Enhancing Indoor Positioning with GNSS-Aided In-Building Wireless Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We present a novel localization architecture that integrates GNSS and IBW systems by repurposing existing distributed antennas as GNSS retransmitters, enabling anchor identification and accurate ranging under LoS conditions. Combined with DoA and inertial cues extracted from downlink CSI, the system supports high-precision positioning without the deployment of multiple signal sources.
- A robust LoS/NLoS detection mechanism is introduced, leveraging signal strength disparities and CSI dynamics. This is incorporated into a Hybrid Adaptive Filter–Graph Fusion (HAF-GF) algorithm, which integrates real-time adaptive filtering with factor graph optimization. The LoS confidence score adaptively modulates measurement noise and influences graph weights for enhanced robustness and convergence.
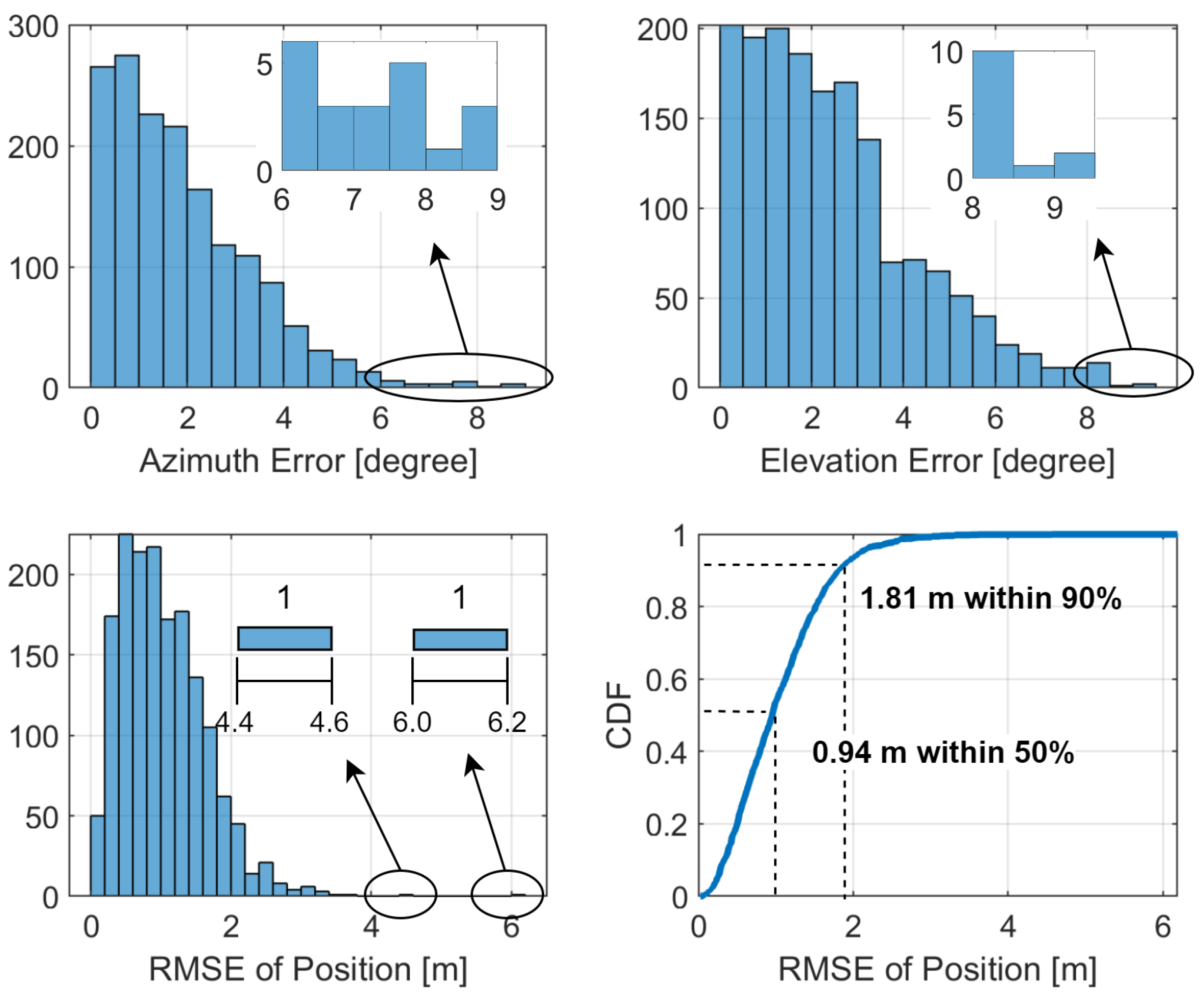
- System-level simulations using 3GPP-compliant signals and ray-tracing in a complex office environment demonstrate 0.69 m accuracy at the 90th percentile, yielding a 30% improvement over baseline fusion algorithms. The proposed system achieves high precision with minimal infrastructure and strong adaptability to varying indoor conditions.
2. Related Work
2.1. Indoor GNSS Solutions
2.2. IBW-Based Positioning
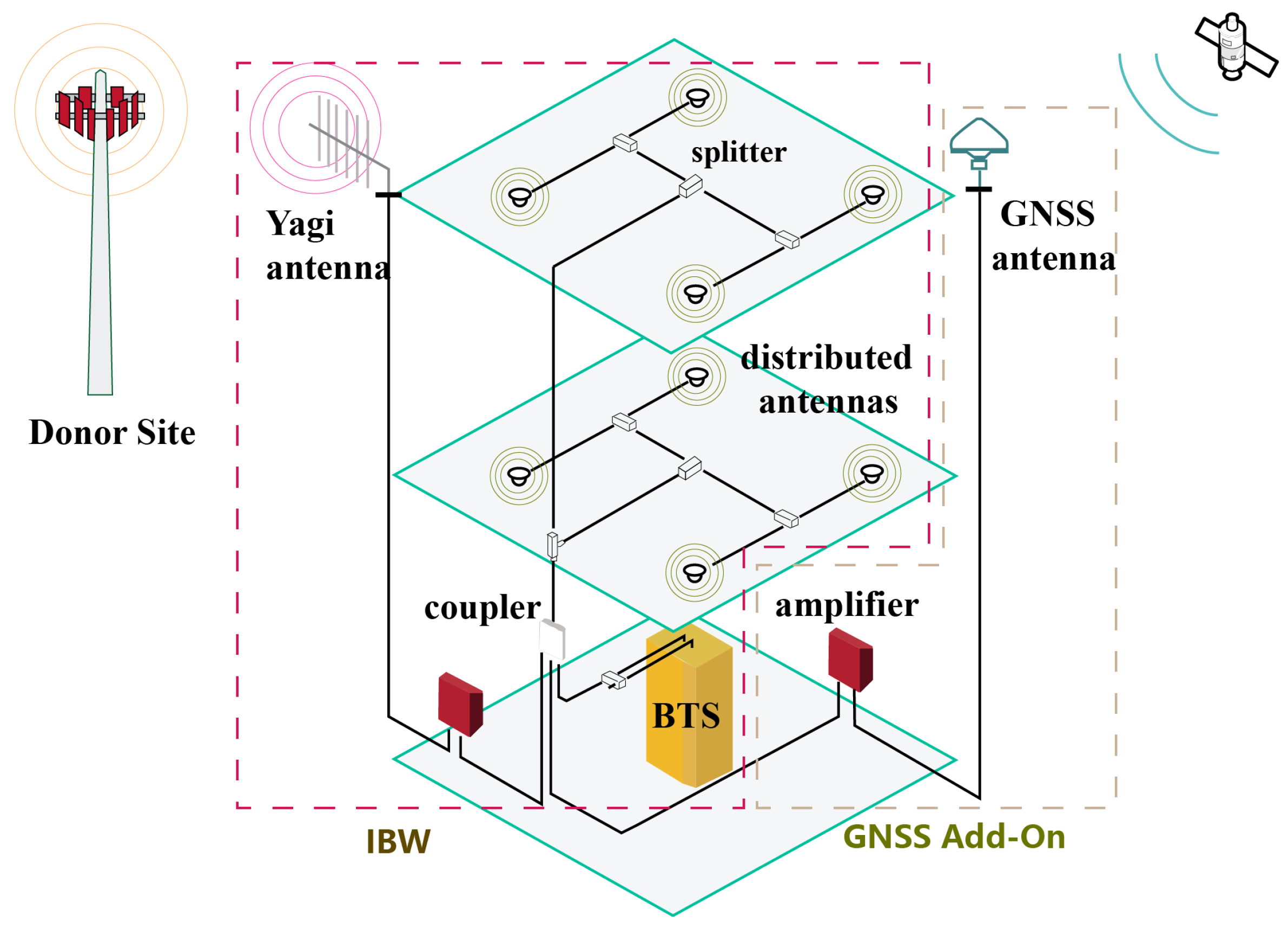
3. Proposed System Structure
3.1. Infrastructure Segment
3.2. User Segment
3.3. Anchor Modeling and Signal Characterization
4. Localization Measurements of the System
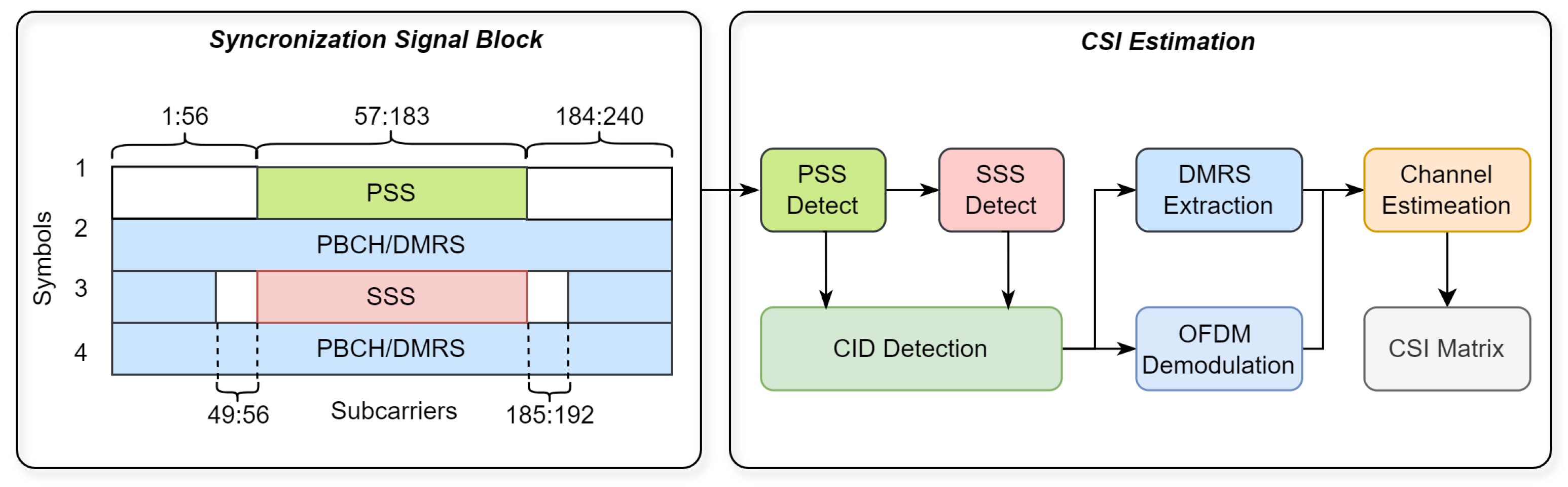
4.1. Anchor Identification and ToA Estimation
4.2. NR CSI Acquisition and DoA Estimation
4.3. LoS Identification
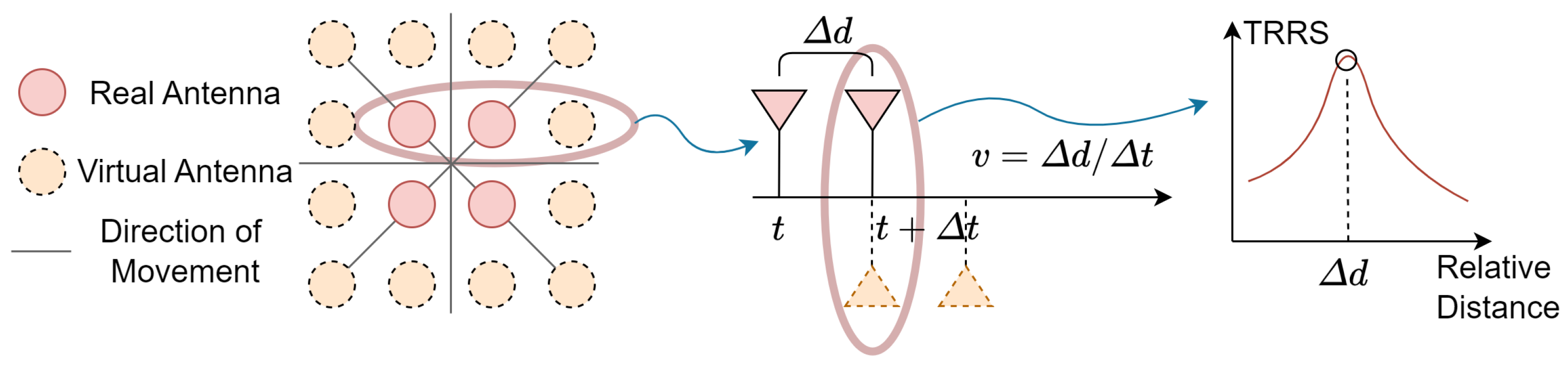
4.4. Inertial Measurements with Virtual Antenna Alignment
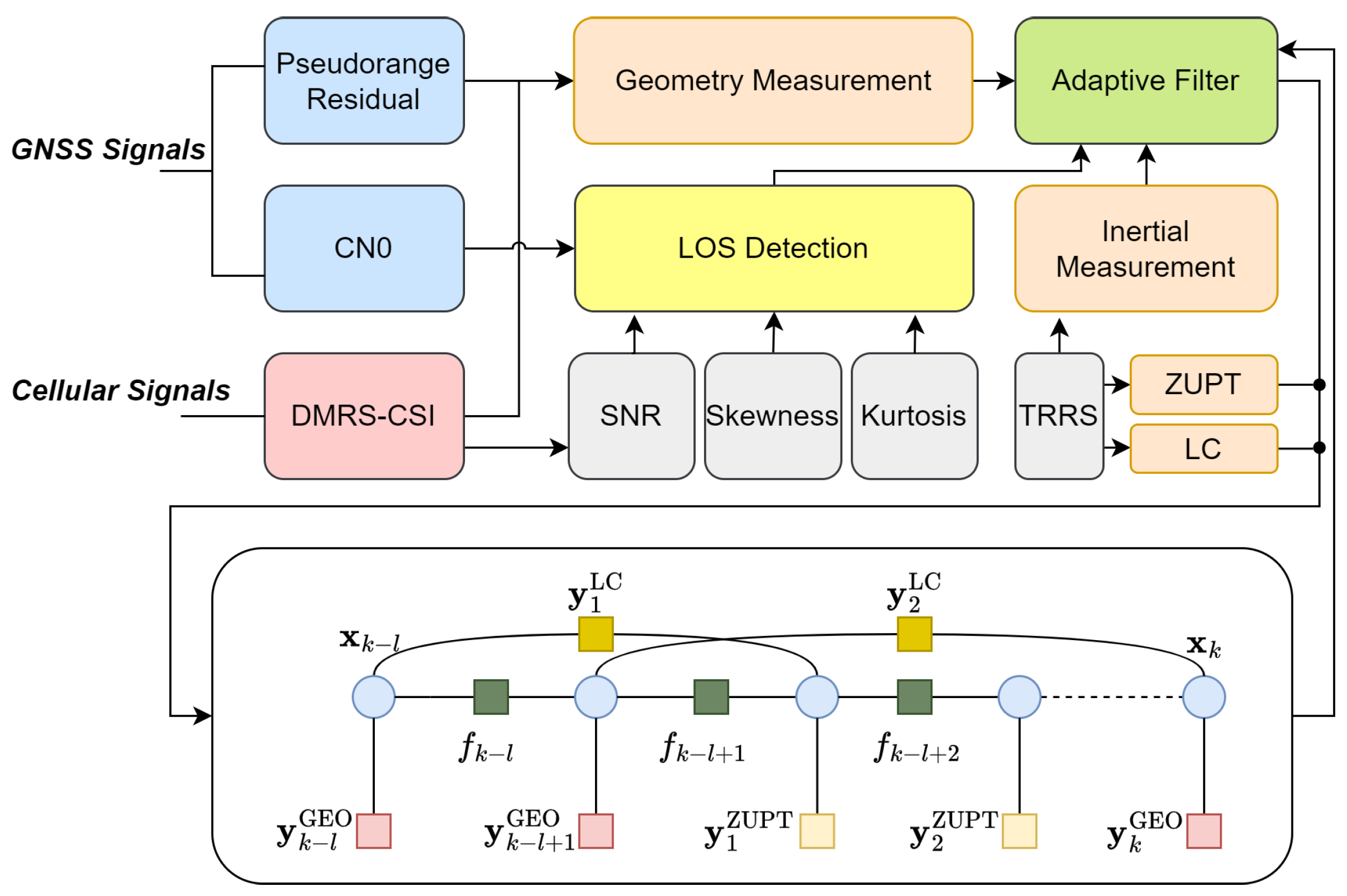
5. Localization Algorithm
5.1. Adaptive Filter
5.2. Factor Graph
6. Experiments and Results
6.1. Analysis of LoS Identification
6.2. Analysis of Inertial Measurement
6.3. Analysis of Static Positioning
6.4. Analysis of Dynamic Positioning
6.5. Complexity Analysis
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farahsari, P.S.; Farahzadi, A.; Rezazadeh, J.; Bagheri, A. A survey on indoor positioning systems for IoT-based applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 7680–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Wu, C.; You, Y.; Yuan, Y. Hybrid indoor positioning method of BLE and PDR based on adaptive feedback EKF with low BLE deployment density. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, J.; Liu, X.; He, X. Secure and reliable indoor localization based on multitask collaborative learning for large-scale buildings. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 22291–22303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, L.; Nardello, M.; Brunelli, D.; Fontanelli, D. UWB-based indoor positioning system with infinite scalability. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Shen, N.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, T.; Chen, R. Indoor Positioning with Smartphone by Using Doppler Observations From Asynchronous Pseudolite System. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 12, 11904–11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. A GPS-based indoor positioning system with delayed repeaters. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 68, 1688–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhani, P.H.; Axelrad, P.; Krumvieda, K.; Thomas, J. Application of successive interference cancellation to the GPS pseudolite near-far problem. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjiashvili, D.; Bosio, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, D. Exact and approximation algorithms for optimal equipment selection in deploying in-building distributed antenna systems. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2014, 14, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerman, A.; Van Kerrebrouck, J.; Caytan, O.; de Paula, I.L.; Bogaert, L.; Torfs, G.; Demeester, P.; Rogier, H.; Lemey, S. Beyond 5G without obstacles: MmWave-over-fiber distributed antenna systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2022, 60, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyez, C.; Bocquet, M.; Lethien, C.; Rolland, N. A distributed antenna system for indoor accurate WiFi localization. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhou, X.; Jiao, Z.; Guo, G.; Chen, R. Machine learning for time-of-arrival estimation with 5G signals in indoor positioning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 9782–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, Z.; Irvine, G.; Smith, R.; Mogyorósi, F.; Revisnyei, P.; Töros, I.; Pašić, A. TDoA based indoor positioning over small cell 5G networks. In Proceedings of the NOMS 2022–2022 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium, Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Yan, J.; Chen, R. Accurate DOA estimation with adjacent angle power difference for indoor localization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 44702–44713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlke, M.; Feigl, T.; García, M.H.C.; Stirling-Gallacher, R.A.; Seitz, J.; Mutschler, C. Transfer learning to adapt 5G AI-based fingerprint localization across environments. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 95th Vehicular Technology Conference: (VTC2022-Spring), Helsinki, Finland, 19–22 June 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Jin, X.; Xia, C.; Xu, C.; Sun, Y.; Duan, Y. 5G1M: Indoor Fingerprint Positioning Using a Single 5G Module. IEEE Sens. J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, M.; Yang, X. Gene-Sequencing-Based Indoor Localization in Distributed Antenna System. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 6019–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Jeon, S.; Lee, T. LTE RSSI Based Vehicular Localization System in Long Tunnel Environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 11102–11114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chu, X.; Zhai, M. Machine learning-based integrated wireless sensing and positioning for cellular network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, G.I.; Choi, J.H.; Bu, S.C. Indoor positioning using TDOA measurements from switching GPS repeater. In Proceedings of the 17th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2004), Long Beach, CA, USA, 21–24 September 2004; pp. 1970–1976. [Google Scholar]
- Im, S.H.; Jee, G.I.; Cho, Y.B. An indoor positioning system using time-delayed GPS repeater. In Proceedings of the 19th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2006), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 26–29 September 2006; pp. 2478–2483. [Google Scholar]
- Vervisch-Picois, A.; Samama, N. Interference mitigation in a repeater and pseudolite indoor positioning system. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2009, 3, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Chen, W.; Xu, Y.; Ji, S. A new indoor positioning system architecture using GPS signals. Sensors 2015, 15, 10074–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Gnss repeater based differential indoor positioning with multi-epoch measurements. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2021, 8, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucciardo, M.; Tinnirello, I.; Dell’Aera, G.M.; Caretti, M. A flexible 4G/5G control platform for fingerprint-based indoor localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; pp. 744–749. [Google Scholar]
- Malmström, M.; Skog, I.; Razavi, S.M.; Zhao, Y.; Gunnarsson, F. 5G positioning-a machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communications (WPNC), Bremen, Germany, 23–24 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, A.A.; Jao, C.S.; Kassas, Z.M.; Shkel, A.M. A pedestrian indoor navigation system using deep-learning-aided cellular signals and ZUPT-aided foot-mounted IMUs. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 5188–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Chai, M.; Xiao, J.; Li, C. A hybrid indoor positioning algorithm for cellular and Wi-Fi networks. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 47, 2909–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Kailath, T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP. Physical Layer Procedures for Control; Technical Report; 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP): Sophia Antipolis, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi, A.; Slock, D.T.; Meilhac, L. On spatio-frequential smoothing for joint angles and times of arrival estimation of multipaths. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 3311–3315. [Google Scholar]
- Retscher, G.; Tatschl, T. Indoor positioning using Wi-Fi lateration—Comparison of two common range conversion models with two novel differential approaches. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on Ubiquitous Positioning, Indoor Navigation and Location Based Services (UPINLBS), Shanghai, China, 2–4 November 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cepeda, R.; Thompson, W.; Beach, M.; McGeehan, J. On the measurement and simulations of the frequency dependent path loss and MB-OFDM. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–11 September 2009; pp. 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W.j.; Zhu, H.b. An empirical path loss model in the indoor stairwell at 2.6 GHz. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Wireless Symposium (IWS 2014), Xi’an, China, 24–26 March 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nkrow, R.E.; Silva, B.; Boshoff, D.; Hancke, G.; Gidlund, M.; Abu-Mahfouz, A. NLOS identification and mitigation for time-based indoor localization systems: Survey and future research directions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Soh, W.S.; Wong, W.C. Indoor localization with channel impulse response based fingerprint and nonparametric regression. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2010, 9, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Xiao, J.; Yi, Y.; Chen, D.; Luo, X.; Ni, L.M. CSI-based indoor localization. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2012, 24, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, F.; Fan, Y.; Liu, K.R. RF-based inertial measurement. In Proceedings of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Beijing, China, 19–23 August 2019; pp. 117–129. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wu, N.; Li, B.; Yuan, W.; Hanzo, L. Indoor localization based on factor graphs: A unified framework. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 4353–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellaert, F. Factor Graphs and GTSAM: A Hands-On Introduction; Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 3GPP. Study on Channel Model for Frequencies from 0.5 to 100 GHz; Technical Report; 3rd Generation PartnershipProject (3GPP): Sophia Antipolis, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, D.; Gibson, K.; Ziebold, R.; Closas, P. Determination of pseudorange error models and multipath characterization under signal-degraded scenarios. In Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, ION GNSS+ 2018, Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Mao, S.; Pandey, S. CSI-based fingerprinting for indoor localization: A deep learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 66, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Wang, Z. Efficient closed-form algorithms for AOA based self-localization of sensor nodes using auxiliary variables. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 2580–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
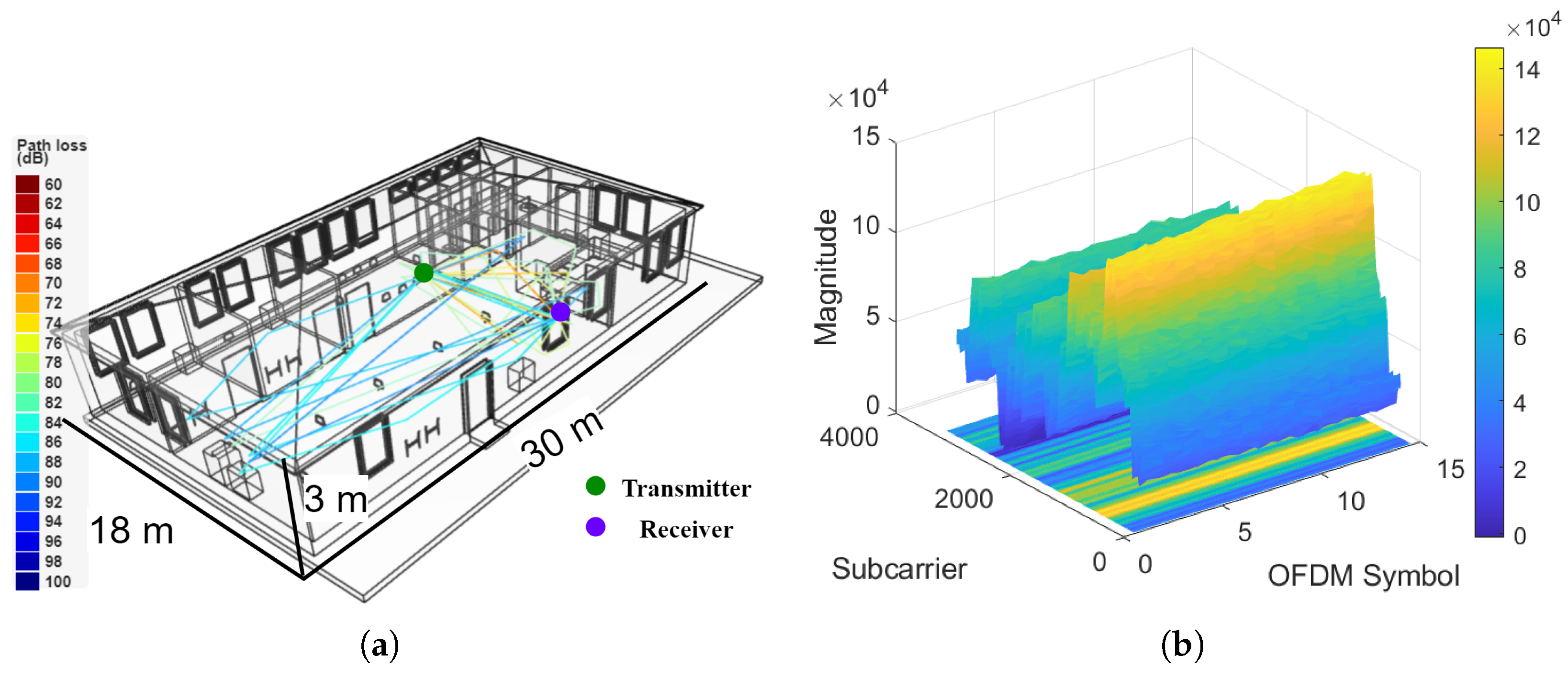

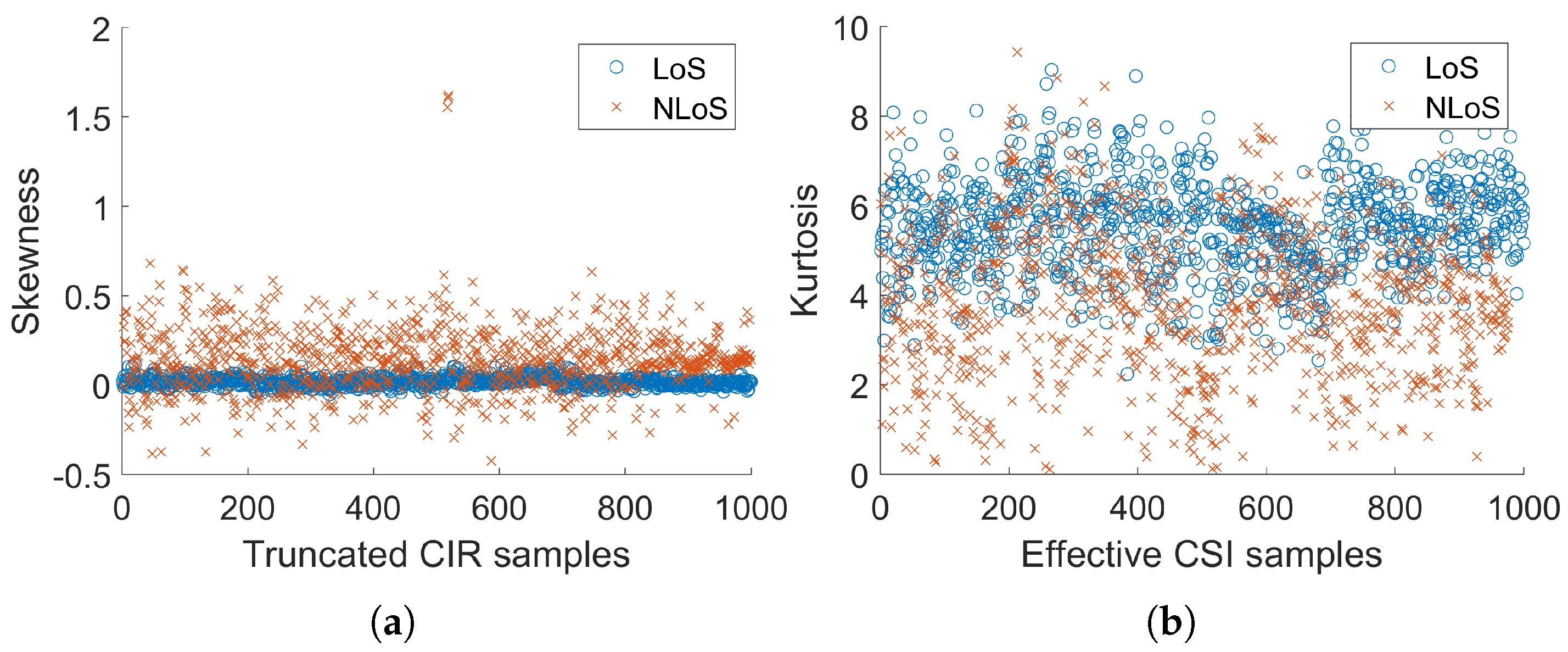

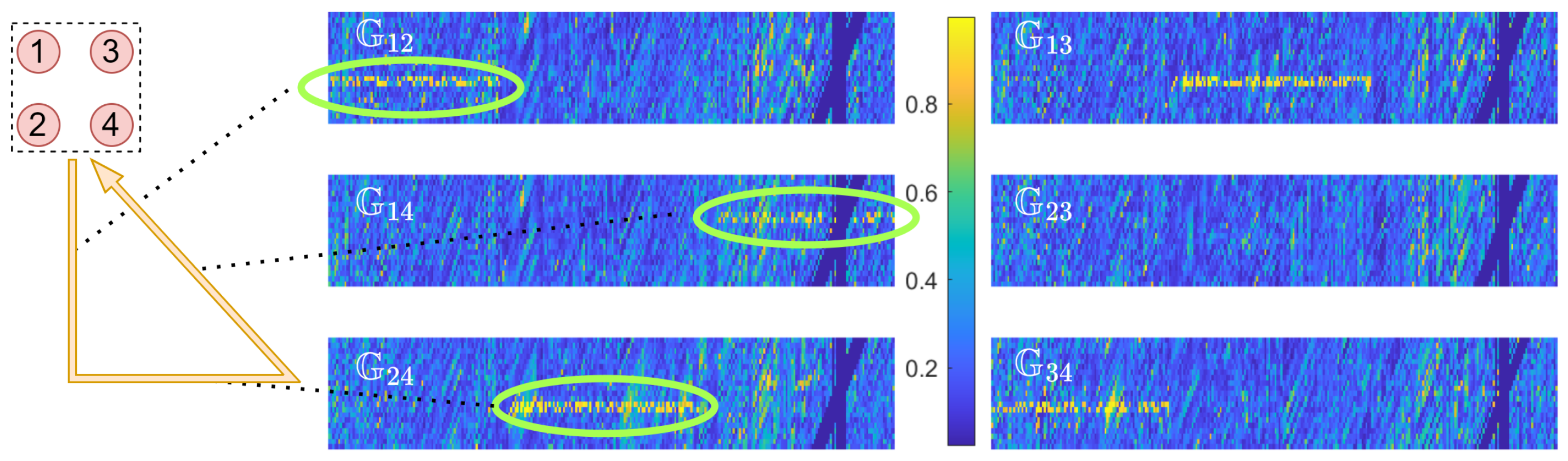

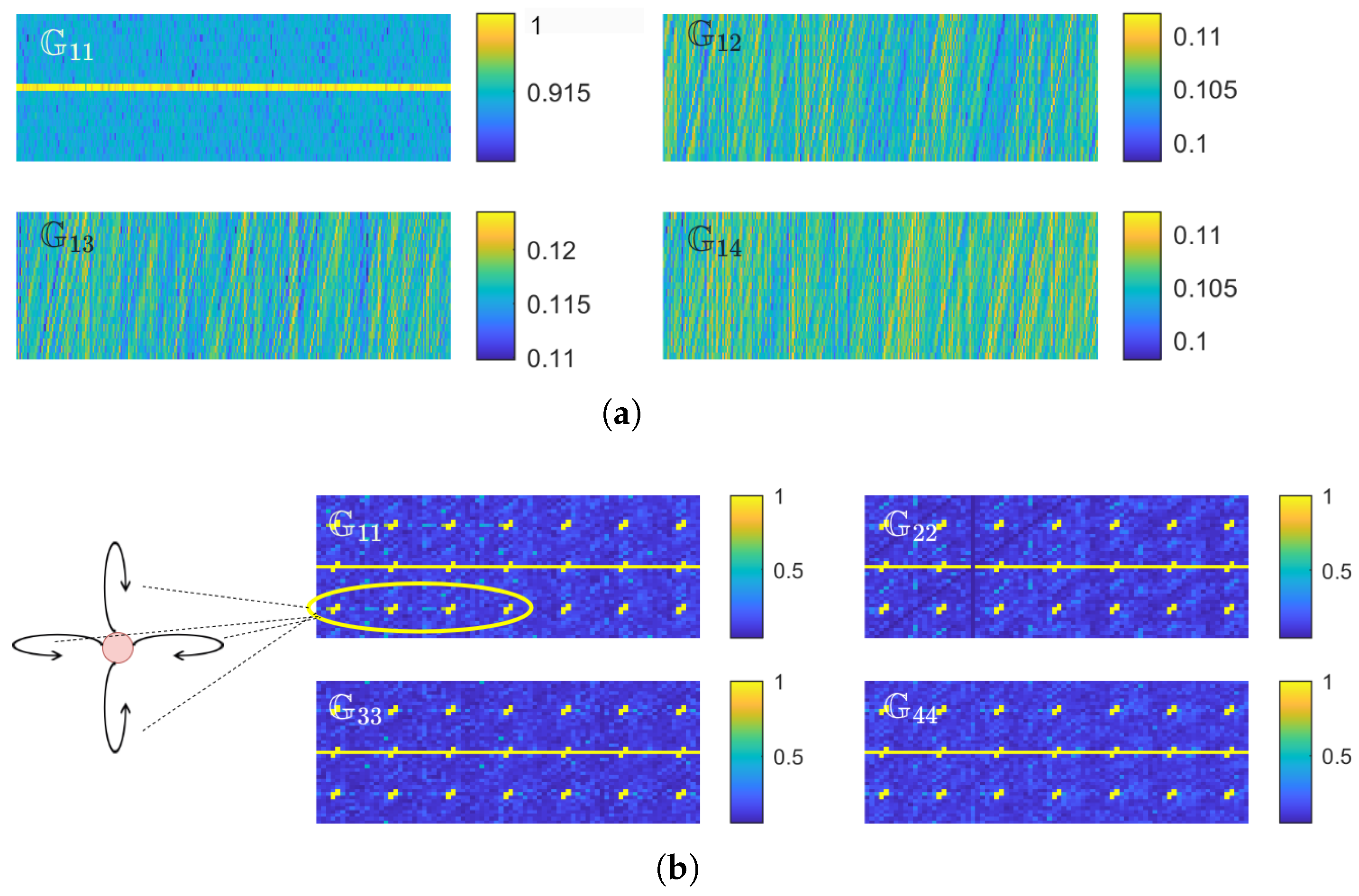



| Method | Number of | MAE | RMSE | CEP75 | CEP90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anchors | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | |
| CSI-fingerprinting | 4 | 1.10 | 1.23 | 1.40 | 1.96 |
| CSI-triangulation | 3 | 1.02 | 1.43 | 1.44 | 2.03 |
| Proposed method | 1 | 1.07 | 1.58 | 1.37 | 1.81 |
| Parameter | Description | Components | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| DR process noise | |||
| ZUPT constraint noise | |||
| LC constraint noise |
| Algorithm | MAE | RMSE | CEP75 | CEP90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | |
| hard-switching EKF | 0.93 | 1.29 | 1.57 | 2.16 |
| soft-switching AEKF | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 1.05 |
| HAF-GF w/o ZUPT | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.56 | 0.69 |
| HAF-GF w/o LC | 0.45 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.85 |
| HAF-GF w/o ZUPT and LC | 0.46 | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.85 |
| HAF-GF with ZUPT and LC | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.69 |
| Method | DoA | Network | LoS | TRRS | Fusion | Average Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimation | Inference | Detection | Computation | Algorithm | Cost (s) | |
| CSI-triangulation | — | — | — | — | 0.224 | |
| +EKF | — | 0.292 | ||||
| CSI-fingerprinting | — | — | — | — | 0.125 | |
| +EKF | — | — | 0.187 | |||
| Proposed Method | — | — | — | — | 0.080 | |
| +HAF-GF | — | 0.427 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Chu, X.; Lu, Z. Enhancing Indoor Positioning with GNSS-Aided In-Building Wireless Systems. Electronics 2025, 14, 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102079
Zhou S, Chu X, Lu Z. Enhancing Indoor Positioning with GNSS-Aided In-Building Wireless Systems. Electronics. 2025; 14(10):2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102079
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shuya, Xinghe Chu, and Zhaoming Lu. 2025. "Enhancing Indoor Positioning with GNSS-Aided In-Building Wireless Systems" Electronics 14, no. 10: 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102079
APA StyleZhou, S., Chu, X., & Lu, Z. (2025). Enhancing Indoor Positioning with GNSS-Aided In-Building Wireless Systems. Electronics, 14(10), 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102079







