Small-Signal Modeling of Grid-Forming Wind Turbines in Active Power and DC Voltage Control Timescale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Control Scheme and Definition of Internal Voltage
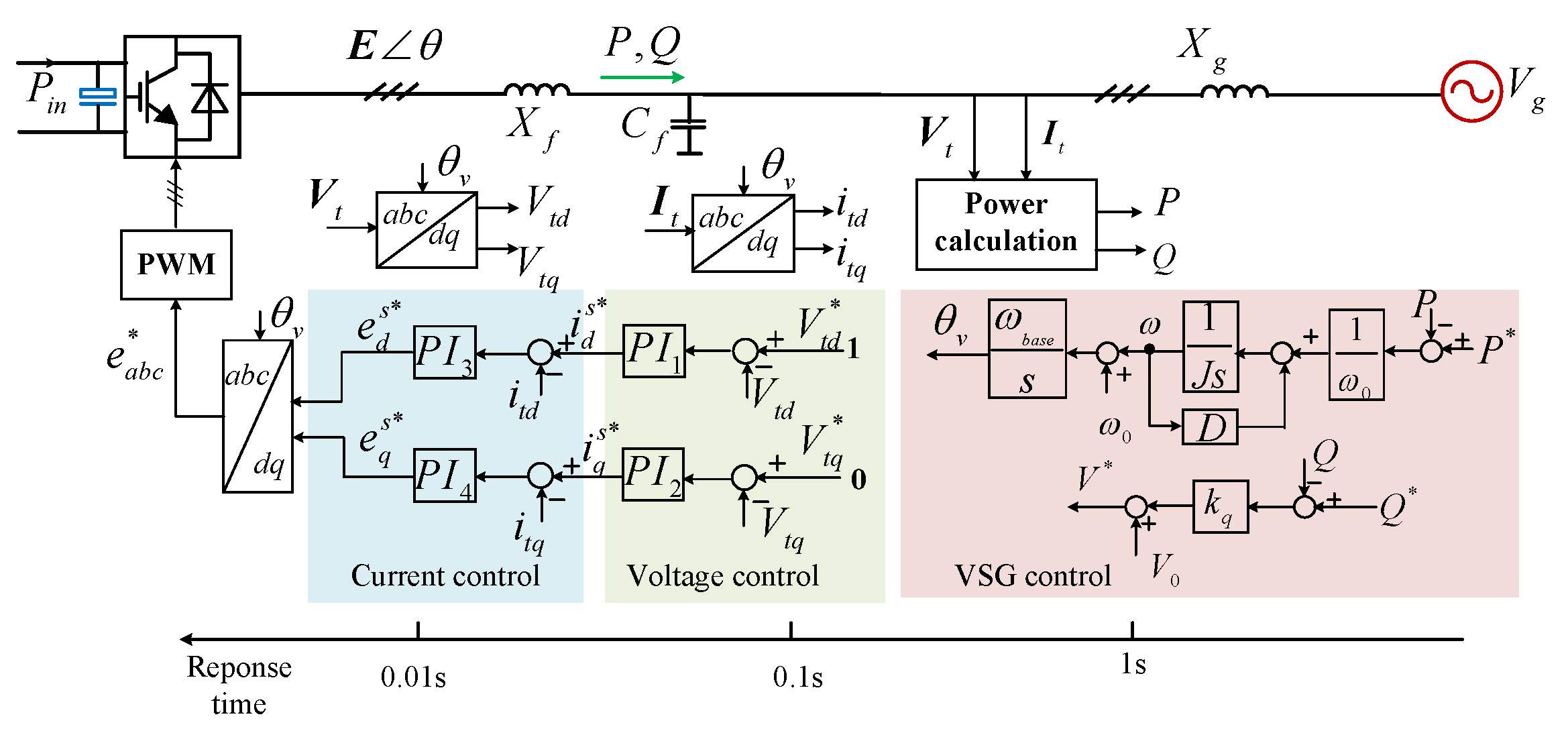
2.1. Basic Control Scheme of a GFM-WT
2.2. Definition of Internal Voltage
3. Proposed a GFM-WT Model
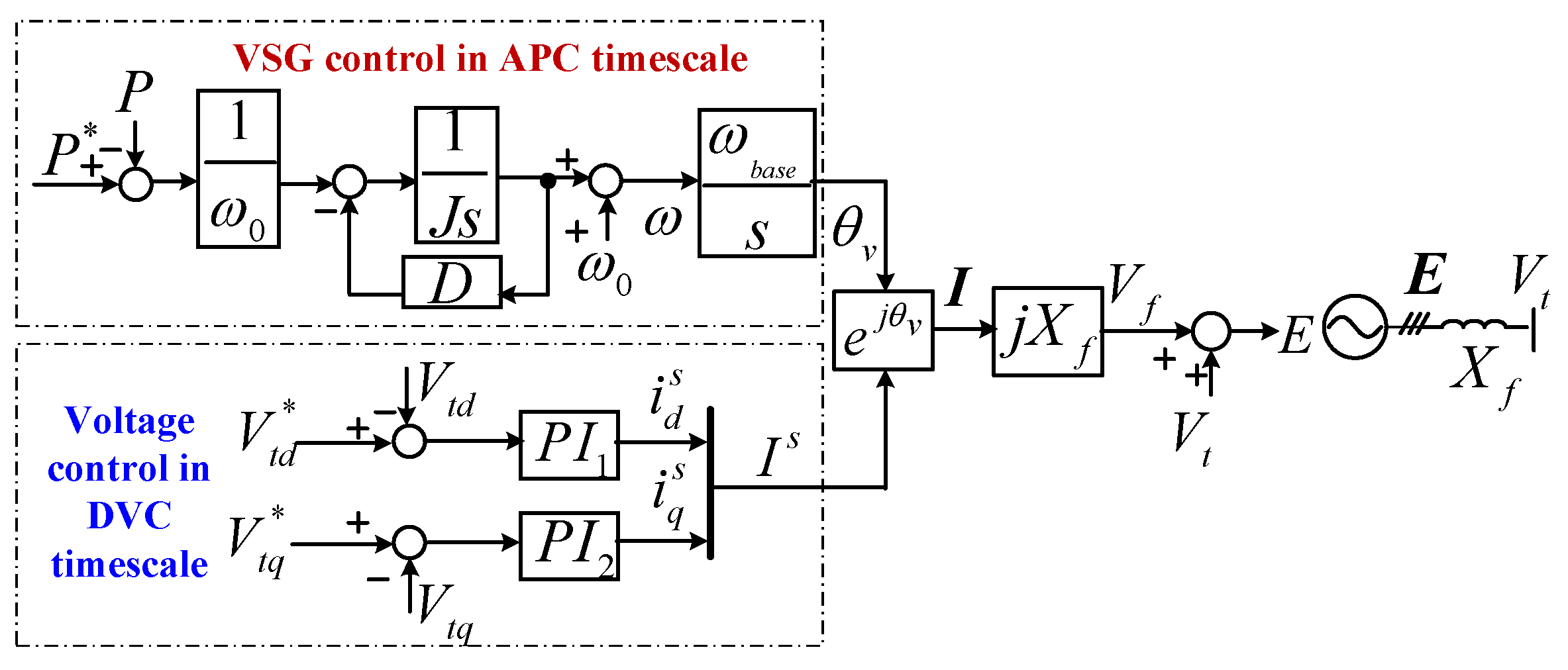
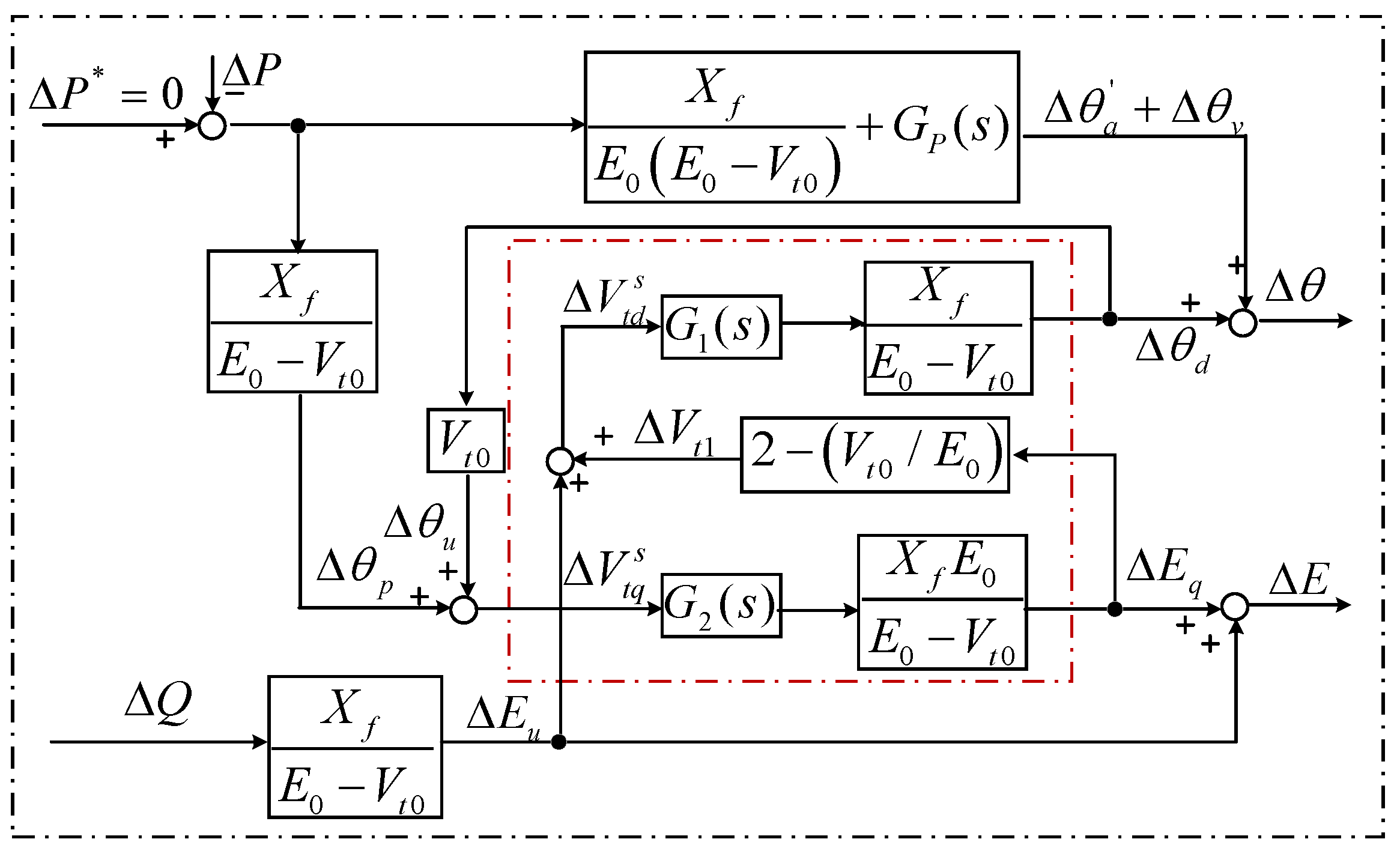
3.1. The Original Small-Signal Model of a GFM-WT
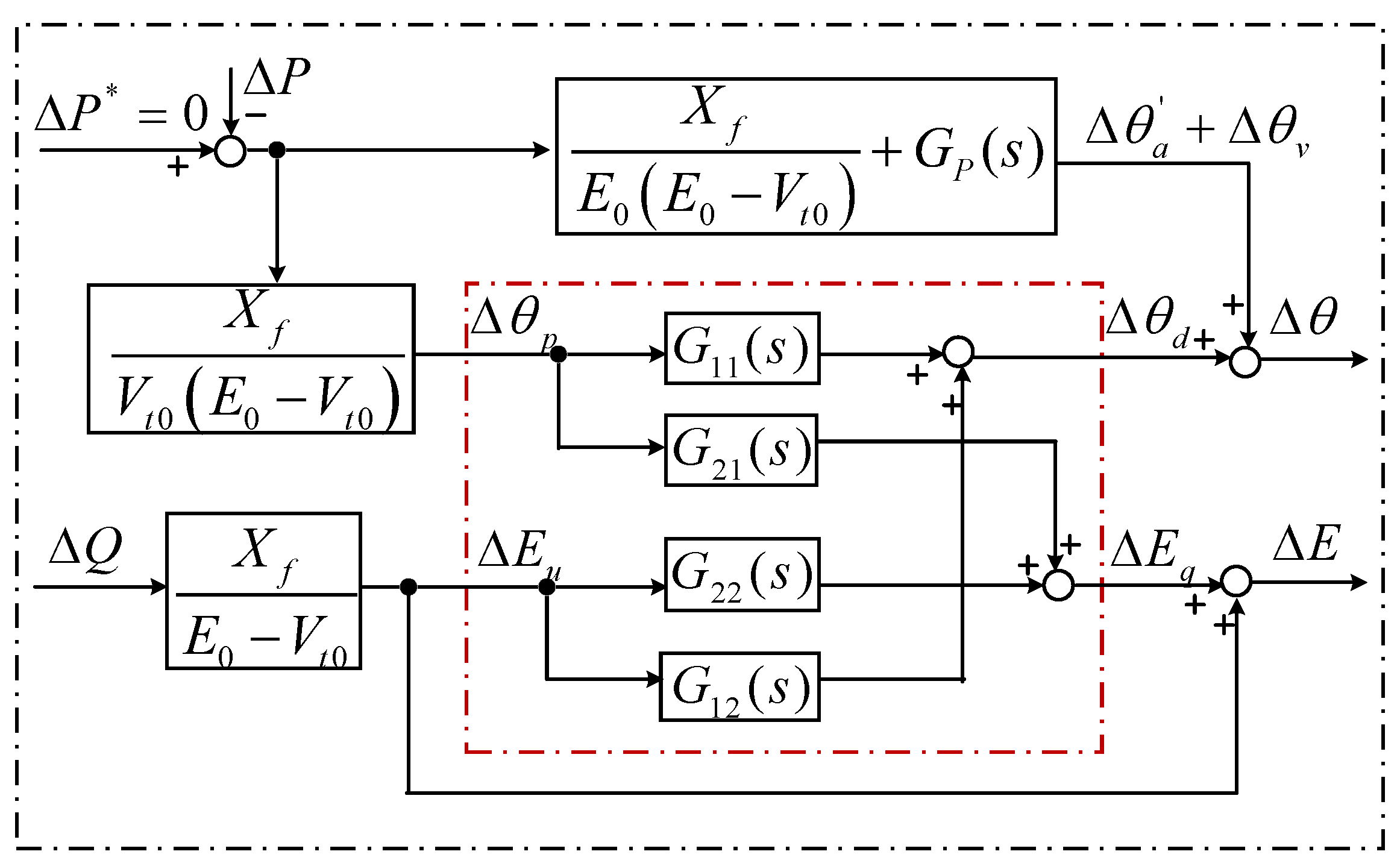
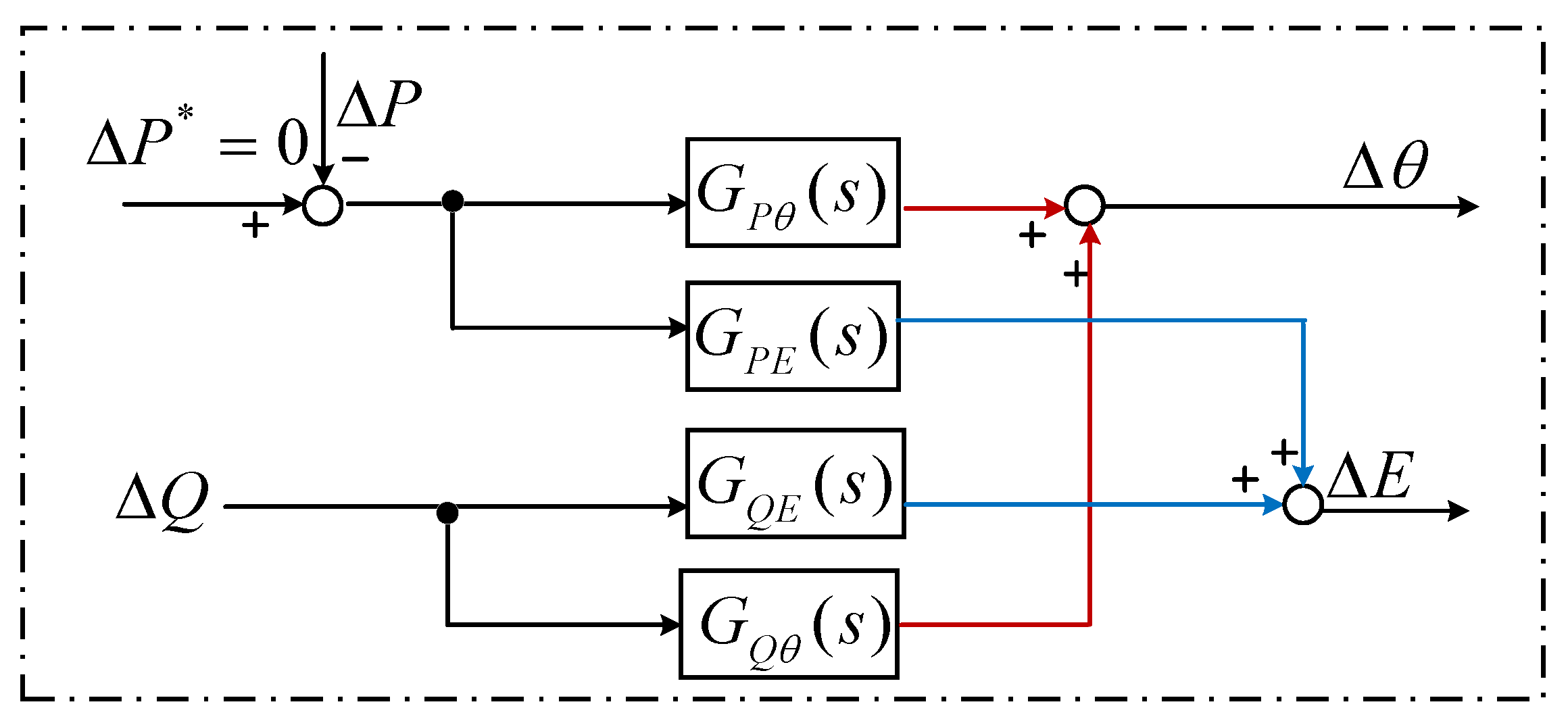
3.2. Simplify the GF-WT Small-Signal Model
3.2.1. Replace the Terminal Voltage
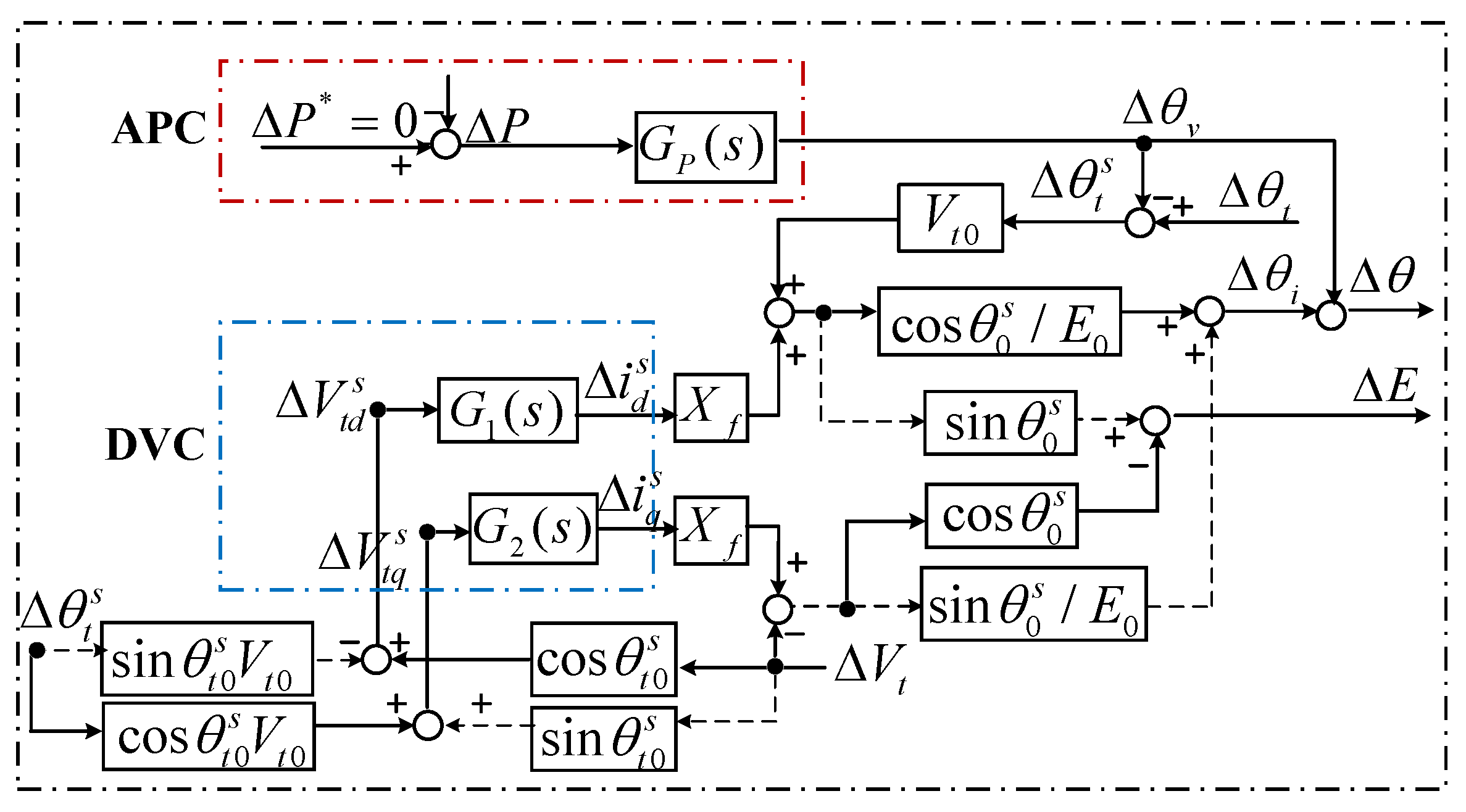
3.2.2. Open the Feedback Loops
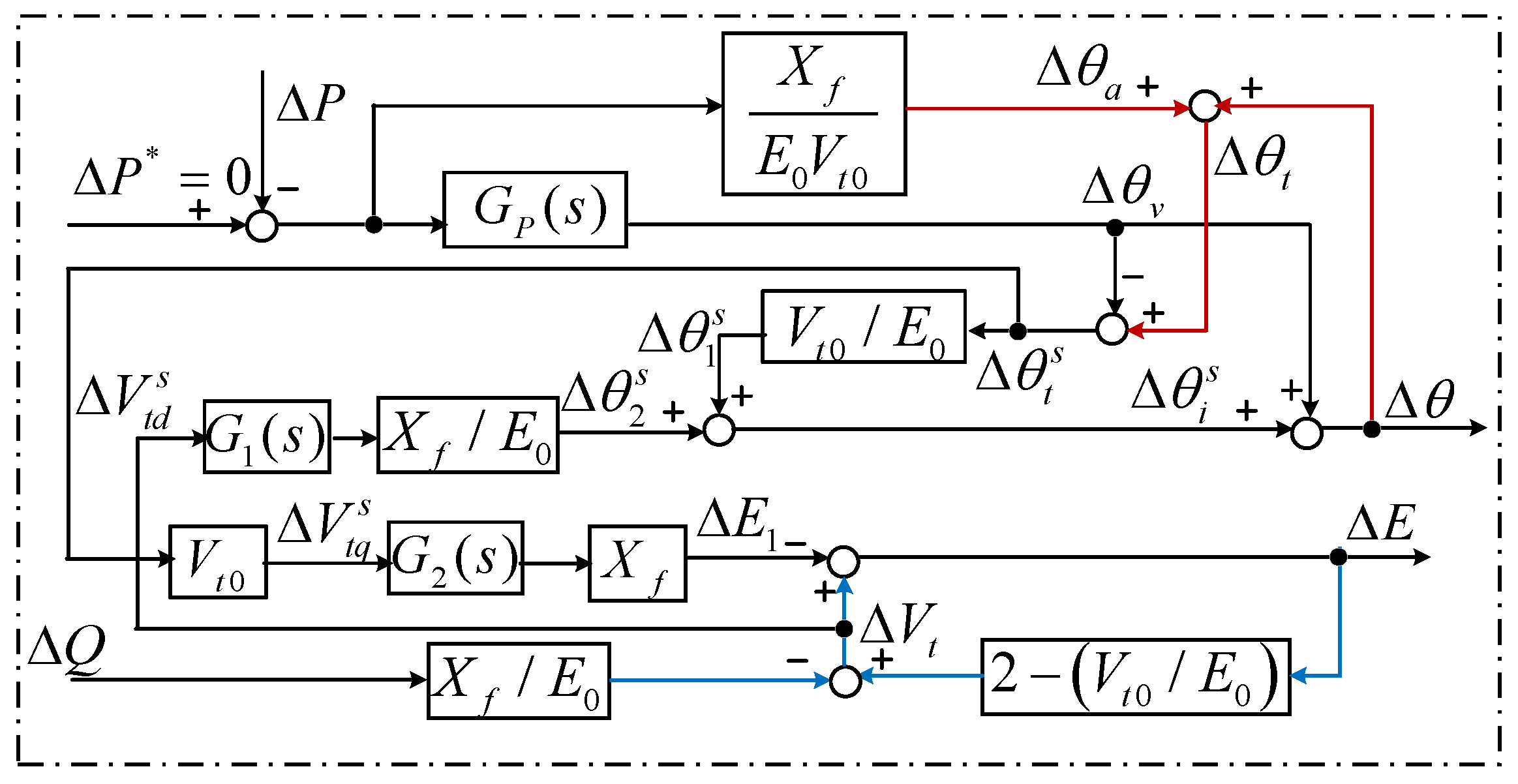
3.2.3. Simplify the Coupled Circuits
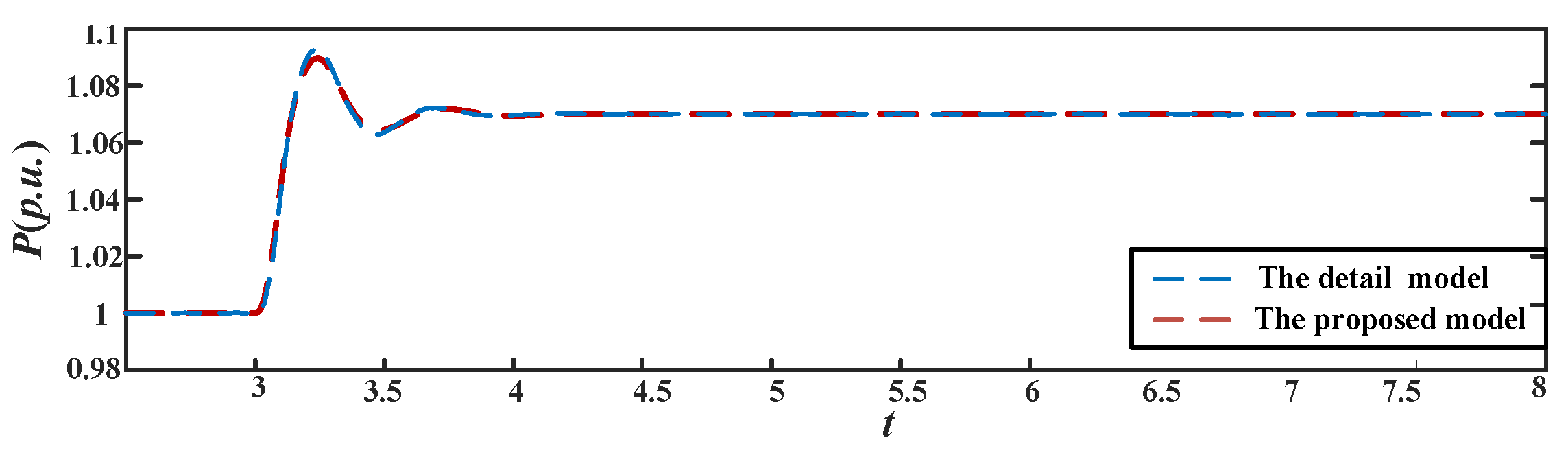
4. Verification of the Proposed GF-WT Model
5. Case Study
5.1. Effect of VSG Parameters
5.2. Effect of Voltage Control Parameters
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Active and reactive power output of GFM VSC | |
| Terminal voltage vector | |
| Magnitude and phase of the terminal voltage | |
| Internal voltage vector | |
| Magnitude and phase of the internal voltage | |
| Vector representation of the AC source | |
| Vector representation and the magnitude of AC current | |
| Output angle of the VSG control | |
| Filter reactance and capacitance of grid-side VSCs | |
| Reactance of the AC transmission line | |
| Reactance of the AC source | |
| Proportional and integral parameters of the PI controller in d-axis voltage controller | |
| Proportional and integral parameters of the PI controller in q-axis voltage controller | |
| Inertia and damping parameters of the VSG control |
| Subscripts: | |
| The subscripts represent the d-axis and q-axis components of the rotation coordinate system | |
| 0 | The subscript represents the initial values in the steady-state condition |
| Superscripts: | |
| * | The subscript represents the reference value |
| s | The subscript represents the signals in VSG-synchronized reference frame |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
Appendix A.2
- (1) Steady-state reference values:
- Inspecting power VA, Impedance ,
- Phase current A, Frequency rad/s,
- Effective value of line voltage V.
- (2) Control parameters and operation points:
- VSG control
- voltage loop control ,
- operation points p.u., p.u., p.u., p.u.
References
- Chen, Z.; Guerrero, J.M.; Blaabjerg, F. A Review of the State of the Art of Power Electronics for Wind Turbines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaabjerg, F.; Ma, K. Future on Power Electronics for Wind Turbine Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xie, X.; Shair, J. Adaptive Hybrid Grid-Forming and Grid-Following Control of IBRs With Enhanced Small-Signal Stability Under Varying SCRs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 6603–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Cheng, L.; Gao, X.; Xu, J.; Blaabjerg, F. A Generic Power Compensation Control for Grid Forming Virtual Synchronous Generator With Damping Correction Loop. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 10908–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasseter, R.H.; Chen, Z.; Pattabiraman, D. Grid-Forming Inverters: A Critical Asset for the Power Grid. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Yang, R.; Long, X.; Chen, G. A Configurable Virtual Impedance Method for Grid-Connected Virtual Synchronous Generator to Improve the Quality of Output Current. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruwa, M.; Fazeli, M. Impact of virtual synchronous machines on low-frequency oscillations in power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 36, 1934–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedian, M.; Sangrody, R.; Shahparasti, M.; Taheri, S.; Pouresmaeil, E. Grid—Following DVI—Based Converter Operating in Weak Grids for Enhancing Frequency Stability. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 37, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedian, M.; Eskandari, B.; Taheri, S.; Hinkkanen, M.; Pouresmaeil, E. A Control Technique Based on Distributed Virtual Inertia for High Penetration of Renewable Energies Under Weak Grid Conditions. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. Impedance Analysis and Stabilization of Virtual Synchronous Generators With Different DC-Link Voltage Controllers Under Weak Grid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 11397–11408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, T.F.; Salazar, A.O. Impedance Model Based Dynamic Analysis Applied to VSG-Controlled Converters in AC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 2720–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z. Modeling and Control of a Two-Bus System with Grid-Forming and Grid-Following Converters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 7133–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, P.; Gao, F. Frequency-Coupled Impedance Modeling of Virtual Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 3692–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yuan, X.; Hu, J. Modeling of Grid-Connected VSCs for Power System Small-Signal Stability Analysis in DC-Link Voltage Control Timescale. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 3981–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhai, X.; Hu, J.; Liu, D.; Lin, C. Modeling of VSCs Modeling and Stability Analysis of VSC Internal Voltage in DC-Link Voltage Control Timescale. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 6, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, D.; Shang, L.; Zhu, G.; Tang, H.; Li, Y. Modeling and Stability Analysis of DC-Link Voltage Control in Multi-VSCs With Integrated to Weak Grid. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers 2017, 32, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Hu, J.; Chai, L.; Liu, B.; Sang, Z. Interaction quantification of MTDC systems connected with weak AC grids. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 10, 3981–3991. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Hu, J.; Yuan, X. Modeling of VSCs Considering Input and Output Active Power Dynamics for Multi-Terminal HVDC Interaction Analysis in DC Voltage Control Timescale. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Peng, J.C.-H.; Yang, H.; Srinivasan, D. Modeling and Analysis of Inner Controls Effects on Damping and Synchronizing Torque Components in VSG-Controlled Converter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Mijatovic, N.; Dragicevic, T. Frequency Stability Assessment of Grid-Forming VSG in Framework of MPME with Feedforward Decoupling Control Strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 6903–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Aleshina, A.; Xu, J.; Blaabjerg, F. Grid Inertia and Damping Support Enabled by Proposed Virtual Inductance Control for Grid-Forming Virtual Synchronous Generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Zha, X.; Tian, Z.; Sun, J. Optimal Virtual Inertia Design for VSG-Based Motor Starting Systems to Improve Motor Loading Capacity. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

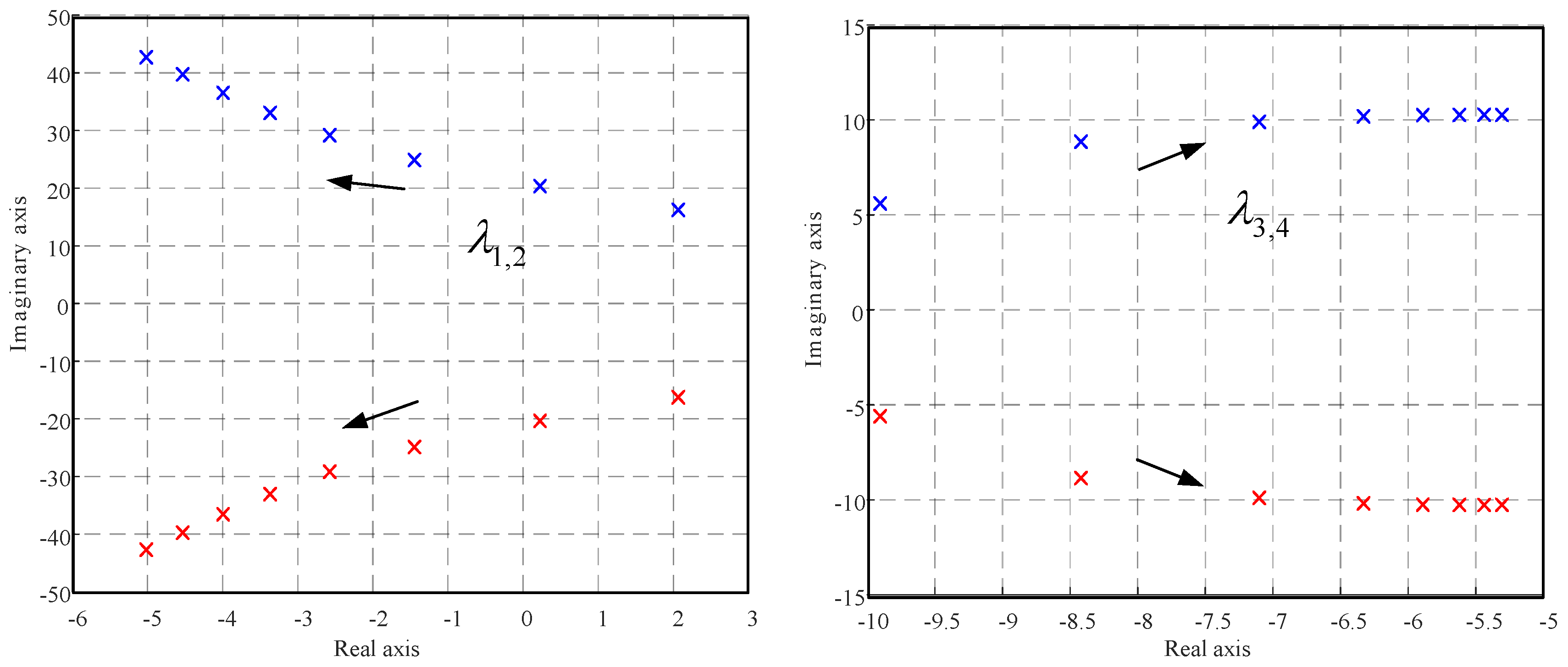
| D | 40 | 60 | 80 |
|---|---|---|---|
| the proposed model | |||
| the detailed model | |||
| Damping Ratio | Damping Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.82 | |||
| 0 | 0.77 | |||
| 0.05 | 0.60 | |||
| 0.10 | 0.49 | |||
| 0.10 | 0.43 | |||
| 0.11 | 0.38 | |||
| 0.11 | 0.35 | |||
| 0.11 | 0.33 |
| Damping Ratio | Damping Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.09 | 0.57 | |||
| −0.01 | 0.69 | |||
| 0.05 | 0.58 | |||
| 0.08 | 0.52 | |||
| 0.10 | 0.49 | |||
| 0.10 | 0.48 | |||
| 0.11 | 0.46 | |||
| 0.11 | 0.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, K.; Ji, X.; Liu, D.; Zheng, W.; Tian, L.; Chen, S. Small-Signal Modeling of Grid-Forming Wind Turbines in Active Power and DC Voltage Control Timescale. Electronics 2024, 13, 4728. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13234728
Jiang K, Ji X, Liu D, Zheng W, Tian L, Chen S. Small-Signal Modeling of Grid-Forming Wind Turbines in Active Power and DC Voltage Control Timescale. Electronics. 2024; 13(23):4728. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13234728
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Kezheng, Xiaotong Ji, Dan Liu, Wanning Zheng, Lixing Tian, and Shiwei Chen. 2024. "Small-Signal Modeling of Grid-Forming Wind Turbines in Active Power and DC Voltage Control Timescale" Electronics 13, no. 23: 4728. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13234728
APA StyleJiang, K., Ji, X., Liu, D., Zheng, W., Tian, L., & Chen, S. (2024). Small-Signal Modeling of Grid-Forming Wind Turbines in Active Power and DC Voltage Control Timescale. Electronics, 13(23), 4728. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13234728





