S-FusionNet: A Multi-Modal Semi-Fusion 3D Object Detection Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Words
2.1. Fusion Position
2.2. Input Data Types
- (1)
- 3D Object Detection Based on BEV/RV + Camera
- (2)
- 3D Object Detection Based on Raw Point Cloud and Camera
- (3)
- 3D Object Detection Based on Voxel and Image Features
2.3. Fusion Strategy
- (1)
- Pixel-Level Fusion Strategy
- (2)
- Decision Fusion Strategy
- (3)
- Feature-Level Fusion Strategy
3. Method
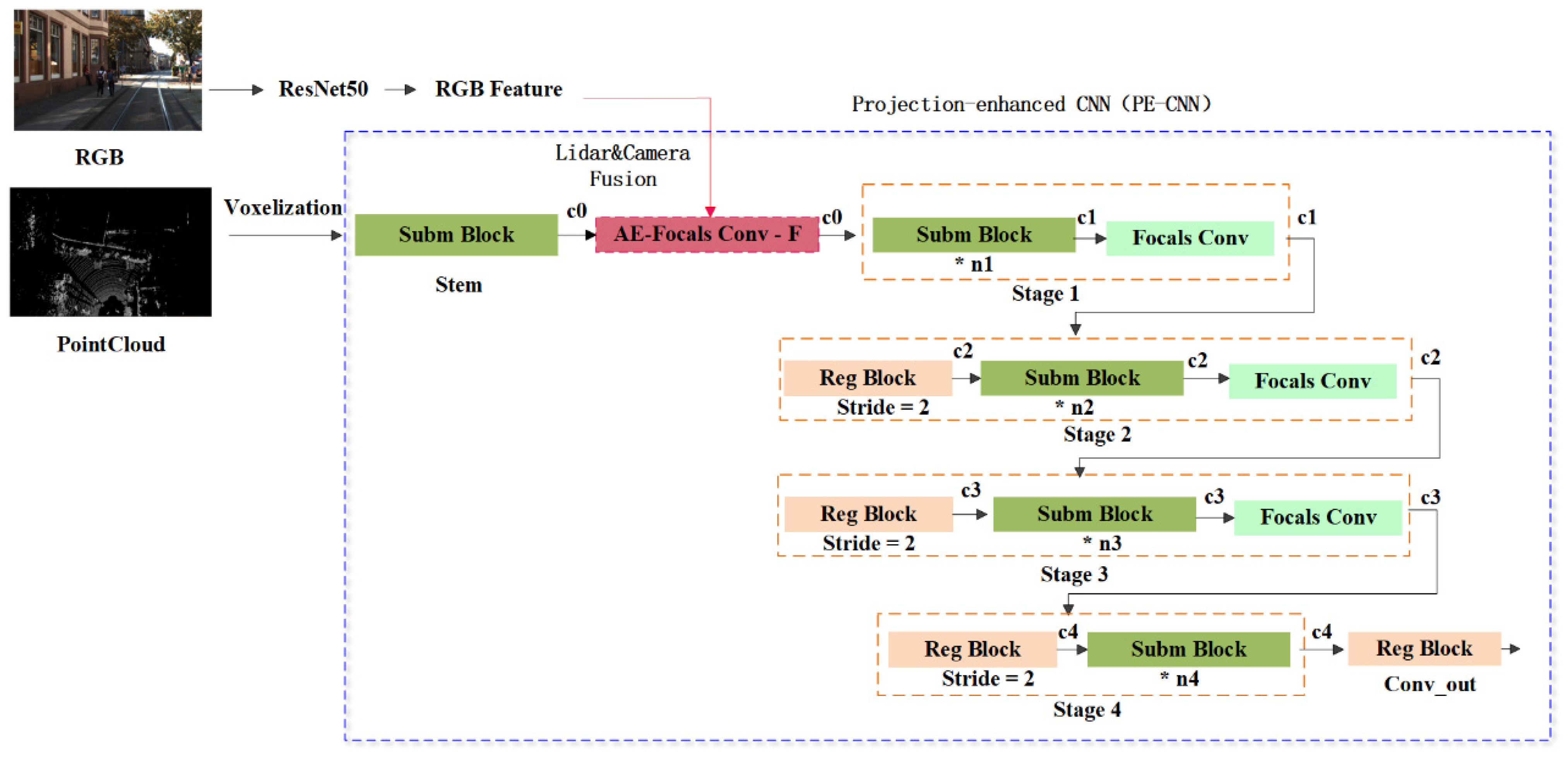
3.1. Multi-Modal Semi-Fusion Network (S-FusionNet)
3.2. Single-View Feature Extraction Module
- (1)
- Voxelization Feature Encoding
- (2)
- Image Feature Encoding
3.3. Projection-Enhanced Convolutional Neural Networks (PE-CNNs)
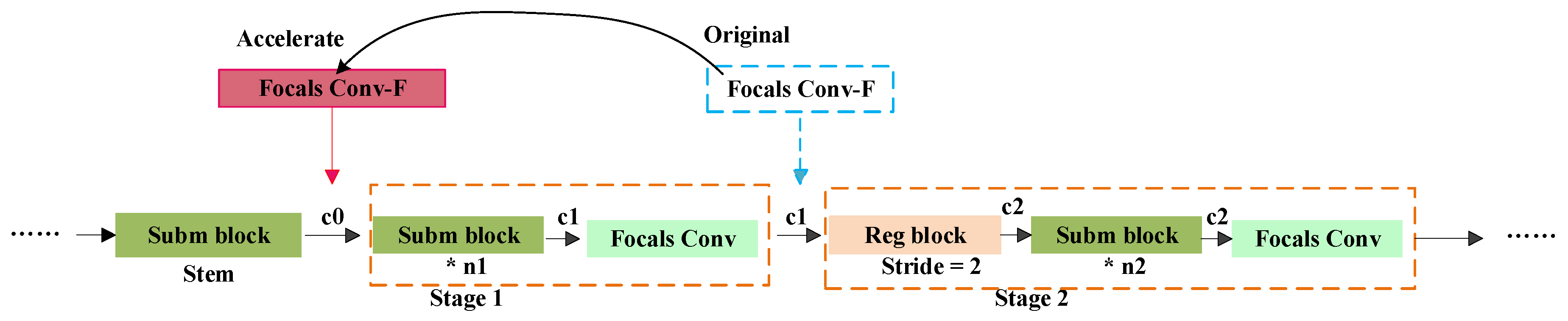
3.4. Voxel Projection Optimization Localization Strategy
- (1)
- Fusion of image features followed by sparse convolution: When this strategy is employed, image features are fused with voxel features on the existing voxel structure, a process that does not result in an increase or decrease in the number of voxels. Additionally, the total number of projection calculations remains unchanged, thus ensuring the consistency and stability of the computational process.
- (2)
- Convolution of voxel features followed by fusion of image features: When voxel features are first subjected to sparse convolution, it may lead to a change in the number of voxels, especially when the convolution operation introduces a dilation effect. This dilation effect can cause an increase in the number of voxels, and in the subsequent fusion stage, the demand for projection calculations will also increase due to the involvement of more voxels, which could potentially double the consumption of computational resources.
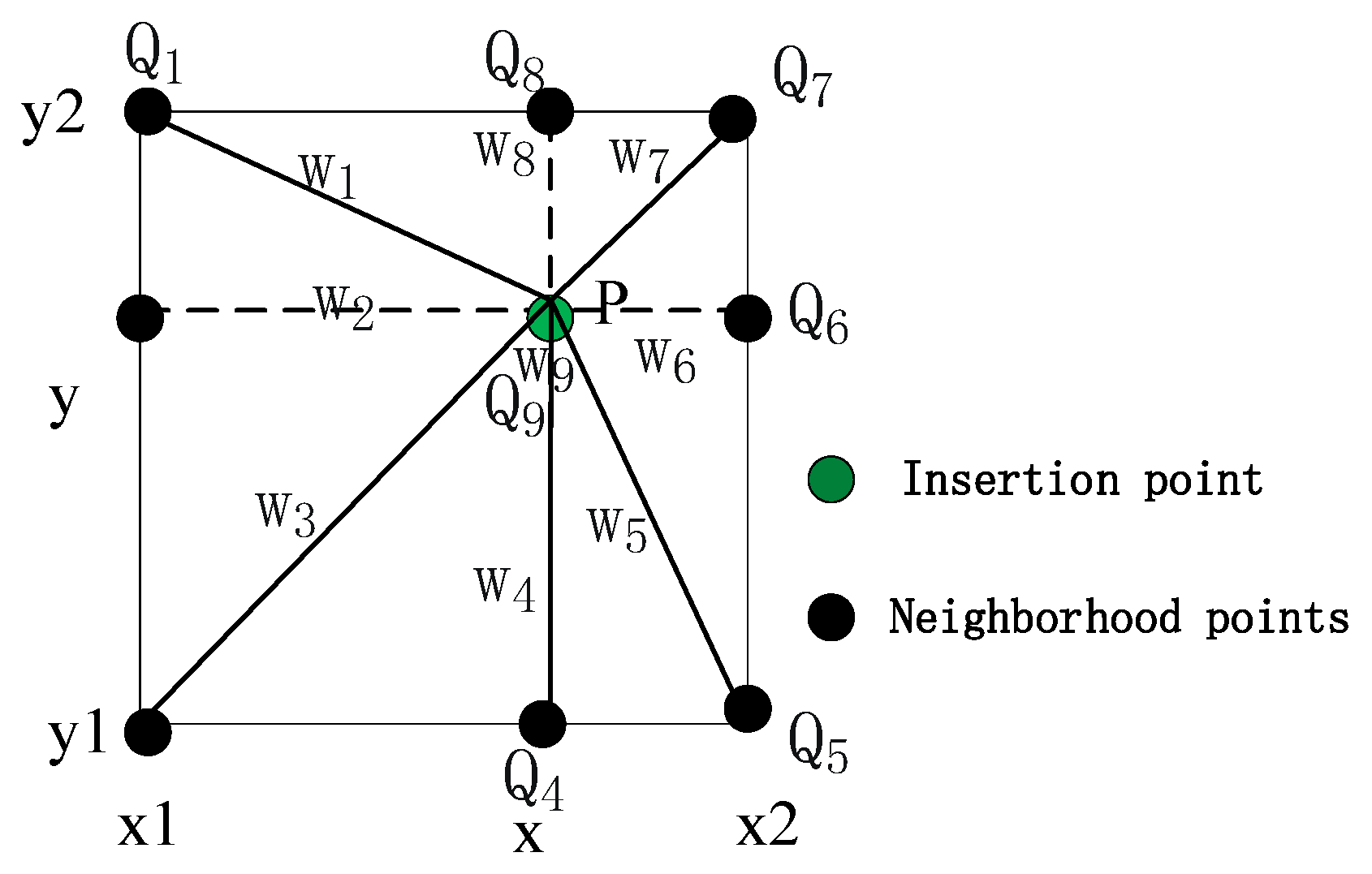
3.5. Neighborhood-Enhanced Feature Interpolation Method
- (1)
- Neighborhood Sampling and Feature Extraction: Traverse the neighborhood coordinates centered on the point P to be interpolated. Remove invalid coordinates that exceed the image size and fill them with zeros. Extract the features corresponding to the valid coordinates from the image feature map.
- (2)
- Feature Weighting: Calculate the cosine similarity between the features of each neighborhood point and the feature of the point to be interpolated (a cosine value closer to 1 indicates that the two feature vectors are more related). Weight each neighborhood feature. Enhance features similar to the center point and suppress irrelevant neighborhood features. The formula for cosine similarity is shown in Equation (1).
- (3)
- Feature Stacking: Combine the nine weighted neighborhood features along the new dimension to form a tensor of [9, N, C], where N represents the number of points in the point cloud and C represents the number of channels of the features. Take the mean along the neighborhood dimension to obtain the final aggregated feature, which is then summed and fused with the voxel feature to serve as the training input.
3.6. Feature Extraction Network
3.7. Object Classification and Parameter Regression Network
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Training Setup
4.3. Experimental Results
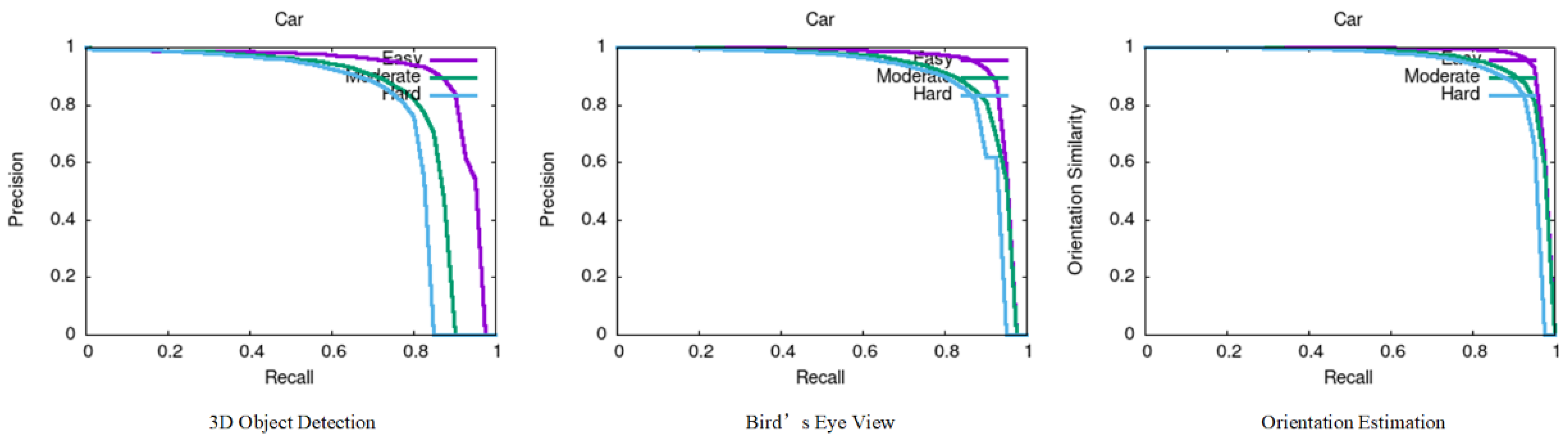
4.3.1. Performance on KITTI Validation Set
4.3.2. Performance on KITTI Test Set
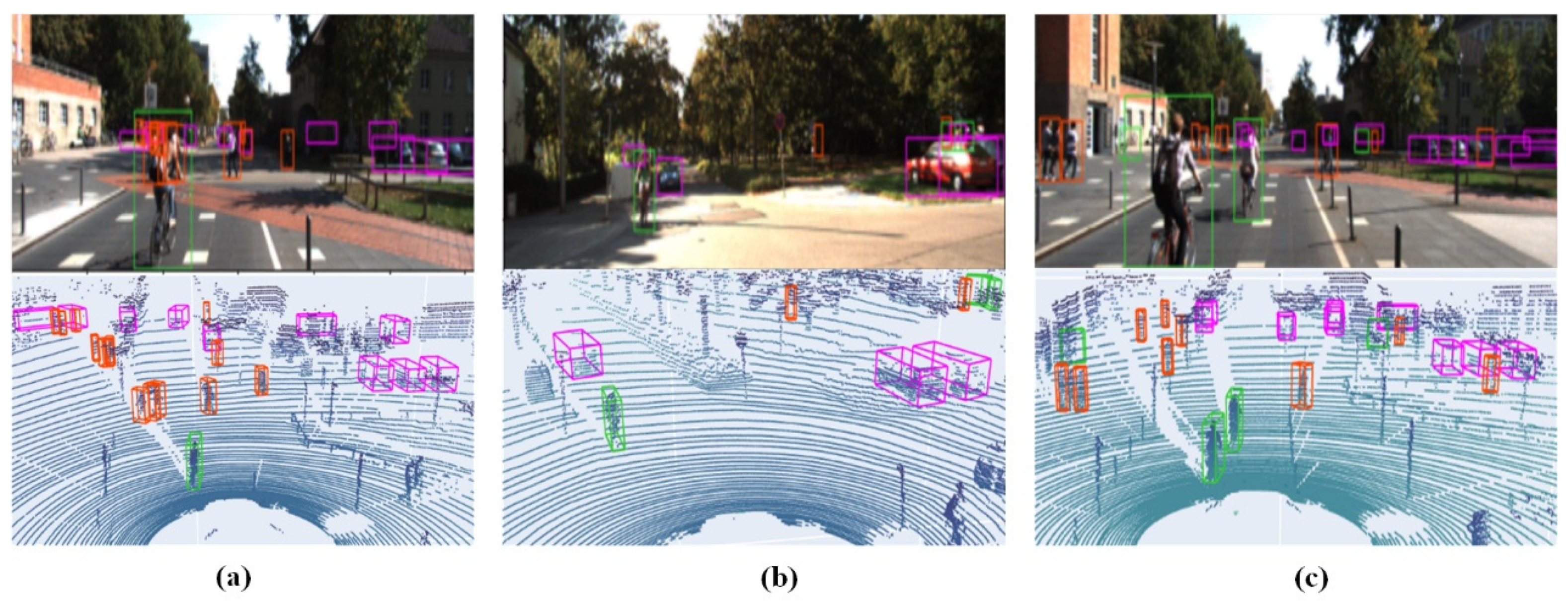
4.4. Visual Analysis
- (1)
- The S-FusionNet network can successfully detect the vast majority of targets. By comparing with the image detection results, we find that there are no missed detections in the three key categories of “Car”, “Pedestrian”, and “Cyclist”, which shows its efficient detection ability.
- (2)
- (3)
- In terms of pedestrian detection, although most pedestrians are accurately identified due to the sparsity of LiDAR data, the point cloud information contained in small target objects is relatively scarce. As a result, some small debris is misjudged as pedestrians, which affects the accuracy of pedestrian detection. This is also a relatively difficult problem to overcome in a 3D object detection task.
- (4)
- In terms of cyclist detection, since there are relatively few samples of this target object, as can be seen from the visualization of the scenario, there are no missed or false detections.
4.5. Ablation Experiment
4.5.1. VPOL Strategy
4.5.2. Neighborhood-Enhanced Feature Interpolation Module
4.5.3. Semi-Fusion Network
4.6. The Scalability of the S-FusionNet Network
4.7. Robustness Testing
- (1)
- Stability
- (2)
- Generalization
- PV-RCNN + KITTI
- b.
- Focals Conv-F + VOD
- c.
- CenterPoint + nuScenes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VPOL | Voxel Projection Optimization Localization |
| PE-RCNN | Projection-Enhanced RCNN |
| A-FocalsConv-F | Accelerated Focal Sparse Convolution Fusion |
| AE-FocalConv-F | Accelerated Enhanced Focal Sparse Convolution Fusion Module |
| NE Interpolation | Neighborhood-Enhanced Feature Interpolation |
| S-FusionNet | Multi-Modal Semi-Fusion Network |
References
- Shi, S.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H. From Points to Parts: 3D Object Detection from Point Cloud with Part-Aware and Part-Aggregation Network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 2647–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.; Qi, C.R.; Deschaud, J.-E.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Guibas, L.J. Kpconv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6411–6420. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, X. A closer look at local aggregation operators in point cloud analysis. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020, Proceedings of the 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XXIII 16; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 326–342. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Kundu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, H.; Fidler, S.; Urtasun, R. 3D Object Proposals Using Stereo Imagery for Accurate Object Class Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Yang, B.; Urtasun, R. Fast and furious: Real time end-to-end 3D detection, tracking and motion forecasting with a single convolutional net. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3569–3577. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Luo, W.; Urtasun, R. Pixor: Real-time 3D object detection from point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7652–7660. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. Voxelnet: End-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4490–4499. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Fang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, H. Autoalign: Pixel-instance feature aggregation for multi-modal 3D object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.06493. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, R.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, W. PTA-Det: Point Transformer Associating Point Cloud and Image for 3D Object Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Morris, D.; Radha, H. CLOCs: Camera-LiDAR object candidates fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 10386–10393. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, W.; Abdelkarim, S.; Zidan, M.; Zahran, M.; El Sallab, A. Yolo3d: End-to-end real-time 3D oriented object bounding box detection from lidar point cloud. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gribbon, K.T.; Bailey, D.G. A novel approach to real-time bilinear interpolation. In Proceedings of the DELTA 2004, Second IEEE International Workshop on Electronic Design, Test and Applications, Perth, Australia, 28–30 January 2004; pp. 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Jia, J. Focal sparse convolutional networks for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5428–5437. [Google Scholar]
- Sindagi, V.A.; Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. Mvx-net: Multimodal voxelnet for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 7276–7282. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Hu, R.; Urtasun, R. Multi-task multi-sensor fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7345–7353. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.W. 3d-cvf: Generating joint camera and lidar features using cross-view spatial feature fusion for 3D object detection. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020, Proceedings of 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XXVII 16; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 720–736. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Bai, X. Epnet: Enhancing point features with image semantics for 3D object detection. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020, Proceedings of the 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XV 16; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Vora, S.; Lang, A.H.; Helou, B.; Beijbom, O. Pointpainting: Sequential fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4604–4612. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. From multi-view to hollow-3D: Hallucinated hollow-3D R-CNN for 3D object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 4722–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. Density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A.; Laio, A. Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. Science 2014, 344, 1492–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhr, J.K.; Jang, J.; Min, D.; Jung, H.G. Sensor fusion-based low-cost vehicle localization system for complex urban environments. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 18, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Lai, X.; Li, X. 3D object detection for autonomous driving: A survey. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 130, 108796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Zhu, H.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Multi-modal 3D object detection in autonomous driving: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 2122–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Shi, S.; Wang, X.; Li, H. 3D object detection for autonomous driving: A comprehensive survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 1909–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Surround-view vision-based 3D detection for autonomous driving: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 3235–3244. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A. Transformer-based sensor fusion for autonomous driving: A survey. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Paris, France, 2–6 October; pp. 3312–3317.
- Wang, X.; Li, K.; Chehri, A. Multi-sensor fusion technology for 3D object detection in autonomous driving: A review. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 1148–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Qin, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, L. Survey on image and point-cloud fusion-based object detection in autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 22772–22789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Bi, J.; Zhang, G.; Wei, H.; Tang, L.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Jia, C. Multi-modal 3D object detection in autonomous driving: A survey and taxonomy. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 3781–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Anguelov, D.; Jain, A. Pointfusion: Deep sensor fusion for 3D bounding box estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Liu, W.; Wu, C.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Frustum pointnets for 3D object detection from rgb-d data. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 918–927. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, K.; Kwon, Y.P.; Tomizuka, M. Roarnet: A robust 3D object detection based on region approximation refinement. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Paris, France, 9–12 June 2019; pp. 2510–2515. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Jia, K. Frustum convnet: Sliding frustums to aggregate local point-wise features for amodal 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 1742–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Fayyad, J.; Jaradat, M.A.; Gruyer, D.; Najjaran, H. Deep Learning Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Vehicle Perception and Localization: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asvadi, A.; Garrote, L.; Premebida, C.; Peixoto, P.; Nunes, U.J. Multimodal vehicle detection: Fusing 3D-LIDAR and color camera data. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 115, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, H.; Wan, J.; Li, B.; Xia, T. Multi-view 3D object detection network for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1907–1915. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, J.; Mozifian, M.; Lee, J.; Harakeh, A.; Waslander, S.L. Joint 3D proposal generation and object detection from view aggregation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, W.; Yun, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, M. FuseSeg: Semantic segmentation of urban scenes based on RGB and thermal data fusion. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Cao, D.; Wu, J. Multi-view adaptive fusion network for 3D object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.00652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecha, C.; Von Hansen, W.; Van Gool, L.; Fua, P.; Thoennessen, U. On benchmarking camera calibration and multi-view stereo for high resolution imagery. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.; Mao, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Vpfnet: Improving 3D object detection with virtual point based lidar and stereo data fusion. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 5291–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltz, E. Multisensor Data Fusion; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.L.; Llinas, J. An introduction to multisensor data fusion. Proc. IEEE 1997, 85, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.; Llinas, J. Multisensor Data Fusion; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Fragonara, L.Z.; Tsourdos, A. RoIFusion: 3D object detection from LiDAR and vision. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 51710–51721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Morris, D.; Radha, H. Fast-CLOCs: Fast camera-LiDAR object candidates fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, G.P.; Charland, J.; Hegde, D.; Laddha, A.; Vallespi-Gonzalez, C. Sensor fusion for joint 3D object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ma, C.; Zhu, M.; Yang, X. Pointaugmenting: Cross-modal augmentation for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11794–11803. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, D.; Fang, J.; Yin, J.; Bin, Z.; Zhang, L. Fusionpainting: Multimodal fusion with adaptive attention for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 3047–3054. [Google Scholar]
- Nabati, R.; Qi, H. CenterFusion: Center-based radar and camera fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 1527–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, M.; Amende, K.; Kraus, A.; Honer, J.; Samann, T.; Kaulbersch, H.; Milz, S.; Michael Gross, H. Complexer-yolo: Real-time 3D object detection and tracking on semantic point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, G.P.; Laddha, A.; Kee, E.; Vallespi-Gonzalez, C.; Wellington, C.K. Lasernet: An efficient probabilistic 3D object detector for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12677–12686. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Yang, B.; Wang, S.; Urtasun, R. Deep continuous fusion for multi-sensor 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 641–656. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xie, J.; Liu, L.; Jia, C.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z. Voxelnextfusion: A simple, unified and effective voxel fusion framework for multi-modal 3D object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Jia, J. Voxel field fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1120–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, C.; Kang, Z.; Ma, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R. SupFusion: Supervised LiDAR-camera fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Paris, France, 2–6 October; pp. 22014–22024.
- Wang, Z.; Zhan, W.; Tomizuka, M. Fusing bird view lidar point cloud and front view camera image for deep object detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.06703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Guo, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Pv-RCNN: Point-voxel feature set abstraction for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10529–10538. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, T.; Zhou, X.; Krahenbuhl, P. Center-based 3D object detection and tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11784–11793. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Shi, S.; Li, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Voxel r-cnn: Towards high performance voxel-based 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Event, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 1201–1209. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.; Engelcke, M.; Van Der Maaten, L. 3D semantic segmentation with submanifold sparse convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 9224–9232. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Stiller, C.; Urtasun, R. Vision meets robotics: The kitti dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, B. SECOND: Sparsely Embedded Convolutional Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Fixing weight decay regularization in adam. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wen, C.; Shi, S.; Wang, C. Virtual Sparse Convolution for Multimodal 3D Object Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.02314. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Ji, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, X.; Chen, J. PeP: A Point enhanced Painting method for unified point cloud tasks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.07591. [Google Scholar]
- Dong Hoang, H.A.; Yoo, M. 3ONet: 3-D Detector for Occluded Object Under Obstructed Conditions. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 18879–18892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wen, C.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, C. Transformation-Equivariant 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 2795–2802. [Google Scholar]
- Palffy, A.; Pool, E.; Baratam, S.; Kooij, J.F.; Gavrila, D.M. Multi-class road user detection with 3+ 1d radar in the view-of-delft dataset. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 4961–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caesar, H.; Bankiti, V.; Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Liong, V.E.; Xu, Q.; Krishnan, A.; Pan, Y.; Baldan, G.; Beijbom, O. Nuscenes: A multimodal dataset for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11618–11628. [Google Scholar]





| Method (L+R) | Car-AP3D (%) | Ped.-AP3D (%) | Cyc.-AP3D (%) | 3D mAP (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | ||
| AVOD-FPN [40] | 84.41 | 74.44 | 68.65 | - | 58.80 | - | - | 49.70 | - | |
| PTA-Det [11] | 84.72 | 74.45 | 69.86 | 60.84 | 52.48 | 45.11 | 72.43 | 49.17 | 46.75 | 61.76 |
| PointFusion [33] | 77.92 | 63.00 | 53.27 | 33.36 | 28.04 | 23.38 | 49.34 | 29.42 | 26.98 | 42.75 |
| F-PointNet [34] | 83.76 | 70.92 | 63.65 | 70.00 | 61.32 | 53.59 | 77.15 | 56.49 | 53.37 | 65.58 |
| CLOCs [12] | 89.49 | 79.31 | 77.36 | 62.88 | 56.20 | 50.10 | 87.57 | 67.92 | 63.67 | 70.50 |
| EPNet [19] | 88.76 | 78.65 | 78.32 | 66.74 | 59.29 | 54.82 | 83.88 | 65.50 | 62.70 | 70.96 |
| 3D-CVF [18] | 89.20 | 80.05 | 73.11 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Voxel R-CNN [63] | 92.38 | 85.29 | 82.86 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FocalsConv-F [15] | 92.26 | 85.32 | 82.95 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ours | 92.87 | 85.46 | 83.13 | 67.77 | 60.75 | 55.93 | 87.75 | 72.44 | 68.57 | 74.97 |
| Method (L+R) | Car-AP3D (%) | Ped.-AP3D (%) | Cyc.-AP3D (%) | 3D mAP (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | ||
| MV3D [39] | 74.97 | 63.63 | 54.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ContFuse [56] | 83.68 | 68.78 | 61.67 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MMF [16] | 88.40 | 77.43 | 70.22 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| EPNet [19] | 89.81 | 79.28 | 74.59 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 3D-CVF [18] | 89.20 | 80.05 | 73.11 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CLOCs [12] | 88.94 | 80.67 | 77.15 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| AVOD-FPN [40] | 83.07 | 71.76 | 65.73 | 50.46 | 42.27 | 39.04 | 63.76 | 50.55 | 44.93 | 56.84 |
| F-PointNet [34] | 82.19 | 69.79 | 60.59 | 50.53 | 42.15 | 38.08 | 72.27 | 56.12 | 49.01 | 57.86 |
| F-ConvNet [36] | 87.36 | 76.39 | 66.69 | 52.16 | 43.38 | 38.80 | 81.98 | 65.07 | 56.54 | 63.15 |
| FocalsConv-F [15] | 90.55 | 82.28 | 77.59 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ours | 90.13 | 81.35 | 76.90 | 52.78 | 44.22 | 41.62 | 79.36 | 64.17 | 59.26 | 65.53 |
| Method | Multi-Modal | Runtime (ms) | Car-AP3D (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Mod | Hard | mAP | |||
| VirConv-S [69] | Full-Fusion | 90 | 92.48 | 87.20 | 82.45 | 87.38 |
| PEP [70] | Full-Fusion | 100 | 91.77 | 86.72 | 82.57 | 87.02 |
| VirConv-T [69] | Full-Fusion | 90 | 92.54 | 86.25 | 81.24 | 86.67 |
| 3ONet [71] | Full-Fusion | 100 | 92.03 | 85.47 | 78.64 | 85.38 |
| TED [72] | Full-Fusion | 100 | 91.61 | 85.28 | 80.68 | 85.86 |
| S-FusionNet | Semi-Fusion | 98.9 | 90.13 | 81.35 | 76.90 | 82.79 |
| Method | Stage | FPS | Car-AP3D (%) | Ped.-AP3D (%) | Cyc.-AP3D (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPOL Strategy | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | ||
| × | (1,) | 6.7 | 92.96 | 85.52 | 84.90 | 71.84 | 64.73 | 59.87 | 88.63 | 71.72 | 68.63 |
| ✓ | (Stem,) | 10.78 | 92.51 | 84.10 | 82.62 | 67.09 | 58.57 | 53.68 | 87.68 | 71.14 | 68.26 |
| Delta | +4.08 | −0.45 | −1.42 | −2.28 | −4.75 | −6.16 | −6.19 | −0.95 | −0.58 | −0.37 | |
| Method | FPS | Car-AP3D (%) | Ped.-AP3D (%) | Cyc.-AP3D (%) | 3D mAP (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | |||
| A-FocalsConv-F | 10.78 | 92.51 | 84.10 | 82.62 | 67.09 | 58.57 | 53.68 | 87.68 | 71.14 | 68.26 | 73.96 |
| AE-FocalsConv-F | 10.11 | 92.87 | 85.46 | 83.13 | 67.77 | 60.75 | 55.93 | 87.75 | 72.44 | 68.57 | 74.96 |
| Delta | −0.67 | +0.36 | +1.36 | +0.51 | +0.68 | +2.18 | +2.25 | +0.07 | +1.3 | +0.31 | +1 |
| Method | Training Time (h) | Car-AP3D (%) | Ped.-AP3D (%) | Cyc.-AP3D(%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | ||
| Full-Fusion | 43.75 | 92.67 | 85.07 | 82.88 | 65.16 | 58.21 | 53.16 | 90.79 | 72.86 | 69.62 |
| Semi-Fusion | 39.40 | 92.87 | 85.46 | 83.13 | 67.77 | 60.75 | 55.93 | 87.75 | 72.44 | 68.57 |
| Delta | +4.35 | +0.2 | +0.39 | +0.25 | +2.61 | +2.54 | +2.77 | −3.04 | −0.42 | −1.05 |
| Method | Time (ms) | Car-AP3D (%) | Ped.-AP3D (%) | Cyc.-AP3D (%) | 3D mAP (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE- FocalsConv-F | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | ||
| Lidar (×) | 71.2 | 92.41 | 82.85 | 80.28 | 64.74 | 56.76 | 50.91 | 89.31 | 74.59 | 70.01 | 73.54 |
| Lidar + RGB (✓) | 98.9 | 92.87 | 85.46 | 83.13 | 67.77 | 60.75 | 55.93 | 87.75 | 72.44 | 68.57 | 74.96 |
| Delta | −27.7 | +0.46 | +2.61 | +2.85 | +3.03 | +3.99 | +5.02 | −1.56 | −2.15 | −1.44 | +1.42 |
| Method | Error Type | Car-AP3D (%) | Ped.-AP3D (%) | Cyc.-AP3D (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angular Error (°) | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | |
| A-FocalsConv-F | a. (0, 0, 0) | 92.51 | 84.10 | 82.62 | 67.09 | 58.57 | 53.68 | 87.68 | 71.14 | 68.26 |
| b. (0.05, 0.05, 0.05) | 92.40 | 82.30 | 81.98 | 67.68 | 59.46 | 54.94 | 87.36 | 70.92 | 67.77 | |
| c. (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) | 89.81 | 78.93 | 77.03 | 67.82 | 59.39 | 54.19 | 88.08 | 71.04 | 67.14 | |
| d. (0.2, 0.2, 0.2) | 82.11 | 62.70 | 61.79 | 65.68 | 57.19 | 52.02 | 83.55 | 63.12 | 59.32 | |
| Delta (b − a) | −0.11 | −1.8 | −0.64 | +0.59 | +0.89 | +1.26 | −0.32 | −0.22 | −0.49 | |
| Delta (c − a) | −2.7 | −5.17 | −5.59 | +0.73 | +0.82 | +0.51 | +0.4 | −0.1 | −1.12 | |
| Delta (d − a) | −10.40 | −21.40 | −20.83 | −1.41 | −1.38 | −1.66 | −4.13 | −8.02 | −8.94 | |
| AE-FocalsConv-F | A. (0, 0, 0) | 92.87 | 85.46 | 83.13 | 67.77 | 60.75 | 55.93 | 87.75 | 72.44 | 68.57 |
| B. (0.05, 0.05, 0.05) | 92.79 | 85.36 | 82.97 | 68.53 | 61.37 | 56.49 | 87.89 | 71.50 | 68.03 | |
| C. (0.1, 0.1, 0.1) | 92.04 | 82.09 | 79.91 | 68.20 | 60.94 | 56.17 | 87.32 | 70.71 | 67.41 | |
| D. (0.2, 0.2, 0.2) | 84.68 | 67.92 | 66.95 | 66.35 | 59.04 | 54.05 | 85.18 | 65.10 | 61.88 | |
| Delta (B − A) | −0.08 | −0.1 | −0.16 | +0.76 | +0.62 | +0.56 | +0.14 | −0.94 | −0.54 | |
| Delta (C − A) | −0.83 | −3.37 | −3.22 | +0.43 | +0.19 | +0.24 | −0.43 | −1.73 | −1.16 | |
| Delta (D − A) | −8.19 | −17.54 | −16.18 | −1.42 | −1.71 | −1.88 | −2.57 | −7.34 | −6.69 | |
| Method | Car-AP3D (%) | Ped.-AP3D (%) | Cyc.-AP3D (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | Easy | Mod | Hard | ||
| PV RCNN* | 3D | 90.89 | 82.67 | 80.11 | 54.46 | 48.37 | 43.13 | 86.57 | 70.94 | 65.33 |
| S-FusionNet | 92.05 | 82.82 | 82.35 | 64.29 | 56.97 | 53.13 | 87.71 | 72.84 | 68.76 | |
| PV RCNN* | BEV | 93.16 | 89.38 | 88.28 | 59.39 | 52.99 | 48.69 | 88.76 | 73.46 | 68.82 |
| S-FusionNet | 95.21 | 90.24 | 88.34 | 69.30 | 62.03 | 58.47 | 89.58 | 75.84 | 71.96 | |
| Method | Time (ms) | Entire Annotated Area | In Driving Corridor | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Ped. | Cyc. | mAP | Car | Ped. | Cyc. | mAP | ||
| FocalsConv-F* | 178 | 61.83 | 49.53 | 65.86 | 59.07 | 90.64 | 64.00 | 82.93 | 79.19 |
| S-FusionNet | 151 | 59.65 | 50.75 | 67.07 | 59.16 | 90.06 | 66.48 | 86.55 | 81.03 |
| Delta | −27 | −2.18 | +1.22 | −1.21 | +0.11 | −0.58 | +2.48 | +3.62 | +1.84 |
| Method | mAP | NDS | Car | Track | C.V. | Bus | Trailer | B.R. | M.T. | Bicycle | Ped. | T.C. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CenterPoint* | 59.82 | 67.21 | 86.55 | 58.17 | 16.32 | 73.43 | 38.31 | 67.15 | 60.38 | 42.89 | 84.35 | 70.65 |
| S-FusionNet | 64.89 | 70.35 | 88.07 | 60.71 | 24.98 | 74.29 | 42.96 | 68.30 | 72.05 | 55.42 | 84.96 | 77.13 |
| Delta | +5.07 | +3.14 | +1.52 | 2.54 | 8.66 | 0.86 | 4.65 | 1.15 | 11.67 | 12.53 | 0.61 | 6.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Su, C.; Cao, G. S-FusionNet: A Multi-Modal Semi-Fusion 3D Object Detection Network. Electronics 2025, 14, 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102008
Zhang B, Su C, Cao G. S-FusionNet: A Multi-Modal Semi-Fusion 3D Object Detection Network. Electronics. 2025; 14(10):2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102008
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Baowen, Chengzhi Su, and Guohua Cao. 2025. "S-FusionNet: A Multi-Modal Semi-Fusion 3D Object Detection Network" Electronics 14, no. 10: 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102008
APA StyleZhang, B., Su, C., & Cao, G. (2025). S-FusionNet: A Multi-Modal Semi-Fusion 3D Object Detection Network. Electronics, 14(10), 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102008






