Abstract
In recent years, pedestrian re-identification technology has made significant progress, with various neural network models performing well under normal conditions, such as good weather and adequate lighting. However, most research has overlooked extreme environments, such as rainy weather and nighttime. Additionally, the existing pedestrian re-identification datasets predominantly consist of well-lit images. Although some studies have started to address these issues by proposing methods for enhancing low-light images to restore their original features, the effectiveness of these approaches remains limited. We noted that a method based on Retinex theory designed a reflectance representation learning module aimed at restoring image features as much as possible. However, this method has so far only been applied in object detection networks. In response to this, we improved the method and applied it to pedestrian re-identification, proposing a transposed convolution reflectance decoder (TransConvRefDecoder) to better restore details in low-light images. Extensive experiments on the Market1501, CUHK03, and MSMT17 datasets demonstrated that our approach delivered superior performance.
1. Introduction
Pedestrian re-identification (Re-ID) is a crucial task in the fields of computer vision and intelligent surveillance, aiming to recognize the same individual across different camera views. However, Re-ID in low-light environments poses significant challenges, due to insufficient lighting, increased image noise, and color distortion.
In recent years, Re-ID has made significant progress under standard lighting conditions [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], thanks to the rapid development of deep learning methods and the availability of large-scale annotated datasets. However, the performance of the traditional methods and existing models significantly declines in low-light conditions. This decline is primarily due to the poor quality of images captured in low-light environments, which makes it difficult to extract pedestrian details and features. Researchers have proposed various strategies, including image enhancement, feature extraction, and model optimization, to improve Re-ID performance in low-light environments.
Image enhancement methods aim to improve the visual quality of low-light images, typically using image preprocessing techniques such as histogram equalization, image denoising, and contrast enhancement. In terms of feature extraction, traditional handcrafted features (e.g., color histograms and histograms of oriented gradients) perform poorly in low-light conditions. Deep learning models, which learn more robust and semantically rich features, have shown great potential for low-light Re-ID. For example, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can extract multi-level features, including edges, textures, and high-level semantic information, effectively improving the recognition performance.
Although the existing image enhancement methods appear effective, they rely on large amounts of low-light images collected from real-world scenarios, and many methods require paired images with good and poor lighting for training [8,9]. For low-light Re-ID, training with low-light images is crucial [10,11]. However, compared to well-lit data, low-light Re-ID datasets are extremely scarce.
To overcome the limitations posed by the scarcity of low-light datasets, we employed a zero-shot daytime domain adaptation scheme [12,13]. As shown in Figure 1, the network can adapt and effectively handle target domain data, even without specific target domain training data. This allows the Re-ID network to be trained only on well-lit images, enabling a performance evaluation on low-light images.

Figure 1.
Zero-shot day–night domain adaptation without access to domain data and only knowing the priors of dark scenarios.
In this paper, we propose a novel transposed convolution reflectance decoder (TransConvRefDecoder) based on the retinex theory of image decomposition, which posits that an image is the product of reflectance and illumination components. Our approach draws inspiration from the zero-shot daytime domain adaptation network (DAI-Net) [14] used in object detection. Specifically, we generate low-light images corresponding to well-lit images using a dark image synthesis network (DarkISP) [10]. These image pairs are then processed through a feature encoder to obtain feature pairs, with the TransConvRefDecoder producing illumination-invariant features related to reflectance. Subsequently, only the feature information from the low-light images is fed into the Re-ID network. Additionally, we use a pre-trained retinex decomposition network (RetinexNet) to decompose the image pairs into reflectance and illumination components, applying a special illumination-invariance strategy for enhancement. Finally, a dual decomposition strategy is employed, where the reflectance components of the image pairs are swapped after the first decomposition. The features are then re-encoded and decoded, with a specific loss function introduced to promote consistency in the decomposition of reflectance components, ensuring that the learned reflectance components are stable and accurate.
The contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
- Our work narrows the performance gap in pedestrian re-identification under low-light conditions, a scenario that is underrepresented in current research.
- We improved the reflectance representation learning module originally applied in the zero-shot daytime domain adaptation network for object detection and proposed a transposed convolution reflectance decoder (TransConvRefDecoder) for pedestrian re-identification.
- We conducted extensive experiments on multiple datasets to validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, demonstrating significant improvements over baseline models.
2. Related Works
2.1. Pedestrian Re-Identification
In recent years, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have made significant advancements in pedestrian re-identification. Existing research primarily focuses on re-identification methods under standard lighting conditions. For instance, Zheng et al. [15] proposed a CNN-based embedding model to generate compact feature vectors describing pedestrians. Wu et al. [16] developed an end-to-end neural network model that learns high-level feature representations and matches them through similarity metrics.
While these methods perform well in well-lit conditions, their performance significantly degrades under low-light conditions. This decline is primarily due to the poor quality of low-light images, which makes it challenging to extract pedestrian details. To address this, Sun et al. [17] proposed the PCB network, which improved upon part-based pooling strategies, providing a robust CNN-based baseline model that enhances feature discrimination through a partitioning strategy. Additionally, Li et al. [18] proposed an attention-aware network that adaptively focuses on key regions in pedestrian images, enhancing the representational capacity of features. In addition, multi-scale feature fusion techniques combine features at different scales to improve the model’s ability to handle variations in pedestrian appearance. However, these existing methods still face limitations when dealing with extreme lighting conditions, such as nighttime or bright sunlight, especially when data scarcity is a concern.
Moreover, generative adversarial networks (GANs) have also been applied to pedestrian re-identification tasks. For example, Qian et al. [19] proposed a pose-normalized GAN to generate pose-normalized pedestrian images, expanding the available training datasets and improving re-identification accuracy. However, these methods still face challenges in low-light scenarios, as they heavily rely on low-light data, which may not always be available, and cannot fully leverage unpaired data.
2.2. Low-Light Image Enhancement
Deep learning methods based on retinex theory have gained significant attention in the field of low-light image enhancement. Retinex theory, first proposed by Land and McCann in 1963, explains how the human visual system perceives color and brightness under varying lighting conditions. Image enhancement methods based on this theory work by decomposing an image into its reflectance and illumination components, effectively enhancing low-light images.
Chen et al. [8] proposed RetinexNet, a classic deep learning model based on retinex theory, which consists of a decomposition network and an enhancement network. The decomposition network separates the input low-light image into reflectance and illumination maps, while the enhancement network adjusts the illumination map to simulate normal lighting conditions. Although RetinexNet improves the visual quality of low-light images, it has limitations when applied to pedestrian re-identification, as it primarily focuses on visual enhancement rather than task-specific feature extraction.
Despite their effectiveness, these enhancement methods rely heavily on large amounts of real-world low-light image datasets paired with well-lit images for training, which are difficult to obtain in practice [9]. To overcome the scarcity of low-light data, some researchers have proposed unsupervised zero-shot domain adaptation techniques, allowing the network to train without access to target domain data [12,13]. These methods use a physics-inspired low-light image synthesis technique to generate low-light images corresponding to well-lit ones, improving the model performance without requiring paired data.
2.3. Low-Light Pedestrian Re-Identification
Most pedestrian re-identification methods focus on scenarios with good lighting conditions, paying less attention to re-identification in low-light environments. However, low-light settings present several challenges, including low illumination, noise interference, and the loss of critical appearance information, all of which severely impact the extraction and matching accuracy of pedestrian features.
To address these challenges, some studies have utilized infrared imaging to capture unique features of pedestrians. For example, Feng et al. [20] proposed the shape-erased feature learning (SEFL) method, which addresses cross-modal re-identification by removing shape information and enhancing texture features. Zhang et al. [21] designed a modality compensation network (MRCN) that restores and compensates for feature differences between different imaging modalities, improving feature discrimination through effective modality fusion. However, these methods depend on infrared images, which are difficult to obtain. Alternatively, some studies used nighttime images. For instance, Lu et al. [22] created a nighttime pedestrian dataset and introduced a light distillation mechanism to enhance images, transferring illumination information from well-lit images to nighttime images, thereby improving the nighttime re-identification performance. However, nighttime images are also challenging to collect, further complicating the data acquisition.
3. Methods
3.1. Overview
Due to the degradation in images caused by changes in lighting, the performance of pedestrian re-identification (Re-ID) decreases. To mitigate the impact of this degradation, we trained a Re-ID network using well-lit pedestrian images and extended its application to low-light images. Our proposed framework is illustrated in Figure 2. We utilized the VGG16 network [23] as the backbone of our Re-ID network. The network’s input consists of a pair of images: one well-lit image and a corresponding low-light image, generated by a physics-inspired low-light synthesis module, DarkISP [10]. Simultaneously, this image pair is also fed into a pre-trained retinex decomposition network to obtain the corresponding reflectance and illumination maps.
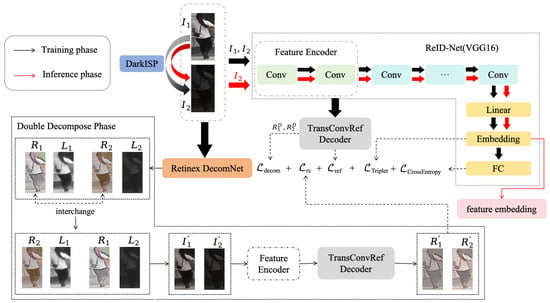
Figure 2.
Structure overview of our method.
The introduction of a reflectance map exchange and re-decomposition strategy accelerates the network’s learning of reflectance representations. Notably, we designed a specialized decoder for decoding the reflectance maps, which is applied within the Re-ID network to better learn the reflectance representations.
To improve the model’s adaptability across various lighting conditions, we leverage prior knowledge from dark scenarios to enhance its robustness. Specifically, dark scenario priors highlight features that are less affected by lighting variations, such as structural and textural elements that remain relatively consistent under different lighting conditions. This decomposition of reflectance and illumination maps helps the model decouple lighting effects from object features, allowing it to perform effective pedestrian re-identification in both well-lit and low-light environments. By learning from these dark priors, the model becomes better equipped to generalize to unseen lighting conditions, as it relies less on specific lighting environments and focuses more on intrinsic object characteristics.
3.2. Pedestrian Re-Identification Network
In this paper, we propose a novel pedestrian re-identification network, as illustrated in Figure 2, aimed at improving the accuracy and robustness of Re-ID in low-light environments. Our network architecture is built upon a deep convolutional neural network and integrates several components to enhance feature extraction and matching.
3.2.1. Backbone
Given the widespread recognition of VGG16 for its simplicity and efficiency in various image recognition tasks, we selected it as the backbone of our Re-ID network. The VGG16 architecture was pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset to extract high-level features from the input images. Notably, we configured the first two convolutional layers of the network as feature encoders because, in the field of computer vision, image decomposition is considered a low-level task. These two convolutional layers efficiently encode the low-level information of the image, laying a solid foundation for subsequent reflectance information decoding. Additionally, in the final linear layers, we designated the penultimate layer as the embedding layer to extract a compact and highly discriminative feature vector. This vector effectively captures the core characteristics of the input image and represents individual objects efficiently in the feature space.
3.2.2. Reflectance Decoder
According to retinex theory [24], an image I can be decomposed into a reflectance map R and an illumination map L, such that . The reflectance map R represents the fundamental features of the image, but lacks realism unless augmented with illumination details such as contrast, shading, and sunlight, provided by L. In low-light Re-ID, the key challenge is to extract clear reflectance map features from low-light images. Therefore, we introduced a transposed convolution reflectance decoder (TransConvRefDecoder) to enhance feature extraction adaptability and performance under low-light conditions.
As shown in the center of Figure 3, this decoder primarily consists of a standard convolutional layer and a transposed convolutional layer. Compared to the reflectance map decoder proposed in DAI-Net [14] (Figure 3, left side), our decoder replaces the traditional upsampling and convolution layer combination with a transposed convolutional layer. The original decoder used interpolation [25] for upsampling, a method that linearly adjusts the size of new pixels based on the values of surrounding pixels, following a fixed algorithm. Since this approach lacks a learning mechanism, it cannot adapt to diverse data characteristics. In contrast, a transposed convolutional layer is capable of learning the optimal upsampling method, optimizing its weights through backpropagation to adapt to specific data features. This enables the network to more effectively learn how to reconstruct high-resolution reflectance components, which can potentially improve the final image’s detail and accuracy, significantly enhancing image quality.
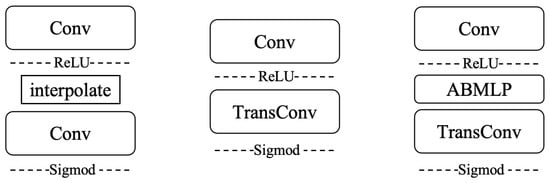
Figure 3.
Comparison of decoders: on the left is the reflectance decoder before improvement (DAI-Net [14]), in the middle is the reflectance decoder after improvement, and on the right is the improved reflectance decoder with ABMLP.
Moreover, by incorporating the ABMLP module [26], we developed an attention-enhanced reflectance decoder (Figure 3, right side). According to our experimental results (see Section 4.4), this improvement improved the overall performance of the network to a certain extent.
For the proposed TransConvRefDecoder, we designed the comparative experiments shown in Table 1 to evaluate its performance in terms of parameter count, computational complexity, and processing time. The results demonstrated that the TransConvRefDecoder, while maintaining the same parameter count as ReflectanceDecoder, significantly reduced the GFLOPs, from 2.9 to 2.5, and shortened the processing time, from 2.6 ms to 1.0 ms, indicating a marked improvement in computational efficiency. Furthermore, with the addition of the ABMLP module, the parameter count increased slightly to 39.2 K, while the computational complexity remained unchanged, and the processing time only increased marginally to 1.2 ms. These results suggest that TransConvRefDecoder and its enhanced version not only maintain a lightweight architecture but also achieve considerable improvements in inference speed, making them highly practical.

Table 1.
Comparison of computational complexity analysis between three decoders.
3.2.3. Retinex DecomNet
To further enhance and accelerate the process of learning reflectance, we introduced an additional image decomposition step using the Retinex DecomNet architecture [8]. Throughout the network training, Retinex DecomNet remained frozen and was used solely for inference. Given an output image pair and , Retinex DecomNet processed these images to generate , , and , . Here, and are essentially the same image (with being a low-light version synthesized from , so ideally, the decomposed reflectance maps and should be identical.
After swapping and (as illustrated in the lower-left corner of Figure 2), new image pairs and can be synthesized. However, in practice, and are not perfectly identical, resulting in significant differences between the synthesized image pairs and and the original images. To address this, we reintroduce the synthesized image pairs into the network’s feature encoding and reflectance decoding modules, applying appropriate constraints to correct this discrepancy (as outlined in Equation (6)).
The optimization is performed by calculating the absolute difference between the reflectance maps obtained after swapping, re-synthesizing, and then re-decomposing them, and the original reflectance maps. Ideally, if the decomposition network accurately extracts and separates the reflectance and illumination maps, then after swapping the reflectance maps, the newly decomposed reflectance map should closely match the original , and should match . During network training, this encourages the network to learn more robust and consistent reflectance representations, thereby improving the overall performance and stability.
3.3. Training
To accelerate the network’s convergence during training, we employed specific loss functions designed to optimize the model’s performance. These loss functions were carefully crafted and adjusted according to the needs of the different sub-networks and tasks.
For the Re-ID backbone network, we utilized different loss functions in the embedding layer and the fully connected layer. In the embedding layer, we applied the triplet loss function [27]. The triplet loss function works by minimizing the distance between the positive sample and the anchor, while maximizing the distance between the negative sample and the anchor, thereby enhancing the model’s discriminative capability.
In this context, represents the anchor sample, the positive sample, and the negative sample. The embedding function is denoted as , and represents the Euclidean distance. The parameter is a hyperparameter used to control the margin between the samples, and denotes the positive part of the expression.
For the fully connected layer, we employed the cross-entropy loss function [28]. Cross-entropy loss measures the difference between the predicted probability distribution and the actual labels, guiding the model in adjusting its weights to improve the classification accuracy.
In this case, represents the actual label, and represents the predicted probability.
For the transposed convolution reflectance decoder, we employed a specialized loss function to further optimize its performance. This loss function is composed of two key components: the mean absolute error (MAE) [29] and the structural similarity index measure (SSIM) [30].
Here, R and represent the pairs of reflectance maps (e.g., (, ) or (, )) generated from well-lit and low-light images, respectively, after being decoded twice.
Additionally, to correct the deviation between the reflectance maps obtained from the decoder and the ground truth reflectance maps, we designed a loss function as described in [8]. This loss function is composed of three terms: the reconstruction loss , the invariant reflectance loss , and the illumination smoothness loss :
In these equations, MSE stands for mean squared error, and I and represent the image pairs (, ) and (, ), respectively.
For Retinex DecomNet, to minimize the discrepancy between the reflectance maps and illumination maps obtained from two instances of image decomposition, we optimized the network by calculating the absolute value difference between the original reflectance maps and those obtained after exchanging the reflectance maps, recomposing, and decomposing them again:
Given all the constraints mentioned above, the overall loss function for the entire network can be expressed as follows:
4. Experiments
4.1. Settings
We conducted experiments using three public pedestrian re-identification datasets: Market1501 [31], CUHK03 [32], and MSMT17 [33]. The detailed information of these datasets is presented in Table 2. Here, “IDs” represent the number of distinct person IDs in each dataset; and “Train”, “Query”, and “Gallery” refer to the number of training images, query images, and gallery images, respectively. The network was trained on the training set, and after the model had been obtained, the features of the images in the query and gallery sets were extracted to calculate the similarity, ultimately finding the most similar image in the gallery for each query.

Table 2.
Comprehensive details of the three datasets.
We used two pre-trained models in the experiments: one pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset [34], and the other being the already trained Retinex DecomNet model.
As described in Section 3.3, we used the stochastic gradient descent (SGD) optimizer [35] with 50 training epochs, a learning rate of 1 × 10−3, and a batch size of 32. These parameters were chosen after extensive preliminary experiments, to strike a good balance between training speed and model convergence.
During training, we carefully tuned the weights of the loss functions to optimize both the pedestrian re-identification accuracy and the image reconstruction quality. The triplet loss weight () was set to 0.01 to ensure the model effectively distinguished between different pedestrian features. The reconstruction loss weight () was set to 0.001, to minimize discrepancies between the reflectance maps generated from well-lit and low-light images. For the invariant reflectance loss () and the illumination smoothness Loss (), we followed the method of Wei et al. [8], setting their values to 0.01 and 0.5, respectively. Based on prior research, these settings strike a good balance between reconstruction quality and feature invariance under varying lighting conditions.
All experiments were conducted on a computer equipped with an NVIDIA RTX 3060 GPU. We used the mean average precision (mAP) and Top-N (1, 5, 10) as metrics to ensure that the model’s performance in practical applications was fully validated.
4.2. Results
Due to the relative scarcity of research focused on pedestrian re-identification in low-light environments, to the best of our knowledge, there are few re-identification networks specifically designed for this purpose. We selected five existing re-identification networks for comparison experiments, four of which were primarily designed for well-lit images: BoT [5], ABD-Net [36], AGW [37], and TransReID [38]. The fifth network, IDF [22], was specifically designed for low-light image processing. It is worth noting that the images in the Market1501, CUHK03, and MSMT17 datasets were all captured under well-lit conditions. To evaluate their performance in low-light environments, we applied DarkISP to simulate low-light conditions for all three datasets. The experimental results are detailed in Table 3. In the table, red text indicates the best performance, while blue text represents the second-best performance.

Table 3.
Comparison of performance across different methods on Market1501, CUHK03, and MSMT17 Datasets.
Using the Market1501 dataset as an example, we randomly selected an image from the query set as the query sample, and then used the five existing pedestrian re-identification networks (BoT, ABD-Net, AGW, TransReID, and IDF) as well as our proposed network to conduct a matching search in the gallery dataset. The task for each network was to find the top 10 most similar images to the query image from the large gallery dataset. These images were ranked in order of similarity, forming a Top-10 list.
In Figure 4, the test results are presented visually, where each row corresponds to a network model and lists the top 10 most similar images retrieved by that network. The images with green captions indicate that the network successfully identified images belonging to the same ID as the query image, signifying accurate results. Images with red captions indicate that the network failed to correctly identify the images belonging to the same ID as the query image, thus representing incorrect matches.
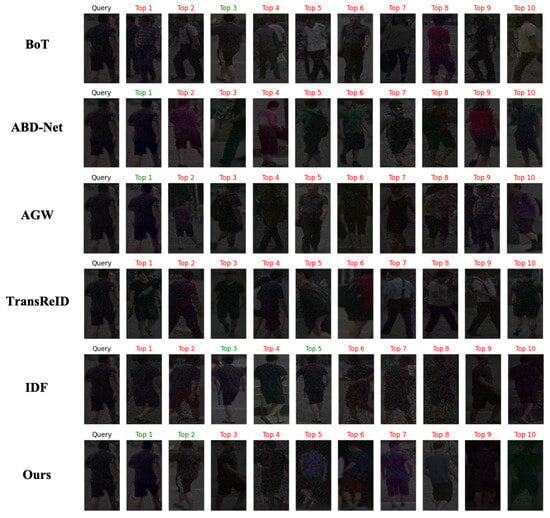
Figure 4.
Visual comparison of person re-identification methods: top-10 ranked matches.
4.3. Analysis
The Market1501 dataset contains a variety of pedestrian images and is widely used to evaluate the performance of pedestrian re-identification (ReID) methods. For this dataset, the TransConvRefDecoder combined with the ABMLP method showed exceptional performance, surpassing the other methods in the R-1, R-5, and R-10 metrics. However, despite its advantage in recognition accuracy, the TransConvRefDecoder and its ABMLP version had lower mAP scores compared to the other methods. This suggests that, while the model excels in recognition accuracy, it has room for improvement in terms of overall precision. This discrepancy may indicate that the model performs well in complex scenarios but still needs to improve its balance of precision across different situations.
On the CUHK03 dataset, which is characterized by its diverse and complex backgrounds, the performance of the TransConvRefDecoder was particularly outstanding, especially for the mAP metric, where it outperformed all other methods. The R-1, R-5, and R-10 metrics also reflected its strong performance, indicating that the model can better balance precision and recall, adapting effectively to the varied pedestrian features in the CUHK03 dataset. However, the introduction of the ABMLP module resulted in a performance decline, which may have been due to the module’s inability to effectively enhance the key feature representation with complex backgrounds, leading to overfitting or blurring of critical features. Future research could focus on optimizing the ABMLP module to better leverage its strengths in diverse datasets, thereby improving its feature extraction and discrimination capabilities.
The MSMT17 dataset, known for its large scale and diverse pedestrian images, poses even greater challenges. On this dataset, the TransConvRefDecoder combined with the ABMLP method performed slightly better than the standalone TransConvRefDecoder. Due to the large scale of the MSMT17 dataset, both methods performed less effectively compared to their performance on the Market1501 and CUHK03 datasets. The R-1, R-5, and R-10 metrics for the TransConvRefDecoder series showed slight improvements, but the mAP remained relatively low. This indicates that these models are constrained by the data diversity and background complexity inherent in large-scale datasets like MSMT17.
In summary, the proposed TransConvRefDecoder series modules demonstrated significant advantages across multiple datasets, particularly in improving the recognition accuracy and handling complex scenarios. The TransConvRefDecoder performed exceptionally well on the CUHK03 dataset, while the TransConvRefDecoder+ABMLP showed strong recognition capabilities on the Market1501 dataset. However, both methods also revealed some shortcomings across different datasets, especially in terms of the average precision and performance on large-scale datasets. These findings highlight the potential of the proposed modules in low-light person re-identification and suggest avenues for future research and improvements.
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. Backbone
To select the most suitable backbone network for optimal performance, we conducted comparison experiments using VGG16, ResNet18, and EfficientNet, as shown in Table 4. On both the Market1501 and CUHK03 datasets, the VGG16 model consistently outperformed the other models across the Rank-1, Rank-5, Rank-10, and mAP metrics. In contrast, the performance of ResNet18 and EfficientNet was notably lower, with EfficientNet achieving only 38.9% Rank-1 and 9.8% mAP on the Market1501 dataset. Therefore, we ultimately chose VGG16 as the backbone, to ensure the best performance.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of different backbone networks with TransConvRefDecoder on Market1501 and CUHK03 datasets.
4.4.2. TransConvRefDecoder
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed TransConvRefDecoder module, we conducted extensive ablation experiments, as shown in Table 5. In these experiments, we used the VGG16 network as the baseline model and compared it with the ReflectanceDecoder module, which was initially introduced by the object detection network DAI-Net [14]. In the table, the results highlighted in red indicate the best performance across all configurations, while the results in blue indicate the second-best performance.
An analysis of the experimental results from the Market1501, CUHK03, and MSMT17 datasets reveals that our proposed TransConvRefDecoder series modules, whether used alone or combined with ABMLP, consistently outperformed the decoder from [14] across multiple evaluation metrics. Notably, the TransConvRefDecoder series modules demonstrated significant improvements and stability in key metrics such as Rank-1, Rank-5, Rank-10, and mAP.
These results further validate the generalizability and superiority of the proposed modules across different datasets and evaluation standards, highlighting their robustness and effectiveness in enhancing performance in pedestrian re-identification tasks.
4.4.3. Robustness
Additionally, to further evaluate the performance of the models under different lighting conditions, we conducted experiments using query images captured in well-lit environments. The experimental setup followed the same visualization method as depicted in Figure 4, with the query images replaced by well-lit ones to test the adaptability of each model in such conditions. The results are shown in Figure 5. As we can see, with the exception of our proposed model, the performance of the other models significantly deteriorated when queried with images under good lighting, demonstrating less-than-ideal retrieval accuracy. This suggests that many models are sensitive to lighting changes, lacking the necessary adaptability and robustness.
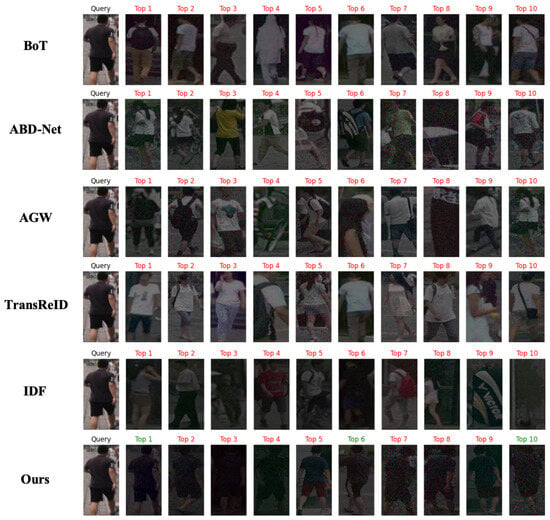

Figure 5.
Visual comparison of person re-identification methods under good lighting conditions: top-10 ranked matches.
Despite this, our model maintained relatively stable performance under well-lit conditions, showing a high degree of robustness. However, compared to its performance when directly queried with low-light images, our model also experienced a slight decline in both accuracy and robustness under good lighting conditions. This is likely because the model’s architecture and training strategy are more focused on handling feature recovery and matching in low-light environments. While it still outperformed the other models overall, its ability to handle fine details may be somewhat diminished in better lighting. Future work could aim to further optimize the model’s adaptability, ensuring that it consistently performs at its best under varying lighting conditions.

Table 5.
Ablation study results of performance across different methods on Market1501, CUHK03, and MSMT17 datasets.
Table 5.
Ablation study results of performance across different methods on Market1501, CUHK03, and MSMT17 datasets.
| Dataset | Methods | R-1 | R-5 | R-10 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market1501 | VGG16 | 68.6 | 81.1 | 84.9 | 17.0 |
| VGG16 + ReflectanceDecoder | 68.9 | 81.6 | 85.5 | 20.5 | |
| VGG16 + TransConvRefDecoder | 74.9 | 85.9 | 89.3 | 21.4 | |
| VGG16 + TransConvRefDecoder + ABMLP | 75.5 | 86.9 | 89.8 | 22.1 | |
| CUHK03 | VGG16 | 62.6 | 80.4 | 85.0 | 24.7 |
| VGG16 + ReflectanceDecoder | 64.4 | 81.7 | 87.6 | 25.3 | |
| VGG16 + TransConvRefDecoder | 67.2 | 84.4 | 88.6 | 26.2 | |
| VGG16 + TransConvRefDecoder + ABMLP | 66.6 | 83.2 | 87.8 | 26.2 | |
| MSMT17 | VGG16 | 40.4 | 54.8 | 60.6 | 7.6 |
| VGG16 + ReflectanceDecoder | 41.9 | 55.8 | 61.6 | 8.1 | |
| VGG16 + TransConvRefDecoder | 42.2 | 56.6 | 62.4 | 8.1 | |
| VGG16 + TransConvRefDecoder + ABMLP | 42.4 | 57.0 | 61.5 | 8.2 |
In the table, red text indicates the best performance, while blue text represents the second-best performance.
5. Conclusions
5.1. Conclusions
To address the challenges posed by the increased image noise, detail loss, and color distortion in low-light environments, this paper introduced a novel transposed convolution reflectance decoder (TransConvRefDecoder) based on retinex theory. This decoder significantly enhances pedestrian re-identification accuracy by restoring detailed features in low-light images.
The innovation of this work lies in improving a reflectance representation learning module originally used in the object detection domain and applying it for the first time to pedestrian re-identification. Specifically, the proposed TransConvRefDecoder replaces the traditional upsampling and convolution layer combination with transposed convolution layers, effectively recovering high-resolution reflectance features and improving the image detail performance and recognition accuracy in low-light conditions. By decomposing the image into reflectance and illumination components and employing multiple decomposition and recombination strategies, the model’s adaptability to low-light environments is further enhanced.
The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed method excelled across multiple datasets, including the Market1501, CUHK03, and MSMT17 datasets, significantly outperforming existing baseline models. These findings confirm the effectiveness and robustness of TransConvRefDecoder in low-light pedestrian re-identification.
In conclusion, this paper not only presents an effective method for low-light pedestrian re-identification but also offers new insights and references for future research. As deep learning technology continues to evolve, pedestrian re-identification in low-light environments is expected to improve further, playing a more significant role in intelligent surveillance and public safety.
5.2. Limitations and Future Work
Although this study achieved positive results in pedestrian re-identification under low-light conditions, some limitations remain. First, while the TransConvRefDecoder improves feature extraction in low-light settings, its performance is less stable in extremely low-light or highly variable lighting conditions, indicating the need for further optimization in handling complex lighting environments.
Additionally, the datasets used in this research, such as Market1501, CUHK03, and MSMT17, mainly consist of well-lit images, with low-light conditions simulated artificially. This limits the model’s real-world applicability, as synthetic low-light images may not fully capture the complexity of real low-light environments. Acquiring more real-world low-light data could help in evaluating the model more comprehensively.
Future work could focus on improving the model by incorporating adaptive modules to better handle different lighting conditions. Another potential direction would be to explore multi-modal approaches, such as combining infrared and visible light data, to enhance the model’s robustness in low-light settings. Moreover, semi-supervised or unsupervised learning methods could be employed to make better use of unpaired low-light data, improving the model’s generalization ability.
Addressing these issues would help to further improve the performance and practical applicability of pedestrian re-identification models in low-light and other challenging environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. and J.X.; methodology, Z.L.; software, Z.L.; validation, Z.L. and J.X.; formal analysis, J.X.; investigation, Z.L.; resources, J.X.; data curation, Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L.; writing—review and editing, J.X.; visualization, Z.L.; supervision, J.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gao, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Hong, R.; Chen, S. DCR: A Unified Framework for Holistic/Partial Person ReID. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 3332–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ye, M.; Lin, G.; Gao, X.; Shen, J. Person Re-Identification by Context-Aware Part Attention and Multi-Head Collaborative Learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 17, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Li, H.; Du, B.; Shen, J.; Shao, L.; Hoi, S.C.H. Collaborative Refining for Person Re-Identification with Label Noise. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 31, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chuang, Y.Y.; Satoh, S. Illumination-Adaptive Person Re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 22, 3064–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Jiang, W.; Gu, Y.; Liu, F.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Gu, J. A Strong Baseline and Batch Normalization Neck for Deep Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 22, 2597–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X.; Wang, P.; Jiao, B.; Zhang, Y. Person Re-Identification in Aerial Imagery. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 23, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Cheng, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. Learning Disentangled Representation Implicitly Via Transformer for Occluded Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 25, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep Retinex Decomposition for Low-Light Enhancement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04560. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.B.; Weng, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Jiang, J. URetinex-Net: Retinex-based Deep Unfolding Network for Low-light Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5891–5900. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Qi, G.J.; Gu, L.; You, S.; Zhang, Z.; Harada, T. Multitask AET with Orthogonal Tangent Regularity for Dark Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 2533–2542. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. HLA-Face: Joint High-Low Adaptation for Low Light Face Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16190–16199. [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel, A.; Garg, S.; Milford, M.; van Gemert, J.C. Zero-Shot Day-Night Domain Adaptation with a Physics Prior. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 4379–4389. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, R.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Similarity Min-Max: Zero-Shot Day-Night Domain Adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 8070–8080. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Shi, M.; Deng, J. Boosting Object Detection with Zero-Shot Day-Night Domain Adaptation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.01220. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y. A Discriminatively Learned CNN Embedding for Person Reidentification. Acm Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (Tomm) 2016, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Shen, C.; van den Hengel, A. PersonNet: Person Re-identification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1601.07255. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, S. Beyond Part Models: Person Retrieval with Refined Part Pooling. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–14 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Harmonious Attention Network for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2285–2294. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.; Fu, Y.; Xiang, T.; Wang, W.; Qiu, J.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Y.G.; Xue, X. Pose-Normalized Image Generation for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–14 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Wu, A.; Zheng, W.S. Shape-Erased Feature Learning for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22752–22761. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H. MRCN: A Novel Modality Restitution and Compensation Network for Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Tang, J.; Wang, L. Illumination Distillation Framework for Nighttime Person Re-Identification and a New Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 26, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Land, E.H. The retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 1977, 237, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukundo, O.; Cao, H. Nearest Neighbor Value Interpolation. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1211.1768. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Lei, S.; Celik, T.; Li, H.C. FER-YOLO-Mamba: Facial Expression Detection and Classification Based on Selective State Space. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.01828. [Google Scholar]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. FaceNet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, A.; Mohri, M.; Zhong, Y. Cross-Entropy Loss Functions: Theoretical Analysis and Applications. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.07288. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image Quality Assessment: From Error Measurement to Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Bu, J.; Tian, Q. Person Re-identification Meets Image Search. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.02171. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhao, R.; Xiao, T.; Wang, X. DeepReID: Deep Filter Pairing Neural Network for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Person Transfer GAN to Bridge Domain Gap for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, H.E. A Stochastic Approximation Method. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ding, S.; Xie, J.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Wang, Z. ABD-Net: Attentive but Diverse Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8350–8360. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Shen, J.; Lin, G.; Xiang, T.; Shao, L.; Hoi, S.C.H. Deep Learning for Person Re-Identification: A Survey and Outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 2872–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, W. TransReID: Transformer-based Object Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 14993–15002. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).