Research on Nonlinear Pitch Control Strategy for Large Wind Turbine Units Based on Effective Wind Speed Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Wind Turbine System Modeling
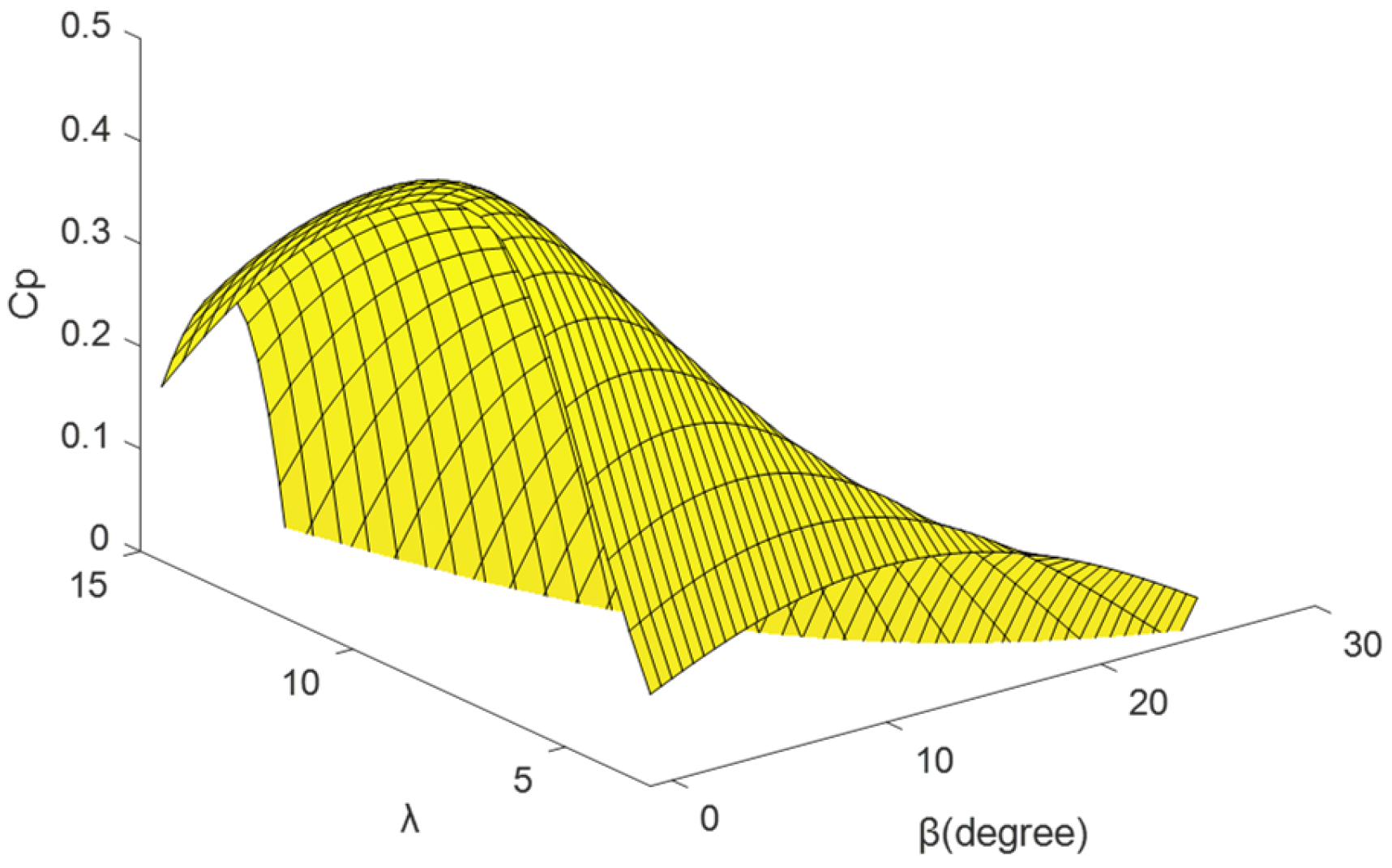
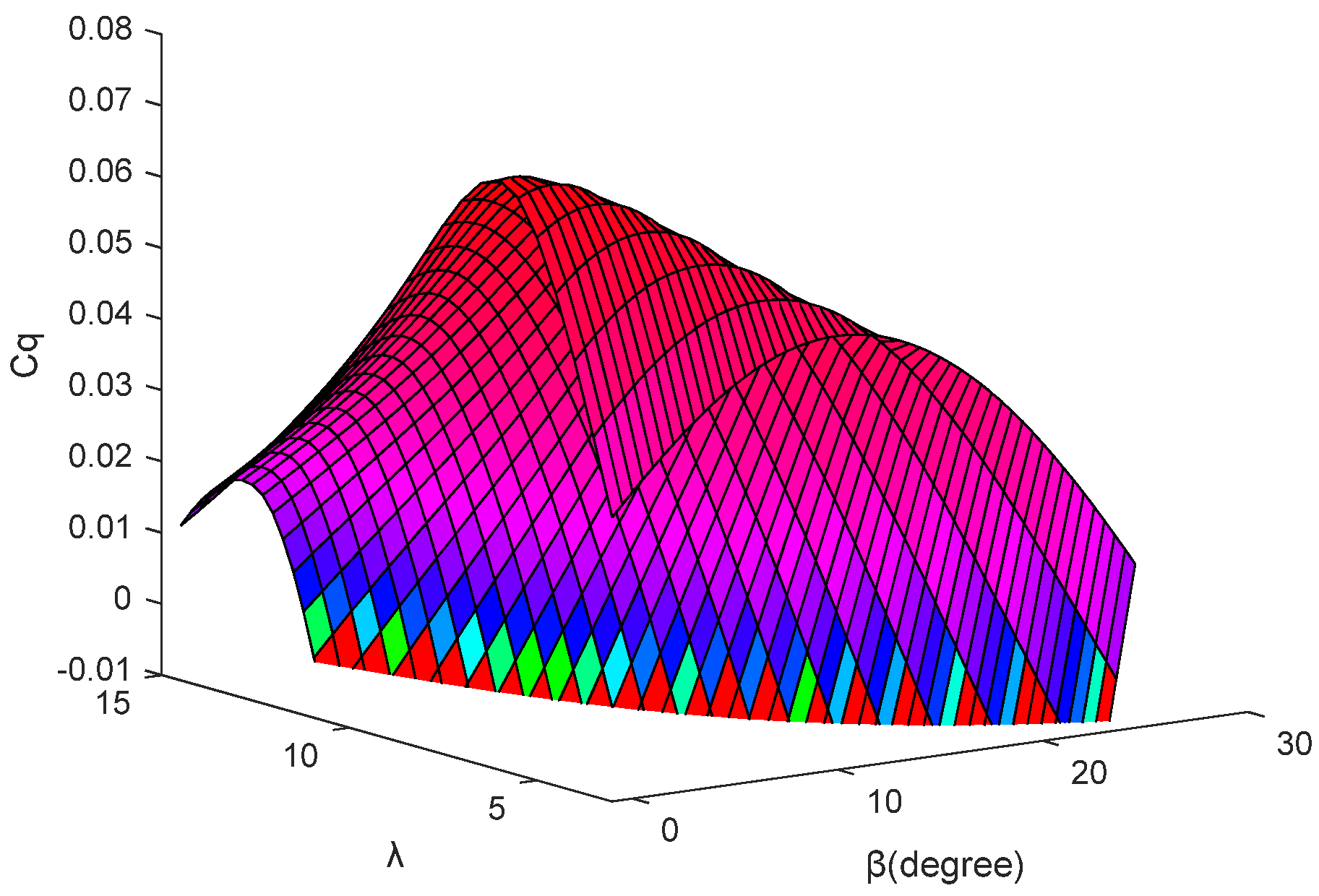
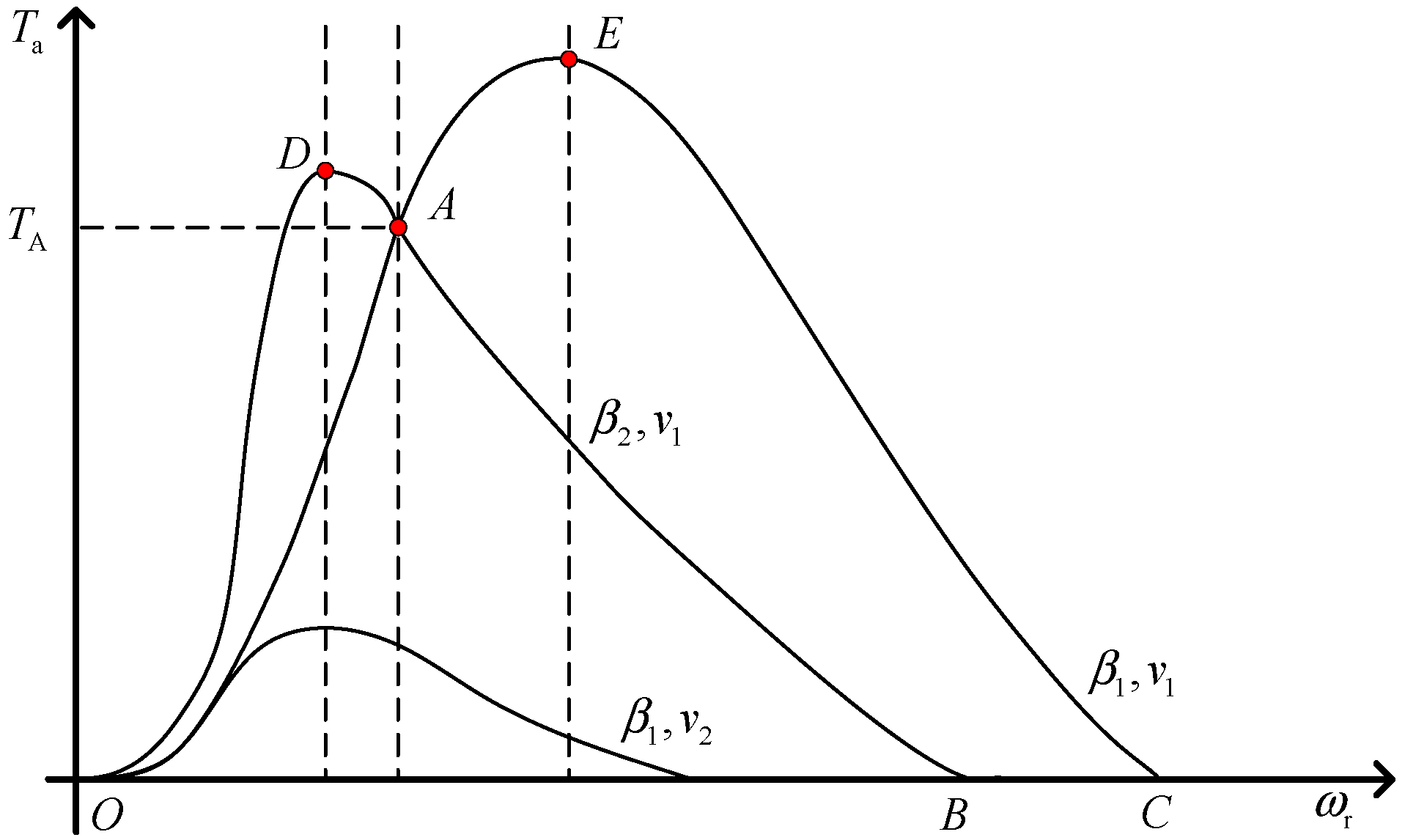
2.1. Wind Turbine Aerodynamic Modeling
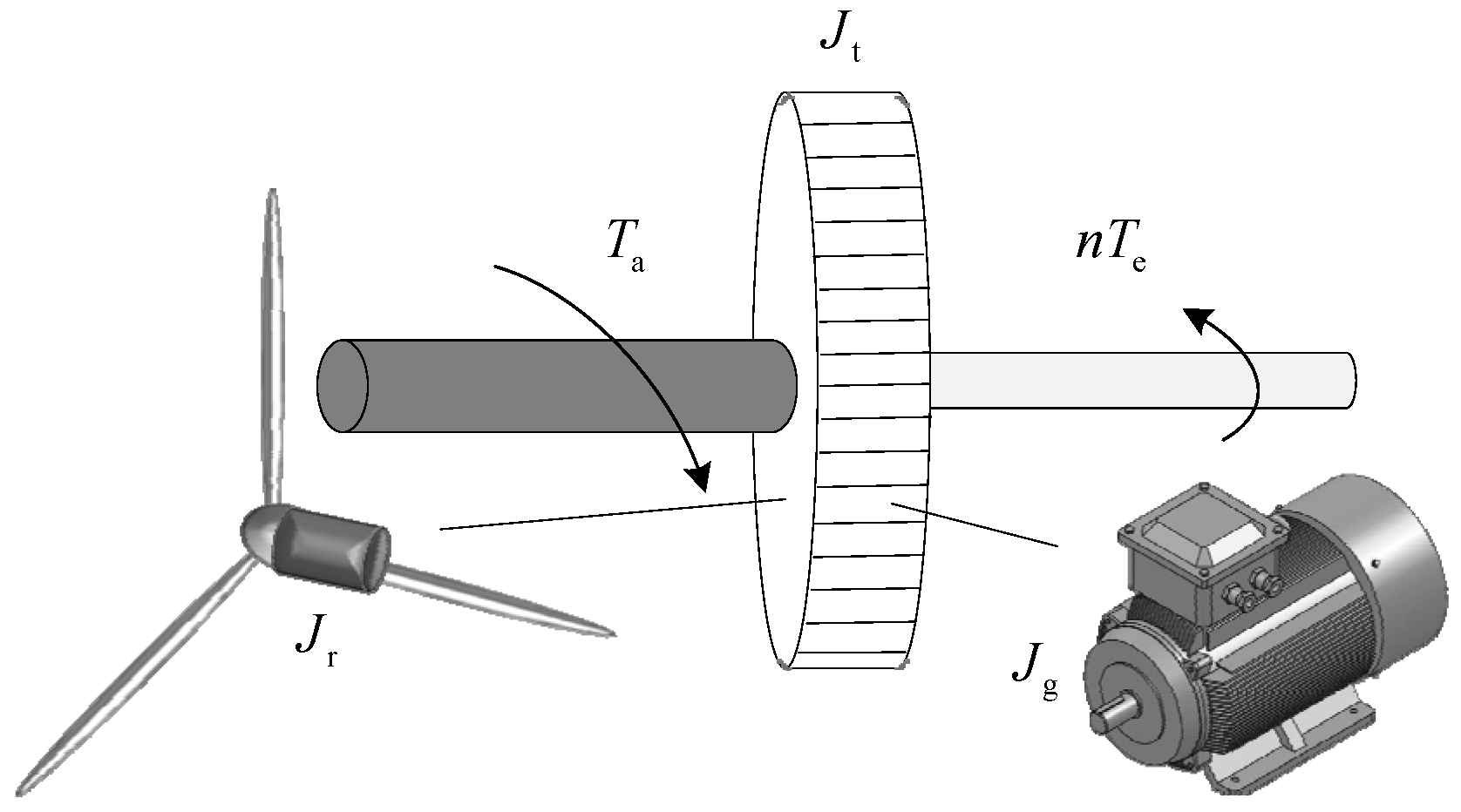
2.2. Wind Turbine Drive Train and Generator Modeling
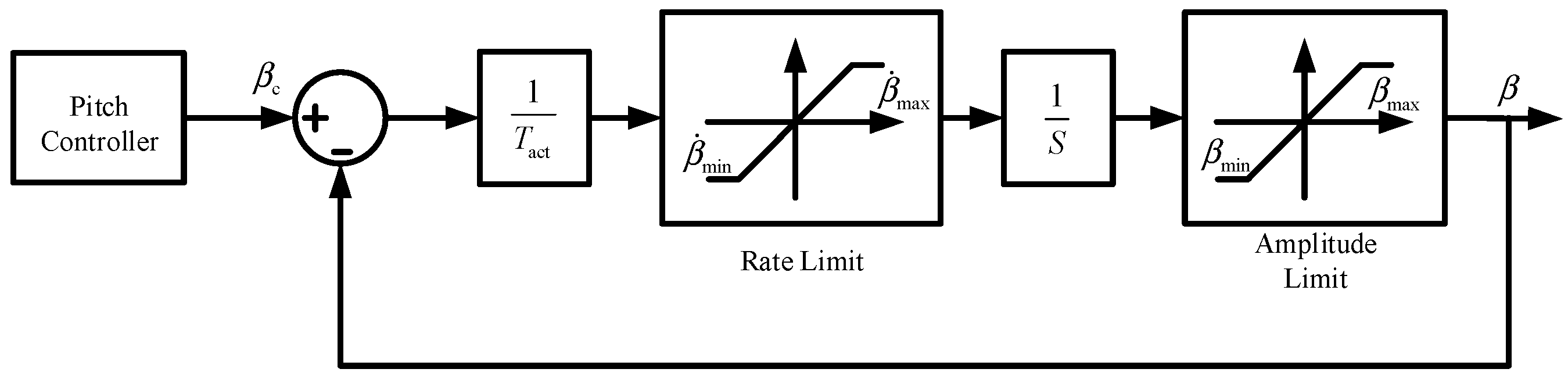
2.3. Modeling of Wind Turbine Pitch Systems
3. Wind Speed Estimation Based on Extended Kalman Filtering
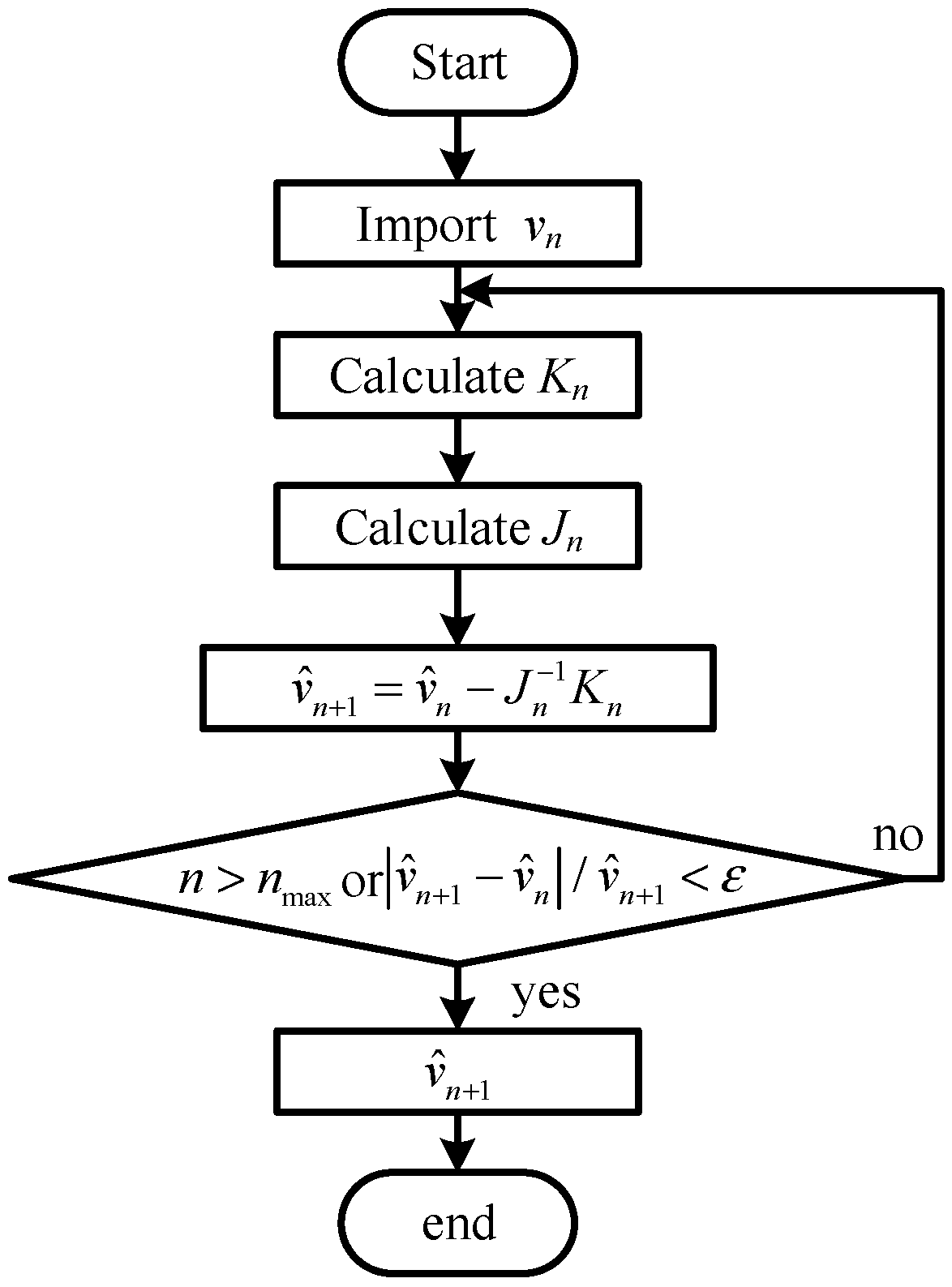
3.1. Extended Kalman Filter Theory
3.2. Pneumatic Torque Estimation
3.3. Wind Speed Estimation
4. Nonlinear Pitch Control Strategy
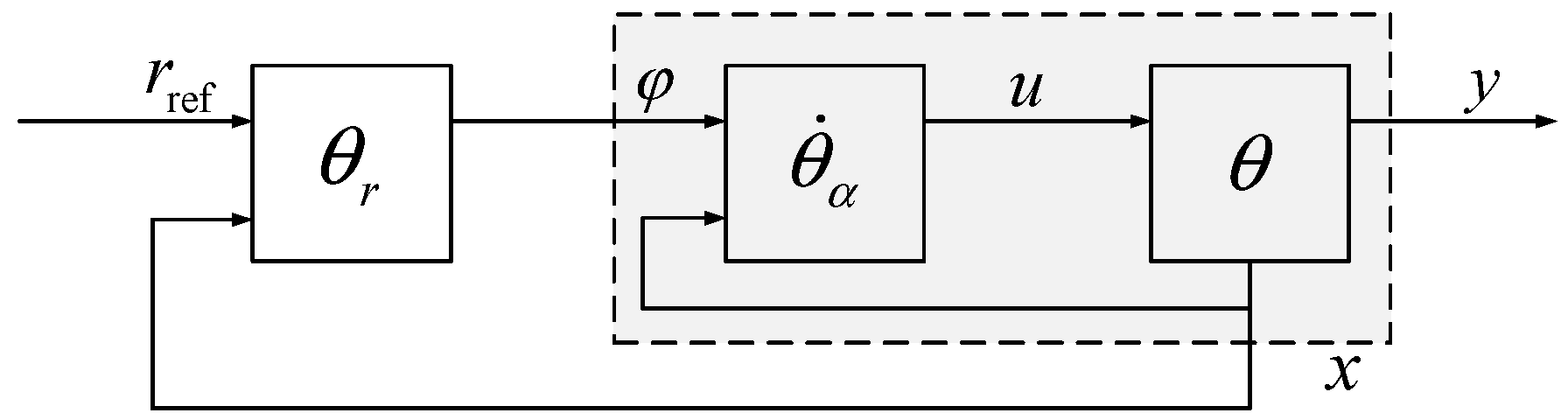
4.1. Fundamentals of Inverse Systems Theory Analysis
- Find the inverse system of the original system Σ and its initial value.
- Find the inverse of the α-order integral system and its initial value.
- Cascade the system Σ with its α-order integral inverse system to form a pseudo-linear composite system , which successfully decouples and linearizes the controlled object.
- Considering each subsystem contained in the above pseudo-linear composite system as a controlled object, the design of the target control system is carried out by utilizing the design method of a single-variable linear system, such as the frequency response method or the root trajectory correction method.
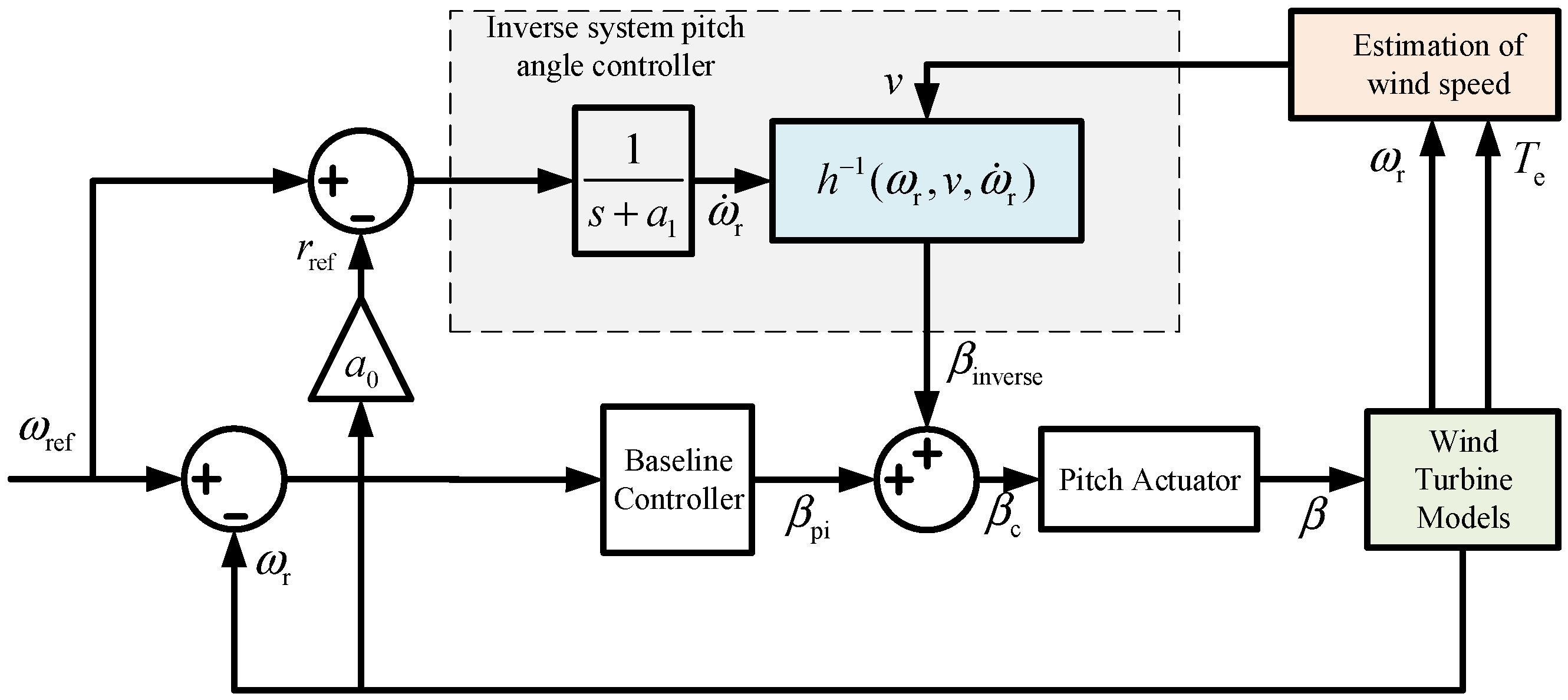
4.2. Pitch Controller Design
5. Simulation Verification
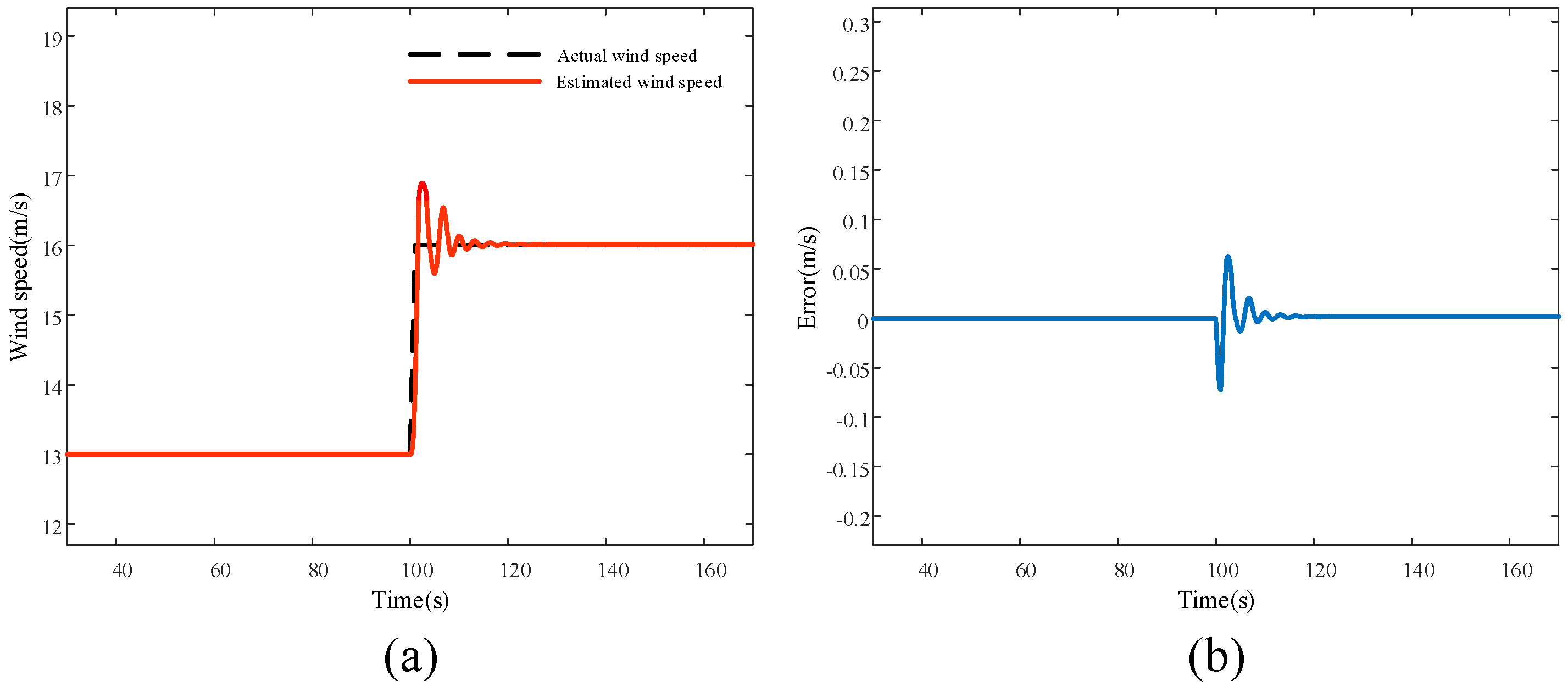
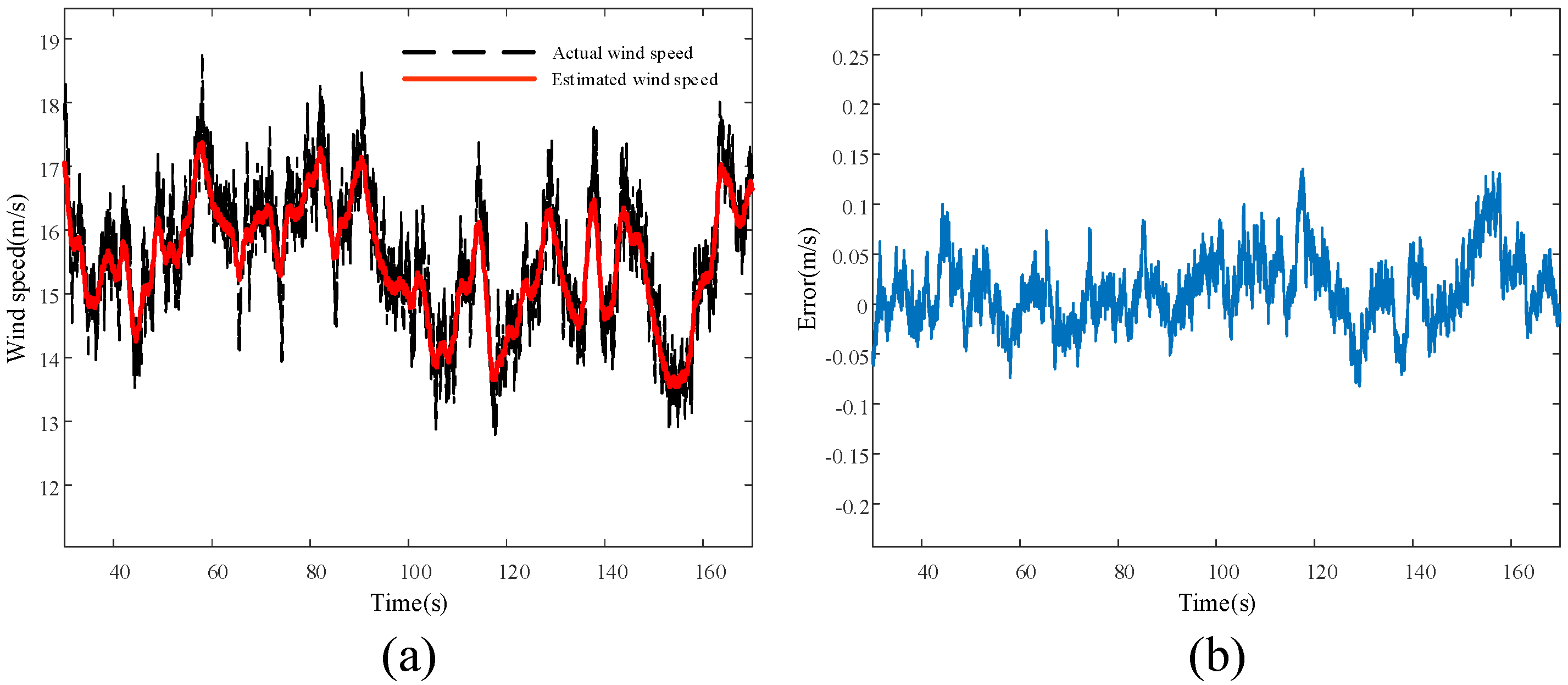
5.1. Simulation Results and Analysis of Wind Speed Estimation
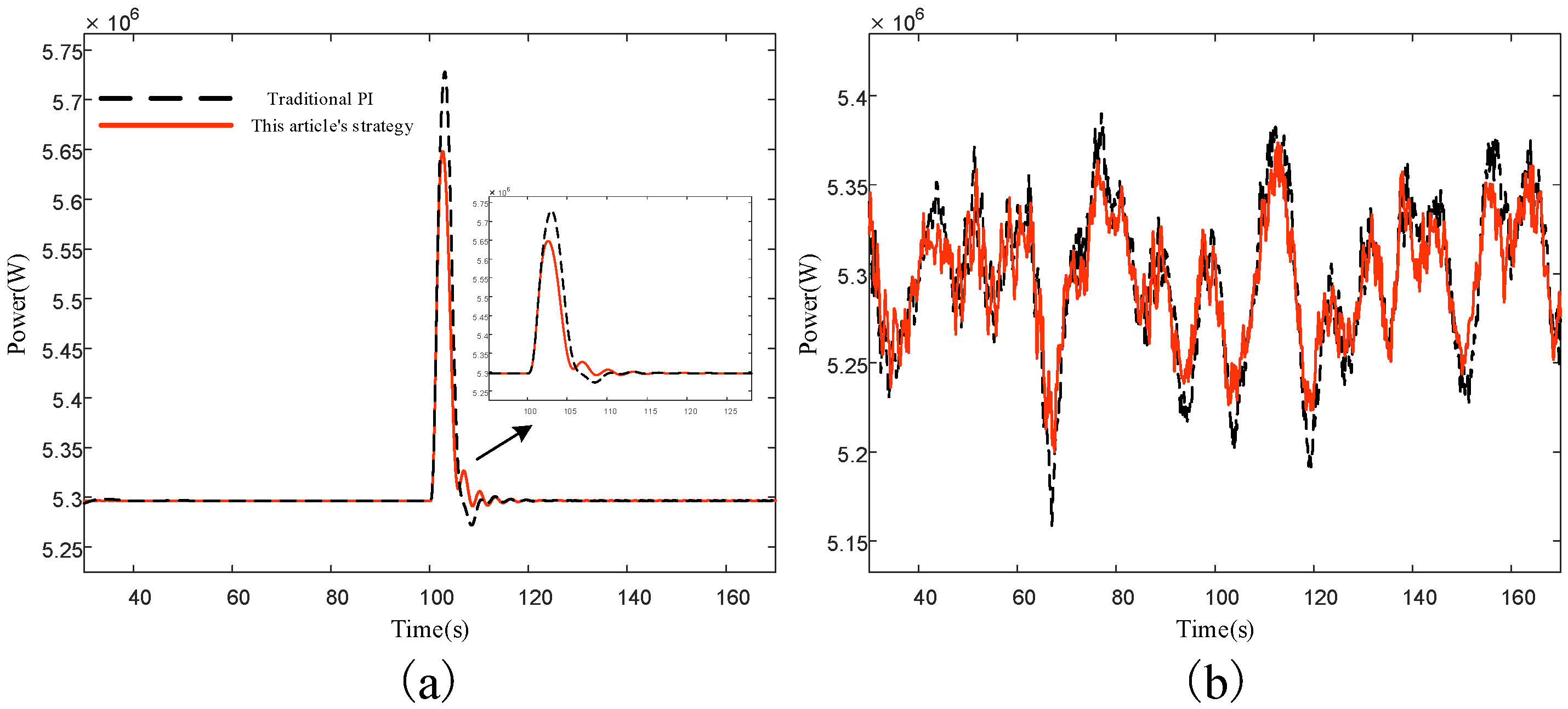
5.2. Pitch Control Simulation Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GWEC. Global Wind Report 2024; Global Wind Energy Council: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Alhrshy, L.; Lippke, A.; Jauch, C. Variable Blade Inertia in State-of-the-Art Wind Turbine Structural-Dynamics Models. Energies 2023, 16, 6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Shi, Y.P. China’s wind power industry enters a stage of high-quality market-oriented development. Wind Energy 2023, 5, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y. Cooperative Control for DFIG-Based Wind Turbine Generation System Covering All Operating Regions. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2025, 16, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheen, A.; Elshafei, L.A. Wind-turbine collective-pitch control via a fuzzy predictive algorithm. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, E.S.; Xu, W. Control design and dynamic performance analysis of a wind turbine-induction generator unit. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2000, 15, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholbrock, A.; Fleming, P.; Schlipf, D.; Wright, A.; Johnson, K.; Wang, N. Lidar-enhanced wind turbine control: Past, present, and future. In Proceedings of the 2016 American Control Conference (ACC), Boston, MA, USA, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 1399–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Haizmann, F.; Schlipf, D.; Raach, S.; Scholbrock, A.; Wright, A.; Slinger, C.; Medley, J.; Harris, M.; Bossanyi, E.; Cheng, P.W. Optimization of a feed-forward controller using a CW-lidar system on the CART3. In Proceedings of the 2015 American Control Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 1–3 July 2015; pp. 3715–3720. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Johnson, K.E.; Wright, A.D. FX-RLS-Based Feedforward Control for LIDAR-Enabled Wind Turbine Load Mitigation. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2012, 20, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z. LIDAR-assisted radial basis function neural network optimization for wind turbines. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 13, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Soltani, M.; Poulsen, N.K.; Niemann, H.H. An MPC approach to individual pitch control of wind turbines using uncertain LIDAR measurements. In Proceedings of the 2013 European Control Conference (ECC), Zurich, Switzerland, 17–19 July 2013; pp. 490–495. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, M.; Hansen, M.H. A LIDAR-assisted model predictive controller added on a traditional wind turbine controller. In Proceedings of the 2016 American Control Conference (ACC), Boston, MA, USA, 6–8 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schlipf, D.; Pao, L.Y.; Cheng, P.W. Comparison of feedforward and model predictive control of wind turbines using LIDAR. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Maui, HI, USA, 10–13 December 2012; pp. 3050–3055. [Google Scholar]
- Schlipf, D.; Grau, P.; Raach, S.; Duraiski, R.; Trierweiler, J.; Cheng, P.W. Comparison of linear and nonlinear model predictive control of wind turbines using LIDAR. In Proceedings of the 2014 American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 June 2014; pp. 3742–3747. [Google Scholar]
- Atsushi, Y.; Iman, Y.; Takeshi, I. Reduction in the Fluctuating Load on Wind Turbines by Using a Combined Nacelle Acceleration Feedback and Lidar-Based Feedforward Control. Energies 2020, 13, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Cai, W.C.; Li, P.; Jia, Z.J.; Chen, H.J.; Song, Y.D. Neuroadaptive Variable Speed Control of Wind Turbine with Wind Speed Estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7754–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Yang, Q.; Xu, B. Hybrid Intelligent Feedforward-Feedback Pitch Control for VSWT with Predicted Wind Speed. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2770–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.H. Short-term wind speed prediction using Extended Kalman filter and machine learning. Energy Rep. 2020, 7, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhong, H.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Geng, A.C.; Zhang, L.; Lei, C.J. Ultra-short-term wind speed prediction based on neural network and wavelet analysis. Renew. Energy 2016, 34, 705–711. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Gu, Z.Y.; Huang, Y. Wind farm wind speed prediction based on hybrid Copula function and whale optimization algorithm. Electr. Power Sci. Eng. 2022, 38, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.Q.; Hao, W.J.; Wang, H.; Sun, Z.H.; Zhou, J.Y. Effective wind speed prediction at wind turbine hub based on LiDAR-Armax. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2020, 57, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.L.; Ang, L.; Fan, Z.M. Real-time rotor effective wind speed estimation using Gaussian processregression and Kalman filtering. Renew. Energy 2021, 169, 670–686. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Cai, X.; Wu, A.; Xu, B.F.; Lin, S.F. Turbulence intensity identification and load reduction of wind turbine under extreme turbulence. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 257, 111710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.B.; Liu, X. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy algorithm to estimate effective wind speed and optimal rotor speed for variable-speed wind turbine. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Song, D.; Xiang, X.; Ge, X.; Joo, Y.H. Sensorless effective wind speed estimation method based on unknown input disturbance observer and extreme learning machine. Energy 2019, 186, 115790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Song, D.; Yang, Y.; Joo, Y.H. An effective wind speed estimation based extended optimal torque control for maximum wind energy capture. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 65959–65969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Zhou, C.K.; Tang, S.Z.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, M.Y.; Deng, Y. MPPT method for large wind turbines based on adaptive model predictive control. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2023, 44, 501–508. [Google Scholar]
- Simley, E.; Pao, Y.L. Evaluation of a wind speed estimator for effective hub-height and shear components. Wind Energy 2016, 19, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.L.; Huang, S.; Du, J.; Su, D.X.; Li, J. Feedforward-based pitch control for wind turbines. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2012, 40, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Tang, H.M.; Bao, G.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liang, C. Disturbance feedforward and predictive feedback composite control for load suppression in wind turbines. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2016, 31, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.Z. Singular perturbation theory. Syst. Eng. Electron. 1988, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]




| Name | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Rated power | 5 MW |
| Number of blades | 3 |
| Impeller diameter | 126 m |
| Hub diameter | 3 m |
| Cut-in wind speed | 3 m/s |
| Rated wind speed | 11.4 m/s |
| Cutting out wind speed | 25 m/s |
| Rated electromagnetic torque | 43,093.55 N·m |
| Rated speed | 12.1 rpm |
| Rotor mass | 110,000 kg |
| Blade initial pitch angle | 0 deg |
| Drive train damping | 6.22 × 106 N·m/(rad/s) |
| Drive train stiffness | 8.67 × 108 N·m/rad |
| Control Strategy | Output Power (W) | Tower Bottom Pitching Moment (kN·m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Values | Overshoot | Maximum Values | Overshoot | |
| PI | 5.74 × 106 | 8.32% | 7.5 × 104 | 63.10% |
| Proposed method | 5.65 × 106 | 6.61% | 7.0 × 104 | 52.13% |
| Control Strategy | Output Power (W) | Tower Bottom Pitching Moment (kN·m) |
|---|---|---|
| Mean Square Error | Mean Square Error | |
| PI | 5.610 × 104 | 3.367 × 103 |
| Proposed method | 3.387 × 104 | 3.137 × 103 |
| Evaluation Metric | Traditional PI Control | Proposed Method |
|---|---|---|
| Rotational Speed Stability | Medium | High |
| Power Fluctuation | Medium | Low |
| Tower Bottom Pitching Moment Fluctuation | Medium | Low |
| Model Complexity | Low | Medium |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Deng, X.; Liu, Y.; Yue, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Cai, Z.; Cai, R. Research on Nonlinear Pitch Control Strategy for Large Wind Turbine Units Based on Effective Wind Speed Estimation. Electronics 2025, 14, 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122460
Li L, Deng X, Liu Y, Yue X, Wang H, Liu R, Cai Z, Cai R. Research on Nonlinear Pitch Control Strategy for Large Wind Turbine Units Based on Effective Wind Speed Estimation. Electronics. 2025; 14(12):2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122460
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Longjun, Xiangtian Deng, Yandong Liu, Xuxin Yue, Haoran Wang, Ruibo Liu, Zhaobing Cai, and Ruiqi Cai. 2025. "Research on Nonlinear Pitch Control Strategy for Large Wind Turbine Units Based on Effective Wind Speed Estimation" Electronics 14, no. 12: 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122460
APA StyleLi, L., Deng, X., Liu, Y., Yue, X., Wang, H., Liu, R., Cai, Z., & Cai, R. (2025). Research on Nonlinear Pitch Control Strategy for Large Wind Turbine Units Based on Effective Wind Speed Estimation. Electronics, 14(12), 2460. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122460






