Abstract
Resistive random-access memory (RRAM) has been attractive as an emerging memory that can be used for computing-in-memory (CIM) and storage-class memory (SCM). However, achieving gradual resistive switching (RS) characteristics and minimizing the variability remain critical challenges. In this work, we investigate the wake-up effect in Al2O3-based RRAM and its role in improving RS properties. Two types of wake-up effects were found: HRS variation improvement and gradual switching during set operation. First, a reduction in current variation in the high-resistance state (HRS), which indicates improvement of filament stability and uniformity. Second, gradual switching during the set voltage sweep, suggesting a more gradual modulation of the conduction mechanism, likely related to interface conductive filament (CF) generation. By harnessing the wake-up effect, it is possible to overcome the limitations of RRAM, which allows writing only during the reset voltage sweep, to enable writing during the set voltage sweep as well.
1. Introduction
Resistive random-access memory (RRAM) has emerged as a promising candidate for next-generation non-volatile memory (NVM) due to its excellent scalability, low power consumption, and suitability for neuromorphic computing. Owing to these features, RRAM is actively being explored for computing-in-memory (CIM) and storage-class memory (SCM) applications, where its fast-switching speed and non-volatility offer significant advantages [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Despite these benefits, several challenges must be addressed to enable large-scale adoption. These include device-to-device variability, abrupt current changes during resistive switching (RS), and unstable switching behavior, all of which hinder the reliability and practicality of RRAM systems [11]. Among these, one of the most critical limitations is the abrupt current surge during the set process, which can lead to uncontrolled filament formation, increased power consumption, and, in severe cases, permanent device failure [12,13,14].
To mitigate these issues, various circuit-level and material-level strategies have been proposed. These include the implementation of current compliance schemes using access transistors [15], the introduction of series resistors [16], and material or structural modifications such as interfacial engineering [17], electrode optimization [18], and tailored stack designs to regulate filament dynamics [19]. While such methods can help alleviate abrupt switching to some extent, they are often accompanied by trade-offs, including increased circuit complexity, slower switching speeds, and limited scalability [20]. In parallel, improving device uniformity and reproducibility both ‘cycle-to-cycle’ and ‘cell-to-cell’ has been another critical objective in recent RRAM research. Various studies have explored approaches such as interface engineering and defect modulation to enhance switching consistency and reliability in large-scale arrays [21,22]. While these efforts have primarily addressed uniformity-related challenges, this study focuses on addressing the abrupt switching behavior observed during the set process.
Due to the instability of the set process, RRAM devices often allow reliable write operations only during the reset phase, where the resistance change tends to be more controlled and predictable [23]. This constraint reduces the architectural flexibility of RRAM-based memory and logic systems. To overcome this limitation, several studies have attempted to achieve more gradual RS behavior by modulating the reset pulse and have demonstrated the feasibility of programming during the set process as well [24], In this context, we investigate the wake-up effect—a phenomenon wherein device switching characteristics evolve through repeated cycling—as a mechanism to gradually suppress abrupt set switching. We explore the potential of leveraging this effect as a built-in strategy to induce more gradual current transitions during the set operation. In addition, we examine the wake-up effect’s ability to reduce variation in the high resistance state (HRS), which is crucial for enhancing overall device stability and reliability.
To investigate this phenomenon, we use Al2O3/TiOx bilayer RRAM devices, which offer a favorable platform due to their combination of material advantages. Al2O3 is known for its high energy bandgap (~8 eV), relatively high dielectric constant (~9), and excellent thermal and chemical stability [25,26,27,28,29]. However, Al2O3 intrinsically lacks a sufficient concentration of oxygen vacancies to reliably form conductive filaments (CFs). By introducing a TiOx layer—which has a higher density of oxygen vacancies—oxide ions can diffuse into the Al2O3 layer, enabling stable RS behavior [30,31]. In addition to this complementary interaction, Al2O3/TiOx bilayer structures provide improved switching characteristics, enhanced thermal stability, and compatibility with existing CMOS processes, making them well-suited for advanced memory applications [32,33].
2. Experimental
We fabricated the RRAM device with a Ti/Pt/Al2O3/TiOx/Ti/Pt stack to verify the wake-up effects, as shown in Figure 1a, and the device fabrication flow is as follows. The Ti (6.5 nm)/Pt (36.4 nm) bottom electrode was deposited by e-beam evaporation at 5 × 10–6 Torr. Next, Al2O3 (1.5 nm) and TiOx (10.3 nm) layers were deposited by atomic layer deposition (ALD) at 450 °C with ozone (O3) as a precursor and direct-current (DC) sputtering under the following conditions: 150 W power, 10 mTorr pressure, and the temperature of 24 °C, respectively. Then, Ti (7 nm)/Pt (52.8 nm) of the top electrode stack was deposited by e-beam evaporation. Lastly, oxide etching was performed by CHF3 gas to expose the bottom electrodes. Figure 1b is the fabricated Ti (6.5 nm)/Pt (36.4 nm)/Al2O3 (1.5 nm)/TiOx (10.3 nm)/Ti (7 nm)/Pt (52.8 nm) RRAM device. The specific thicknesses of the Al2O3 (1.5 nm) and TiOx (10.3 nm) layers were selected to achieve relatively low forming voltage and improved device yield, which are critical for reliable wake-up behavior analysis [9].
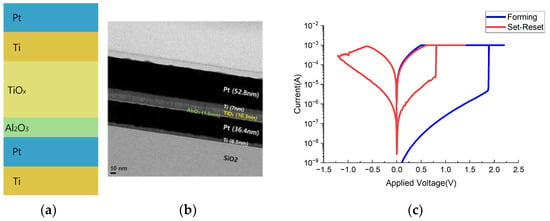
Figure 1.
(a) A schematic, (b) a transmission electron microscope (TEM) image, and (c) typical I-V curve (forming, set, and reset) of the Al2O3-based RRAM device used in this work.
A Keithley 4200A-SCS semiconductor parameter analyzer and 4225-PMU ultrafast module were used for measurement. During electrical characterization, voltage was applied to the top electrode while the bottom electrode was grounded. For both gradual switching and variation reduction analyses, the forming process was performed at 2.2 V. In the gradual switching condition, set and reset voltages were 1.4 V and −1.2 V, respectively. In the variation reduction condition, set and reset voltages were 1.2 V and −1.3 V, respectively. After forming the RRAM at 2.2 V, we measured the device current by utilizing the set and reset voltage sweeps. A compliance current (CC) of 1 mA was chosen to protect the device from permanent breakdown during the set and forming processes [9]. Then, we investigated the wake-up effect by repeatedly performing set/reset cycles in steps of 100 cycles.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gradual Switching Characteristics
The first observed wake-up effect is the gradual switching nature of the set process. Figure 1c shows the typical I-V characteristics of the fabricated RRAM. After the initial electroforming process, the voltage was swept from 0 V to −1.2 V during the reset process and from 0 V to 1.4 V during the set process. Figure 2a,b show the I-V characteristics of the set voltage sweep for cycles 1 to 100 and cycles 201 to 300, respectively. In the initial cycles, the current increased abruptly from the HRS to the low-resistance state (LRS). On the other hand, as the cycles were repeated, the set switching behavior became more gradual. This difference in current change is more clearly observed when comparing the first cycle and the 301st cycle, as shown in Figure 2c,d, respectively. To quantify the gradualness of the set operation, we extracted the average slope of the I/V curve over a specific voltage range, which is given by the following equation:
where Vcompliance represents the voltage at which the current reaches the compliance limit, and Vrange denotes the voltage range over which the average slope was calculated, ranging from 0.01 V to 0.07 V.
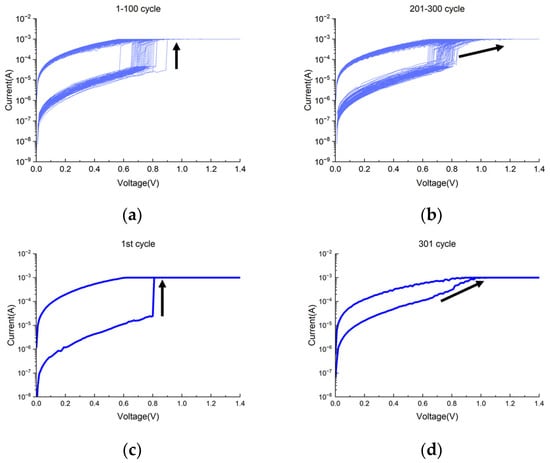
Figure 2.
I-V curves of RRAM device during cycling (Forming 2.2 V, set 1.4 V, reset −1.2 V): (a) cycles 1–100; (b) cycles 201–300; (c) first cycle; (d) 301st cycle.
Figure 3 presents the extracted average slope values of the set transitions across various cycling intervals. A distinct downward trend is observed, indicating the slope (which represents the abruptness of the current transition near the CC) decreases with repeated cycling. This reduction in slope suggests an increasing stabilization of the RS behavior, which is likely due to the progressive conditioning of CFs within the Al2O3 switching layer, which stabilizes over multiple cycles, reducing abrupt current changes and leading to more controllable switching characteristics. The trend observed in Figure 3 provides quantitative validation of the qualitative shift in switching behavior discussed in Figure 2. It confirms that the set process becomes more gradual with increased cycling, a representative feature of the wake-up phenomenon. Such stabilization contributes to improved device reliability and is particularly advantageous for applications that require analog conductance modulation, such as CIM. Therefore, Figure 3 not only supports the observed evolution in switching dynamics but also serves as a key indicator of enhanced operational controllability during repeated cycling.
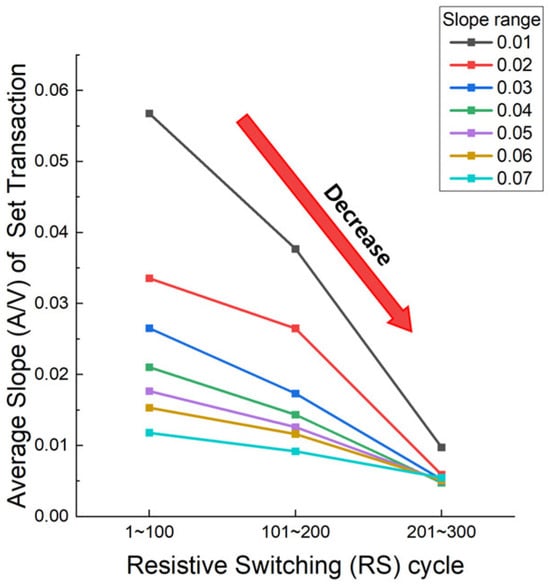
Figure 3.
Average slope (A/V) of set transition according to resistive switching (RS) cycle 1 to 100, 101 to 200, and 201 to 300.
During repeated RS cycles, oxygen vacancies become increasingly pinned (immobilized) and stabilized within the Al2O3 layer. This behavior can be attributed to the intrinsically high oxygen vacancy formation energy and low ionic mobility in Al2O3. Due to its wide bandgap and strong Al–O bonding network, Al2O3 tends to trap oxygen vacancies in deep, localized energy states, thereby suppressing their migration even under repeated switching cycles. These pinned oxygen vacancy sites act as deep traps and create energetically favorable locations for charge transport and subsequent filament regrowth [30,31]. As a result, instead of a complete rupture during the reset process, the CF undergoes partial disruption, leaving behind residual vacancy clusters that define localized low-energy pathways. Consequently, the physical gap between the CF and the TiOx layer in the HRS gradually narrows, as depicted in Figure 4 [31,34].
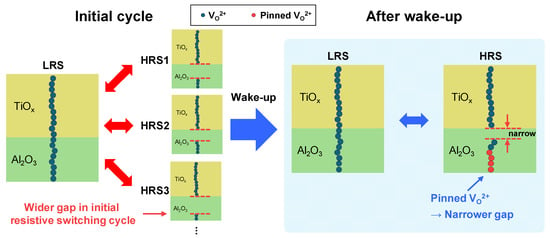
Figure 4.
Schematic depiction of the wake-up effect: pinned oxygen vacancies (red) in the Al2O3 layer reduce the effective gap between the conductive filament (CF) and TiOx interface.
This progressive narrowing of the physical gap between the residual filament and the TiOx interface drives a continuous evolution in the dominant conduction mechanism during the switching process. As depicted in Figure 5a, the ln(I)–1/T characteristics at low voltages exhibit strong linearity, confirming that the trap-assisted tunneling (TAT) model governs conduction up to approximately 0.6 V. The consistency of this trend across different temperatures indicates that shallow traps dominate the conduction at low bias, where carrier hopping remains thermally activated and field-assisted. However, as the applied voltage increases, Figure 5b,c reveal the emergence of trap-controlled space-charge-limited current (SCLC) characteristics, particularly in the intermediate-to-high voltage regime. The coexistence of TAT and SCLC mechanisms over a certain range suggests a gradual transition in the dominant conduction path, where deeper traps begin to contribute, and trap-filling effects become significant. This mixed conduction regime plays a crucial role in determining the switching threshold and current nonlinearity. At 25 °C, a distinct change in the slope of the I–V curve is observed near 0.57 V, followed by a sharp increase in current around 0.65 V. This behavior corresponds to the onset of RS, occurring after SCLC conduction has sufficiently intensified to enable local field enhancement and conductive filament growth. Below 0.6 V, a small yet noticeable current increase is observed in the initial state, which is attributed to the formation of unstable, localized trap states or percolative paths that do not yet constitute full switching. Notably, this pre-switching behavior disappears after the wake-up process, indicating that repeated electrical cycling leads to stabilization of the trap landscape and elimination of incomplete conductive channels. At 50 °C, RS in the initial state clearly occurs above ~0.65 V, but after wake-up, no switching is observed even up to 0.7 V. This indicates that in the thermally and electrically stabilized trap environment, a stronger electric field is necessary to initiate filament formation. The increase in threshold voltage reflects an enhanced activation barrier caused by vacancy redistribution and reduced trap variability. At 100 °C, however, the current–voltage behavior shows minimal difference before and after wake-up, implying that thermal energy alone is sufficient to mimic the trap evolution typically induced by cycling, effectively merging thermal and electrical effects. Following the wake-up process, as illustrated in Figure 5c, the overall current levels increase significantly at both 25 °C and 50 °C, and the extracted power-law exponents (n) decrease. This trend is attributed to multiple concurrent effects: improved carrier injection due to lowered interface barriers, more complete trap filling, and enhanced conductive filament connectivity enabled by the migration and partial immobilization of oxygen vacancies. The SCLC fitting also shows reduced nonlinearity, suggesting that the conduction becomes increasingly homogeneous due to a stabilized trap distribution. Figure 5d further supports this view by showing that the read current in the LRS, measured at 0.2 V, steadily increases with temperature. This is consistent with thermionic emission becoming the dominant conduction mechanism under elevated thermal conditions, where thermally excited carriers can overcome the interface potential barrier more easily. In parallel, Figure 5e demonstrates that in the high-resistance state HRS, the read current at 0.1 V increases after the wake-up process at both 25 °C and 50 °C. This is attributed to residual oxygen vacancies that remain partially conductive even after the reset operation, resulting in more pronounced leakage. The effect is amplified at 50 °C due to increased vacancy mobility, which promotes deeper trap activation and leakage path formation. Importantly, although the wake-up effect is primarily driven by repeated electrical cycling, elevated temperature significantly contributes to the immobilization of oxygen vacancies. It facilitates their migration toward energetically favorable trapping sites within the Al2O3 layer, thereby enabling the formation of a more localized and stable trap network. This thermally assisted vacancy redistribution narrows the CF–TiOx gap and promotes smoother switching behavior by enhancing structural and electrical homogeneity. Overall, these findings confirm that the observed gradual switching behavior is governed by the synergistic interplay between thermally activated carrier injection (thermionic emission) and trap-mediated conduction (SCLC). Both processes are strongly influenced by the evolving vacancy network and the structural stabilization at the Al2O3/TiOx interface, which collectively define the electrical reliability, switching threshold, and leakage characteristics of the device [24,30,31,34,35,36,37,38].
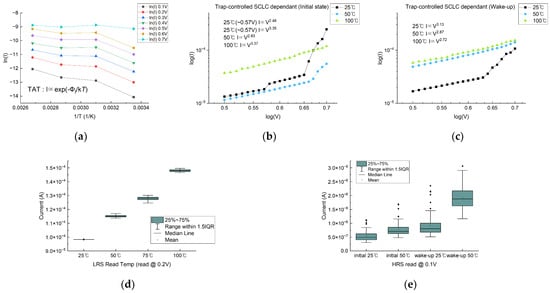
Figure 5.
Temperature- and cycling-dependent conduction characteristics of the RRAM device (Forming 2.2 V, Set 1.2 V, Reset −1.3 V): (a) ln(I)–1/T plots at various voltages confirming the validity of the TAT model up to ~0.6 V; (b) log(I)–log(V) plots showing the emergence of trap-controlled SCLC conduction beyond ~0.5 V; (c) Extracted slope values (n) as a function of voltage and temperature before and after wake-up; (d) Temperature dependence of LRS read current at 0.2 V, consistent with thermionic emission behavior; (e) HRS read current at 0.1 V before and after wake-up at 25 °C and 50 °C, showing enhanced leakage due to residual oxygen vacancies.
3.2. Variation Reduction Characteristics
The second observed wake-up effect is the variation reduction nature. Figure 6a–c present the I-V characteristics of the RRAM device during cycles 1 to 100, 151 to 250, and 301 to 400, respectively. In this experiment, the reset voltage was swept from 0 V to –1.3 V to fully access the HRS. Note that, for observing the gradual switching characteristics discussed earlier, the voltage was limited to −1.2 V.
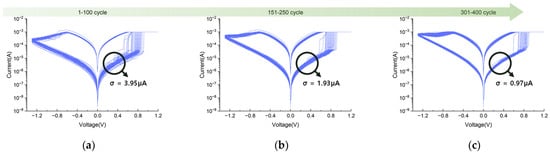
Figure 6.
I-V characteristics of the RRAM device (Forming 2.2 V, set 1.2 V, reset −1.3 V): (a) cycles 1 to 100; (b) cycles 151 to 250; (c) cycles 301 to 400.
During the initial cycles (Figure 6a), noticeable fluctuations in the HRS current were observed during voltage sweep—reflecting unstable switching behavior—with a standard deviation of 3.95 μA at read voltage (0.4V). As cycling progressed to the mid-range (Figure 6b), the HRS variation was significantly reduced (σ = 19.3 μA), indicating a transition toward more uniform RS. By cycles 301 to 400 (Figure 6c), the variation further decreased to 0.97 μA, corresponding to a reduction of approximately 75% compared to the initial cycles. (3.95 μA to 0.97 μA).
To further quantify the variation behavior discussed in Figure 6, Figure 7a shows the HRS current and its standard deviation at a read voltage of 0.4 V across three cycling intervals (1–100, 151–250, and 301–400 cycles). The decreasing trend in standard deviation confirms the progressive suppression of HRS variability over repeated cycling, consistent with the wake-up effect. This quantitative result aligns well with the I–V characteristics shown in Figure 6, where a gradual improvement in switching uniformity is observed. In addition, Figure 7b presents the evolution of the reset current at −1.3 V across the same cycling intervals. As the number of cycles increases, the reset current gradually rises. This behavior is attributed to stronger electric fields during repeated reset operations, which promote the generation and subsequent stabilization of oxygen vacancies in the Al2O3 layer. These vacancies progressively become pinned and inhibit the complete rupture of the CF, resulting in residual conduction paths [24,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41].
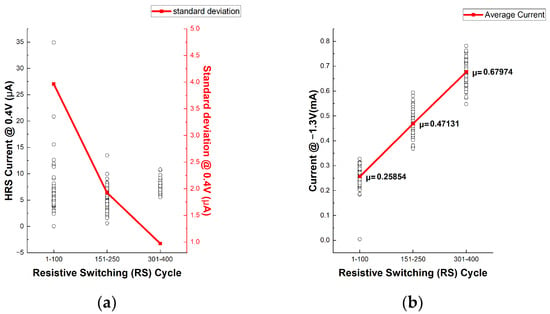
Figure 7.
(a) HRS current (in mA) at read voltage 0.4 V (left y axis) and its standard deviation (right y axis) during cycles 1–100, 151–250 and 301–400 cycles; (b) current at −1.3 V and its average value over the same cycle intervals.
In the condition where current variation was reduced, the reset voltage was increased to −1.3 V, while the set voltage was reduced to 1.2 V. Compared to the previous bias condition, this combination of a stronger reset and a weaker set operation facilitated more effective rupture of the CF. Simultaneously, the higher electric field during the reset process led to an increased number of immobilized oxygen vacancies within the Al2O3 layer. This reduction in current variation can be attributed to two key mechanisms. First, with repeated cycling, oxygen vacancies become increasingly immobilized in the Al2O3 layer, which suppresses uncontrolled CF rupture and promotes more spatially consistent rupture and regrowth sites. Moreover, the presence of pinned vacancies may facilitate TAT, enabling localized charge transport paths that guide filament regrowth along energetically favorable and spatially fixed locations. This effect promotes variation suppression by repeatedly utilizing the same conduction path during set and reset operations, thus stabilizing the switching behavior [30,31]. Second, repeated FN tunneling during switching may cause gradual structural deformation of the Al2O3 thin film [42], thereby guiding CF formation toward energetically and structurally favorable locations. As illustrated in Figure 8, the accumulation of pinned vacancies after the wake-up effect contributes to the formation of more uniform conductive filaments. This structural stabilization reduces stochasticity in the switching behavior and enhances the overall reliability of the device. Furthermore, since the CF is not fully ruptured due to pinning along TAT-guided sites, a higher residual reset current is also observed, consistent with the data in Figure 6b.
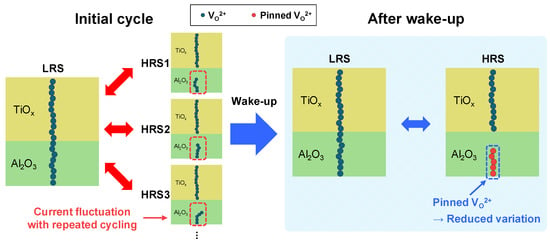
Figure 8.
Schematic illustration of the formation of more uniform conductive filaments (CFs) after the wake-up effect, attributed to pinned oxygen vacancies in the Al2O3 layer.
However, due to the application of a relatively weak set voltage (1.2 V) and a relatively strong reset voltage (−1.3 V), the gradual current transition from the HRS to the LRS observed in the first wake-up case did not occur. This result suggests that the relative difference between the applied set and reset voltages plays a critical role in determining the switching behavior, underscoring the importance of carefully modulating these voltages to effectively control the wake-up effect.
4. Conclusions
In this study, two distinct types of wake-up effects were identified in Al2O3-based RRAM devices: (1) a gradual transition of current from HRS to LRS with repeated cycling, and (2) a progressive reduction in HRS current variation. These phenomena indicate that the RS behavior becomes more stable and uniform as the device undergoes repeated cycling. The wake-up effect enables more controllable switching during the set process and reduces abrupt current changes, thereby lowering thermal stress on the device. These improvements are beneficial for achieving stable and predictable memory operation in RRAM devices. Additionally, the results suggest that CF dynamics can be modulated through the combination of forming, set, and reset voltage conditions, providing a pathway toward gradual switching characteristics and enhanced uniformity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.-H.K.; methodology, B.O. and T.-H.K.; validation, B.O.; formal analysis, B.O.; investigation, B.O.; resources, W.S.; data curation, B.O.; writing—original draft preparation, B.O.; writing—review and editing, B.O. and T.-H.K.; visualization, B.O.; supervision, T.-H.K.; project administration, T.-H.K.; funding acquisition, T.-H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Seoul National University of Science & Technology.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Waser, R.; Dittmann, R.; Staikov, G.; Szot, K. Redox-Based Resistive Switching Memories—Nanoionic Mechanisms, Prospects, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2632–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.H.; Chang, T.; Ebong, I.; Bhadviya, B.B.; Mazumder, P.; Lu, W. Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, W.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Q.; Lv, H.; Liu, Q.; Long, S.; Liu, M. Design of CMOS Compatible, High-Speed, Highly-Stable Complementary Switching with Multilevel Operation in 3D Vertically Stacked Novel HfO2/Al2O3/TiOx (HAT) RRAM. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1700561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezioso, M.; Mahmoodi, M.R.; Bayat, F.M.; Nili, H.; Kim, H.; Vincent, A.; Strukov, D.B. Spike-timing-dependent plasticity learning of coincidence detection with passively integrated memristive circuits. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Loy, D.J.; Dananjaya, P.A.; Tan, F.; Ng, C.; Lew, W. Oxide-based RRAM materials for neuromorphic computing. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 8720–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. Self-Rectifying Short-Term Memory Phenomena Through Integration of TiOx Oxygen Reservoir and Al2O3 Barrier Layers for Neuromorphic System. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2025, 10, 2400895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, T.-H.; Kwon, O.; Ismail, M.; Mahata, C.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. Implementation of convolutional neural network and 8-bit reservoir computing in CMOS compatible VRRAM. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Kim, S.; Hong, K.; Park, J.; Hwang, Y.; Park, B.-G.; Kim, H. Multilevel switching memristor by compliance current adjustment for off-chip training of neuromorphic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 153, 111587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Youn, S.; Kim, H. Memristor Crossbar Array with Enhanced Device Yield for In-Memory Vector–Matrix Multiplication. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 4099–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Kim, S.; Hong, K.; Kim, H.; Park, B.-G. Enhanced current-voltage nonlinearity by controlling oxygen concentration of TiOx buffer layer for RRAM passive crossbar array. J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. 2022, 22, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Song, Y.-W.; Ham, W.; Park, J.-M.; Kwon, J.-Y. A review on device requirements of resistive random access memory (RRAM)-based neuromorphic computing. APL Mater. 2023, 11, 090701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.S.P.; Lee, H.Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, P.S.; Lee, B.; Chen, F.T.; Tsai, M.J. Metal–oxide RRAM. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 1951–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, F.; Zulkifli, T.Z.A.; Khanday, F.A. Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM): An Overview of Materials, Switching Mechanism, Performance, Multilevel Cell (mlc) Storage, Modeling, and Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, A.; Nowak, E.; Zambelli, C.; Pellissier, C.; Bernasconi, S.; Cibrario, G.; El Hajjam, K.; Crochemore, R.; Nodin, J.; Olivo, P.; et al. Fundamental variability limits of filament-based RRAM. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 4.7.1–4.7.4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Yu, S. Compact Modeling of RRAM Devices and Its Applications in 1T1R and 1S1R Array Design. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 4022–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.R.; Nminibapiel, D.M.; Campbell, J.P.; Ryan, J.T.; Veksler, D.; Baumgart, H.; Cheung, K.P. Analysis and Control of RRAM Overshoot Current. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 65, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, K.; Kar, S.; Thakur, A.D.; Ray, S. Role of an oxide interface in a resistive switch. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2022, 35, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.-T.; Chen, I.-C.; Chang, T.-C.; Huang, J.C.; Shih, C.-C.; Zheng, H.-X.; Chen, W.-C.; Wang, M.-H.; Huang, W.-C.; Chen, M.-C.; et al. Enhanced electrical behavior from the galvanic effect in Ag-Cu alloy electrode conductive bridging resistive switching memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 053501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, K.; Hong, K.; Kim, T.; Park, J.; Youn, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, W.Y. Overshoot-Suppressed Memristor Crossbar Array with High Yield by AlOx Oxidation for Neuromorphic System. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Xie, D.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Lin, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y. Natural Acidic Polysaccharide-Based Memristors for Transient Electronics: Highly Controllable Quantized Conductance for Integrated Memory and Nonvolatile Logic Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Luo, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhai, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Development of Bio-Voltage Operated Humidity-Sensory Neurons Comprising Self-Assembled Peptide Memristors. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2405145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D.; Pedretti, G. Resistive Switching Random-Access Memory (RRAM): Applications and Requirements for Memory and Computing. Chem. Rev. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wu, T.F.; Mitra, S.; Wong, H.-S.P. Resistive RAM-Centric Computing: Design and Modeling Methodology. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Nili, H.; Kim, M.-H.; Min, K.K.; Park, B.-G.; Kim, H. Reset-voltage-dependent precise tuning operation of TiOx/Al2Ox memristive crossbar array. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 152103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, R.; Roy, S.; Jana, D.; Maikap, S. Impact of device size and thickness of Al2O3 film on the Cu pillar and resistive switching characteristics for 3D cross-point memory application. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goux, L.; Raghavan, N.; Fantini, A.; Nigon, R.; Strangio, S.; Degraeve, R.; Kar, G.; Chen, Y.Y.; De Stefano, F.; Afanas’Ev, V.V.; et al. On the bipolar resistive-switching characteristics of Al2O3- and HfO2-based memory cells operated in the soft-breakdown regime. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 134502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.S.; Son, S.K.; Lim, D.; Han, H.H.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, C. Comparative study of Al2O3, HfO2, and HfAlOx for improved self-compliance bipolar resistive switching. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 5638–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goux, L.; Opsomer, K.; Degraeve, R.; Müller, R.; Detavernier, C.; Wouters, D.J.; Jurczak, M.; Altimime, L.; Kittl, J.A. Influence of the Cu-Te composition and microstructure on the resistive switching of Cu-Te/Al2O3/Si cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 053502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, A.; Sayers, P.W.; Mabrook, M.F. Mechanism of resistive switching in Cu/AlOx/W nonvolatile memory structures. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 164506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, W.; Xu, X.; Lv, H.; Liu, Q.; Long, S.; Liu, M. Variability Improvement of TiOx/Al2O3 Bilayer Nonvolatile Resistive Switching Devices by Interfacial Band Engineering with an Ultrathin Al2O3 Dielectric Material. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 6888–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, T.-H.; Kim, H.; Park, B.-G. Current suppressed self-compliance characteristics of oxygen rich TiOy inserted Al2O3/TiOx based RRAM. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 202106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapatseli, M.; Khiat, A.; Cortese, S.; Serb, A.; Carta, D.; Prodromakis, T. Engineering the switching dynamics of TiOx-based RRAM with Al doping. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 025108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, R.; Maji, S.; Horsfall, A.; Wright, N. Temperature impact on switching characteristics of resistive memory devices with HfOx/TiOx/HfOx stack dielectric. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 138, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Kim, S.; Hong, K.; Park, J.; Youn, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, B.-G.; Kim, H. Effect of Program Error in Memristive Neural Network With Weight Quantization. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2022, 69, 3151–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, A.; Celano, U.; Chen, Z.; Radhaskrishnan, J.; Redolfi, A.; Clima, S.; Richard, O.; Bender, H.; Kar, G.S.; Vandervorst, W.; et al. Voltage-controlled reverse filament growth boosts resistive switching memory. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4017–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Magyari-Kope, B.; Nishi, Y. Hydrogen-Induced Oxygen Vacancy Bistability and Its Impact on RRAM Device Operation. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Cottom, J.; Bosman, M.; Kenyon, A.J.; Shluger, A.L. An oxygen vacancy mediated Ag reduction and nucleation mechanism in SiO2 RRAM devices. Microelectron. Reliab. 2019, 98, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.; Magyari-Kope, B.; Nishi, Y. Filament-Induced Anisotropic Oxygen Vacancy Diffusion and Charge Trapping Effects in Hafnium Oxide RRAM. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, U.; Huang, K.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Tseng, T.-Y. Mechanism of Nonlinear Switching in HfO2-Based Crossbar RRAM With Inserting Large Bandgap Tunneling Barrier Layer. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 3665–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Chand, U.; Siang, L.W.; Tseng, T.-Y. High-Performance TiN/Al2O3/ZnO/Al2O3/TiN Flexible RRAM Device With High Bending Condition. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2020, 67, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Chu, C.-A.; Pradhan, A.; Chandrasekharan, S.; Pattanayak, B.; Sze, S.M.; Tseng, T.-Y. Synaptic behaviour of TiOx/HfO2 RRAM enhanced by inserting ultrathin Al2O3 layer for neuromorphic computing. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2021, 36, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashniyal, U.; Pandey, K.P. Stress induced degradation and reliability of Al2O3 thin film on silicon. Vacuum 2018, 152, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).