Laser Radar and Micro-Light Polarization Image Matching and Fusion Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminary
2.1. Matching of LiDAR and Low-Light Polarization Images
2.2. Fusion Algorithm of LiDAR and Micro-Light Polarization Images
2.3. Optimization of Fusion Between LiDAR and Low-Light Polarization Images
3. The Proposed Fusion System
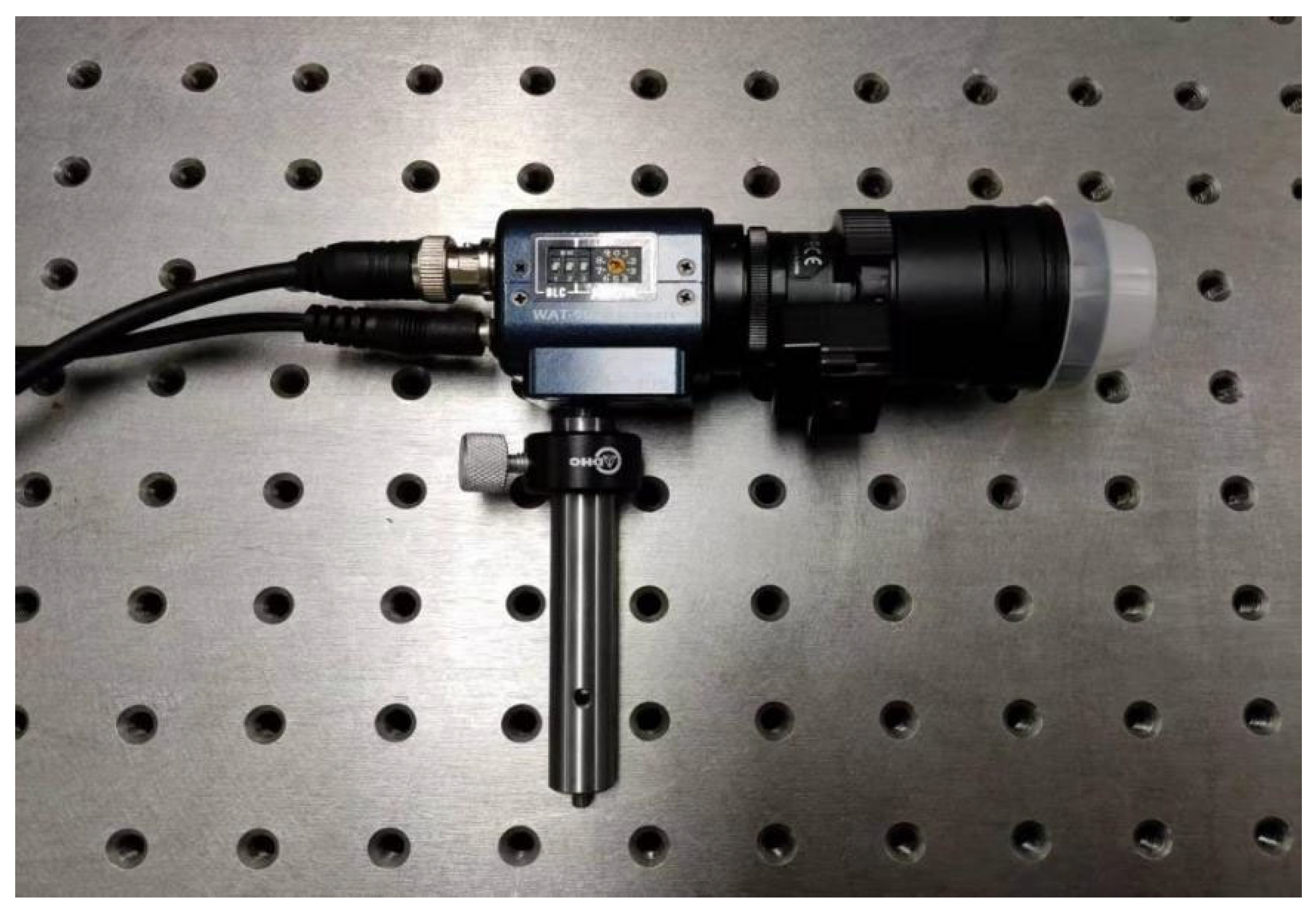
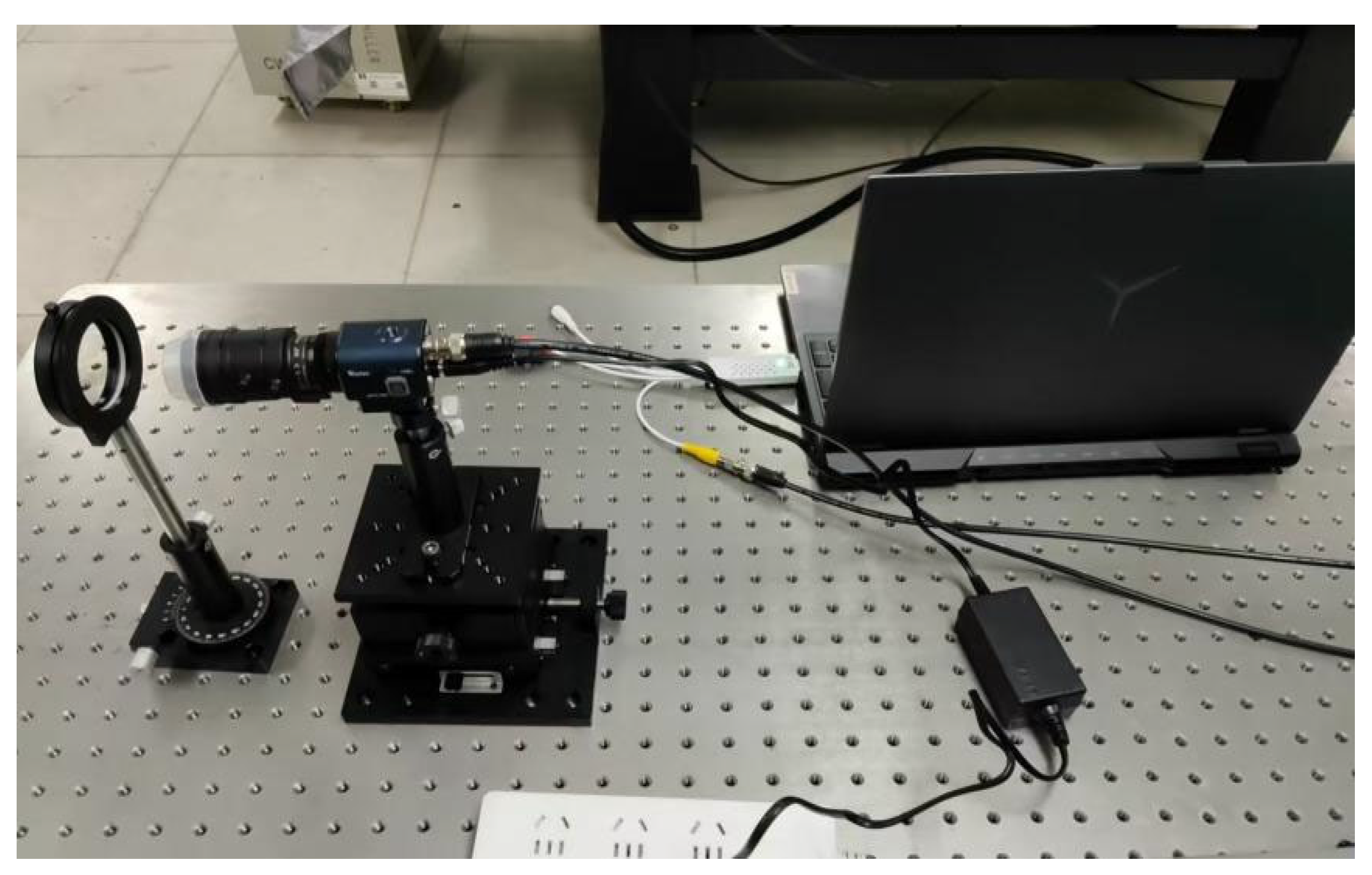
3.1. Imaging System Design and Construction
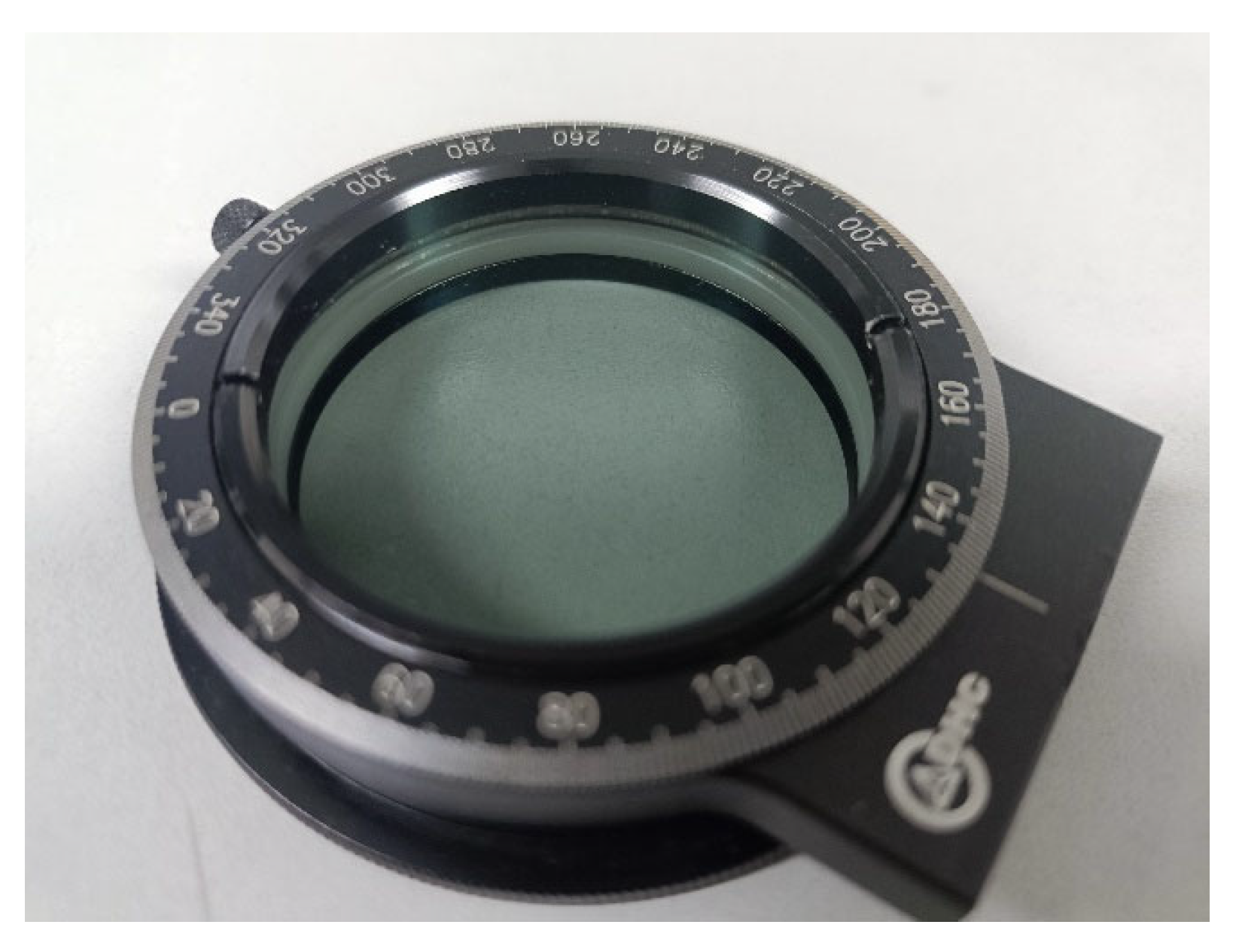
3.1.1. Micro-Light Polarization Imaging System
3.1.2. LiDAR Imaging System
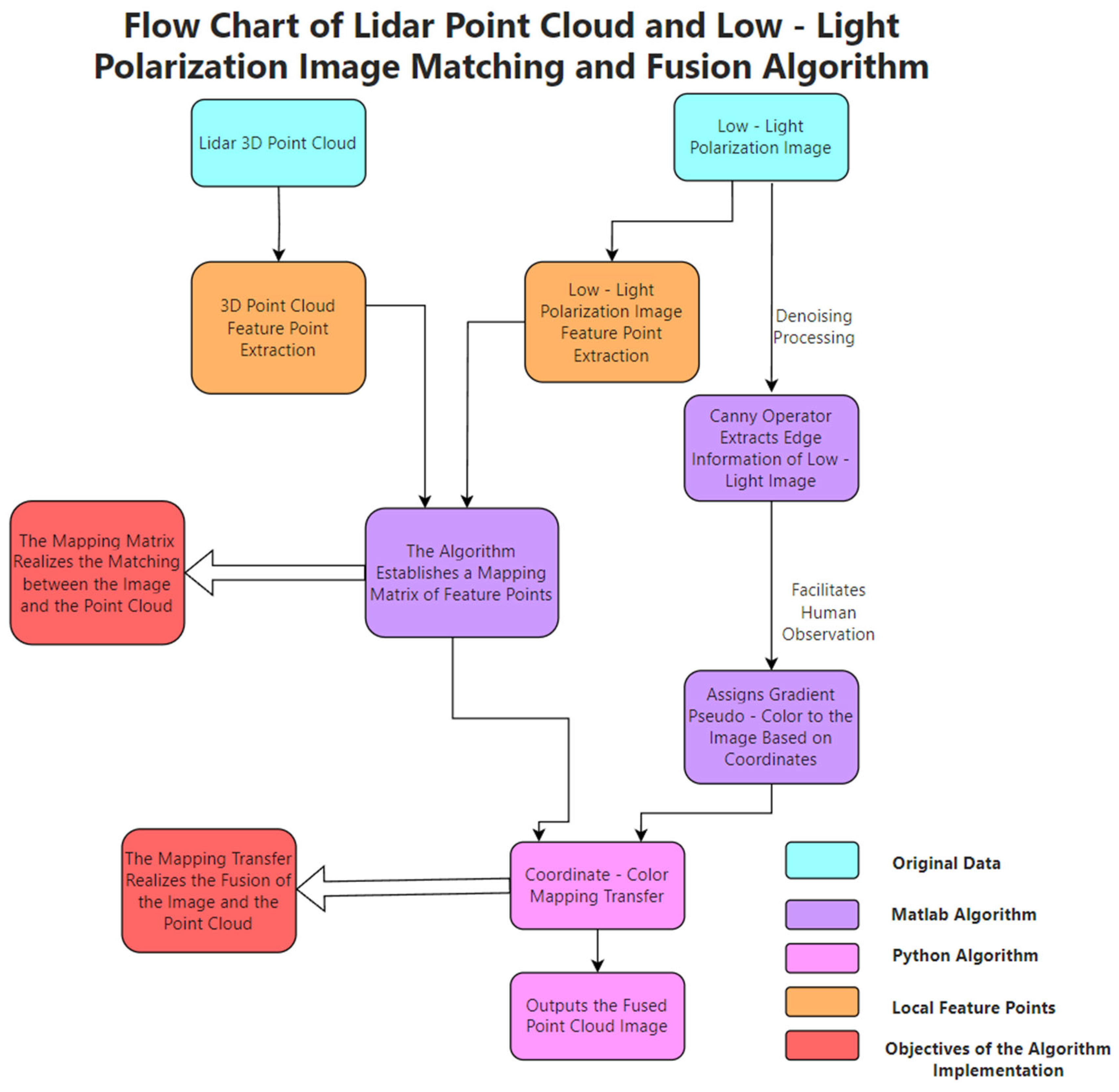
3.2. Matching and Fusion Processing
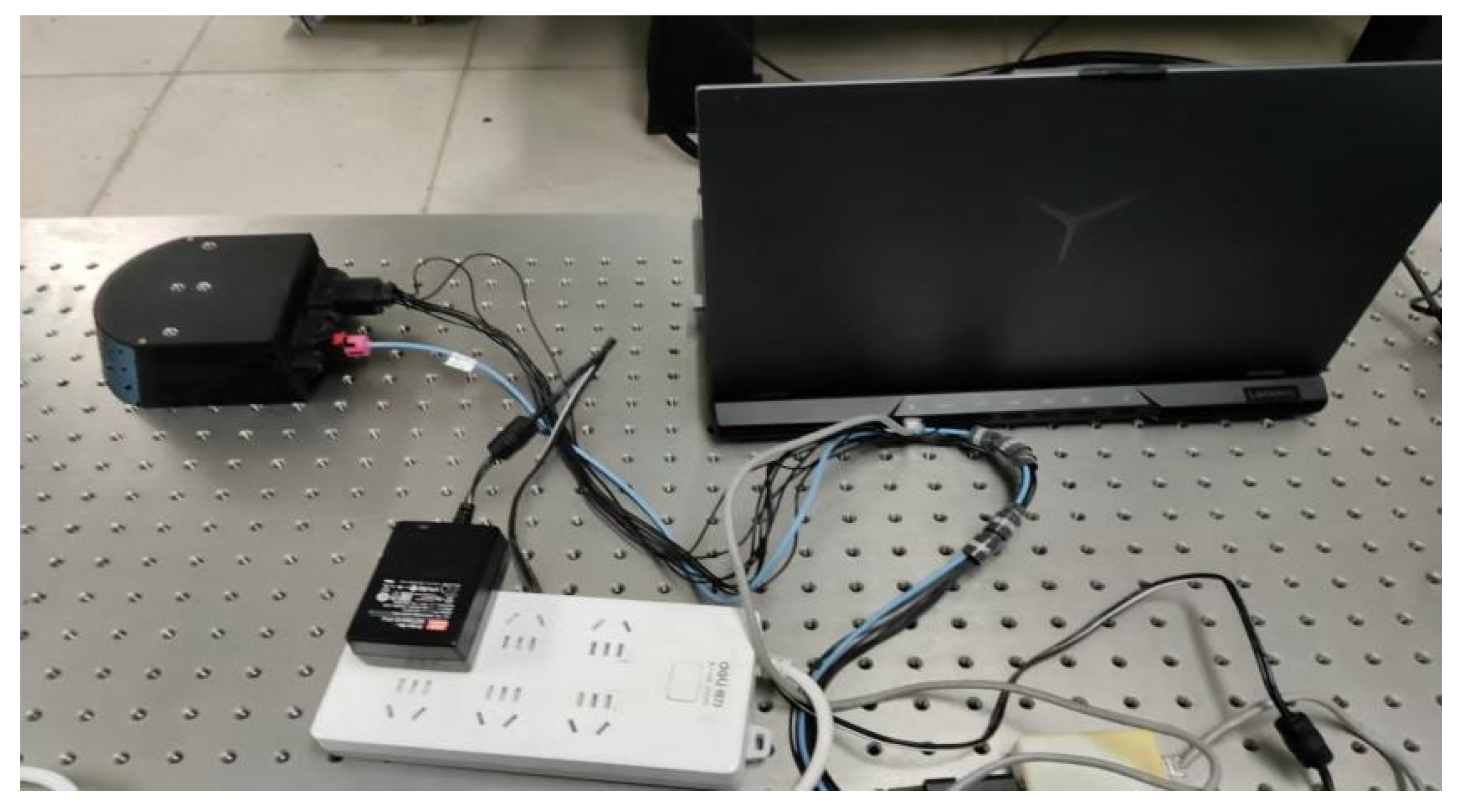
3.2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
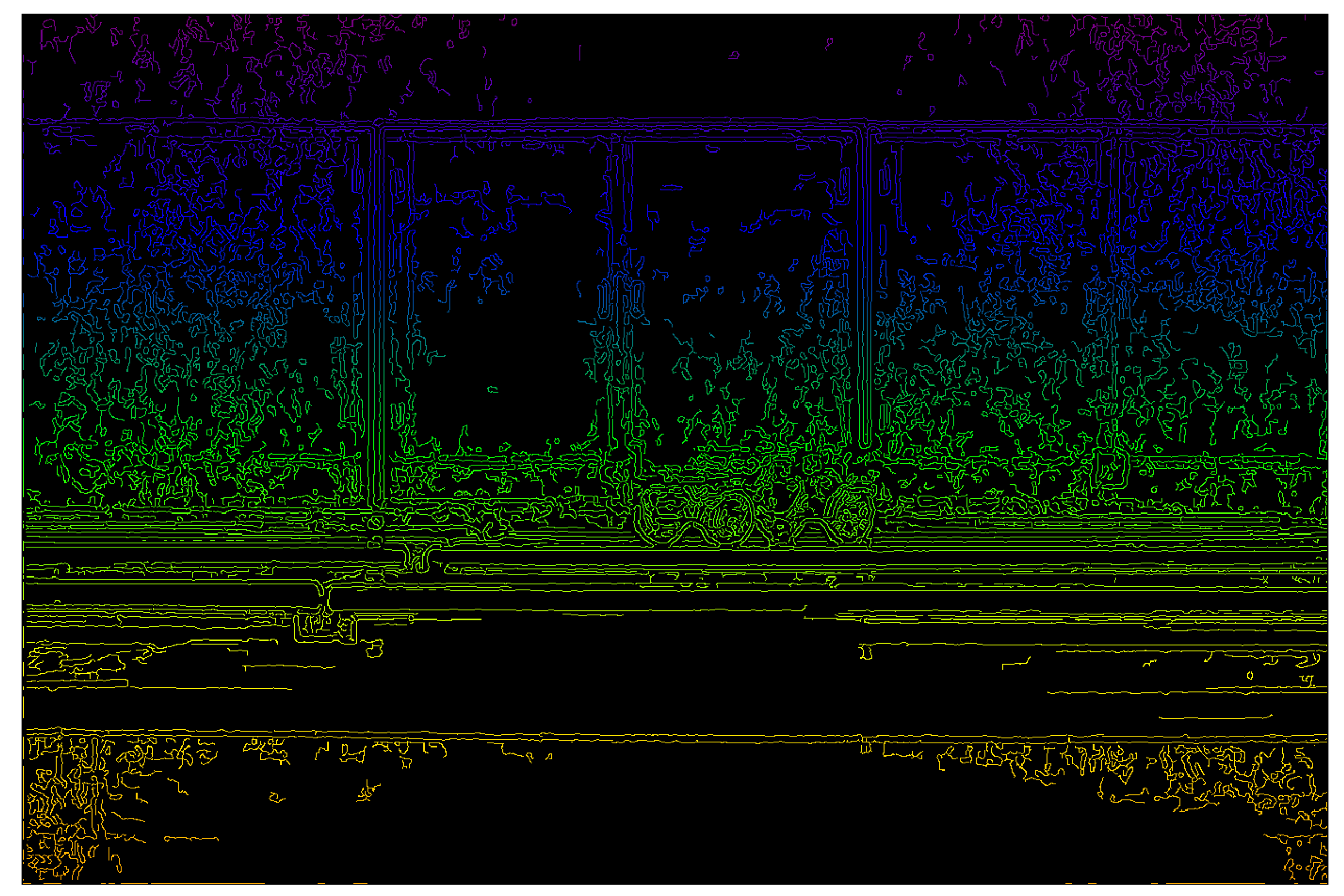
3.2.2. LiDAR and Micro-Light Polarization Image Matching
3.2.3. LiDAR and Micro-Light Polarization Image Fusion
4. Experiment and Analysis
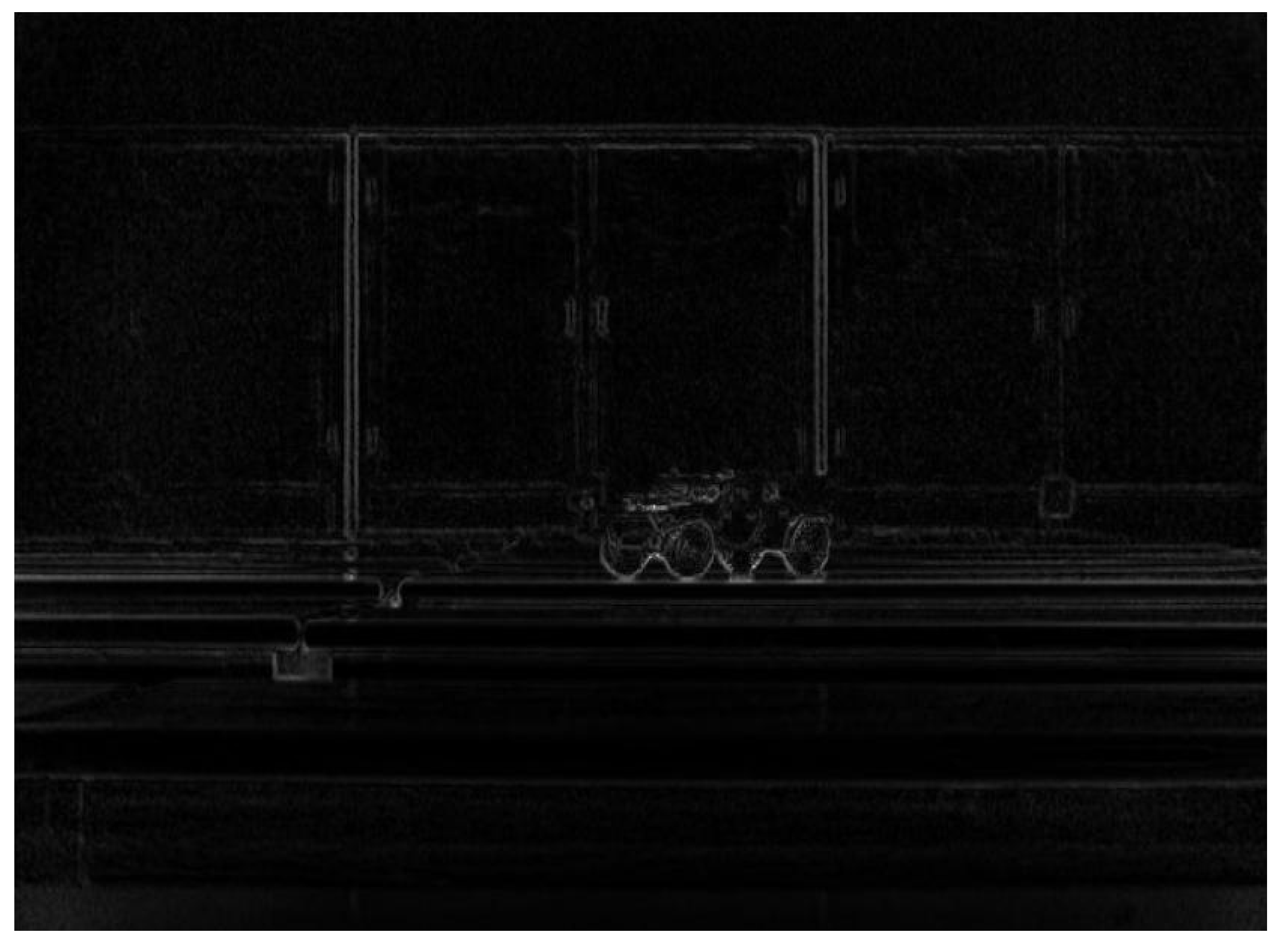
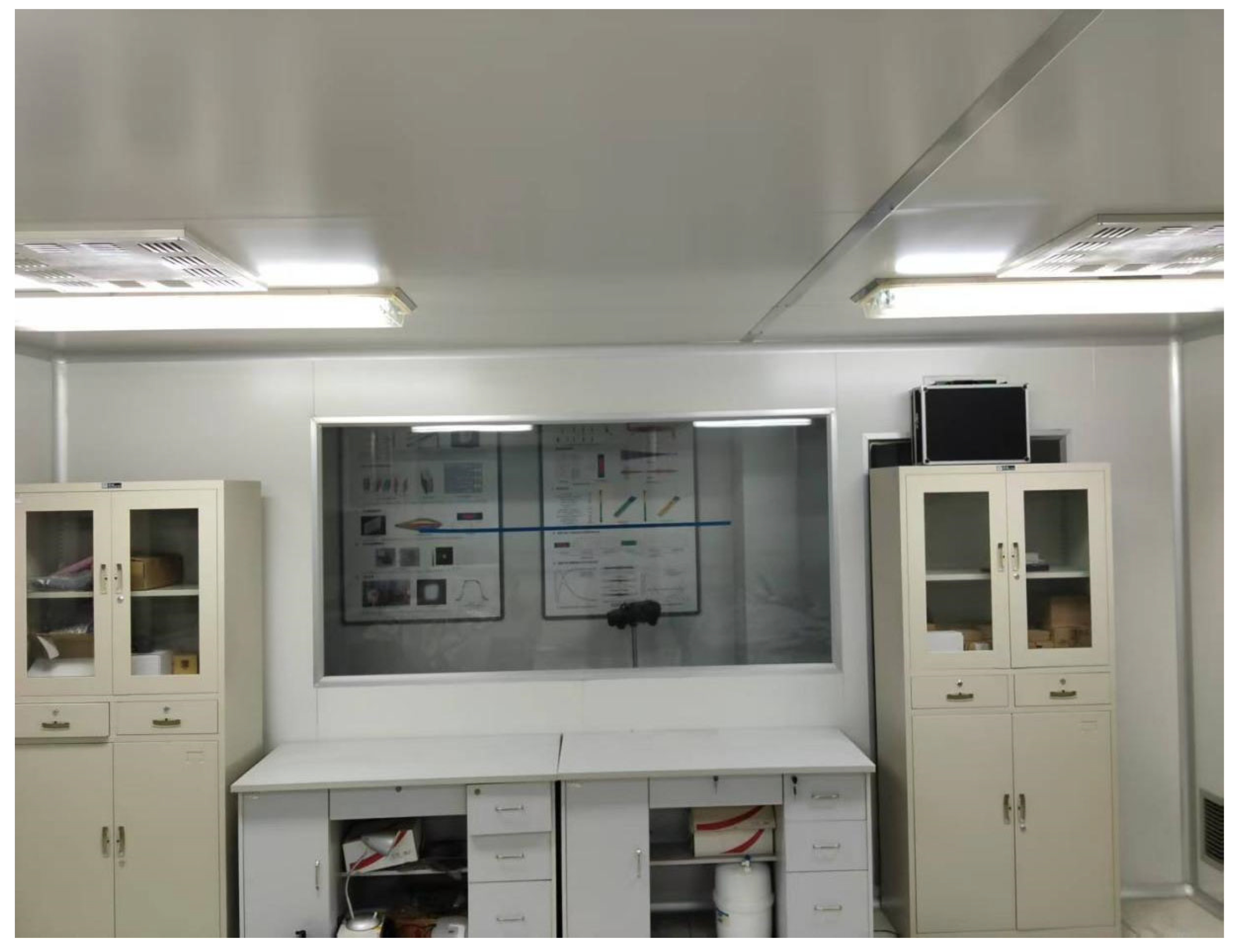
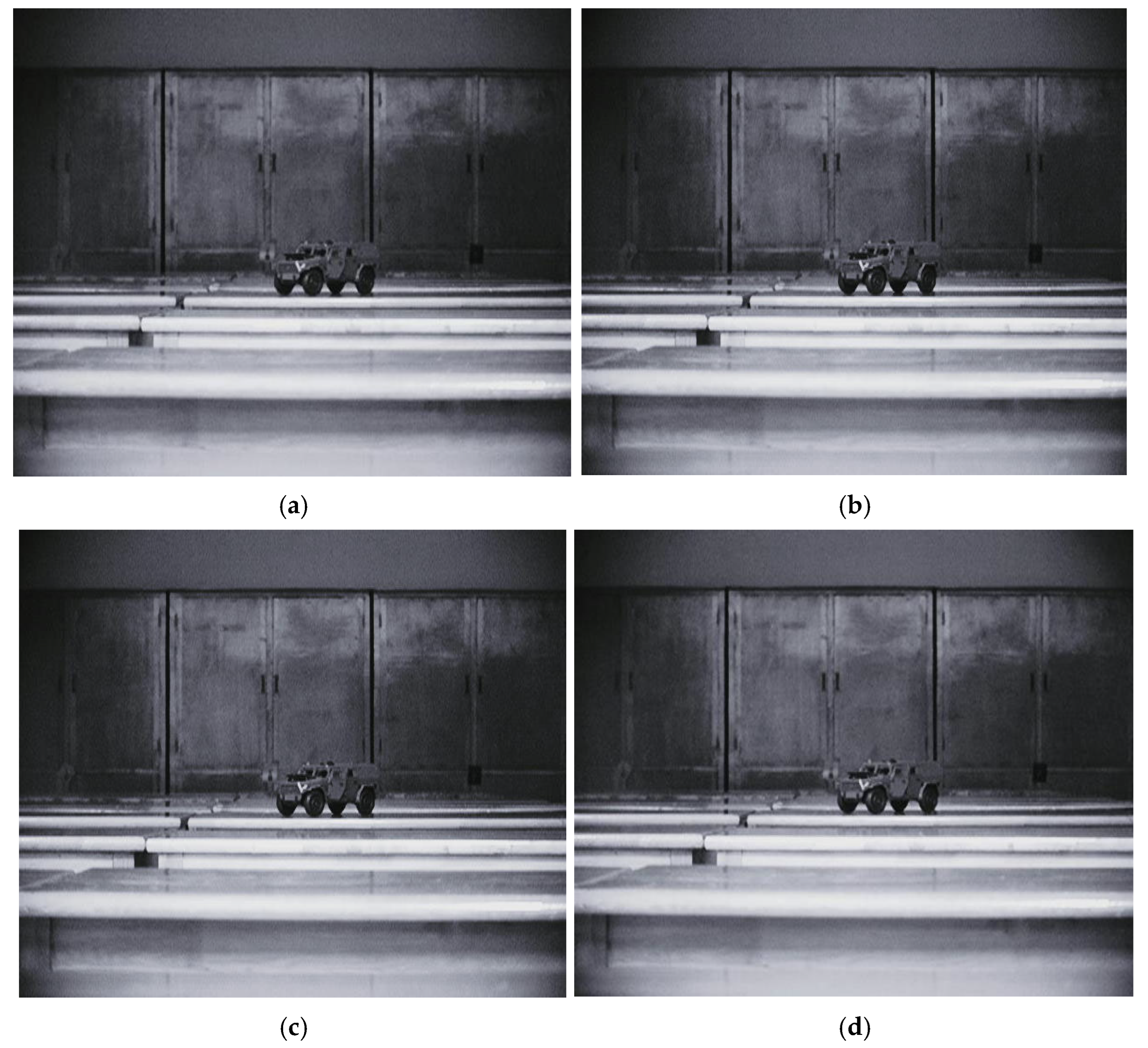
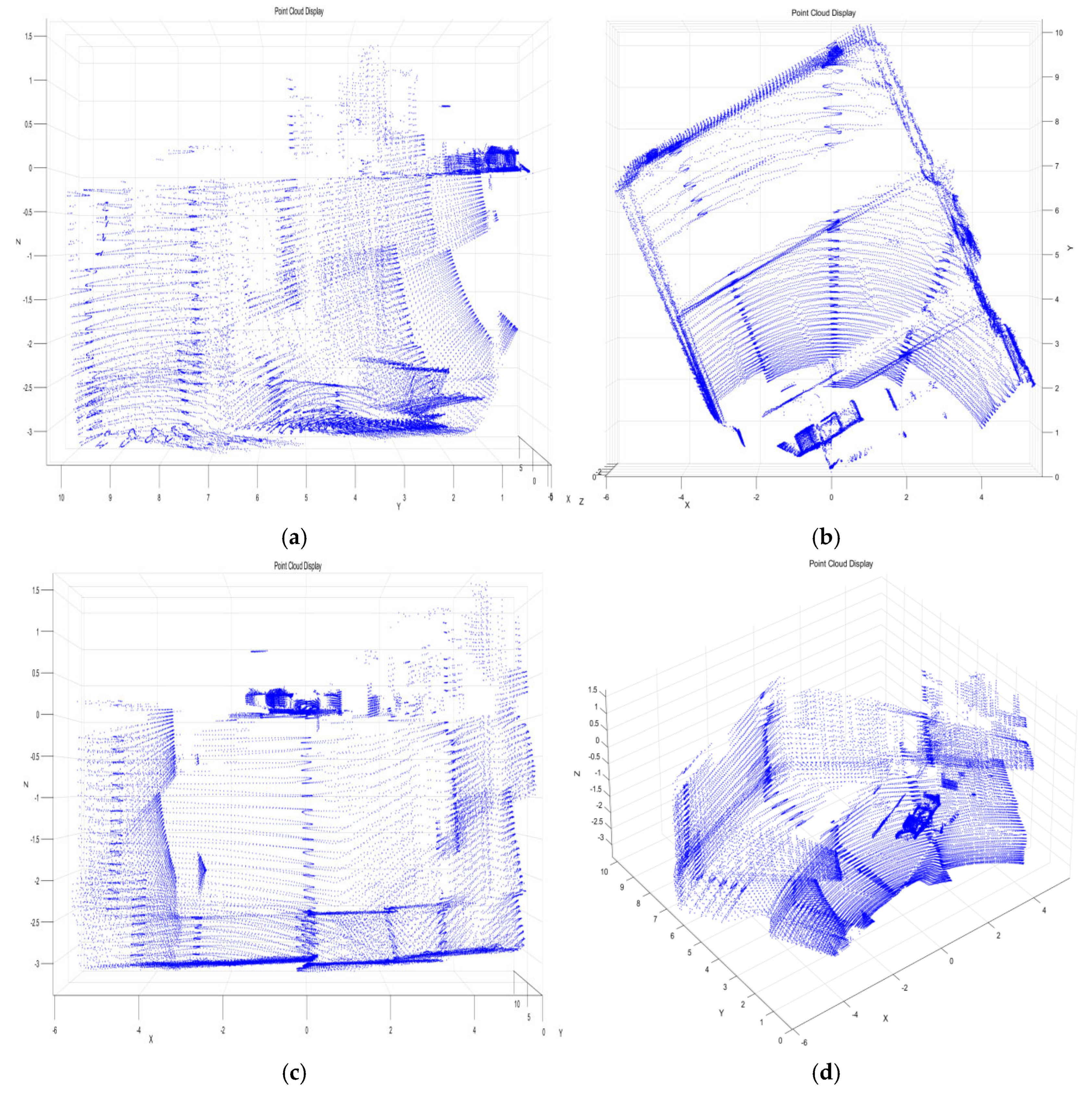
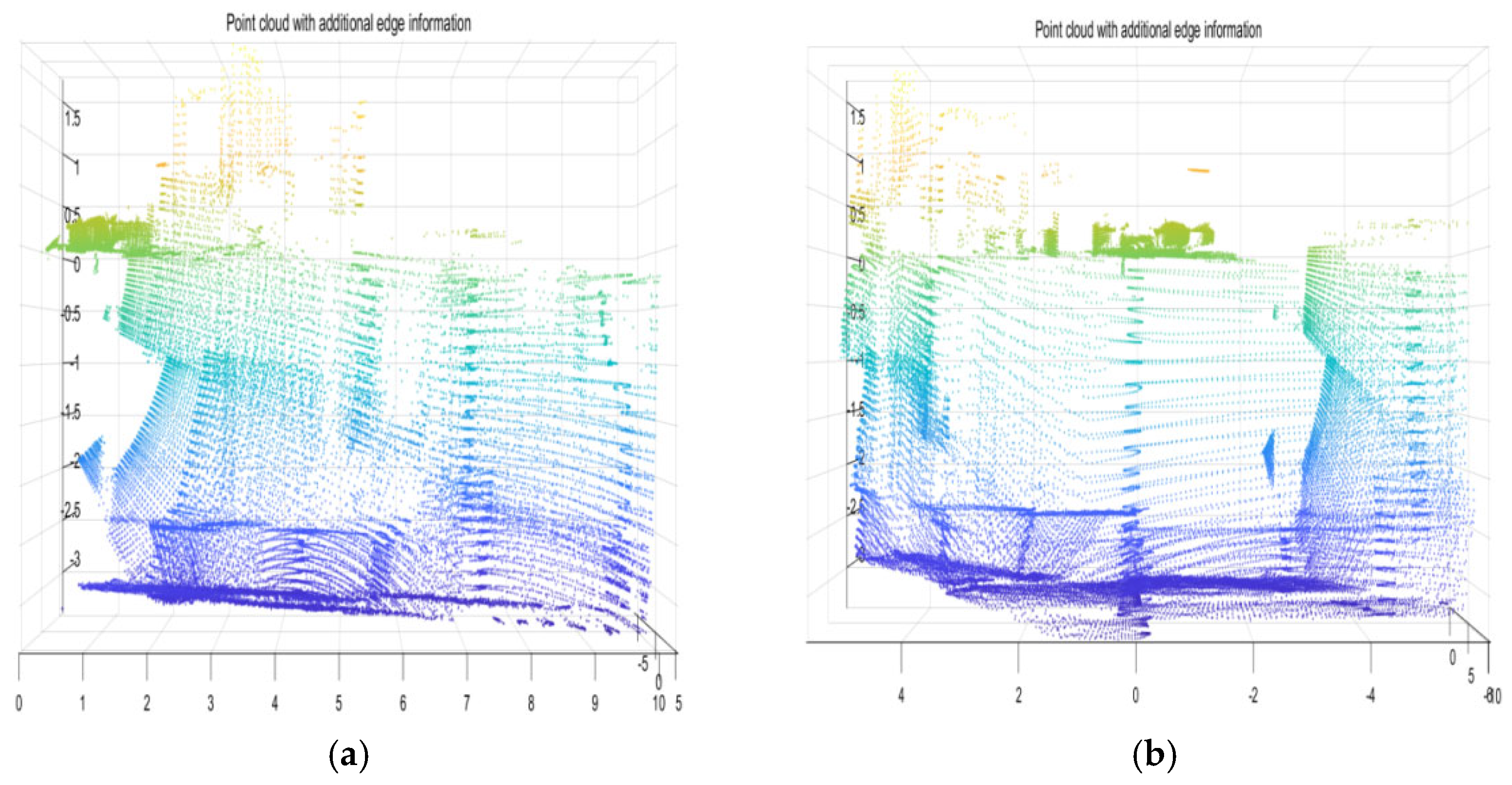
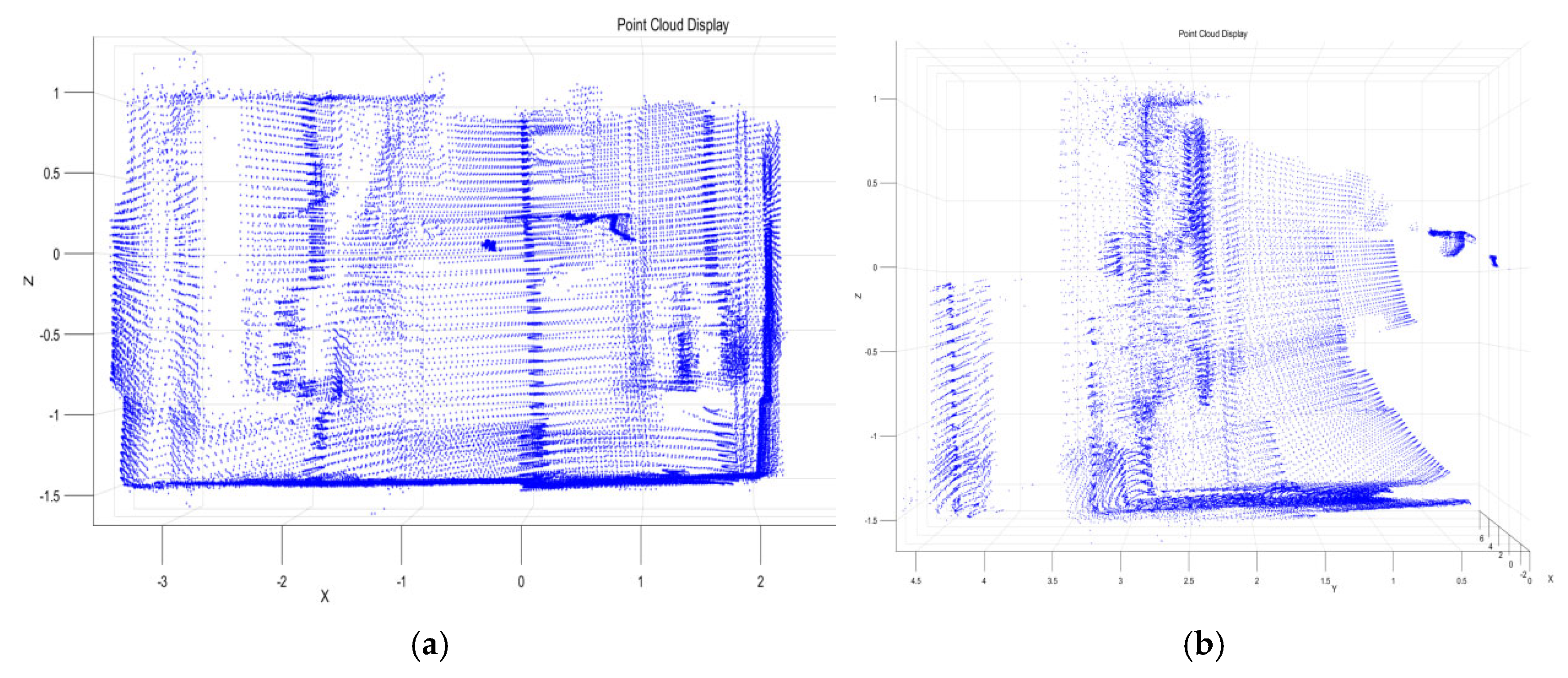
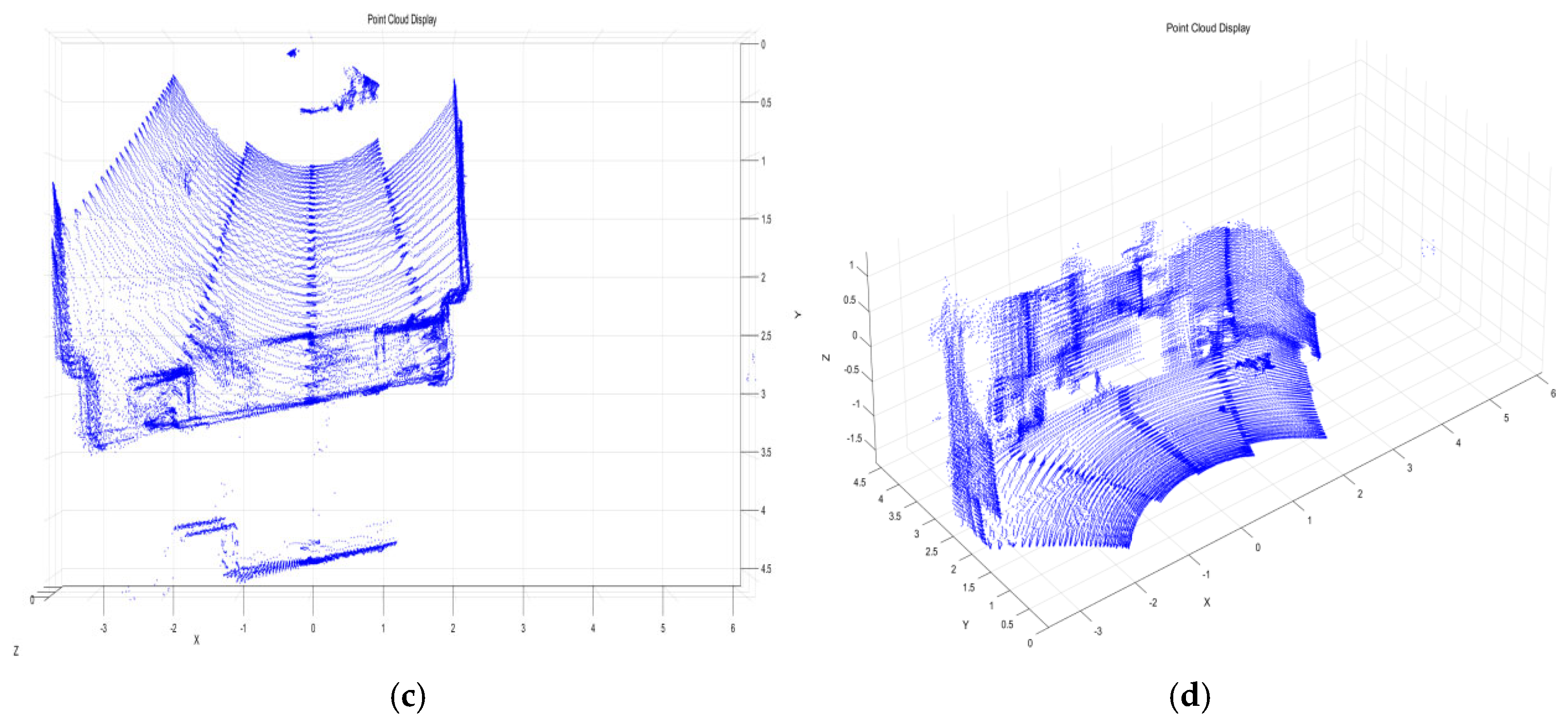
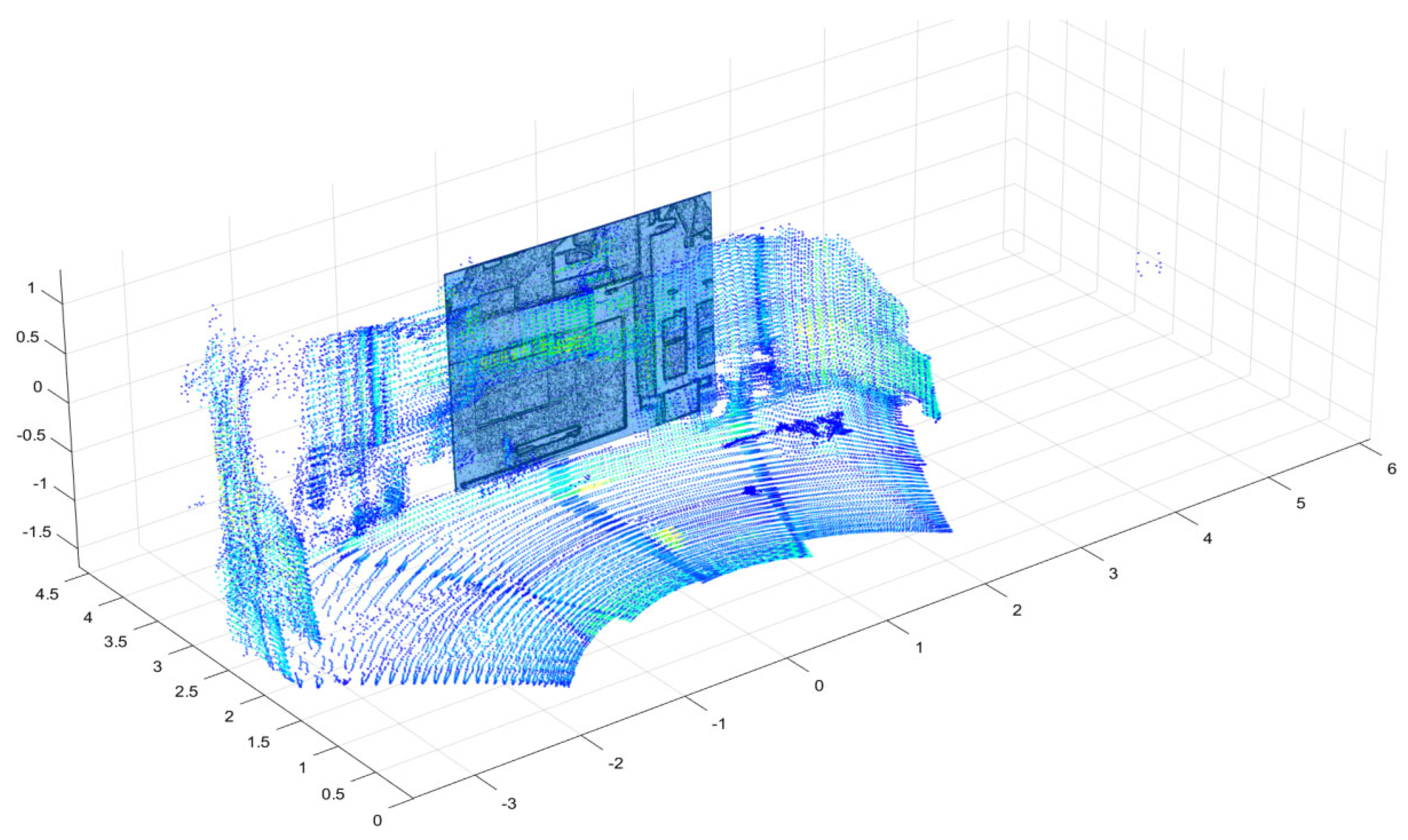
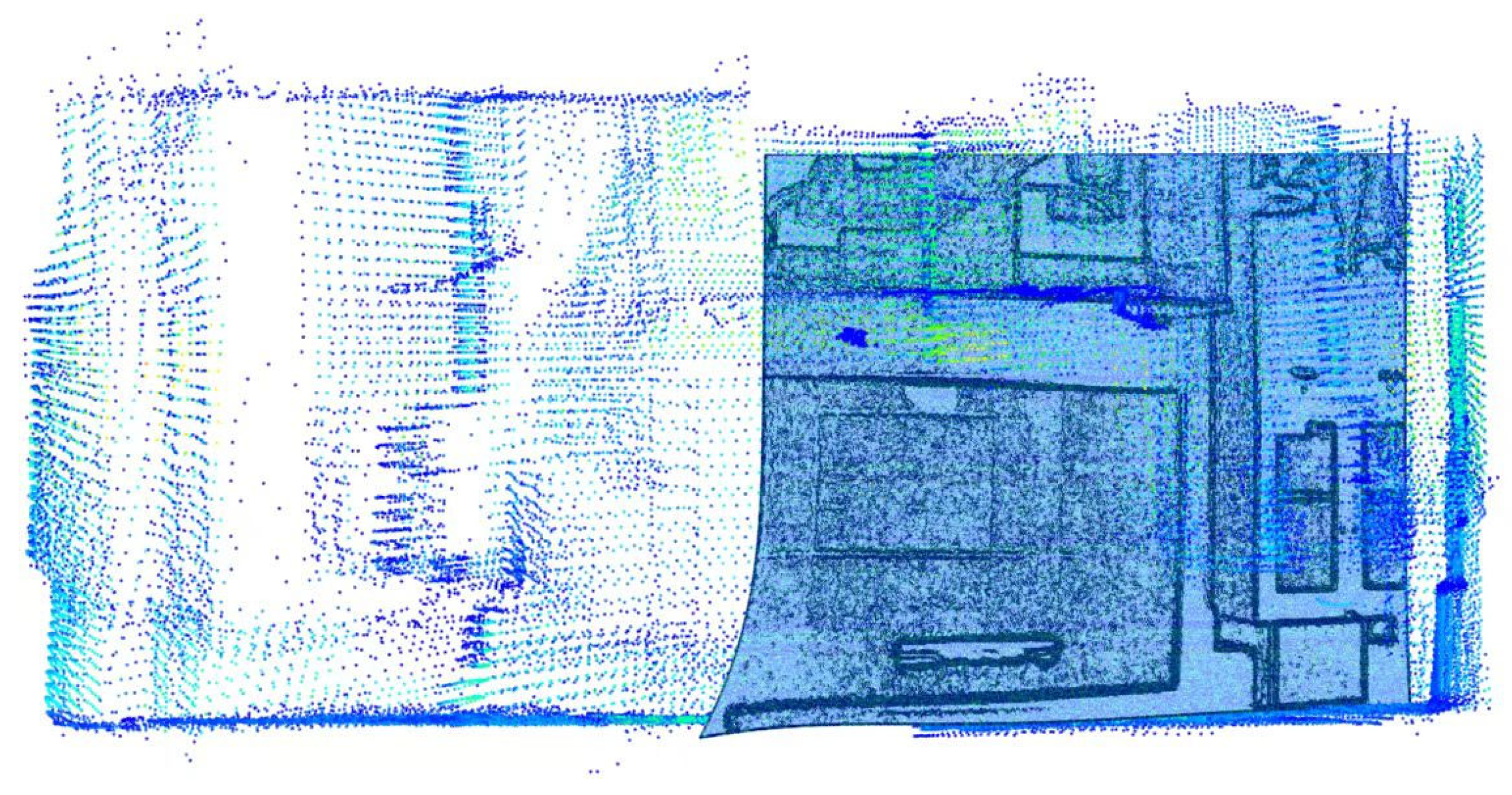
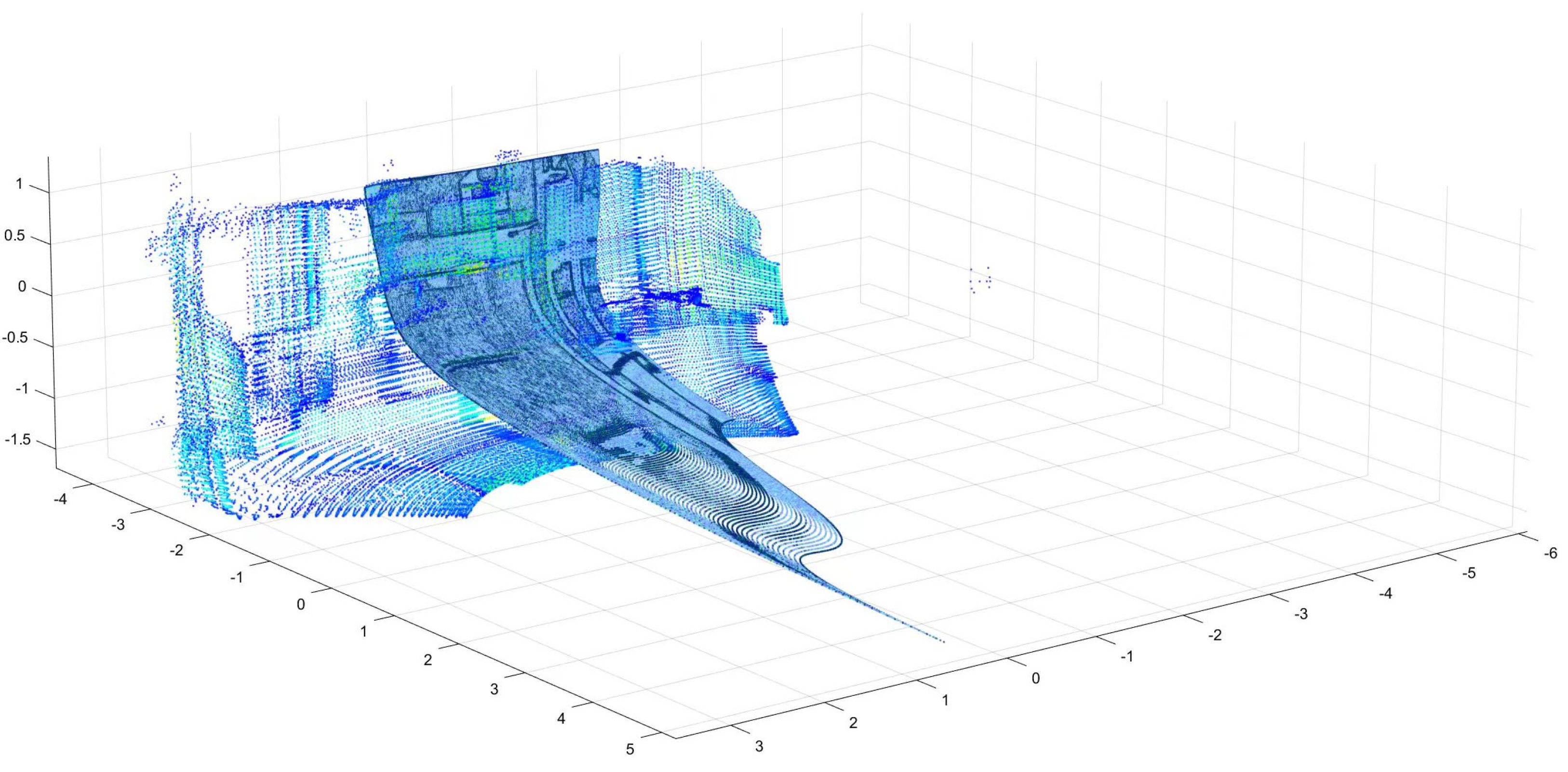
4.1. Fusion Data
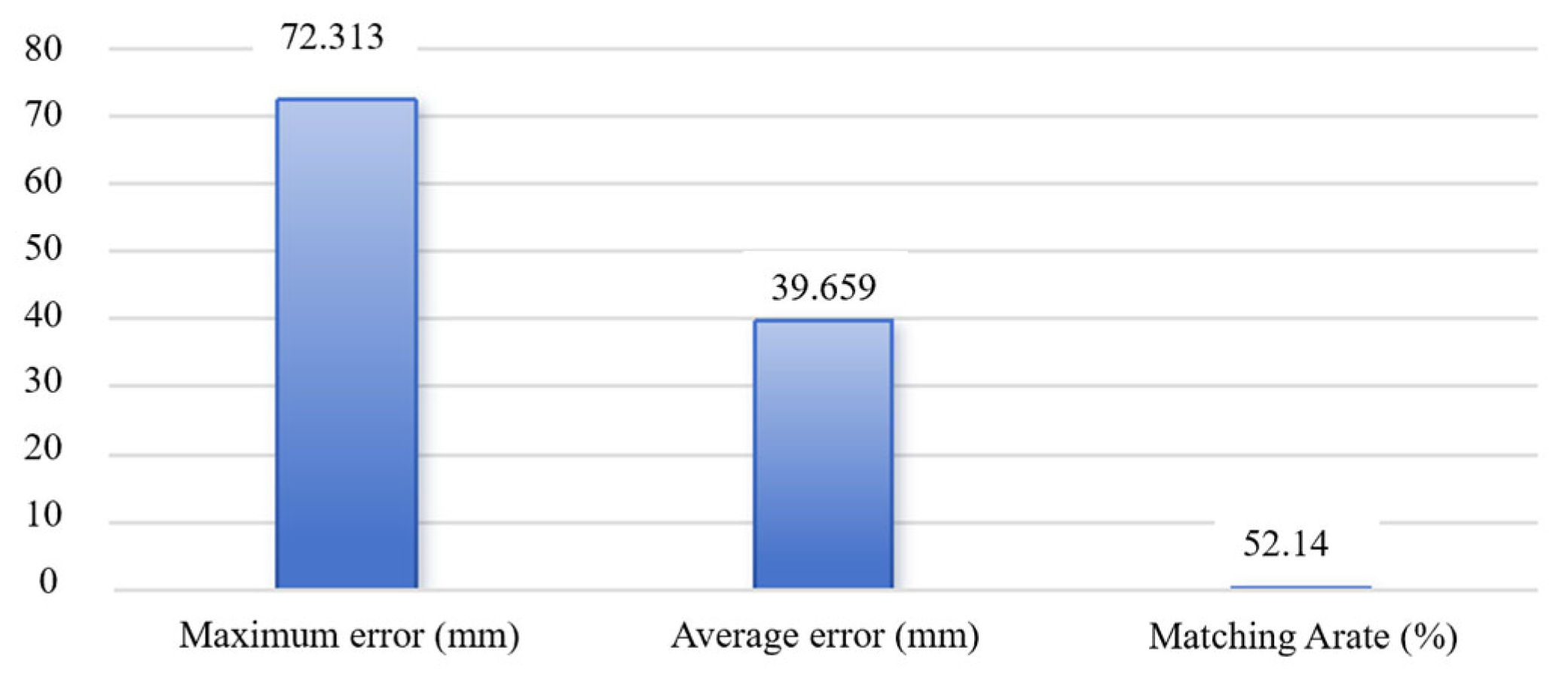
4.2. Matching Effect Evaluation
4.3. System Optimization
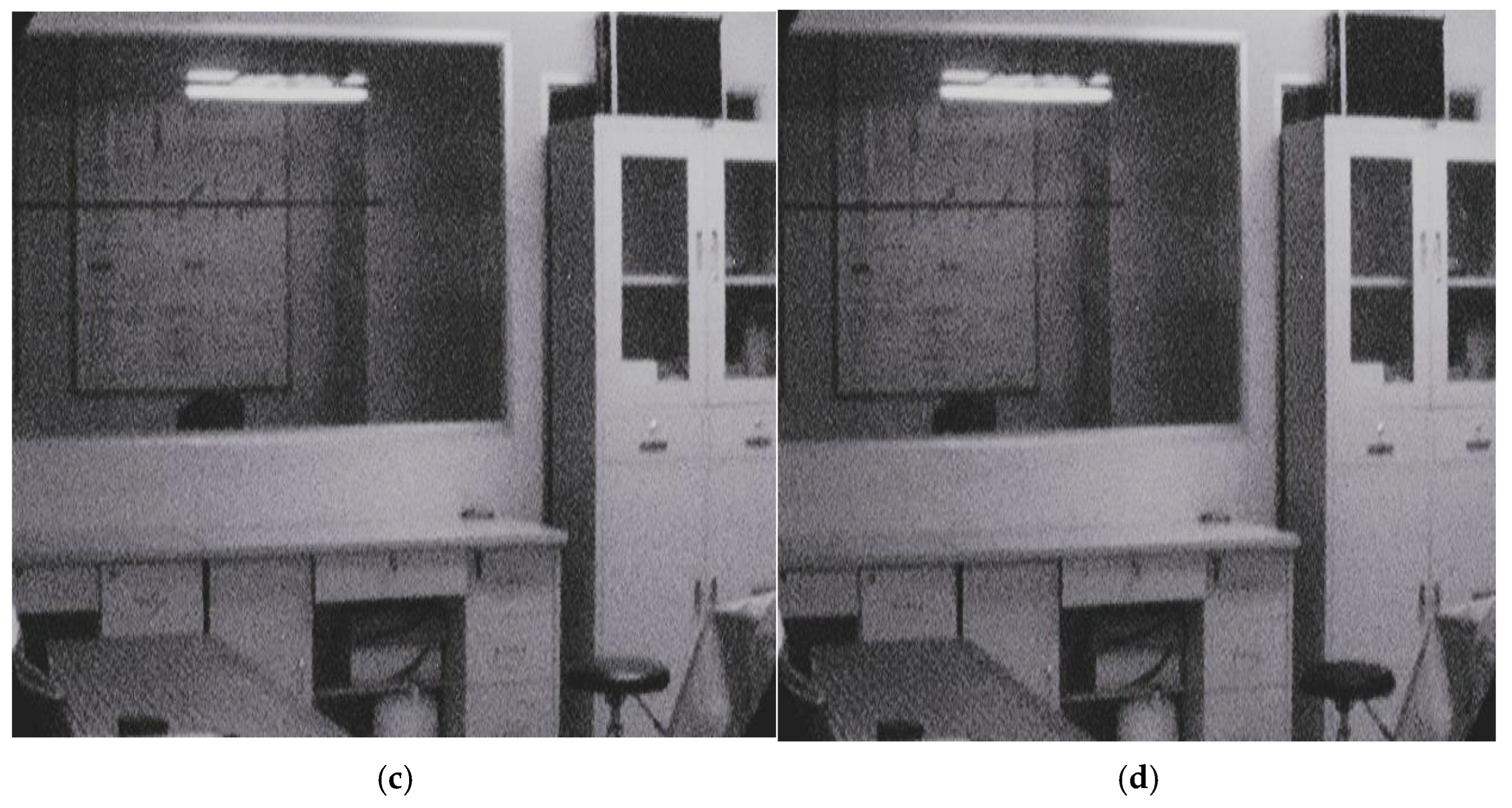
4.3.1. System Design Optimization
4.3.2. Optimization of the System Feature Extraction Algorithm
4.3.3. System Response Optimization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, J.; Che, K.; Gong, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, J.; Que, L.; Liu, H.; Len, Y. Fast and Accurate Detection of Dim and Small Targets for Smart Micro-Light Sight. Electronics 2024, 13, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kong, F.; Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Ruan, Y.; Cao, S.; Guo, Y. Biomimetic Polarized Light Navigation Sensor: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhu, D.; Gong, X.; Ye, Y.; Lee, H.F. CIRSM-Net: A Cyclic Registration Network for SAR and Optical Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5610619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Song, A.; Li, J.; Jin, K.; Luo, X.; Wei, K. Laser Phase Noise Compensation Method Based on Dual Reference Channels in Inverse Synthetic Aperture Lidar. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Shao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, P.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, H. GLO: General LiDAR-Only Odometry With High Efficiency and Low Drift. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 3518–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Ishikawa, R.; Oishi, T. Stereo-LiDAR Fusion by Semi-Global Matching With Discrete Disparity-Matching Cost and Semidensification. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 4548–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, H. Impact of Phase Error on Coherent LiDAR: Analysis and Validation. J. Light. Technol. 2025, 43, 4149–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraez, D.C.; Zeller, M.; Wang, D.; Behley, J.; Heidingsfeld, M.; Stachniss, C. RaI-SLAM: Radar-Inertial SLAM for Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 5257–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, T.; Fischer, T.; Milford, M. Matched Filtering Based LiDAR Place Recognition for Urban and Natural Environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 2566–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y. Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Method for LiDAR and IMU Using Surface Features. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2025, 62, 0415004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, W.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q. LNIFT: Locally Normalized Image for Rotation Invariant Multimodal Feature Matching. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5621314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Singh, S. Low-drift and Real-time LiDAR Odometry and Mapping. Auton. Robot. 2017, 41, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzo, I.; Guadagnino, T.; Mersch, B.; Wiesmann, L.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. KISS-ICP: In Defense of Point-to-Point ICP—Simple, Accurate, and Robust Registration If Done the Right Way. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, S.; He, R. Collaborative Contrastive Learning for Hyperspectral and LiDAR Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5507714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, R.; Chu, W.; Chen, L.; Tian, D.; Li, Y.; Cao, D. Deep Learning for Image and Point Cloud Fusion in Autonomous Driving: A Review. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 722–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitta, K.; Prakash, A.; Jaeger, B.; Yu, Z.; Renz, K.; Geiger, A. TransFuser: Imitation With Transformer-Based Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 12878–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, R.; Li, Z.; Ghamisi, P.; Hong, D.; Xia, G.; Liu, Q. Classification of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Using Coupled CNNs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4939–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liang, J.; Guo, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Integrated Precision Evaluation Method for 3D Optical Measurement System. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Manuf. 2011, 225, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, W.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, T.; Hu, X.; Ma, L. Deep-Learning-Based Point Cloud Completion Methods: A Review. Graph. Models 2024, 136, 101233. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, A.; Deng, Y. Precision Detection and Identification Method for Apparent Damage in Timber Components of Historic Buildings Based on Portable LiDAR Equipment. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Wei, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Intangible Cultural Heritage Based on Finite Element Analysis: Force Analysis of Chinese Traditional Garden Rockery Construction. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Advancements in point cloud data augmentation for deep learning: A survey. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 153, 110532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Dong, K.; Cheng, L.; Tiwari, P.; Ning, X. Coarse to Fine-Based Image–Point Cloud Fusion Network for 3D Object Detection. Inf. Fusion 2024, 112, 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Chen, J. 3D Modelling Method and Application to a Digital Campus by Fusing Point Cloud Data and Image Data. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Su, C.; Cao, G. Enhanced DetNet: A New Framework for Detecting Small and Occluded 3D Objects. Electronics 2025, 14, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, F.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Gao, X. Fringe Projection Profilometry(FPP) Based Point Clouds Fusion for the Binocular and Monocular Structured Light Systems. J. Opt. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Bian, Z.; Sun, T.; Zhong, K. Fusion and Visualization of Three-Dimensional Point Cloud and Optical Images. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2023, 60, 0611001. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Gai, X.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Development Status and Prospects of Polarization Imaging Technology (Invited). Infrared Laser Eng. 2022, 51, 20210987. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Gai, X. Polarization Image Interpolation Algorithm via Tensor Non-Negative Sparse Factorization. Acta Opt. Sin. 2021, 41, 1411001. [Google Scholar]
















| Minimum Illumination | Signal-to-Noise Ratio | Gain Mode |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0003 LuxF1.4 (AGC:High) | 46 dB | Automatic |
| Machine version | ML-30s B1 | ||
| FOV (°) | Horizontal FOV: 140° (70°~+70°) Vertical FOV: 70° (FOV1: −10°~+20°) (fov2: −50°~−10°) | ||
| Detection distance (m) | 100 k Lux | Resolution | HXV: 320 × 160 |
| Maximum detection distance (m) | 40 m | Minimum detection distance (m) | 20 cm |
| Frame rate (FPS) | 10 | Data interface | 100Base-T1 (data: UDP; control: TCP) |
| Data Type | Distance, reflectivity, azimuth and altitude Angle | Points per second | 512,000 points per second |
| −0.04235 | −3.456867 | 0.0916 | 9.1191 |
| 0 | 2.670461 | 0 | 5.673622 |
| 0 | 6.916017 | 0 | 6.666525 |
| Method | Matching Rate (%) | Average Error (mm) | Maximum Error (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original method | 52.14 | 39.659 | 72.313 |
| Optimizing method | 74.82 | 21.893 | 63.256 |
| Standard ICP | 60.37 | 30.880 | 68.934 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Li, G.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, L. Laser Radar and Micro-Light Polarization Image Matching and Fusion Research. Electronics 2025, 14, 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14153136
Yin J, Li G, Zhou B, Cheng L. Laser Radar and Micro-Light Polarization Image Matching and Fusion Research. Electronics. 2025; 14(15):3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14153136
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jianling, Gang Li, Bing Zhou, and Leilei Cheng. 2025. "Laser Radar and Micro-Light Polarization Image Matching and Fusion Research" Electronics 14, no. 15: 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14153136
APA StyleYin, J., Li, G., Zhou, B., & Cheng, L. (2025). Laser Radar and Micro-Light Polarization Image Matching and Fusion Research. Electronics, 14(15), 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14153136





