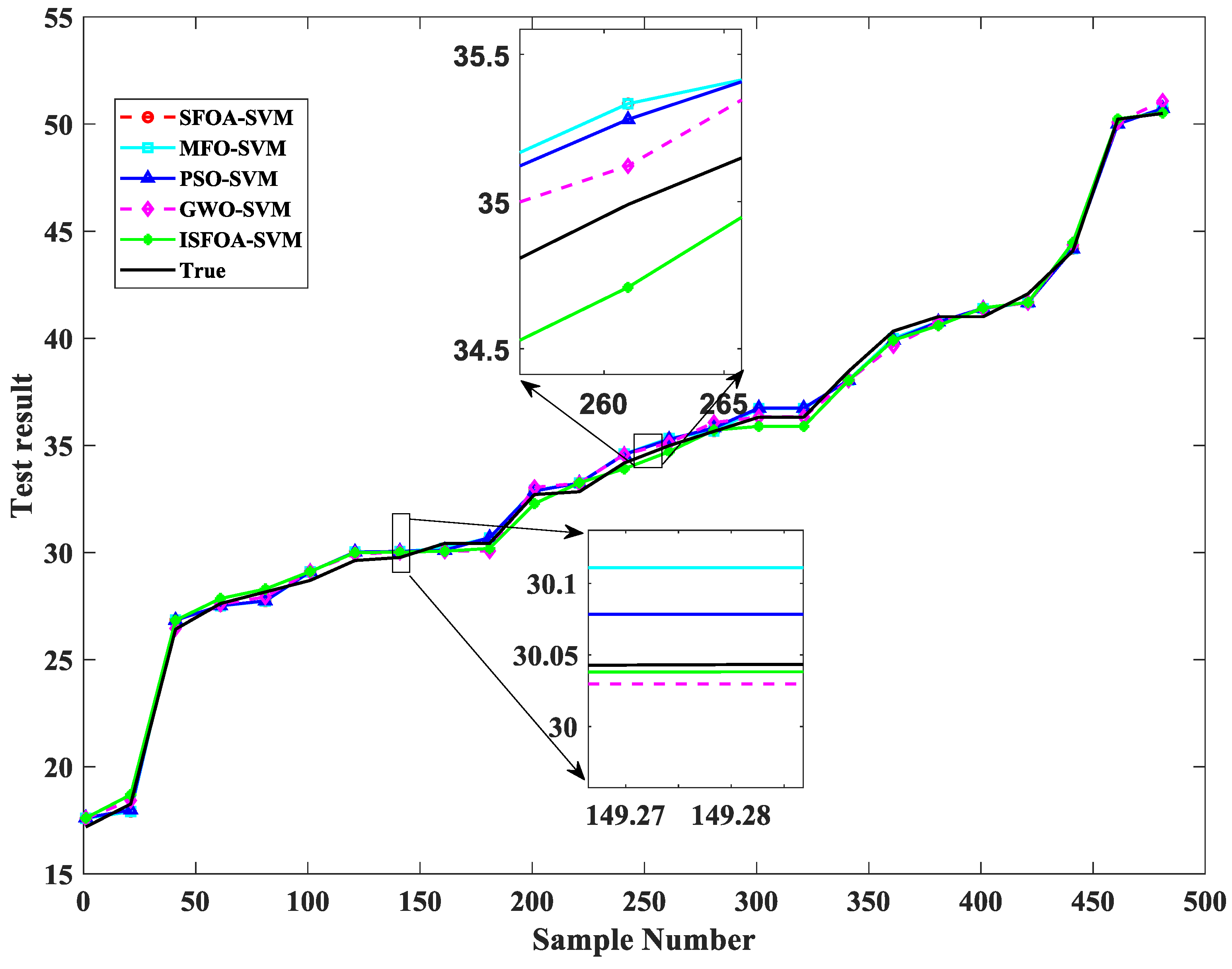
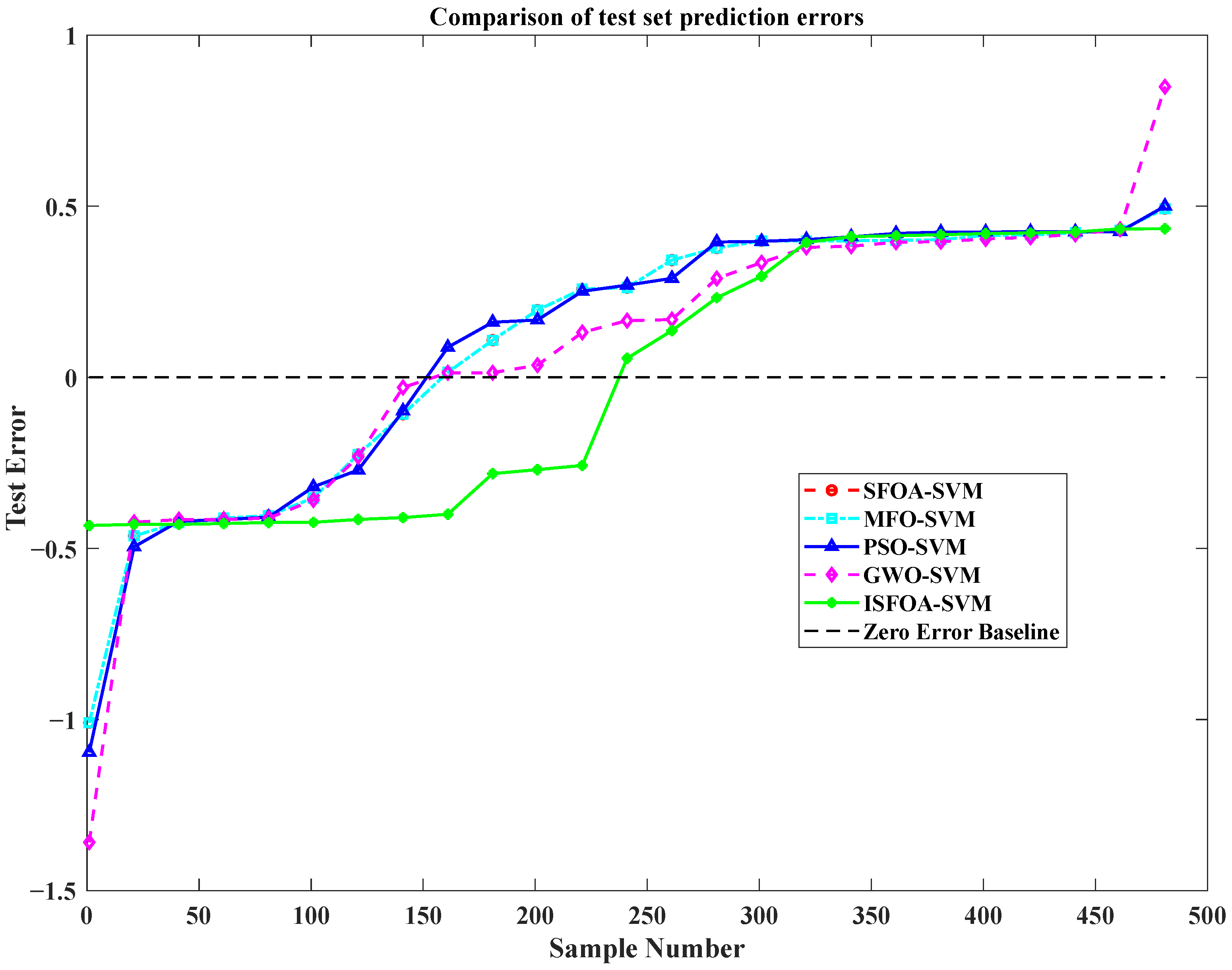
5.2. Results and Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SFOA | Superb Fairy-wren Optimization Algorithm |
| ISFOA | improved Superb Fairy-wren Optimization Algorithm |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MBE | Mean Bias Error |
| R2 | R-squared |
| PSO | particle swarm optimization |
| EAO | Enzyme Action Optimizer |
| SCA | Sine Cosine Algorithm |
| COA | Crayfish Optimization Algorithm |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| MFO | Moth-Flame Optimization |
| DE | Differential Evolution |
References
- Jiao, R.; Huang, X.; Ma, X.; Han, L.; Tian, W. A Model Combining Stacked Auto Encoder and Back Propagation Algorithm for Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 17851–17858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, M.; Hodge, B.M.; Florita, A.; Freedman, J. Ramp forecasting performance from improved short-term wind power forecasting over multiple spatial and temporal scales. Energy 2017, 122, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wei, T.; Li, J.; Ling, B.; Xu, J.; Wu, Z. Short-Term Power Load Forecasting Based on DPSO-LSSVM Model. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 32211–32224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, H.; Si, C. Improved composite model using metaheuristic optimization algorithm for short-term power load forecasting. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 241, 111330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Kong, L.; Su, Z.; Hu, M.; Wang, G. Approach for Short-Term Power Load Prediction Utilizing the ICEEMDAN–LSTM–TCN–Bagging Model. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2025, 20, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Tang, Z. An Improved CNN-BILSTM Model for Power Load Prediction in Uncertain Power Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Huang, H.; Liu, J. Fusion of Hierarchical Optimization Models for Accurate Power Load Prediction. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wen, B.; Yu, Z.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; Xu, C.; Huang, H. Multi-objective optimization method for power supply and demand balance in new power systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 161, 110204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qin, T.; Yang, B. Short-Term Power Load Forecasting Based on PSO-Optimized VMD-TCN-Attention Mechanism. Energies 2023, 16, 4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad Santjago, A.; Pelaez, C.; Perez-Aracil, J.; Sanz Justo, J.; Casanova Mateo, C.; Salcedo Sanz, S. Hybridizing Machine Learning Algorithms With Numerical Models for Accurate Wind Power Forecasting. Expert Syst. 2025, 42, e13830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, M.; Tao, G.; Mirza, A.F.; Irfan, M.; Chen, W. Feature fusion temporal convolution: Wind power forecasting with light hyperparameter optimization. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 2468–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xing, F.; Kang, L.; Zhang, M.; Qin, C. Ultra-Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on DT-DSCTransformer Model. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 22919–22930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, C.; Liao, B.; Cao, X.; Li, S. Wind Power Forecasting Based on WaveNet and Multitask Learning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Bai, J. Ultra-Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on the MSADBO-LSTM Model. Energies 2024, 17, 5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamari, R.C.; Mani, S.; Bodkhe, R.G.; Singh, A.K. Enhancing wind power forecasting accuracy: A hybrid SNGF-RERNN-SCSO approach. Sol. Energy 2025, 295, 113513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, T.; Hatziargyriou, N. Regional Wind Power Forecasting Based on Bayesian Feature Selection. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2025, 40, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, J.; Cheng, P. Ultra-Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on CGAN-CNN-LSTM Model Supported by Lidar. Sensors 2023, 23, 4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Y.; Li, S. Study on short-term network forecasting based on SVM-MFA algorithm. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 65, 102646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. Electric Power Load Forecasting Method Based on a Support Vector Machine Optimized by the Improved Seagull Optimization Algorithm. Energies 2022, 15, 9197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tang, J.; Ma, H.; Fan, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, J. Load Prediction Based on Optimization Ant Colony Algorithm. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 18, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, S.; Sahoo, A. Prediction of suspended sediment concentration using hybrid SVM-WOA approaches. Geocarto Int. 2021, 37, 5609–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshmand, F.; Seilsepour, F.; MirHassani, S. Adjustable robust optimization approach for SVM under uncertainty. Omega 2025, 131, 103206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Lashin, M.M.A.; Alrowais, F.; Karamti, H. A Dual Soft-Computing Based on Genetic Algorithm and Fuzzy Logic Defect Recognition for Gearbox and Motors: Attempts Toward Optimal Performance. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 73956–73968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouachi, S.; Bourouba, N.; Mebarkia, K.; Laidani, I. Analog Circuits Fault Diagnosis Using ISM Technique and a GA-SVM Classifier Approach. Electron. ETF 2024, 28, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojae Chaeikar, S.; Manaf, A.A.; Alarood, A.A.; Zamani, M. PFW: Polygonal Fuzzy Weighted—An SVM Kernel for the Classification of Overlapping Data Groups. Electronics 2020, 9, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Mirjalili, S. Superb Fairy-wren Optimization Algorithm: A novel metaheuristic algorithm for solving feature selection problems. Clust. Comput. 2025, 28, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Qin, Y.; Cao, K.; Du, T.; Dai, Q. Software defect prediction based on support vector machine optimized by reverse differential chimp optimization algorithm. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodan, A.; Al-Tamimi, A.K.; Al-Alnemer, L.; Mirjalili, S.; Tiňo, P. Enzyme action optimizer: A novel bio-inspired optimization algorithm. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Cheng, J. A Modified Sine Cosine Algorithm for Numerical Optimization. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Appl. 2024, 23, 2450015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Abualigah, L.; Yildiz, A.R.; Hussien, A.G. Modified crayfish optimization algorithm for solving multiple engineering application problems. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, K. Particle Swarm Optimization-A Survey. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2009, E92-D, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Y. Hybrid-Driven Car-Following Model Based on Improved Composite Network and IDM. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 50, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. Moth-flame optimization algorithm: A novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 89, 228–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cite | Method | Applicable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| [5] | ICEEMDAN-LSTM-TCN-Bagging | Short-term power load prediction |
| [6] | CNN-BiLSTM | Power load prediction |
| [7] | CMPLF | Power load prediction |
| [8] | TSMO | Power supply and demand balance |
| [19] | ISOA-SVM | Electric power load forecasting |
| [20] | ACA-LSSV | Load prediction |
| [10] | ERA5 and ML | Wind power forecasting |
| [11] | FFN-TCN | Wind power forecasting |
| [12] | DT-DSCTransformer | Ultra-short-term wind power forecasting |
| [13] | WaveNet | Multi-step wind power prediction |
| [14] | LSTM embedded with MSADBO | Ultra-short-term wind power forecasting |
| [15] | SNGF-RERNN-SCSO pipeline | Wind power forecasting |
| [16] | Bayesian Feature Selection | Regional wind power forecasting |
| [17] | CGAN-CNN-LSTM framework | Ultra-short-term wind power forecasting |
| [9] | TCN | Short-term power load forecasting |
| F* | Name | ISFOA | SFOA | COA | EAO | PSO | SCA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Std | 1.06 | 1.80 | 1.81 | 1.47 | 1.01 | 9.14 |
| Mean | 1.43 | 1.09 | 6.35 | 3.44 | 2.93 | 2.95 | |
| F2 | Std | 2.59 | 2.92 | 5.75 | 6.47 | 2.82 | 1.62 |
| Mean | 4.60 | 7.50 | 5.73 | 5.67 | 4.71 | 1.00 | |
| F3 | Std | 3.32 | 1.80 | 1.37 | 9.59 | 8.53 | 5.62 |
| Mean | 6.04 | 7.11 | 6.46 | 6.81 | 6.16 | 6.55 | |
| F4 | Std | 3.27 | 3.94 | 1.28 | 1.55 | 2.10 | 1.89 |
| Mean | 8.80 | 1.09 | 8.98 | 9.73 | 8.74 | 9.68 | |
| F5 | Std | 7.18 | 3.75 | 4.18 | 7.72 | 1.43 | 5.50 |
| Mean | 9.76 | 1.32 | 3.20 | 2.95 | 1.05 | 3.10 | |
| F6 | Std | 3.36 | 3.59 | 2.57 | 4.45 | 1.40 | 1.73 |
| Mean | 5.25 | 5.53 | 2.69 | 9.59 | 1.78 | 2.47 | |
| F7 | Std | 3.09 | 9.96 | 1.19 | 3.49 | 5.31 | 2.56 |
| Mean | 2.08 | 2.48 | 2.19 | 2.24 | 2.13 | 2.21 | |
| F8 | Std | 3.30 | 1.07 | 5.99 | 6.20 | 8.06 | 5.69 |
| Mean | 2.23 | 7.98 | 2.29 | 2.29 | 2.29 | 2.31 | |
| F9 | Std | 2.27 | 4.31 | 3.43 | 3.35 | 3.87 | 4.73 |
| Mean | 2.48 | 3.77 | 2.51 | 2.53 | 2.52 | 2.68 | |
| F10 | Std | 9.66 | 1.42 | 1.58 | 1.51 | 7.04 | 1.62 |
| Mean | 2.81 | 7.49 | 5.29 | 2.99 | 3.40 | 3.33 | |
| F11 | Std | 1.63 | 5.10 | 1.07 | 1.02 | 1.21 | 1.48 |
| Mean | 3.05 | 1.55 | 4.48 | 5.02 | 3.27 | 9.26 | |
| F12 | Std | 1.90 | 1.68 | 4.67 | 1.14 | 3.13 | 6.84 |
| Mean | 2.98 | 3.76 | 3.01 | 3.11 | 2.99 | 3.15 |
| F* | vs. SFOA | vs. COA | vs. EAO | vs. PSO | vs. SCA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 7.22 | 5.86 | 1.53 | 2.55 | 3.41 |
| F2 | 7.80 | 5.51 | 1.32 | 2.29 | 1.70 |
| F3 | 4.69 | 1.91 | 8.42 | 7.76 | 1.01 |
| F4 | 4.45 | 5.69 | 1.88 | 2.22 | 2.78 |
| F5 | 2.78 | 1.97 | 2.09 | 6.92 | 2.31 |
| F6 | 1.15 | 3.02 | 7.52 | 8.06 | 1.23 |
| F7 | 9.91 | 2.12 | 8.53 | 2.83 | 6.73 |
| F8 | 1.13 | 1.34 | 1.64 | 4.61 | 4.41 |
| F9 | 1.63 | 8.92 | 1.99 | 1.47 | 8.41 |
| F10 | 4.28 | 8.28 | 5.53 | 1.83 | 9.77 |
| F11 | 6.40 | 1.08 | 2.20 | 2.54 | 2.60 |
| F12 | 2.63 | 1.03 | 1.69 | 1.96 | 3.65 |
| SFOA-SVM | PSO-SVM | MFO-SVM | GWO-SVM | ISFOA-SVM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 0.3193 | 0.3378 | 0.3619 | 0.7456 | 0.3158 |
| MBE | 0.0278 | 0.0331 | 0.0342 | 0.0173 | 0.0126 |
| RMSE | 1.0038 | 0.3902 | 0.4142 | 0.5621 | 0.3304 |
| R2 | 0.9948 | 0.9975 | 0.9973 | 0.9820 | 0.9982 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z. Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on ISFOA-SVM. Electronics 2025, 14, 3172. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163172
Chen L, Liu X, Zhou Z. Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on ISFOA-SVM. Electronics. 2025; 14(16):3172. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163172
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Li, Xufeng Liu, and Zupeng Zhou. 2025. "Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on ISFOA-SVM" Electronics 14, no. 16: 3172. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163172
APA StyleChen, L., Liu, X., & Zhou, Z. (2025). Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on ISFOA-SVM. Electronics, 14(16), 3172. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163172





