A Novel FMCW LiDAR Multi-Target Denoising Method Based on Optimized CEEMDAN with Singular Value Decomposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Integration of the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm optimizes the noise addition frequency and standard deviation parameters in the CEEMDAN method. This optimization enhances decomposition, minimizes mode mixing, and ensures modal functions do not carry excess interference or lose valuable information. Envelope entropy serves as the optimization fitness function, refining the CEEMDAN algorithm’s effectiveness.
- (2)
- For the IMFs generated by the CEEMDAN algorithm, this study proposes a method that performs windowed FFT operations on the original signal and the CEEMDAN-processed IMFs, and then uses a comparison algorithm that combines frequency and amplitude spectra to determine the IMFs containing useful signals and filter out other IMFs that are mainly noise.
- (3)
- The SVD algorithm is used to further decompose the retained IMF components. The value with the largest change in the singular value difference is used as the basis for determining the reconstruction order, so as to achieve a low-rank singular value matrix and thereby achieve efficient signal denoising.
2. Methodology
2.1. CEEMDAN Method
2.2. CEEMDAN Parameters Optimized by PSO Method
2.3. IMF Decomposition by SVD Method
3. Performance Evaluation
3.1. Synthetic Signal Evaluation
3.2. Real Signal Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behroozpour, B.; Sandborn, P.A.; Wu, M.C.; Boser, B.E. Lidar system architectures and circuits. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, D.; Monteiro, P.P.; Oliveira, A.S.; Drummond, M.V. An overview of LiDAR requirements and techniques for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the 2021 Telecoms Conference (ConfTELE), Leiria, Portugal, 11–12 February 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.; Song, C.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Deng, M.; Su, H. Accurate ranging of dual wavelength FMCW laser fuze under different types of aerosol interference. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 18953–18960. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Liu, B.; Yang, Z. Noise reduction in Lidar signal using correlation-based EMD combined with soft thresholding and roughness penalty. Opt. Commun. 2018, 407, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.T.; Huang, D.S.; Wu, Y.H. Antinoise approximation of the lidar signal with wavelet neural networks. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.T.; Huang, D.S. Noise reduction in lidar signal based on discrete wavelet transform. Opt. Commun. 2004, 233, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Gao, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q. Seismic time–frequency analysis via STFT-based concentration of frequency and time. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 14, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dang, B.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Ma, H. Applications of savitzky-golay filter for seismic random noise reduction. Acta Geophys. 2016, 64, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, S. Application of fourier transform and butterworth filter in signal denoising. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi’an, China, 9–11 April 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1277–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Safdar, M.F.; Nowak, R.M.; Pałka, P. A denoising and fourier transformation-based spectrograms in ECG classification using convolutional neural network. Sensors 2022, 22, 9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldi, K.; Alouane, M.T.H.; Boudraa, A.O. A new EMD denoising approach dedicated to voiced speech signals. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd International Conference on Signals, Circuits and Systems, Acapulco, Mexico, 25–27 January 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z. EMD interval thresholding denoising based on similarity measure to select relevant modes. Signal Process. 2015, 109, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wei, G. An integrated EMD adaptive threshold denoising method for reduction of noise in ECG. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Cao, X.; Liang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yi, N.; Wang, L.; Cheng, X. Improved empirical mode decomposition based denoising method for lidar signals. Opt. Commun. 2014, 325, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudraa, A.O.; Cexus, J.C. EMD-based signal filtering. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Hua, D.; Cui, Y.; Sui, L. An EMD-based denoising method for lidar signal. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Yantai, China, 16–18 October 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 8, pp. 4016–4019. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Li, J.; Mao, F.; Zhang, J. Comparison of simultaneous signals obtained from a dual-field-of-view lidar and its application to noise reduction based on empirical mode decomposition. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2011, 9, 050101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaci, S. A new ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) denoising method for seismic signals. Energy Procedia 2016, 97, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Li, Q.; Mohamed, M.A. A novel adaptive EEMD method for switchgear partial discharge signal denoising. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 58139–58147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 4144–4147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Tan, D.; Liu, L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: An overview. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Mao, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, C.; Gong, X.; Rao, Z. An EEMD-SVD-LWT algorithm for denoising a lidar signal. Measurement 2021, 168, 108405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xiang, M.; Li, C. Denoising FMCW ladar signals via EEMD with singular spectrum constraint. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pouls, J.; Wu, M.C. Laser frequency sweep linearization by iterative learning pre-distortion for FMCW LiDAR. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 9965–9974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorigo, M.; Birattari, M. Swarm intelligence. Scholarpedia 2007, 2, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; He, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z. Feature extraction based on hierarchical improved envelope spectrum entropy for rolling bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 3518912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Q. Machine learning-based prediction approach for ranging resolution enhancement of FMCW LiDAR system with LSTM networks. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 179, 111299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Q. Denoising method for a lidar bathymetry system based on a low-rank recovery of non-local data structures. Appl. Opt. 2021, 61, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, N.; Kiuchi, H.; Yasaka, H. Directly modulated optical negative feedback lasers for long-range FMCW LiDAR. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 11693–11703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Li, X.; Ma, Z. A Fast Close-target Ranging Method for LiDAR in Fog Using Gauss-Newton Global Optimization. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 8505411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

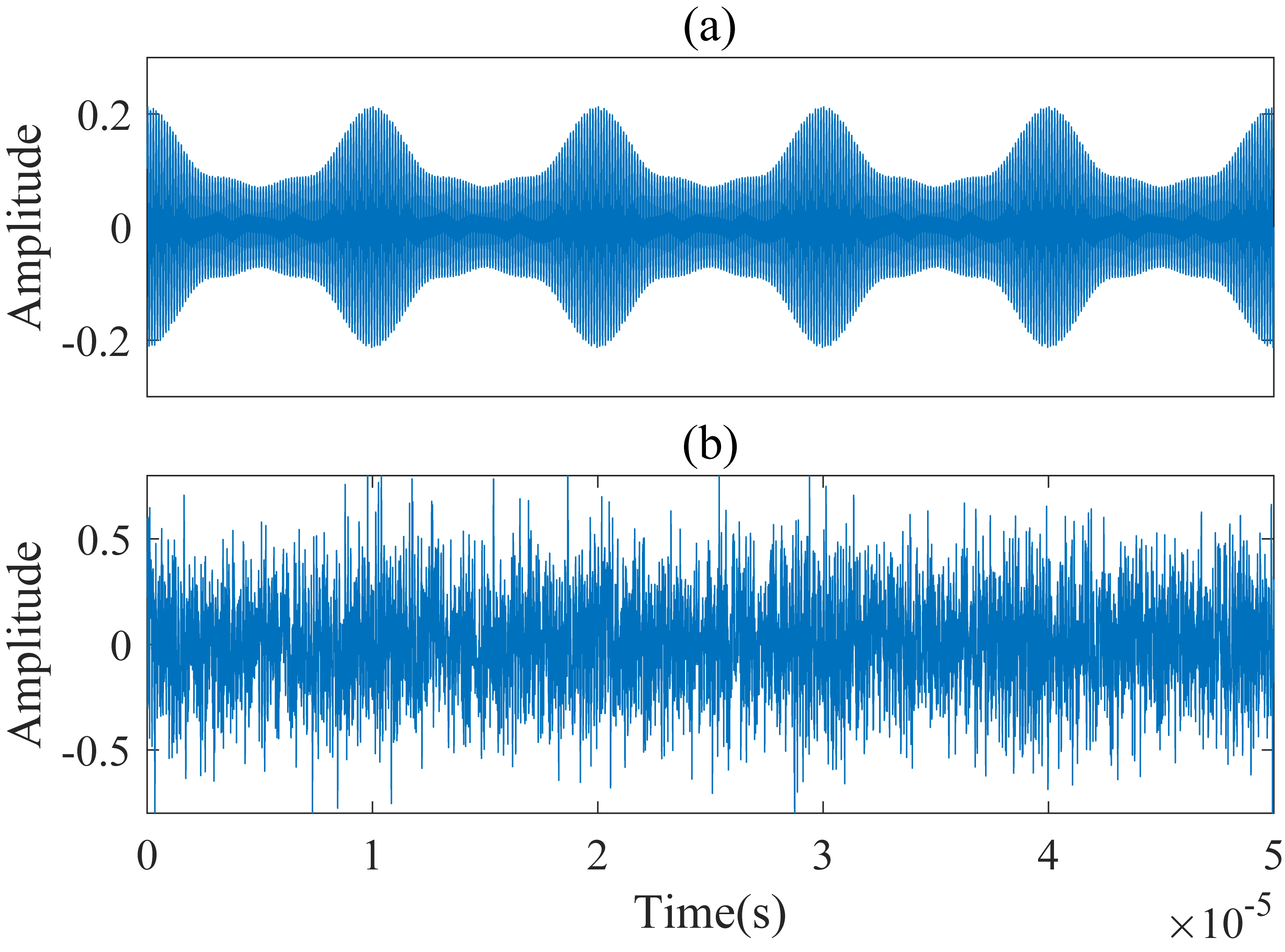
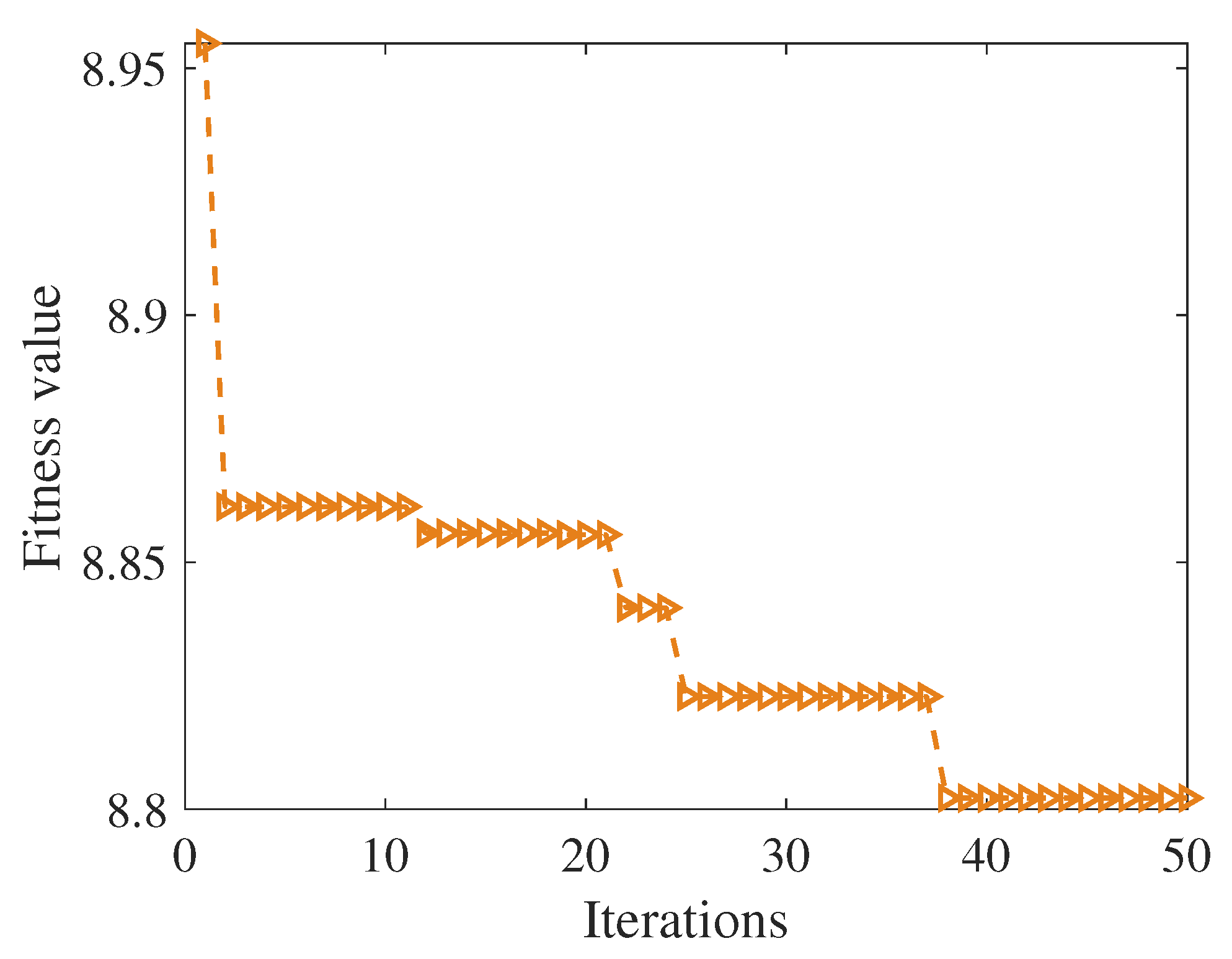
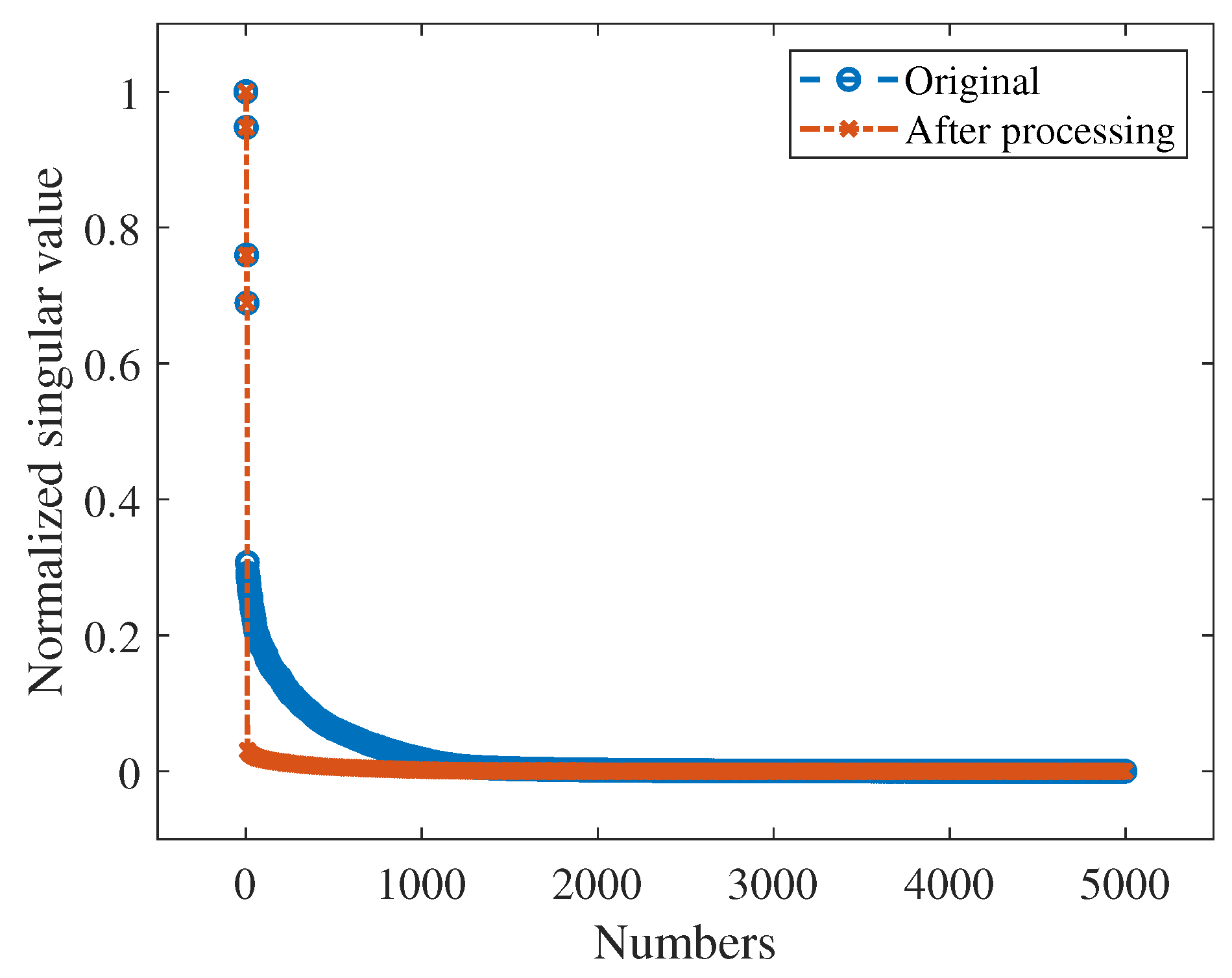



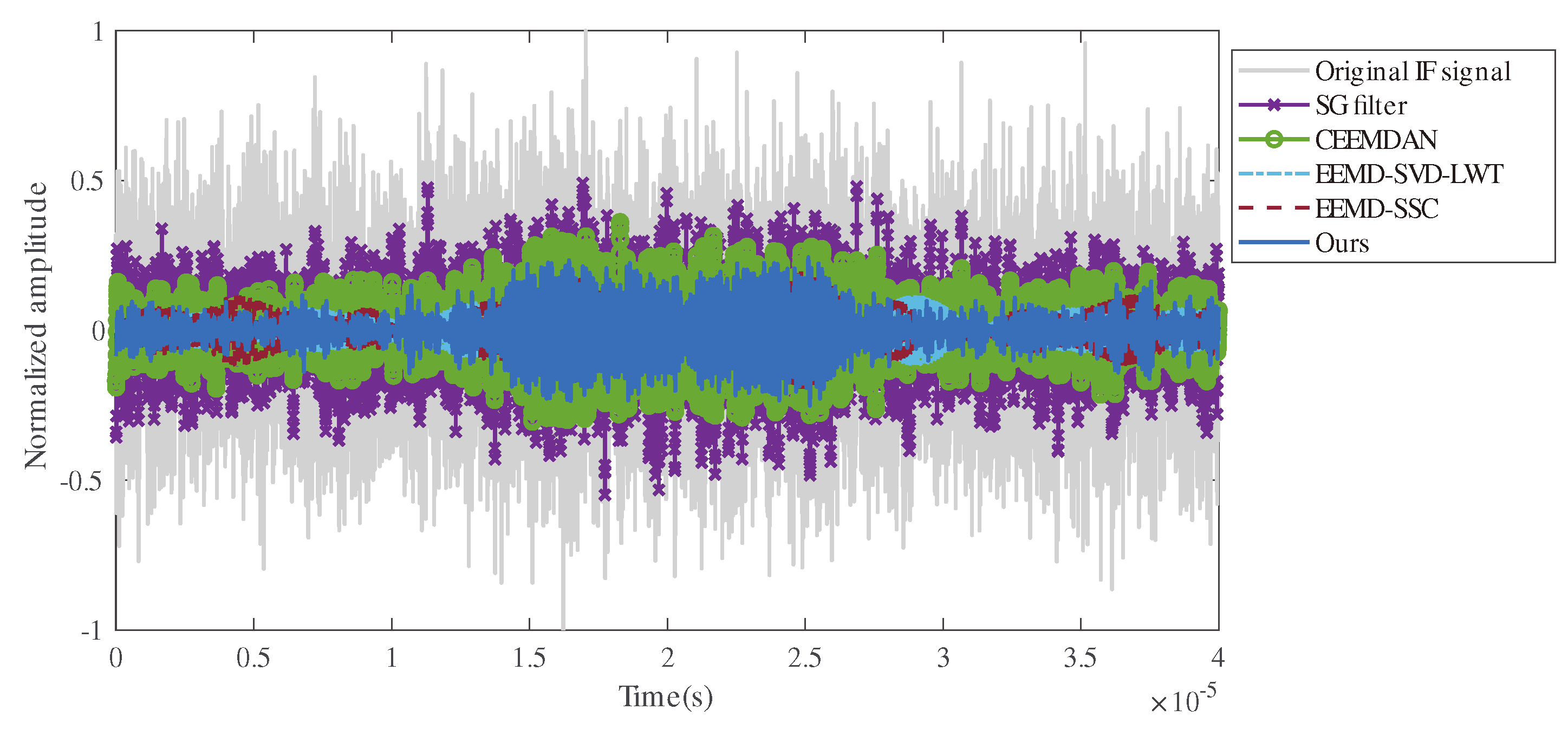
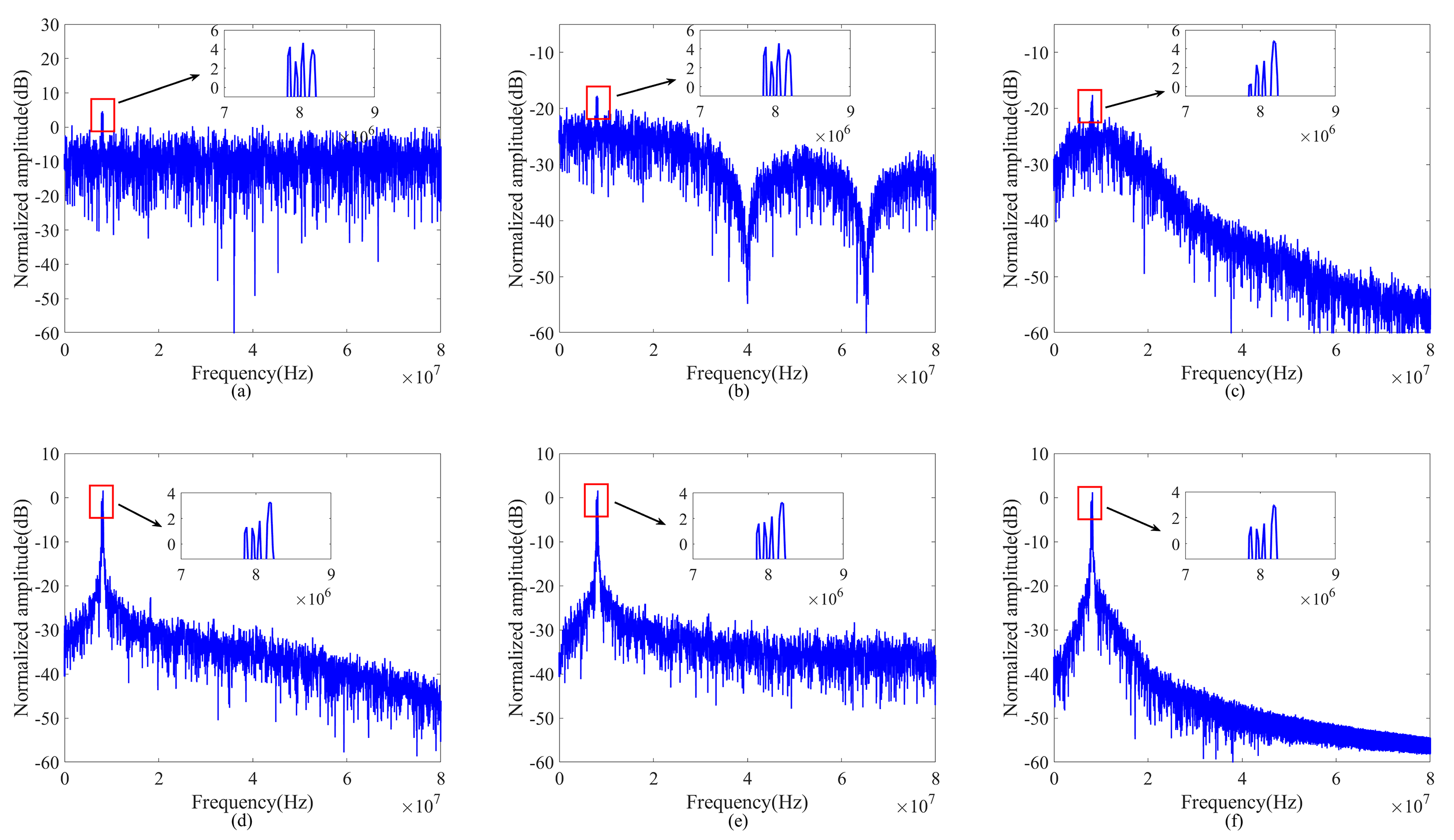
| Target #1 | Target #2 | Target #3 | Target #4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (MHz) | 8 | 8.1 | 8.2 | 8.3 |
| Amplitude | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.1 |
| Phase | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Populations number () | 30 |
| Maximum iterations () | 50 |
| Inertial weight () | 0.5 |
| Individual learning factor () | 1.5 |
| Social learning factor () | 1.5 |
| Noisy Signal SNR (dB) | Evaluation | Savitzky–Golay Filtering Algorithm [8] | CEEMDAN Algorithm [22] | EEMD-SVD-LWT [24] | EEMD-SSC [25] | Our Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −2 | MAE MSE SNR PSNR | 0.1163 0.0213 4.8514 5.9042 | 0.1081 0.0187 5.29 6.8394 | 0.0731 0.007 5.6915 11.5421 | 0.0682 0.0072 5.6567 11.4650 | 0.0497 0.0057 6.2357 12.2653 |
| −4 | MAE MSE SNR PSNR | 0.1311 0.0268 2.7755 4.9657 | 0.1186 0.0215 3.2592 5.5787 | 0.0669 0.0136 4.7871 10.7408 | 0.0747 0.0152 4.7701 10.5025 | 0.0426 0.0106 5.1223 11.9339 |
| −6 | MAE MSE SNR PSNR | 0.1481 0.0342 0.7687 3.25 | 0.1287 0.0348 2.9031 4.587 | 0.0358 0.0229 3.3966 9.8118 | 0.0378 0.0246 3.3683 9.7274 | 0.0254 0.0202 4.2331 10.9917 |
| −8 | MAE MSE SNR PSNR | 0.1674 0.0466 −1.6726 2.0293 | 0.1439 0.041 1.1631 3.0822 | 0.0533 0.0353 2.4632 8.2079 | 0.0506 0.0397 2.1478 8.9841 | 0.0341 0.0304 3.4871 9.4492 |
| Algorithms | Execution Time (s) |
|---|---|
| Savitzky–Golay filter [8] | 1.2 |
| CEEMDAN algorithm [22] | 2.3 |
| EEMD-SVD-LWT [24] | 5.1 |
| EEMD-SSC [25] | 4.6 |
| Our method | 6.2 |
| DAQ Parameter | ADC’s Sampling Rate | 200 MHz |
|---|---|---|
| FMCW laser parameters | Amplitude | 2.8 V |
| Voltage bias | 1.5 V | |
| Sweeping period | 100 μs | |
| Modulation range | 3.4 GHz | |
| Start wavelength | 1550.101 nm | |
| Final wavelength | 1550.74 nm | |
| Modulation slope | 68 THz/s | |
| Repeated frequency | 10 kHz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Zhao, Y. A Novel FMCW LiDAR Multi-Target Denoising Method Based on Optimized CEEMDAN with Singular Value Decomposition. Electronics 2025, 14, 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132697
Li Z, Wang N, Li Y, He J, Zhao Y. A Novel FMCW LiDAR Multi-Target Denoising Method Based on Optimized CEEMDAN with Singular Value Decomposition. Electronics. 2025; 14(13):2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132697
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhiwei, Ning Wang, Yao Li, Jiaji He, and Yiqiang Zhao. 2025. "A Novel FMCW LiDAR Multi-Target Denoising Method Based on Optimized CEEMDAN with Singular Value Decomposition" Electronics 14, no. 13: 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132697
APA StyleLi, Z., Wang, N., Li, Y., He, J., & Zhao, Y. (2025). A Novel FMCW LiDAR Multi-Target Denoising Method Based on Optimized CEEMDAN with Singular Value Decomposition. Electronics, 14(13), 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132697






