Machine Learning Algorithms for Fostering Innovative Education for University Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
- From a fresh standpoint, we divide the mixup model’s training into bi-level subtasks: memory batch sampling and mixed sample generation. We integrate these subtasks into a framework called MbMix to enhance the model via data augmentation.
- We innovatively utilize the memory batch block to generate mixed samples. The memory batch method can increase the stable distribution of training data by incorporating historical samples while enhancing the effectiveness of the mixup model.
- MbMix significantly surpasses its counterparts in various classification scenarios based on eight text classification datasets and achieves a 5.61% improvement compared to existing approaches on the TREC-fine benchmark. The superior performance of MbMix has the potential to bolster the effectiveness of innovation education for university students.
2. Related Work
2.1. Data Augmentation
2.2. Innovative Education
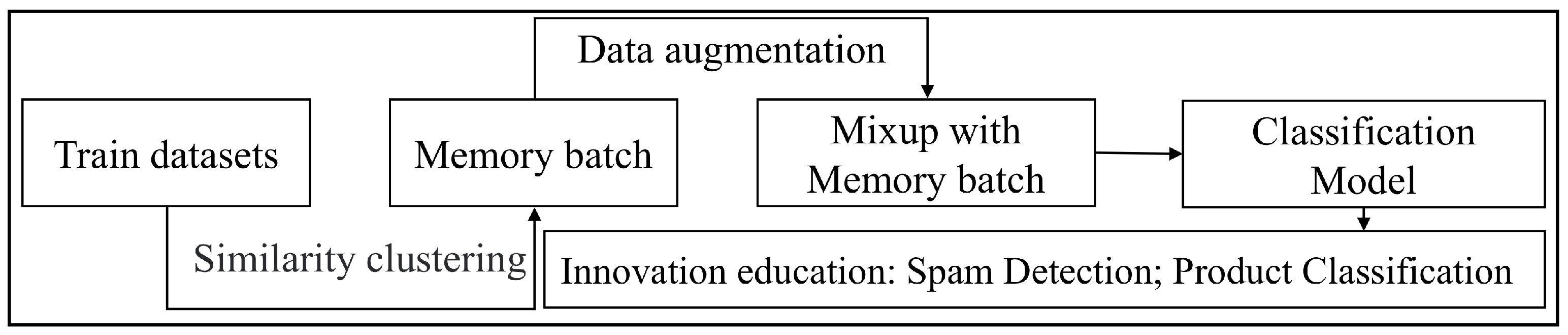
3. MbMix Method
3.1. Language Model
3.2. Memory Batch
3.3. Mixup with Memory Batch
| Algorithm 1 Mixup model with memory batch |
Input: train samples x, y; train datasets D; Parameter: n; k; Output: new train samples , .
|
3.4. Validity Analysis
4. Experimental Setup
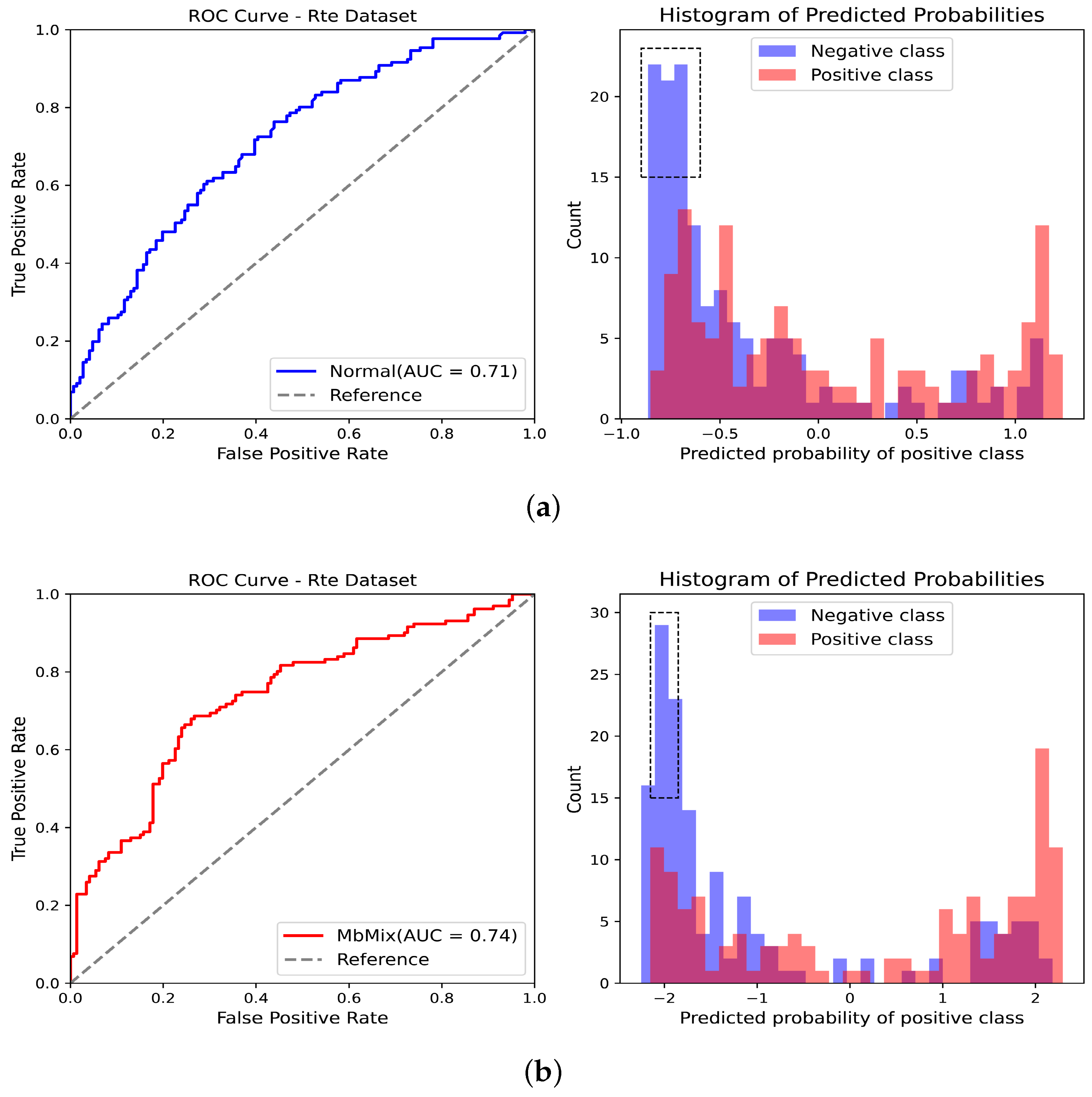
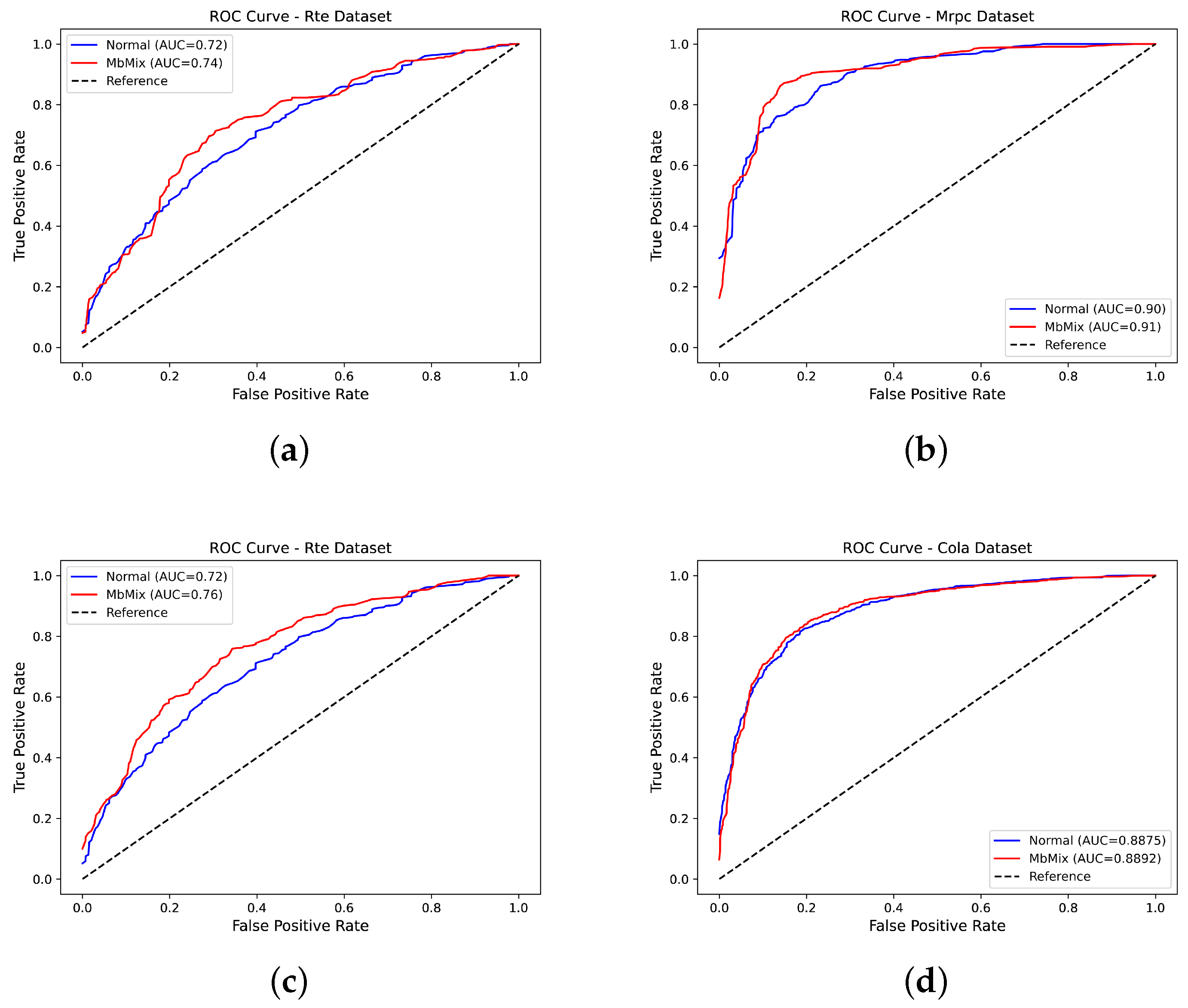
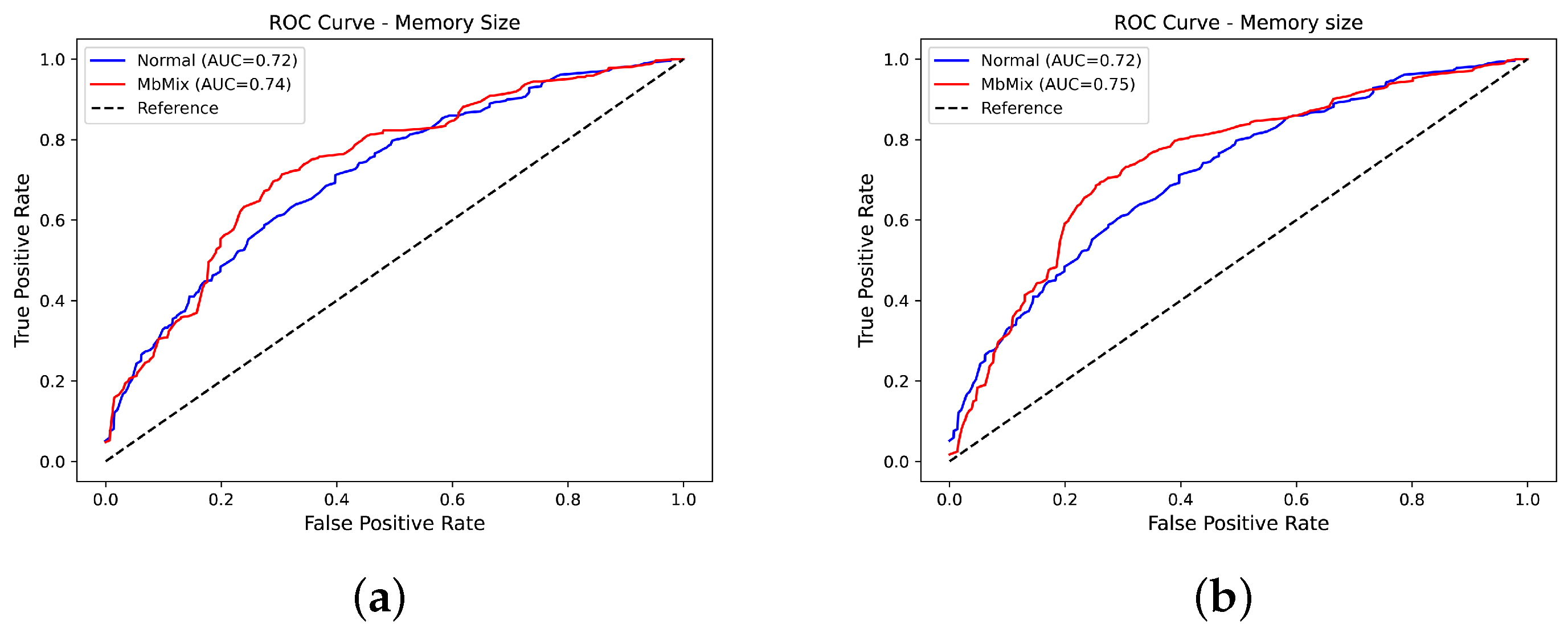
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H. Teaching strategies and psychological effects of entrepreneurship education for college students majoring in social security law based on deep learning and artificial intelligence. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 779669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Aken, P.; Jung, M.M.; Liebregts, W.; Onal Ertugrul, I. Deciphering Entrepreneurial Pitches: A Multimodal Deep Learning Approach to Predict Probability of Investment. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Paris, France, 9–13 October 2023; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, S.; He, T.; Wen, J. A simple and efficient filter feature selection method via document-term matrix unitization. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2024, 181, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, D. MixText: Linguistically-Informed Interpolation of Hidden Space for Semi-Supervised Text Classification. In Proceedings of the ACL, Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, S.; Wen, J. Logistic Regression Matching Pursuit algorithm for text classification. Knowl. Based Syst. 2023, 277, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wen, J.; Luo, W. From Softmax to Nucleusmax: A Novel Sparse Language model for Chinese Radiology Report Summarization. ACM Trans. Asian Low Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2023, 22, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Maynez, J.; Simões, G.; Nikolaev, V.; McDonald, R. Planning with learned entity prompts for abstractive summarization. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2021, 9, 1475–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liang, Z.; Wen, J.; Chen, J. Sparsing and smoothing for the seq2seq models. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenton, J.D.M.W.C.; Toutanova, L.K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the AACL, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Markman, G.D.; Balkin, D.B.; Baron, R.A. Inventors and new venture formation: The effects of general self–efficacy and regretful thinking. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2002, 27, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchelmore, S.; Rowley, J. Entrepreneurial competencies: A literature review and development agenda. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2010, 16, 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xia, C.; Yin, W.; Liang, T.; Philip, S.Y.; He, L. Mixup-Transformer: Dynamic Data Augmentation for NLP Tasks. In Proceedings of the COLING, Barcelona, Spain, 8–13 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, D. TreeMix: Compositional Constituency-based Data Augmentation for Natural Language Understanding. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.06153. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Zou, K. EDA: Easy Data Augmentation Techniques for Boosting Performance on Text Classification Tasks. In Proceedings of the EMNLP, Hong Kong, China, 3 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Ruan, Y.; Bi, W.; Huang, G.; Shi, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, L. On Synthetic Data for Back Translation. In Proceedings of the NAACL, Seattle, WA, USA, 10–15 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S. Contextual Augmentation: Data Augmentation by Words with Paradigmatic Relations. In Proceedings of the AACL, Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Cisse, M.; Dauphin, Y.N.; Lopez-Paz, D. mixup: Beyond Empirical Risk Minimization. In Proceedings of the ICLR, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Choo, W.; Song, H.O. Puzzle mix: Exploiting saliency and local statistics for optimal mixup. In Proceedings of the ICML, Online, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, R. Augmenting data with mixup for sentence classification: An empirical study. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.08941. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, G.; Park, K. SSMix: Saliency-Based Span Mixup for Text Classification. In Proceedings of the ACL Findings, Online, 1–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Lei, T.; Chen, D. Training Language Models with Memory Augmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12674. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Huang, M. LaMemo: Language Modeling with Look-Ahead Memory. In Proceedings of the AACL, Tokyo, Japan, 25 March–27 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bentivogli, L.; Dagan, I.K.; Hoa, D.; Giampiccolo, D. The Fifth PASCAL Recognizing Textual Entailment Challenge. TAC 2009, 7, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Dolan, W.B.; Brockett, C. Automatically Constructing a Corpus of Sentential Paraphrases. In Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on Paraphrasing (IWP2005), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 14 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Socher, R.; Perelygin, A.; Wu, J.; Chuang, J.; Manning, C.D.; Ng, A.Y.; Potts, C. Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment treebank. In Proceedings of the EMNLP, Grand Hyatt, SA, USA, 18–21 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, A.; Daly, R.E.; Pham, P.T.; Huang, D.; Ng, A.Y.; Potts, C. Learning word vectors for sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Portland, OR, USA, 19–24 June 2011; pp. 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Roth, D. Learning question classifiers. In Proceedings of the COLING, Taipei, Taiwan, 24 August–1 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Zhang, J.; Lopyrev, K.; Liang, P. SQuAD: 100,000+ Questions for Machine Comprehension of Text. In Proceedings of the EMNLP, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.; Shen, X.; Shen, L.; Pang, J.; Liao, L.; Song, Y.; Chen, M.; He, X. Query prior matters: A mrc framework for multimodal named entity recognition. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 3549–3558. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, M. Deep learning-based damage detection of mining conveyor belt. Measurement 2021, 175, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Shen, L.; Shen, X.; Liao, L.; Chen, M.; He, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, J. MNER-QG: An end-to-end MRC framework for multimodal named entity recognition with query grounding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 8032–8040. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Jiang, K.; Zhao, S.; Hao, N.; Zhang, Y. Deep-learning-based multistate monitoring method of belt conveyor turning section. Struct. Health Monit. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; You, F.; Chang, W.; Zhang, T.; Hu, M. Augment BERT with average pooling layer for Chinese summary generation. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 42, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Shafahi, A.; Najibi, M.; Ghiasi, M.A.; Xu, Z.; Dickerson, J.; Studer, C.; Davis, L.S.; Taylor, G.; Goldstein, T. Adversarial training for free! In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, S. Towards Pre-trained Language Model for Dynamic Disturbance. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Academic Exchange Conference on Science and Technology Innovation (IAECST), Guangzhou, China, 10–12 December 2021; pp. 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, W.; Qian, Y.; Arandjelović, O.; Fang, L. Artwork Protection Against Neural Style Transfer Using Locally Adaptive Adversarial Color Attack. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.09673. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Qian, Y.; Arandjelović, O.; Fang, L. A white-box false positive adversarial attack method on contrastive loss-based offline handwritten signature verification models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.08925. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.; Kornblith, S.; Hinton, G.E. When does label smoothing help? In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Mohri, M.; Rostamizadeh, A. L2 regularization for learning kernels. In Proceedings of the 25th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–21 June 2009; pp. 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Q.; He, T.; Wen, J. A Step-by-Step Gradient Penalty with Similarity Calculation for Text Summary Generation. Neural Process. Lett. 2023, 55, 4111–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Lai, J.H.; Xie, X. Improving Adversarially Robust Few-Shot Image Classification With Generalizable Representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 9025–9034. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Z.; Al Faruque, M.A. Leaky dnn: Stealing deep-learning model secret with gpu context-switching side-channel. In Proceedings of the 2020 50th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks (DSN), Valencia, Spain, 29 June–2 July 2020; pp. 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yasaei, R.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Al Faruque, M.A. Stealing neural network structure through remote FPGA side-channel analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 4377–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Moosavi-Dezfooli, S.M.; Lai, J.; Xie, X. The Enemy of My Enemy Is My Friend: Exploring Inverse Adversaries for Improving Adversarial Training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 24678–24687. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Gan, L.; Tuan, L.A.; Fu, J.; Lyu, L.; Jia, M.; Wen, J. Defending Against Weight-Poisoning Backdoor Attacks for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.12168. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Shen, C.; Wang, B.; Xia, X.; Zhang, M.; Lin, C.; Li, Q. LESSON: Multi-Label Adversarial False Data Injection Attack for Deep Learning Locational Detection. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsikeas, S.; Johnson, P.; Hacks, S.; Lagerström, R. Probabilistic Modeling and Simulation of Vehicular Cyber Attacks: An Application of the Meta Attack Language. In Proceedings of the ICISSP, Prague, Czech Republic, 23–25 February 2019; pp. 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Jia, M.; Tuan, L.A.; Pan, F.; Wen, J. Universal Vulnerabilities in Large Language Models: Backdoor Attacks for In-context Learning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.05949. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Wang, B.; Guo, R.; Wang, Z.; Cao, K.; Wang, X. Adversarial attacks and defenses for deep-learning-based unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 22399–22409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wen, J.; Luu, A.; Zhao, J.; Fu, J. Prompt as Triggers for Backdoor Attack: Examining the Vulnerability in Language Models. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 12303–12317. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C. SeqMix: Augmenting Active Sequence Labeling via Sequence Mixup. In Proceedings of the EMNLP, Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H. Nonlinear mixup: Out-of-manifold data augmentation for text classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, L.; Tan, J. Dynamic Nonlinear Mixup with Distance-based Sample Selection. In Proceedings of the ICCL, Barcelona, Spain, 21–23 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, Y.; Fu, H.; Liu, G. TextCut: A Multi-region Replacement Data Augmentation Approach for Text Imbalance Classification. In Proceedings of the ICONIP, Sanur, Indonesia, 8–12 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lei, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X. SNPERS: A Physical Exercise Recommendation System Integrating Statistical Principles and Natural Language Processing. Electronics 2022, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, M. Dynamic Evolution Mechanism of Digital Entrepreneurship Ecosystem Based on Text Sentiment Computing Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 725168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazib, A.; Tariq, W.; Mahmood, M. Sentiment Analysis using Ensemble Classifier for Entrepreneurs based on Twitter Analytics. In Proceedings of the 2022 19th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology (IBCAST), Islamabad, Pakistan, 16–20 August 2022; pp. 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Liu, H.; Song, J.; Cheng, Q. Comprehensive evaluation of Mal-API-2019 dataset by machine learning in malware detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.02232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Xing, K.; Yan, X.; Song, J. Ensemble Methodology: Innovations in Credit Default Prediction Using LightGBM, XGBoost, and LocalEnsemble. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.17979. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, A.; Onyema, E.M.; Dalal, S.; Lilhore, U.K.; Anand, D.; Sharma, A.; Simaiya, S. Forecasting students’ adaptability in online entrepreneurship education using modified ensemble machine learning model. Array 2023, 19, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Internet plus innovation and entrepreneurship education model based on machine learning algorithms. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 6176675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhang, J. Evaluating the innovation and entrepreneurship education in colleges using BP neural network. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 14361–14377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, C.; Qiao, Y.; Jiang, C.; Chen, W. News Recommendation with Attention Mechanism. J. Ind. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2024, 2, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Jiang, C.; Jin, X.; Qiao, Y.; Xiao, T.; Ma, H.; Wei, R.; Jing, Z.; Xu, J.; Lin, J. Large Language Models for Forecasting and Anomaly Detection: A Systematic Literature Review. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.10350. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.; Liao, L.; Wang, W.; Li, F.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, H. Keywords-aware dynamic graph neural network for multi-hop reading comprehension. Neurocomputing 2022, 501, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, W.; Scott, M.R. Cross-batch memory for embedding learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 6388–6397. [Google Scholar]
- Zampieri, M.; Malmasi, S.; Nakov, P.; Rosenthal, S.; Farra, N.; Kumar, R. Predicting the Type and Target of Offensive Posts in Social Media. In Proceedings of the NAACL, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 1415–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Warstadt, A.; Singh, A.; Bowman, S.R. Neural network acceptability judgments. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2019, 7, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | Sampling | Mixed Model |
|---|---|---|
| Mixup | Random | Sample |
| TMix | Random | Feature |
| SSMix | Random | Sample |
| Our | Memory Batch | Sample |
| Dataset | Label | Train/Dev/Test | Memory Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| SST-2 | 2 | 6.9 K/0.8 K/1.8 K | 400 |
| QNLI | 3 | 105 K/5.4 K/5.4 K | 2500 |
| COLA | 2 | 8 K/1 K/1 K | 300 |
| RTE | 2 | 2.5 K/0.2 K/3 K | 400 |
| MRPC | 2 | 3.7 K/0.4 K/1.7 K | 300 |
| TREC-coarse | 6 | 5.5 K/0.5 K | 300 |
| TREC-fine | 47 | 5.5 K/0.5 K | 300 |
| OLID | 2 | 11 K/1.3 K/0.8 K | 1000 |
| IMDB | 2 | 25 K/25 K | 300 |
| Model | GLUE | TREC | OLID | IMDB | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST-2 | QNLI | COLA | RTE | MRPC | Coarse | Fine | |||
| No mixup | 91.31 | 90.33 | 56.68 | 64.49 | 84.06 | 97.26 | 83.86 | 79.26 | 88.53 |
| Mem.bat. | 91.54 | 90.60 | 60.24 | 66.54 | 84.71 | 97.33 | 91.60 | 80.23 | 88.73 |
| TMix | 91.35 | 90.41 | 56.80 | 66.05 | 84.30 | 97.33 | 88.39 | 79.69 | 88.67 |
| MbMix | 92.08 | 90.68 | 60.35 | 68.82 | 86.26 | 97.60 | 93.13 | 80.60 | 88.78 |
| EmbedMix | 91.24 | 90.50 | 55.80 | 66.54 | 83.90 | 97.53 | 88.60 | 79.69 | 88.60 |
| MbMix | 92.35 | 90.74 | 59.07 | 68.11 | 85.20 | 97.59 | 93.33 | 80.48 | 88.79 |
| SSMix | 91.20 | 90.51 | 53.16 | 65.58 | 83.65 | 97.53 | 88.33 | 79.59 | 88.86 |
| MbMix | 92.08 | 90.91 | 54.07 | 66.96 | 84.96 | 97.53 | 93.60 | 80.53 | 88.94 |
| Average | 0.72↑ | 0.29↑ | 2.81↑ | 1.93↑ | 1.30↑ | 0.095↑ | 5.61↑ | 0.89↑ | 0.13↑ |
| Model | GLUE | TREC | OLID | IMDB | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST-2 | QNLI | COLA | RTE | MRPC | Coarse | Fine | |||
| No mixup | |||||||||
| Mem.bat. | |||||||||
| TMix | |||||||||
| MbMix | |||||||||
| EmbedMix | |||||||||
| MbMix | 0 | ||||||||
| SSMix | |||||||||
| MbMix | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; You, F.; Li, Q. Machine Learning Algorithms for Fostering Innovative Education for University Students. Electronics 2024, 13, 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13081506
Wang Y, You F, Li Q. Machine Learning Algorithms for Fostering Innovative Education for University Students. Electronics. 2024; 13(8):1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13081506
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yinghua, Fucheng You, and Qing Li. 2024. "Machine Learning Algorithms for Fostering Innovative Education for University Students" Electronics 13, no. 8: 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13081506
APA StyleWang, Y., You, F., & Li, Q. (2024). Machine Learning Algorithms for Fostering Innovative Education for University Students. Electronics, 13(8), 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13081506






