A Wireless Ad Hoc Network Communication Platform and Data Transmission Strategies for Multi-Bus Instruments
Abstract
1. Introduction
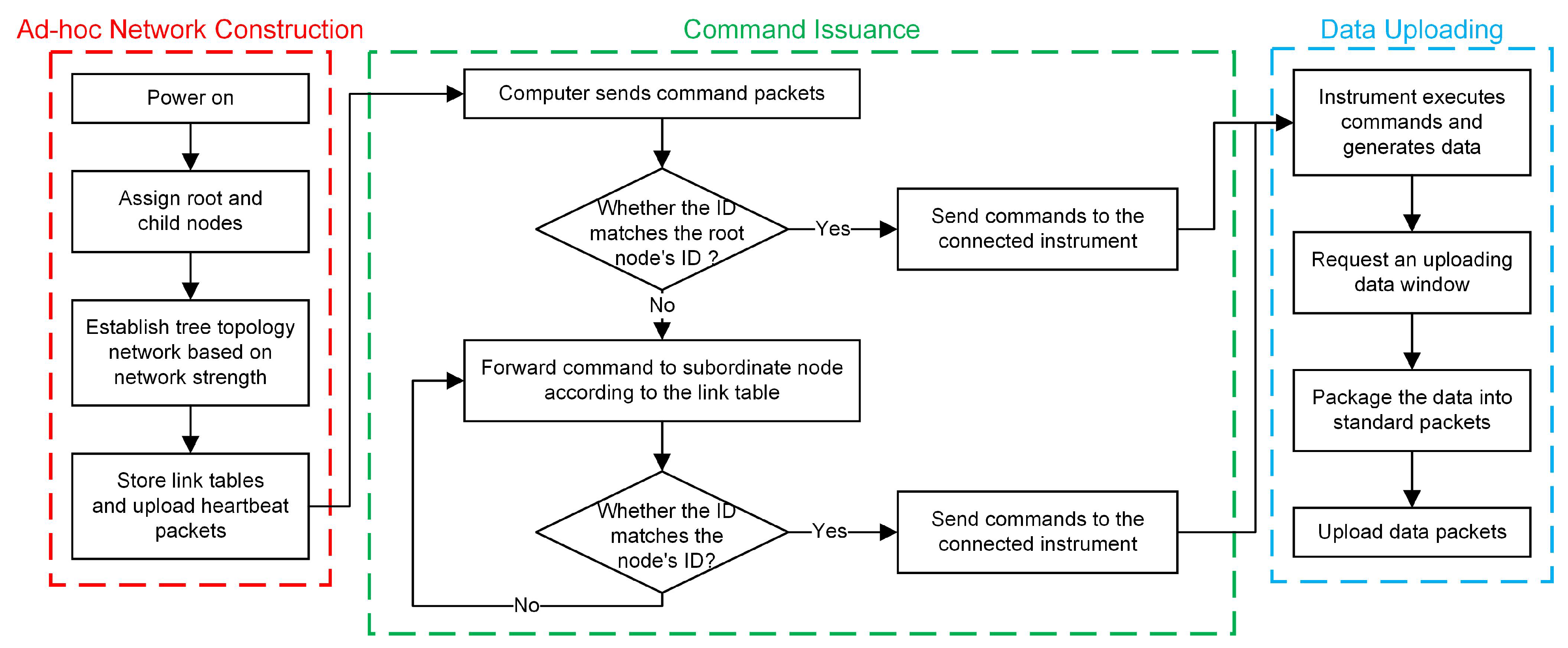
2. Design of Ad Hoc Network Communication Platform
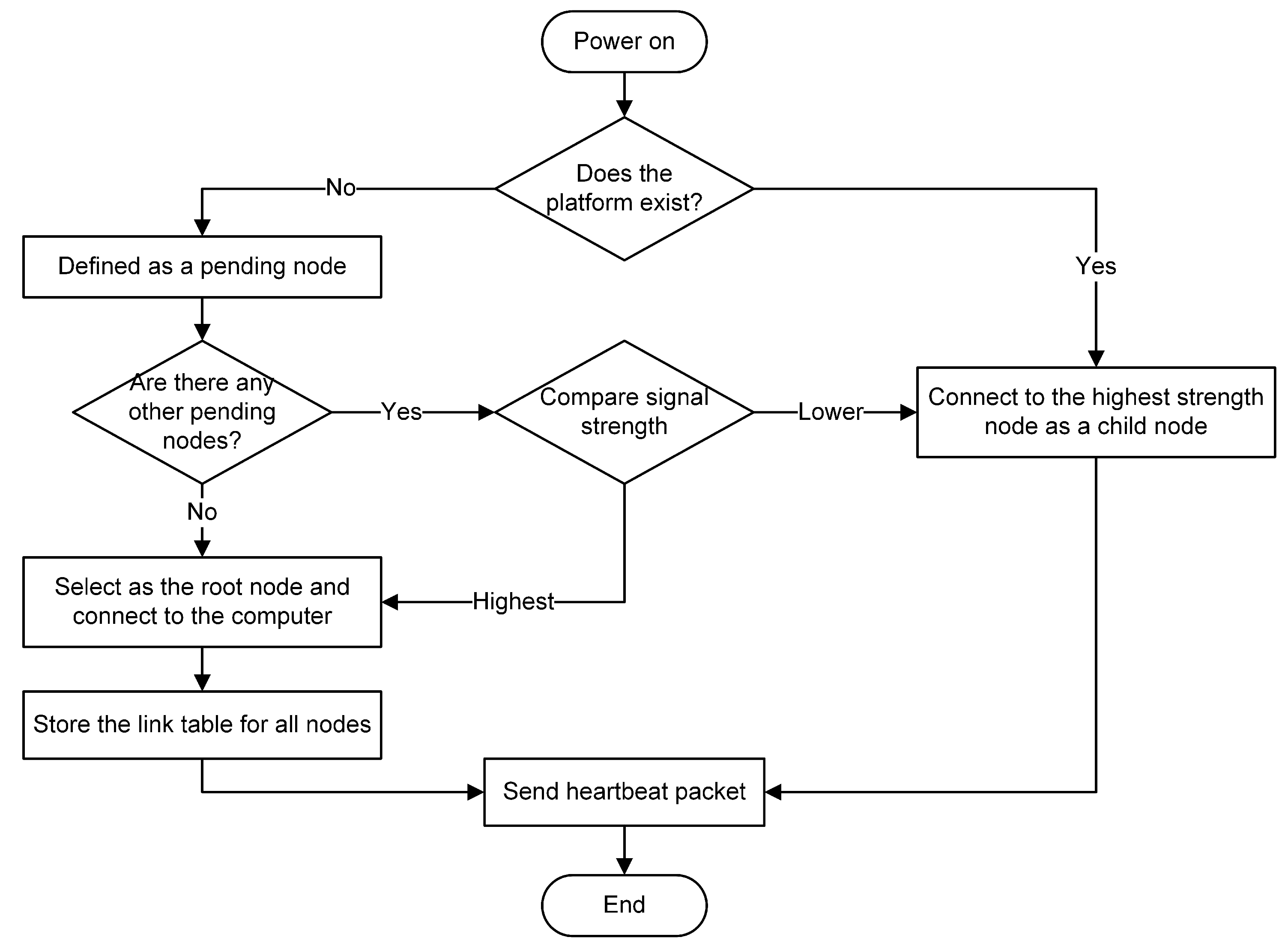
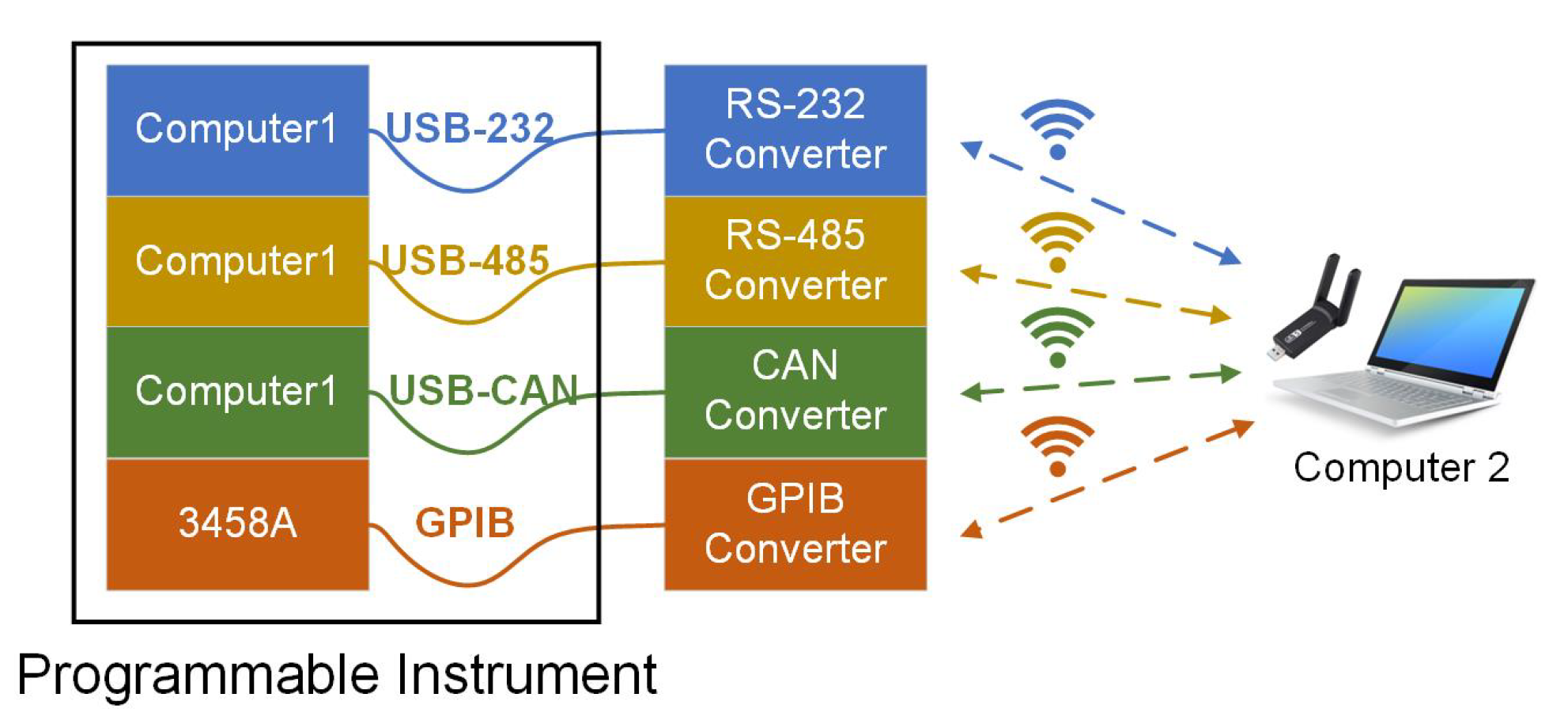
2.1. Platform Structure and Ad Hoc Network Method
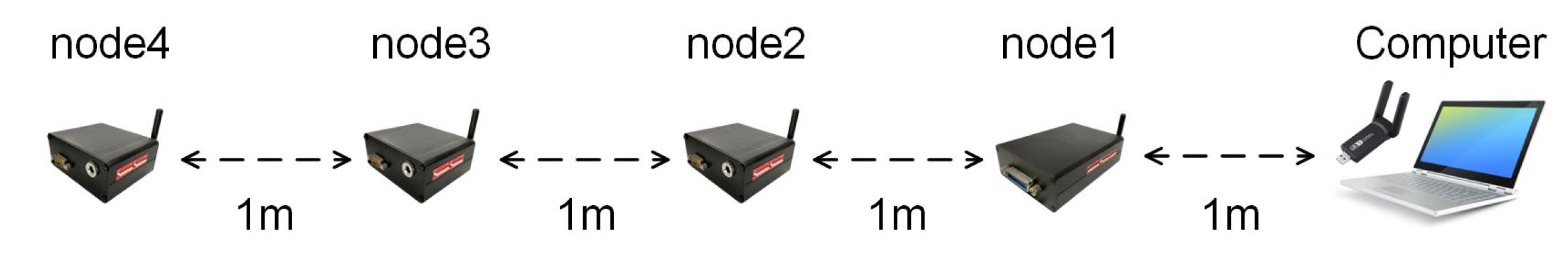
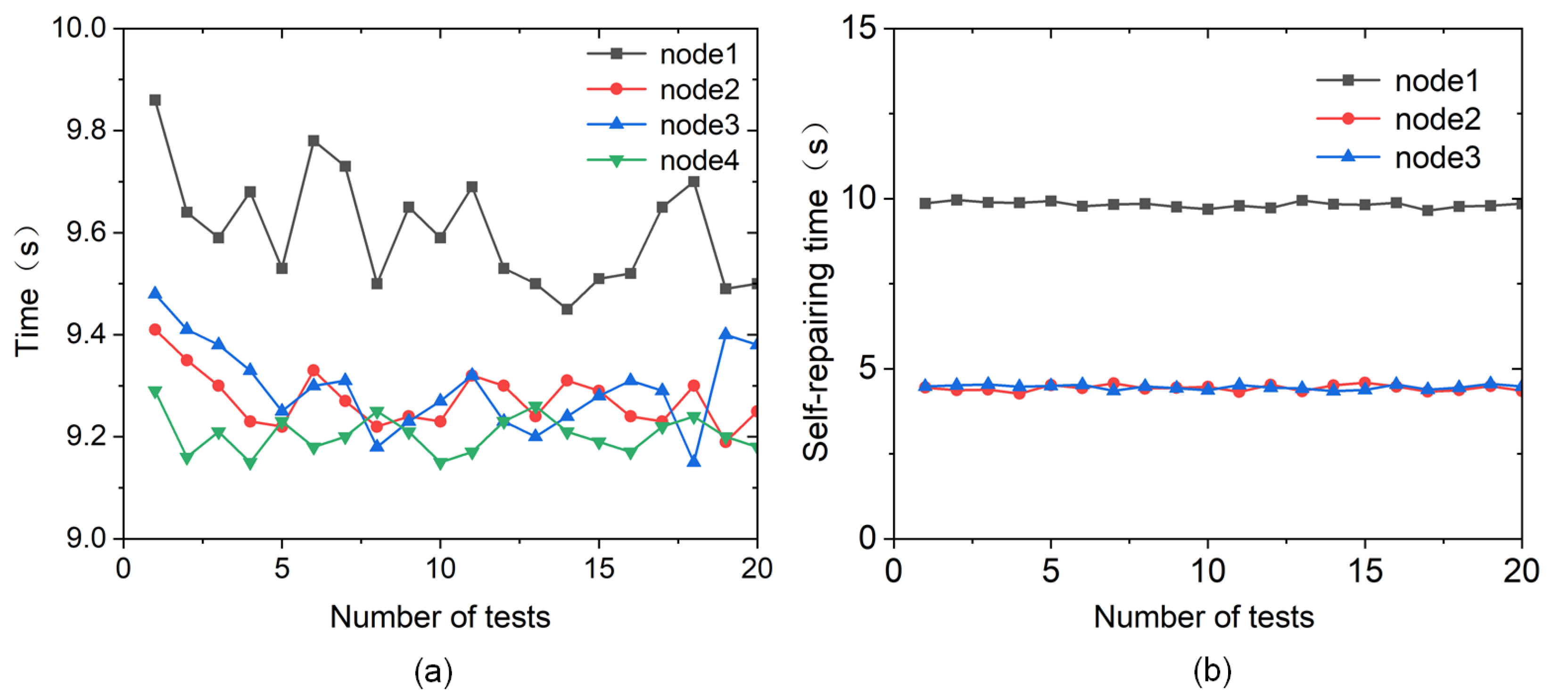
2.2. Self-Repairing Capability
3. Bus Protocol Converters
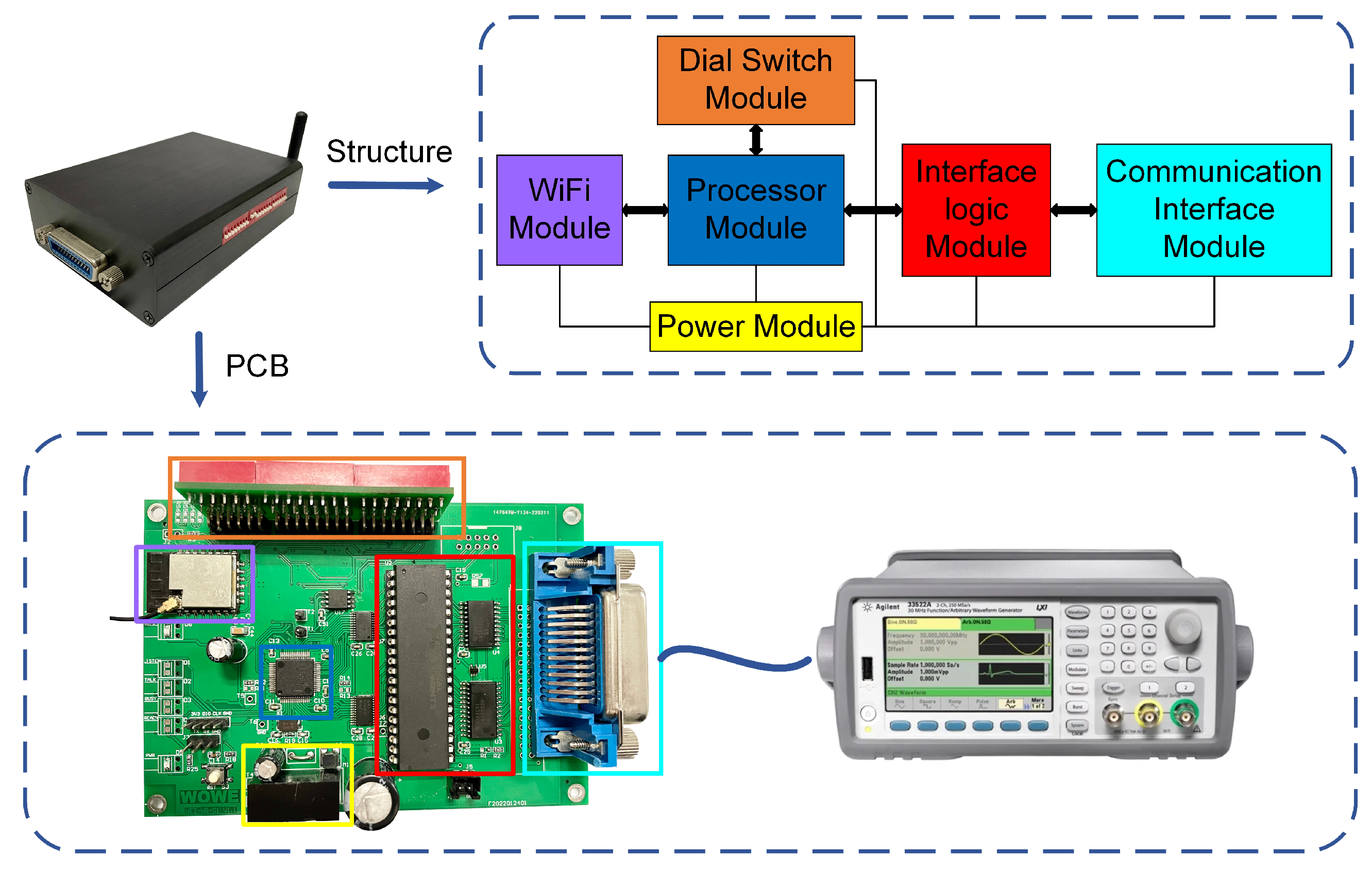
3.1. Converter Hardware Structure
3.2. Converter Control Logic
4. Data Transmission Strategy
4.1. Issues in Data Transmission
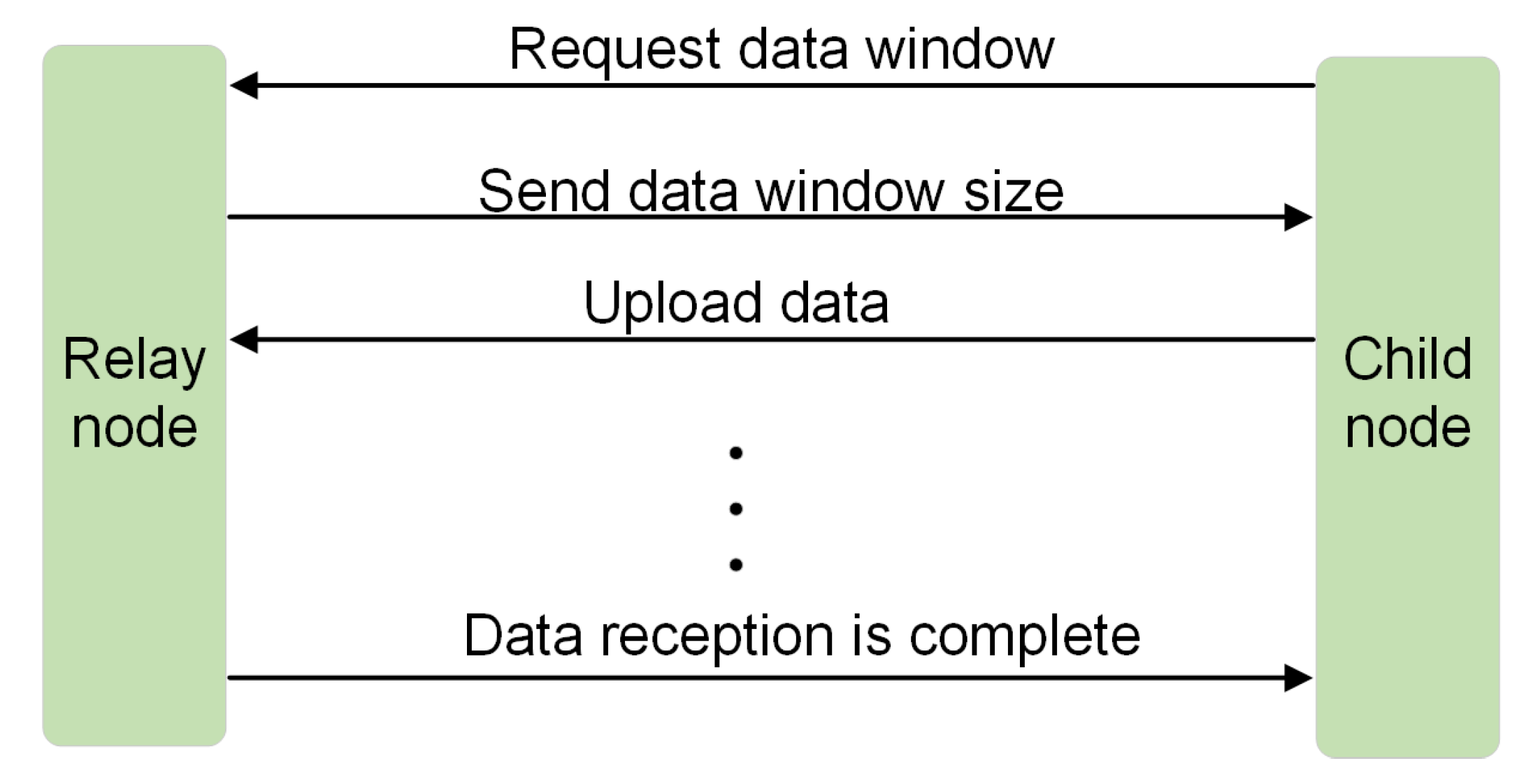
4.2. Approaches to Optimize Large Data Packet Transmission
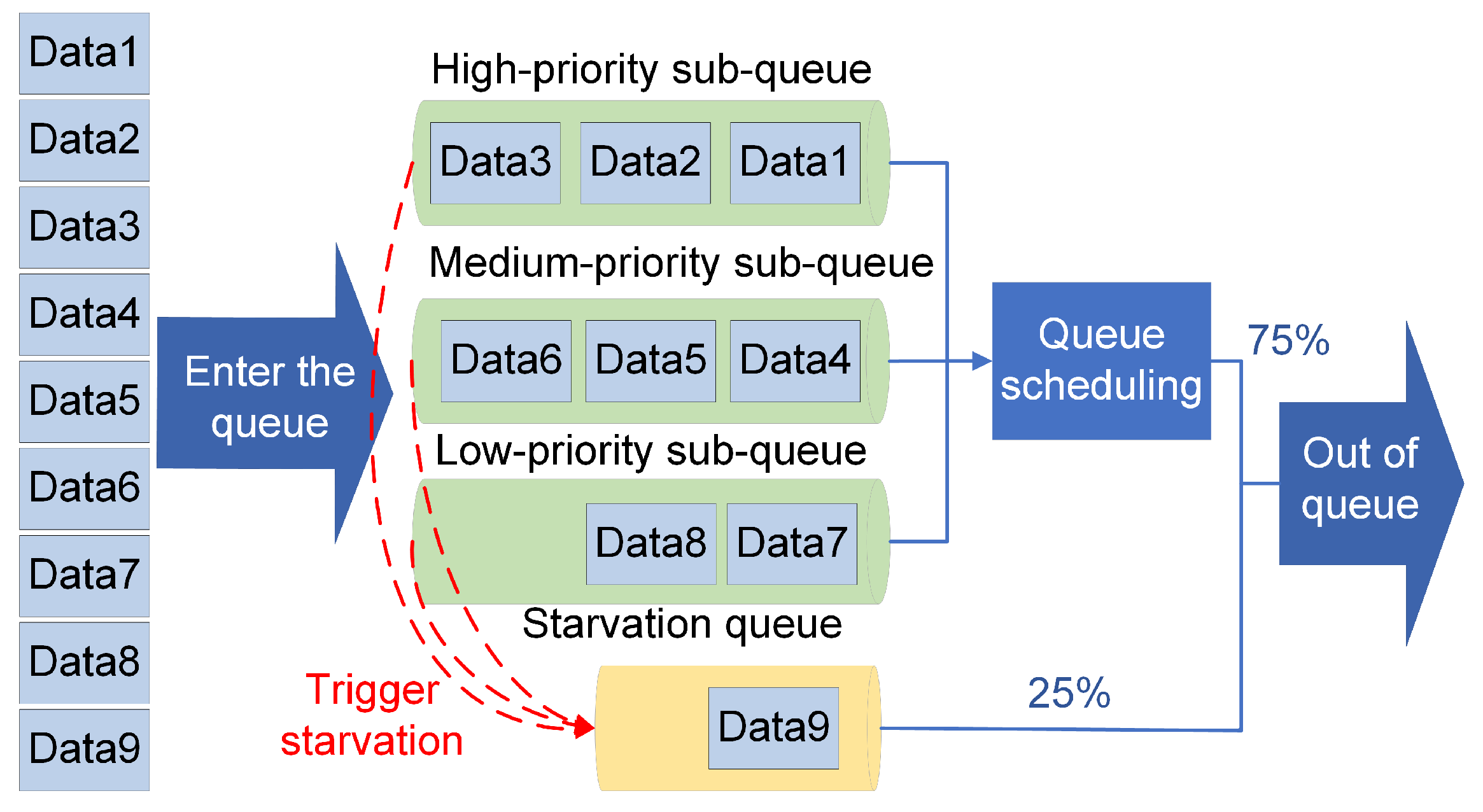
4.3. Approaches to Optimize Data Packet Conflicts
4.4. Validation of Optimized Data Transmission Strategy
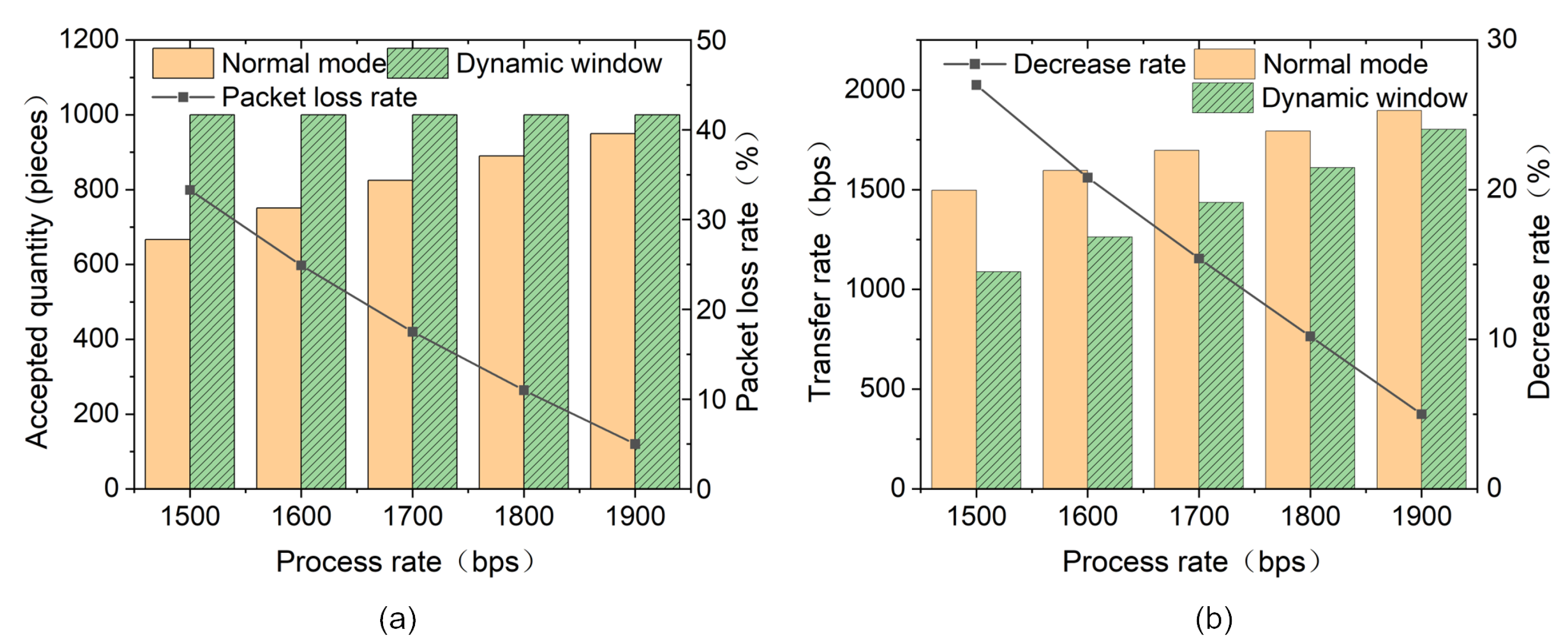
4.4.1. Validation of the Dynamic Window Receiving Mode
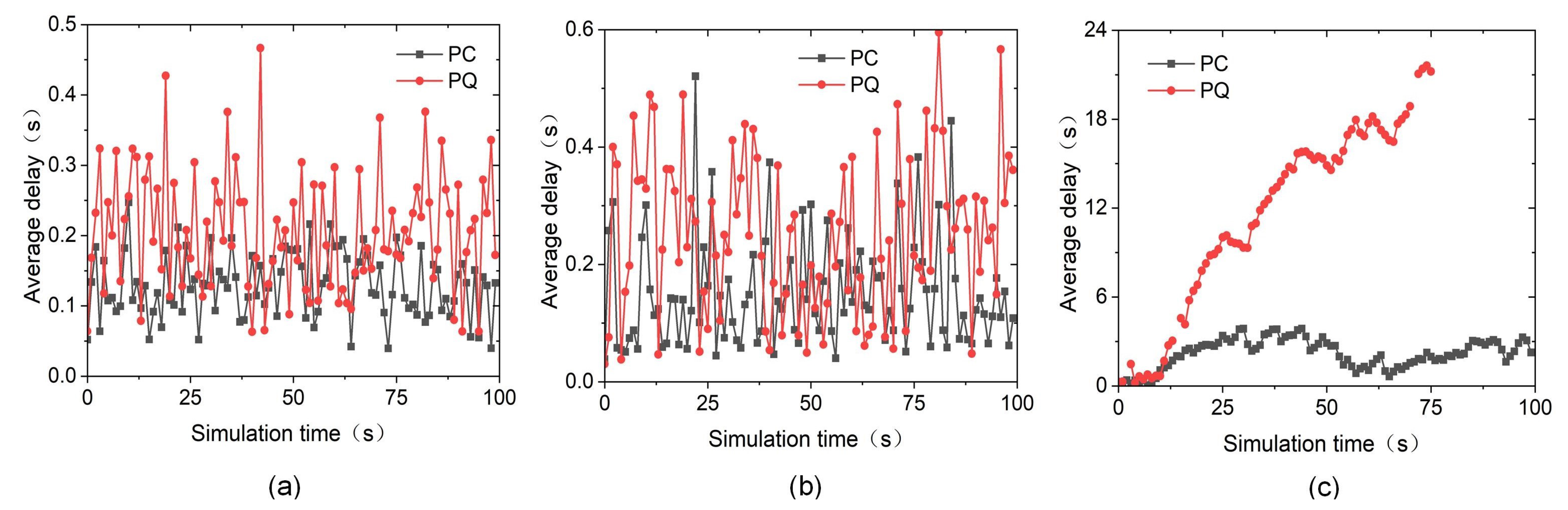
4.4.2. Validation of the PC Mechanism
5. Platform Performance Test
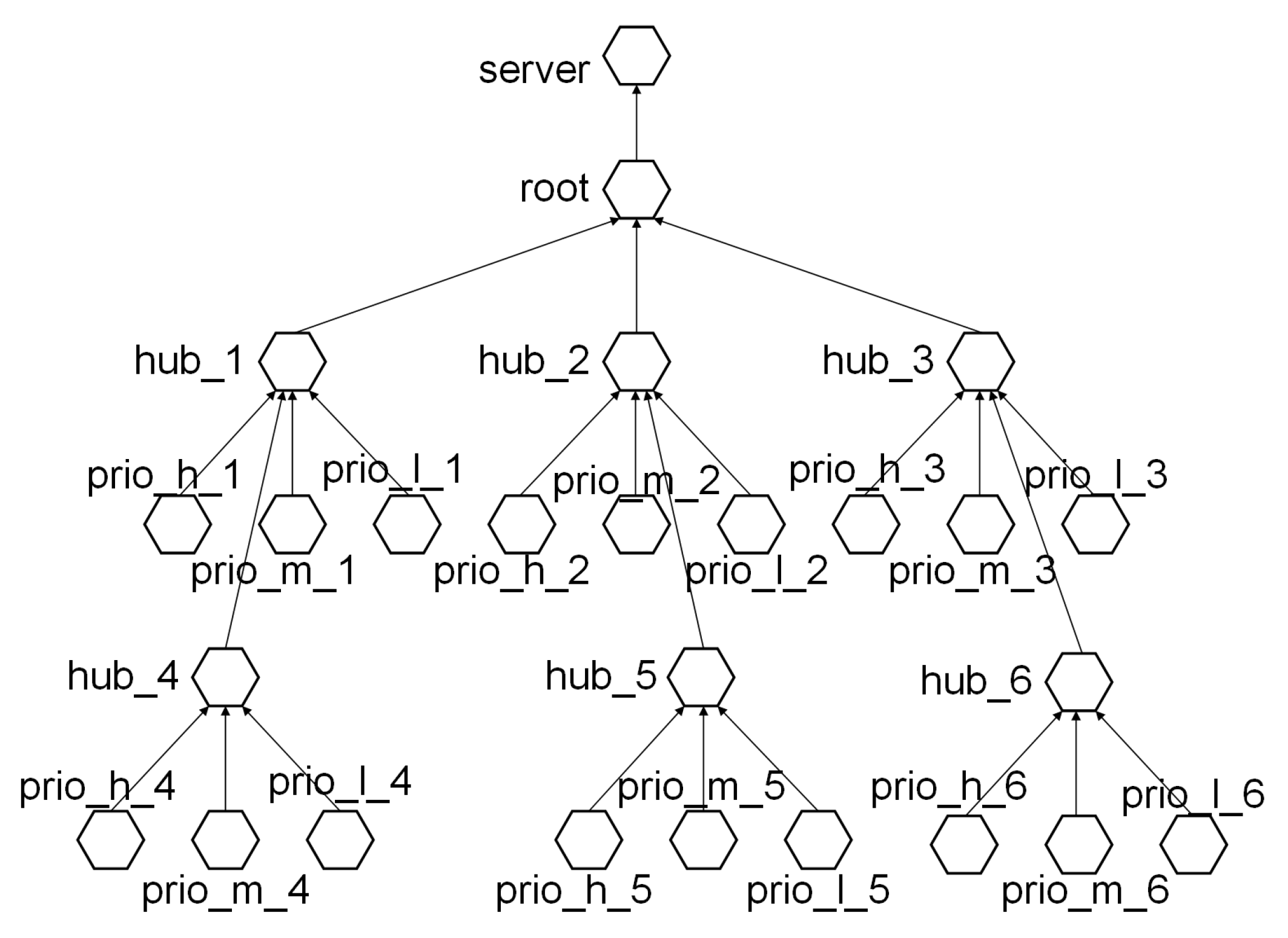
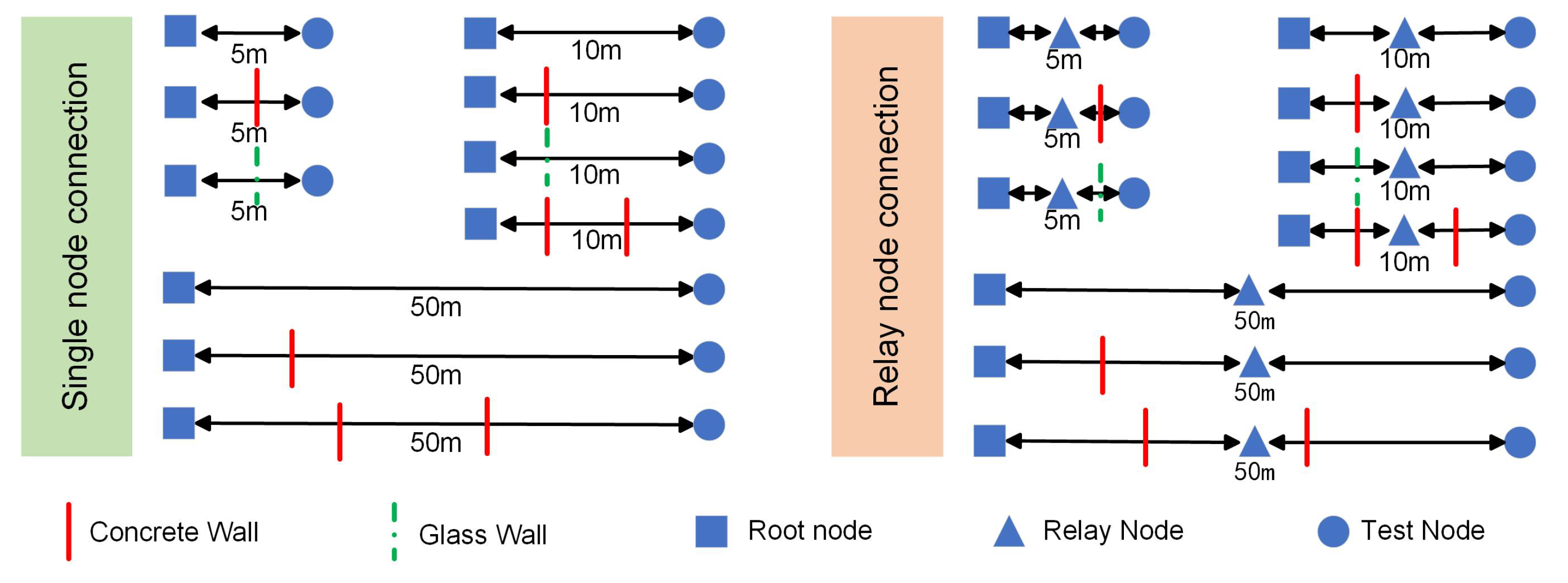
5.1. Networking Performance
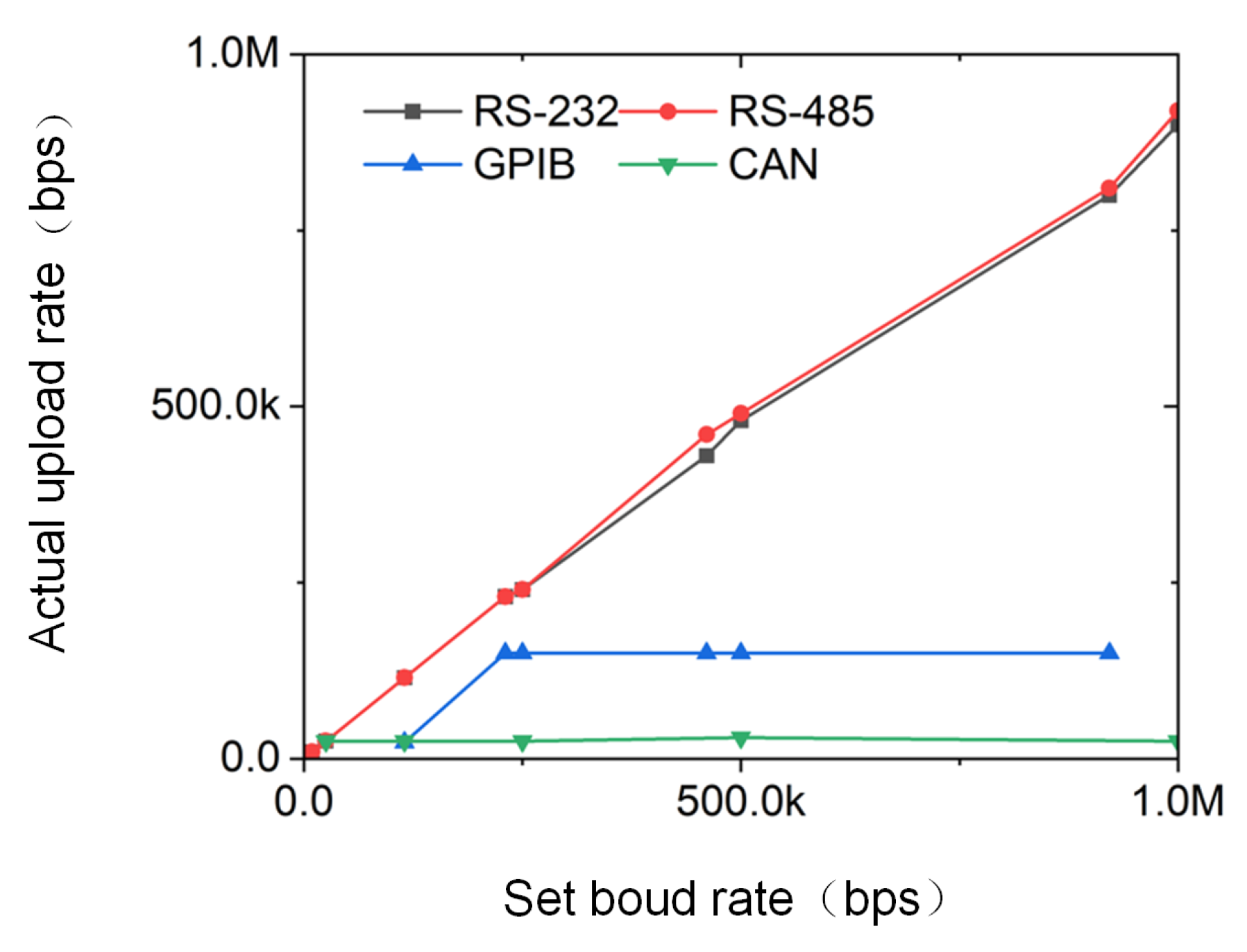
5.2. Upload Rate
5.3. Stability of Data Transmission
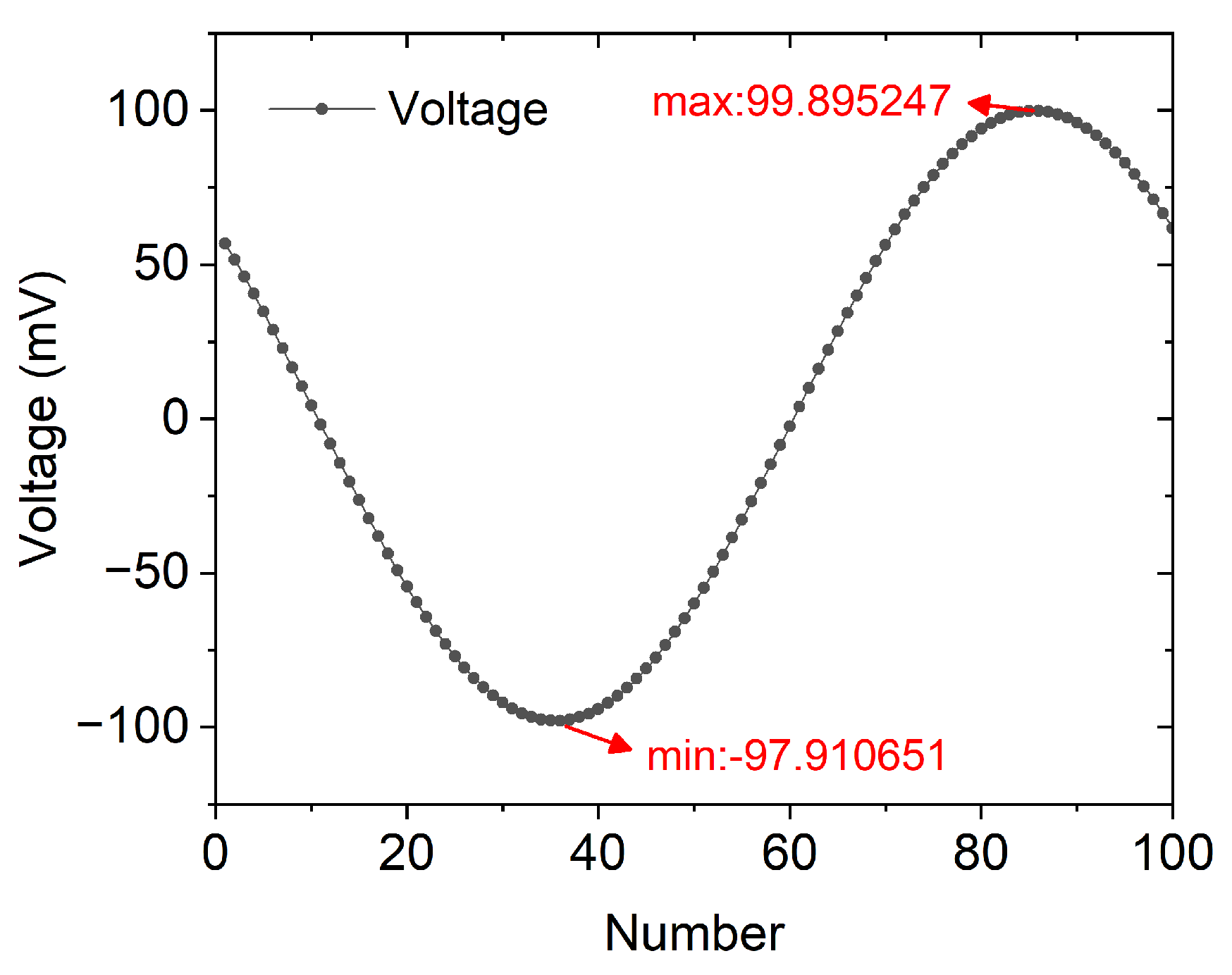
5.3.1. Practicality of Data Transmission
5.3.2. The Targeted Testing of Data Transmission Problems
5.3.3. Long-Term Stability Testing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, M.; Agarwal, N.; Reddy, S.R.N. Design and Development of Daughter Board for USB-UART Communication between Raspberry Pi and PC. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Communication & Automation (ICCCA), Noida, India, 15–16 May 2015; pp. 944–948. [Google Scholar]
- Abaceoae, C.; Postolache, M. Design and Implementation of a CAN-USB Interface for Networked Embedded Systems. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Sinaia, Romania, 10–12 October 2018; pp. 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sumathi, P.; Peter, D. Instrument Control through GPIB-USB Communication with LabVIEW. In Proceedings of the 28th IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (IEEE-ISIE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 1583–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.S.; Liu, H.B.; Luo, W.L. Development of a Novel Settlement Monitoring System Using Fiber-Optic Liquid-Level Transducers with Automatic Temperature Compensation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.P.; Huang, T.; Li, J.Q.; Yang, Z.H.; Li, B. Automatic test system of full electrical parameters for space traveling-wave tubes. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 065009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carni, D.L.; Lamonaca, F. Toward an Automatic Power Quality Measurement System: An Effective Classifier of Power Signal Alterations. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 2514208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobes, T.S.; Murphy, C. Deciding to Use Wireless Control and Instruments in the UK Nuclear Industry. Meas. Control 2014, 47, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mois, G.; Folea, S.; Sanislav, T. Analysis of Three IoT-Based Wireless Sensors for Environmental Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folea, S.C.; Mois, G.D. Lessons Learned From the Development of Wireless Environmental Sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 3470–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keysight E5810B LAN/GPIB/USB Gateway User’s Guide. Keysight Technologies. Available online: https://www.keysight.com/us/en/assets/9018-03842/user-manuals/9018-03842.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- TekScope Analysis Datasheet. Tektronix. Available online: https://www.tek.com/en/datasheet/tekscope-analysis-datasheet-analyze-anywhere-anytime (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Ferrigno, L.; Pietrosanto, A. A Bluetooth-based proposal of instrument wireless interface. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Symposium on Virtual and Intelligent Measurement Systems (IEEE Cat. No. 02EX545), Girdwood, AK, USA, 19–20 May 2002; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrigno, L.; Paciello, V.; Pietrosanto, A. Performance Characterization of a Wireless Instrumentation Bus. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 3253–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enériz, D.; Medrano, N.; Calvo, B.; Pérez-Bailón, J. A Wireless Instrumentation Control System Based on Low-Cost Single Board Computers. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Orta, D.E.; Medrano, N.; Calvo, B. A Wireless Instrumentation Control System Based on Low-Cost Single Board Computer Gateways. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 115632–115642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEE Std 802.11-2020 (Revision of IEEE Std 802.11-2016); IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems—Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Specific Requirements—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–4379. [CrossRef]
- Ova, K.; Watanabe, T.; Koga, H. Parametric spanning tree generation method for network topology design. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 13–15 January 2016; pp. 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Lubobya, S.C.; Dlodlo, M.E.; Jager, G.D. Performance Evaluation of the Wireless Tree Wi-Fi Video Surveillance System. In Proceedings of the 2014 UKSim-AMSS 16th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation, Cambridge, UK, 26–28 March 2014; pp. 511–516. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.D.; Wang, Y.X. Construction of Tree Network with Limited Delivery Latency in Homogeneous Wireless Sensor Networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2014, 78, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, T.; Medvecky, M. Performance Evaluation of WFQ, WF2Q + And WRR Queue Scheduling Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Budapest, Hungary, 18–20 August 2011; pp. 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hirchoren, G.A.; Porrez, N.; La Sala, B.; Buraczewski, I. Quality of service in networks with self-similar traffic. In Proceedings of the 17th Workshop on Information Processing and Control (RPIC), Mar del Plata, Argentina, 20–22 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.Z.; Islam, M.S.; Haque, A.K.M.F.; Ahmed, M. A comparative analysis of different real time applications over various queuing techniques. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 18–19 May 2012; pp. 1118–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, M.E.G.; Talab, S.A. The Effect of Queuing Mechanisms First in First out (FIFO), Priority Queuing (PQ) and Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) on Network’s Routers and Applications. WSN 2016, 8, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, B.; Kim, J.; Bueker, O. Equilibrium analysis of a partially observable priority queue. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 182, 109434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceco, A.; Mrdovic, S. Test bed for network protocols optimization. In Proceedings of the 26th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 20–21 November 2018; pp. 116–120. [Google Scholar]




| Name | Size |
|---|---|
| Packet generation interval | 1 s |
| Buffer size | 5 kbit |
| Buffer processing rate | 1.5 kbps/1.6 kbps/1.7 kbps/1.8 kbps/1.9 kbps |
| Link transmission rate | 1 Mbps |
| Name | Interval | Size |
|---|---|---|
| prio_h | 1 s | 40 kbit |
| prio_m | 1 s | 30 kbit |
| prio_l | 0.5 s | 20 kbit |
| hub | 1 s | 30 kbit |
| Distance/m | Indoor No Obstacle | One Glass Wall | One Concrete Wall | Two Concrete Walls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 100% | 100% | 100% | / |
| 10 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 0% |
| 50 | 100% | / | 0% | 0% |
| Distance/m | Indoor No Obstacle | One Glass Wall | One Concrete Wall | Two Concrete Walls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 100% | 100% | 100% | / |
| 10 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| 50 | 100% | / | 100% | 100% |
| Networking Module | Baud Rate | Sent Count | Received Count | Packet Loss Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPIB | 115,200 | 301 | 301 | 0% |
| RS232(1) | 115,200 | 301 | 301 | 0% |
| RS232(2) | 9600 | 299 | 299 | 0% |
| RS232(3) | 921,600 | 299 | 299 | 0% |
| RS232(4) | 460,800 | 298 | 298 | 0% |
| RS485 | 115,200 | 20 | 20 | 0% |
| CAN | 115,200 | 296 | 296 | 0% |
| Networking Module | Sent Count | Received Count |
|---|---|---|
| GPIB 1 (3458A) | 15,364 | 15,364 |
| GPIB 2 (8508A) | 15,282 | 15,282 |
| GPIB 2 (33220A) | 17,379 | 17,379 |
| RS232 1 | 40,466 | 40,466 |
| RS232 2 (F200) | 17,286 | 17,286 |
| RS232 3 | 40,383 | 40,383 |
| RS232 4 | 20,182 | 20,182 |
| RS485 | 40,451 | 40,451 |
| CAN | 4050 | 4050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, L.; Gu, K.; Fu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xu, S. A Wireless Ad Hoc Network Communication Platform and Data Transmission Strategies for Multi-Bus Instruments. Electronics 2024, 13, 3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183596
Qian L, Gu K, Fu Y, Shen Y, Xu S. A Wireless Ad Hoc Network Communication Platform and Data Transmission Strategies for Multi-Bus Instruments. Electronics. 2024; 13(18):3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183596
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Lushuai, Kexin Gu, Yaqiong Fu, Yuli Shen, and Suan Xu. 2024. "A Wireless Ad Hoc Network Communication Platform and Data Transmission Strategies for Multi-Bus Instruments" Electronics 13, no. 18: 3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183596
APA StyleQian, L., Gu, K., Fu, Y., Shen, Y., & Xu, S. (2024). A Wireless Ad Hoc Network Communication Platform and Data Transmission Strategies for Multi-Bus Instruments. Electronics, 13(18), 3596. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183596






