Design of a High-Gain X-Band Electromagnetic Band Gap Microstrip Patch Antenna for CubeSat Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
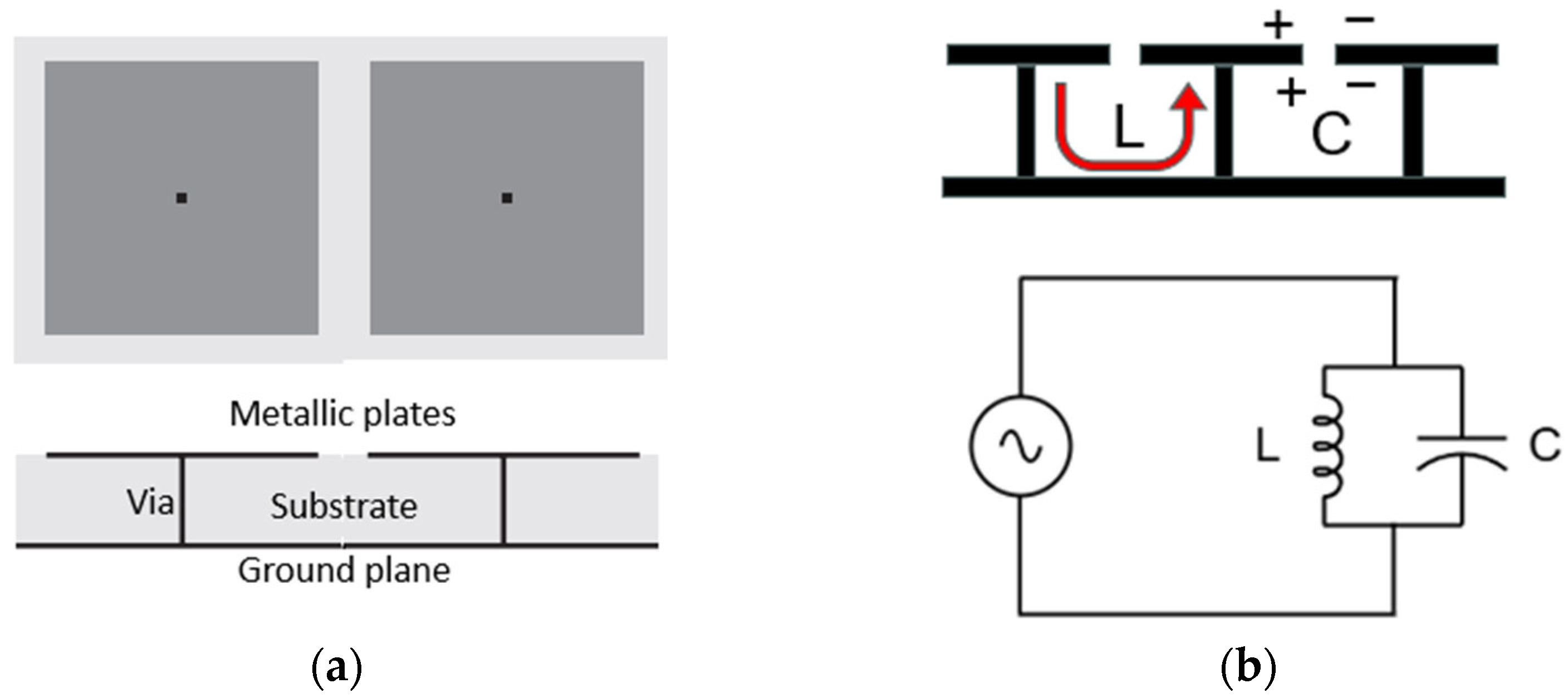
2. EBG for Microstrip Patch Antenna
3. Antenna Design and Parameters Study
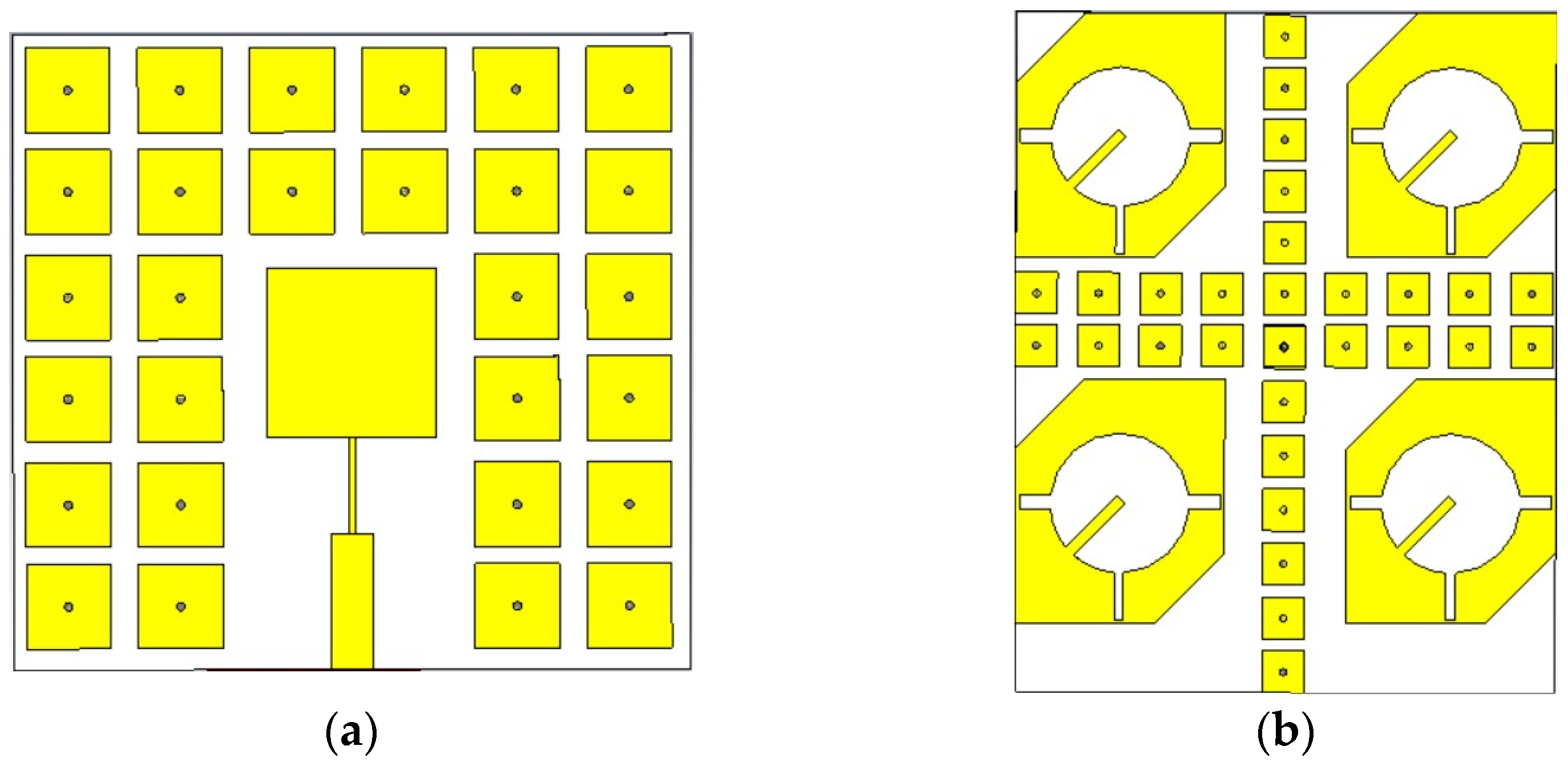
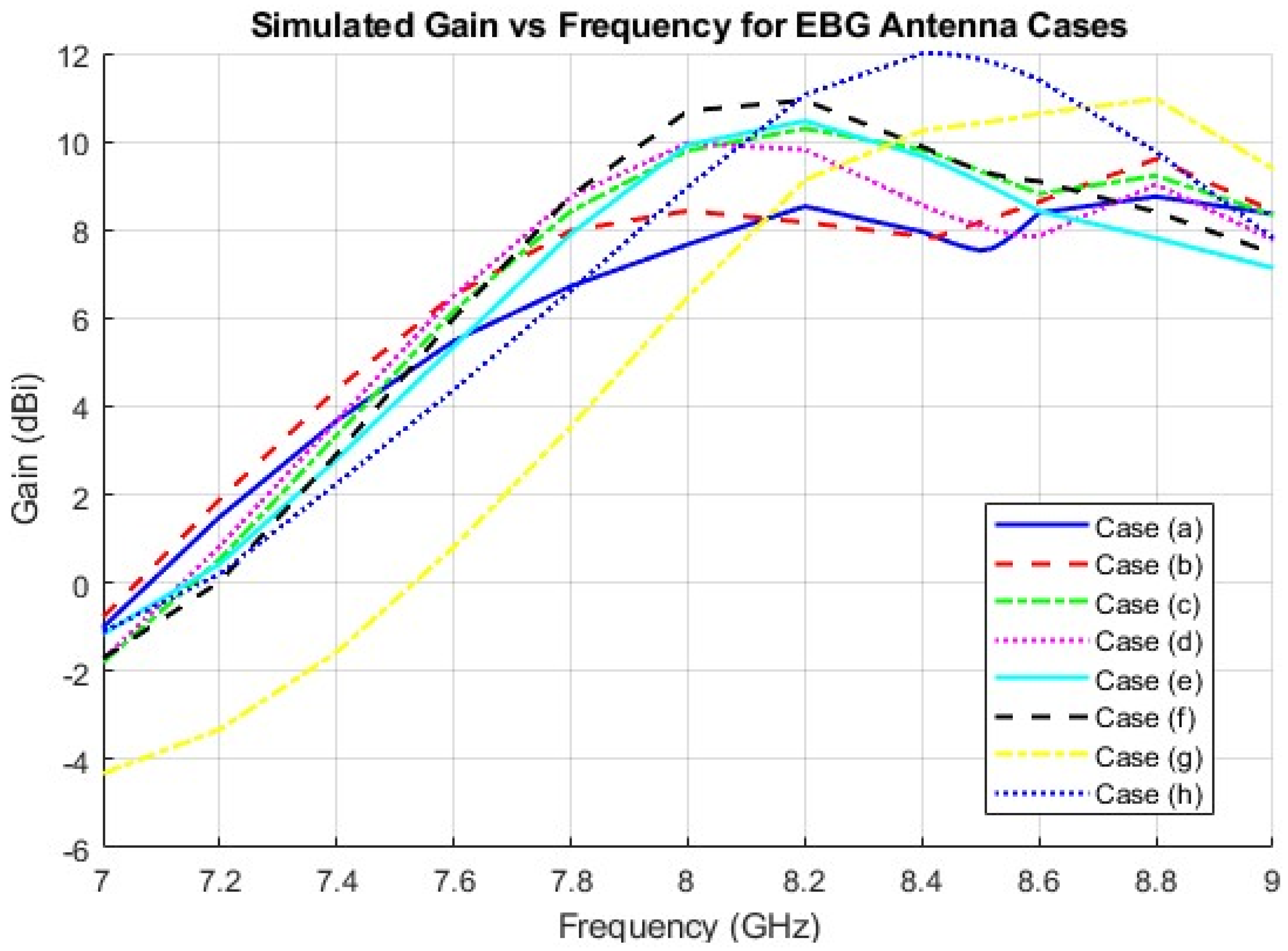
3.1. Design and Simulation of the EBG MPAs
- Design and simulate the original CP MPA in the available surface area with only the center radiator, at the target frequency of 8.483 GHz;
- Design and simulate the MPA with the mushroom-like EBG structure added;
- Optimize the related parameters to satisfy the requirements of gain and CP.
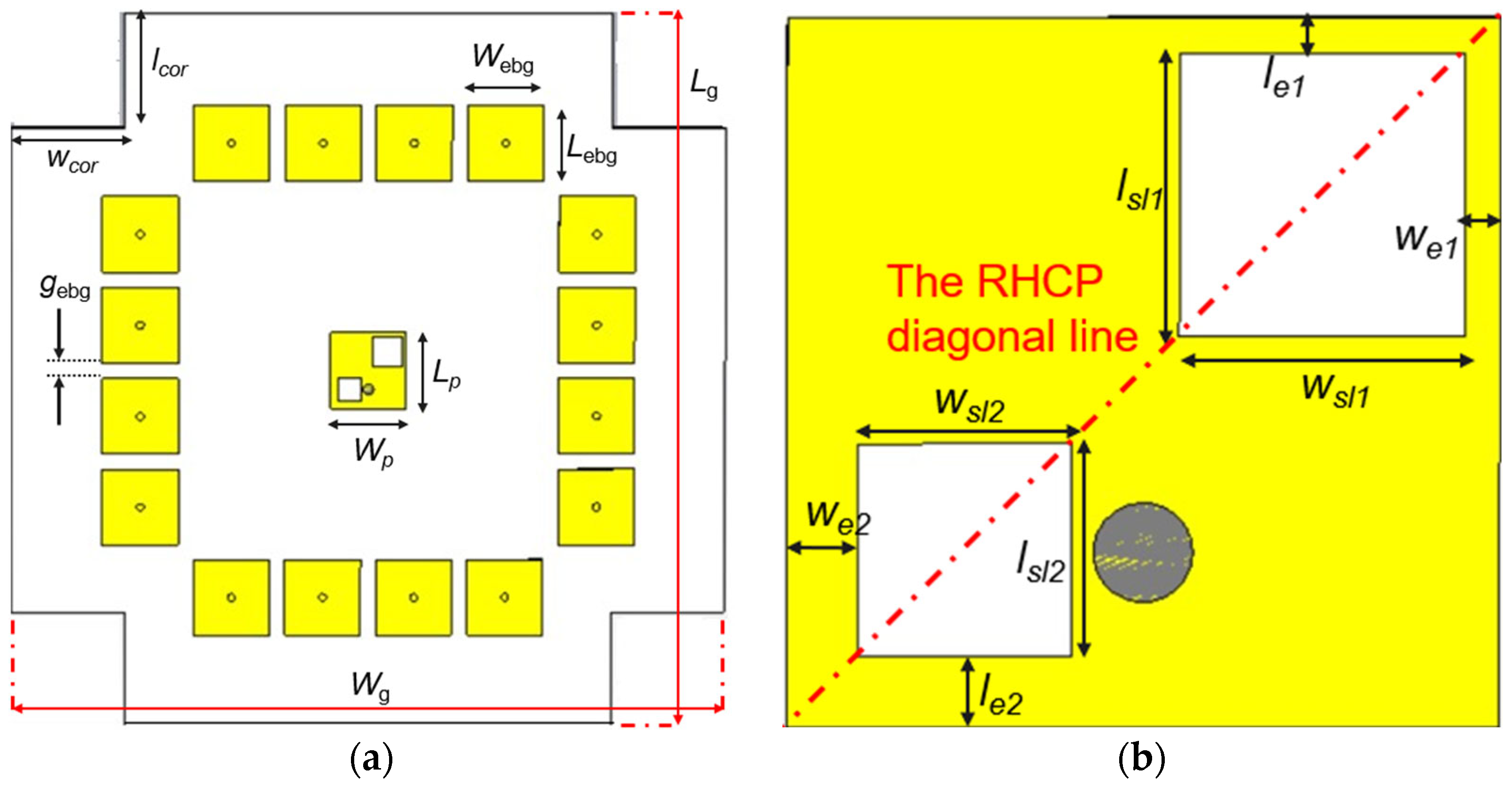
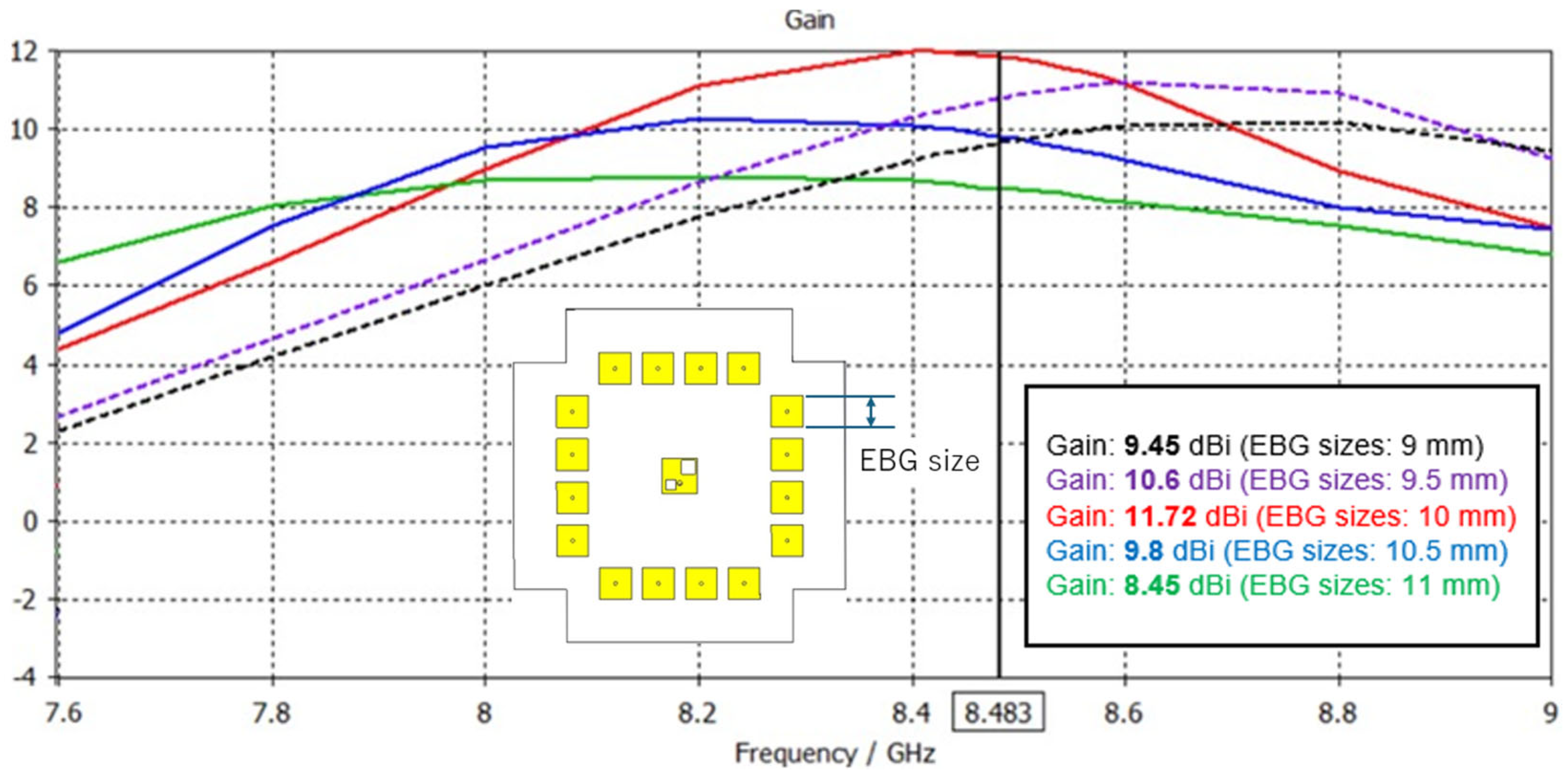
3.2. Parameters Study
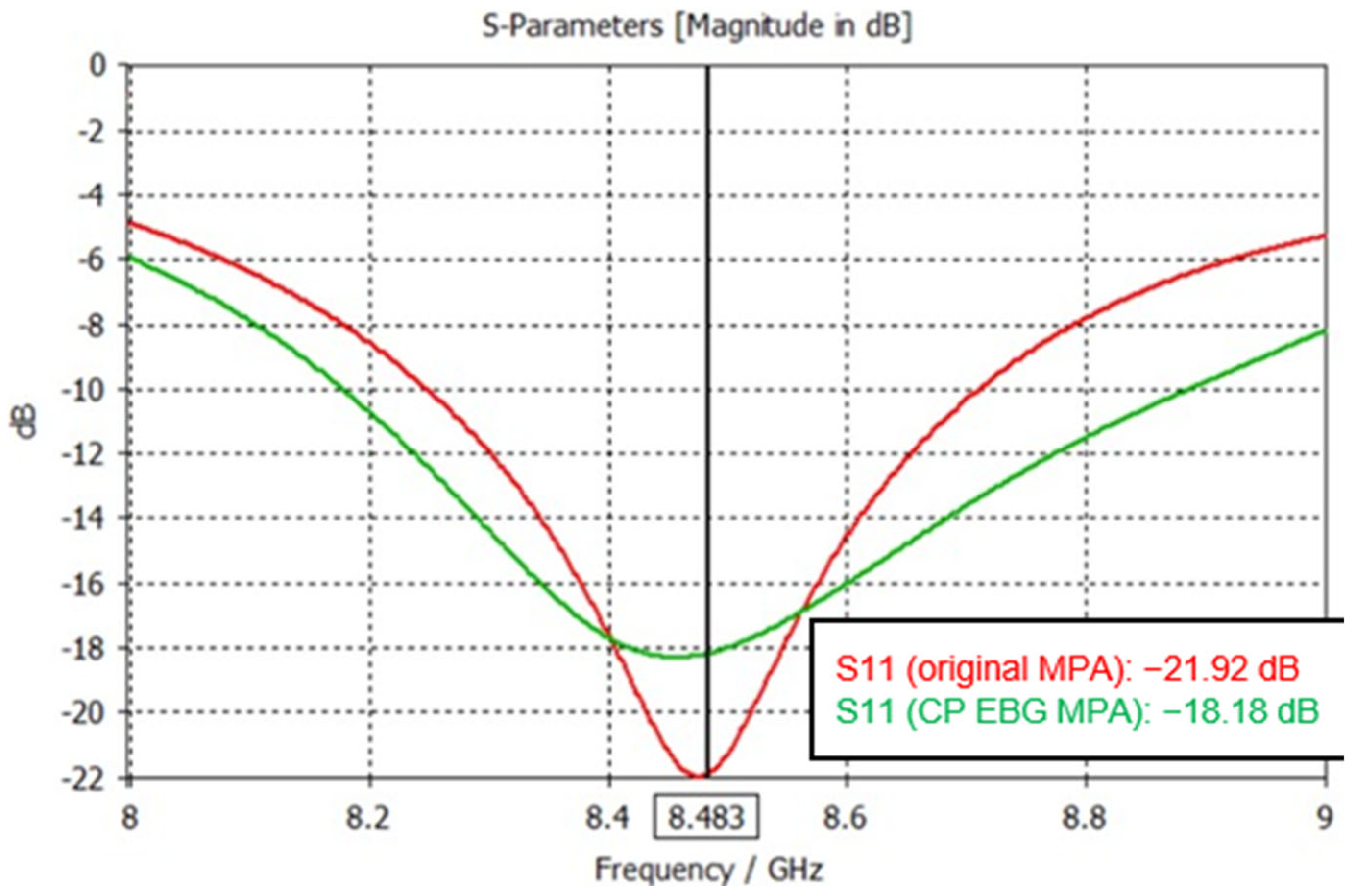
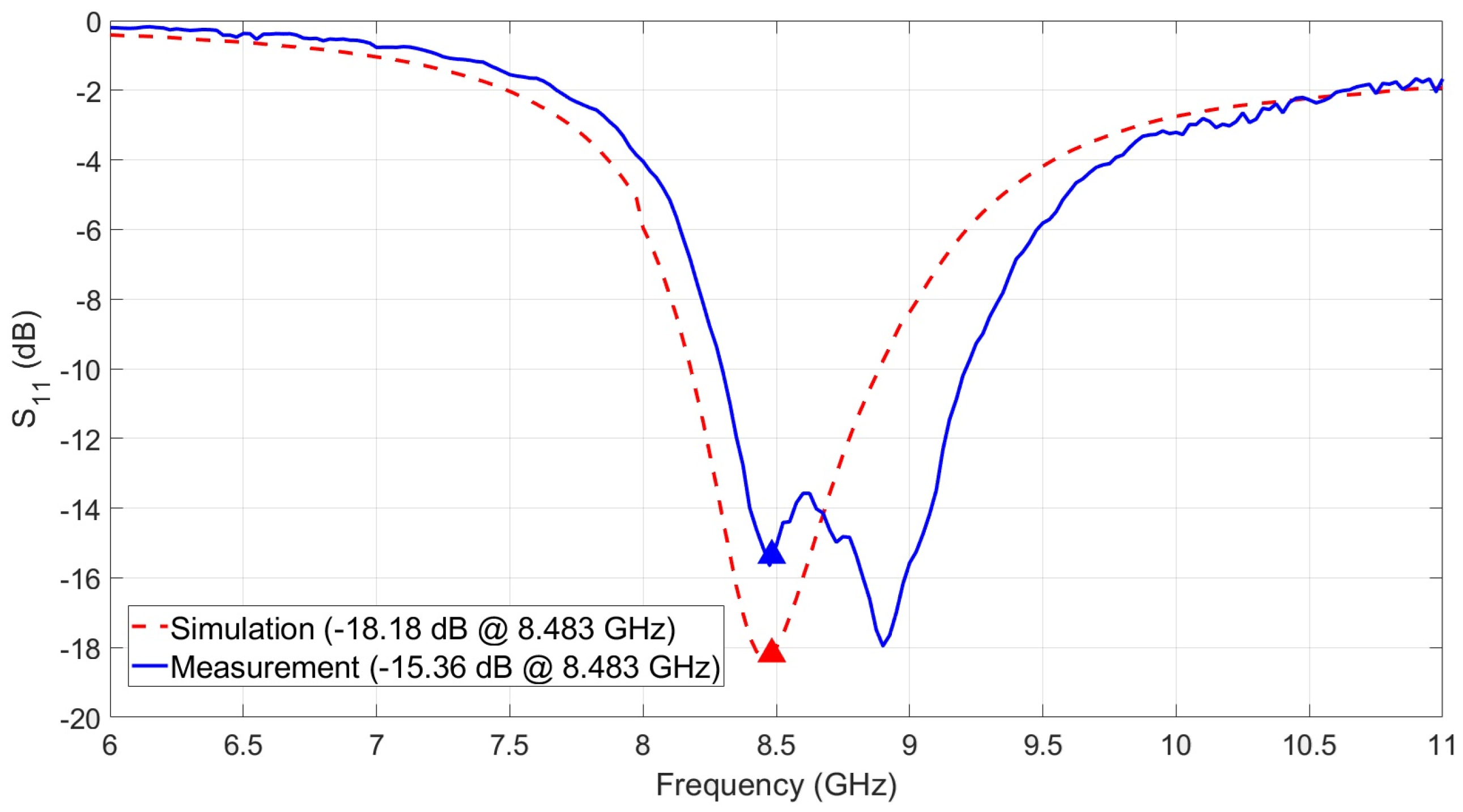
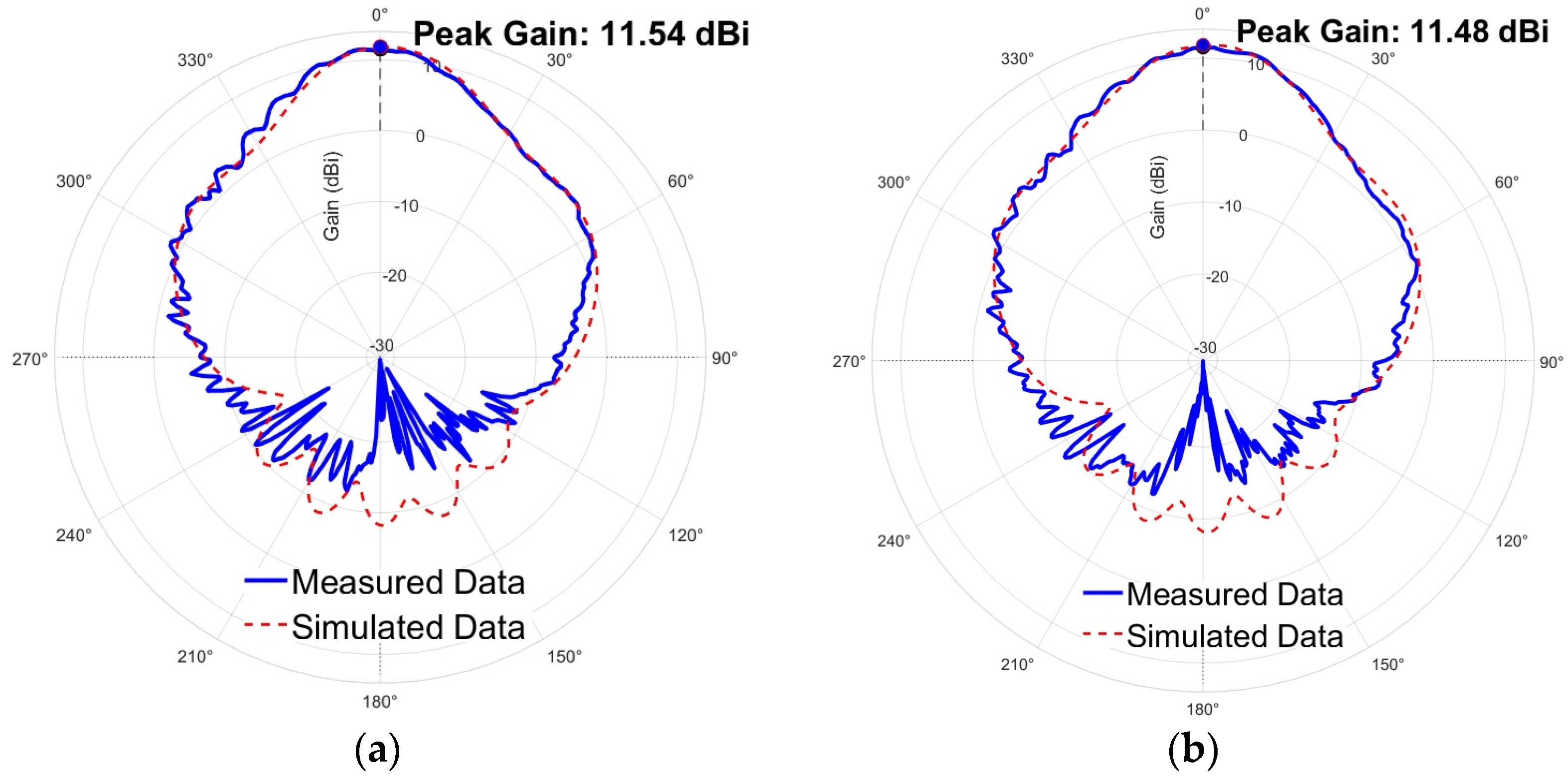
4. Antenna Measurement Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghaderi, M.R.; Amiri, N. CubeSat Antenna Designs in the Last 2 Decades (2002–2023): A Survey. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2024, 26, 327–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahat, N.; Decrossas, E.; Kobayashi, M.M. Mars Cube One. In CubeSat Antenna Design, 1st ed.; Nacer, C., Ed.; Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 35–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, M.; Lodi, M.B.; Curreli, N.; Pavone, S.C.; Maccio, C.; Marongiu, E.; Mariani, L.; Muntoni, G.; Mazzarella, G.; Fanti, A. A Deep Space Ka-band Antenna for CubeSat: Design and Multiphysics Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 16th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Madrid, Spain, 27 March–1 April 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, B.; Capet, N.; Romier, M. Compact S-band and X-band antennas for CubeSats. CEAS Space J. 2020, 12, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High-Gain Circularly Polarised Planar Antennas for Cubesat Systems. Available online: https://www.electronicspecifier.com/products/communications/high-gain-circularly-polarised-planar-antennas-for-cubesat-systems (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- CubeSat Design Specification Rev. 14.1. The CubeSat Program, Cal Poly SLO. Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5418c831e4b0fa4ecac1bacd/t/62193b7fc9e72e0053f00910/1645820809779/CDS%2BREV14_1%2B2022-02-09.pdf? (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Babuscia, A. Telecommunication Systems for Small Satellites Operating at High Frequencies: A Review. Information 2020, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoubiri, B.; Mayouf, A.; Mayouf, F.; Abdelkebir, S.; Devers, T. Rectangular microstrip antenna gain enhancement using elliptical EBG structure. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th International Conference on Sciences of Electromagnetics, Technologies of Information and Telecommunications (SETIT), Hammamet, Tunisia, 18–20 December 2016; pp. 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Thakur, A.; Srivastava, V.M. Miniaturization and Gain Enhancement of Microstrip Patch Antenna Using Defected Ground with EBG. J. Commun. 2018, 13, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.; Dinesh, K.V. Gain enhancement of microstrip patch antenna for Wi-Fi applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 Loughborough Antennas and Propagation Conference (LAPC), Loughborough, UK, 10–11 November 2014; pp. 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errifi, H.; Baghdad, A.; Badri, A.; Sahel, A. Improving Microstrip Patch Antenna Directivity using EBG Superstrate. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2014, 3, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, D.; Shafai, L.; Foroozesh, A. Improving microstrip patch antenna performance using EBG substrates. IEE Proc.-Microw. Antennas Propag. 2007, 153, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasimuddin, N.; Chen, Z.N.; Qing, X. Slotted Microstrip Antennas for Circular Polarization with Compact Size. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2013, 55, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yablonovitch, E. Photonic Crystals. J. Mod. Opt. 1994, 41, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat-Samii, Y.; Mosallaei, H. Electromagnetic band-gap structures: Classification, characterization, and applications. In Proceedings of the 2001 Eleventh International Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Manchester, UK, 17–20 April 2001; pp. 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Electromagnetic Band Gap Structures in Antenna Engineering; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sievenpiper, D.; Zhang, L.; Broas, R.; Alexopolous, N.; Yablonovitch, E. High-impedance electromagnetic surfaces with a forbidden frequency band. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1999, 47, 2059–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Liu, H.-X.; Liang, C.-H. Locally resonant cavity cell model for electromagnetic band gap structures. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2006, 54, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharamappa, K.; Jagadeesha, S. Gain Enhancement of Microstrip Antenna using Ebg Structure for Wi-Fi Application. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 9, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketkuntod, P.; Hongnara, T.; Thaiwirot, W.; Akkaraekthalin, P. Gain enhancement of microstrip patch antenna using I-shaped Mushroom-like EBG structure for WLAN application. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Phuket, Thailand, 30 October–2 November 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.K.; Sharma, N. Improving the Performance Parameters of Microstrip Patch Antenna by Using EBG Substrate. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2013, 2, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhameed, M.; Isa, M.S.B.M.; Zakaria, Z.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Mohsen, M.K.; Attiah, M.L.; Dinar, A.M. Radiation control of microstrip patch antenna by using electromagnetic band gap. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2019, 110, 152835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhameed, M.K.; Isa, M.S.M.; Zakaria, Z.; Mohsin, M.K.; Attiah, M.L. Mushroom-Like EBG to Improve Patch Antenna Performance for C-Band Satellite Application. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2019, 8, 3875–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Microstrip antennas integrated with electromagnetic band-gap (EBG) structures: A low mutual coupling design for array applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2003, 51, 2936–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.M.; Rahman, T.A.; Rahim, S.K.A.; Ali, M.T.; Jamlos, M.F. Antenna array enhancement using mushroom-like electromagnetic band gap (EBG). In Proceedings of the Fourth European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Barcelona, Spain, 12–16 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sokunbi, O.; Attia, H.; Sheikh, S.I. Microstrip Antenna Array with Reduced Mutual Coupling Using Slotted-Ring EBG Structure for 5G Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting, Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–12 July 2019; pp. 1185–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaglan, N.; Gupta, S.D. Surface waves minimisation in microstrip patch antenna using EBG substrate. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication (ICSC), Noida, India, 16–18 March 2015; pp. 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccioli, R.; Yang, F.-R.; Ma, K.-P.; Itoh, T. Aperture-coupled patch antenna on UC-PBG substrate. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1999, 47, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, R.; De Maagt, P.; Sorolla, M. Enhanced patch-antenna performance by suppressing surface waves using photonic-bandgap substrates. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1999, 47, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colburn, J.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Patch antennas on externally perforated high dielectric constant substrates. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1999, 47, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CubeSat Concept. Available online: https://www.eoportal.org/other-space-activities/cubesat-concept#p-pod-poly-picosatellite-orbital-deployerta (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Toorian, A.; Diaz, K.; Lee, S. The CubeSat Approach to Space Access. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 1–8 March 2008; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








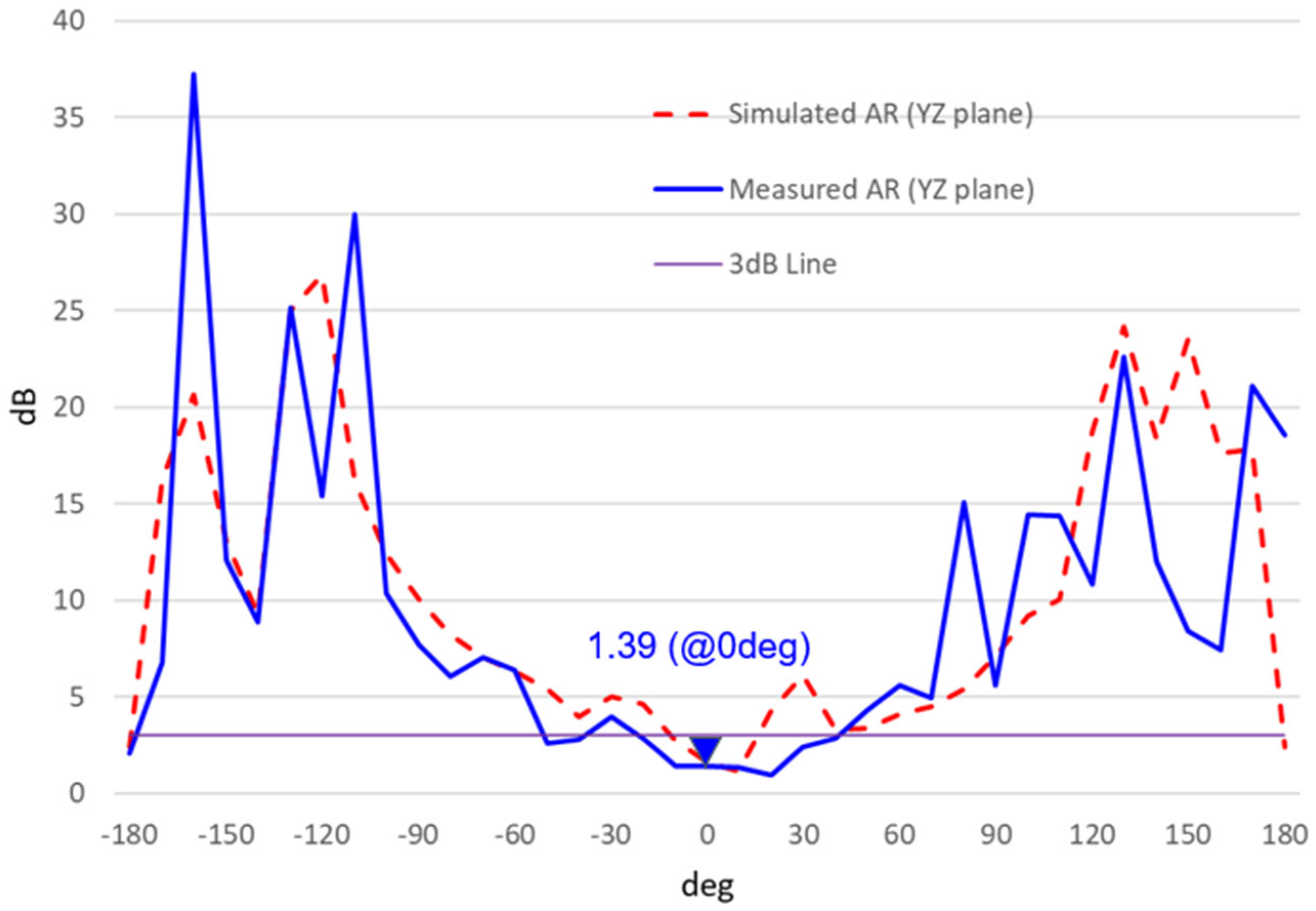
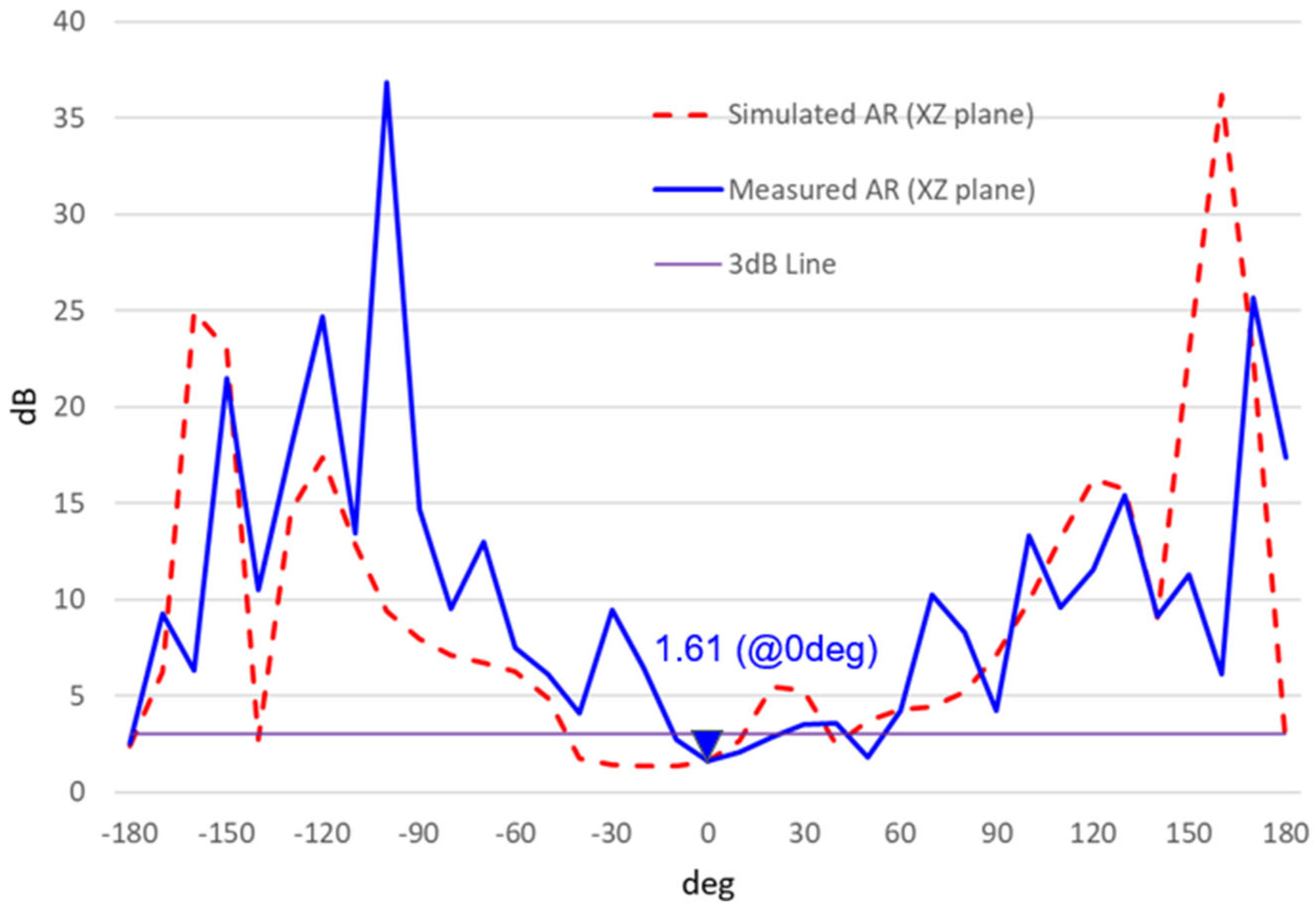
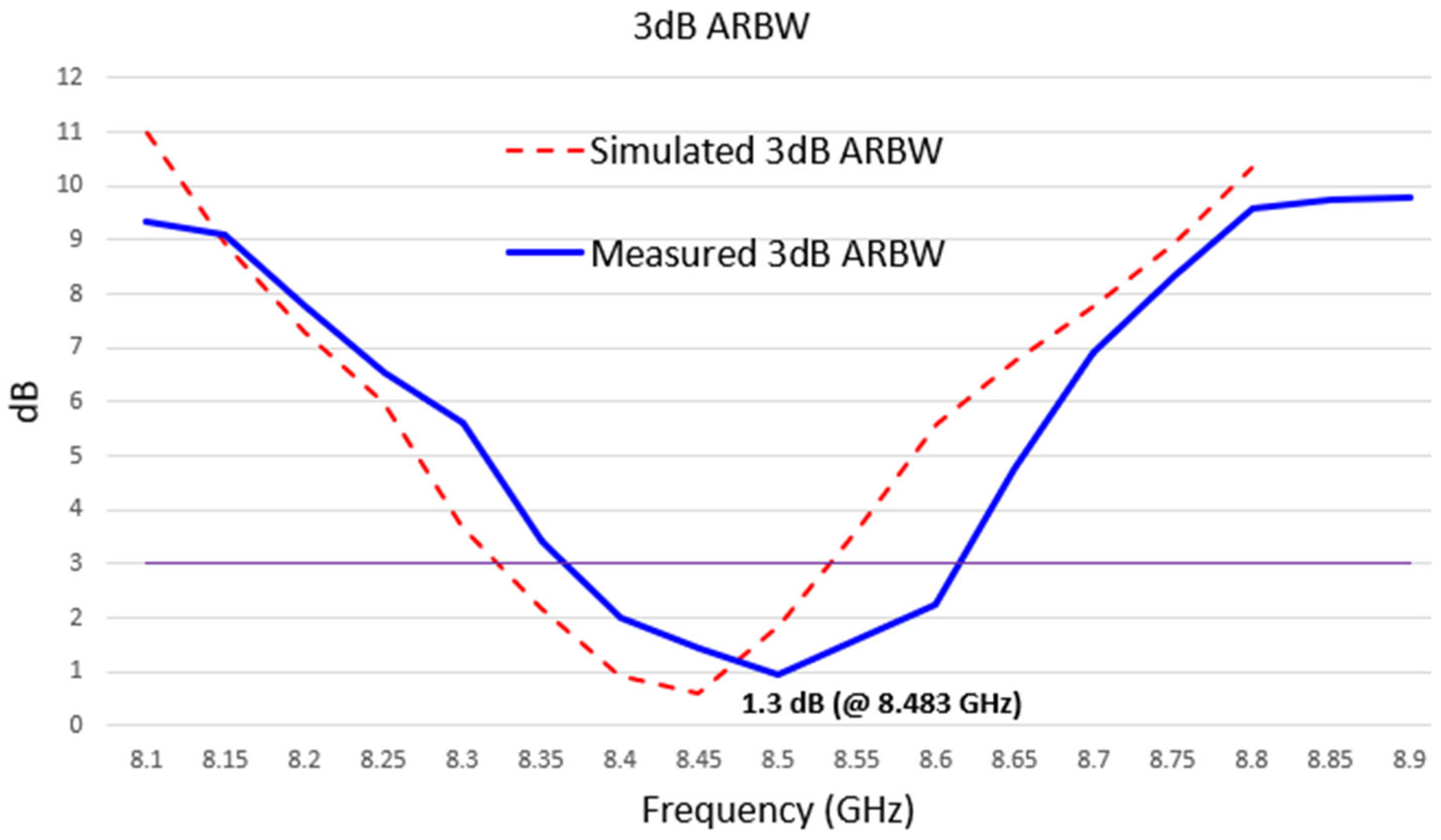
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Gain | 10 dBi |
| Gain Bandwidth | 13 MHz |
| S11 Bandwidth | 13 MHz |
| AR Bandwidth | 13 MHz |
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Lp | 10 | Patch length |
| Wp | 10 | Patch width |
| Lg | 91.3 | Ground length |
| Wg | 91.3 | Ground width |
| Lebg | 10 | Length of an EBG element |
| Webg | 10 | Width of an EBG element |
| gebg | 2 | Gap between two adjacent EBGs |
| lsl1 | 4 | Length of the upper square |
| wsl1 | 4 | Width of the upper square |
| lsl2 | 3 | Length of the lower square |
| wsl2 | 3 | Width of the lower square |
| le1 | 0.5 | Distance from the upper square to the upper edge |
| we1 | 0.5 | Distance from the upper square to the right edge |
| le2 | 1 | Distance from the lower square to the lower edge |
| we2 | 1 | Distance from the lower square to the left edge |
| lcor | 15 | Truncated corner length |
| wcor | 15 | Truncated corner width |
| h | 1.6 | Substrate thickness |
| hc | 0.035 | Conductive part thickness |
| Antenna Parameters | Specifications | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Operation frequency | 8.483 | GHz |
| −10 dB Impedance bandwidth | 900 | MHz |
| Polarization | RHCP | - |
| Measured Gains | 11.72 | dBi |
| Measured AR at 8.483 GHz | 1.4 | dB |
| Measured 3 dB ARBW | 250 | MHz |
| Antenna efficiency | 95 | % |
| Dielectric substrate | Rogers RT5880 | - |
| RF input | 50 | Ω |
| Feed type | Single probe (SMA) |
| Ref. No. | Center Freq. (GHz) | Antenna Size (mm) | Max. Gain (dBi) | Polarization | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [4] | 8.2 | 72.6 × 72.6 × 11 | 11.5 | CP | - Complicated design. - Feed network needed. - The height exceeded the 6.5 mm threshold specified in Cal Poly’s CDS. |
| [5] | 8.25 | 100 × 100 | 17 (dBic) | CP | - Need 4 feed points to create differential pairs of excited signals for CP. - The height is not mentioned. However, it exceeded 6.5 mm and cannot be applied to CubeSats that follow Cal Poly’s CDS. |
| [7] | 7.19 (RX) 8.45 (TX) | 120 × 80 | 9 | CP | - Too big for 1U CubeSat surface. - Feed network needed. - The height is not mentioned. |
| [11] | 7 | 60 × 45 | 11.78 (directivity) | LP | - Only simulation result of the directivity, not the realized gain. - The height is not mentioned. However, the 2 EBG superstrates makes the structure too high to apply to CubeSats that follow Cal Poly’s CDS. |
| [12] | 9.9 | 60 × 60 × 3.2 | 9.77 | LP | - Complicated design with mushroom-like EBG as the middle layer. - The airgap between layers can significantly affect the antenna performance. |
| [21] | 10.67 | 50 × 35 | 7.7 | LP | - The gain is not so high. - No measured results. Only simulation. - The height is not mentioned. |
| Our work | 8.48 | 91.3 × 91.3 × 1.6 | 11.72 | CP | - Simple design. - No feed network needed. - Highly compatible with CubeSat platforms. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ta, L.P.; Nakayama, D.; Hirose, M. Design of a High-Gain X-Band Electromagnetic Band Gap Microstrip Patch Antenna for CubeSat Applications. Electronics 2025, 14, 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112216
Ta LP, Nakayama D, Hirose M. Design of a High-Gain X-Band Electromagnetic Band Gap Microstrip Patch Antenna for CubeSat Applications. Electronics. 2025; 14(11):2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112216
Chicago/Turabian StyleTa, Linh Phuong, Daisuke Nakayama, and Miyuki Hirose. 2025. "Design of a High-Gain X-Band Electromagnetic Band Gap Microstrip Patch Antenna for CubeSat Applications" Electronics 14, no. 11: 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112216
APA StyleTa, L. P., Nakayama, D., & Hirose, M. (2025). Design of a High-Gain X-Band Electromagnetic Band Gap Microstrip Patch Antenna for CubeSat Applications. Electronics, 14(11), 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112216








