A Distributed Multi-Microgrid Cooperative Energy Sharing Strategy Based on Nash Bargaining
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A multi-microgrid system with wind–solar-storage-load and combined heat and power (CHP) is established. Compared with the conventional microgrids [8,9,27], this paper takes into account various factors such as the adjustable heat-to-electrical ratio, power load, heat load, ladder-type positive and negative carbon trading and peak–valley electricity price, thereby aligning more closely with the actual development needs of the power grid.
- (2)
- A distributed multi-microgrid cooperative energy sharing strategy is proposed. Compared with other optimal scheduling strategies [19,20,21,22,23,24,26], this strategy establishes a cooperative energy sharing optimization model for multi-microgrids based on Nash bargaining, and divides it into two stages of the cost minimization of multi-microgrids and fair distribution of cooperative benefits, so as to realize low-carbon and economic scheduling, and improve the utilization rate of renewable energy.
- (3)
- The alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) is adopted to address cost minimization and fair distribution problems. Compared with other centralized optimization scheduling methods [10,11,12,14], the ADMM can update and iterate the multipliers according to the constraints of the multi-microgrid system after the objective function of each microgrid is solved by itself, which can fully protect the privacy of each microgrid.
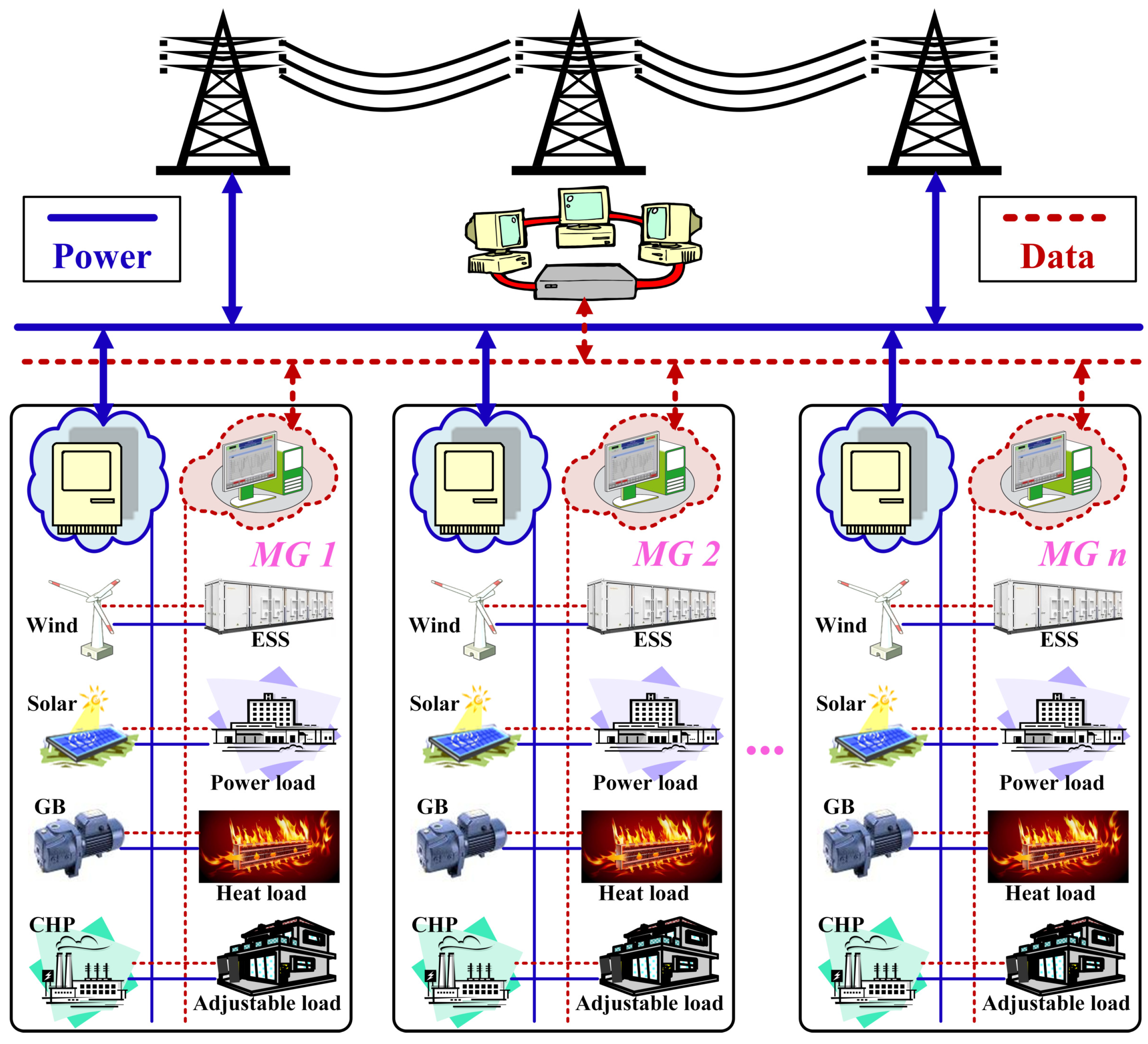
2. The Modeling of Multi-Microgrid Systems
2.1. Multi-Energy Microgrids
2.2. Demand Response
2.3. Energy Interaction
2.4. Ladder-Type Positive and Negative Carbon Trading
3. Multi-Microgrid Energy Sharing Strategy and ADMM Algorithm
3.1. Cost Minimization of Multi-Microgrids
- Step 1.
- The augmented Lagrange relaxation method is applied as follows:where and are Lagrange multiplier and penalty term in cost minimization.
- Step 2.
- Each microgrid updates its own power traded locally to protect privacy, so the update strategy of MGi can be expressed as:where k denotes the number of iterations. Then the update strategy of MGj is:and an iteration is not completed until the strategy is updated for each microgrid.
- Step 3.
- Then the Lagrange multiplier is updated as follows:
- Step 4.
- By calculating the raw residuals of the distributed algorithm, the convergence of the algorithm is judged as follows:where is a small constant. Therefore, if the judgment condition (24) is satisfied, the iteration can be stopped; otherwise, go to Step 2. Then, the details are implemented as shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Cost Minimization of Multi-Microgrids |
| Initialization: |
| Import new energy and load data, as well as electricity price parameters; |
| Establish the cost minimization objective function for each microgrid based on (1)–(17); |
| Set the Lagrange multiplier , penalty term and tolerances ; |
| Establish augmented Lagrangian function (20) of cost minimization for multi-microgrids; |
Iterative:
|
3.2. Fair Distribution of Cooperative Benefits
- Step 1.
- The augmented Lagrange relaxation method is applied as follows:where and are the Lagrange multiplier and penalty term in a fair distribution.
- Step 2.
- Each microgrid updates its own power trading unit price locally to protect privacy, so the update strategy of MGi can be expressed as:where k denotes the number of iterations. Then the update strategy of MGj is:and an iteration is not completed until the strategy is updated for each microgrid.
- Step 3.
- Then the Lagrange multiplier is updated as follows:
- Step 4.
- By calculating the raw residuals of the distributed algorithm, the convergence of the algorithm is judged as follows:where is a small constant. Therefore, if the judgment condition (32) is satisfied, the iteration can be stopped; otherwise, go to Step 2. Then, the details are implemented as shown in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2 Fair Distribution of Cooperative Benefits |
| Initialization: |
| Calculate Equation (25) based on the optimal interaction results obtained by Algorithm 1; |
| Establish the benefit distribution model based on the asymmetric bargaining theory (27); |
| Set the Lagrange multiplier , penalty term and tolerances ; |
| Establish augmented Lagrangian function (28) of fair distribution for cooperative benefits; |
Iterative:
|
4. Simulation Results
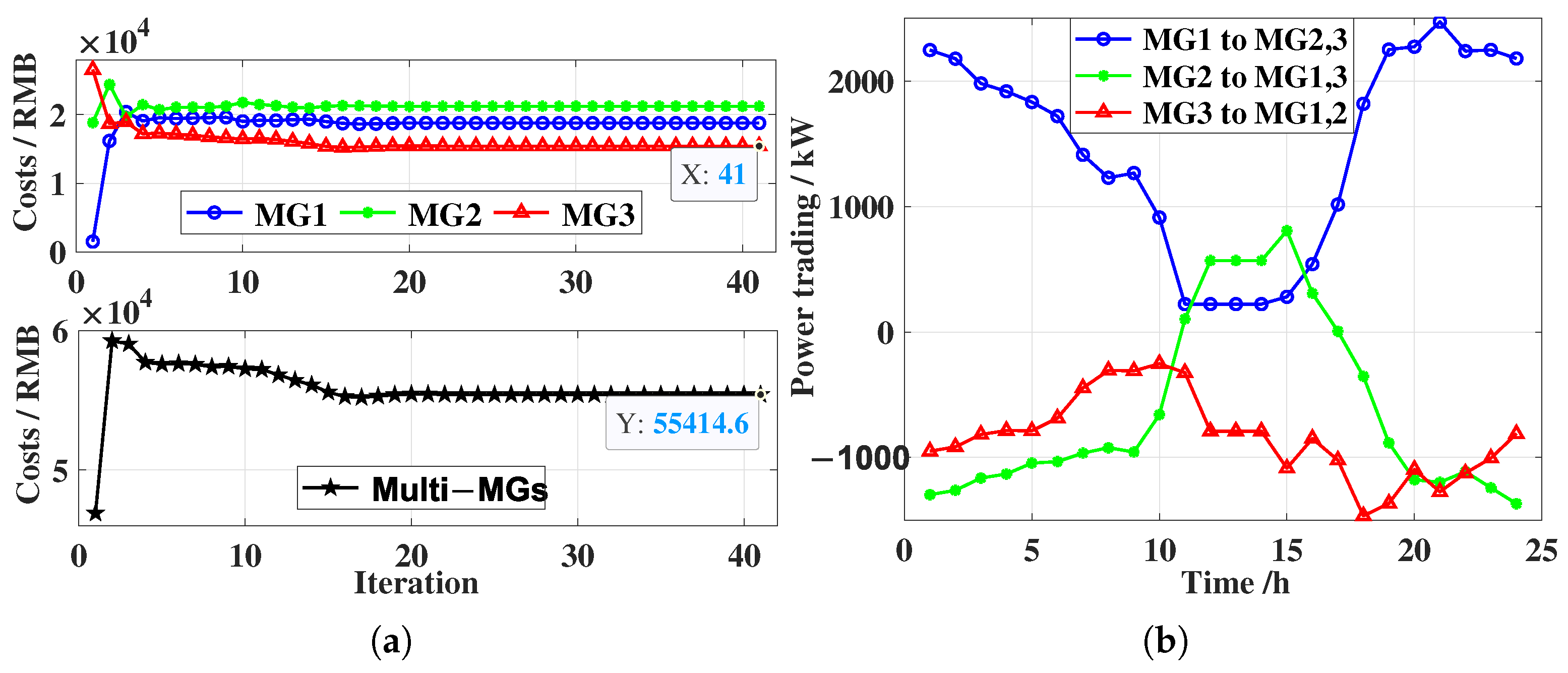
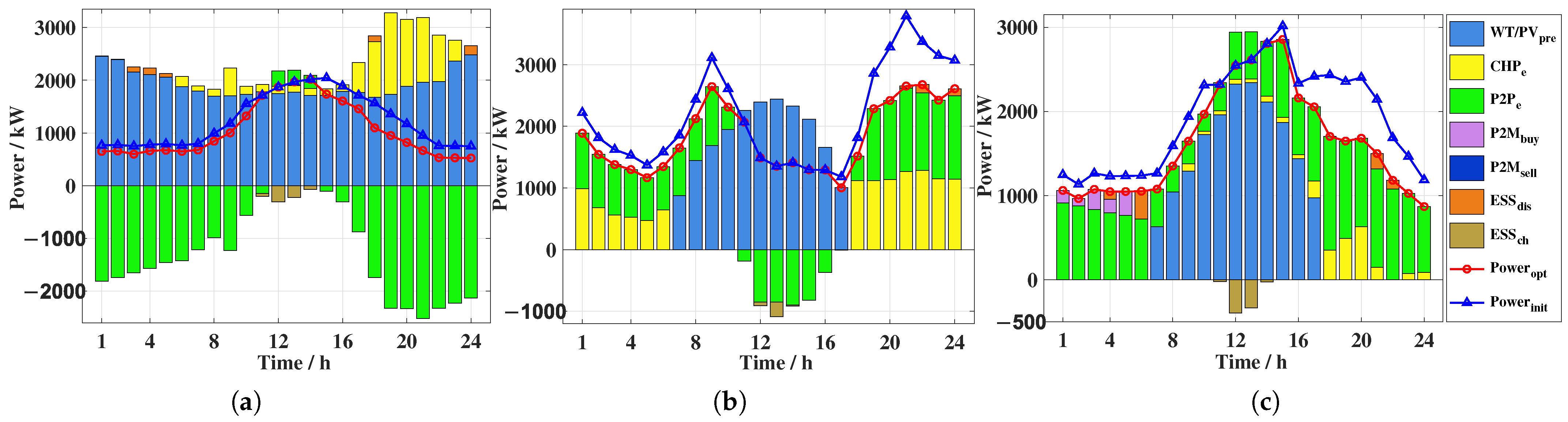
4.1. Optimization Results for Cost Minimization of Multi-Microgrids
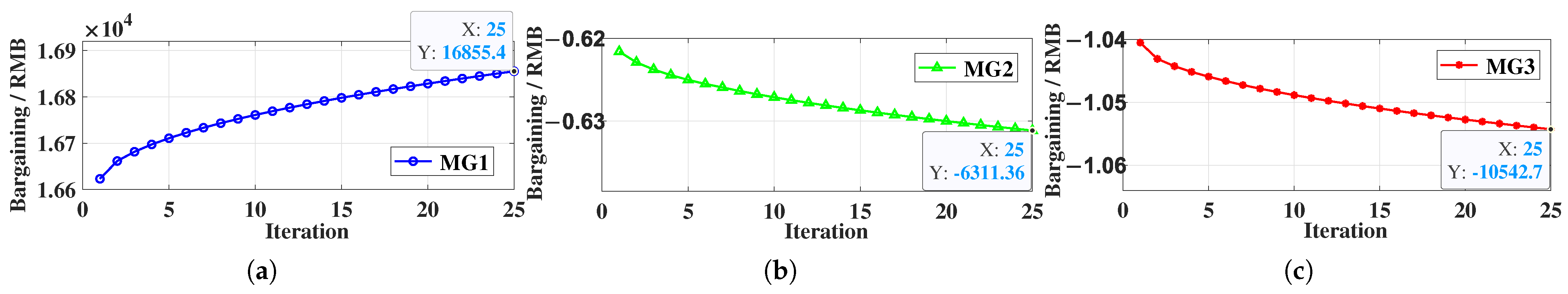
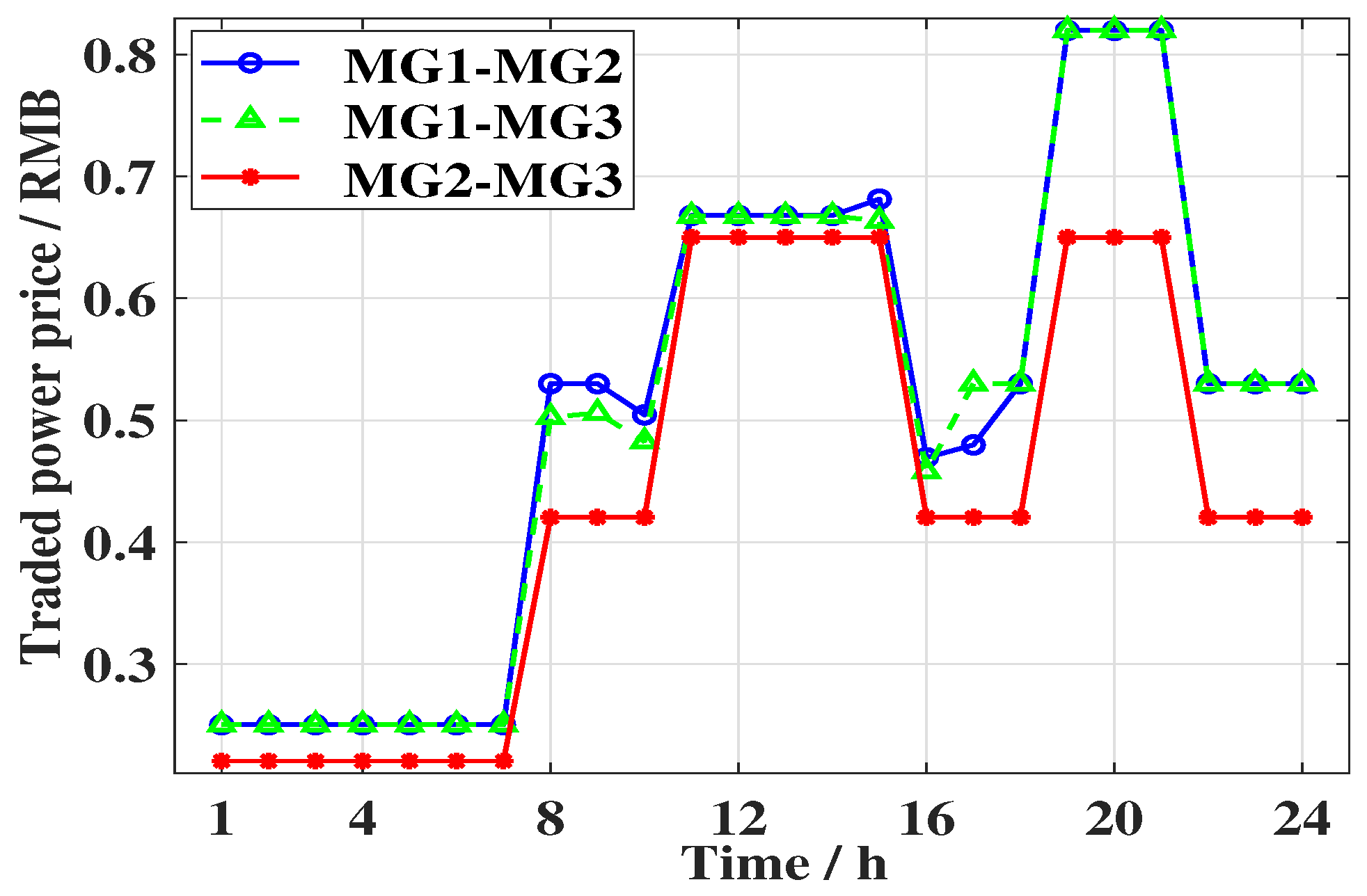
4.2. Optimization Results for Fair Distribution of Cooperative Benefits
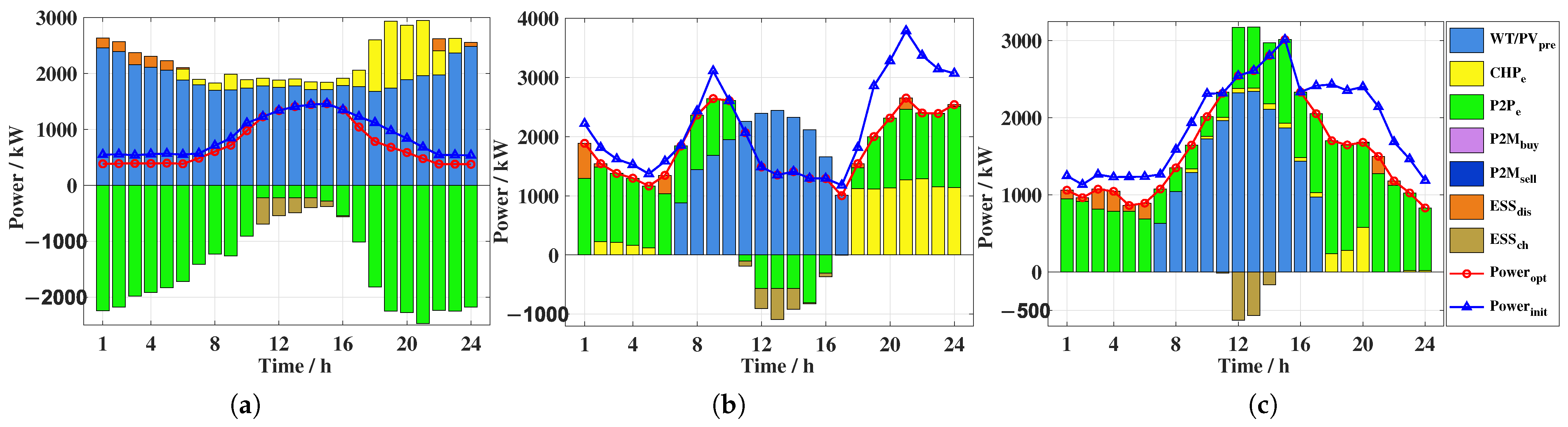
4.3. Comparative Analysis with Independent Operation of Multi-Microgrids
4.4. Validation of Scenarios with Increased Load of Multi-Microgrids
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daneshvar, M.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Zare, K. A Fair Risk-Averse Stochastic Transactive Energy Model for 100% Renewable Multi-Microgrids in the Modern Power and Gas Incorporated Network. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.H.; Hussain, A.; Kim, H.M. A Multiagent-Based Hierarchical Energy Management Strategy for Multi-Microgrids Considering Adjustable Power and Demand Response. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Tang, F.; Dragicevic, T.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M. A Control Architecture to Coordinate Renewable Energy Sources and Energy Storage Systems in Islanded Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Su, J.; Wang, N.; Chen, B. Distributed Optimal Control of Energy Storages in DC Microgrids for Operation Loss Minimization with Communication Delays. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2024, 15, 5284–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Singh, B. Resilient Control Algorithm for Wind-Hydro Based Distributed Generation System with Grid Synchronization Capability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 4687–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Chen, M.; Zhao, B.; Li, B.; Qian, Z. Design of Control System for Smooth Mode-Transfer of Grid-Tied Mode and Islanding Mode in Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 6419–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Yan, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, N. Hierarchical Hybrid Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Among Multiple Heterogeneous Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 4649–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Liu, W.; Tang, N.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, R.; Li, H. Joint Optimization of Renewable Energy Utilization and Multi-Energy Sharing for Interconnected Microgrids with Carbon Trading. Electronics 2024, 13, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirugnanam, K.; Moursi, M.S.E.; Khadkikar, V.; Zeineldin, H.H.; Al Hosani, M. Energy Management of Grid Interconnected Multi-Microgrids Based on P2P Energy Exchange: A Data Driven Approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 1546–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Wei, F.; Wu, C.; Lin, X.; Li, Z. Day-Ahead Energy Management for Pelagic Island Microgrid Groups Considering Non-Integer-Hour Energy Transmission. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 5249–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Bao, Z.; Liu, C. Centralized Distributionally Robust Chance-Constrained Dispatch of Integrated Transmission-Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 2947–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, C.; Feng, T.; Wang, K.; Yao, W.; Zhang, Z. Day-Ahead and Intraday Joint Optimal Dispatch in Active Distribution Network Considering Centralized and Distributed Energy Storage Coordination. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 4832–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, A.; Sampath, L.P.M.I.; Yang, J.; Gooi, H.B. Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading in Smart Grid Considering Power Losses and Network Fees. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 4727–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; He, Y.; Tian, Y.; Sun, K.; Jiao, L.; Wang, H. Capacity Optimization of Wind–Solar–Storage Multi-Power Microgrid Based on Two-Layer Model and an Improved Snake Optimization Algorithm. Electronics 2024, 13, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinejad, M.; Shayanfar, H.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B. Peer-to-Peer Decentralized Energy Trading Framework for Retailers and Prosumers. Appl. Energy 2022, 308, 118310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, J.; Luo, X.; Lai, C.S.; Yang, P.; Lai, L.L.; Li, P.; Guerrero, J.M.; Shahidehpour, M. Distributed Robust Model Predictive Control-Based Energy Management Strategy for Islanded Multi-Microgrids Considering Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2107–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wu, W.; Zhang, B.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y. A Fully Distributed Reactive Power Optimization and Control Method for Active Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Pinson, P.; Chen, S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Z. Chance-Constrained Peer-to-Peer Joint Energy and Reserve Market Considering Renewable Generation Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yu, F.; Wang, D.; Li, N. Optimization Strategy for Integrated Energy Microgrids Based on Shared Energy Storage and Stackelberg Game Theory. Electronics 2024, 13, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, F.; Han, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Q. Cloud-edge-based We-Market: Autonomous Bidding and Peer-to-peer Energy Sharing Among Prosumers. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2023, 11, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Xu, Q.; Fang, J.; Li, F. Non-Iterative Decentralized Peer-to-Peer Market Clearing in Multi-Microgrid Systems via Model Substitution and Network Reduction. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 2922–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Guo, J.; Choi, J.K.; Zukerman, M. Distributed Energy Trading in Microgrids: A Game-Theoretic Model and Its Equilibrium Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3524–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, A.; Chaudhari, K.; Long, C.; Gooi, H.B. Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading in a Prosumer-Based Community Microgrid: A Game-Theoretic Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 6087–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Shahidehpour, M.; Paaso, A.; Zhang, L.; Alabdulwahab, A.; Abusorrah, A. Distribution Network-Constrained Optimization of Peer-to-Peer Transactive Energy Trading Among Multi-Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, J. Incentivizing Energy Trading for Interconnected Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 2647–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiş, A.; Koivunen, V. Coalitional Game-Based Cost Optimization of Energy Portfolio in Smart Grid Communities. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Huang, L.; Lan, J. Research on Multi-Microgrid Electricity–Carbon Collaborative Sharing and Benefit Allocation Based on Emergy Value and Carbon Trading. Electronics 2024, 13, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lai, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Guerrero, J.M. Distributed Coordination of Islanded Microgrid Clusters Using a Two-Layer Intermittent Communication Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 3956–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
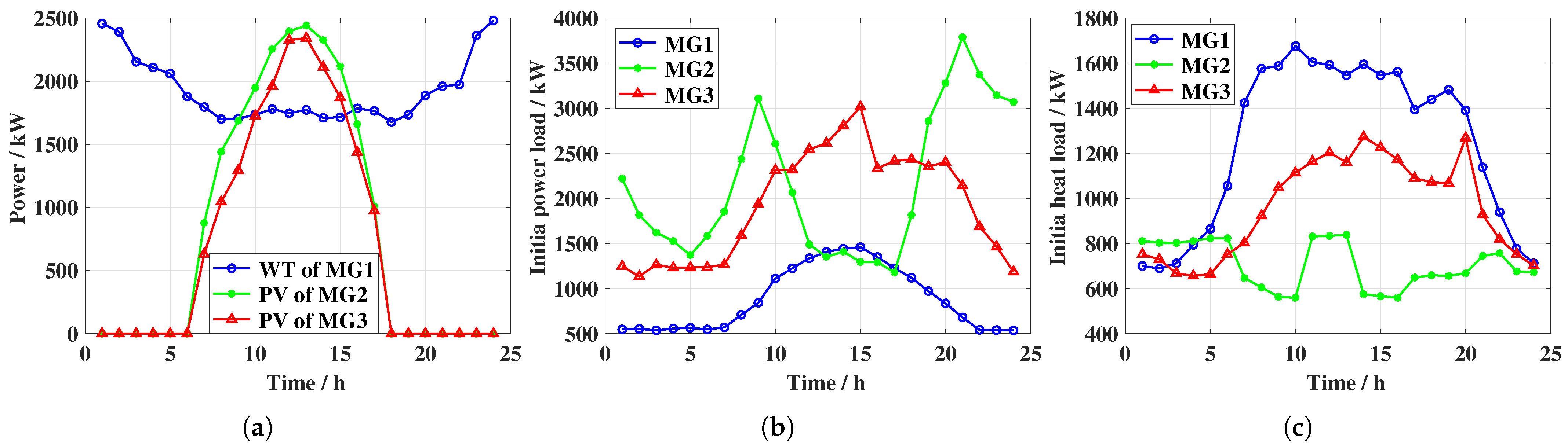

| Items | Capacity (kW) | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| PV/WT | and are in line with Figure 2a | , |
| ESS | , | , , , |
| CHP | , , , | , , , |
| GB | , , , | |
| Valley: 1:00–7:00 | , | |
| Price | Normal: 8:00–10:00, 16:00–18:00, 22:00–24:00 | , |
| Peak: 11:00–15:00, 19:00–21:00 | , | |
| Demand | is in line with Figure 2b | , , = 0.1, |
| is in line with Figure 2c | , | |
| Trading | , , | and follow the peak-valley price |
| Carbon | ||
| , , , , , , , | ||
| ADMM | , , , | |
| Operating | Cost/Carbon | MG1 | MG2 | MG3 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent | Cost/RMB | 2155.3 | 47,998 | 43,353 | 93,506.3 |
| Carbon/kg | 17,439 | 24,514 | 24,554 | 66,507 | |
| Interactive | Cost/RMB | 18,777 | 21,216 | 15,422 | 55,415 |
| Carbon/kg | 20,156 | 14,271 | 13,590 | 48,017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, Q. A Distributed Multi-Microgrid Cooperative Energy Sharing Strategy Based on Nash Bargaining. Electronics 2025, 14, 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14153155
Su S, Zhang Q, Xie Q. A Distributed Multi-Microgrid Cooperative Energy Sharing Strategy Based on Nash Bargaining. Electronics. 2025; 14(15):3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14153155
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Shi, Qian Zhang, and Qingyang Xie. 2025. "A Distributed Multi-Microgrid Cooperative Energy Sharing Strategy Based on Nash Bargaining" Electronics 14, no. 15: 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14153155
APA StyleSu, S., Zhang, Q., & Xie, Q. (2025). A Distributed Multi-Microgrid Cooperative Energy Sharing Strategy Based on Nash Bargaining. Electronics, 14(15), 3155. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14153155






