Abstract
We propose a deep learning-based face anti-spoofing method that utilizes both RGB and depth images for face recognition. The proposed method can detect spoofing attacks across various domain types using domain adversarial learning for preventing overfitting to a specific domain. A pre-trained face detection model and a face segmentation model are employed to detect a facial region from RGB images. The pixels outside the facial region in the corresponding depth image are replaced with the depth values of the nearest pixels in the facial region to minimize background influence. Subsequently, a network comprising convolutional layers and a self-attention layer extracts features from RGB and depth images separately, then fuses them to detect spoofing attacks. The proposed network is trained using domain adversarial learning to ensure robustness against various types of face spoofing attacks. The experiment results show that the proposed network reduces the average Attack Presentation Classification Error Rate (APCER) to 11.12% and 8.00% compared to ResNet and MobileNet, respectively.
1. Introduction
Currently, various biometric authentication technologies are being utilized in fields, such as access control and finance. Biometric authentication verifies an individual’s identity using unique biological or behavioral characteristics, including fingerprints, face features, iris patterns, voice, and signature. However, concerns over infection transmission, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, have shifted interest toward non-contact authentication methods, such as facial and iris recognition. Video-based facial recognition is widely adopted due to its cost-effectiveness compared to other biometric methods. However, it is vulnerable to presentation attacks, which are attempts to deceive a biometric authentication system by using fake or manipulated samples [1]. To ensure secure biometric authentication in real-world applications, additional techniques are required to prevent such spoofing attempts.
A face presentation attack involves deceiving facial recognition systems using a third-party facial image, a printed photograph, or an image of a 3D facial model. Face Anti-Spoofing (FAS) aims to distinguish genuine faces from spoofed ones. FAS methods can be categorized into dynamic signal analyses, handcrafted feature-based methods, and deep learning-based approaches. Dynamic signal analysis relies on sequential video frames to detect natural facial behaviors, such as eye blinking [2,3], subtle movements caused by breathing [4,5], and lip movement during speech [6], for spoof detection. However, this approach struggles against replay attacks, in which pre-recorded videos of real individuals are played back to deceive the system. FAS methods based on handcrafted features detect fake faces using Local Binary Pattern (LBP) [7,8,9] or difference of Gaussian (DoG) [10,11]. However, these methods may be vulnerable to previously unknown types of snooping attacks. More recently, deep learning-based FAS methods utilizing convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and DenseNet have been proposed [12,13,14,15]. However, these methods suffer from low detection performance when encountering unseen attack types. To address the limitations of RGB image-based FAS techniques, multimodal approaches incorporating RGB-D images [16,17] and infrared imaging [18] have been introduced. However, as technology advances, the diversity of face spoofing attack types continues to grow. Therefore, a robust FAS method capable of handling various spoofing techniques is required.
In this paper, we propose a face anti-spoofing method utilizing RGB-D images. The proposed method first applies pixel correction to the depth image during input processing and then employs a network designed to extract both local features and global relationships through domain adversarial learning. This approach ensures that the model remains robust against domain variations, such as lighting conditions, devices, and attack types without significant performance degradation.
This paper proposes three key contributions to address the limitations of existing face anti-spoofing techniques. First, a self-attention mechanism is applied to both RGB and depth streams, allowing the network to effectively emphasize fine-grained spatial features within each modality. Second, domain adversarial learning based on a domain classifier is introduced to enhance generalization performance across various acquisition environments and sensor types. Lastly, a feature fusion strategy combining representations from RGB and depth modalities is employed, and the experimental results demonstrate that it enables more accurate and stable spoof detection compared to single-modality models.
The structure of this paper is as follows. Section 2 reviews existing research on face anti-spoofing. Section 3 introduces the proposed RGB-D image-based FAS method, which is robust to domain variations. Section 4 presents the evaluation of the proposed method by measuring network performance across various domain shifts. Finally, Section 5 provides conclusion.
2. Background and Previous Works
Face spoofing attacks are classified into print attacks, replay attacks, and 3D mask attacks. Research on dynamic motion-based detection utilizes the natural movement characteristics of humans. Pan et al. [2] and Li [3] proposed a spoof detection method by analyzing eye blinking, one of the most common human dynamic movements, at the frame level in video input. Kollreider et al. [4] and Bao et al. [5] introduced a method that analyzes facial liveness by using optical flow fields to measure pixel movements between consecutive frames. However, dynamic motion-based face anti-spoofing approaches face limitations, as replay attacks involving pre-recorded videos of real individuals can also exhibit detectable dynamic movements. To address this issue, Kollreider et al. [6] proposed a method that detects spoofing by analyzing both lip movements and speech in videos where a person pronounces randomly selected numbers. Since the system requires a response to random numbers, it can effectively prevent pre-recorded replay attacks. However, this method is challenging in real-world environments due to ambient noise interference. Additionally, the synchronization between lip contour tracking and speech input is not always precise. Dynamic motion-based face anti-spoofing requires multiple input frames for analysis, making real-time processing difficult. Since face anti-spoofing is a part of the face recognition pipeline, ensuring fast real-time operation is crucial. However, frame-based analysis imposes computational burdens, making real-time processing infeasible. Moreover, most previous studies have primarily focused on detecting print attacks, limiting their ability to generalize to a wider range of existing and future spoofing attack types.
Määttä et al. [8] and Chingovska et al. [9] proposed using LBP to analyze the texture of input facial images, classifying spoofing attacks with a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier. Zhang et al. [19] introduced a Lambertian model-based method for spoof detection, leveraging differences in light reflection between real skin and fake materials. Although light reflection-based approaches do not require additional user interaction, their performance is highly dependent on light intensity, leading to reduced effectiveness under varying illumination conditions. Handcrafted feature-based anti-spoofing methods extract predefined features, making them highly susceptible to variations in environmental conditions. Thus, an effective anti-spoofing method must maintain generalized performance across diverse environments.
Recently, deep learning-based face anti-spoofing research has gained significant attention. Deep learning-based approaches can be categorized based on the number of input modalities: single-modality and multi-modality methods. Single-modality methods use only RGB images as an input, while multi-modality approaches incorporate two or more types of input, such as RGB, depth, or infrared images. Early single-modality methods utilized powerful image classification networks, such as ResNet [20] and DenseNet [21], for spoof detection [13,22]. However, these models struggle to handle unseen types of spoofing attacks due to their tendency to be biased toward the training images. PatchNet [12] addressed this limitation by constructing a fine-grained patch-level recognition problem rather than a binary classification task. By embedding camera devices and attack types into the patch space, PatchNet enables the differentiation of spoofing characteristics across patches. However, this method heavily depends on the attack types and camera conditions within the dataset, making it ineffective against unknown attacks or unseen domains. Domain Transfer Networks (DTNs) [16] attempted to improve spoof detection by generating depth images from RGB inputs using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and CNNs. However, DTN research focused only on 2D attacks, leaving it ineffective against 3D mask attacks. Convolutional Vision Transfomer (CVT) [23] combines the local feature extraction capabilities of CNNs with the global context modeling of Vision Transformers, enhancing generalization performance across diverse domains. While it takes an approach toward domain generalization, an explicit domain adversarial learning strategy is not employed.
Next, we discuss multi-modality approaches. While depth images were not directly used, Wang et al. [17] proposed improving face anti-spoofing performance by generating auxiliary depth images from multiple input frames. However, since these depth images are generated artificially, their accuracy remains questionable. Nonetheless, this approach suggests that combining RGB and depth images can enhance detection accuracy. Central Difference Convolutional Networks (CDCNs) [18] proposed a multi-modality approach utilizing RGB, depth, and infrared images for face anti-spoofing. The CDC [24] framework calculates the differences between central and surrounding pixels to effectively learn texture and structural differences in images. The Transformer-based network FM-ViT [25] maintains independent branches for each modality, such as RGB, Depth, and IR, to effectively handle diverse input types. It introduces the Cross-Modal Transformer Block (CMTB), which facilitates interactions between modalities and enables the learning of modality-invariant features.
Since CDCN and FM-Vit employ three different modalities, they achieve high detection accuracy. However, processing three different modalities simultaneously demands significant computational resources. Furthermore, since face anti-spoofing operates as a component of real-time face recognition systems, the high computational cost of multi-modality methods imposes practical limitations on deployment.
3. Face Anti-Spoofing Method Using RGB-D Image
We propose a method for preventing face spoofing. The proposed model is trained using domain adversarial learning to ensure robust performance across multiple domains. The flow of the proposed method is shown in Figure 1. First, a face is captured as RGB and depth images. A facial region is detected from the RGB image using a pre-trained face segmentation model. Afterward, the depth image is corrected. Finally, both the depth image and RGB image are fed into the face anti-spoofing network to determine whether the given face image is a real or spoofed face.
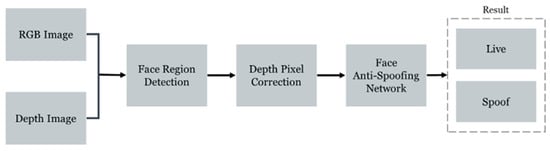
Figure 1.
Flow of the proposed method.
3.1. Facial Region Detection
The facial region is first detected from the input RGB image. Figure 2 illustrates the facial region detection processes. First, a bounding box corresponding to the facial region is detected from the RGB image. Both the RGB and depth images are cropped to the region corresponding to the detected bounding box to reduce the overall image range to focus on the face. FaceNet [26] is adopted for detecting the face bounding box. Figure 3 shows the result of face bounding box detection.
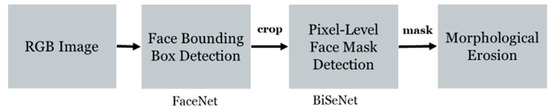
Figure 2.
Process of facial region detection.

Figure 3.
Detection of face bounding box.
A pixel-wise facial region mask is extracted using a BiSeNet [27] based a segmentation network [28]. This network divides the face into 18 distinct parts, allowing for precise selection and extraction of desired facial regions. In this study, we define the facial region as including the skin, eyebrows, eyes, glasses, nose, and mouth while excluding the ears and hair. Depth cameras that employ stereoscopic vision capture the same scene from two slightly different angles and calculate depth using the disparity between the two images. Due to this mechanism, depth values cannot be measured at object boundaries where the background and the object overlap, resulting in missing pixels. Since both hair and ears often suffer from such depth measurement issues, they are excluded to ensure accurate classification. However, for individuals wearing glasses, the glasses are included in the facial region. Figure 4a,b shows a cropped RGB image and a mask of the facial region, respectively.
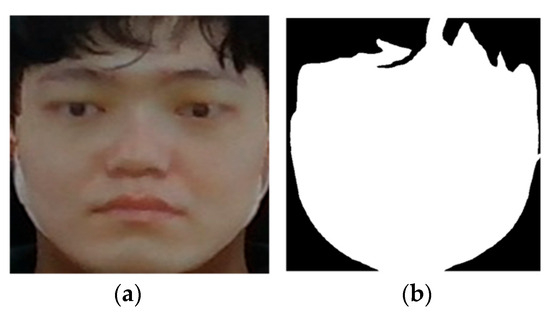
Figure 4.
RGB image and corresponding facial region mask: (a) cropped RGB image based on bounding box and (b) extracted facial region mask.
If the extracted facial mask is directly applied to the depth image, certain pixels at object boundaries may remain unmeasured. Directly feeding such incomplete depth data into the network could lead to learning unintended features. This issue is particularly pronounced in distinguishing between real faces and 3D mask attacks. To address this, we apply morphological erosion operations [29] to refine the mask. The morphological erosion operation is performed three times consecutively. When applying morphological erosion operations, one or two iterations are insufficient to effectively remove background noise, whereas iterations exceeding three often cause an excessive loss of important facial regions, particularly in low-contrast depth images. The morphological erosions with three iterations can reduce image noise with facial structural preservation. Figure 5 shows the mask images before and after applying the morphological erosion operation. This process helps prevent the network from learning erroneous features caused by unmeasured boundary pixels, ultimately improving its robustness against sophisticated spoofing attacks, such as 3D mask attacks.
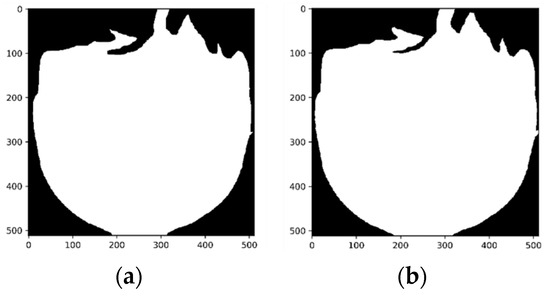
Figure 5.
Face mask refinement using morphological erosion: (a) before erosion and (b) after erosion.
3.2. Pixel Correction of Depth Image
The depth image pixel correction process consists of three steps, as illustrated in Figure 6. The depth image and the previously extracted facial mask are used as inputs, where the depth values are assigned to the facial region based on the mask. The subsequent steps involve correcting both the facial region and background pixels.
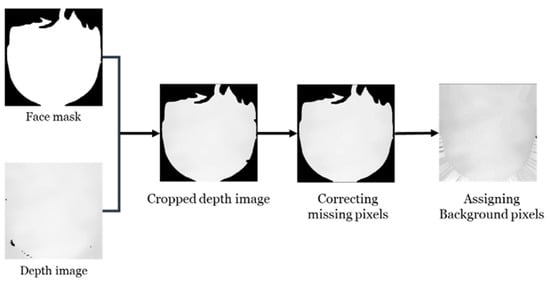
Figure 6.
Pixel correction process.
Figure 7a shows an image where the input depth values have been assigned to the facial region based on the mask. Although the mask was refined using morphological erosion, some pixels within the facial region are missing due to the inherent limitations of the depth camera. Since adjacent pixels in the depth image often have similar values, a 5 × 5 mode filter is applied to correct these missing pixels. Figure 7b illustrates this correction as applied to Figure 7a. Afterward, background pixels are assigned specific values to minimize the influence of their background during network training. Since the depth values are only applied to the facial region using the extracted mask, all background pixels in the current depth image are set to zero. Additionally, since the facial region pixels have already been corrected, any remaining missing pixels represent the background. To further refine the image, background pixels are filled with the depth value of the nearest facial region pixel. Figure 7c illustrates the final result, where the background pixels in (b) have been filled. This process ensures that all missing pixels in the depth image are properly assigned. By filling the background with depth values derived from the facial region rather than arbitrary values or empty spaces, the network can better emphasize the facial region during training [30,31].
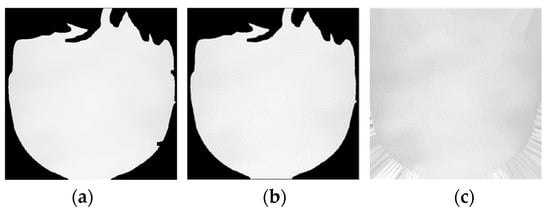
Figure 7.
Pixel correction of depth image: (a) cropping depth image to facial region; (b) filling missing depth pixels; and (c) replacing pixels within background region.
3.3. Network for Face Anti-Spoofing
A deep learning network is proposed to detect spoofing attacks using an RGB-D image. Figure 8 shows the structure of the proposed network. The color and depth images are fed into separate networks with identical architectures. The networks are structured with four CNN layers with ReLU activation and 2 × 2 max pooling, and a final self-attention layer [32]. The CNN layers and self-attention layer extract the local features and the global features, respectively. The self-attention layer consists of a single head with a feature dimension of 256. By using only one head, the layer reduces computational overhead while effectively capturing spatial relationships between positions. Then, the extracted features from both color and depth images are fused and classified as a real or spoofed face through the two FC layers with a Softmax activation. A domain classifier with two FC layers and ReLU activation is attached to the proposed network. This classifier determines domain, which means spoofing attack types, from the image features. The output of the domain classifier does not affect spoofing attack detection directly, but it encourages the model to be domain-invariant during training.

Figure 8.
Structure of the proposed network.
The performance of face anti-spoofing typically deteriorates in new domains, such as different lighting conditions, capturing images with different cameras, and unseen attack types. The anti-spoofing model should perform well across various domains to effectively counter diverse attack scenarios, even though these domains are not included in the training process. In other words, the face anti-spoofing model should maintain high generalization performance regardless of variations in illumination, camera devices, or spoofing techniques. Domain-Adversarial Neural Networks (DANNs) [33] employ domain adversarial learning to reduce the distribution gap between the source and target domains, preventing the network from overfitting to a specific domain. By adopting this training strategy, our proposed face anti-spoofing network aims to achieve improved generalization performance across different domains. During training, a gradient reversal layer (GRL) is employed to ensure adversarial training in backpropagation between the main network and the domain classifier. The GRL applies a negative scalar to reverse the gradient of the domain loss, which forces the feature extractor to learn domain-invariant representations. This process confuses the domain classifier, thereby reducing domain discrepancies and ensuring more generalized feature learning. The loss function for training the proposed network using domain adversarial learning is as follows:
where LossFAS represents the loss from spoof detection, Lossdomain represents the loss from the domain classifier, and λ is a weighting parameter. Through this adversarial training process, the network learns domain-independent features, allowing it to maintain high generalization performance even when tested on previously unseen domains.
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
We evaluated the performance of the proposed face anti-spoofing network by conducting simulations on depth image pixel correction, performance improvements achieved through self-attention, and the effectiveness of domain adversarial learning. The experiments were conducted on a system equipped with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 GPU and 32 GB of memory.
For the experiments, we used the “Liveness Detection” dataset provided by AiHub [34]. The images in this dataset feature faces of various individuals captured under diverse lighting conditions and using different camera devices, including both real faces and a range of spoofing attack types. Therefore, this dataset allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the generalization performance of spoofing detection models.
The RGB-D images in this dataset were captured by RealSense SR305 and RealSense D435 RGB-D cameras, both of which are manufactured by Intel Corporation (Santa Clara, CA, USA), under three different lighting conditions. The dataset includes a total of 11 attack types: eight print attacks, two replay attacks, and one 3D mask attack. The print attacks are further classified into two categories: flat printed paper and printed paper curved to match the face. Additionally, print attacks involve cutting out specific facial features from the printed image (eyes, eyes/nose, eyes/nose/mouth) and replacing them with real facial features. The spoofing attack types, including this dataset, are divided into two cases: one where the printed sheet is flat and another where it is curved to match the face. As a result, print attacks are categorized into a total of eight types—two non-cut print attacks and six cut-and-replaced feature print attacks. Replay attacks involve playing a video of the target face on an electronic device to deceive the recognition system. These attacks are categorized based on the device used: one attack type using a smartphone and another using a tablet. The 3D mask attack involves wearing a 3D mask designed to match the facial structure of a real person, comprising a single attack type. Figure 9 presents examples of the face spoofing attack types included in the Liveness Detection dataset. In the following discussions, each attack type will be referred to by its corresponding number in Figure 9. The single 3D mask attack type is denoted as “3D Mask 1”.

Figure 9.
Types of face spoofing attacks in the dataset.
Face anti-spoofing must maintain consistent performance despite domain variations, such as lighting and equipment. Therefore, in this study, we classified the experimental protocols based on four datasets with different domain variations. Each network was trained and tested according to the classified datasets. The four protocols are as follows: Protocol 1 consists of lighting variations, Protocol 2 consists of attack-type variations, Protocol 3 consists of camera-type variations, and Protocol 4 consists of a dataset where all three domain variations (lighting, attack type, and camera) are changed. Table 1 shows the composition of training, validation, and test datasets for each protocol.

Table 1.
Dataset composition for four experimental protocols based on domain variations.
In the model training, the batch size and epochs were set to 64 and 100, respectively. We trained the proposed network with the Adam optimizer, setting the initial learning rate to 0.001. The learning rate was halved if the loss for the validation set did not decrease for five consecutive epochs. The optimal model was selected based on the lowest ACER observed on the validation set.
To evaluate the performance of the face anti-spoofing model, we used the Attack Presentation Classification Error Rate (APCER), Bona Fide Presentation Classification Error Rate (BPCER), and Average Classification Error Rate (ACER) as evaluation metrics for the face anti-spoofing model [35]. The mathematical definitions of these metrics are as follows:
where the APCER represents the rate at which spoofing attacks are misclassified as bona fide faces, calculated by dividing the number of falsely classified spoofing attacks (FP) by the total number of spoofing attempts (the sum of correctly classified spoofing attacks (TN) and falsely classified ones (FP)); BPCER represents the rate at which bona fide faces are misclassified as spoofing attacks, calculated by dividing the number of falsely classified bona fide faces (FN) by the total number of bona fide samples (the sum of correctly classified bona fide samples (TP) and falsely classified ones (FN)); and ACER is the average of the APCER and BPCER. Therefore, in this study, the ACER is used as the primary metric to evaluate the overall misclassification rate of the network.
4.1. Depth Image Correction Performance
To evaluate the effectiveness of depth image pixel correction, we conducted an experiment using 3D mask attacks, where the depth difference between real faces and spoofing attacks is minimal. A dataset was configured specifically for testing 3D mask attacks. For training and validation, we used data captured with the D435 camera under three different lighting conditions (high, normal, and low illumination), consisting of print attacks 1, 2, 7, 8, and 3D mask attacks. For testing, we used data from the D435 RGB-D camera under the same three lighting conditions, but with only 3D mask attacks.
We conducted experiments by comparing networks trained with and without depth image pixel correction. To focus solely on evaluating the performance of depth image correction, we used a simplified face anti-spoofing network that consists of four consecutive convolution layers, with only depth images as input. Table 2 shows the experimental results, indicating that the network trained without depth image correction achieved an ACER of 26.22%, whereas the network trained with corrected depth images achieved an ACER of 24.41%. These results confirm that using corrected depth images improves network performance, particularly by reducing the APCER, which measures the misclassification rate of 3D mask attacks as real faces.

Table 2.
Performance of depth image pixel correction on 3D mask attacks.
Figure 10 illustrates depth images of different spoofing types, with and without pixel correction. The uncorrected depth images in Figure 10b show cases where the network mistakenly classifies paper regions in print attacks as part of a real face, similar to the upper-right example. When observed with the naked eye, the uncorrected depth images in Figure 10a (real face) and Figure 10c (3D mask) appear visually similar to real faces. Only the print attack in Figure 10b clearly deviates from real facial boundaries, making it easier to detect as a spoofing attempt. Consequently, the network learns to rely heavily on such boundary differences during training. In contrast, the corrected depth images shown in Figure 10d–f appear visually indistinguishable between real and fake faces. This forces the network to rely on more refined and detailed spoofing detection features rather than simple boundary differences. By utilizing corrected depth images, the network learns to extract more intricate features, making it more robust against sophisticated spoofing attacks. The experimental results demonstrate that using corrected depth images reduces the ACER by 1.81 percentage points, confirming its effectiveness in improving face anti-spoofing performance.

Figure 10.
Depth images of different spoofing types: (a) real face; (b) Print Attack 1; (c) 3D Mask Attack 1; (d) corrected real face; (e) corrected image of Print Attack 1; and (f) corrected image of 3D Mask Attack 1.
4.2. Face Anti-Spoofing Performances Across Various Protocols
We evaluated face anti-spoofing performance using the four previously defined protocols. For all experiments, the input modality consisted of both RGB images and corrected depth images, ensuring consistency in the input format. However, the structure of the feature extraction network for spoof detection varied across models. We compared the spoofing detection performance of the proposed model with ResNet-50 [20], known for its strong image classification capabilities, MobileNetV2 [36], a lightweight and efficient network architecture, and VGG19 [37], which is the best model for facial detection. Additionally, we compared a version of our proposed network without self-attention against the full proposed network that integrates CNNs and self-attention mechanisms.
Table 3 presents the performance evaluation of different models under the four protocols. The VGG19 model demonstrated the highest accuracy in detecting spoofing attacks across all protocols, which can be attributed to its deep network architecture structure. However, this model is unsuitable for use as a real-time spoofing attack detector due to its large number of parameters and high computational complexity. For Protocols 1, 3, and 4, MobileNet outperformed ResNet-50. Since this study evaluates models under domain shifts (lighting, camera types, and attack types), ResNet-50, being a deeper network, overfits the training domain, resulting in a large error when tested on unseen domains. The proposed model exhibits the second-best accuracy among all protocols, excluding Protocol 1. For Protocol 1 (variation in lighting conditions), the proposed model achieves the third-highest accuracy, following VGG19 and MobileNet. Notably, the proposed model with self-attention outperformed its counterpart without self-attention by 7.84 percentage points. This result suggests that adding self-attention helps the model learn not only pixel-based features but also the structural characteristics of the entire image, reducing its sensitivity to lighting variations. For Protocol 2 (variation in attack types), all models achieved ACERs below 4%. This suggests that incorporating both RGB and depth images provides sufficient information for detecting new types of spoofing attacks effectively. For Protocol 3 (variation in camera types) with different pixel value distributions, as shown in Figure 11, the proposed model with self-attention achieved an ACER at 7.21%, while the proposed model without self-attention had an ACER at 10.86%, highlighting a significant gap of 3.65% between the two models. This suggests that relying solely on pixel-level features is insufficient when adapting to a new domain. The poor performance of the proposed model without self-attention confirms this difficulty. The proposed model with self-attention addresses this issue by capturing both local features through convolutional layers and global dependencies through self-attention. The accuracies in Protocol 3 are the worst among the Protocols 1–3 for all models. This indicates that face anti-spoofing remains challenging when adapting to unseen camera types. For Protocol 4 (combined variations in lighting, attack types, and camera types), all networks showed poor performance. This suggests that face anti-spoofing remains highly challenging when multiple domain variations occur simultaneously and requires further improvements to enhance generalization across different domains.

Table 3.
Performance comparison for spoofing detection models.
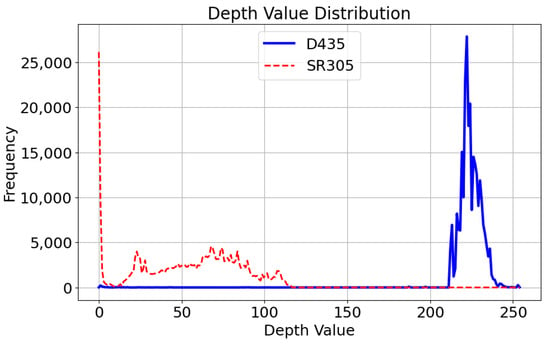
Figure 11.
Comparison of depth pixel value distributions between two RGB-D cameras.
Table 4 compares the computational performances of the spoofing detection models. While VGG19 achieves the highest accuracy for spoofing detection, it has the largest computational load and the slowest speed. Therefore, VGG19 is not feasible for real-time applications. Despite the proposed model having the fewest parameters, it achieves spoofing attack detection accuracies comparable to other models and demonstrates robustness across various domains.

Table 4.
Computational performance comparison for spoofing detection models.
4.3. Face Anti-Spoofing Performances Using Domain Adversarial Learning
We trained the proposed deep learning network using domain adversarial learning to ensure generalization across different domains. We compared the performance of the network trained with and without domain adversarial learning. Additionally, we investigated the impact of different domain loss weight values to determine the optimal weight. The network was tested across four protocols using weight values λ ranging from 0 to 0.5.
Table 5 shows that the networks trained using domain adversarial learning achieved a lower ACER than those trained without it. In Protocol 1 (lighting variation dataset), the lowest ACER (3.68%) was achieved with a weight of 0.03, indicating the best performance. The next lowest ACER (4.72%) was obtained with a weight of 0.07. In contrast, with a weight of 0.5, the ACER reached 15.1%, making it the worst performing configuration, with a 10.38 percentage point increase compared to the non-adversarial trained network. For Protocol 2 (attack-type variation dataset), the lowest ACER (1.18%) was obtained with a weight of 0.07. The ACERs generally remained within the 4% range, with the highest ACER (3.7%) occurring at a weight of 0.5. Similar to Protocol 1, performance degradation was observed at 0.5, but the difference among weight values was less pronounced. This indicates that the proposed network maintains high spoof detection performance even when attack types vary. For Protocol 3 (camera-type variation dataset), the best ACER (6.14%) was obtained with a weight of 0.05. However, weights of 0.03 and 0.5 resulted in significantly higher ACERs of 12.73% and 10.25%, respectively. In Protocol 4 (lighting, camera, and attack-type variation dataset), the performance significantly decreased across all weight values. The best ACER (12.75%) was achieved with a weight of 0.07, showing a 18.31 percentage point improvement compared to the non-adversarial trained network (ACER = 31.06%). Even the worst performing adversarial trained network, with a weight of 0.3, had an ACER of 27.28%, which was still 3.78 percentage points lower than the non-adversarial trained network, indicating better performance. However, excessive or insufficient weighting led to unstable training and degraded performance, sometimes even resulting in worse performance than the non-adversarial trained network. This was particularly observed when the weight value was 0.3 or 0.5 (too large) or 0.03 (too small). Therefore, identifying an appropriate weight value through experimentation was necessary. In this study, 0.07 was selected as the optimal weight. Although the ACER for Protocol 3 was higher than that of the non-adversarial trained network when using adversarial learning, this method showed better performance in other protocols, particularly achieving the greatest improvement in Protocol 4. These results demonstrate that domain adversarial learning enables the face anti-spoofing. Figure 12 shows the ACER curves with respect to λ. In most protocols, the optimal performance was achieved when λ was set to 0.07.

Table 5.
Performance evaluation of domain adversarial learning with different weights.
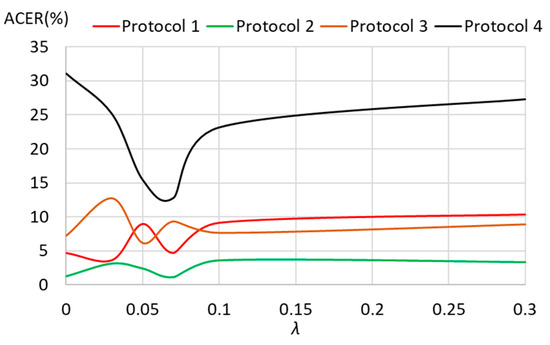
Figure 12.
ACER curves with respect to λ.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we proposed a face anti-spoofing method using a RGB-D image. The pre-trained model segmented the face region, excluding the hair and ears, and the background region from the RGB image. Each pixel within the background region of the corresponding depth image was replaced with the pixel value of the nearest face region. The features from the RGB and depth images were captured through the network composed of a CNN and self-attention layers, separately, then fused. The network was trained using domain adversarial learning to eliminate domain-specific characteristics. The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed model is robust to various domain shifts, achieving high accuracy in spoofing attack detection while maintaining lower computational complexity. The proposed method is expected to enhance the security of video-based biometric recognition systems. Future research will focus on light-weighting for applying it to real-time authentication applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-j.K. and S.-k.K.; software, H.-j.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-j.K. and S.-k.K.; supervision, S.-k.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partly supported by the Innovative Human Resource Development for Local Intellectualization program through the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (IITP-2025-RS-2020-II201791, 100%) and by the BB21plus funded by Busan Metropolitan City and Busan Techno Park.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
This research used datasets from ‘The Open AI Dataset Project (AI-Hub, S. Korea)’. All data information can be accessed through ‘AI-Hub (www.aihub.or.kr)’.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Agarwal, A.; Singh, R.; Vatsa, M. Face Anti-Spoofing Using Haralick Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems, Arlington, VA, USA, 13–16 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.; Sun, L.; Wu, Z.; Lao, S. Eyeblink-Based Anti-Spoofing in Face Recognition from a Generic Webcamera. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Eye Blink Detection Based on Multiple Gabor Response Waves. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Kunming, China, 12–15 July 2008; pp. 2852–2856. [Google Scholar]
- Kollreider, K.; Fronthaler, H.; Bigun, J. Evaluating Liveness by Face Images and the Structure Tensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Automatic Identification Advanced Technologies (AutoID), Buffalo, NY, USA, 17–18 October 2005; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, W.; Li, H.; Li, N.; Jiang, W. A Liveness Detection Method for Face Recognition Based on Optical Flow Field. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Analysis and Signal Processing, Taizhou, China, 11–13 April 2009; pp. 233–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kollreider, K.; Fronthaler, H.; Faraj, M.I.; Bigun, J. Real-Time Face Detection and Motion Analysis with Application in “Liveness” Assessment. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2007, 2, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulkenafet, Z.; Komulainen, J.; Hadid, A. Face Anti-Spoofing Based on Color Texture Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 2636–2640. [Google Scholar]
- Maatta, J.; Hadid, A.; Pietikainen, M. Face Spoofing Detection from Single Images Using Micro-Texture Analysis. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Washington, DC, USA, 11–13 October 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chingovska, I.; Anjos, A.; Marcel, S. On the Effectiveness of Local Binary Patterns in Face Anti-Spoofing. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 6–7 September 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L. Face Liveness Detection from a Single Image with Sparse Low Rank Bilinear Discriminative Model. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2010, 6316, 504–517. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, B.; Michelassi, C.; Rocha, A. Face Liveness Detection under Bad Illumination Conditions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 3557–3560. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Lu, Y.-D.; Yang, S.-T.; Lai, S.-H. PatchNet: A Simple Face Anti-Spoofing Framework via Fine-Grained Patch Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 20249–20258. [Google Scholar]
- Asim, M.; Ming, Z.; Javed, M.Y. CNN Based Spatio-Temporal Feature Extraction for Face Anti-Spoofing. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Chengdu, China, 2–4 June 2017; pp. 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Hadiprakoso, R.B.; Setiawan, H.; Girinoto, G. Face Anti-Spoofing Using CNN Classifier & Face Liveness Detection. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Information and Communications Technology (ICOIACT), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 24–26 March 2020; pp. 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, J.; Li, S.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, C. 3D Convolutional Neural Network Based on Face Anti-Spoofing. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Multimedia and Image Processing (ICMIP), Wuhan, China, 24–26 March 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Xu, T.; Feng, Z.; Wu, X.-J. From RGB to Depth: Domain Transfer Network for Face Anti-Spoofing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 4280–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lei, Z. Deep Spatial Gradient and Temporal Depth Learning for Face Anti-Spoofing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 5041–5050. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Lei, Z.; Zhao, G. Multi-Modal Face Anti-Spoofing Based on Central Difference Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2766–2774. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yi, D.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Face Liveness Detection by Learning Multispectral Reflectance Distributions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; pp. 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- George, A.; Marcel, S. Deep Pixel-Wise Binary Supervision for Face Presentation Attack Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Crete, Greece, 4–7 June 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, G. Searching Central Difference Convolutional Networks for Face Anti-Spoofing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 5295–5305. [Google Scholar]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, G.; Shen, C.; Sang, N. Bisenet V2: Bilateral Network with Guided Aggregation for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3051–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Face-Parsing. Available online: https://github.com/zllrunning/face-parsing.PyTorch (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Serra, J.; Soille, P. Mathematical Morphology and Its Applications to Image Processing, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, P.; Parmar, N.; Vaswani, A.; Bello, I.; Levskaya, A.; Shlens, J. Stand-Alone Self-Attention in Vision Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 68–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ganin, Y.; Ustinova, E.; Ajakan, H.; Germain, P.; Larochelle, H.; Laviolette, F.; Lempitsky, V. Domain-Adversarial Training of Neural Networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2016, 17, 2030–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Images for Liveness Detection. Available online: https://aihub.or.kr/ (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 37 Biometrics: Information Technology Biometric Presentation Attack Detection Part 1: Framework. 2016. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/iso (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. MobilenetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Kwak, Y.; Shin, J. Robust face anti-spoofing framework with Convolutional Vision Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–11 October 2023; pp. 1015–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Tan, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wan, J.; Liang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.Z.; Guo, G. Fm-vit: Flexible modal vision transformers for face anti-spoofing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 18, 4775–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, S.; Borghi, G.; Vezzani, R.; Maltoni, D.; Cucchiara, R. A systematic comparison of depth map representations for face recognition. Sensors 2021, 21, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, M.T.; Cheng, H.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Lai, S.H. High-accuracy RGB-D face recognition via segmentation-aware face depth estimation and mask-guided attention network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Jodhpur, India, 15–18 December 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional neural network based image classification using small training sample size. In Proceedings of the IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 3–6 November 2015; pp. 730–734. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).