Advances in Gecko-Inspired Climbing Robots: From Biology to Robotics—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
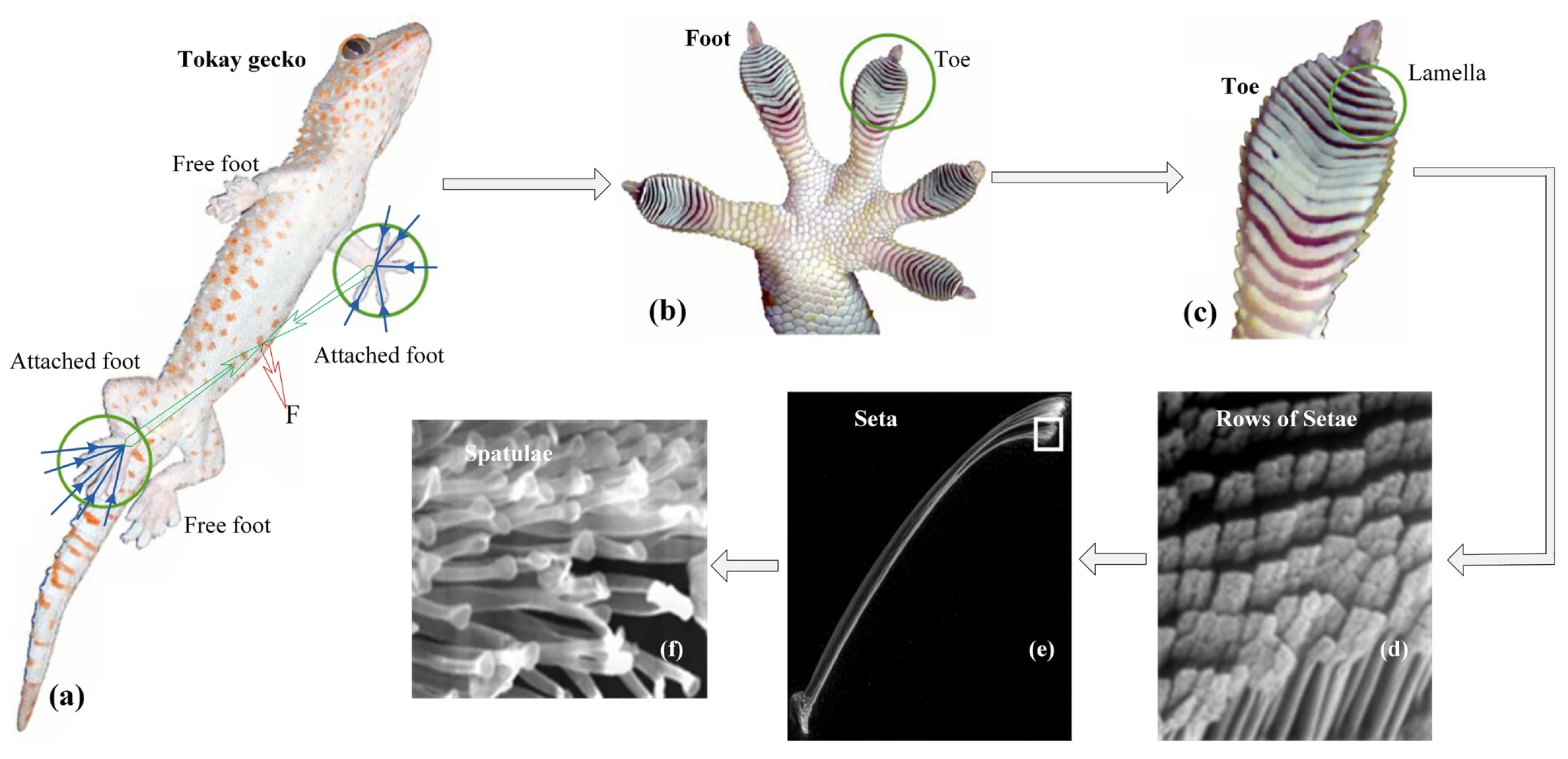
2. Biological Inspiration
3. Classification and Development of Bioinspired Gecko Robots
3.1. Classification Based on Spine Flexibility
3.1.1. Rigid-Spine Gecko Robots
3.1.2. Flexible-Spine Gecko Robots
3.2. Classification by Attachment Mechanisms
3.2.1. Claw-Based Attachment
3.2.2. Adhesive-Based Attachment

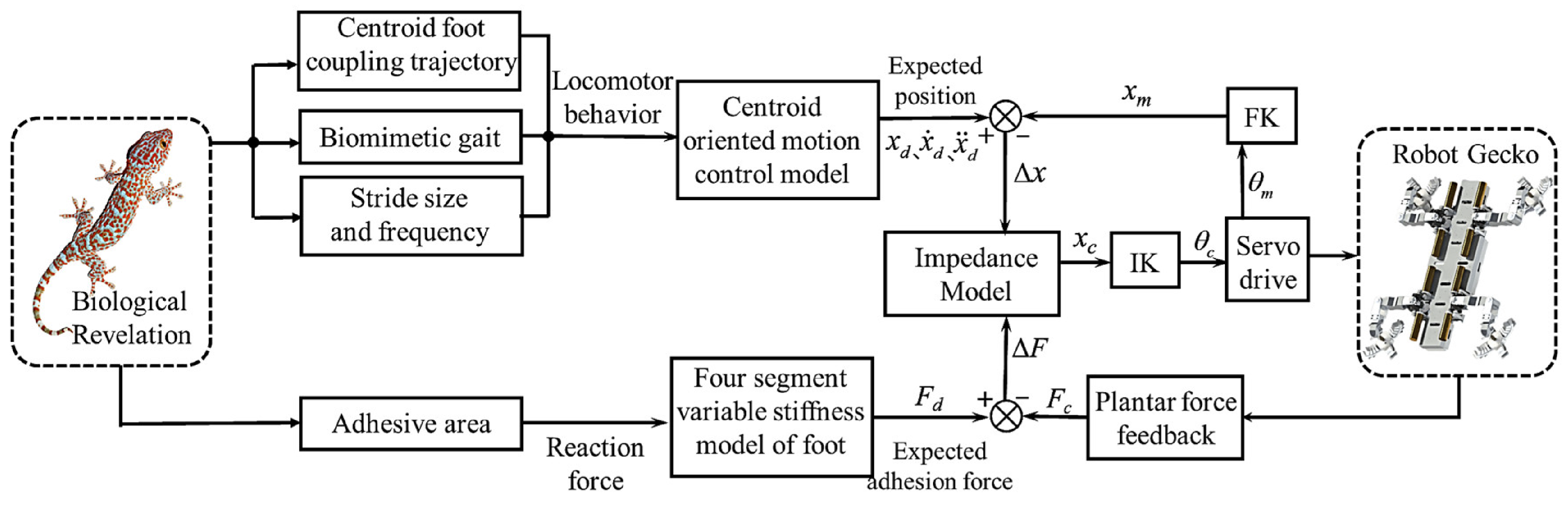
4. Motion Control Strategy of Bioinspired Gecko Robot
5. Applications of Gecko-Inspired Robots
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez-Aguirre, J.A.; Osorio-Oliveros, R.; Rodríguez-Hernández, K.L.; Lizárraga-Iturralde, J.; Morales Menendez, R.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R.A.; Ramirez-Moreno, M.A.; Lozoya-Santos, J.d.J. Service robots: Trends and technology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nansai, S.; Mohan, R.E. A survey of wall climbing robots: Recent advances and challenges. Robotics 2016, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusell, A.; Andrikopoulos, G.; Nikolakopoulos, G. A survey on pneumatic wall-climbing robots for inspection. In Proceedings of the 2016 24th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED), Athens, Greece, 21–24 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, D.; Berns, K. Climbing robots for maintenance and inspections of vertical structures—A survey of design aspects and technologies. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 1288–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wu, X. Survey on bioinspired adhesive methods and design and implementation of a multi-mode biomimetic wall-climbing robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Auckland, New Zealand, 9–12 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 688–693. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, T.; Jeon, Y.; Park, C.; Kim, J. Survey on glass and façade-cleaning robots: Climbing mechanisms, cleaning methods, and applications. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2019, 6, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, S.; Bi, Q.; Cui, D.; Yan, C. Design and technical development of wall-climbing robots: A review. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 877–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Ji, A.; Zhu, K.; Han, Q.; Wang, W.; Qi, Q.; Chen, G. A gecko-inspired robot with a flexible spine driven by shape memory alloy springs. Soft Robot. 2023, 10, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Yan, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W. A small climbing robot for the intelligent inspection of nuclear power plants. In Proceedings of the 2014 4th IEEE International Conference on Information Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China, 26–28 April 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 484–487. [Google Scholar]
- Saadat, S.; Salichs, J.; Noori, M.; Hou, Z.; Davoodi, H.; Bar-On, I.; Suzuki, Y.; Masuda, A. An overview of vibration and seismicapplications of NiTi shape memory alloy. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Noh, K.; Jang, M.; Kim, S. Wall-climbing robot with active sealing for radiation safety of nuclear power plants. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 2020, 194, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Hirai, M.; Hirose, S. Gunryu III: Reconfigurable magnetic wall-climbing robot for decommissioning of nuclear reactor. Adv. Robot. 2013, 27, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Pan, H.; Shen, W. Multifunctional robot to maintain boiler water-cooling tubes. Robotica 2009, 27, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneewarn, T.; Thung-od, K. ICP-EKF localization with adaptive covariance for a boiler inspection robot. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 7th International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) and IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM), Angkor Wat, Cambodia, 15–17 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, Z.; Deng, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Xiao, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Dong, N.; Wu, J. Design and experimental verification of an intelligent wall-climbing welding robot system. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2014, 41, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Tian, W.; Wei, R.; Pan, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S. Application of a wall-climbing, welding robot in ship automatic welding. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 106, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Pan, G.; Zhang, T.; Chen, S.; Zhuang, F.; Yan-zheng, Z. Design and optimal research of a non-contact adjustable magnetic adhesion mechanism for a wall-climbing welding robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zheng, J. A real-time weld line detection for derusting wall-climbing robot using dual cameras. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 27, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Gui, H.; Li, D.; Li, Z. Identification of the deviation of seam tracking and weld cross type for the derusting of ship hulls using a wall-climbing robot based on three-line laser structural light. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 35, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Sun, L.; Li, M. Optimization design and flexible detection method of wall-climbing robot system with multiple sensors integration for magnetic particle testing. Sensors 2020, 20, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.V.; Kyaw, P.T.; Veerajagadheswar, P.; Muthugala, M.V.J.; Elara, M.R.; Kumar, M.; Nhan, N.H.K. Reinforcement learning-based optimal complete water-blasting for autonomous ship hull corrosion cleaning system. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 220, 108477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Hua, S. Predictor-based adaptive feedback control for a class of systems with time delay and its application to an aircraft skin inspection robot. IET Control. Theory Appl. 2020, 14, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Mohsin, I.; Wei, Y.; He, K. Influence of processing parameters on coating removal for high pressure water jet technology based on wall-climbing robot. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Liu, Q. Adhesion-adaptive control of a novel bridge-climbing robot. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control and Intelligent Systems, Chengdu, China, 19–22 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Q.; Luo, X.; Qiao, Z.; Li, Q. Design and motion planning of a biped climbing robot with redundant manipulator. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Kawamura, Y. Development of climbing robot for steel bridge inspection. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2016, 43, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Guo, J.; Cho, C.; Wang, Y.; Lee, K.M. Wireless mobile sensor network for the system identification of a space frame bridge. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 17, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiting, W.; Shili, T.; Junjian, D.; Liwen, Y. Complete coverage path planning of wall-cleaning robot using visual sensor. In Proceedings of the 2007 8th International Conference on Electronic Measurement and Instruments, Xian, China, 16–18 August 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 4–159. [Google Scholar]
- Soeda, T.; Okada, N.; Kiguchi, K. A simple wall-climbing mechanism for a window cleaning robot. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics 2013 (AROB 18th ’13), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 30 January–1 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Jeon, Y.; Yoo, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J. Development of a wall-climbing platform with modularized wall-cleaning units. Autom. Constr. 2017, 83, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. Mechanism design and mechanical analysis of multi-suction sliding cleaning robot used in glass curtain wall. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2019, 34, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Heredia, M.; Mohan, R.E.; Wen, T.Y.; Siti’Aisyah, J.; Vengadesh, A.; Ghanta, S.; Vinu, S. Design and modelling of a modular window cleaning robot. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, T.; Kushwaha, S.K.; Roslin, S.E.; Nandhitha, N. Flux controlled BLDC motor for automated glass cleaning robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 Third International Conference on Science Technology Engineering & Management (ICONSTEM), Chennai, India, 23–24 March 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 955–959. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, F.; Honjo, A.; Makino, T.; Kwon, S. Inspection robot system using duct fan and deterioration estimation of building wall that can be applied even in disaster. In Proceedings of the 2018 18th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), PyeongChang, Republic of Korea, 17–20 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 331–334. [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi, Y.; Kojima, S.; Ohno, K.; Okada, Y.; Hamada, R.; Suzuki, T.; Tadokoro, S. Attempt at climbing of spiral staircase for tracked vehicles using reaction force of stairs’ handrail. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Taipei, Taiwan, 11–14 December 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 456–462. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.G.; Wang, H.G.; Liu, A.H.; Li, Z.H. Design and analysis of a novel wall-climbing robot mechanism. In Proceedings of the Advanced Engineering Forum; Trans Tech Publ: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Altaf, M.; Ahmad, E.; Xu, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Na, H. Design of a climbing robot platform with protection device. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417716382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Peng, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, X. Research status and development trend of wall climbing robot. J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 59, 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Guangqing, C.; Lei, Z.; Jinze, X.; Kunyuan, L.; Aiqin, S.; Yahui, C.; Liang, Y. Analysis and future prospects of adsorption techniques employed by wall-climbing. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2024, 21, 17298806241279611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rivaz, S.D.; Goldberg, B.; Doshi, N.; Jayaram, K.; Zhou, J.; Wood, R.J. Inverted and vertical climbing of a quadrupedal microrobot using electroadhesion. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaau3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, R.S.; Pathak, P.M.; Panigrahi, S.K. Design and development of a glass façade cleaning robot. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 168, 104585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintov, A.; Avramovich, T.; Shapiro, A. Design and motion planning of an autonomous climbing robot with claws. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2011, 59, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Kim, H.; Seo, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.S. MultiTrack: A multi-linked track robot with suction adhesion for climbing and transition. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 72, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parness, A.; Frost, M.; Thatte, N.; King, J.P.; Witkoe, K.; Nevarez, M.; Garrett, M.; Aghazarian, H.; Kennedy, B. Gravity-independent rock-climbing robot and a sample acquisition tool with microspine grippers. J. Field Robot. 2013, 30, 897–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatsu, M.; Kawasaki, Y.; Kawasaki, S.; Kikuchi, K. Development of cm-scale wall climbing hexapod robot with claws. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Design Engineering and Science—ICDES, Pilsen, Czech Republic, 31 August–3 September 2014; pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakoli, M.; Viegas, C.; Marques, L.; Pires, J.N.; De Almeida, A.T. OmniClimbers: Omni-directional magnetic wheeled climbing robots for inspection of ferromagnetic structures. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.H.; Sreekumar, M.; Ponnambalam, S. Hybrid electrostatic and elastomer adhesion mechanism for wall climbing robot. Mechatronics 2016, 35, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, S.; Rahman, M.H.; Siddaiah, A.; Menezes, P.L. Gecko-Inspired Adhesive Mechanisms and Adhesives for Robots—A Review. Robotics 2022, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Li, W.; Ji, A.; Wang, W. How do the substrate reaction forces acting on a gecko’s limbs respond to inclines? Sci. Nat. 2015, 102, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maderson, P. Keratinized epidermal derivatives as an aid to climbing in gekkonid lizards. Nature 1964, 203, 780–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.P. A contribution to the functional analysis of the foot of the Tokay, Gekko gecko (Reptilia: Gekkonidae). J. Zool. 1975, 176, 437–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Liang, Y.A.; Hsieh, S.T.; Zesch, W.; Chan, W.P.; Kenny, T.W.; Fearing, R.; Full, R.J. Adhesive force of a single gecko foot-hair. Nature 2000, 405, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, R.; Byrnes, G.; Full, R.J.; Jusufi, A. Tails stabilize landing of gliding geckos crashing head-first into tree trunks. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jusufi, A.; Goldman, D.I.; Revzen, S.; Full, R.J. Active tails enhance arboreal acrobatics in geckos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4215–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Ji, A.; Ren, L.; Xing, Q.; Dai, L. Biomechanics of gecko locomotion: The patterns of reaction forces on inverted, vertical and horizontal substrates. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 016019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Full, R.J. Role of multiple, adjustable toes in distributed control shown by sideways wall-running in geckos. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R. A gecko-inspired electroadhesive wall-climbing robot. IEEE Potentials 2015, 34, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ji, A. Dynamics of gecko locomotion: A force-measuring array to measure 3D reaction forces. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaf, A.; Van Damme, R.; Herrel, A.; Aerts, P. Limb joint kinematics during vertical climbing and level running in a specialist climber: Gekko gecko Linneus, 1758 (Lacertilia: Gekkonidae). Belg. J. Zool. 2001, 131, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, L.; Li, W.; Ji, A.; Wang, W.; Dai, Z. Effect of slope degree on the lateral bending in Gekko geckos. J. Bionic Eng. 2015, 12, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, A.; Wakasugi, Y.; Watanabe, K. Design of a robot capable of moving on a vertical wall. Adv. Robot. 1986, 1, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, A. Development of wall-climbing robots. Comput. Electr. Eng. 1996, 22, 123–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Cheng, J. Advances in climbing robots for vertical structures in the past decade: A review. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, S.; Kim, D.W.; Park, Y.; Lee, T.J.; Ho Bhang, S.; Pang, C. A wet-tolerant adhesive patch inspired by protuberances in suction cups of octopi. Nature 2017, 546, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, S. Role of locust Locusta migratoria manilensis claws and pads in attaching to substrates. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Ji, A.; Han, Q.; Shen, H.; Liu, S.; Xiang, W.; Zhang, Q. Advances in Research of Wall-climbing Robots: From Biology to Bionics-A Review. J. Bionic Eng. 2025, 22, 945–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.; Rahn, C.D.; Kier, W.M.; Walker, I.D. Soft robotics: Biological inspiration, state of the art, and future research. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2008, 5, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaf, A.; Van Damme, R.; Herrel, A.; Aerts, P. Spatio-temporal gait characteristics of level and vertical locomotion in a ground-dwelling and a climbing gecko. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasiliotis, K.; Ijspeert, A.J. Analysis of the terrestrial locomotion of a salamander robot. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 5015–5020. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, W.; Seo, T.; Kim, B.; Jeon, D.; Cho, K.J.; Kim, J. Kinematic analysis and experimental verification on the locomotion of gecko. J. Bionic Eng. 2009, 6, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ji, A.; Chen, G.; Ravi, S.; Shen, H.; Gorb, S.N.; Dai, Z. Kinematics of gecko climbing: The lateral undulation pattern. Zoology 2020, 140, 125768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haomachai, W.; Shao, D.; Wang, W.; Ji, A.; Dai, Z.; Manoonpong, P. Lateral undulation of the bendable body of a gecko-inspired robot for energy-efficient inclined surface climbing. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7917–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Hsieh, S.T.; Dudek, D.M.; Chen, J.; Chitaphan, C.; Full, R.J. Dynamics of geckos running vertically. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Peattie, A.; Autumn, K.; Full, R. Differential leg function in a sprawled-posture quadrupedal trotter. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, D.I.; Chen, T.S.; Dudek, D.M.; Full, R.J. Dynamics of rapid vertical climbing in cockroaches reveals a template. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 2990–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, S.; Zhu, P.; Liu, R. Analysis on the dynamic climbing forces of a gecko inspired climbing robot based on GPL model. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 3314–3319. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Ji, A.; Dai, Z.; Qin, G.; Ren, T.; Han, Q. Angular variables of climbing geckos in two lateral undulation patterns. Zoology 2021, 145, 125892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, M. Further studies on locomotion of the cheetah. J. Mammal. 1961, 42, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z. Research on the Movement Behavior of the Gecko and the Development of a Gecko-like Robot. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, J.L. The evolution of terrestrial locomotion. In Major Patterns in Vertebrate Evolution; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1977; pp. 553–577. [Google Scholar]
- Cartmill, M.; Hildebrand, M.; Bramble, D.; Liem, K.; Wake, D. Functional Vertebrate Morphology; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, A.P. Integrative Functional Morphology of the Gekkotan Adhesive System (Reptilia: Gekkota)1. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruibal, R.; Ernst, V. The structure of the digital setae of lizards. J. Morphol. 1965, 117, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Puthoff, J. Biological Adhesives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 225–255. [Google Scholar]
- Kasar, A.K.; Ramachandran, R.; Menezes, P.L. Natural adhesion system leads to synthetic adhesives. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2018, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, U. Untersuchungen zum Feinbau und zur Funktion der Haftborsten von Reptilien. Z. Morphol. Tiere 1968, 62, 307–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, U. Correlation between corona-discharge of polyethylene-films and the adhering power of Tarentola m. mauritanica (Rept.). Forma Funct. 1969, 1, 350–352. [Google Scholar]
- Hiller, U. Walking upside down: The mystery of climbing ability in gekkonid lizards. Gekko 2000, 1, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Autumn, K.; Sitti, M.; Liang, Y.A.; Peattie, A.M.; Hansen, W.R.; Sponberg, S.; Kenny, T.W.; Fearing, R.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Full, R.J. Evidence for van der Waals adhesion in gecko setae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12252–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autumn, K.; Peattie, A.M. Mechanisms of adhesion in geckos. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, N.; Gardner, K.; Walls, D.e.a.; Keiper-Hrynko, N.; Ganzke, T.; Hallahan, D. Characterization of the structure and composition of gecko adhesive setae. J. R. Soc. Interface 2006, 3, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L. Ultrastructural autoradiographic and immunocytochemical analysis of setae formation and keratinization in the digital pads of the gecko Hemidactylus turcicus (Gekkonidae, Reptilia). Tissue Cell 2003, 35, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peattie, A.M.; Majidi, C.; Corder, A.; Full, R.J. Ancestrally high elastic modulus of gecko setal β-keratin. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Majidi, C.; Groff, R.; Dittmore, A.; Fearing, R. Effective elastic modulus of isolated gecko setal arrays. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 3558–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z. Gecko-like dry adhesive surfaces and their applications: A review. J. Bionic Eng. 2021, 18, 1011–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Hwang, I.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.; Lim, H.; Tahk, D.; Sung, M.; Bae, W.G.; Choi, S.J.; Kwak, M.K.; et al. Continuous and scalable fabrication of bioinspired dry adhesives via a roll-to-roll process with modulated ultraviolet-curable resin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14590–14599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, A.; Jiang, R.; Li, D.; Zhang, M.; Gan, Z.; Tao, W.; Guo, H.; Mei, T. Surface properties of bionic micro-pillar arrays with various shapes of tips. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, C.B.; Chun, S.; Krishna-Subbaiah, N.; Drotlef, D.M.; Akolpoglu, M.B.; Sitti, M. 3D printing of elastomeric bioinspired complex adhesive microstructures. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liimatainen, V.; Drotlef, D.M.; Son, D.; Sitti, M. Liquid-superrepellent bioinspired fibrillar adhesives. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siles, I.; Walker, I. Continuum robotic elements for enabling negotiation of uneven terrain in unstructured environments. WSEAS Trans. Appl. Theor. Mech. 2013, 8, 258–273. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, T.V.; Conard, G.G.; Sanchez, A.G.; Sun, Y.; Onal, C.D. Lizard: A Novel Origami Continuum Mobile Robot for Complex and Unstructured Environments. Robot. Rep. 2025, 2, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxerbaum, A.S.; Oro, J.; Peterson, G.; Quinn, R.D. The latest generation Whegs™ robot features a passive-compliant body joint. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1636–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Karakasiliotis, K.; Thandiackal, R.; Melo, K.; Horvat, T.; Mahabadi, N.K.; Tsitkov, S.; Cabelguen, J.M.; Ijspeert, A.J. From cineradiography to biorobots: An approach for designing robots to emulate and study animal locomotion. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20151089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, A.; Karakasiliotis, K.; Guignard, A.; Ijspeert, A.J. Salamandra robotica II: An amphibious robot to study salamander-like swimming and walking gaits. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 29, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zang, H.; Liao, B.; Qi, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, M.; Lang, X.; Wang, Y. A quadruped soft robot for climbing parallel rods. Robotica 2021, 39, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrey, J.M.; Lambrecht, B.; Horchler, A.D.; Ritzmann, R.E.; Quinn, R.D. Highly mobile and robust small quadruped robots. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2003) (Cat. No. 03CH37453), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27 October–1 November 2003; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Saranli, U.; Buehler, M.; Koditschek, D.E. RHex: A simple and highly mobile hexapod robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2001, 20, 616–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altendorfer, R.; Moore, N.; Komsuoglu, H.; Buehler, M.; Brown, H.; McMordie, D.; Saranli, U.; Full, R.; Koditschek, D.E. Rhex: A biologically inspired hexapod runner. Auton. Robot. 2001, 11, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.J.; Quinn, R.D.; Bachmann, R.J.; Ritzmann, R.E. Abstracted biological principles applied with reduced actuation improve mobility of legged vehicles. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2003) (Cat. No. 03CH37453), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27 October–1 November 2003; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1370–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Ding, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Gao, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, G.; Hossain, M. SoSpider: A bio-inspired multimodal untethered soft hexapod robot for planetary lava tube exploration. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2023, 66, 3090–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, O.; Uneri, A.; Aydemir, A.; Sitti, M. Geckobot: A gecko inspired climbing robot using elastomer adhesives. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 2329–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Spenko, M.; Trujillo, S.; Heyneman, B.; Mattoli, V.; Cutkosky, M.R. Whole body adhesion: Hierarchical, directional and distributed control of adhesive forces for a climbing robot. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Heyneman, B.; Kim, S.; Esparza, N.; Cutkosky, M.R. Gecko-inspired climbing behaviors on vertical and overhanging surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, E.W.; Eason, E.V.; Asbeck, A.T.; Cutkosky, M.R. The Gecko’s Toe: Scaling Directional Adhesives for Climbing Applications. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, P. Review of advancements in wall climbing robot techniques. Frankl. Open 2024, 8, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, E.W.; Ulmen, J.; Esparza, N.; Cutkosky, M.R. Scaling walls: Applying dry adhesives to the real world. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 5100–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Buehler, M.; Cutkosky, M.; Fearing, R.; Full, R.J.; Goldman, D.; Groff, R.; Provancher, W.; Rizzi, A.A.; Saranli, U.; et al. Robotics in scansorial environments. In Proceedings of the Unmanned Ground Vehicle Technology VII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5804, pp. 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Spenko, M.J.; Haynes, G.C.; Saunders, J.A.; Cutkosky, M.R.; Rizzi, A.A.; Full, R.J.; Koditschek, D.E. Biologically inspired climbing with a hexapedal robot. J. Field Robot. 2008, 25, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, G.C.; Khripin, A.; Lynch, G.; Amory, J.; Saunders, A.; Rizzi, A.A.; Koditschek, D.E. Rapid pole climbing with a quadrupedal robot. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 2767–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalouche, S.; Wiltsie, N.; Su, H.J.; Parness, A. Inchworm style gecko adhesive climbing robot. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 2319–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xie, J.; Yang, S.X.; Dai, Z. Design and analysis of a bionic adhesive foot for gecko robot climbing the ceiling. Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2018, 33, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.; Wei, Y.; Xu, F.; Kong, D. A four-legged wall-climbing robot with spines and miniature setae array inspired by longicorn and gecko. J. Bionic Eng. 2021, 18, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Liu, S.; Wei, A.; Shi, R.; Dai, Z. Bioinspired Rigid–Flexible Coupled Adaptive Compliant Motion Control of Robot Gecko for Space Stations. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ji, A.; Manoonpong, P.; Shen, H.; Hu, J.; Dai, Z.; Yu, Z. Lateral undulation of the flexible spine of sprawling posture vertebrates. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2018, 204, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Lin, T.; Lodewijks, G.; Ji, A. Design of an active flexible spine for wall climbing robot using pneumatic soft actuators. J. Bionic Eng. 2023, 20, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, L.; Seibel, A.; Schlattmann, J. Toward a Gecko-Inspired, Climbing Soft Robot. Front. Neurorobot. 2019, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.K.; Schultz, J.T.; Clemente, C.J. A bio-inspired robotic climbing robot to understand kinematic and morphological determinants for an optimal climbing gait. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2022, 17, 016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadan, P.; Backus, S.; Johnson, A.M. LORIS: A Lightweight Free-Climbing Robot for Extreme Terrain Exploration. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 18480–18486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; Sitti, M. Waalbot: An Agile Small-Scale Wall-Climbing Robot Utilizing Dry Elastomer Adhesives. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 12, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; Kute, C.; Mengüç, Y.; Sitti, M. Waalbot II: Adhesion Recovery and Improved Performance of a Climbing Robot using Fibrillar Adhesives. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2011, 30, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Higuchi, T. A Crawler Climbing Robot Integrating Electroadhesion and Electrostatic Actuation. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2014, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Dai, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, L. A wheeled wall climbing robot by using bio-inspired adhesive material. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhai, J.; Yan, W.; Zhao, Y. The Design and the Gait Planning Analysis of Hexapod Wall-Climbing Robot. In Intelligent Robotics and Applications; Kubota, N., Kiguchi, K., Liu, H., Obo, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 619–631. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Yan, W.; Chen, L.; Cui, R. CPG-based Motion Planning of Hybrid Underwater Hexapod Robot for Wall Climbing and Transition. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 12299–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Casteren, A.; Codd, J.R. Foot morphology and substrate adhesion in the Madagascan hissing cockroach, Gromphadorhina portentosa. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, Y.; Lin, X.; Tanaka, Y.; Mehta, A.; Hong, D. Risk-Aware Motion Planning for a Limbed Robot with Stochastic Gripping Forces Using Nonlinear Programming. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4994–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housecroft, C.E. Geckos, Ceilings and van der Waals: Chemical Education. Chimia 2018, 72, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dong, X.; Kim, J.k.; Wang, C.; Sitti, M. Wireless soft millirobots for climbing three-dimensional surfaces in confined spaces. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lim, B.; Lee, J.W.; Park, J.; Kim, T.; Seo, T. Steerable dry-adhesive linkage-type wall-climbing robot. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 153, 103987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Jiang, G. Design and analysis of a wall-climbing robot based on a mechanism utilizing hook-like claws. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2012, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhihui, Z. Hook-Claw Type Quadruped Wall-Climbing Robot. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, J. Opposing-Grasp Hexapod Wall-Climbing Robot. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, S.; Xu, F.; Wei, Y.; Kong, D. a novel type of wall-climbing robot with a gear transmission system arm and adhere mechanism inspired by Cicada and Gecko. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, L.; Cheng, G.; Chen, S.; Xu, H.; Shi, J.; Liang, X. Analysis and optimization of the wall-climbing robot with an adsorption system and adhesive belts. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1729881420926409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Asbeck, A.T.; Cutkosky, M.R.; Provancher, W.R. SpinybotII: Climbing hard walls with compliant microspines. In Proceedings of the ICAR’05, 12th International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–20 July 2005; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 601–606. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Dong, E.; Cheng, G.; Jin, H.; Yang, J.; Sun, D. Inchworm-inspired soft climbing robot using microspine arrays. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 5800–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Agrawal, K.; Yadav, R.; Srivstava, R. Design of out pipe crawler for oil refinery based on analysis & classification of locomotion and adhesion techniques. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th IEEE Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (UPCON), Gorakhpur, India, 2–4 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Hui, Y.; Fu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, T. Recent advances in Gecko-inspired adhesive materials and application. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 2275–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbeck, A.T.; Kim, S.; Cutkosky, M.R.; Provancher, W.R.; Lanzetta, M. Scaling hard vertical surfaces with compliant microspine arrays. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2006, 25, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xiong, X.; Duan, J.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Z. Compliant detachment of wall-climbing robot unaffected by adhesion state. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Spenko, M.; Trujillo, S.; Heyneman, B.; Santos, D.; Cutkosky, M.R. Smooth vertical surface climbing with directional adhesion. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, T. Biomimetic soft adhesion robot: From biology to bionics. Sci. Sin. Technol. 2018, 48, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkmeyer, P.; Gillies, A.G.; Fearing, R.S. Dynamic climbing of near-vertical smooth surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 286–292. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, R.; Lin, L.J.; Fedor, C. Autonomous task control for mobile robots. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control 1990, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 5–7 September 1990; Volume 2, pp. 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfes, A. A distributed control architecture for an autonomous mobile robot. Artif. Intell. Eng. 1986, 1, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majorana, S.; Chua, L.O. A unified framework for multilayer high order CNN. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 1998, 26, 567–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Openpose: Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, P.; Fortuna, L.; Frasca, M.; Patane, L.; Pavone, M. Climbing obstacles via bio-inspired CNN-CPG and adaptive attitude control. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Kobe, Japan, 23–26 May 2005; Volume 5, pp. 5214–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar]
- Haarnoja, T.; Zhou, A.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Pmlr, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1861–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. Kinematics of Lateral Undulation Pattern in Gekko gecko and Biomimetic Robot Design. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ijspeert, A.J. Central pattern generators for locomotion control in animals and robots: A review. Neural Netw. 2008, 21, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K. Sustained oscillations generated by mutually inhibiting neurons with adaptation. Biol. Cybern. 1985, 52, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, A.; Kurokawa, H.; Yoshida, E.; Tomita, K.; Kokaji, S.; Murata, S. Distributed adaptive locomotion by a modular robotic system, M-TRAN II. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37566), Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; Volume 3, pp. 2370–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, A.; Badertscher, A.; Guignard, A.; Ijspeert, A.J. AmphiBot I: An amphibious snake-like robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2005, 50, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Q.; Luo, W.H.; Xu, Z.D.; Shu, B.M.; Yang, D.K. Research on the Design and Gait Planning of a Hexapod Robot Based on Improved Triangular Gait for Lunar Exploration. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C. Design and Analysis of Gecko-like Robot. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2011, 24, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadehyazdi, V.; Modabberifar, M.; Mahmoudzadeh Akherat, S.J.; Spenko, M. Electrostatic self-cleaning gecko-like adhesives. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20170714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuchinnawong, A.; Shao, D.; Ngamkajornwiwat, P.; Teerakittikul, P.; Dai, Z.; Ji, A.; Manoonpong, P. Neural Control for Gait Generation and Adaptation of a Gecko Robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 19th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2–6 December 2019; pp. 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gorb, S.N.; Dai, Z. Control strategies of gecko’s toe in response to reduced gravity. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Wang, Z.; Ji, A.; Dai, Z.; Manoonpong, P. A gecko-inspired robot with CPG-based neural control for locomotion and body height adaptation. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2022, 17, 036008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Zong, W.; Zhang, L.; Ji, K.; Manoonpong, P.; Dai, Z. A Neural Coordination Strategy for Attachment and Detachment of a Climbing Robot Inspired by Gecko Locomotion. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2023, 4, 0008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, F.W.; Rachkov, M.; Seevers, J.; Hahn, M. High tractive power wall-climbing robot. Autom. Constr. 1995, 4, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunete, A.; Hernando, M.; Torres, J.E.; Gambao, E. Heterogeneous multi-configurable chained microrobot for the exploration of small cavities. Autom. Constr. 2012, 21, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepolina, F.; Michelini, R.; Razzoli, R.; Zoppi, M. Gecko, a climbing robot for walls cleaning. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Advances in Service Robotics (ASER03), Bardolino, Italy, 13–15 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Yang, H.; Lee, K.; Seo, K.; Chang, D.; Kim, J. Development of a wall-climbing robot using a tracked wheel mechanism. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2008, 22, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Jung, K.; Han, C.S.; Hong, D. A survey of climbing robots: Locomotion and adhesion. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2010, 11, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, L.; Bustamante, P.; Serna, M.A. Robicen: A wall-climbing pneumatic robot for inspection in nuclear power plants. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 1994, 11, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, B.; Collie, A.; Cooke, D.; Chen, S. Walking and climbing service robots for safety inspection of nuclear reactor pressure vessels. Meas. Control. 2006, 39, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsimpelis, I.; Taylor, C.J.; Lennox, B.; Joyce, M.J. A review of ground-based robotic systems for the characterization of nuclear environments. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2019, 111, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabanov, V.; Gulimova, V.; Berdiev, R.; Saveliev, S. Object play in thick-toed geckos during a space experiment. J. Ethol. 2015, 33, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabanov, V.; Gulimova, V.; Berdiev, R.; Saveliev, S. Individual features of play behavior in thick-toed geckos in weightlessness and normal gravity conditions. Life Sci. Space Res. 2019, 22, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















| Classification | Rigid-Spine Robots | Flexible-Spine Robots |
|---|---|---|
| Structural features | Rigid torso with fixed geometry | Flexible torso that can be actively bent or twisted |
| Few joints and simple mechanical structure | Multi-degree-of-freedom spinal joint design | |
| Advantage | High stability | High flexibility of movement and strong adaptability to complex terrain [100,101] |
| Disdvantage | Poor steering flexibility [8,102] | Complex control algorithm |
| Drive mode | Servo motors | Motors, pneumatic fluid, rope or SMA [8,103,104,105] |
| Representative models | Mini-Whegs IV [106], RHex [107,108] | Whegs II [109], SoSpider [110] |
| Robots | Spine Flexibility | Movement Mode | Accuracy | Cost | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geckobot | Rigid-Spine | Adhesion | Low | Low | [111] |
| SpinybotII | Rigid-Spine | Adhesion | Medium | Low | [145] |
| StickybotI | Rigid-Spine | Adhesion | Low | Low | [112] |
| StickybotII | Rigid-Spine | Adhesion | Medium | Low | [151] |
| StickybotIII | Rigid-Spine | Adhesion | High | Medium | [114] |
| RiSE V3 | Rigid-Spine | Claw | Low | Medium | [119] |
| ACROBOT | Rigid-Spine | Adhesion | High | High | [120] |
| Ji et al. | Rigid-Spine | Claw | Medium | Low | [141] |
| Kong et al. | Rigid-Spine | Claw | Medium | Medium | [142] |
| Yu et al. | Rigid-Spine | Adhesion | Medium | Medium | [121] |
| Bian et al. | Rigid-Spine | Claw | High | Medium | [122] |
| Lars et al. | Flexible-Spine | Adhesion | Medium | Medium | [126] |
| Pei et al. | Rigid-Spine | Adhesion | Medium | Medium | [123] |
| Wang et al. | Rigid-Spine | Adhesion | Medium | High | [150] |
| X4 | Flexible-Spine | Claw | High | High | [127] |
| Slalom | Flexible-Spine | Adhesion | High | High | [72] |
| Qiu et al. | Flexible-Spine | Claw | Medium | High | [8] |
| LORIS | Flexible-Spine | Claw | Low | High | [128] |
| Control Method | Description | Advantages | Limitations | Example Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical control | Multi-layered system integrating perception and action | Modular, adaptive, task-specific | Complex integration, latency issues | Simmons [154], Rosenblatt [155] |
| CPG-based neural control | Uses biological-like oscillators to generate rhythmic motion | Rhythmic, low computational load, biologically plausible | Sensitive to parameters, hard to stabilize | Kim et al. [129], Cai et al. [164] |
| Reinforcement learning | Learns policies from trial-and-error in simulation | High adaptability, end-to-end training | Data-hungry, sim-to-real gap | PPO/SAC in simulation |
| Impedance control | Adjusts force compliance via dynamic equations | Effective for interaction tasks | Requires accurate force/torque estimation | Pei et al. [123] |
| Motion matching | Learns and reconstructs periodic joint data from biological gaits | Accurate reproduction, biologically inspired | Relies heavily on training data | Wang et al. [158] |
| Application | Task | Key Technologies | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure inspection | Bridge/high-rise crack detection | Force-sensitive adhesion, CPG control | Wang et al. [150] |
| Building maintenance | Glass wall/window cleaning | Modular cleaning unit, suction adhesion | Kim et al. [30] |
| Nuclear power plants | Radiation measurement, NDT in DCSS | Vacuum suction, active sealing, PID control, SLAM | Kim et al. [11] |
| Space applications | Surface mobility in microgravity | Gecko-inspired adhesion, pneumatic-electric hybrid | Pei et al. [123] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, W.; Honarvar Shakibaei Asli, B. Advances in Gecko-Inspired Climbing Robots: From Biology to Robotics—A Review. Electronics 2025, 14, 2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142810
Xiang W, Honarvar Shakibaei Asli B. Advances in Gecko-Inspired Climbing Robots: From Biology to Robotics—A Review. Electronics. 2025; 14(14):2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142810
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Wenrui, and Barmak Honarvar Shakibaei Asli. 2025. "Advances in Gecko-Inspired Climbing Robots: From Biology to Robotics—A Review" Electronics 14, no. 14: 2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142810
APA StyleXiang, W., & Honarvar Shakibaei Asli, B. (2025). Advances in Gecko-Inspired Climbing Robots: From Biology to Robotics—A Review. Electronics, 14(14), 2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142810







