Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Despeckling Based on a Deep Learning Network Employing Frequency Domain Decomposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Statistical Model of SAR Speckle
2.2. Frequency Domain Decomposition Model
3. Methodology
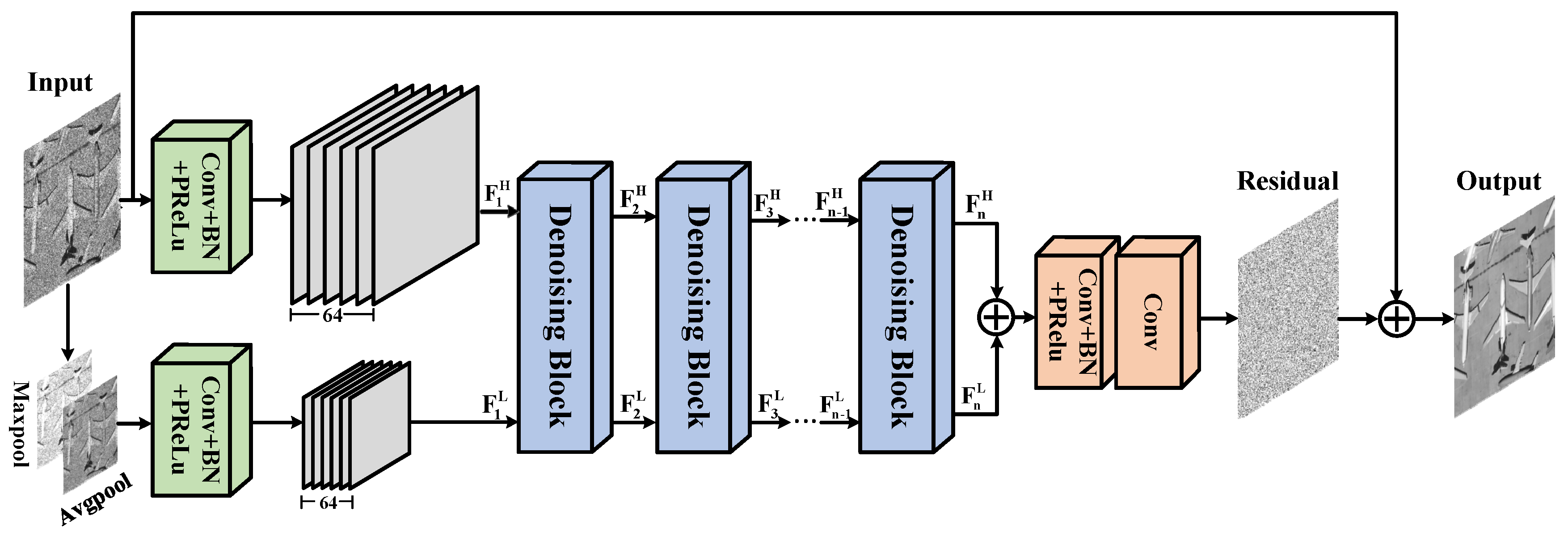
3.1. General Network Architecture
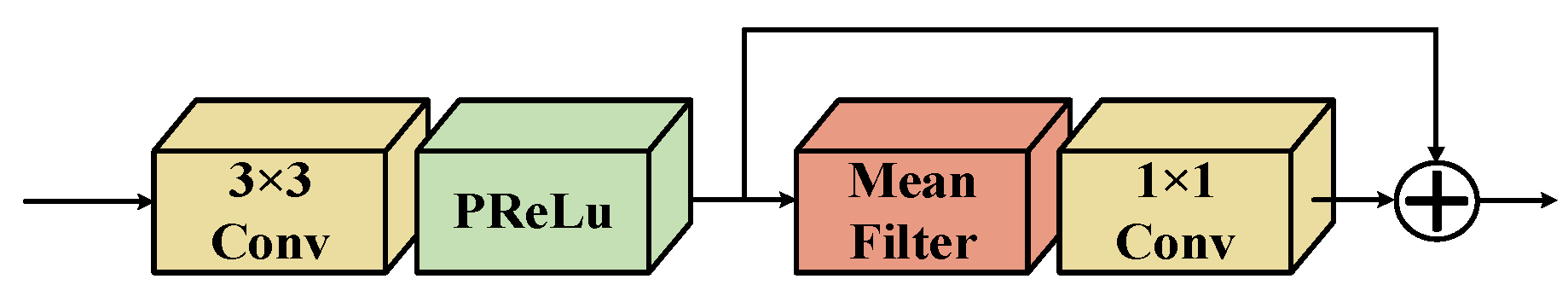
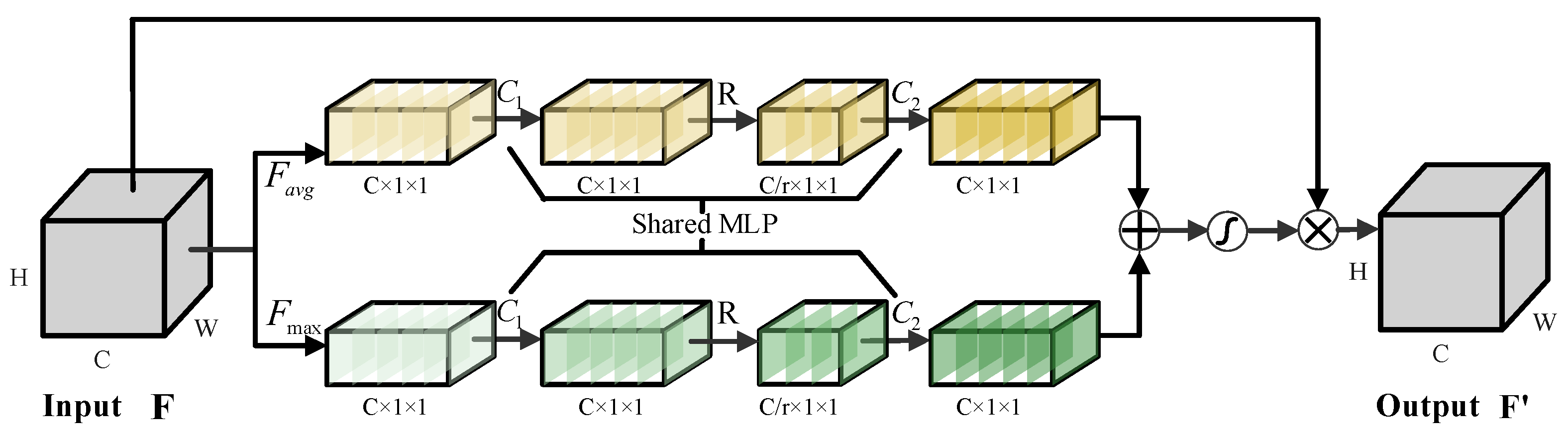
3.2. Network Subblock Structure
3.3. Overall Network Training
4. Results and Discussion
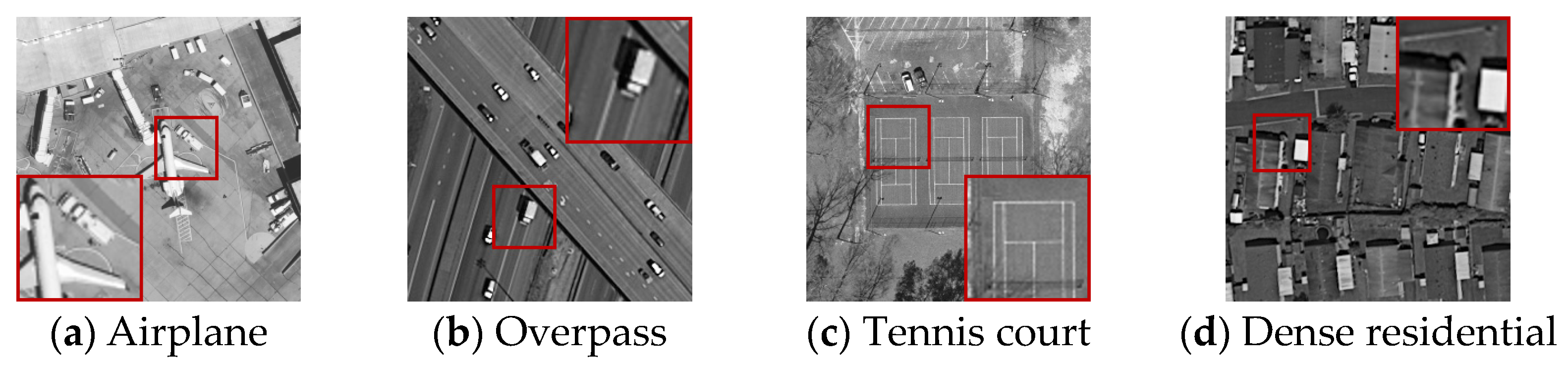
4.1. Experimental Setting
4.2. Comparative Methods and Quantitative Evaluations
4.3. Simulated Data Experiments
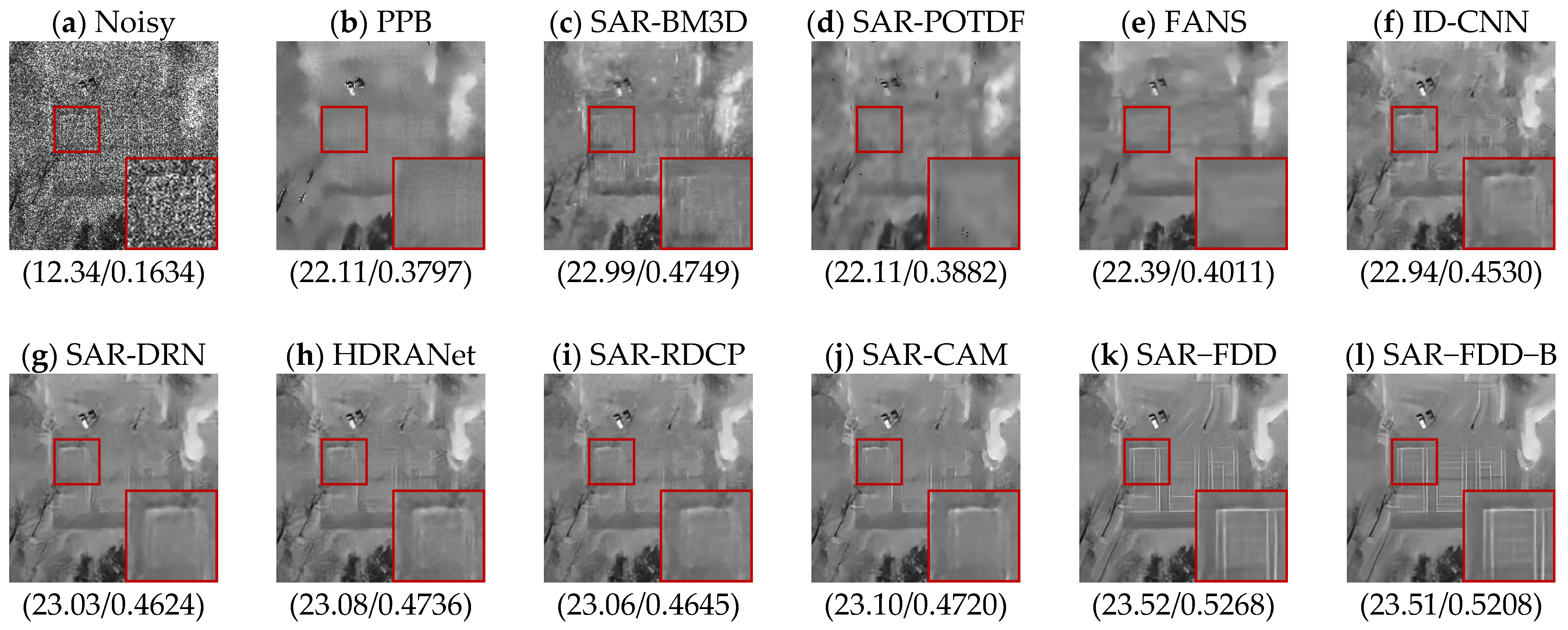
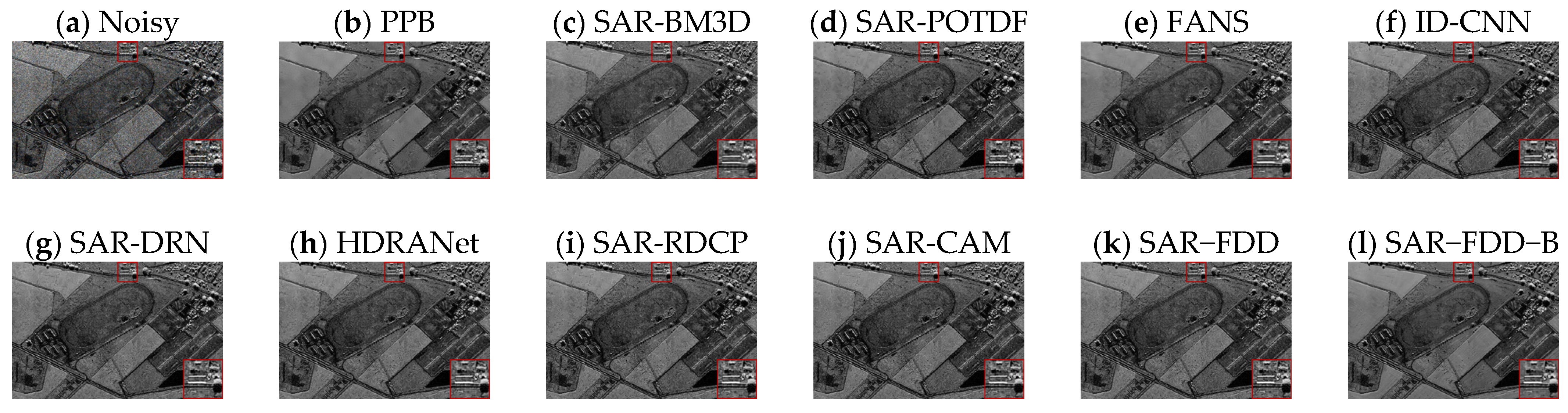
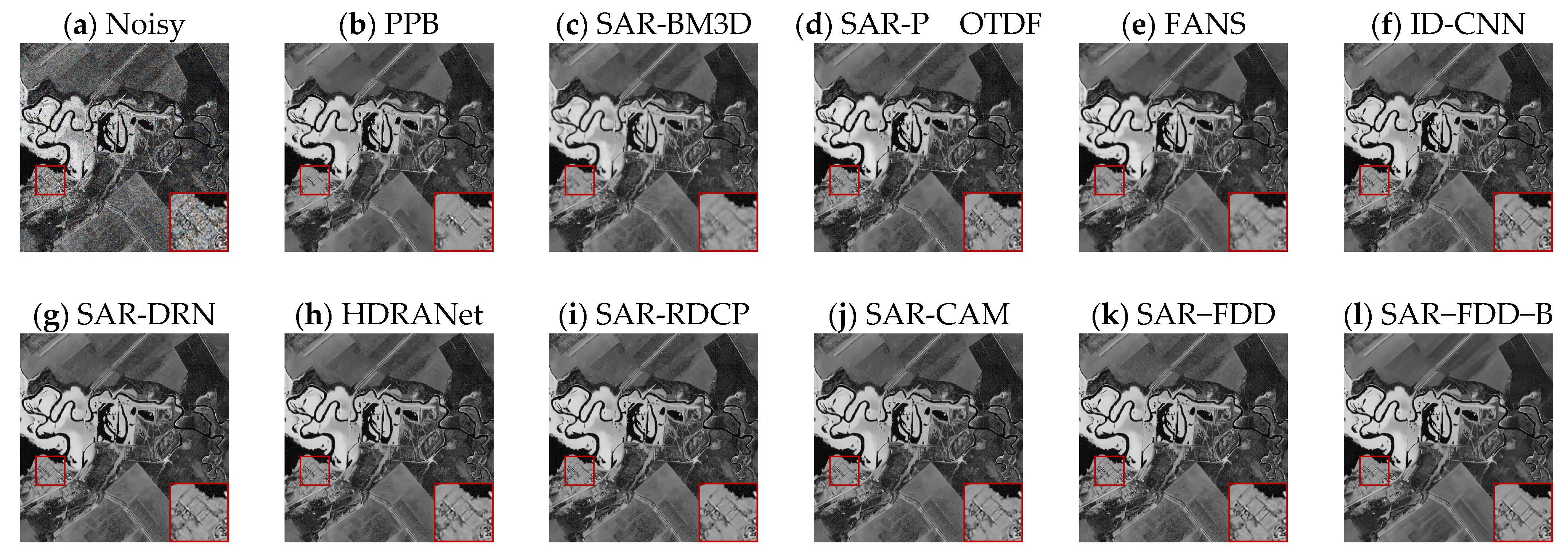
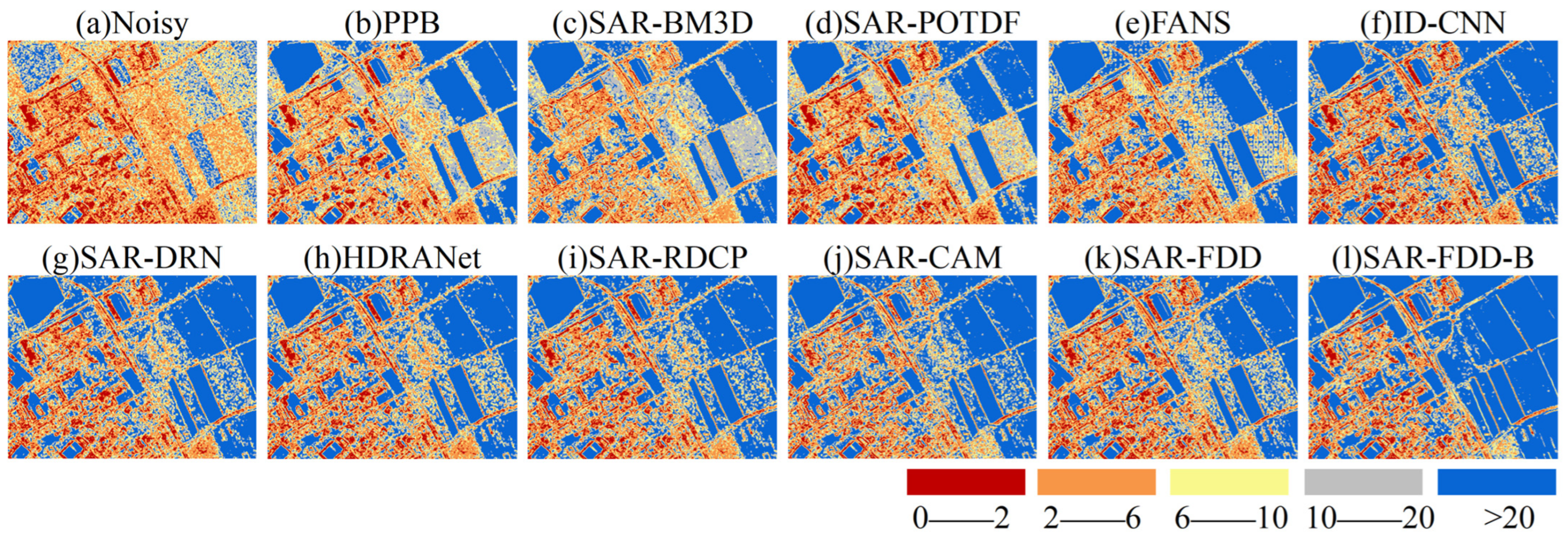
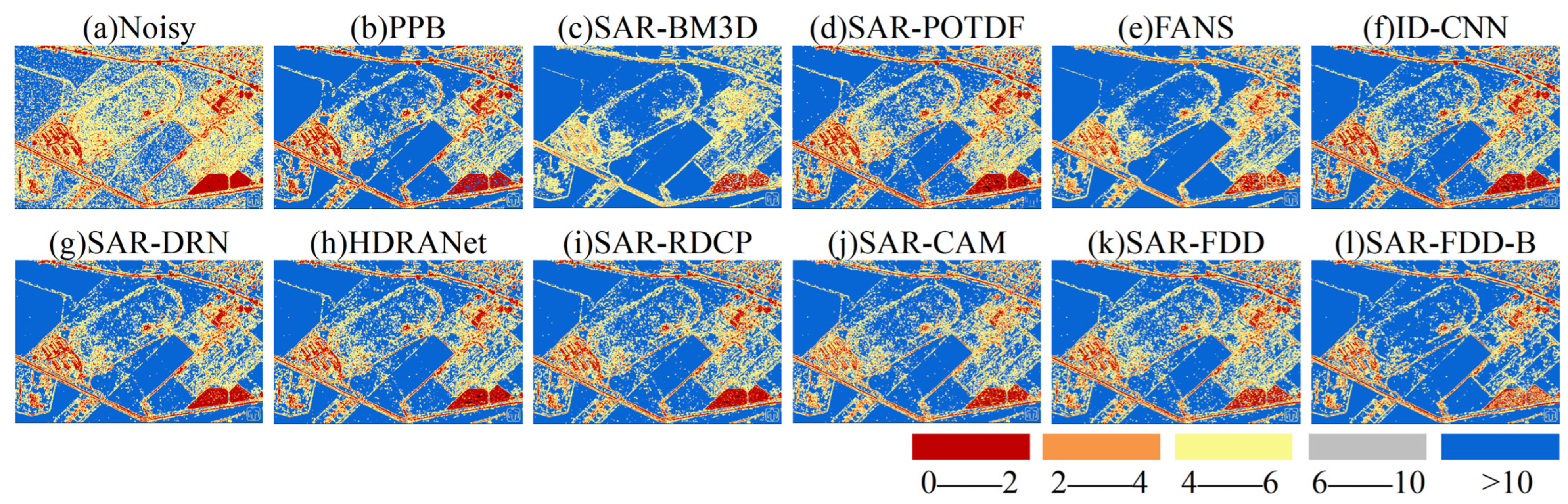
4.4. Real SAR Data Experiments
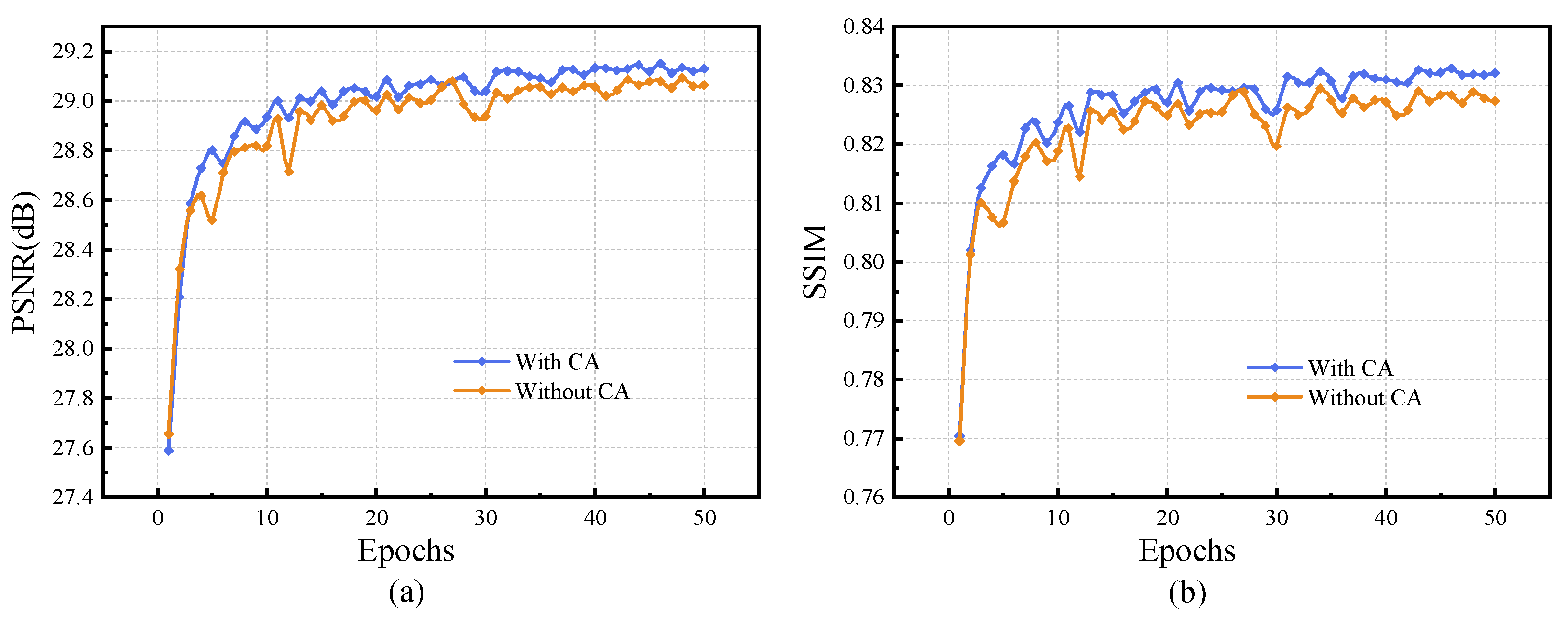
4.5. Ablation Study
4.6. About Runtime and Number of Parameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Statistical properties of laser speckle patterns. In Laser Speckle and Related Phenomena; Springer: Berling/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975; pp. 9–75. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Pu, H.; Chen, B.; Gao, L. Prediction of InSAR Deformation Time-Series Using a Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 6921–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Digital Image Enhancement and Noise Filtering by Use of Local Statistics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1980, 2, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, D.T.; Sawchuk, A.A.; Strand, T.C.; Chavel, P. Adaptive Noise Smoothing Filter for Images with Signal-Dependent Noise. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1985, 7, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, V.S.; Stiles, J.A.; Shanmugan, K.S.; Holtzman, J.C. A Model for Radar Images and Its Application to Adaptive Digital Filtering of Multiplicative Noise. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1982, 4, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucher, S.; Benie, G.B.; Boucher, J.M. Multiscale MAP filtering of SAR images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Odegard, J.E.; Lang, M.; Gopinath, R.A.; Selesnick, I.W.; Burrus, C.S. Wavelet based speckle reduction with application to SAR based ATD/R. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Image Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 13–16 November 1994; pp. 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschetti, G.; Pascazio, V.; Schirinzi, G. Iterative homomorphic technique for speckle reduction in synthetic-aperture radar imaging. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1995, 12, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, L.; Jouan, A. Speckle filtering of SAR images: A comparative study between complex-wavelet-based and standard filters. Wavelet Applications in Signal and Image Processing V. SPIE 1997, 3169, 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.G.; Yu, B.; Vetterli, M. Spatially adaptive wavelet thresholding with context modeling for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argenti, F.; Alparone, L. Speckle removal from SAR images in the undecimated wavelet domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deledalle, C.A.; Denis, L.; Tupin, F. Iterative Weighted Maximum Likelihood Denoising with Probabilistic Patch-Based Weights. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrilli, S.; Poderico, M.; Angelino, C.V.; Verdoliva, L. A Nonlocal SAR Image Denoising Algorithm Based on LLMMSE Wavelet Shrinkage. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, D.; Parrilli, S.; Scarpa, G.; Poggi, G.; Verdoliva, L. Fast Adaptive Nonlocal SAR Despeckling. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, W.; Zhang, D.; Shi, G. Two-stage image denoising by principal component analysis with local pixel grouping. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 1531–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, L.I.; Osher, S.; Fatemi, E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1992, 60, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, G.; Aujol, J.F. A Variational Approach to Removing Multiplicative Noise. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2008, 68, 925–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Osher, S. A Nonlinear Inverse Scale Space Method for a Convex Multiplicative Noise Model. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2008, 1, 294–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, L. SAR Image Despeckling Based on Combination of Fractional-Order Total Variation and Nonlocal Low Rank Regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 2056–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Zhou, R.R. Optimization model for multiplicative noise and blur removal based on Gaussian curvature regularization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2018, 35, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krichen, M. Convolutional Neural Networks: A Survey. Computers 2023, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. FFDNet: Toward a Fast and Flexible Solution for CNN-Based Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4608–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, N.K.; Jha, D.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, H.D.; Johansen, D.; Rittscher, J.; Halvorsen, P.; Ali, S. Fanet: A Feedback Attention Network for Improved Biomedical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 9375–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, N.K.; Jha, D.; Bagci, U.; Ali, S. TGANet: Text-Guided Attention for Improved Polyp Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Singepore, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Hu, S.; Liu, S. Ship detection in SAR images based on region growing and multi-scale salienc. In Proceedings of the Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV), Nanjing, China, 16–18 October 2020; pp. 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Chierchia, G.; Cozzolino, D.; Poggi, G.; Verdoliva, L. SAR image despeckling through convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 5438–5441. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Patel, V.M. SAR Image Despeckling Using a Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Ma, X. Learning a dilated residual network for SAR image despeckling. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, P.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, Z.; Hou, X.; Cottrell, G. Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 1451–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Bai, Y. HDRANet: Hybrid Dilated Residual Attention Network for SAR Image Despeckling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Xue, L.; Li, X. SAR image despeckling using a dilated densely connected network. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattari, F.; Gonzalez Leon, B.; Asaro, F.; Rucci, A.; Prati, C.; Matteucci, M. Deep Learning for SAR Image Despeckling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Yuan, Q. SAR Image Despeckling Employing a Recursive Deep CNN Prior. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaei, H.; Ferraioli, G.; Vitale, S.; Zamani, R.; Schirinzi, G.; Pascazio, V. Nonlocal Model-Free Denoising Algorithm for Single- and Multichannel SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsasso, E.; Denis, L.; Tupin, F. SAR2SAR: A Semi-Supervised Despeckling Algorithm for SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4321–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molini, A.B.; Valsesia, D.; Fracastoro, G.; Magli, E. Speckle2Void: Deep Self-Supervised SAR Despeckling With Blind-Spot Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsasso, E.; Denis, L.; Tupin, F. As if by Magic: Self-supervised Training of Deep Despeckling Networks with MERLIN. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perona, P.; Malik, J. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1990, 12, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, H.; Xu, B.; Yan, Z.; Kalantidis, Y.; Rohrbach, M.; Yan, S.; Feng, J. Drop an octave: Reducing spatial redundancy in convolutional neural networks with octave convolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3435–3444. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Wang, W.; Cheng, G.; Wei, M.; Xie, H.; Wang, F.L. FDDL-Net: Frequency domain decomposition learning for speckle reduction in ultrasound images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 42769–42781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Wei, M.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Liang, L.; Xie, H.; Wang, F.L.; Wang, M. Detail-recovery image deraining via context aggregation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 14560–14569. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lillie, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, J.; Lee, S. SAR image despeckling using continuous attention module. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Hou, B.; Gong, M. SAR Image Despeckling Based on Local Homogeneous-Region Segmentation by Using Pixel-Relativity Measurement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2724–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papafitsoros, K.; Schönlieb, C.B. A combined first and second order variational approach for image reconstruction. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2014, 48, 308–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Newsam, S. Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification. In Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 2–5 November 2010; pp. 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gong, H.; Feng, D.; Zhang, Y. An Adaptive Method of Speckle Reduction and Feature Enhancement for SAR Images Based on Curvelet Transform and Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3105–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cui, Y.; Li, Z.; Zuo, B.; Yang, J.; Song, J. Patch Ordering-Based SAR Image Despeckling Via Transform-Domain Filtering. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Pierce, L.E.; Ulaby, F.T. SAR speckle reduction using wavelet denoising and Markov random field modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2196–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, G.; Poderico, M.; Poggi, G.; Riccio, D.; Verdoliva, L. Benchmarking Framework for SAR Despeckling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 1596–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


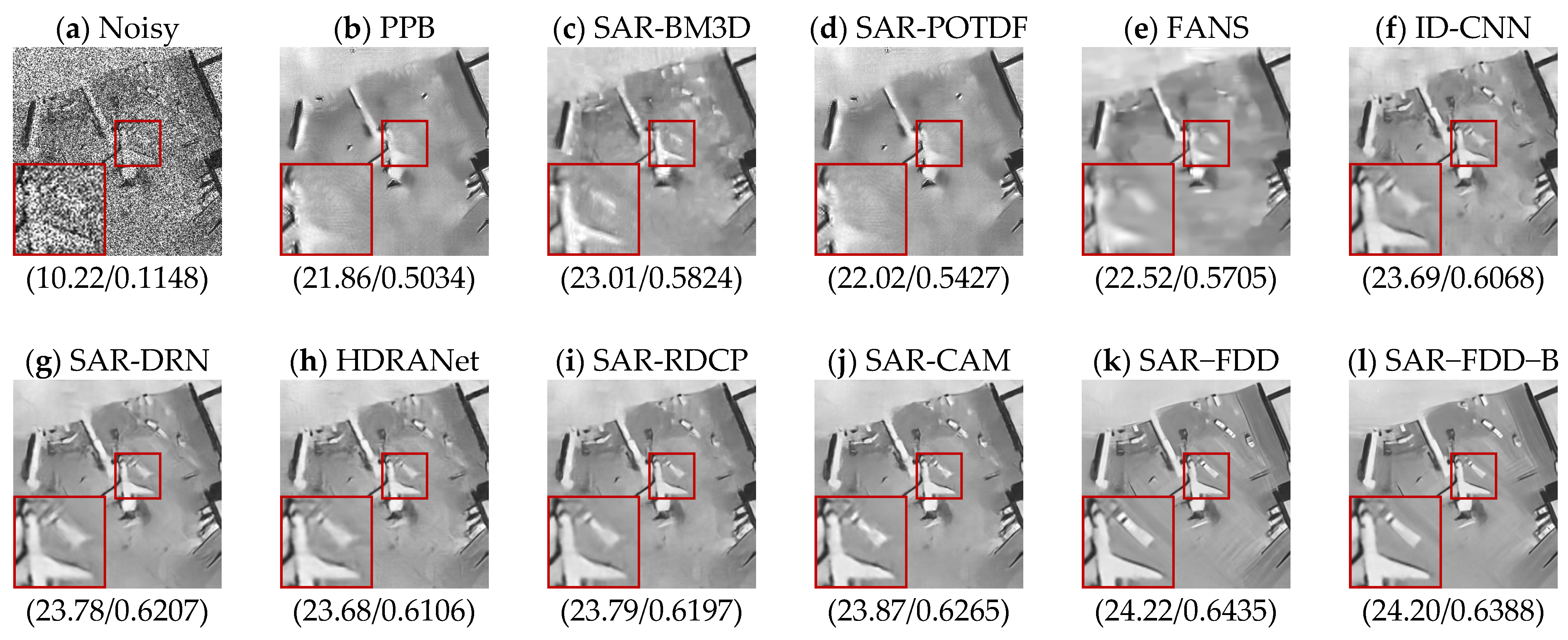
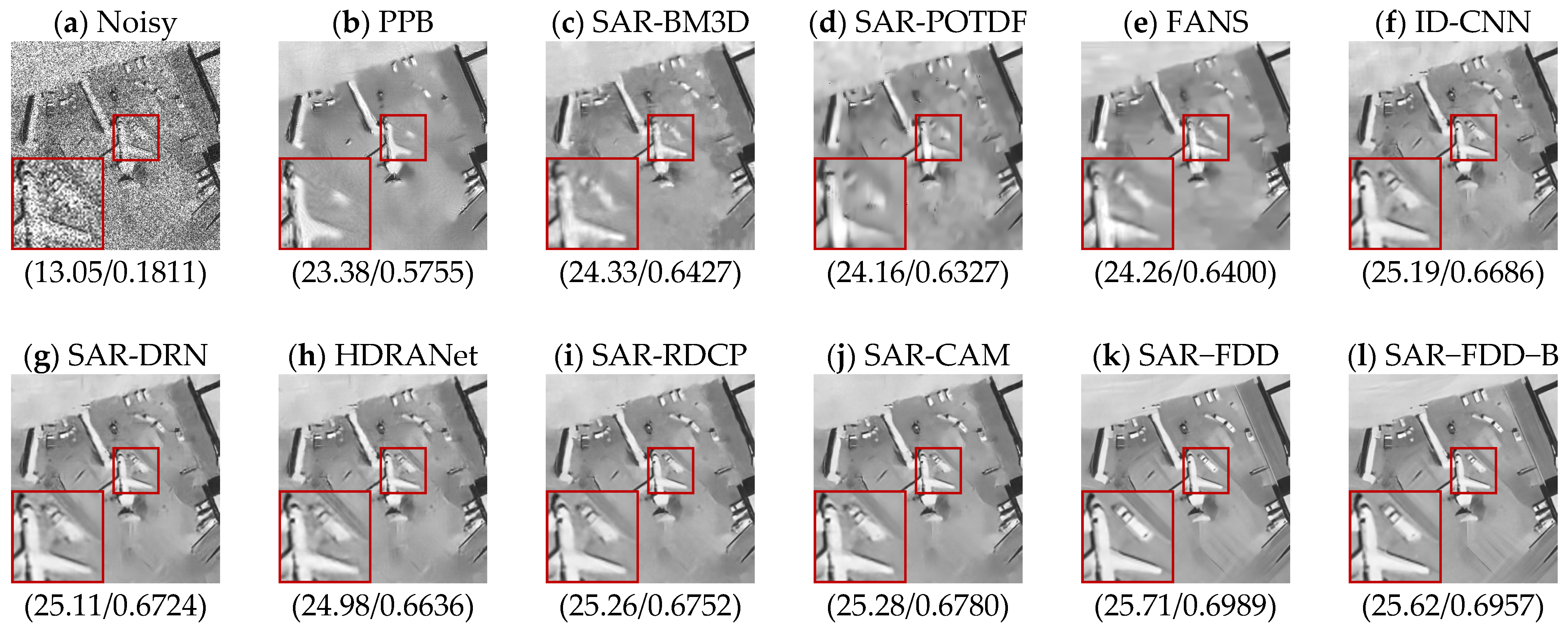
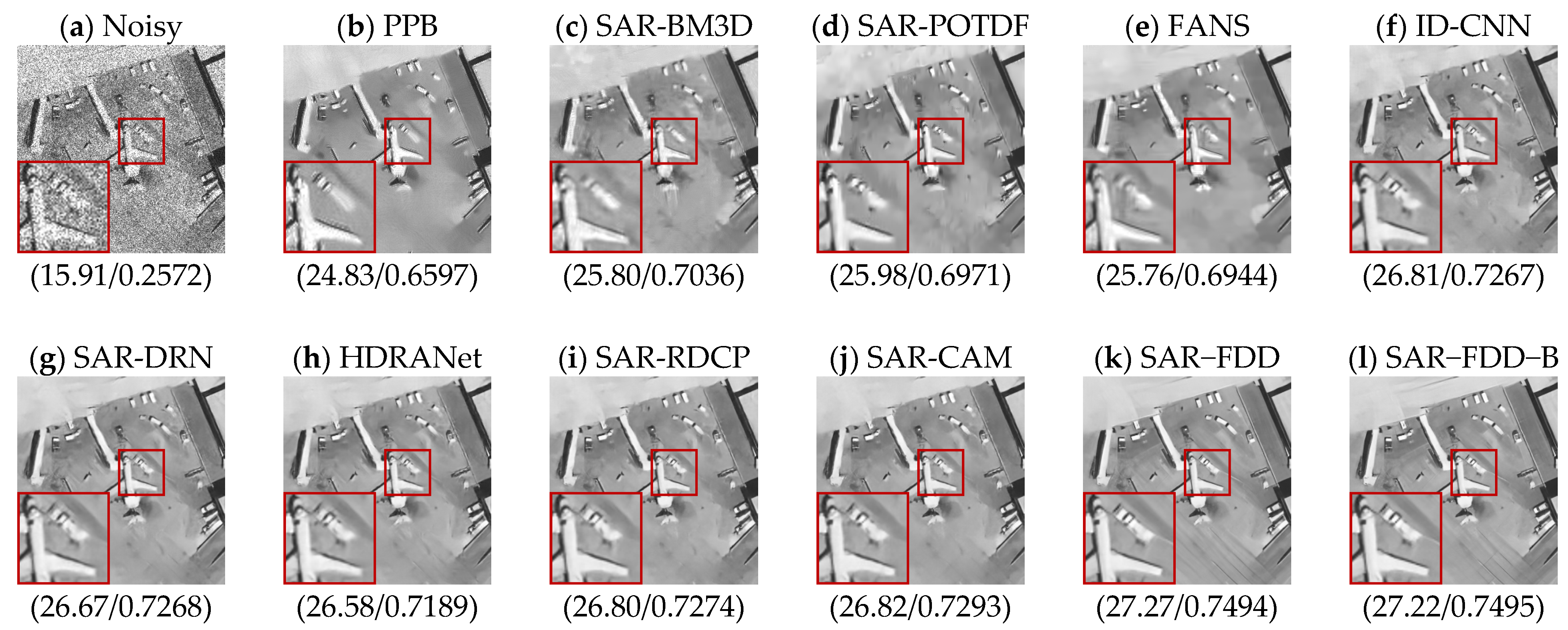

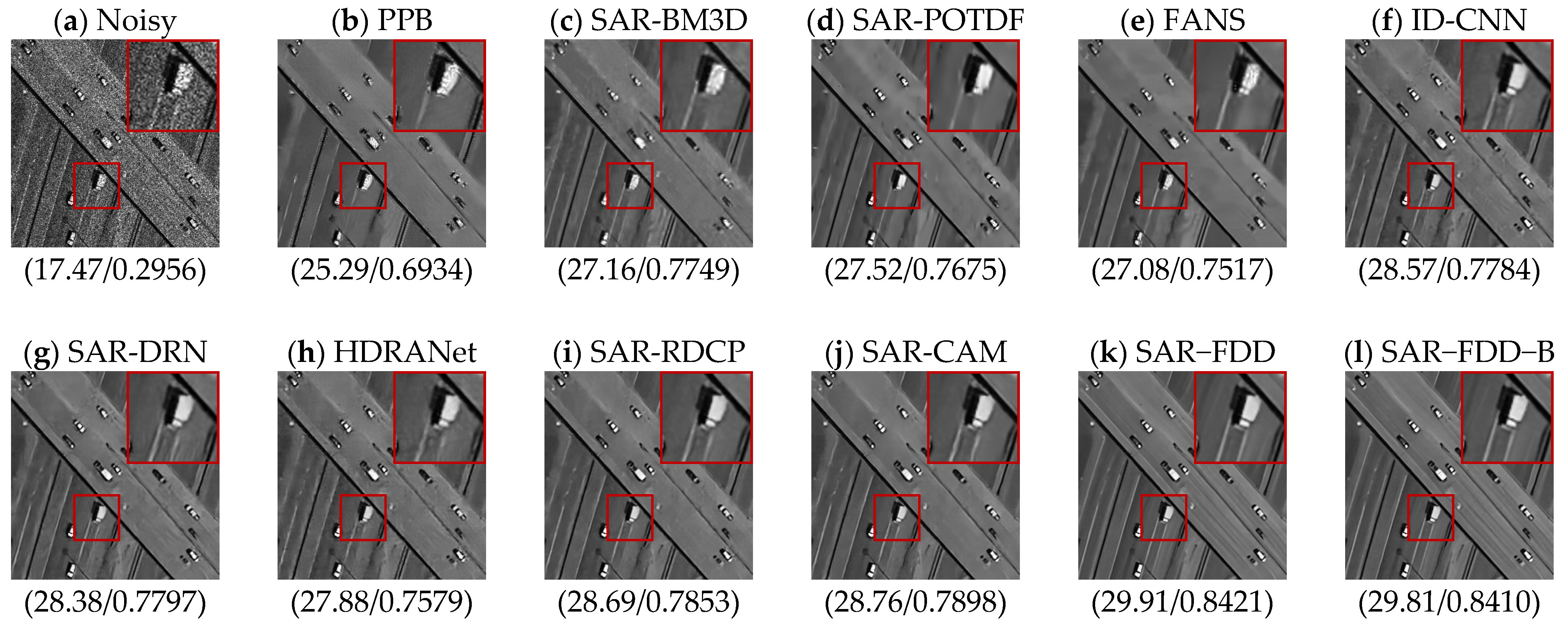
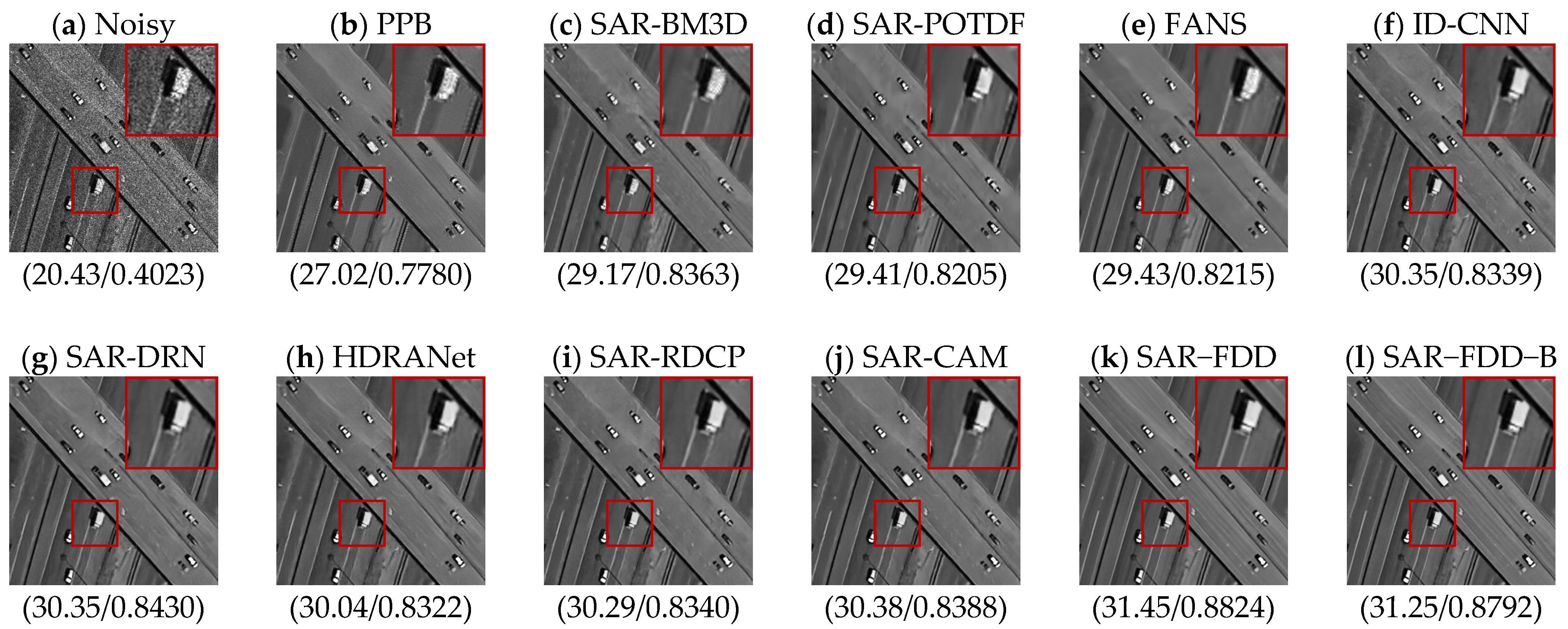



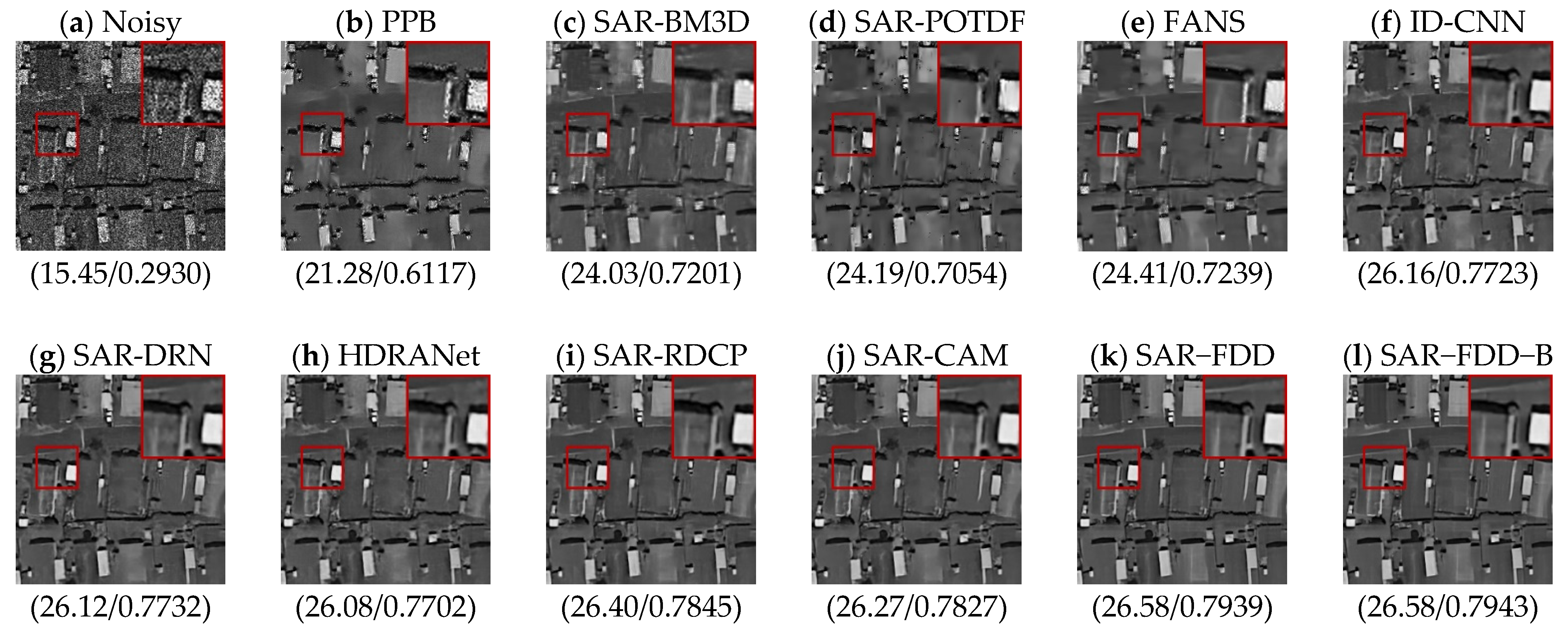
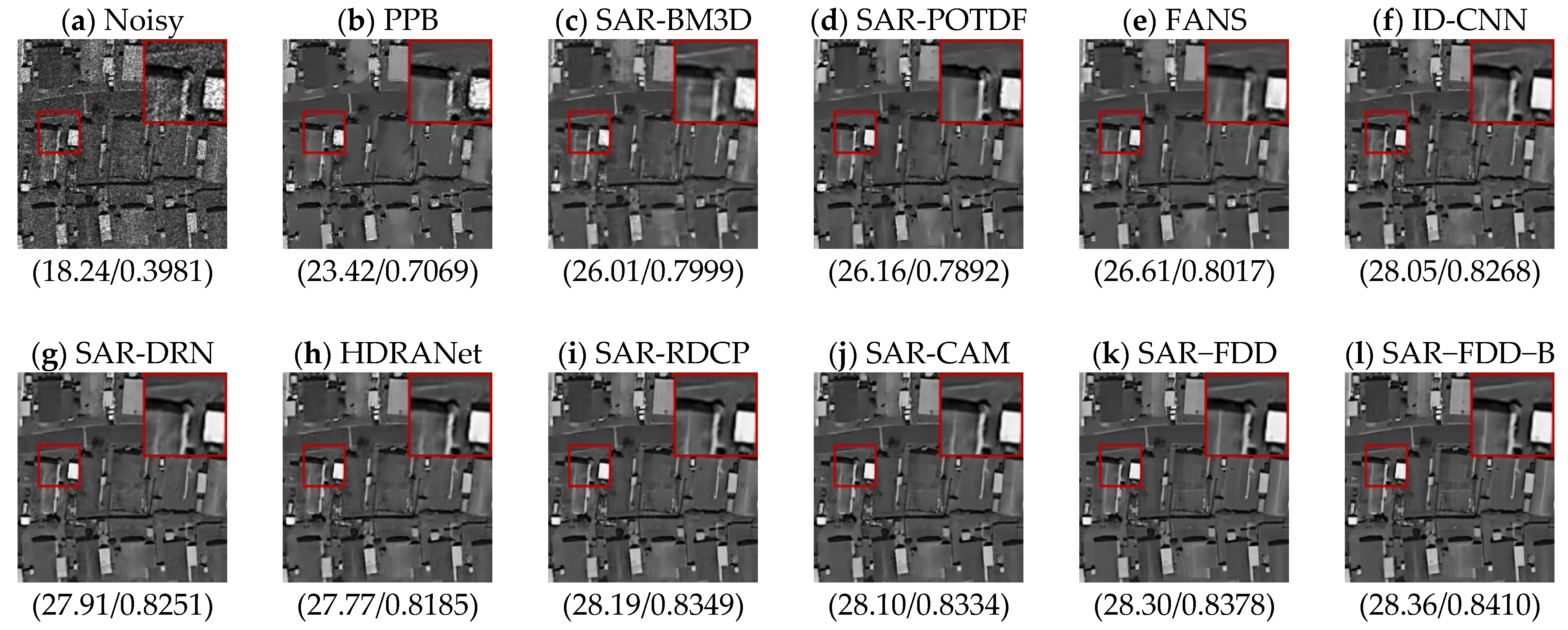
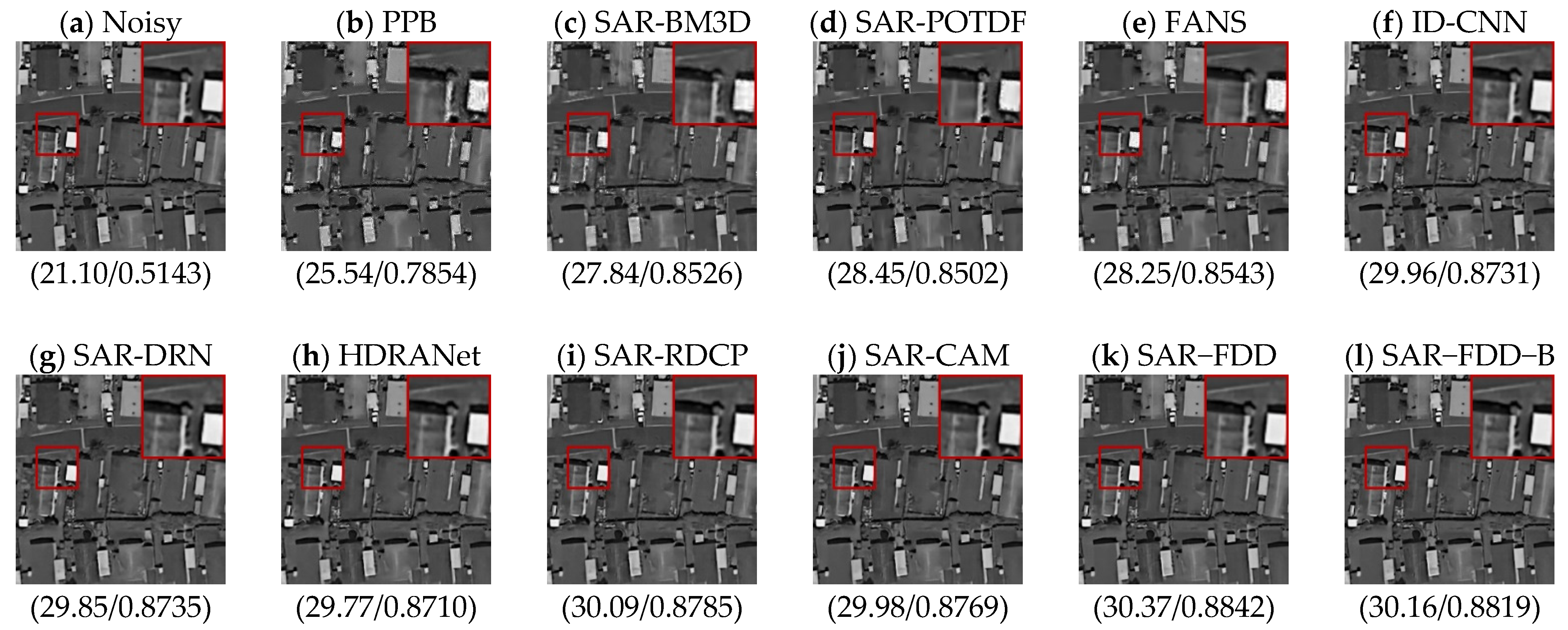



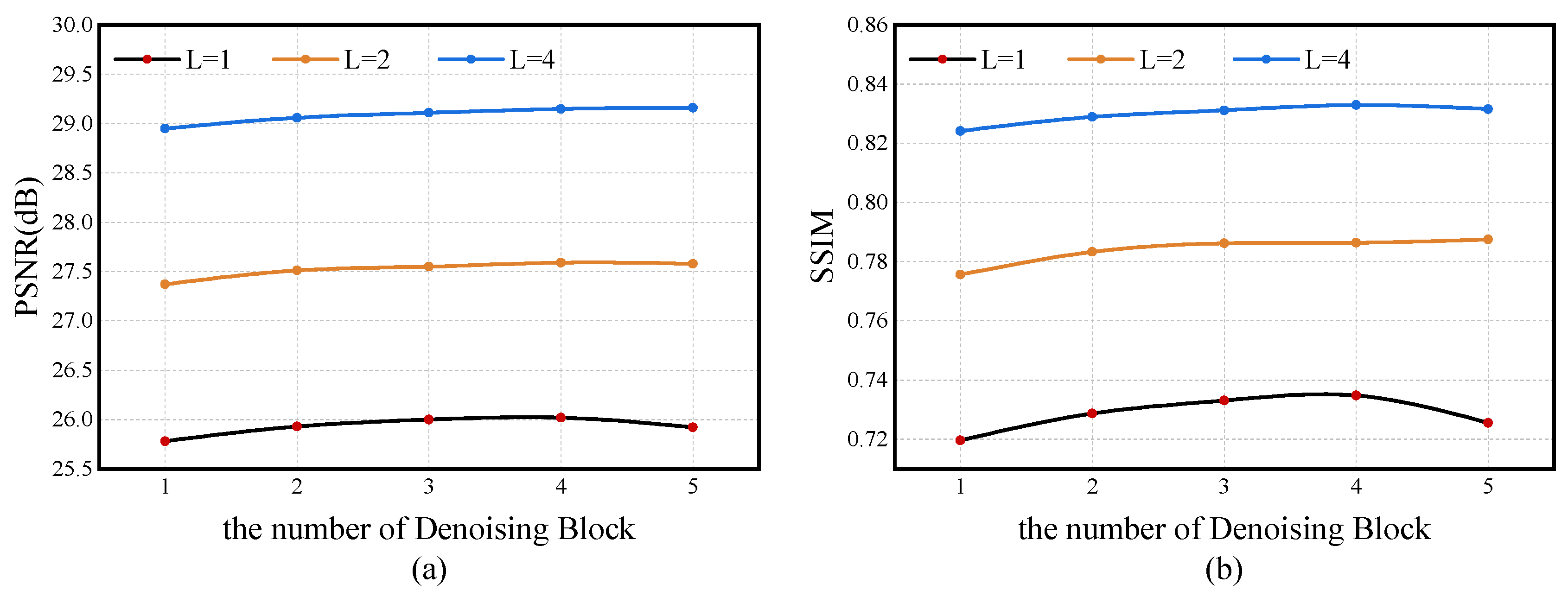
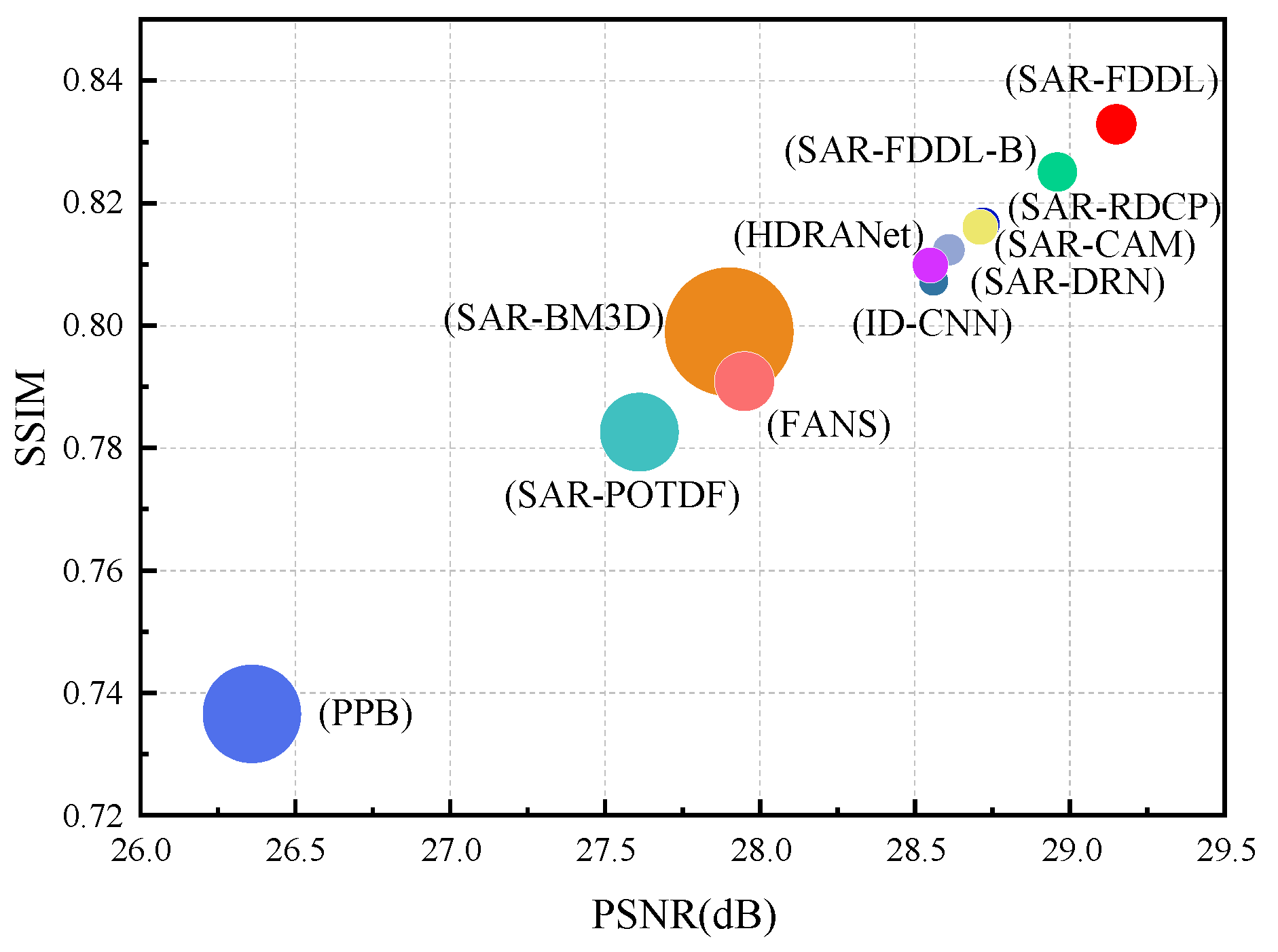
| Methods | L = 1 (PSNR/SSIM) | L = 2 (PSNR/SSIM) | L = 4 (PSNR/SSIM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPB | 23.19/0.5790 | 24.81/0.6637 | 26.36/0.7366 |
| SAR-BM3D | 24.65/0.6733 | 26.28/0.7407 | 27.90/0.7990 |
| SAR-POTDF | 23.32/0.6120 | 25.58/0.7086 | 27.61/0.7826 |
| FANS | 24.43/0.6601 | 26.22/0.7313 | 27.95/0.7909 |
| ID-CNN | 25.21/0.6871 | 26.92/0.7535 | 28.56/0.8073 |
| SAR-DRN | 25.42/0.7035 | 27.01/0.7623 | 28.61/0.8124 |
| HDRANet | 25.41/0.7010 | 26.83/0.7528 | 28.55/0.8099 |
| SAR-RDCP | 25.53/0.7095 | 27.19/0.7690 | 28.72/0.8166 |
| SAR-CAM | 25.61/0.7142 | 27.19/0.7693 | 28.71/0.8161 |
| SAR−FDD | 26.02/0.7348 | 27.59/0.7864 | 29.15/0.8329 |
| SAR−FDD−B | 25.94/0.7263 | 27.48/0.7797 | 28.96/0.8251 |
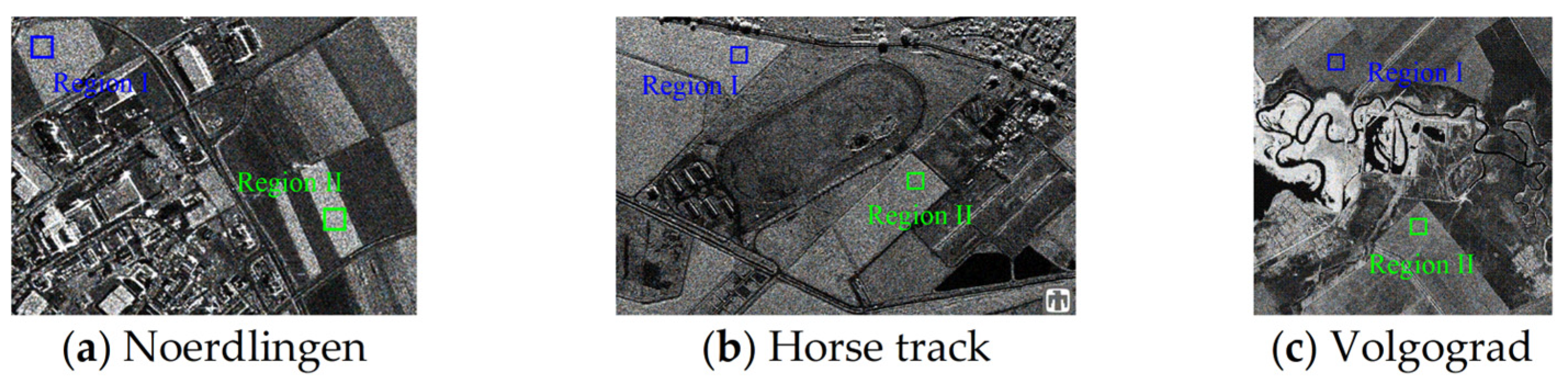
| Sensor | Method | ENL | MoI | MoR | EPD-ROA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region I | Region II | HD | VD | ||||
| Noerdlingen | PPB | 137.91 | 340.42 | 0.9624 | 0.9626 | 0.9432 | 0.9511 |
| SAR-BM3D | 111.11 | 51.51 | 0.9656 | 0.9654 | 0.9366 | 0.9515 | |
| SAR-POTDF | 167.94 | 367.51 | 0.9632 | 0.9665 | 0.9319 | 0.9316 | |
| FANS | 152.18 | 481.57 | 0.9598 | 0.9634 | 0.9211 | 0.9380 | |
| ID-CNN | 163.55 | 179.27 | 0.9615 | 0.9626 | 0.8898 | 0.8923 | |
| SAR-DRN | 169.27 | 188.83 | 0.9635 | 0.9643 | 0.9288 | 0.9308 | |
| HDRANet | 179.32 | 222.61 | 0.9654 | 0.9661 | 0.9282 | 0.9312 | |
| SAR-RDCP | 171.92 | 259.43 | 0.9649 | 0.9656 | 0.9266 | 0.9347 | |
| SAR-CAM | 179.52 | 557.32 | 0.9682 | 0.9699 | 0.8883 | 0.9063 | |
| SAR−FDD | 174.40 | 177.04 | 0.9675 | 0.9663 | 0.9411 | 0.9395 | |
| SAR−FDD−B | 172.01 | 609.34 | 0.9643 | 0.9660 | 0.9040 | 0.9138 | |
| Horse track | PPB | 138.42 | 117.20 | 0.9523 | 0.9478 | 0.9469 | 0.9457 |
| SAR-BM3D | 86.64 | 39.31 | 0.9587 | 0.9529 | 0.9462 | 0.9731 | |
| SAR-POTDF | 112.57 | 84.70 | 0.9712 | 0.9680 | 0.9558 | 0.9555 | |
| FANS | 135.09 | 130.45 | 0.9532 | 0.9537 | 0.9268 | 0.9518 | |
| ID-CNN | 135.24 | 99.11 | 0.9587 | 0.9540 | 0.9008 | 0.9073 | |
| SAR-DRN | 94.83 | 84.75 | 0.9587 | 0.9540 | 0.9479 | 0.9473 | |
| HDRANet | 107.91 | 70.47 | 0.9604 | 0.9594 | 0.9386 | 0.9457 | |
| SAR-RDCP | 118.20 | 90.98 | 0.9598 | 0.9537 | 0.9415 | 0.9525 | |
| SAR-CAM | 127.56 | 117.71 | 0.9611 | 0.9565 | 0.9315 | 0.9581 | |
| SAR−FDD | 93.42 | 73.23 | 0.9651 | 0.9567 | 0.9685 | 0.9726 | |
| SAR−FDD−B | 342.87 | 494.92 | 0.9588 | 0.9580 | 0.9494 | 0.9700 | |
| Volgograd | PPB | 93.28 | 146.67 | 0.9668 | 0.9548 | 0.9256 | 0.9327 |
| SAR-BM3D | 94.75 | 115.61 | 0.9747 | 0.9631 | 0.9037 | 0.9269 | |
| SAR-POTDF | 179.10 | 102.52 | 0.9911 | 0.9762 | 0.9163 | 0.9276 | |
| FANS | 125.86 | 121.59 | 0.9779 | 0.9725 | 0.8998 | 0.9210 | |
| ID-CNN | 360.75 | 178.11 | 0.9749 | 0.9603 | 0.8782 | 0.8939 | |
| SAR-DRN | 470.37 | 164.41 | 0.9723 | 0.9577 | 0.9019 | 0.9153 | |
| HDRANet | 509.75 | 255.59 | 0.9752 | 0.9621 | 0.9059 | 0.9257 | |
| SAR-RDCP | 424.98 | 178.73 | 0.9711 | 0.9556 | 0.9030 | 0.9210 | |
| SAR-CAM | 754.82 | 284.08 | 0.9746 | 0.9620 | 0.8706 | 0.8953 | |
| SAR−FDD | 249.87 | 106.28 | 0.9624 | 0.9533 | 0.9283 | 0.9443 | |
| SAR−FDD−B | 954.39 | 849.73 | 0.9656 | 0.9632 | 0.8880 | 0.9082 | |
| Loss Function | PSNR (dB) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|
| MSE | 29.1388 | 0.8315 |
| DG | 29.1418 | 0.8318 |
| 29.1357 | 0.8317 | |
| 29.1423 | 0.8316 | |
| 29.1501 | 0.8329 |
| Method | ID-CNN | SAR-DRN | HDRANet | SAR-RDCP | SAR-CAM | SAR−FDD | SAR- FDDL-B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 223,104 | 185,857 | 112,611 | 272,196 | 3,317,284 | 377,537 | 377,537 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Ren, F.; Sun, H.; Qi, Q. Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Despeckling Based on a Deep Learning Network Employing Frequency Domain Decomposition. Electronics 2024, 13, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030490
Zhao X, Ren F, Sun H, Qi Q. Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Despeckling Based on a Deep Learning Network Employing Frequency Domain Decomposition. Electronics. 2024; 13(3):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030490
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xueqing, Fuquan Ren, Haibo Sun, and Qinghong Qi. 2024. "Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Despeckling Based on a Deep Learning Network Employing Frequency Domain Decomposition" Electronics 13, no. 3: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030490
APA StyleZhao, X., Ren, F., Sun, H., & Qi, Q. (2024). Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Despeckling Based on a Deep Learning Network Employing Frequency Domain Decomposition. Electronics, 13(3), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030490






