Improved Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search Combined with Simulated Annealing (IALNS-SA) Algorithm for Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup and Time Windows
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Review of the Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup and Time Windows (VRPSDPTWs)
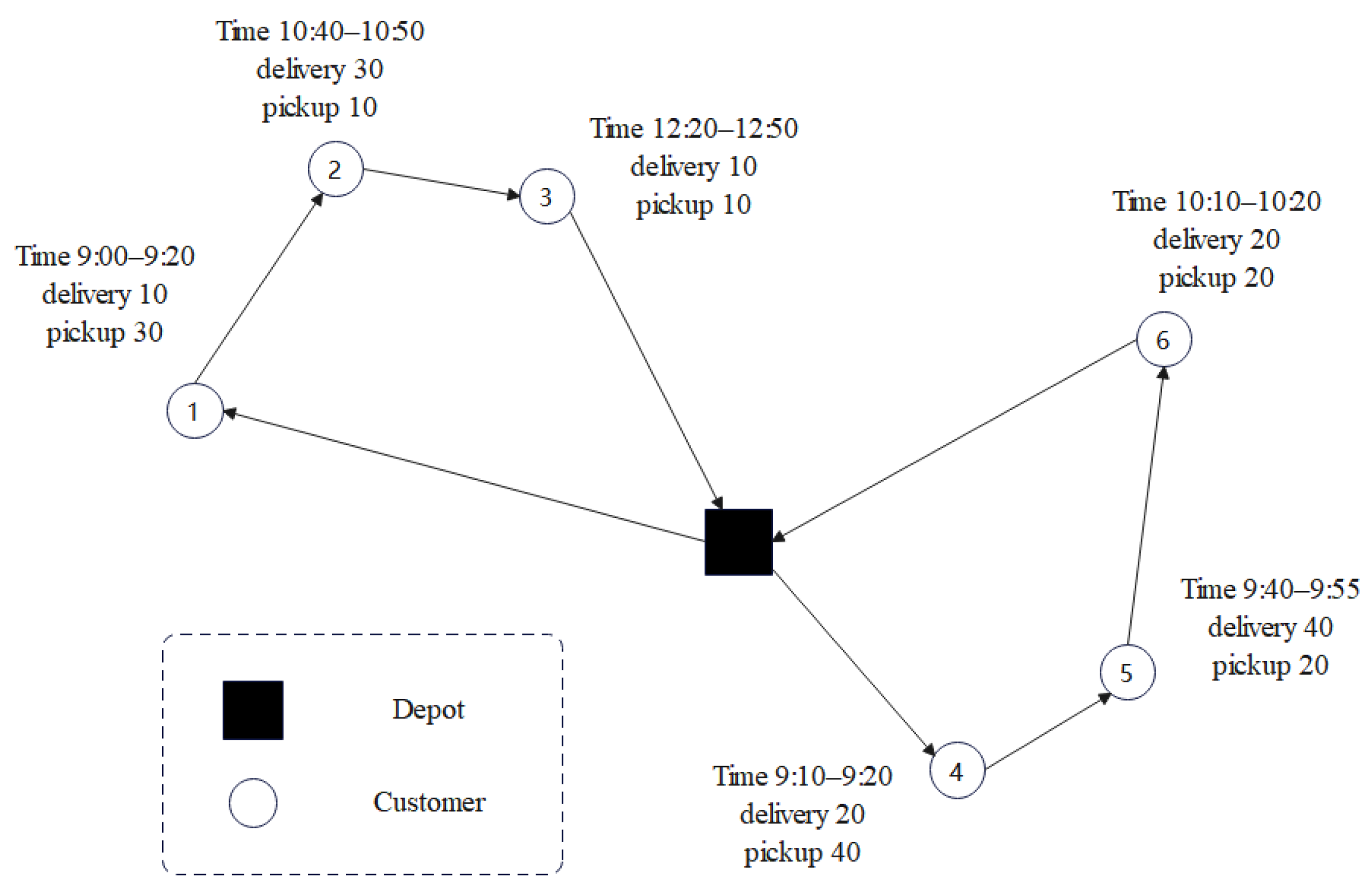
2.2. The Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup and Time Windows (VRPSDPTWs)
2.3. The Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup and Time Windows (VRPSDPDTWs) Mathematical Model
2.4. Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search (ALNS)
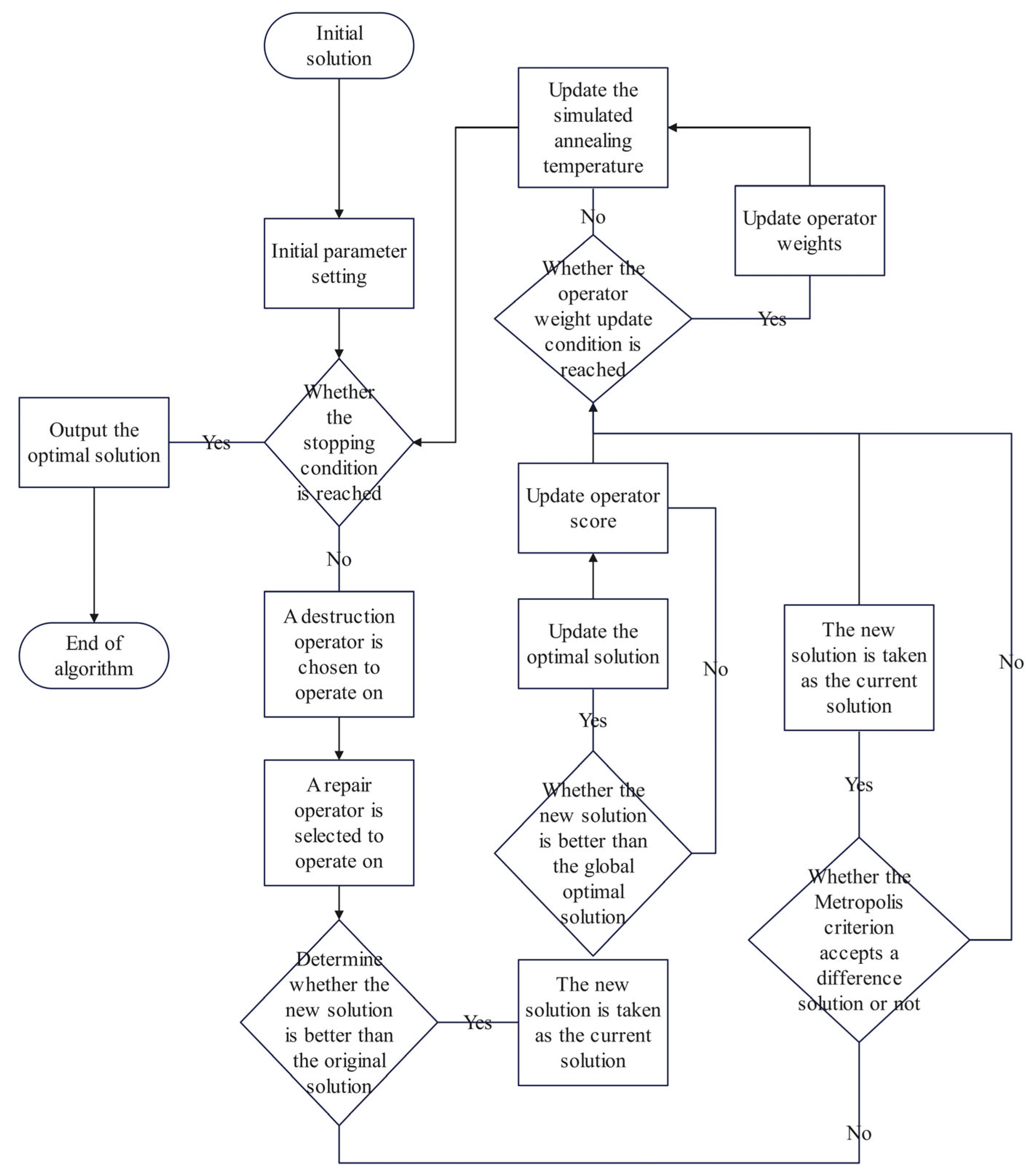
3. Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search Integrated with Simulated Annealing (IALNS-SA) Algorithm
3.1. Initialization Solution
3.2. Solution Optimization
3.2.1. Destroy Operator
- Random Destroy Operator
- 2.
- Similarity Destroy Operator
| Algorithm 1 Similarity Destroy Operator |
| Input: Current solution , number of customers to remove , random element Output: Destroyed solution , set of removed customers Randomly select a customer from the solution , and add to the set while do Randomly select a customer from the set Sort the customers that are in the current solution but not in the set as follows: , then store the sorting result in the sequence Calculate the index of randomly selected customers end while Remove the customers in the set from the solution to obtain the destroyed solution return and |
- 3.
- Maximum Saving Cost Destroy Operator
- 4.
- Destroying Vehicle Destroy Operator
- 5.
- Maximum Waiting Time Destroy Operator
3.2.2. Repair Operator
- 1.
- Global Optimal Repair Operator
- 2.
- Minimum Insertion Cost Repair Operator
| Algorithm 2 Minimum Insertion Cost Repair Operator |
| Input: The solution after destruction , the set of removed customers Output: The repaired solution while do Calculate the minimum insertion cost for each customer in , and correspond to the insertion path number and the position on that route Select customer from with the among all customers in , which is the customer with the largest minimum insertion cost from Insert customer into the at position of route , which is the position with the minimum insertion cost from , which means removing customer from end while return |
- 3.
- Random K Repair Operator
- 4.
- Regret Criterion Repair Operator
- 5.
- Minimum Waiting Time Repair Operator
4. Adaptive Selection Strategy
| Algorithm 3 Roulette Wheel Selection |
| Input: Operator weights list W = [w1, w2, ..., w10] Output: Selected operator index i total_weight = sum(W) r = random(0, total_weight) cumulative = 0 for i in 1 to 10: cumulative += W[i] if r ≤ cumulative: return i |
Acceptance Criterion
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Experimental Settings
5.2. Ablation Experiment
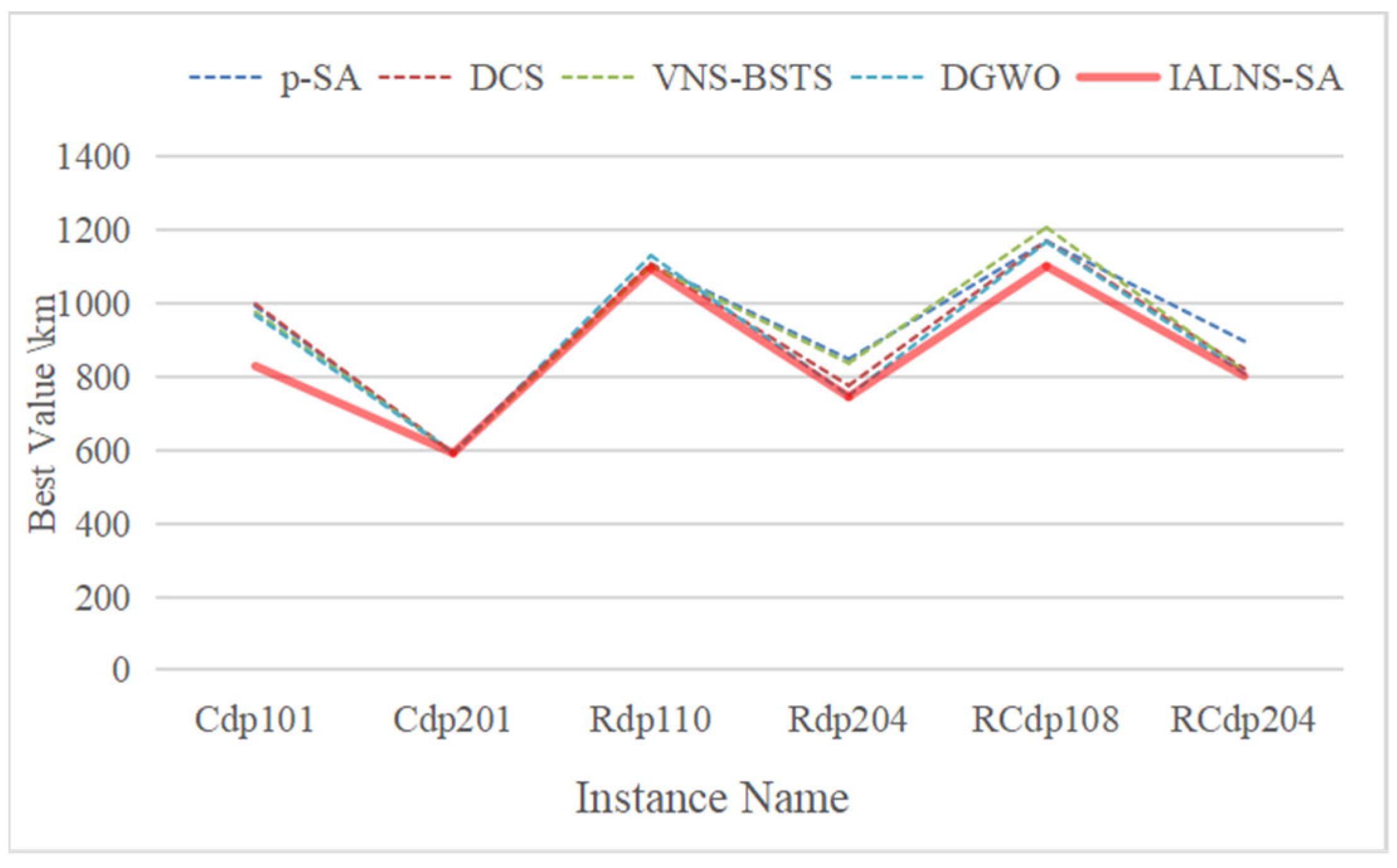
5.3. Results and Comparisons
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdumutaliyev, R.; Narimonov, S. Ways to Balance International Trade Operations in Our Country. Dev. Pedagog. Technol. Mod. Sci. 2024, 3, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, S.; Hou, D.; Dai, L. The mediation effect of innovation in the domestic and international economic development circulation. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2024, 36, 989–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Sezer, S.; Abasiz, T. The impact of logistics industry on economic growth: An application in OECD countries. Eurasian J. Soc. Sci. 2017, 5, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, M.; Rey, A.; Maglio, R.; Panetti, E. Determinants in adopting the Internet of Things in the transport and logistics industry. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 131, 584–590. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Mu, D.; Wang, C. A solution for the full-load collection vehicle routing problem with multiple trips and demands: An application in Beijing. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 89381–89394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Meng, L.; Wang, Z. Improved NSGA-II Algorithm-Based SDVRP Considering Simultaneously Pickup and Delivery of Multi-Commodity. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Duan, J.; Wang, G. Mathematical models for truck-drone routing problem: Literature review. Appl. Math. Model. 2025, 144, 116074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, G. Approaches to the truck-drone routing problem: A systematic review. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2025, 92, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazlollahtabar, H. Genetic Algorithm-based optimization for the fuzzy capacitated Location-Routing Problem with simultaneous pickup and delivery. J. Eng. Manag. Syst. Eng. 2025, 4, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chung, S.H.; Kwon, C. An adaptive large neighborhood search method for the drone—truck arc routing problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2025, 176, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucq, D.; Lopez, A.J.; Aghezzaf, E.H.; Semanjski, I.; Gautama, S. A Viability Study of Pickup and Delivery Locations Using Genetic Algorithm in Intelligent Transportation Systems. In Intelligent Systems Conference; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 847–861. [Google Scholar]
- Bocewicz, G.; Banaszak, Z.; Wikarek, J.; Rutczyńska-Wdowiak, K.; Sitek, P. Optimization of capacitated vehicle routing problem with alternative delivery, pick-up and time windows, A modified hybrid approach. Neurocomputing 2021, 423, 670–678. [Google Scholar]
- Kurniawati, W.; Wahyuningsih, S.; Yasin, M. Study of ALNS-TS algorithm on VRPSDPTW and its implementation. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 3235. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Wei, L.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Du, W. A diagnostic method of freight wagons hunting performance based on wayside hunting detection system. Measurement 2024, 227, 114274. [Google Scholar]
- Simic, V.; Pamucar, D.; Riffi, M.E.; Mzili, I.; Abualigah, L.; Almohsen, B.; Mzili, T. Hybrid genetic and penguin search optimization algorithm (GA-PSEOA) for efficient flow shop scheduling solutions. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2024, 22, 77–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xu, M.; Fan, J.; Guan, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Collaborative multi-depot pickup and delivery vehicle routing problem with split loads and time windows. Knowl. Based Syst. 2021, 231, 107412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, E.; Paredes, F.; Lagos, C.; Guerrero, G.; Johnson, F.; Moltedo, A. An improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for the VRP with simultaneous pickup and delivery and time windows. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2018, 16, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantakopoulos, G.D.; Gayialis, S.P.; Kechagias, E.P. Vehicle routing problem and related algorithms for logistics distribution: A literature review and classification. Oper. Res. 2022, 22, 2033–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, M.; Al-e, S.M.J.M. Green vehicle routing problem: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 231, 107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi Sarbijan, M.; Behnamian, J. Emerging research fields in vehicle routing problem: A short review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 2473–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.J.; Miyazawa, F.K.; Xavier, E.C.; Amorim, P.; Rios, B.H.O.; Curcio, E. Recent dynamic vehicle routing problems: A survey. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 160, 107604. [Google Scholar]
- Benyettou, A.; Salimifard, K.; Moghdani, R.; Demir, E. The green vehicle routing problem: A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123691. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Sánchez, A.; Rocha-Medina, L.B. VRP variants applicable to collecting donations and similar problems: A taxonomic review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 164, 107887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelelli, E.; Mansini, R. The vehicle routing problem with time windows and simultaneous pick-up and delivery. In Quantitative Approaches to Distribution Logistics and Supply Chain Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 249–267. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.H. Applications of smart technologies in logistics and transport: A review. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 153, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malisetty, S.; Pasupuleti, V.; Thuraka, B.; Kodete, C.S. Enhancing supply chain agility and sustainability through machine learning, Optimization techniques for logistics and inventory management. Logistics 2024, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingfei, Y.; Mengze, Z.; Zeyu, L.; Ki-Hyung, B.; Avotra, A.A.R.N.; Nawaz, A. Green logistics performance and infrastructure on service trade and environment-measuring firm’s performance and service quality. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groër, C.; Golden, B.; Wasil, E. The consistent vehicle routing problem. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2009, 11, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Mu, D. Solving the vehicle routing problem with time windows and simultaneous delivery and pickup based on discrete cuckoo search algorithm. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 24, 570–582. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Deng, Z.; Gong, Y. Discrete grey wolf optimization algorithm for solving VRPSPDTW problem. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2023, 32, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Grunder, O.; Boudouh, T.; Shi, Y. A lexicographic-based two-stage algorithm for vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pickup—Delivery and time window. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 95, 103901. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Mu, D.; Sutherland, J.W.; Wang, C. A parallel simulated annealing method for the vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pickup–delivery and time windows. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 83, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Pureza, V.; Morabito, R.; Reimann, M. Vehicle routing with multiple deliverymen, Modeling and heuristic approaches for the VRPTW. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 218, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyasiry, A.M.; Forbes, M.; Bulmer, M. An exact algorithm for the pickup and delivery problem with time windows and last-in-first-out loading. Transp. Sci. 2019, 53, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gao, Y. An ant colony optimization based on local search for the vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pickup–delivery and time window. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 139, 110203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, L. Comparative analysis of several new intelligent optimization algorithms. J. Front. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2022, 16, 88–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ropke, S.; Pisinger, D. An adaptive large neighborhood search heuristic for the pickup and delivery problem with time windows. Transp. Sci. 2006, 40, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Chen, Y.Y. A Genetic Algorithm for the Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup Problems with Time Window. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 62, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Condition | Score Weight |
|---|---|
| New solution cost < global optimal solution cost | 6 |
| Current solution cost > New solution cost > Global optimal solution cost | 3 |
| New solution cost = current solution cost | 1 |
| New solution cost > current solution cost | 0 |
| Combination | Total Path Length (km) | Running Time (s) | Convergence Rate (Number of Iterations) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combination 1 | 829.21 | 1252 | 12 |
| Combination 2 | 951.47 | 2053 | 100 |
| Combination 3 | 895.32 | 1424 | 31 |
| Combination 4 | 887.95 | 1561 | 35 |
| Instance | p-SA | DCS | VNS-BSTS | DGWO | IALNS-SA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cdp101 | 1512 | 1459 | 1807 | 1442 | 1252 |
| Rdp101 | 2034 | 1915 | 1751 | 1517 | 1653 |
| RCdp101 | 2207 | 2120 | 2433 | 2098 | 1812 |
| AVG | 1917 | 1831 | 1997 | 1685 | 1572 |
| Instance | p-SA | DCS | VNS-BSTS | DGWO | IALNS-SA | SD | AVG | GAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cdp101 | 992.88 | 998.29 | 976.04 | 967.42 | 828.94 | 9.87 | 835.21 | −16.71% |
| Cdp102 | 955.31 | 954.31 | 942.45 | 936.74 | 821.93 | 10.52 | 829.45 | −13.97% |
| Cdp103 | 958.66 | 923.05 | 896.28 | 890.23 | 860.59 | 8.95 | 867.83 | −3.44% |
| Cdp104 | 944.74 | 931.26 | 872.39 | 885.79 | 826.66 | 9.23 | 834.17 | −5.53% |
| Cdp105 | 989.86 | 981.45 | 1080.63 | 981.45 | 822.84 | 9.54 | 830.76 | −19.28% |
| Cdp106 | 878.29 | 878.45 | 963.45 | 878.29 | 828.94 | 8.91 | 835.89 | −5.95% |
| Cdp107 | 911.90 | 912.37 | 987.64 | 915.64 | 820.61 | 8.97 | 827.35 | −11.12% |
| Cdp108 | 1063.73 | 978.82 | 934.41 | 924.65 | 820.61 | 10.68 | 829.42 | −12.68% |
| Cdp109 | 947.90 | 940.49 | 909.27 | 922.67 | 855.91 | 9.75 | 863.24 | −6.23% |
| Cdp201 | 591.56 | 591.56 | 591.56 | 591.56 | 591.56 | 0 | 591.56 | 0.00% |
| Cdp202 | 591.56 | 591.56 | 591.56 | 591.56 | 591.56 | 0 | 591.56 | 0.00% |
| Cdp203 | 591.17 | 591.17 | 591.17 | 591.17 | 591.17 | 0 | 591.17 | 0.00% |
| Cdp204 | 590.60 | 590.60 | 599.33 | 591.17 | 590.60 | 0 | 590.60 | 0.00% |
| Cdp205 | 588.88 | 588.88 | 588.88 | 588.88 | 588.88 | 0 | 588.88 | 0.00% |
| Cdp206 | 588.49 | 588.49 | 588.49 | 588.49 | 588.49 | 0 | 588.49 | 0.00% |
| Cdp207 | 588.29 | 588.29 | 588.29 | 588.29 | 588.29 | 0 | 588.29 | 0.00% |
| Cdp208 | 588.32 | 588.32 | 588.32 | 588.32 | 588.32 | 0 | 588.32 | 0.00% |
| Instance | p-SA | DCS | VNS-BSTS | DGWO | IALNS-SA | SD | AVG | GAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rdp101 | 1660.98 | 1658.65 | 1650.80 | 1646.27 | 1648.05 | 13.21 | 1653.28 | 0.11% |
| Rdp102 | 1491.75 | 1490.13 | 1486.12 | 1477.60 | 1486.64 | 11.93 | 1491.87 | 0.61% |
| Rdp103 | 1226.77 | 1228.48 | 1294.75 | 1234.60 | 1218.77 | 9.78 | 1224.15 | −0.66% |
| Rdp104 | 1000.65 | 1005.99 | 984.81 | 1012.03 | 1002.71 | 8.06 | 1007.45 | 1.82% |
| Rdp105 | 1399.81 | 1340.06 | 1377.11 | 1345.76 | 1364.35 | 10.94 | 1369.72 | 1.81% |
| Rdp106 | 1275.69 | 1270.29 | 1261.50 | 1256.76 | 1265.11 | 10.17 | 1269.93 | 0.66% |
| Rdp107 | 1082.92 | 1084.00 | 1144.02 | 1076.49 | 1079.09 | 8.68 | 1083.85 | 0.24% |
| Rdp108 | 962.48 | 964.38 | 968.32 | 959.90 | 954.96 | 7.67 | 959.15 | −0.52% |
| Rdp109 | 1181.92 | 1156.90 | 1224.86 | 1151.96 | 1164.47 | 9.36 | 1169.35 | 1.09% |
| Rdp110 | 1106.52 | 1108.81 | 1101.33 | 1130.63 | 1095.19 | 8.79 | 1099.76 | −0.56% |
| Rdp111 | 1073.62 | 1077.65 | 1117.76 | 1084.35 | 1075.92 | 8.63 | 1080.63 | 0.21% |
| Rdp112 | 966.06 | 977.59 | 961.29 | 962.36 | 969.99 | 7.79 | 974.14 | 0.91% |
| Rdp201 | 1286.55 | 1281.63 | 1254.57 | 1177.92 | 1159.24 | 9.31 | 1164.06 | −1.61% |
| Rdp202 | 1150.31 | 1152.65 | 1202.27 | 1039.02 | 1046.64 | 8.41 | 1051.04 | 0.73% |
| Rdp203 | 997.84 | 950.79 | 949.42 | 885.70 | 903.73 | 7.26 | 907.69 | 2.04% |
| Rdp204 | 848.01 | 776.00 | 837.13 | 748.13 | 745.08 | 5.98 | 748.26 | −0.41% |
| Rdp205 | 1046.06 | 1051.38 | 1027.49 | 986.12 | 978.46 | 7.86 | 982.57 | −0.78% |
| Rdp206 | 959.94 | 957.81 | 938.63 | 894.48 | 912.75 | 7.33 | 916.55 | 2.04% |
| Rdp207 | 899.82 | 890.52 | 912.26 | 809.41 | 802.24 | 6.44 | 805.62 | −0.89% |
| Rdp208 | 739.06 | 737.05 | 737.26 | 719.60 | 722.16 | 5.80 | 725.26 | 0.36% |
| Rdp209 | 947.80 | 930.26 | 940.29 | 871.14 | 877.77 | 7.05 | 881.52 | 0.76% |
| Rdp210 | 1005.11 | 1005.11 | 945.97 | 921.91 | 930.99 | 7.48 | 934.95 | 0.98% |
| Rdp211 | 812.44 | 819.88 | 805.22 | 772.36 | 781.37 | 6.27 | 784.68 | 1.17% |
| Instance | p-SA | DCS | VNS-BSTS | DGWO | IALNS-SA | SD | AVG | GAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCdp101 | 1659.59 | 1654.32 | 1708.21 | 1664.79 | 1629.79 | 16.38 | 1637.82 | −1.51% |
| RCdp102 | 1522.76 | 1522.76 | 1526.36 | 1500.12 | 1472.74 | 14.81 | 1481.35 | −1.86% |
| RCdp103 | 1344.62 | 1344.63 | 1336.05 | 1334.65 | 1289.89 | 12.97 | 1296.48 | −3.47% |
| RCdp104 | 1268.43 | 1269.31 | 1177.21 | 1226.51 | 1124.46 | 11.31 | 1130.82 | −4.69% |
| RCdp105 | 1581.54 | 1581.26 | 1548.38 | 1557.46 | 1553.08 | 15.61 | 1560.89 | 0.30% |
| RCdp106 | 1418.16 | 1419.26 | 1408.19 | 1420.46 | 1374.96 | 13.82 | 1381.97 | −2.42% |
| RCdp107 | 1360.17 | 1360.17 | 1295.43 | 1304.31 | 1228.99 | 12.36 | 1235.63 | −5.41% |
| RCdp108 | 1169.57 | 1170.12 | 1207.60 | 1167.82 | 1101.47 | 11.07 | 1107.48 | −6.02% |
| RCdp201 | 1513.72 | 1520.56 | 1437.48 | 1304.13 | 1286.93 | 12.94 | 1293.67 | −1.34% |
| RCdp202 | 1273.26 | 1242.92 | 1412.52 | 1114.42 | 1107.63 | 11.14 | 1113.58 | −0.61% |
| RCdp203 | 1123.58 | 1087.37 | 1064.95 | 957.63 | 945.44 | 9.50 | 950.28 | −1.29% |
| RCdp204 | 897.14 | 822.02 | 813.74 | 808.50 | 802.39 | 8.07 | 806.8 | −0.76% |
| RCdp205 | 1357.44 | 1357.44 | 1316.06 | 1164.32 | 1173.41 | 11.80 | 1179.76 | 0.78% |
| RCdp206 | 1166.88 | 1166.88 | 1154.36 | 1076.57 | 1070.43 | 10.76 | 1076.08 | −0.57% |
| RCdp207 | 1089.85 | 1093.37 | 1098.64 | 966.37 | 991.56 | 9.97 | 996.79 | 2.61% |
| RCdp208 | 862.89 | 862.89 | 843.30 | 796.04 | 796.27 | 8.01 | 800.54 | 0.03% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Yang, T. Improved Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search Combined with Simulated Annealing (IALNS-SA) Algorithm for Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup and Time Windows. Electronics 2025, 14, 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122375
Ma H, Yang T. Improved Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search Combined with Simulated Annealing (IALNS-SA) Algorithm for Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup and Time Windows. Electronics. 2025; 14(12):2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122375
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Huan, and Tianbin Yang. 2025. "Improved Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search Combined with Simulated Annealing (IALNS-SA) Algorithm for Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup and Time Windows" Electronics 14, no. 12: 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122375
APA StyleMa, H., & Yang, T. (2025). Improved Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search Combined with Simulated Annealing (IALNS-SA) Algorithm for Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup and Time Windows. Electronics, 14(12), 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122375





