Abstract
In recent years, there has been significant progress in human pose estimation, fueled by the widespread adoption of deep convolutional neural networks. However, despite these advancements, multi-person 2D pose estimation still remains highly challenging due to factors such as occlusion, noise, and non-rigid body movements. Currently, most multi-person pose estimation approaches handle joint localization and association separately. This study proposes a direct regression-based method to estimate the 2D human pose from a single image. The authors name this network YOLO-Rlepose. Compared to traditional methods, YOLO-Rlepose leverages Transformer models to better capture global dependencies between image feature blocks and preserves sufficient spatial information for keypoint detection through a multi-head self-attention mechanism. To further improve the accuracy of the YOLO-Rlepose model, this paper proposes the following enhancements. Firstly, this study introduces the C3 Module with Swin Transformer (C3STR). This module builds upon the C3 module in You Only Look Once (YOLO) by incorporating a Swin Transformer branch, enhancing the YOLO-Rlepose model’s ability to capture global information and rich contextual information. Next, a novel loss function named Rle-Oks loss is proposed. The loss function facilitates the training process by learning the distributional changes through Residual Log-likelihood Estimation. To assign different weights based on the importance of different keypoints in the human body, this study introduces a weight coefficient into the loss function. The experiments proved the efficiency of the proposed YOLO-Rlepose model. On the COCO dataset, the model outperforms the previous SOTA method by 2.11% in AP.
1. Introduction
The task of multi-person 2D keypoint detection aims to enable computers to understand all instances in an image and simultaneously identify the motion joints of each individual. Human pose estimation is one of the fundamental tasks in the field of computer vision, with extensive applications in numerous areas, including activity recognition [1], human–robot interaction [2], pedestrian tracking [3], and the re-identification of individuals [4].
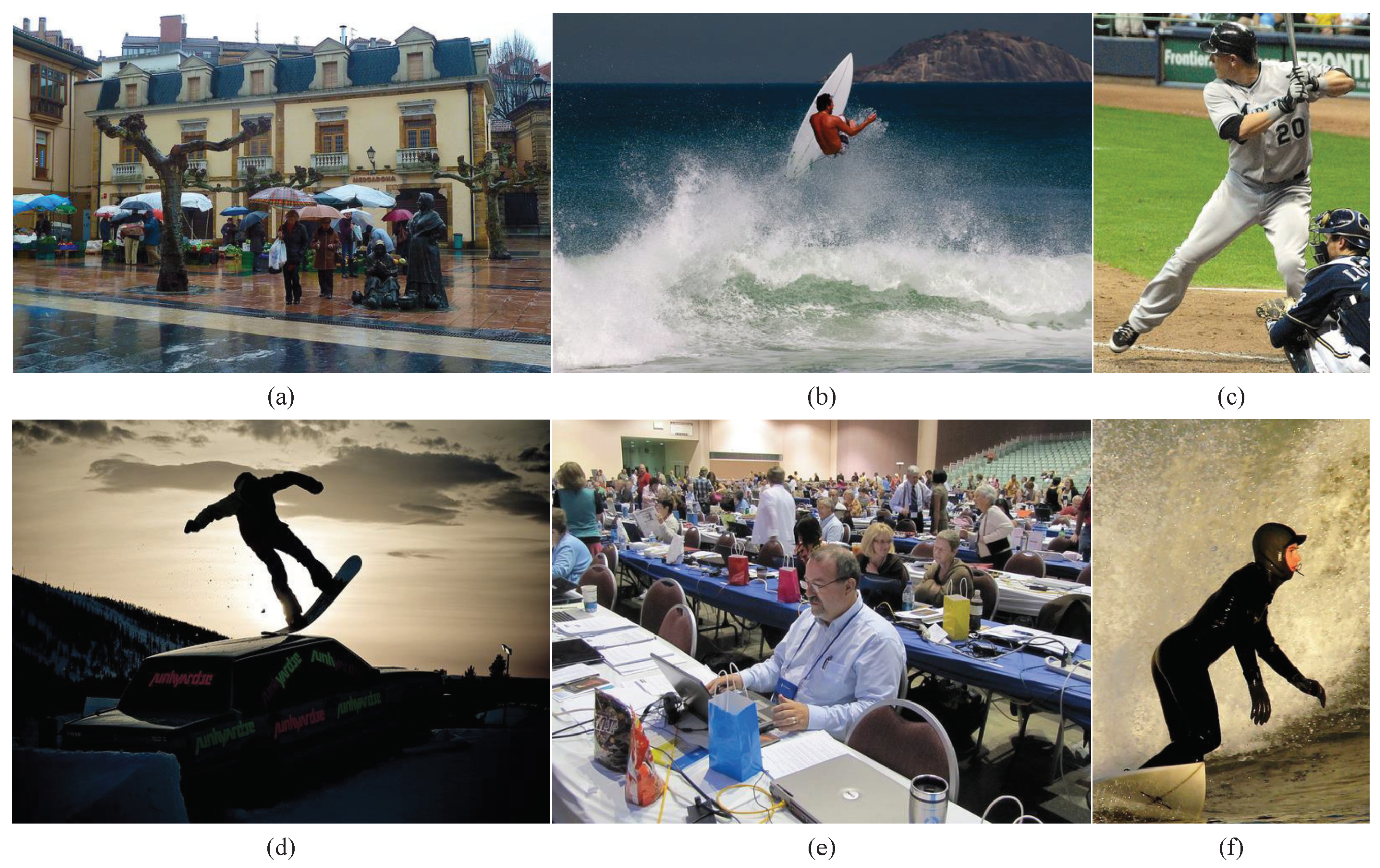
Due to the various bending, stretching, or twisting movements of joints during human activities, as shown in Figure 1c,d,f, human joints may also be occluded by other objects, body parts, or themselves, as shown in Figure 1a,b,e. These factors make it challenging for pose estimation algorithms to accurately detect the positions and angles of joints. Therefore, pose estimation algorithms need to accurately capture these non-rigid variations to provide accurate pose estimation results. As a result, multi-person 2D human pose estimation is a challenging task.

Figure 1.
The challenges in multi-person 2D pose estimation are illustrated using images from the COCO dataset. (c,d,f) illustrate the joints bending, stretching, and twisting movements caused by human activities. (a,b,e) illustrate the joints may also be occluded by other objects, body parts, or themselves.
Human pose estimation algorithms can be classified based on two criteria. The first criterion is the algorithm’s workflow, which categorizes human pose estimation approaches into three types: top-down, bottom-up, and single-stage pose estimation. The second criterion is the method used for predicting keypoints, which can be divided into regression-based pose estimation and heatmap-based pose estimation.
However, existing human pose estimation approaches still have some drawbacks. Firstly, top-down algorithms heavily rely on the performance of the human detector for accurate keypoint detection. If the human detector performs poorly, the accuracy of keypoint detection will also be affected. Additionally, this approach has a high computational cost [5], especially when there are a large number of human instances in the image, resulting in longer running times. Secondly, although heatmap-based methods show excellent performance, they require significant computational and storage resources, making it challenging to use them in single-stage approaches at the current stage.
In the task of object detection, the YOLO series [6] plays a significant role as a one-stage detector. In this study, the authors propose an improved model named YOLO-Rlepose based on YOLO to address the aforementioned issues. This study utilizes CSP-Darknet53 and PANet [7] as the backbone and neck of YOLO-Rlepose, respectively. In the head part, YOLO-Rlepose consists of four detection heads, each dedicated to detecting small, medium, and large objects. Each detection head includes an object box detection head, a keypoint detection head, and a convolutional layer for computing the loss. Additionally, the authors replace the original C3 module with an improved C3 module with Swin Transformer (C3STR) in the neck, enabling the network to better capture global information and rich contextual information.
This study proposes a regression-based single-stage human pose estimation method. To reduce the impact of noise on regression-based methods, a new loss function named Rle-Oks loss is introduced. The loss function simulates the distribution of the output by exploring maximum-likelihood estimation, thereby improving the accuracy of human pose regression. The contributions are described as follows:
- This study adds the Swin Transformer to the C3 module and proposes C3STR, enabling the network to better capture global information.
- This study introduces the Rle-Oks loss and applies it to human pose estimation, enabling the model to have keypoint weights when calculating the error between predicted and ground-truth keypoint values.
- On the COCO dataset, the proposed YOLO-Rlepose achieved 65.01 (AP), outperforming YOLO-Pose (previous SOTA method) by 2.11%.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation
The existing approaches to multi-person pose estimation can be broadly categorized into top-down methods, bottom-up methods, and single-stage human pose estimation based on their algorithmic workflows.
2.1.1. Top-Down Methods
Top-down methods first use a human detector to determine the bounding boxes of each human instance in the image and then crop these instances. Next, keypoints are detected among the obtained multiple-person instances. Representative algorithms of this kind include Hourglass [8] and CPN [9]. The Hourglass network is a sequential architecture that utilizes pooling and upsampling operations to capture different spatial relationships associated with the human body. By processing and integrating features, it aims to generate accurate predictions. This architecture is referred to as the ’stacked hourglass’ network. CPN locates simple keypoints through the feature pyramid network GlobalNet and then integrates all features from GlobalNet using RefineNet to obtain the remaining keypoints. Generally, top-down methods tend to have slower inference speed during the inference process due to the need for image cropping before human keypoint detection. Additionally, the efficiency of the detection of the human body plays a crucial role in the performance of top-down methods.
2.1.2. Bottom-Up Methods
Bottom-up methods detect the keypoints in the image first and then connect the detected keypoints to form the human skeleton. Currently, most bottom-up methods are primarily based on the association of detected keypoints belonging to the same individual. Representative algorithms of this type of approach include Openpose [10] and HigherHRNet [11]. Openpose is the first real-time deep-learning-based algorithm for multi-person 2D pose estimation. It can track the facial expressions, torsos, limbs, and even fingers of individuals, making it suitable for both single-person and multi-person pose estimation with good robustness. HigherHRNet adopts a novel high-resolution feature pyramid module to generate high-resolution heatmaps, making the network more efficient. It also proposes a Multi-Resolution Supervision strategy, which assigns the training objectives of varying resolutions to their respective feature pyramid levels. Compared to top-down methods, bottom-up methods usually run faster but have lower performance due to the difficulty of grouping processing.
2.1.3. Single-Stage Human Pose Estimation
To address the drawbacks of both top-down and bottom-up methods, single-stage human pose estimation has been proposed. FCPose [5] is a fully convolutional framework for multi-person pose estimation that employs dynamic instance-aware convolution for keypoint estimation. This approach allows FCPose to eliminate the need for ROIs and post-processing after grouping. SPM [12] was proposed as the first single-stage model to improve the efficiency of multi-person pose estimation. The paper introduces a novel Structured Pose Representation, SPR, which unifies the position representation of both human instances and body keypoints, enabling the model to directly predict the poses of multiple individuals in a single stage. To adapt the network parameters to each instance, InsPose [13] introduces an instance-aware module. InsPose significantly improves the network’s ability to recognize various poses. DirectPose [14] employs a novel Keypoint Alignment mechanism that overcomes the main challenge of the feature misalignment between convolutional features and predicted features in an end-to-end framework. PointSetNet [15] introduces a new object representation that can be viewed as an extension and generalization of traditional bounding boxes. YOLO-Pose [16] is a novel heatmap-free keypoint detection method based on the YOLO object detection framework. This method does not require the use of bottom-up post-processing methods to group the detected keypoints into a skeleton. This is because each bounding box is associated with a specific pose, which naturally groups the keypoints. Unlike top-down methods, instance cropping from bounding boxes is not needed since the poses of all individuals in the image are localized in a single inference.
2.2. Transformer in Vision
Transformers have been widely applied in natural language processing and have achieved significant progress in machine translation, text classification, and other tasks. Recently, many papers have attempted to introduce the Transformer architecture into computer vision tasks.
Early research focused on using Transformers as better decoders. For example, TransPose [17] introduces a Transformer model for human pose estimation, which directly processes the features extracted by a convolutional neural network to model global relationships, enabling the model to effectively capture dependencies between predicted keypoints. TokenPose [18] is a token-based approach to human pose estimation, where each keypoint is embedded with a token to estimate the position of occluded keypoints and model relationships between different keypoints. These methods are based on heatmaps and use complex Transformer encoders to enhance the model capacity. To improve the keypoint detection performance while maintaining high computational efficiency, Poseur [19] was proposed as a regression-based approach with a lightweight Transformer decoder.
Vision Transformer (ViT) demonstrated that the Transformer architecture can be directly applied to process images by treating them as a sequence of patches. ViT has achieved a performance comparable to that of convolutional networks in the field of computer vision. ViTPose [20] showcases the surprising capability of Vision Transformer in pose estimation, highlighting the simplicity of the model structure, the scalability of model size, the flexibility of training paradigms, and the portability of knowledge between models.
In computer vision tasks, the scale of input images varies significantly and is not fixed. To enable models to handle images of different scales more flexibly, the Swin Transformer [21] adopts a hierarchical structure similar to that of a convolutional neural network to process images, thereby improving computational efficiency. The hierarchical structure offers the flexibility to model at multiple scales, and its computational complexity scales linearly with the image size.
2.3. Heatmap-Based Pose Estimation and Regression-Based Pose Estimation
Currently, keypoint localization tasks can be roughly divided into two categories based on the method for predicting keypoints: heatmap-based and regression-based.
2.3.1. Heatmap-Based Pose Estimation
TompSon et al. [22] first proposed a 2D pose estimation method based on heatmaps, which represents the joint positions of the human body by estimating the per-pixel likelihood of each keypoint location. Since then, heatmap-based methods have become dominant in the field of 2D human pose estimation. To maintain high-resolution feature maps, some works have attempted to design powerful backbone networks for heatmap supervision. RSN [23] efficiently aggregates features with the same spatial size, resulting in fine-grained local representations that preserve rich spatial information at lower levels and achieve precise keypoint localization. HRNet [24] performs repeated multi-scale fusion, generating rich high-resolution representations that lead to more accurate keypoint predictions. Some works [25,26] have also focused on mitigating biases in heatmap data.
2.3.2. Regression-Based Pose Estimation
In the research of 2D human pose estimation, only a few studies have employed regression-based approaches. Although regression-based methods have faster inference speeds, their accuracy is not as good as heatmap-based methods. Therefore, it receives less attention from researchers. Carreira et al. [27] proposed the Iterative Error Feedback (IEF) network to improve the performance of regression models. Wei et al. [15] employed Point-Set Anchors for object detection, instance segmentation, and human pose estimation. To achieve comparable performance between regression-based methods and heatmap-based methods in human pose estimation, RLE [28] was proposed as a method that utilizes maximum-likelihood estimation and flow models for keypoint prediction.
In the field of 3D human pose estimation, Rogez et al. [29] proposed an end-to-end architecture named LCR-Net, which can detect 2D and 3D poses in natural images. This network locates individuals by extracting candidate regions. Then, a classification branch is used to score each proposed pose and independently regress each anchored pose. Pavllo et al. [30] demonstrated that 3D poses in videos can be effectively estimated using a fully convolutional model with extended temporal convolutions based on 2D keypoints. In the field of human pose estimation, Wang et al. [31] proposed an innovative technique that accurately generates high-quality 3D pose information in outdoor images without being limited by internal conditions. Zeng et al. [32] introduced a segmentation and recombination method named SRNet, which can easily adapt to single-image and temporal models, and it shows significant improvement in predicting rare and unseen poses. Choi et al. [33] proposed Pose2Mesh, a novel system based on Graph Convolutional Neural Networks (GraphCNNs), which directly estimates the 3D coordinates of human mesh vertices from 2D human pose estimation. Fang et al. [34] introduced a pose grammar to address the problem of 3D human pose estimation, further improving the model’s generalization ability.
3. Proposed Method
The proposed network architecture in this paper is a hybrid model named YOLO-Rlepose, which combines both convolutional and Swin Transformer models, primarily based on CSP-Darknet53. YOLO-Rlepose consists of three main parts. In the first part, the model utilizes CSP-Darknet53 as the backbone network and incorporates the C3STR module, which is a fusion with the Swin Transformer, into the backbone network to extract features more efficiently. The integration of the Swin Transformer helps enhance the feature extraction process. In the second part, the model employs the PANet structure to further refine the features. In the third part, keypoint detection heads and object box detection heads are introduced to predict keypoints and bounding boxes on four different scales of feature maps.
In addition, this study proposes a novel loss function named Rle-Oks loss. This loss function can estimate the potential distribution of errors between predicted and ground-truth keypoint values and facilitate human pose regression.
3.1. YOLO-Pose
Currently, the majority of human pose estimation approaches utilize top-down or two-stage methods. They first detect the locations of each person in the image and then perform single-person pose estimation for the detected individuals. The complexity of this top-down approach increases linearly with the number of individuals in the image. Due to its complexity and unstable runtime, it is challenging to apply this method to real-time applications.
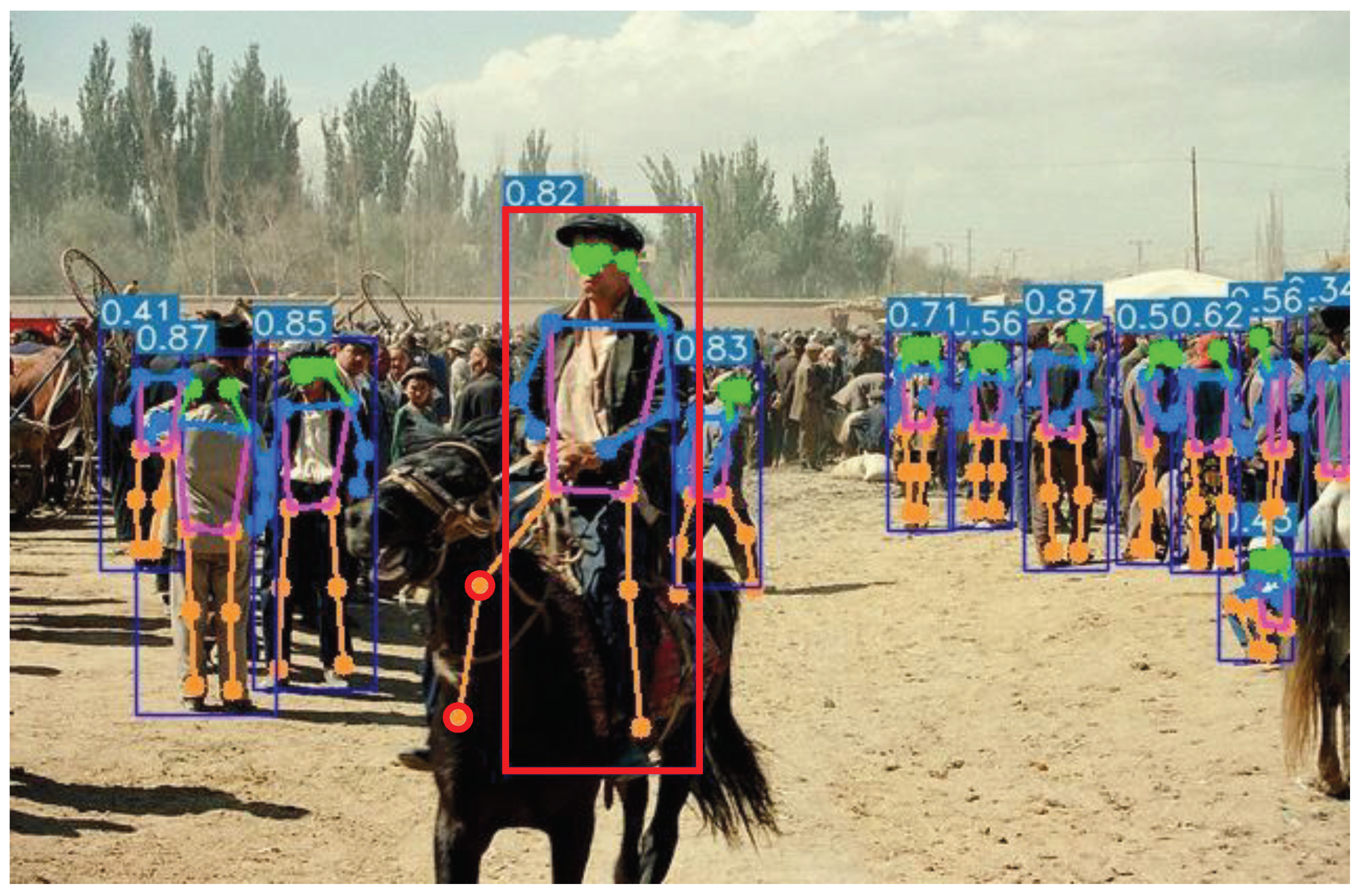
YOLO-Pose is a human pose estimation algorithm that employs a similar approach to bottom-up methods. Unlike most bottom-up human pose estimation algorithms, it does not use heatmaps. Instead, it associates all keypoints of a person with an anchor. For a given image, the anchor associated with a person stores not only the bounding box but also the complete 2D pose keypoints. The size of the detection box is normalized based on the height and width of the anchor, but the keypoints are not constrained by the anchor’s dimensions. Therefore, YOLO-Pose can still predict keypoints that are outside the bounding box, as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
YOLO-Pose accurately predicts occluded keypoints that are located outside the bounding box in images from the COCO dataset.
The results in Figure 2 demonstrate the output of the human pose estimation model, including the predicted bounding boxes and the estimated human skeletons. The bounding boxes not only indicate the position of the human body but also reflect the accuracy of the algorithm’s predictions. The predicted human skeletons showcase the algorithm’s ability to recognize keypoints on the human body. By overlaying these two pieces of information, we can visually assess the performance of the human pose estimation model.
3.2. C3 Module with Swin Transformer
For multi-person human pose estimation in complex scenes, collecting relevant keypoint information from neighboring regions can help alleviate keypoint confusion. However, convolutional neural networks have limitations in capturing global contextual information due to the nature of convolutional operations.
Compared to convolutional operations, the Transformer model leverages multi-head self-attention mechanism to effectively capture spatial information among keypoints in an image, resulting in more accurate keypoint detection. Compared to convolutional neural networks, Transformers exhibit higher robustness to perturbations and displacements.
In existing Transformer-based models, the scale of tokens is fixed, which is not suitable for the computer vision domain. Moreover, the pixel resolution of images is much larger than the number of words in text paragraphs. In many visual tasks, such as semantic segmentation, dense predictions need to be made at the pixel level. Therefore, Transformers struggle to handle high-resolution images. To address this issue, Swin Transformer introduces hierarchical feature maps.
The Swin Transformer is an approach that replaces the standard multi-head self-attention module (MSA) with a shifted-window-based module. In the Swin Transformer, all layers remain unchanged except for the replacement of the MSA module. The structure of the Swin Transformer is illustrated in Figure 3a.
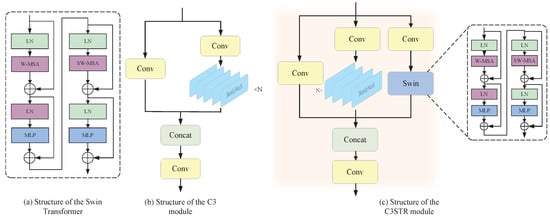
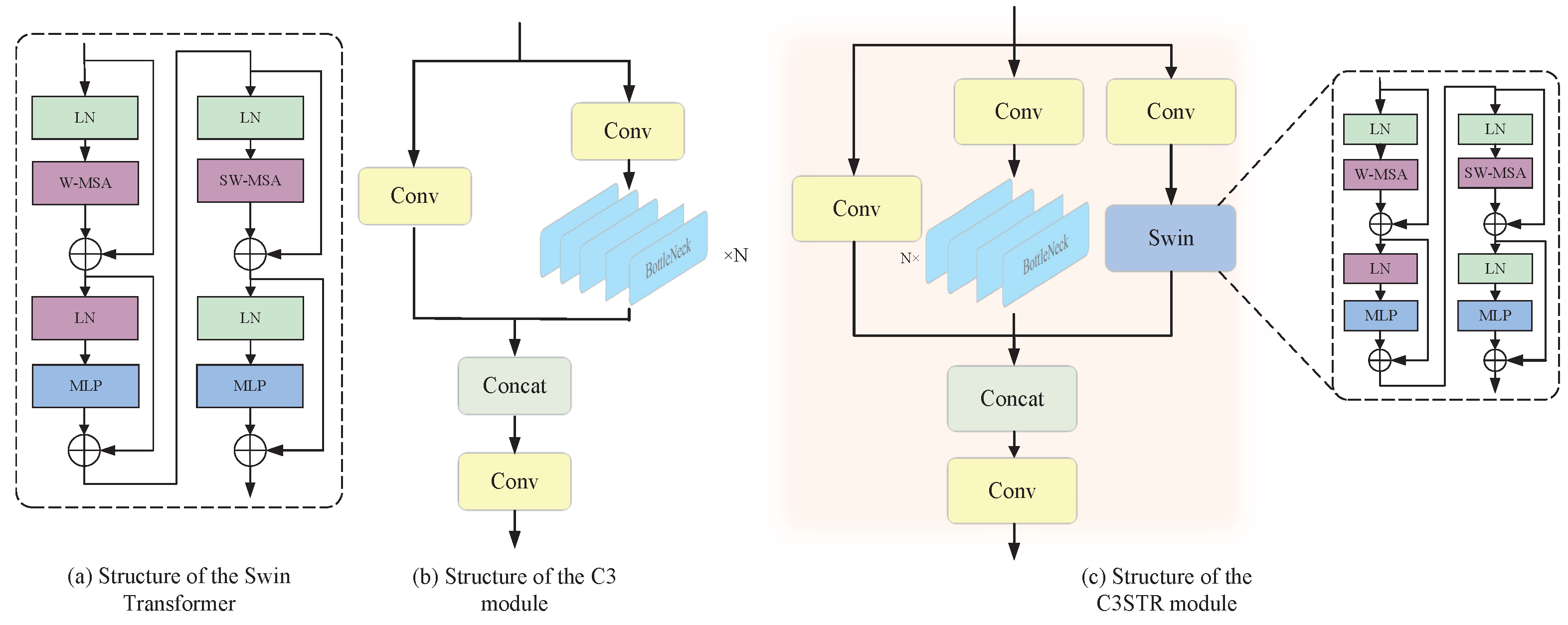
Figure 3.
(a) W-MSA and SW-MSA are multi-head self-attention modules with regular and shifted-window configurations, respectively. (b) The left branch of the module consists of a single basic convolutional module, while the right branch is composed of convolutional layers and multiple Bottleneck units. The main purpose of this module is to learn residual features. Finally, the outputs from the two branches of the C3 module are concatenated together. (c) In addition to the C3 module, the C3STR module incorporates a Swin Transformer branch, which consists of a Swin Transformer module and three standard convolutional layers.
This study modified the C3 module in the original YOLOv5 architecture using the Swin Transformer module named C3STR. Compared to the original C3 module, the modified C3STR module can better capture global information and enrich contextual information. Figure 3b illustrates the structure of the C3 module.
The C3 module is an important component of the YOLOv5 network, that aims to increase the depth and receptive field of the network, thereby enhancing the feature extraction capability. The C3 module consists of three basic convolutional blocks and N Bottleneck modules. The first convolutional block has a stride of 2, which reduces the size of the feature map by half, while the second and third convolutional blocks have a stride of 1. The convolutional blocks in the C3 module utilize 3 × 3 convolutional kernels. Additionally, Batch Normal layers and LeakyReLU activation functions are incorporated between convolutional blocks to improve the stability and generalization ability of the model.
To enable the C3 module to gather relevant keypoint information from neighboring regions, this study integrated the Swin Transformer into the C3 module, resulting in the C3STR module. The structure of the C3STR module is illustrated in Figure 3c.
This module consists of three parallel branches, each playing a different role in feature extraction.
Firstly, the leftmost branch contains a convolutional module with the SiLU activation function. This branch focuses on directly processing the input feature map through convolutional operations to preserve the spatial information integrity.
Secondly, the middle branch has a more complex structure composed of a convolutional module and N Bottleneck modules. Each Bottleneck module employs a residual connection structure to facilitate the training of deep networks. In this module, the channel number of the input feature map is halved by a convolutional kernel to reduce the parameter count and computational complexity. Subsequently, a convolutional kernel is used to expand the channel number, restoring it to the original dimension. This process ensures that the channel number of the input and output feature maps remains unchanged.
The rightmost branch combines a standard convolutional module with a Swin Transformer module. The Swin Transformer utilizes a self-attention mechanism, enabling it to capture long-range dependencies, which is particularly important for understanding complex human poses.
Finally, the outputs of these three branches are merged by concatenating their feature maps along the channel dimension. Then, the concatenated feature map is processed again by a standard convolutional module to integrate the information from different branches and output the final feature representation. This design allows the C3STR module to fully leverage the advantages of different network architectures, thus achieving more accurate predictions in the task of human pose estimation.
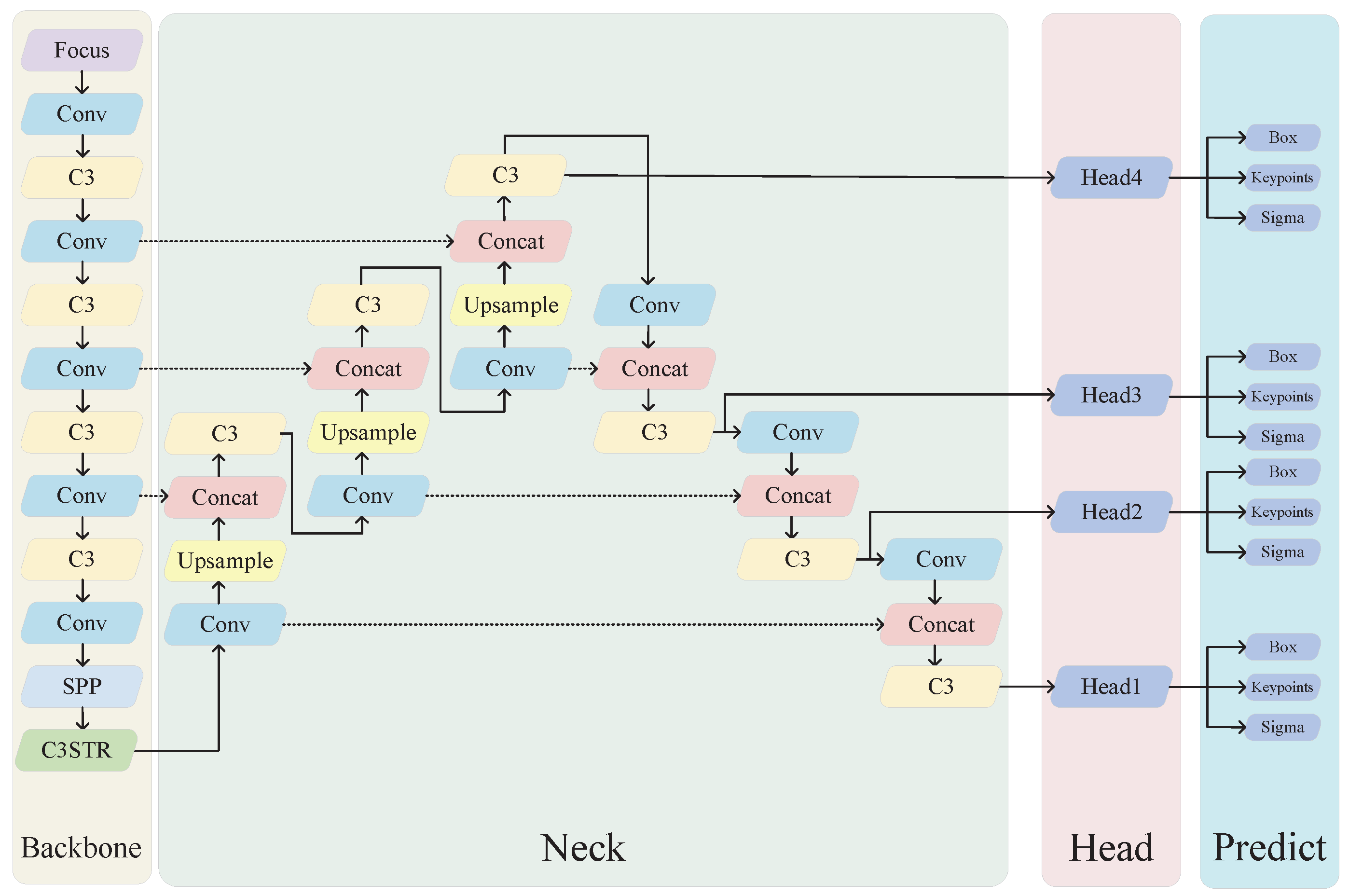
Using the Transformer too early in the network may result in the loss of meaningful contextual information. Therefore, this study only modified a subset of the C3 modules, specifically the ones directly connected to the head. The network architecture is illustrated in Figure 4.
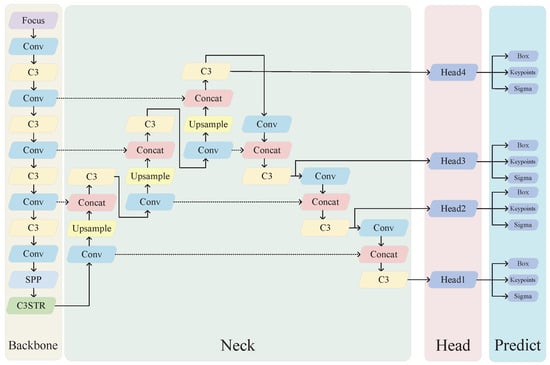
Figure 4.
YOLO-Rlepose network architecture.
3.3. Rle-Oks Loss
In the field of human pose estimation, heatmap-based methods have dominated the landscape. These methods generate likelihood heatmaps for each keypoint and locate the keypoints through argmax and soft-argmax operations. While heatmap-based methods exhibit excellent performance, they come with high computational and storage requirements.
In contrast, regression-based methods for human pose estimation are more efficient but often exhibit lower performance. During human pose estimation, real-time edge devices often directly map the input to the output joint coordinates. Regression-based methods are highly effective in such cases. However, in practical applications, the presence of occlusion, motion blur, and truncation issues leads to ambiguous ground-truth labels, resulting in the poor performance of regression-based methods in these scenarios. Heatmap-based methods leverage likelihood heatmaps to make the network robust to such ambiguities, but regression-based methods are still susceptible to the influence of these noisy labels.
Therefore, to mitigate the impact of noise on regression-based methods, maximum-likelihood estimation can be employed to model the distribution of the output, thereby facilitating human pose regression [28]. The regression paradigm employed to capture the potential output distribution is referred to as Residual Log-likelihood Estimation (RLE).
A generative model, in simple terms, is a model that generates new samples that follow the same distribution as the given training data. Assuming the training data follow the distribution , the generated samples follow the distribution , and our goal is to make these two distributions, and , similar. Therefore, the essence of a generative model is to fit the given training samples using a known probability model, which can be represented by a parameterized distribution .
Since different regression losses essentially make different assumptions about the output probability distribution, utilizing a flow-based model [35] to learn the distribution of errors between predicted and ground-truth keypoint values can help construct a better regression loss function.
Normalizing flows helps the model learn to construct complex distributions by transforming simple distributions through invertible mappings. Firstly, a flow model is used to map a zero-mean initial distribution to a zero-mean deformed distribution . Then, a regression model is used to predict and to control the location and scale of the distribution. The final distribution is obtained by shifting and rescaling to X, where . Therefore, the loss function can be written as Equation (1) [28]:
Given an input image , the regression model predicts a distribution , which represents the probability of the ground truth occurring at position X. In the equation, and , where represents the error between the predicted value and the ground-truth value, and is a constant. With this design, the flow model can now reveal the deviation between the output and the ground truth.
However, in the problem of human pose estimation, certain keypoints are more crucial than others. For instance, keypoints on the human body, such as shoulders, knees, and hips, are more important compared to keypoints on the head. Obviously, the less important keypoints are penalized more heavily for the same pixel-level error.
OKS (Object Keypoint Similarity) is the most popular evaluation metric for assessing keypoint detection. This metric is inspired by the IoU (Intersection over Union) metric used in object detection, with the purpose of measuring the similarity between the ground-truth and predicted human body keypoints. The OKS can be calculated as Equation (2):
In this equation, represents the Euclidean distance between the ground-truth and detected keypoints, and is the visibility flag for the ground-truth keypoints. is the standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution; here, s is the scale parameter of the target, which represents the size or dimension of the target in the image. represents the weights of the individual keypoints of the human body, and represents the total number of keypoints in the human body.
The RLE loss only considers the direct difference between predicted and ground-truth values, failing to fully account for variations in human target size and the relative importance of different keypoints. This approach neglects the possibility that the distribution of keypoint errors may vary with changes in target size and keypoint importance, potentially resulting in the model’s inability to accurately fit the true data distribution. To address this issue, this paper proposes a new loss function, named Rle-Oks loss, by referencing the OKS evaluation metric. This loss function not only considers the direct differences between keypoints but also normalizes these differences, similar to the OKS evaluation metric. Specifically, the Rle-Oks loss refers to the OKS evaluation metric and divides each keypoint error, denoted by , by a normalization factor determined by the target size s and keypoint-specific weight . This provides a more detailed and fair measurement of the error. Through this approach, the Rle-Oks loss can more accurately reflect the error between predicted keypoints and ground-truth keypoints and helps the model better adapt to targets of different sizes and keypoints of different importance.
In the task of human pose estimation, the prediction error of each target is usually accumulated from the keypoint errors it consists of. Considering that a target may contain 17 keypoints (e.g., head, neck, shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, and ankles), this paper defines the total loss function as the sum of the losses of these 17 keypoints. Therefore, the Rle-Oks loss function is represented by Equation (3):
where , , and is a constant.
At the beginning stage of training, the flow-based model may struggle to learn the correct distribution of errors, leading to increased difficulty in training the regression model and potentially decreasing the model’s performance. To address this issue, the target probability distribution formula can be written as Equation (4):
where the first term represents a simple distribution (such as a Gaussian or Laplace distribution), is the distribution that the flow model needs to learn, and the third term is a constant. Through this transformation, it can be observed that the dependence of the regression model on the flow model is greatly reduced, as the learned results of the flow model are only used to complement the simple distribution.
The presence of occlusions poses a challenge for keypoint detection tasks, as occlusions can prevent algorithms from accurately identifying the position and pose of the target. Therefore, the Rle-Oks loss takes into account the occlusions of keypoints, which can improve the accuracy and robustness of keypoint detection.
4. Experiments
The proposed model was evaluated on the COCO dataset. The COCO dataset consists of over 200,000 images with a total of 250,000 human instances, each annotated with 17 keypoints. The training set contains 57,000 images, while the validation and test sets contain 5000 and 20,000 images, respectively. The proposed model was trained on the training set, and the performance was evaluated on the test set. To evaluate the performance, this study uses the Average Precision (AP) based on the Object Keypoint Similarity (OKS) as the main evaluation metric on the COCO dataset. The experimental results are reported as the Average Precision (AP), Average Recall score (AR), and other metrics, such as AP50, AP75, and APL at different thresholds and target sizes.
In the field of human pose estimation, Average Precision (AP) is a crucial performance evaluation metric. The calculation of AP involves a threshold value, denoted by t, which is used to determine whether a keypoint detection is considered correct. Specifically, OKS is employed to measure the similarity between the predicted keypoints and the ground-truth keypoints. For a given threshold value t, if the OKS of a predicted keypoint is greater than t, it is regarded as a successful detection. Conversely, if the OKS is less than t, the detection is considered unsuccessful, indicating potential false positives, false negatives, or other errors. For each threshold value t, we count the number of detections with an OKS greater than the threshold and compare it to the total number of detections, resulting in a ratio. This ratio represents the proportion of correctly detected keypoints by the model at the current threshold, with a higher value indicating better detection performance. AP provides a comprehensive measure by aggregating the performance evaluations at different thresholds.
During the training process, to ensure the consistency of the input images, we first resized them to the desired size while maintaining a fixed aspect ratio. To maintain the consistency of the aspect ratio, we performed padding operations at the bottom of the image. This ensures that each sample has the same size and aspect ratio when performing pose estimation on the input images. The SGD optimizer with a cosine scheduler was used in training.
4.1. Implementation Details
YOLO-Rlepose was implemented with the help of PyTorch 1.11. All models were trained and tested on NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti. The device is a graphics card introduced by NVIDIA, located in Santa Clara, California, United States. During the training phase, partially pre-trained models from YOLO-Pose were utilized to accelerate the training progress. Since YOLO-Rlepose shares a significant portion of the backbone and some parts of the head with YOLO-Pose, many weights can be transferred, which significantly saves training time.
During the training phase, both the regression model and the flow model are optimized simultaneously. The initial density distribution of the flow model is set to a Laplace distribution. During inference, there is no need to run the flow model, allowing the loss function to be flexibly applied to various regression algorithms without increasing the testing time. Since the flow model is lightweight, it has a minimal impact on the training speed. Due to the generality of this loss function, it can also be applied to other versions of YOLO.
4.2. Results on COCO Test Set
Table 1 compares the proposed model with other methods based on Higher, HRNet, and EfficientHRNet. The proposed model demonstrates competitive performance in terms of AP values compared to existing methods. The achievements in AP values are particularly significant.

Table 1.
Comparison with bottom-up methods on the COCO dataset.
One of the reasons why the proposed model performs well in terms of AP values is the adoption of a novel loss function and network module, which enables the network to better understand the spatial relationships between keypoints. Through this approach, the model gains a better understanding of the structure and relationships of human poses.
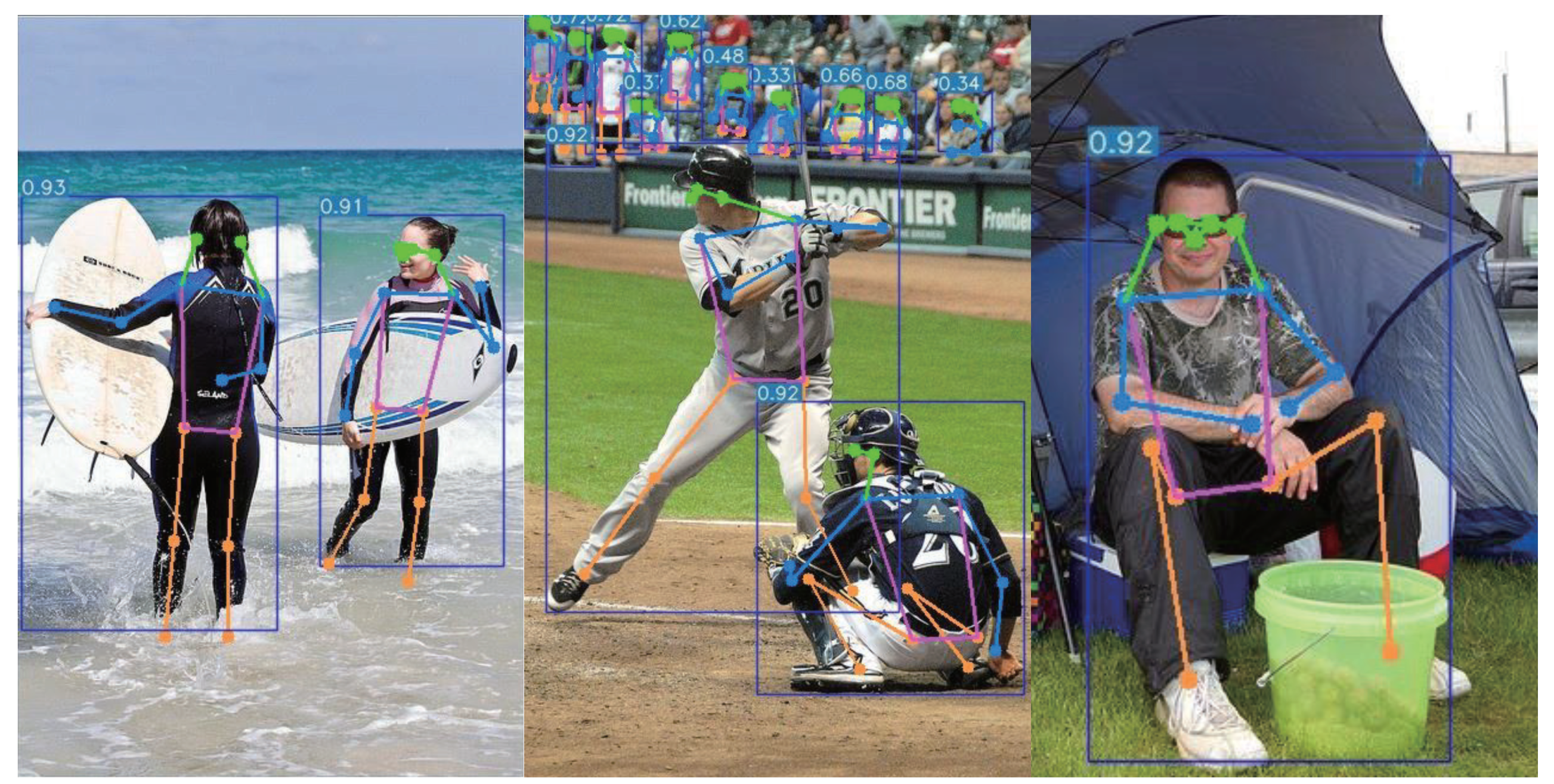
Furthermore, the proposed model exhibits superiority in predicting keypoints that are partially occluded. As shown in Figure 5, the model accurately predicts partially occluded keypoints, which is crucial for practical applications where occlusions may occur.

Figure 5.
YOLO-Rlepose accurately predicts partially occluded keypoints in images from the COCO dataset.
Experiments indicate that the proposed model is competitive in keypoint detection tasks and achieves notable results in terms of AP values and predicting keypoints in occluded body parts. The authors believe that the proposed model can play an important role in various practical applications, such as human action analysis and human–computer interaction.
4.3. Comparison of Rle-Oks Loss with Rle Loss and OKS Loss
One of the main contributions of this model is the Rle-Oks loss. The advantage of the Rle-Oks loss lies in its consideration of both the spatial relationships between keypoints and the weights between keypoints. In contrast, the traditional OKS loss only considers the distance between keypoints, while the Rle-Oks loss fails to take into account the visibility of keypoints and their weights. Therefore, the Rle-Oks loss can more accurately reflect the error in keypoint localization and better capture the distribution of real errors.
In the experiments, the authors compared the performance of OKS loss, Rle loss, and Rle-Oks loss in the yolov5s6-rlepose model. The results in Table 2 clearly show that the Rle-Oks loss, with the inclusion of keypoint weighting coefficients, exhibited better performance. This indicates that the Rle-Oks loss can more accurately estimate the localization error of keypoints and provide more precise loss feedback, thereby facilitating model training and optimization.

Table 2.
Comparison of different loss functions. It can be observed that the Rle-Oks loss performs the best in terms of AP.
The experiments demonstrate that the Rle-Oks loss is an effective loss function that can model the error distribution better and provide more accurate loss estimation. Using the Rle-Oks loss in keypoint localization tasks can lead to improved performance, thereby enhancing the accuracy and stability of the model.
4.4. Ablation Experiments
In this section, the impact of different components on the network performance is evaluated, as shown in Table 3. This study is based on the baseline model YOLOv5s6-Pose, where YOLOv5s6-Rlepose was incorporated as the backbone network, and the C3STR module was integrated into the original network. Additionally, the original loss function was replaced with the Rle-Oks loss.

Table 3.
Ablation experiments on the COCO dataset.
To assess the influence of different components on the network performance, we conducted a series of experiments. Firstly, we compared the performance of the baseline model YOLOv5s6-Pose with the modified YOLOv5s6-Rlepose, which includes the Rle loss, on the COCO dataset. The results showed that the modified model did not perform well in the human pose estimation task, indicating that the inclusion of the Rle-Oks loss did not yield desirable prediction results.
Next, this study further investigated the impact of the Rle-Oks loss on the network performance. The experimental results demonstrated that the network using the Rle-Oks loss achieved improvements in AP and AP75, confirming the effectiveness of the Rle-Oks loss in human pose estimation tasks.
Furthermore, the effects of the combination of the Rle-Oks loss and the C3STR module were studied on the experimental results. The results showed that the simultaneous use of the Rle-Oks loss and the C3STR module exhibited better robustness and accuracy in the human pose estimation task. Compared to the baseline model YOLOv5s6-Pose on the COCO dataset, the AP value achieved the greatest improvement, with a gain of .
The experimental results demonstrate significant performance improvements in the human pose estimation task by incorporating the C3STR module and the Rle-Oks loss to enhance the baseline model. These findings indicate the crucial roles played by the C3STR module and the Rle-Oks loss in human pose estimation tasks.
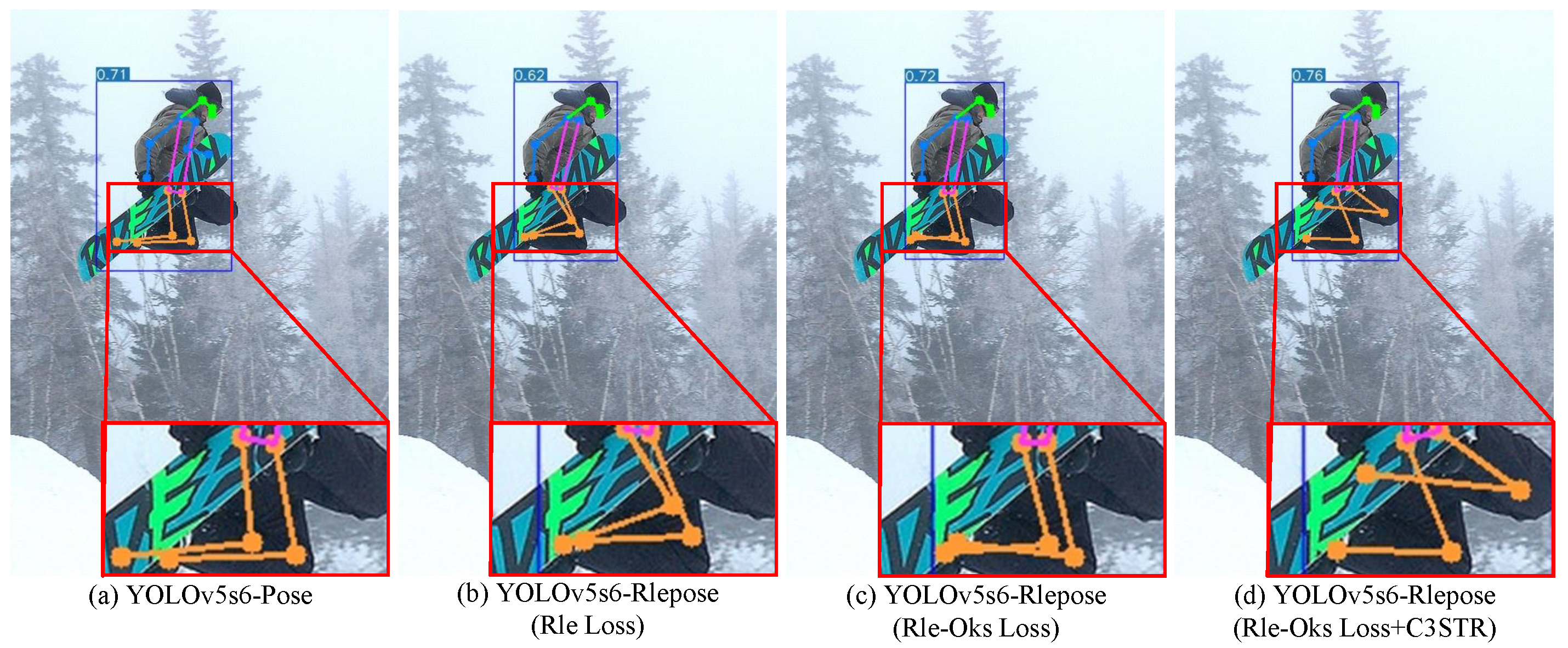
Figure 6 presents the results of the ablation experiments, as recorded in Table 3. In this experiment, the proposed YOLO-Rlepose model achieved a performance improvement of 2.11% compared to the YOLO-Pose model. Although this improvement may not be very apparent in the visual results, a careful zoom-in analysis reveals an enhancement in the accuracy of keypoint predictions.
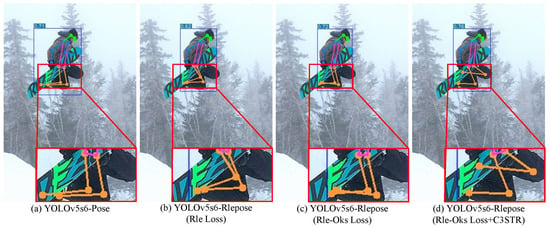
Figure 6.
Comparison of results from ablation experiments. The red border indicates the enlarged section.
Although the model in this study has achieved improvements in accuracy, it must be noted that this performance enhancement comes at the cost of increased computational complexity. The detailed numbers are given in Table 4.

Table 4.
Comparing the parameter and computation complexities of various experiments.
It should be clarified that the loss function only affects the model during the training process. During this stage, the loss function evaluates the difference between the ground-truth values and the predicted values of the model and adjusts the model’s parameters through backpropagation to minimize this difference. Once the model training is completed, the loss function no longer plays a role. Therefore, the Rle-Oks loss does not impact the computational complexity during the inference stage.
5. Conclusions
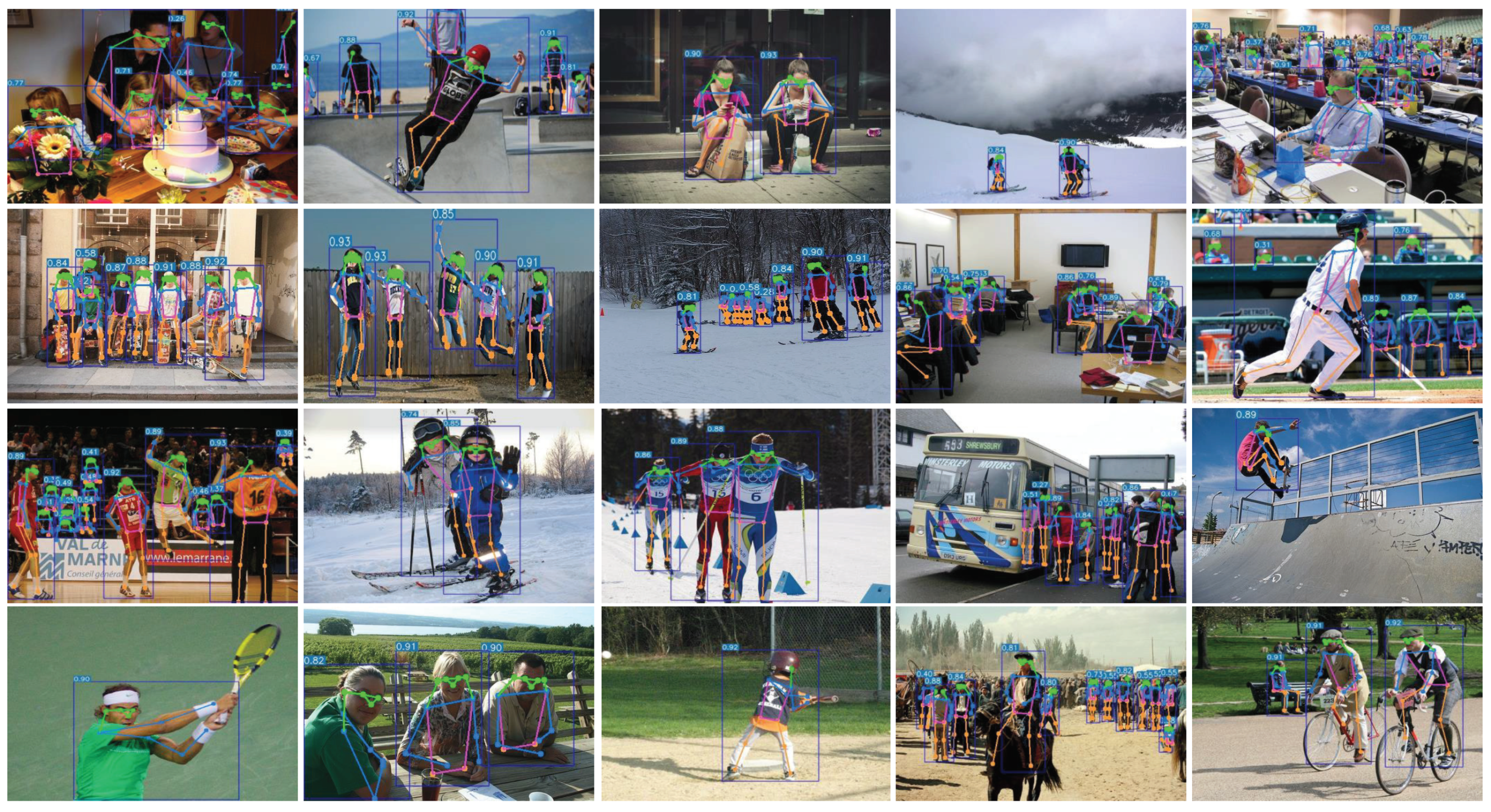
This study incorporated several state-of-the-art techniques, such as the Swin Transformer and an improved flow-based loss function, into YOLOv5 to create an effective human keypoint detector named YOLO-Rlepose. The results of our approach on the COCO dataset are shown in Figure 7. The detector excels at detecting keypoints for small objects. The introduction of the C3STR module allows for the better capture of global information and richer contextual information, thereby effectively improving the model’s keypoint detection capability. Additionally, the adoption of Rle-Oks loss reduces the impact of noise on regression-based methods, resulting in the more accurate detection of keypoints by the network. The experiments demonstrate that YOLO-Rlepose achieves favorable performance on the COCO dataset. The authors hope that this report can assist developers and researchers in gaining better insights into and experiences in the analysis and processing of human pose estimation.

Figure 7.
Results of human pose estimation by YOLO-Rlepose on the COCO dataset. The method demonstrates excellent keypoint detection performance for small objects.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.J.; software, K.Y.; writing—original draft, K.Y. and J.Z.; visualization, L.Q.; supervision, Y.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://cocodataset.org/.
Acknowledgments
The authors give their thanks the editor and anonymous referees for their comments, which helped improve the quality of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Du, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, L. Hierarchical recurrent neural network for skeleton based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 8–10 June 2015; pp. 1110–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, H.P.; Subramanian, A.; Das, S.; Mittal, A. Real-time upper-body human pose estimation using a depth camera. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision/Computer Graphics Collaboration Techniques: 5th International Conference, MIRAGE 2011, Rocquencourt, France, 10–11 October 2011; Proceedings 5. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Iqbal, U.; Insafutdinov, E.; Pishchulin, L.; Milan, A.; Gall, J.; Schiele, B. Posetrack: A benchmark for human pose estimation and tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 5167–5176. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ni, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, P.; Cheng, S.; Hu, J. Pose transferrable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 4099–4108. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, C. Fcpose: Fully convolutional multi-person pose estimation with dynamic instance-aware convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9034–9043. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part VIII 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Sun, J. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 7103–7112. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7291–7299. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J.; Shi, H.; Huang, T.S.; Zhang, L. Higherhrnet: Scale-aware representation learning for bottom-up human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5386–5395. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S. Single-stage multi-person pose machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6951–6960. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.; Wei, X.; Yu, X.; Tan, W.; Ren, Y.; Pu, S. Inspose: Instance-aware networks for single-stage multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 3079–3087. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, H.; Shen, C. Directpose: Direct end-to-end multi-person pose estimation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.07451. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, S. Point-set anchors for object detection, instance segmentation and pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part X 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 527–544. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, D.; Nagori, S.; Mathew, M.; Poddar, D. Yolo-pose: Enhancing yolo for multi person pose estimation using object keypoint similarity loss. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 2637–2646. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Quan, Z.; Nie, M.; Yang, W. Transpose: Keypoint localization via transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11802–11812. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.; Xia, S.T.; Zhou, E. Tokenpose: Learning keypoint tokens for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11313–11322. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Ge, Y.; Shen, C.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; den Hengel, A.v. Poseur: Direct human pose regression with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 72–88. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, D. Vitpose: Simple vision transformer baselines for human pose estimation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 38571–38584. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Tompson, J.J.; Jain, A.; LeCun, Y.; Bregler, C. Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Proceedings of the NIPS 2014, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc. (NeurIPS): San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Yin, B.; Du, A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, E.; Sun, J. Learning delicate local representations for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part III 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Shang, J.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y. Compositional human pose regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2602–2611. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Dai, H.; Ye, M.; Zhu, C. Distribution-aware coordinate representation for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 7093–7102. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Agrawal, P.; Fragkiadaki, K.; Malik, J. Human pose estimation with iterative error feedback. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4733–4742. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Bian, S.; Zeng, A.; Wang, C.; Pang, B.; Liu, W.; Lu, C. Human pose regression with residual log-likelihood estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11025–11034. [Google Scholar]
- Rogez, G.; Weinzaepfel, P.; Schmid, C. Lcr-net: Localization-classification-regression for human pose. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3433–3441. [Google Scholar]
- Pavllo, D.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Grangier, D.; Auli, M. 3D human pose estimation in video with temporal convolutions and semi-supervised training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7753–7762. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Z.; Qian, K.; Lin, M.; Li, H.; Ren, J.S. Generalizing monocular 3D human pose estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 4024–4033. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.; Sun, X.; Huang, F.; Liu, M.; Xu, Q.; Lin, S. Srnet: Improving generalization in 3D human pose estimation with a split-and-recombine approach. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XIV 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 507–523. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Moon, G.; Lee, K.M. Pose2mesh: Graph convolutional network for 3D human pose and mesh recovery from a 2D human pose. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part VII 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 769–787. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhu, S.C. Learning pose grammar to encode human body configuration for 3D pose estimation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Rezende, D.; Mohamed, S. Variational inference with normalizing flows. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; PMLR. pp. 1530–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Zhu, T.; Chen, L.C.; Gidaris, S.; Tompson, J.; Murphy, K. Personlab: Person pose estimation and instance segmentation with a bottom-up, part-based, geometric embedding model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss, S.; Bertoni, L.; Alahi, A. Pifpaf: Composite fields for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11977–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Neff, C.; Sheth, A.; Furgurson, S.; Tabkhi, H. Efficienthrnet: Efficient scaling for lightweight high-resolution multi-person pose estimation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.08090. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; PMLR; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Z.; Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Bottom-up human pose estimation via disentangled keypoint regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14676–14686. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).