A 0.59 nW/kHz Clock Circuit with High-Precision Clock Calibration for Passive Internet of Things Chips
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Traditional Methods
3. Proposed Design
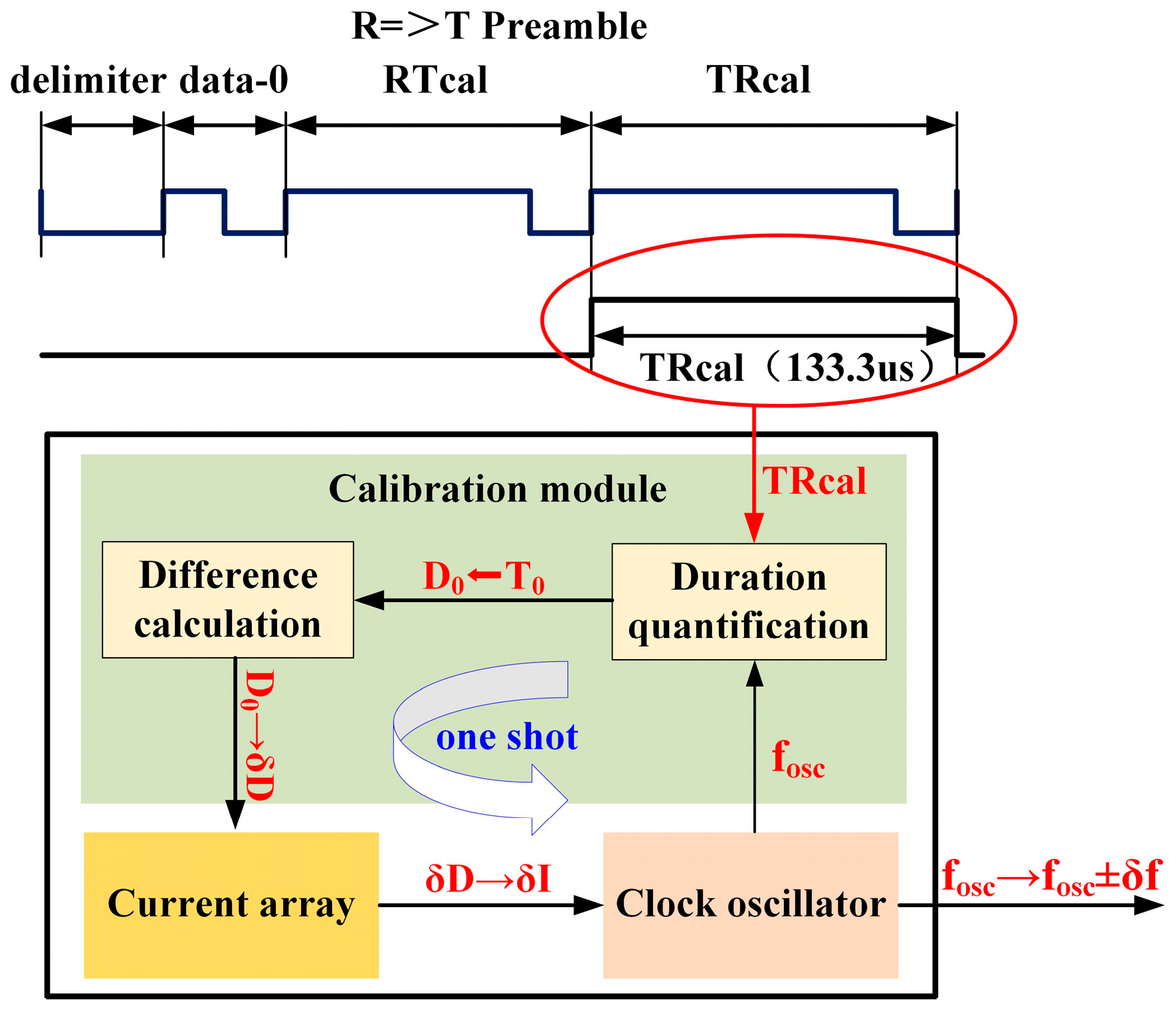
3.1. TDIF Single-Shot Calibration Method
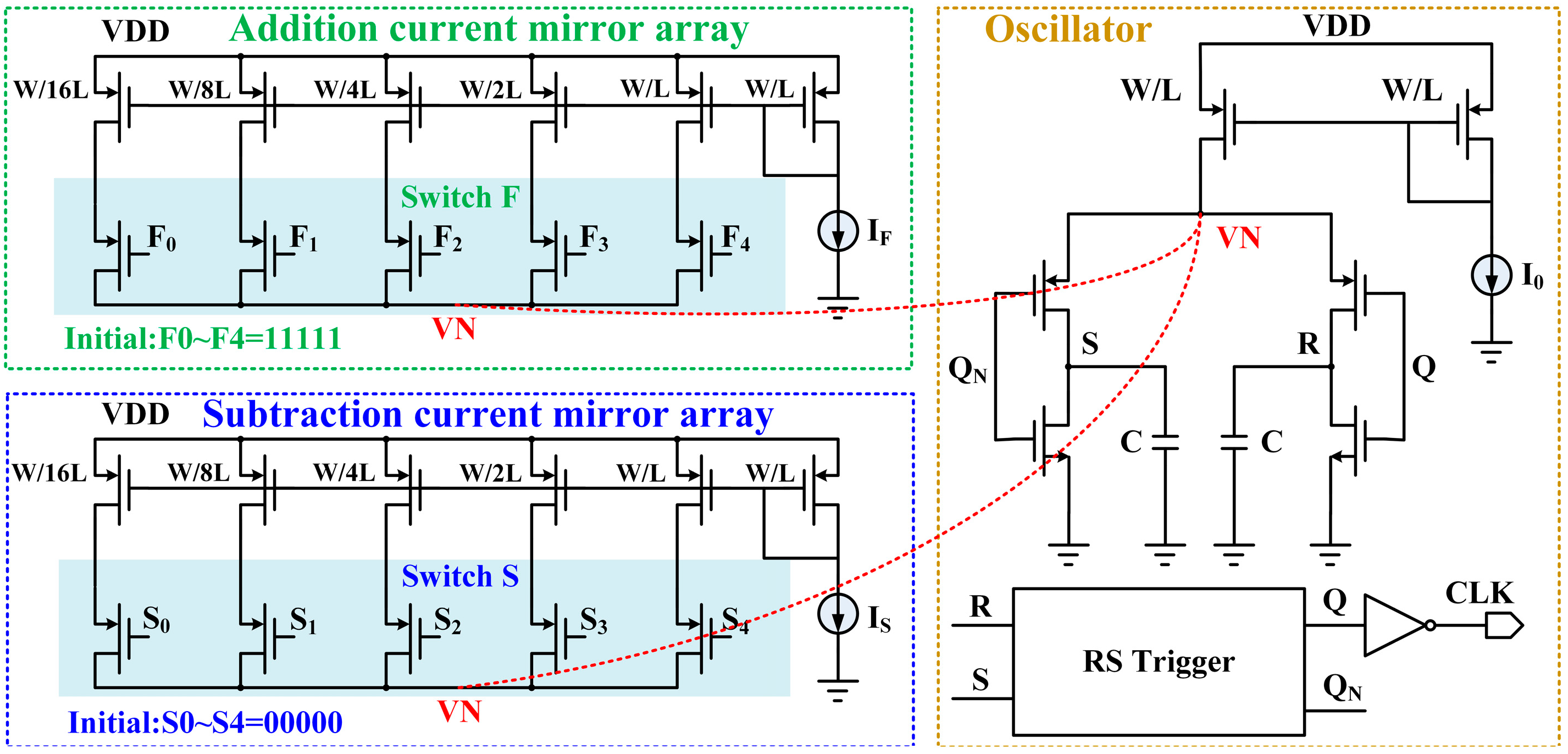
3.2. Circuits Scheme of Clock Generator
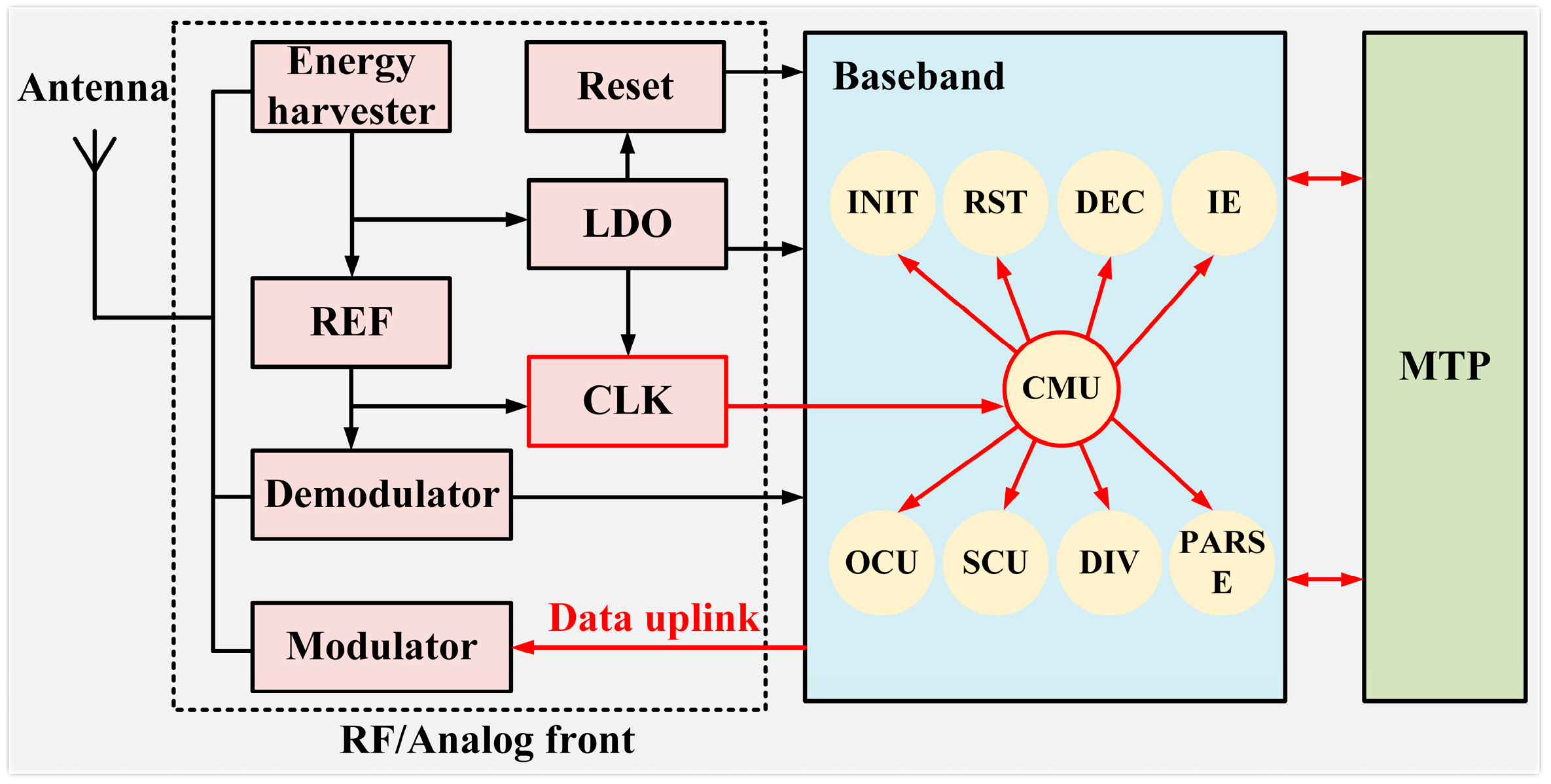
4. Circuit Implementation
4.1. Collaborative Design of Clock Oscillator and Current Array
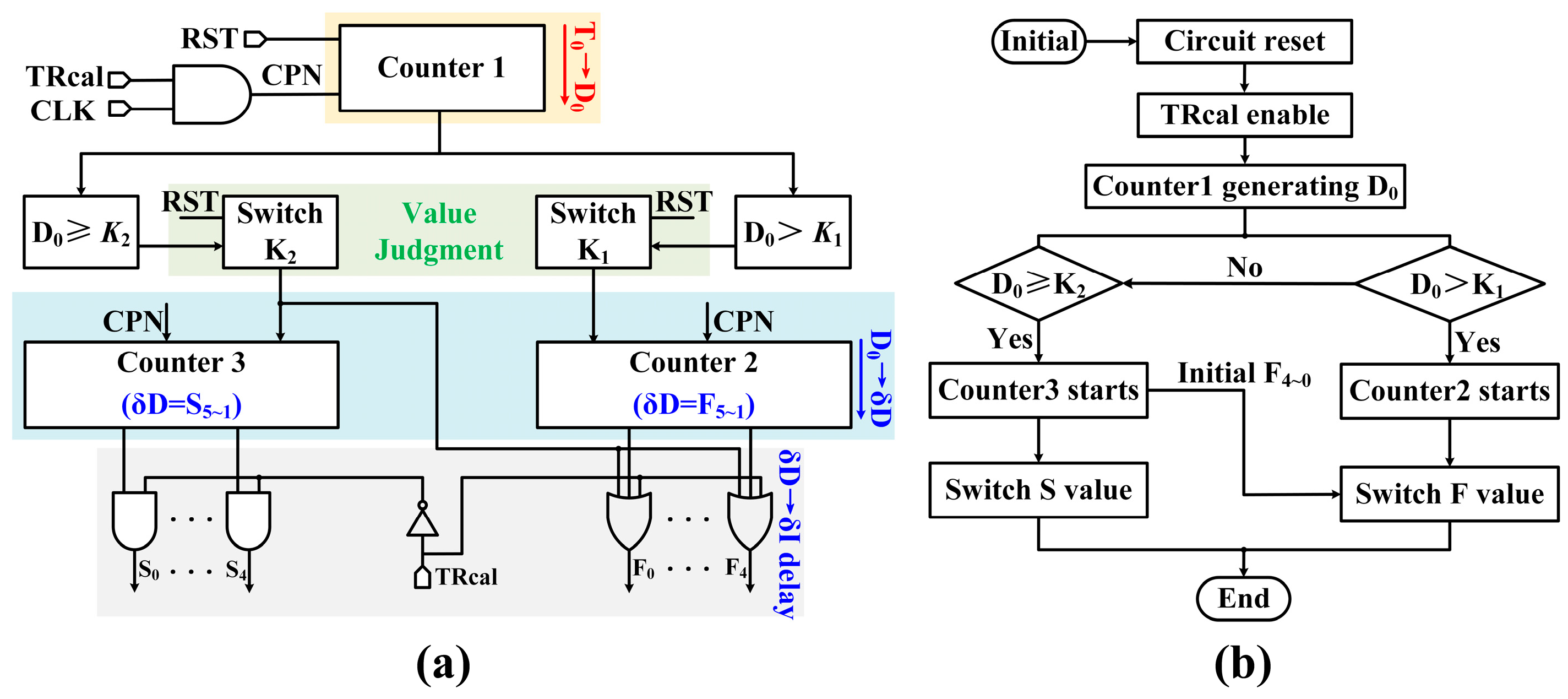
4.2. Calibration Module
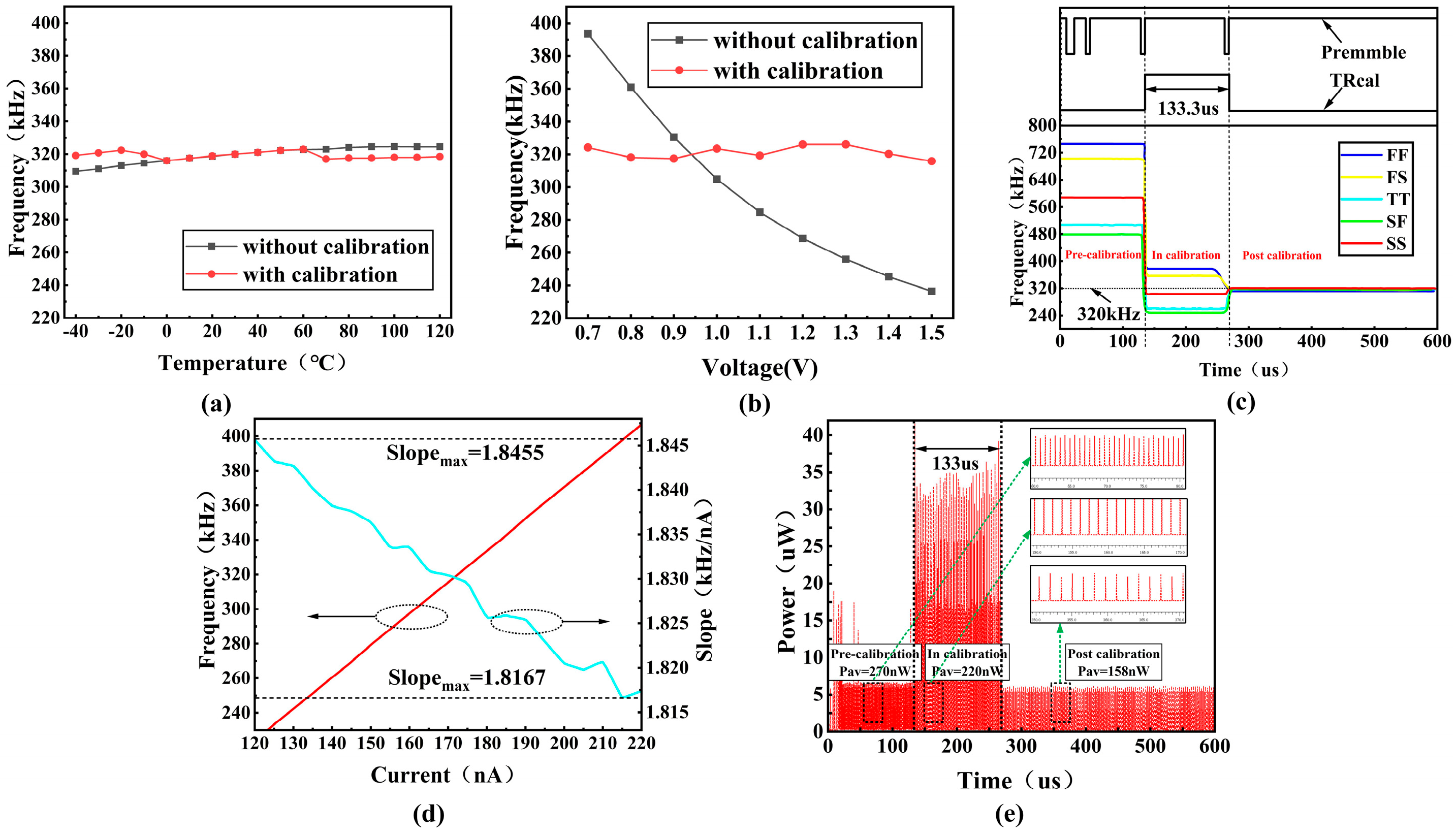
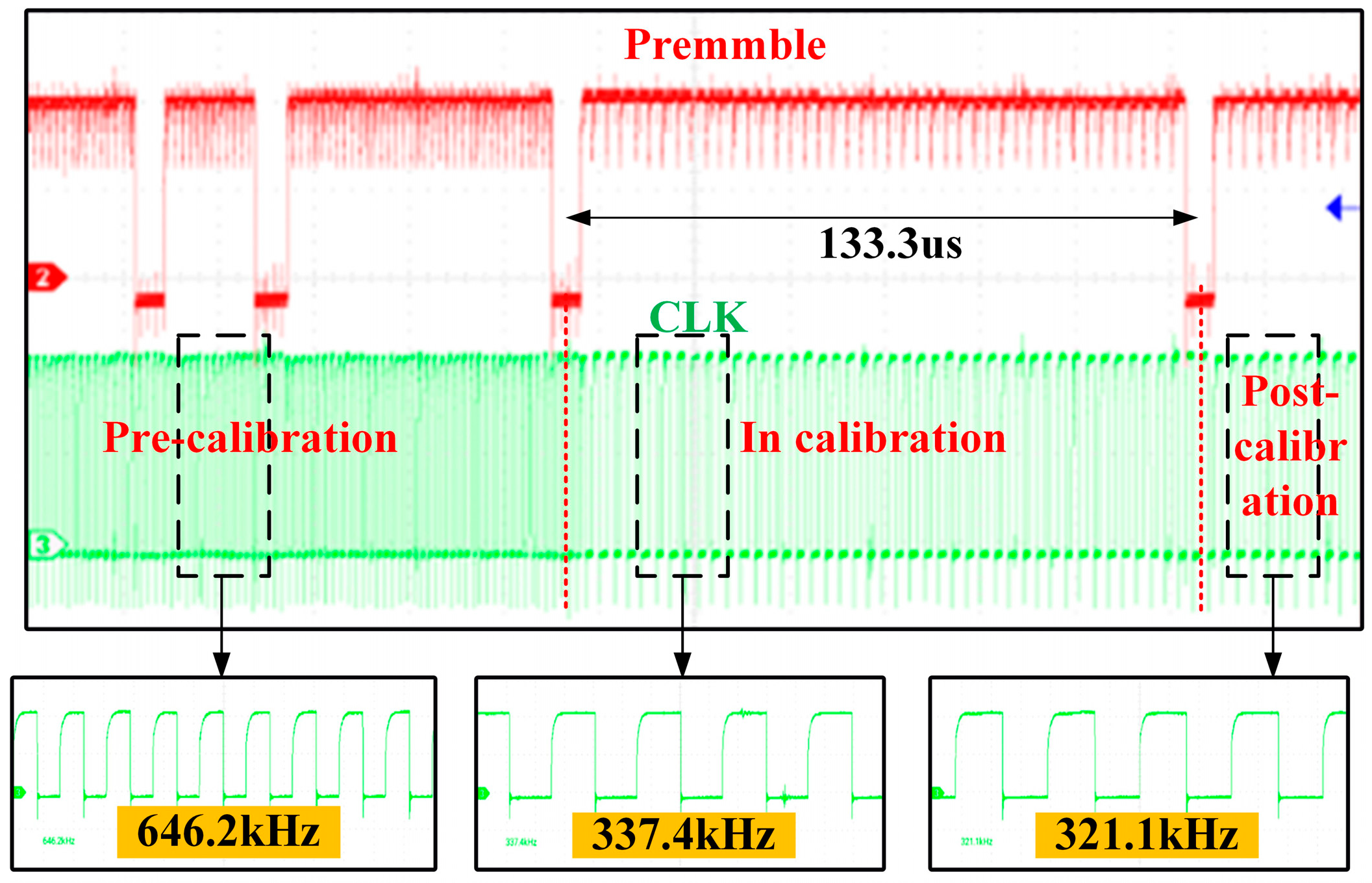
5. Simulation and Test Result
5.1. Simulation Result
5.2. Test Result
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, H.; Liang, Y.-C.; Long, R.; Zhang, Q. Cooperative ambient backscatter system: A symbiotic radio paradigm for passive IoT. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 8, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.W.; Liao, J.W.; Arjmandpour, S.; Novello, A.; Sim, J.-Y.; Jang, T. A Second-Order Temperature-Compensated On-Chip R-RC Oscillator Achieving 7.93ppm/°C and 3.3pj/Hz in −40 °C to 125 °C Temperature Range. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–26 February 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam, T.; Sotoudeh, H.H. An efficient 2.4GHz radio frequency identicication (RFID) in a standard CMOS process. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2013, 36, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Pirbhulal, S.; Zhang, H.; E Alahi, M.E.; Ghayvat, H.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Wu, W. A Novel Secure IoT-Based Smart Home Automation System Using a Wireless Sensor Network. Sensors 2016, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilek, F.; Seemann, K.; Holweg, G.; Weigel, R. Impact of the local oscillator on baseband processing in RFID transponder. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Symposium on Signals, Systems and Electronics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 30 July–2 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Usami, M.; Sato, A.; Sameshima, K.; Watanabe, K.; Yoshigi, H.; Imura, R. Powder LSI: An ultra small RF identification chip for individual recognition applications. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers, ISSCC, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Savanth, A. A Sub nW/kHz Relaxation Oscillator with Ratioed Reference and Subclock Power-Gated Comparator. IEEE JSSC 2019, 54, 3097–3106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, P.B.; Ruo, H.Y. Process, voltage and temperature compensation in a 1-MHz 130nm CMOS monolithic clock oscillator with 2.3% accuracy. Int. J. Electron. 2014, 102, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Pan, S.; Gürleyük, Ç.; Makinwa, K.A.A. 31.3 A 0.14mm2 16MHz CMOS RC Frequency Reference with a 1-Point Trimmed Inaccuracy of ±400ppm from −45°C to 85 °C. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–22 February 2021; pp. 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byondi, F.K.; Chung, Y. Longest-Range UHF RFID Sensor Tag Antenna for IoT Applied for Metal and Non-Metal Objects. Sensors 2019, 19, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, J.; Gong, W.; Liu, J. Reliable and practical Bluetooth backscatter with commodity devices. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2021, 29, 1717–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensworth, J.F.; Hoang, A.T.; Reynolds, M.S. A low power 2.4 GHz superheterodyne receiver architecture with external LO for wirelessly powered backscatter tags and sensors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on RFID (RFID), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 9–11 May 2017; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, V.; Talla, V.; Kellogg, B.; Gollakota, S.; Smith, J. Inter-technology backscatter: Towards internet connectivity for implanted devices. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGCOMM Conference, Florianopolis, Brazil, 22–26 August 2016; pp. 356–369. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, J.D.; Mandal, A.; Sathe, V.; Reynolds, M.S. An All-Digital 1 Mbps, 57 pJ/bit Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Backscatter ASIC in 65 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on RFID (RFID), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 17–19 May 2022; pp. 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.; Das, D.K. A comprehensive review on the application of Internet of Thing (IoT) in smart agriculture. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 122, 1807–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo Espinosa, Á.; Lopez, J.L.; Mata Mata, F.; Estevez, M.E. Application of IoT in healthcare: Keys to implementation of the sustainable development goals. Sensors 2021, 21, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miraz, M.H.; Ali, M.; Excell, P.S.; Picking, R. A review on Internet of Things (IoT), Internet of everything (IoE) and Internet of nano things (IoNT). In Proceedings of the 2015 Internet Technologies and Applications (ITA), Wrexham, UK, 8–11 September 2015; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Ahmed, O.H.; Ahmed, S.H.; Trinh, C.; Bagheri, N.; Kumari, S.; Lansky, J.; Huynh, B. An enhanced authentication protocol for RFID systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 126977–126987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Lin, K.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J. Design and implementation of a high sensitivity fully integrated passive UHF RFID tag. J. Semicond. 2014, 35, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansraj, B.; Prdro, I. A 2-MHZ, Process and Voltage Compensated Clock Oscillator for BIomedical Implantable SoC in 0.18-μm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Beijing, China, 19–23 May 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kelam, M.; Battu, B.Y.; Abbas, Z. A Compact, Power Efficient, Self-Adaptive and PVT Invariant CMOS Relaxation Oscillator. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), Limassol, Cyprus, 6–8 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/IEC 18000-6:2013; Information Technology—Radio Frequency Identification for Item Management—Part 6: Parameters for Air Interface Communications at 860 MHz to 960 MHz. International Organization for Standardization—ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Impinj, G. Gen 2 Tag Clock Rate-What You Need to Know. 2009. Available online: https://www.impinj.com/ (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Shimada, M. Model-based polarimetric SAR calibration method using forest and surface-scattering targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1712–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A. SAR calibration: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keishi, T.; Tetsuya, H.; Nobutaka, K.; Masahiro, N. A 32-kHz Real-Time Clock Oscillator with On-Chip PVT Variation Compensation Circuit for Ultra-Low Power MCUs. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2015, 98, 446–453. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.F.; Yang, X.; Feng, X.X.; Shen, J.-P.; Wang, X.-A.; Huang, R. 360nW Self-calibrated Clock Generator Operating from −50°C to 120 °C. In Proceedings of the 2010 10th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology, Shanghai, China, 1–4 November 2010. [Google Scholar]



| Reference | [20] | [21] | [26] | [27] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process (nm) | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 |
| Operating voltage (V) | 1.8 | 0.7–1.2 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 0.7–1.6 |
| Frequency | 2.02 MHz | 32.7 kHz | 32.55 kHz | 320 kHz | 320 kHz |
| Temperature range | - | −20 °C~100 °C | - | −50 °C~120 °C | −40 °C~120 °C |
| Precision | ±2.81% | ±1.525% | - | ±4% | ±3% |
| Power consumption | 12 μW | 54 nW@0.7 V | 472 nW | 360 nW@0.7 V | 158 nW@0.7 V |
| Energy efficiency (nW/kHz) | 5.9 | 1.65 | 8.1 | 1.125 | 0.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Xu, H.; An, Y.; Feng, X. A 0.59 nW/kHz Clock Circuit with High-Precision Clock Calibration for Passive Internet of Things Chips. Electronics 2024, 13, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13061094
Li X, Xu H, An Y, Feng X. A 0.59 nW/kHz Clock Circuit with High-Precision Clock Calibration for Passive Internet of Things Chips. Electronics. 2024; 13(6):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13061094
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoming, Hui Xu, Yabin An, and Xiting Feng. 2024. "A 0.59 nW/kHz Clock Circuit with High-Precision Clock Calibration for Passive Internet of Things Chips" Electronics 13, no. 6: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13061094
APA StyleLi, X., Xu, H., An, Y., & Feng, X. (2024). A 0.59 nW/kHz Clock Circuit with High-Precision Clock Calibration for Passive Internet of Things Chips. Electronics, 13(6), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13061094





