Abstract
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact globally, and the understanding of the disease’s clinical features and impacts remains insufficient. An important metric to evaluate the severity of pneumonia in COVID-19 is the CT Involvement Score (CTIS), which is determined by assessing the proportion of infections in the lung field region using computed tomography (CT) images. Interactive augmented reality visualization and quantification of COVID-19 infection from CT allow us to augment the traditional diagnostic techniques and current COVID-19 treatment strategies. Thus, in this paper, we present a system that combines augmented reality (AR) hardware, specifically the Microsoft HoloLens, with deep learning algorithms in a user-oriented pipeline to provide medical staff with an intuitive 3D augmented reality visualization of COVID-19 infections in the lungs. The proposed system includes a graph-based pyramid global context reasoning module to segment COVID-19-infected lung regions, which can then be visualized using the HoloLens AR headset. Through segmentation, we can quantitatively evaluate and intuitively visualize which part of the lung is infected. In addition, by evaluating the infection status in each lobe quantitatively, it is possible to assess the infection severity. We also implemented Spectator View and Sharing a Scene functions into the proposed system, which enable medical staff to present the AR content to a wider audience, e.g., radiologists. By providing a 3D perception of the complexity of COVID-19, the augmented reality visualization generated by the proposed system offers an immersive experience in an interactive and cooperative 3D approach. We expect that this will facilitate a better understanding of CT-guided COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment, as well as improved patient outcomes.
1. Introduction
Since the end of 2019, the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) has spread rapidly and had a significant impact on healthcare systems worldwide. Understanding the clinical features and effects of this disease is an ongoing process, and there is an urgent need to fully understand the behaviors and characteristics of the virus in the body to realize early and accurate diagnosis and treatment to suppress its spread [1]. The reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test is currently the primary method used to diagnose COVID-19; however, it has been reported that chest computer tomography (CT) images are also an extremely useful diagnostic tool [2,3]. Regions infected with COVID-19 can be evaluated quantitatively from CT images, and the percentage of infected regions in the lung field (CT Involvement Score (CTIS)) can act as an indicator of disease severity [4]. In addition, artificial intelligence-assisted diagnostic methods using chest CT images for COVID-19 have been reported, and they can be divided into classification problems (COVID-19 or non-COVID-19 pneumonia) [5,6,7] and segmentation problems (extraction of infected regions of COVID-19) [8,9,10,11]. The segmentation problem of infected regions is a recognition problem of infected region information at the pixel or voxel level, which is a more challenging task. In a previous study, we proposed a graph-based pyramid global context reasoning (Graph-PGCR) method to realize the automatic segmentation of infected regions in COVID-19 using a graph convolutional network [12]. The Graph-PGCR method performs convolutional feature extraction in a graph space, which enables long-range feature extraction and is particularly effective for extracting COVID-19-infected regions that are widely distributed in the lung region. We also developed an interactive COVID-19 diagnosis visualization system that allows radiologists to intuitively perform quantitative evaluations and make diagnoses of COVID-19 based on the Graph-PGCR [13] segmentation method. This system includes an automatic infected region segmentation function, an interactive correction function for insufficient segmentation results, an automatic calculation function for CTISs (indicating the degree of progression in the infected regions), and a three-dimensional (3D) display function to present inflammatory areas. The visualization of reconstructed 3D models on computers can provide radiologists with detailed information to facilitate the diagnosis of COVID-19. However, the use of contact devices, e.g., mice, keyboards, or touch panels, to display these models is frequently required, which presents a challenge in terms of maintaining sterile environments during the diagnostic processes. Specifically, the need for re-sterilization of visualization devices after each use can be both inefficient and ineffective. This issue highlights the importance of exploring alternative methods to visualize 3D models, e.g., using augmented reality (AR) or virtual reality (VR), which may resolve the challenges faced by traditional visualization methods.
Recently, there has been a significant increase in the popularity and use of AR and VR devices in the medical field [14], and the COVID-19 pandemic has further emphasized the importance of using such technologies in the qualification and assessment of the disease [15,16]. An accurate understanding of 3D infected regions is critical to realizing the effective treatment and management of COVID-19, and AR technology is a powerful tool to achieve this goal. AR enables true 3D visualization with effective depth perception, which facilitates interactions with medical data without the need for physical contact. This feature is particularly advantageous in maintaining a sterile environment and minimizing the risk of infected regions during the diagnosis and assessment of COVID-19.
The goal of this study is to establish a 3D augmented reality visualization system for infected regions in each lobe using AR HoloLens technology. The main objective is to provide a more precise and comprehensive 3D perception of COVID-19 to improve both disease management and treatment. To demonstrate the feasibility of using 3D HoloLens visualization in COVID-19 studies, a pilot cooperative scenario study was conducted.
2. Proposed Method
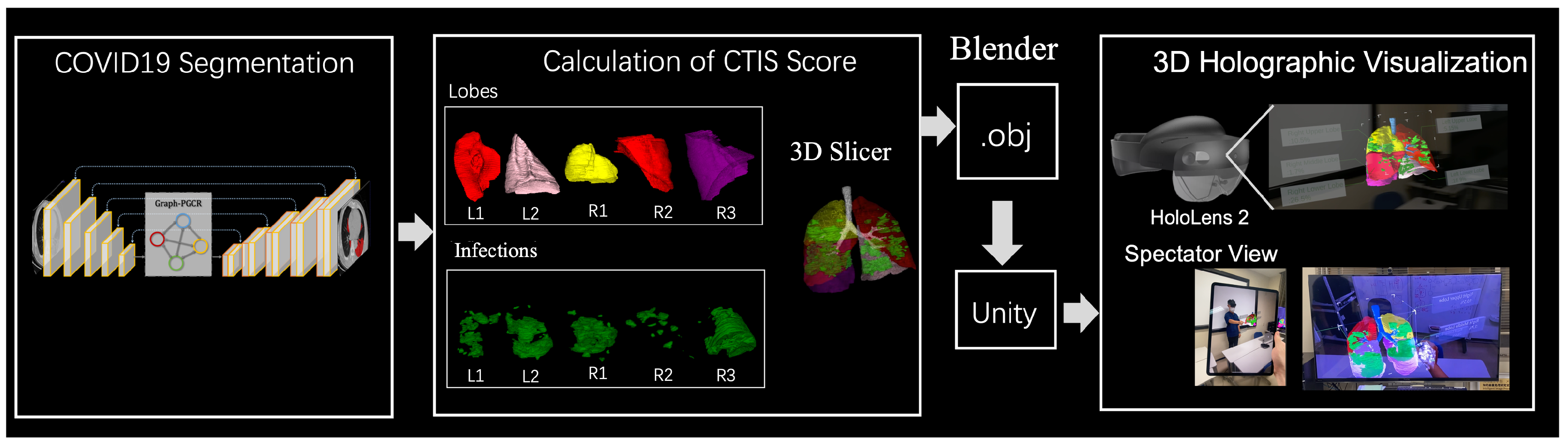
Here, we propose the 3D augmented reality visualization system based on CT-based COVID-19 segmentation results to generate a 3D COVID-19 model and visualize infected lung regions on the HoloLens. An overview of the proposed system, which involves several modules, is shown in Figure 1. The first module performs automatic segmentation of COVID-19-infected regions using Graph-PGCR on the input CT images. Then, 3D surface rendering is performed based on the lung lobes and infected regions. The volume of the accurately segmented infected regions is then calculated, and the CTIS is computed accordingly. The system displays the determined COVID-19 severity based on the calculated CTIS and provides a 3D augmented reality visualization of the infected regions using the HoloLens. Segment processing is discussed in further detail in the following sections.
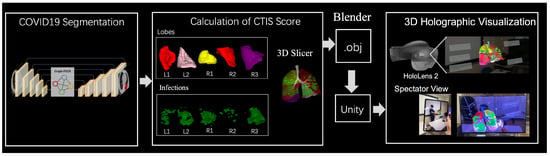
Figure 1.
Proposed system for augmented reality visualization of COVID-19.
2.1. Segmentation of COVID-19-Infected Lung Regions
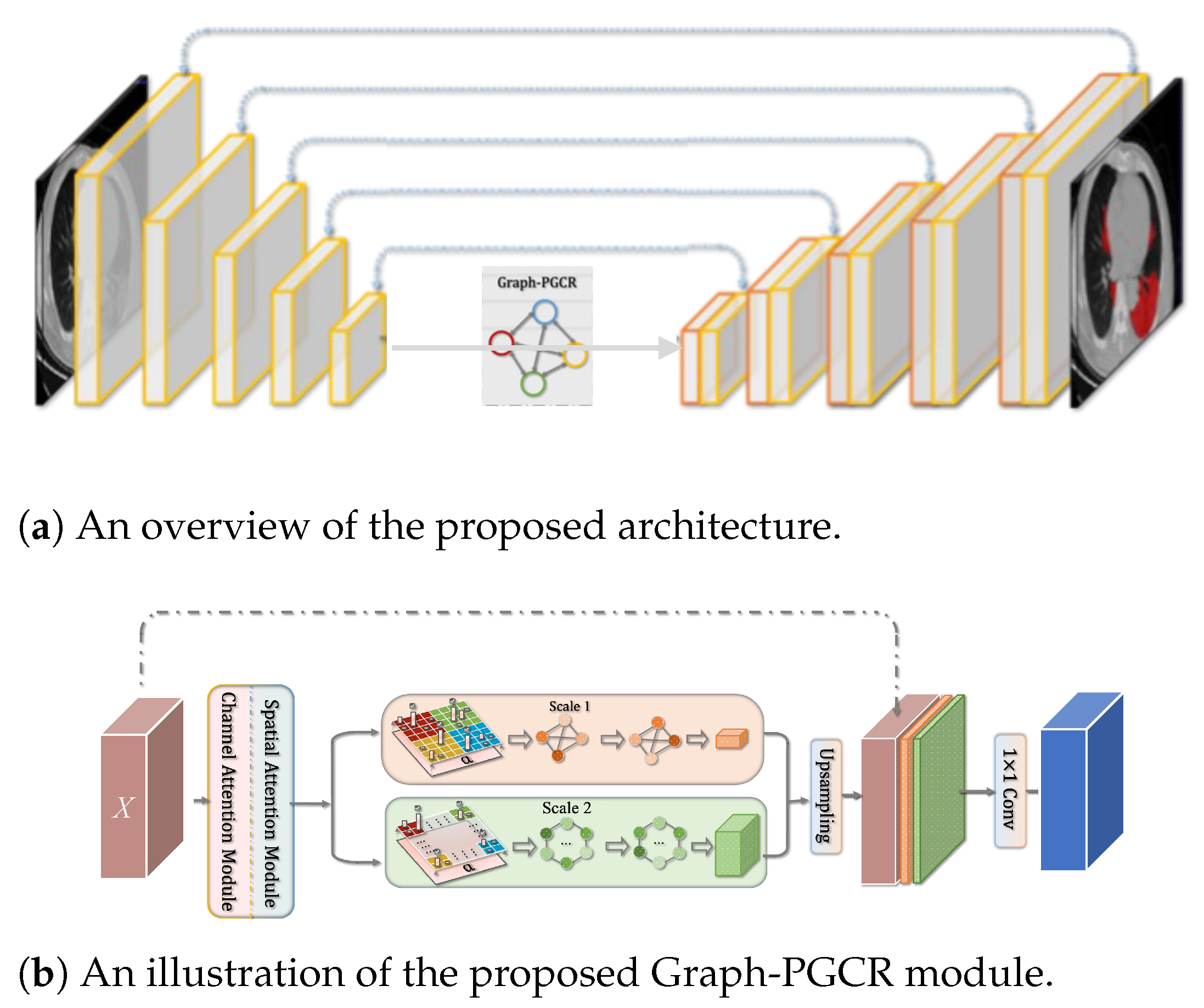
The first stage of the proposed system involves the segmentation of the lung regions infected by COVID-19. For the automatic segmentation of COVID-19 inflammation regions from CT images, we utilized our previously developed Graph-based Pyramid Global Context Reasoning (Graph-PGCR) method [12]. An overview of the Graph-PGCR model is shown in Figure 2. We used U-Net [17], which is a widely used neural network that is frequently used for medical image segmentation, as the backbone network. To address the challenge of varying infected region sizes and locations in different lobes, we incorporated graph convolutional layers into the U-Net encoder to enable long-range feature extraction, which proved particularly effective in extracting COVID-19-infected regions distributed over large areas of the lung. The first step of automatic segmentation using Graph-PGCR is to extract feature maps from the input images using a U-Net encoder. The extracted feature map is then converted into a graph structure using the saliency-aware projection method [12]. First, the feature map is divided into grid-like subregions. The number of subregions is given by , where H and W are the height and width of the feature map, respectively, and the size of the subregions is 5. For each subregion, we identify the most salient pixel based on both channel attention and spatial attention, which is then used as a vertex in the fully connected graph. The feature of the salient pixel is utilized as the feature of the vertex.
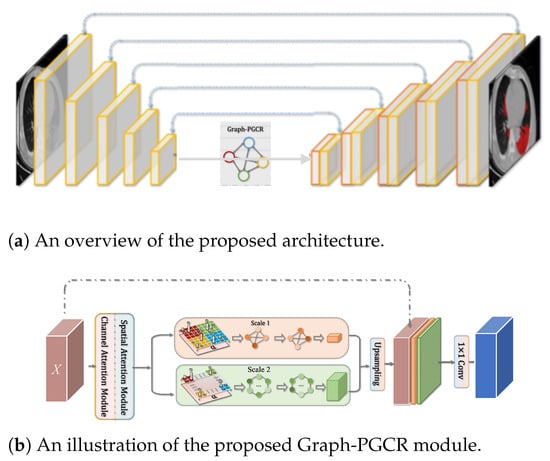
Figure 2.
An overview of the Graph-PGCR module in the UNet architecture.
Here, an adjacency matrix is calculated based on the similarity between vertices. The graph vertex feature is denoted by , where S is the dimension of the original feature map X. Note that the number of vertices is determined by the number of subregions (subregion size); thus, the subregion size (i.e., 5) can be considered the scale of the graph. In the Graph-PGCR method, three graphs with different scales are generated to extract multiscale features.
We perform graph convolution in the graph space using the graph convolution described in Equation (1):
where is a linear transformation obtained by learning, is a learned weight parameter, is the ReLU activation function, is the output of the convolution, and k represents the scale. In the proposed method, we generate three graphs with different scales to extract multiscale features. The graph convolution can extract long-range features via reasoning interactions between distant vertices (regions), thereby making it particularly effective in segmenting COVID-19-infected regions spread over large areas.
We then combine the features obtained from each graph-scale space and project them back to the image space. The inverse projected feature map is then input to the U-Net decoder to perform segmentation.
2.2. Calculation of CTIS
The infected regions of the lungs are segmented by applying the segmentation methods described in Section 2.1. Overlaying the prelabeled lung lobe masks (i.e., the right upper, right middle, right lower, left upper, and left lower lobes) onto the segmented infected regions allows us to separate the infected regions in each lobe. As a result, the volume and proportion of the infected regions in each lobe can be calculated automatically. Based on the calculated proportions, the CT Involvement Score (CTIS) is estimated, as shown in Table 1. Here, the sum of the CTIS values in the five lobes (ranging from 0 to 25) is used as an indicator of COVID-19 severity, where a score of 18 or higher indicates the highest severity level [3].

Table 1.
Quantitative assessment of CTIS.
2.3. HoloLens-Based 3D Visualization Module
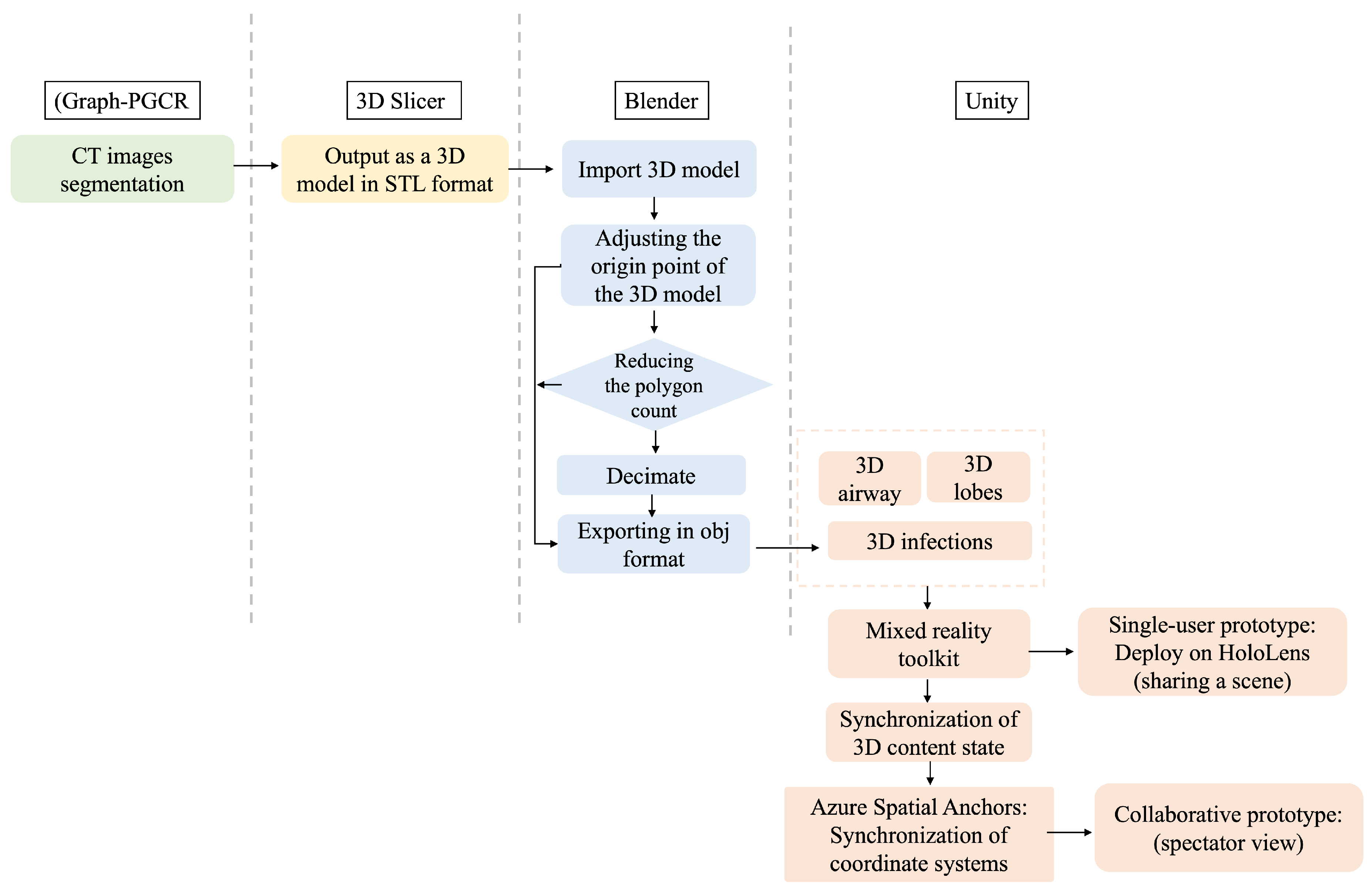
We developed an interactive visualization system based on the HoloLens to observe the expansion of the COVID-19 infection in the lung regions. The system utilizes 11 models, including the airway, five lung lobe models, and infected regions in each of the five lung lobe regions segmented by the system. The infected regions in each lung lobe region can be viewed intuitively by adjusting the opacity of the lung regions. The wireless HoloLens device can be operated via hand gestures. This contactless interaction allows doctors to visualize COVID-19 while wearing AR glasses under sterile conditions without the need to touch any other surfaces or devices, which could compromise the sterile environment. The workflow is illustrated in Figure 3.
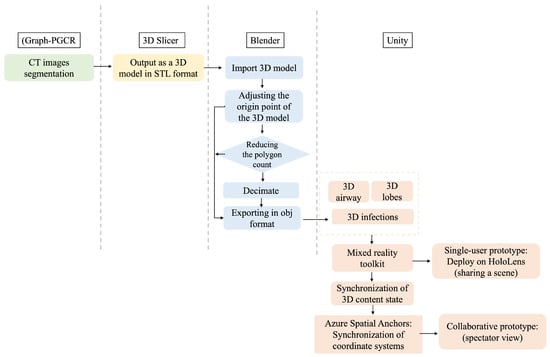
Figure 3.
The development workflow from CT images (green box), which are exported in an appropriate format (yellow box) and converted to 3D geometry (blue boxes). The generated 3D models can be imported into Unity and integrated with various mixed reality toolkit components (pink boxes) to create both single- and collaborative-user applications deployed on HoloLens2.
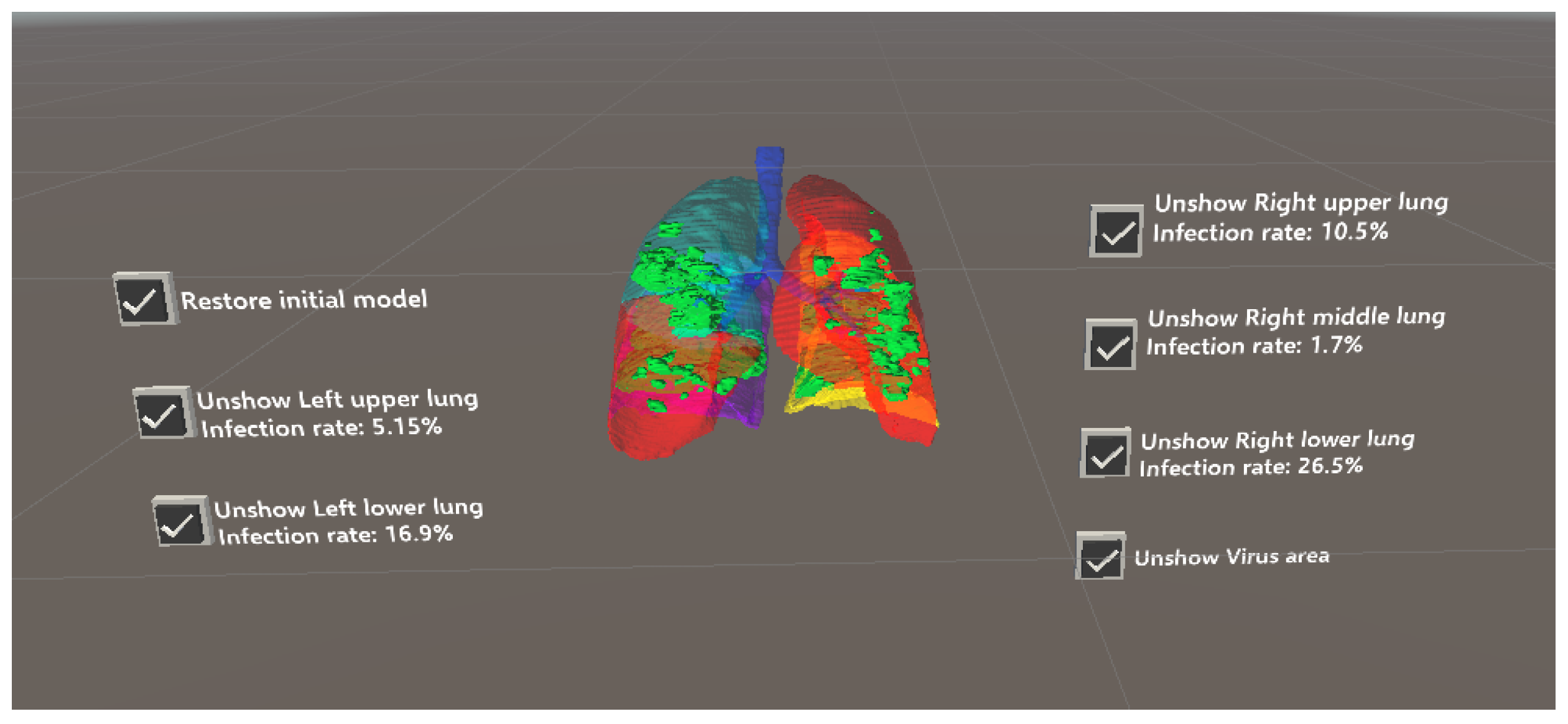
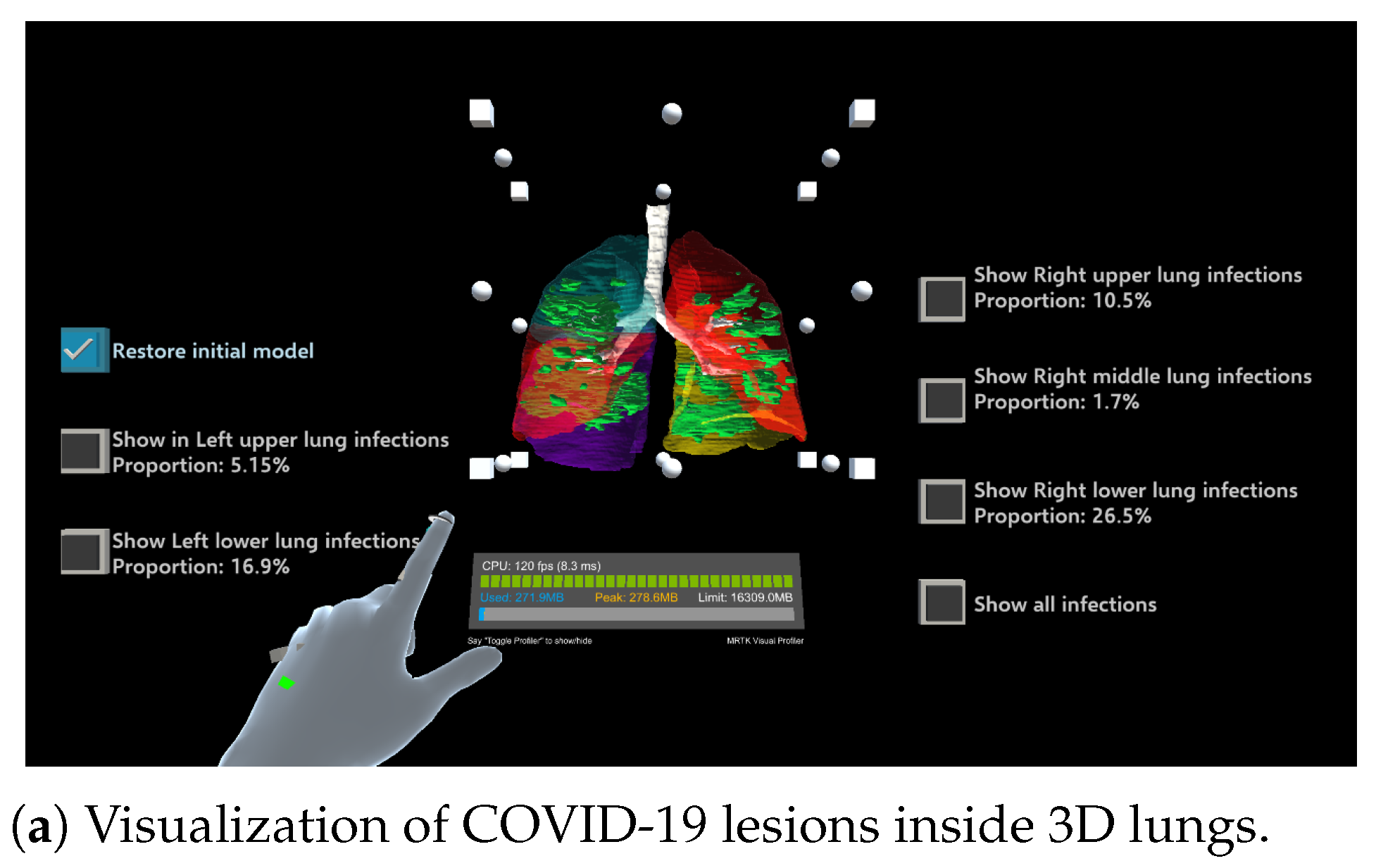
An example is shown in Figure 4, where the operation menu for each lung lobe region is provided on the left and right sides of the screen. This menu provides information about the corresponding lung lobe region, infected regions within that region, and a visualization of their superposition.
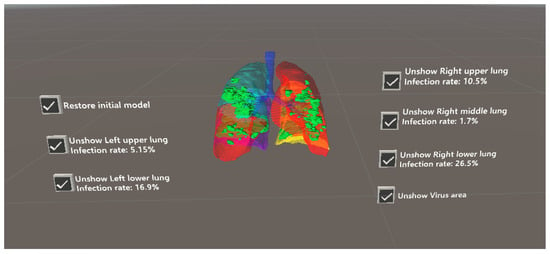
Figure 4.
Visualization of COVID-19-infected regions in lung fields.
Note that the utilization of a third-person perspective offers a unique opportunity for a broader audience to observe the interactions between the HoloLens user and virtual objects in the real world. This can facilitate improved communication among medical professionals by providing a shared, visual understanding of the AR experience, which can be realized through various features, e.g., the Spectator View and Sharing a Scene features.
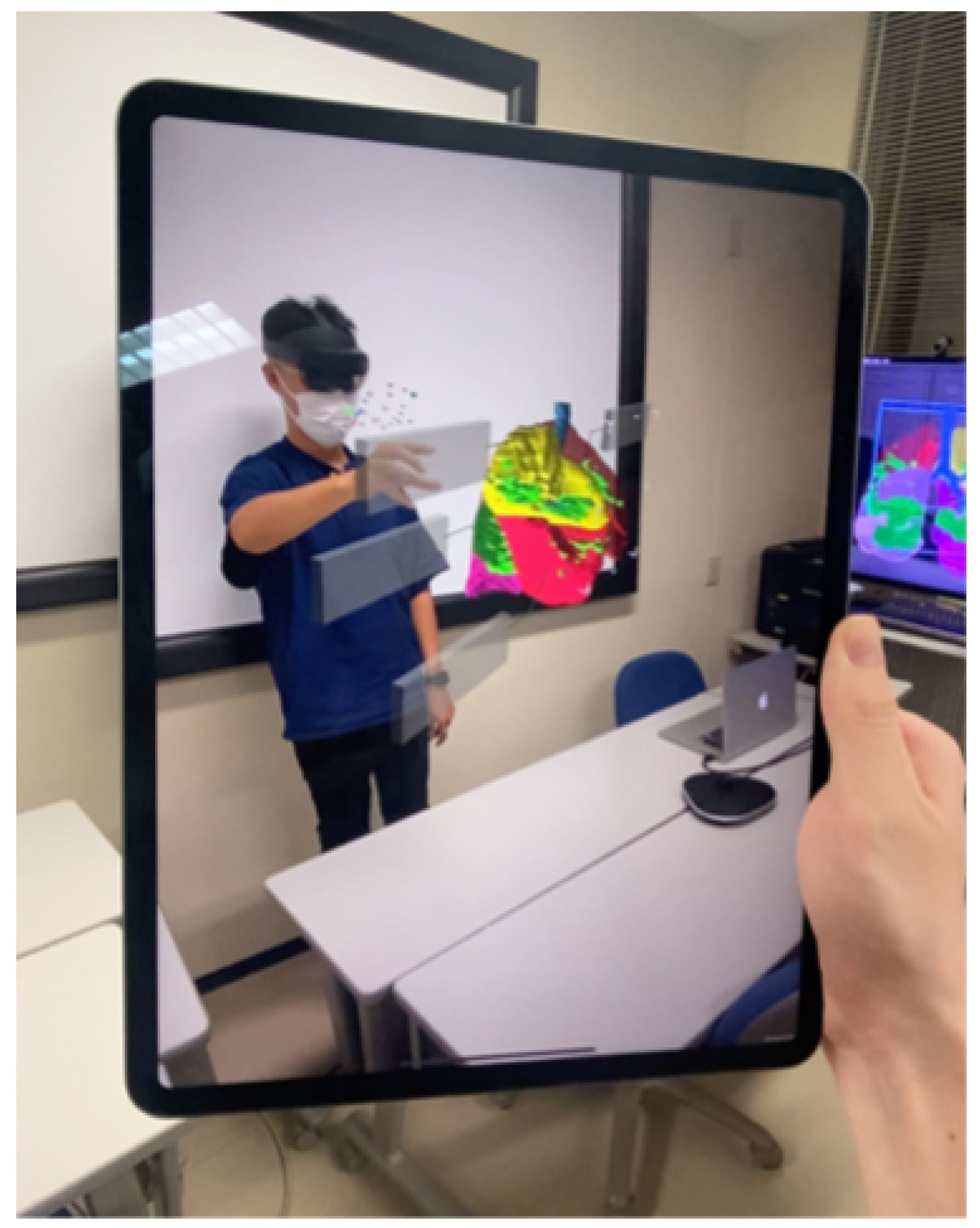
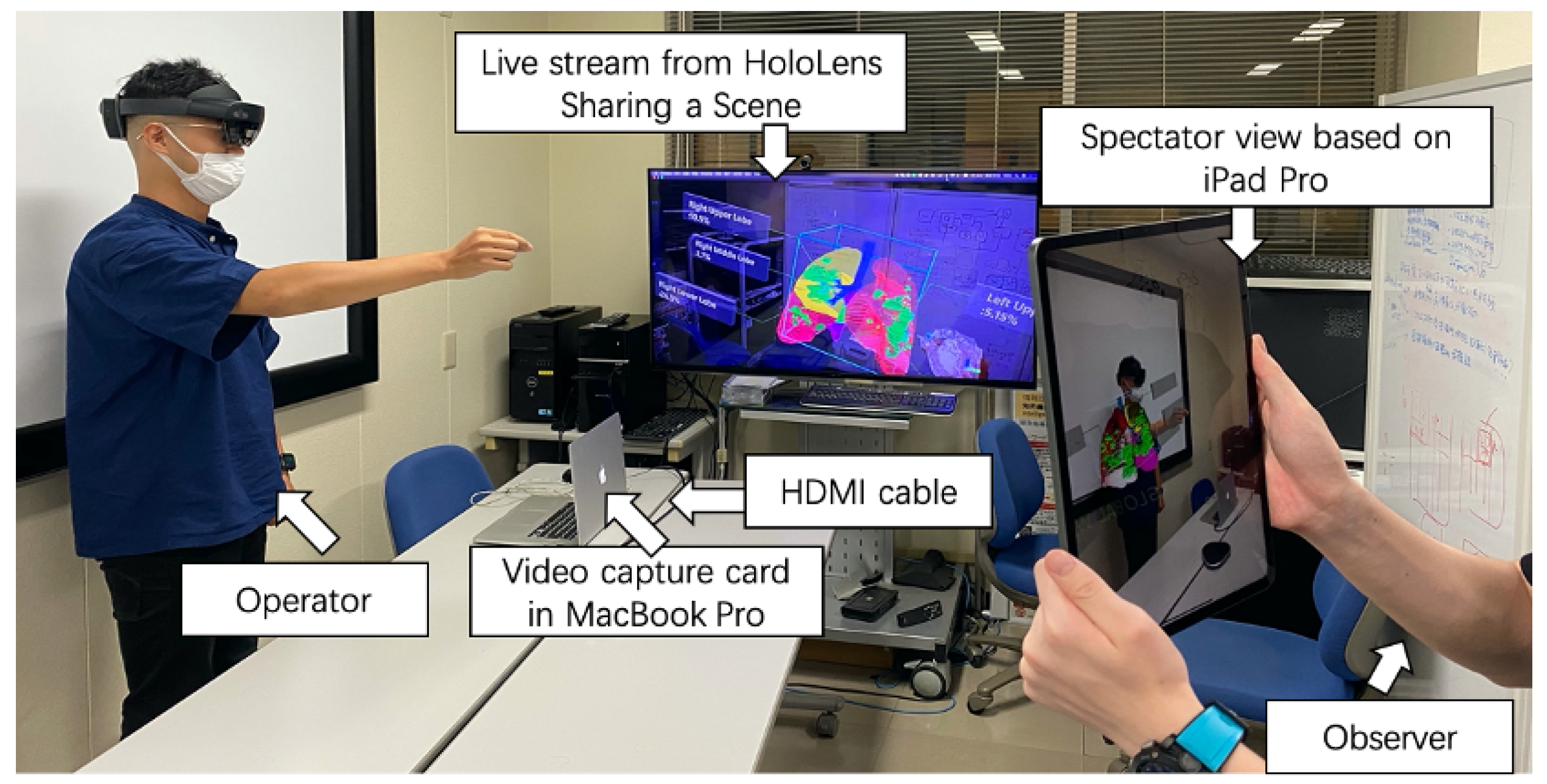
With the Spectator View feature, a device can be placed in the AR environment to capture the HoloLens user’s actions and display them on a separate screen (Figure 5). In this study, a HoloLens device and an iPad Pro were utilized to realize the Spectator View functionality. Here, the HoloLens is worn by the user interacting with the AR application, and the iPad Pro captures real-world information from a third-person perspective, which is then superimposed with the virtual objects using the Unity game engine running on a computer. In addition, Microsoft offers the Calibration application [18], which is used to obtain the field of view of the external camera (i.e., the iPad Pro’s camera) and the spatial relationship between the external camera and the RGB color camera on the HoloLens device.

Figure 5.
Third-person perspective (Spectator View function).
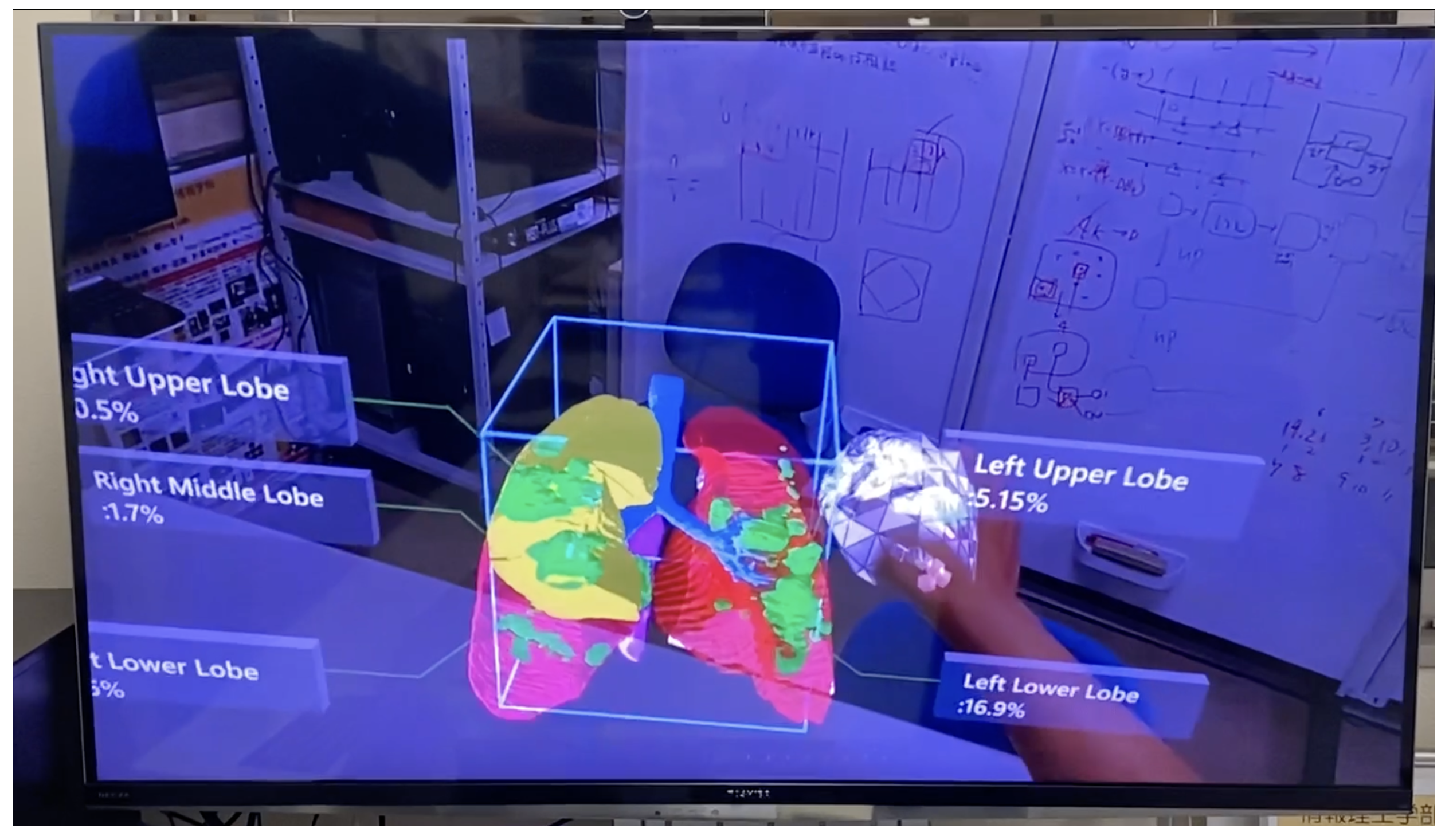
The Sharing a Scene feature allows multiple users to experience the same AR environment. As shown in Figure 6, the real-world view from this device was live-streamed to a computer using the Microsoft HoloLens application.
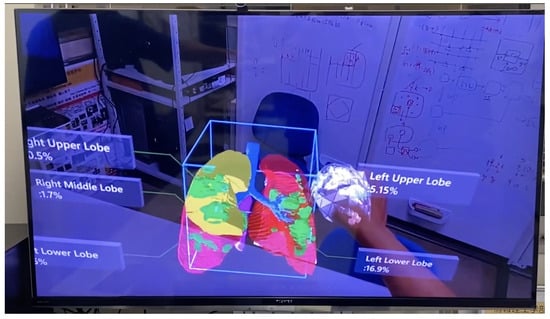
Figure 6.
User’s perspective (Sharing a Scene function).
The configuration of the Sharing a Scene function, the Spectator View functions, and the cooperative scenario are shown in Figure 7. whole system demonstration video can be found in Supplementary Materials.
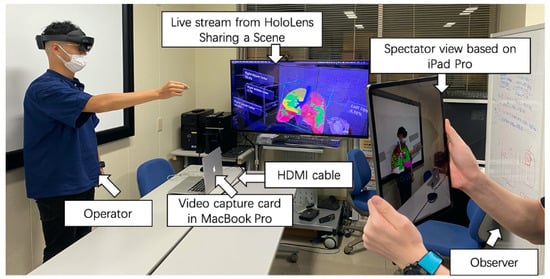
Figure 7.
Sharing a Scene function, Spectator View function, and cooperative scenario.
3. Performance Evaluation
In this section, we present the segmentation results and discuss an evaluation conducted by a radiologist to assess the performance of the proposed system. Here, a publicly available COVID-19 dataset [19] was used in the experiment. This dataset contains 20 cases with infected regions caused by COVID-19, and all the infected regions were pre-annotated by clinical experts.
3.1. Automatic Segmentation Results Using Graph-PGCR
We conducted experiments using 16 cases as training data and four cases as validation data. For details about the experimental conditions, please refer to the literature [12]. Table 2 compares the segmentation accuracy (Dice) between Graph-PGCR and existing methods. As can be seen, the average accuracy of the proposed method [12] was 80.58%, which is higher than that obtained by the existing methods.

Table 2.
Comparison of segmentation accuracy with Graph-PGCR.
3.2. Calculation of CTIS and Evaluation of Severity
An inconsistency between the estimated CTIS values and the ground-truth scores was observed in only two cases, i.e., the cases with the worst automatic segmentation accuracy. Here, the occupancy ratio of the infected regions and the estimated CTIS for each lung lobe region in these two cases are shown in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively. A difference of −1 was observed in the CTIS values for the right middle lobe region (case 1 in Table 3) and the right lower lobe region (case 2 in Table 4).
3.3. Three-Dimensional Visualization of Inflamed Region
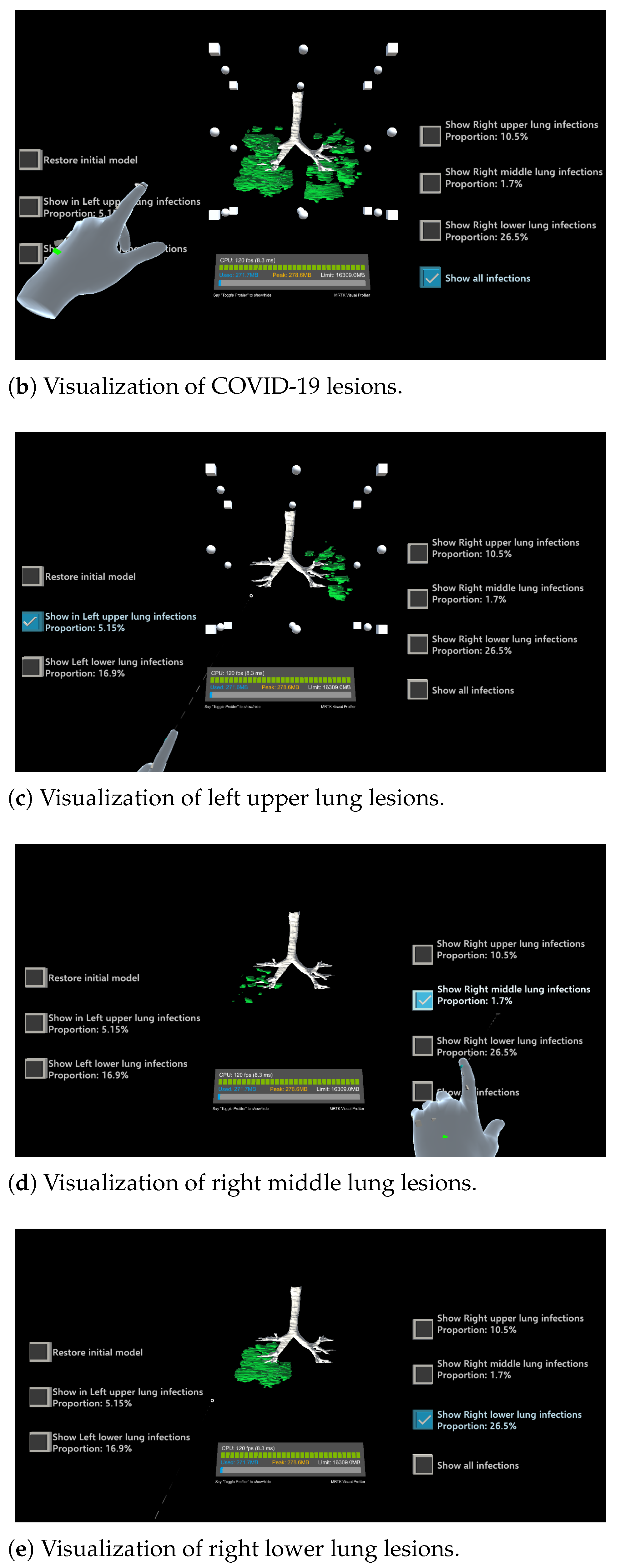
Figure 8 shows five examples of 3D visualizations based on the segmentation results (Section 2.1 and Section 2.2). Here, the infected regions are highlighted in green, and the right upper, right middle, right lower, left upper, and left lower lobes are shown in blue, pink, purple, red, and yellow, respectively. By simply touching the button, the display and non-display settings can be toggled. As shown in Figure 8, the proposed system allows for the superimposition of the entire lung field and infected regions or the display of only the infected areas in a specific lung lobe. This visualization and more intuitive interactive operations can improve the visibility of the infection status in each area, thereby contributing to the diagnostic support in terms of determining the severity of a COVID-19 infection.
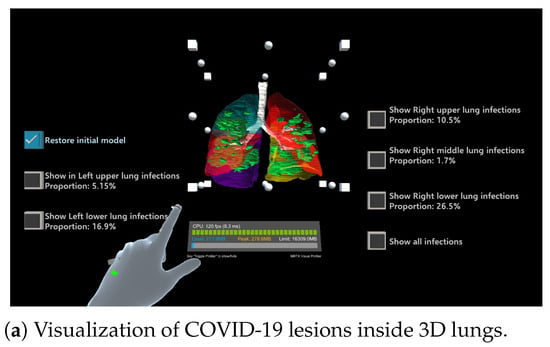
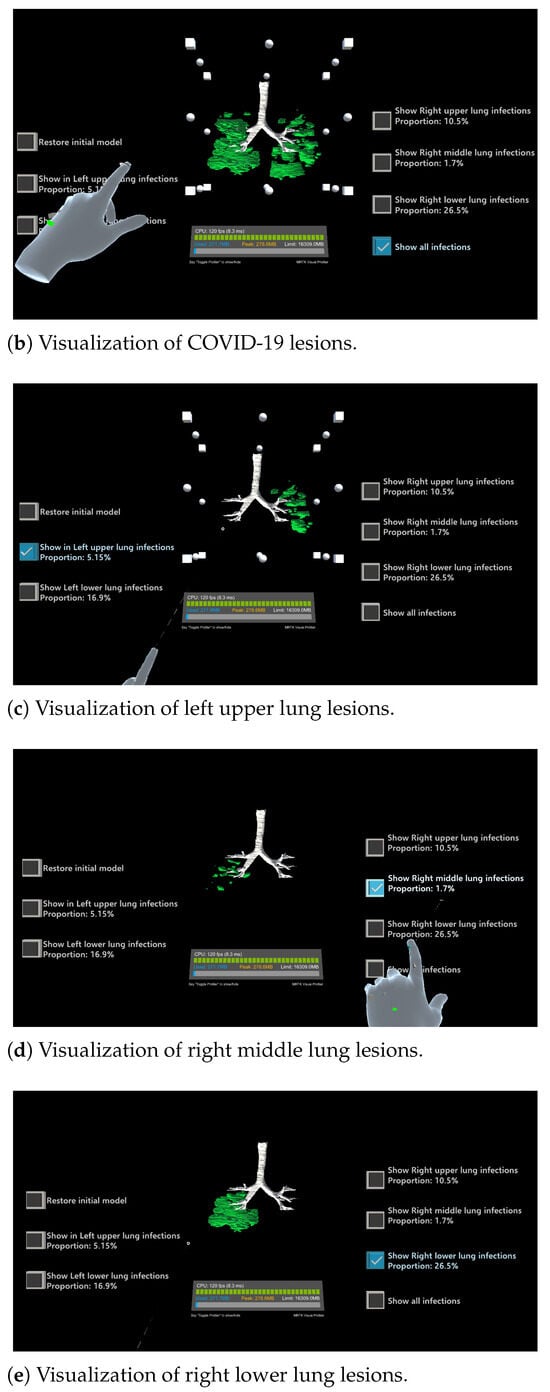
Figure 8.
Examples of three-dimensional visualizations of segmented COVID-19-infected regions. The buttons located in the upper left and upper right of the screen are used to toggle the display of each lung region on or off.

Table 3.
Proportion of infected regions in each lung lobe and CTIS (case 1).
Table 3.
Proportion of infected regions in each lung lobe and CTIS (case 1).
| Region | GT | Results | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left lung upper | Ratio (%) | 16.89 | 10.87 |
| CTIS | 2 | 2 | |
| Left lung lower | Ratio (%) | 44.4 | 39.61 |
| CTIS | 3 | 3 | |
| Right lung upper | Ratio (%) | 19.9 | 25.24 |
| CTIS | 2 | 2 | |
| Right lung middle | Ratio (%) | 28.17 | 21.04 |
| CTIS | 3 | 2 | |
| Right lung lower | Ratio (%) | 9.67 | 5.63 |
| CTIS | 1 | 1 |

Table 4.
Proportion of infected regions in each lung lobe and CTIS (case 2).
Table 4.
Proportion of infected regions in each lung lobe and CTIS (case 2).
| Region | GT | Results | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left lung upper | Ratio (%) | 18.59 | 20.05 |
| CTIS | 3 | 3 | |
| Left lung lower | Ratio (%) | 0.32 | 0.7 |
| CTIS | 1 | 1 | |
| Right lung upper | Ratio (%) | 4.34 | 4.1 |
| CTIS | 1 | 1 | |
| Right lung middle | Ratio (%) | 0.38 | 0.94 |
| CTIS | 1 | 1 | |
| Right lung lower | Ratio (%) | 58.91 | 43.79 |
| CTIS | 4 | 3 |
3.4. Subjective Evaluation
In addition, a radiologist was recruited to evaluate the usability of the proposed system. The questionnaire items and results are shown in Table 5, where the evaluation results are enclosed within circular symbols. This evaluation was conducted using a five-point Likert scale (1: poor; 5: excellent). As can be seen, high evaluations were received for all questionnaire items, which suggest that the proposed system is sufficiently satisfactory for practical application in clinical settings. For example, the “useful for medical education” items received high evaluation scores, which indicate that the proposed system can support the diagnosis of COVID-19 severity and medical education for COVID-19 infections.

Table 5.
Question items and scores.
3.5. Limitations of the Proposed Method
While the proposed system for the visualization and quantification of COVID-19 infections in the lungs shows promising results, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. Our experiments utilized a publicly available COVID-19 dataset comprising only 20 cases. The relatively small sample size and lack of diversity in this dataset might limit the generalizability of our findings. Larger datasets featuring a wider variety of cases are necessary to further validate the robustness of our proposed methods. Additionally, while the average accuracy of the proposed Graph-PGCR method is commendable, there is noticeable variability in segmentation accuracy across different cases. Furthermore, the subjective evaluation of the system’s usability was conducted with only one radiologist. A more extensive evaluation involving multiple radiologists would provide a broader understanding of the system’s usability and its practicality in clinical settings. By addressing these limitations, future work can aim to enhance the robustness, accuracy, and applicability of the proposed system, aiding in the diagnosis and severity assessment of COVID-19 infections.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we developed a system to enable the quantitative evaluation and augmented reality visualization of regions infected with COVID-19 in lung fields through interactive operations. We also confirmed the accurate estimation of the CTIS, which has been identified as an effective indicator when assessing the severity of the disease. The proposed system enables an intuitive and accurate understanding of the spatial infection status in lung fields. In addition, an evaluation of the system’s usability by a radiologist demonstrated a high level of satisfaction. However, it is important to note the limitations of our approach. The system’s performance was evaluated using a limited dataset of 20 COVID-19 cases, raising concerns about the generalizability of our results. Moreover, the variability in segmentation accuracy across different cases highlights the need for further refinement of the algorithm. The system’s usability evaluation was based on feedback from a single radiologist, suggesting the need for broader clinical validation. These results demonstrate the usefulness of the proposed visualization support system for COVID-19. Moving forward, we plan to gather additional feedback from more clinical professionals to further improve the proposed system. We also aim to conduct clinical support experiments for COVID-19 to verify the effectiveness of our system in a real-world clinical diagnosis setting. Finally, since the segmentation method of the proposed system can be changed, it can be applied to various organs and tumors; thus, we also plan to verify its applicability in those areas, potentially broadening its clinical utility. By addressing the identified limitations and continuing to refine our system, we believe that it holds significant promise for improving the diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19 and other pathologies in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/electronics13061158/s1, Video S1: System demonstration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and Y.C.; methodology, J.L. and H.H.; software, L.L. (Liang Lyu) and S.C.; validation, T.T.; formal analysis, F.W.; investigation, T.T.; resources, F.W.; data curation, F.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, J.L.; visualization, L.L. (Liang Lyu); supervision, Y.C., L.L (Lanfen Lin); project administration, Y.C.; funding acquisition, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported in part by the Japan Society of Promotion of Science (JSPS) under Grant Nos. 22K21316 and 23K16909.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The COVID-19-CT-Seg datasets, which were used and analyzed during the current study, are accessible at the following URL: https://zenodo.org/records/3757476#.Xpz8OcgzZPY (last accessed on 14 March 2024). This dataset is distributed under the CC BY-NC-SA License.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- WHO World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report, 88. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- Shi, F.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; He, K.; Shi, Y.; Shen, D. Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation and diagnosis for COVID-19. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, S.; Kay, F.U.; Abbara, S.; Bhalla, S.; Chung, J.H.; Chung, M.; Henry, T.S.; Kanne, J.P.; Kligerman, S.; Ko, J.P.; et al. Radiological Society of North America Expert Consensus Statement on Reporting Chest CT Findings Related to COVID-19. Endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Radiology, the American College of Radiology, and RSNA. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francone, M.; Iafrate, F.; Masci, G.M.; Coco, S.; Cilia, F.; Manganaro, L.; Panebianco, V.; Andreoli, C.; Colaiacomo, M.C.; Zingaropoli, M.A.; et al. Chest CT score in COVID-19 patients: Correlation with disease severity and short-term prognosis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6808–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Feng, J.; Jin, C.; Han, X.; Wu, H.; Shi, H. Longitudinal assessment of COVID-19 using a deep learning–based quantitative CT pipeline: Illustration of two cases. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Jie, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. Deep learning enables accurate diagnosis of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) with CT images. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Gong, D.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zheng, B.; et al. Deep learning-based model for detecting 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia on high-resolution computed tomography: A prospective study. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Shi, N.; Han, M.; Xue, Z.; Shen, D.; Shi, Y. Lung infected regions Quantification of COVID-19 in CT Images with Deep Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04655. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Wang, B.; Xu, H.; Luo, C.; Wei, L.; Zhao, W.; Hou, X.; Ma, W.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; et al. AI-assisted CT imaging analysis for COVID-19 screening: Building and deploying a medical AI system in four weeks. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Deng, X.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Feng, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Deep learning-based detection for COVID-19 from chest CT using weak label. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Zhou, T.; Ji, G.P.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.Y.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Inf-Net: Automatic COVID-19 Lung infected regions Segmentation from CT Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2626–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y. Graph-based pyramid global context reasoning with a saliency-aware projection for COVID-19 lung infected regionss segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Tateyama, T.; Iwamoto, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, Y.W. Touch-Based Interactive System for Assessment and Visualization of COVID-19. IEICE Trans. 2022, J105-D, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan, M.; Mohan, H.; Ryan, J.R.; Schürch, C.M.; Nolan, G.P.; Frakes, D.H.; Coskun, A.F. Virtual and augmented reality for biomedical applications. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, A.; Benlamri, R. Augmented reality, virtual reality and new age technologies demand escalates amid COVID-19. In Novel AI and Data Science Advancements for Sustainability in the Era of COVID-19; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, F.; Samad-Soltani, T.; Rezaei-Hachesu, P. Applications of virtual and augmented reality in infectious disease epidemics with a focus on the COVID-19 outbreak. J. Med. Syst. 2021, 45, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Microsoft, SpectatorView Pro Code on GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/Microsoft/MixedRealityCompanionKit/tree/master/SpectatorView (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; An, X.; Ge, C.; Yu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Q.; Dong, G.; He, J.; He, Z.; et al. Towards Efficient COVID-19 CT Annotation: A Benchmark for Lung and Infection Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.12537. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).