Abstract
Deep learning (DL) has brought new perspectives and methods to automatic modulation recognition (AMR), enabling AMR systems to operate more efficiently and reliably in modern wireless communication environments through its powerful feature learning and complex pattern recognition capabilities. However, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), which are used for sequence recognition tasks, face two main challenges, respectively: the ineffective utilization of global information and slow processing speeds due to sequential operations. To address these issues, this paper introduces CTRNet, a novel automatic modulation recognition network that combines a CNN with Transformer. This combination leverages Transformer’s ability to adequately capture the long-distance dependencies between global sequences and its advantages in sequence modeling, along with the CNN’s capability to extract features from local feature regions of signals. During the data preprocessing stage, the original IQ-modulated signals undergo sliding-window processing. By selecting the appropriate window sizes and strides, multiple subsequences are formed, enabling the network to effectively handle complex modulation patterns. In the embedding module, token vectors are designed to integrate information from multiple samples within each window, enhancing the model’s understanding and modeling ability of global information. In the feedforward neural network, a more effective Bilinear layer is employed for processing to capture the higher-order relationship between input features, thereby enhancing the ability of the model to capture complex patterns. Experiments conducted on the RML2016.10A public dataset demonstrate that compared with the existing algorithms, the proposed algorithm not only exhibits significant advantages in terms of parameter efficiency but also achieves higher recognition accuracy under various signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions. In particular, it performs relatively well in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, with clearer classification of higher-order modulations and notable overall accuracy improvement.
1. Introduction
In modern wireless communications, the accurate recognition of the modulation types of input signal is crucial, especially in applications such as dynamic spectrum access, anomaly detection, interference monitoring and localization, spectrum management, wireless communication parameter estimation, and signal demodulation. Automatic modulation identification (AMR) methods play a crucial role. They rely on the pre-synchronization code of the received signal to provide the details about the modulation scheme and determine their modulation pattern by analyzing the electromagnetic, spectral, and statistical characteristics of the unknown signal. This capability allows receivers to accurately recognize modulation patterns and transmit them to the corresponding demodulation processes [1]. AMR aids in optimizing spectrum utilization efficiency and enables the heterogeneous deployment of wireless networks. In fields such as military electronic warfare and civilian communication supervision [2], accurate and efficient AMR technology is the key means for spectrum resource monitoring and management.
However, in today’s complex wireless communication environments, multiple diverse communication systems coexist in a non-cooperative manner, posing significant challenges for designing high-precision AMR schemes. This challenge is particularly pronounced in cognitive radio (CR) networks and software-defined radio (SDR) systems, where performing AMR tasks is more demanding due to their support for various wireless communication services across a wide range of frequencies. In CR and SDR environments, dynamic spectrum sensing and access occur non-cooperatively over broad bandwidths. In such environments, signal reception is often inconsistent and incomplete. It is particularly important that the AMR systems must be able to accurately identify the modulation patterns, even when the received samples may contain only partial information or information is available only in the middle or at the end [3]. Therefore, with the development of wireless communication technologies and the diversification of application scenarios, the design of efficient AMR systems capable of handling incomplete signals in such non-cooperative environments is crucial for improving the performance and efficiency of communication systems.
AMR primarily comprises two architectures: (I) likelihood-based (LB) and (II) feature extraction-based (FB) methods [4]. LB methods [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12] construct the judgment criteria by computing the corresponding likelihood function, which relies on the ideal parameter estimation in the transmission environment and utilizes extensive prior knowledge of target modulations to achieve high-precision classification. However, as the number of modulation patterns increases and potentially more diverse modulation patterns appear, the computational complexity of LB methods also increases, which may lead to difficulties in mathematical computation. In contrast, the recognition rate of FB methods mainly depends on the extraction of signal feature parameters and the design of the classifier. These features primarily include instantaneous time features [13,14], spectral features [15], higher-order cumulants and moments [16,17,18,19,20,21], zero-crossing features [22], transformation features, and correlation entropy [23]. Compared with LB methods, FB methods require either no or less prior information. Generally speaking, FB methods can be divided into three steps: signal preprocessing, feature parameter extraction, and classification recognition [18,24,25,26]. Although theoretically these methods may be suboptimal, they are often simpler in implementation and application than LB methods. However, the traditional algorithms each have their limitations. For example, LB methods require comprehensive prior knowledge, whereas FB methods rely more on the effectiveness of feature extraction.
In recent years, with the rapid development of computer hardware processing speed, attention has increasingly focused on the deep learning (DL) methods within the context of FB methods. In AMR, signals are usually complex multidimensional data. DL can effectively extract more representative and distinguishable high-level feature representations from these signal data through multi-layer neural networks. DL is capable of learning and generalizing the features of various modulation patterns from extensive data so that the system can better cope with the diversity and variability in complex environmental conditions such as varying signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs), multipath effects, and so on [27]. By employing an end-to-end learning approach, DL can directly learn from the original data and optimize the entire recognition process, thus enhancing system performance and robustness in practical applications, ultimately improving the accuracy of modulation recognition.
O’Shea et al. [28,29] introduced a convolutional neural network (CNN) in the area of AMR, pioneering the direct use of original in-phase and quadrature signals as network inputs to extract local features for modulation mode differentiation. They extensively studied AMR network designs and established high-quality public datasets, focusing on modulation signal recognition [30]. CNN-based AMR methods have shown improved performance in complex environments [31,32,33]. However, these methods come with certain limitations: they require input data with a fixed size and cannot adapt to different operational modes composed of variable numbers of pulses. This necessitates adjusting or padding input data when the length of the input signal or number of component elements in the input signal varies to ensure CNN networks can handle these changes. These limitations may restrict the flexibility and applicability of these methods in dealing with real-time and dynamic environments. Subsequent research [34,35] introduced recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to optimize modulation signal recognition by continuously extracting time-series features, demonstrating higher accuracy compared to contemporaneous CNN-based approaches. However, RNN methods may incur a higher time cost, especially when dealing with long time-series data [36,37,38,39]. To fully utilize temporal and spatial information, researchers have begun exploring hybrid methods combining CNNs and RNNs [40,41,42,43,44]. These methods can significantly improve the accuracy of modulation recognition but usually require more parameters and computing resources. An effective architecture recommendation involves a two-layer gated recurrent unit (GRU) structure [35]. Researchers demonstrated that a model based on a long-term and short-term memory network (LSTM) effectively learns the representation of variable-length time series. Further improvements were made by introducing sequential convolutional recurrent networks (SCRNs) [45], combining the strengths of CNNs and LSTMs and validating the efficiency of this network structure through simulations. Another advancement proposed an end-to-end sequential network comprising shallow CNNs, bidirectional LSTMs with self-attention mechanisms, and dense neural networks [46]. This network extracts critical information in the past and future from cross-domain feature sequences, automatically discovering useful features to further enhance modulation signal recognition performance.
The attention mechanism has played a crucial role in the field of DL for a long time. For example, research simulated human visual information processing, paying special attention to the combination of RNNs with attention mechanisms, thus resulting in significant performance improvement in image classification tasks. Concurrently, research [47] pioneered the application of the attention mechanism in the field of machine translation, achieving the effect of synchronous translation and alignment, marking a groundbreaking innovation in natural language processing (NLP). The introduction of attention mechanisms has not only enhanced model performance on specific tasks but also significantly boosted model generalization capabilities. In recent years, with the emergence of the Transformer Network [48], this architecture based entirely on self-attention mechanisms [49,50,51] has revolutionized the field of deep learning, especially in handling long-sequence data and addressing challenges associated with high computational complexity. Transformer successfully integrates the strengths of CNNs and RNNs into a unified architecture with efficient performance, achieving remarkable accomplishments across multiple domains such as natural language processing [52,53,54] and image processing [55]. In sequence classification tasks, particularly in AMR-like tasks, it has become a hot topic to introduce Transformer-related structures [56,57,58].
Existing convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) face limitations in effectively leveraging global information for sequence classification tasks. While CNNs excel at extracting information from local feature regions, they lack an understanding of the overall sequence structure. On the other hand, RNNs can process sequence data but struggle with capturing long-range global dependencies due to their serial processing nature. This serial processing characteristic of RNNs results in slower model performance, particularly when dealing with large-scale data, leading to inefficient computation. This paper introduces a Transformer-based modulation recognition network named CTRNet, which has been further improved accordingly. The approach combines the strengths of Transformers in capturing long-range dependencies and sequence modeling, along with a CNN in local feature extraction and spatial relationship modeling. During the data preprocessing stage, the raw IQ modulation signals are processed using a sliding-window approach. By selecting appropriate window sizes and step lengths, multiple subsequences are generated. This method facilitates the network’s ability to effectively handle different modulation patterns. And it is optimized in the embedding module: token vectors are designed to integrate information from multiple samples within each window, thereby enhancing the model’s ability to understand and model global information. In contrast to traditional AMR algorithms, we primarily adopt the encoder structure [55] as the core unit of the network; in the feedforward neural network, a more effective Bilinear layer was introduced to enhance the model’s capability to capture higher-order relationships between input features. Through extensive evaluation, CTRNet effectively leverages the advantages of the two neural network architectures, demonstrating superior performance with fewer parameters compared to existing algorithms. Additionally, it offers certain advantages in computational speed.
The structure of the remaining sections of this paper is as follows: Section 2 provides background information related to the AMR problem, including the modeling of signal transmission channels. Section 3 presents an overview, the motivation, and a detailed description of the proposed CTRNet approach. Section 4 conducts relevant simulation experiments on publicly available datasets, discusses factors influencing the network performance, and compares it with other deep models. Section 5 summarizes the findings of this study.
2. Signal Modeling for the AMR Problem
In this paper, we employ a deep neural network as a classifier for receiving wireless signal modulation patterns. The advantage of deep learning as an end-to-end classification approach lies in its ability to automatically learn necessary parameters from training data.
Typically, a receiver processes a wireless signal modulated in a noisy fading environment to obtain its baseband complex envelope with the following general expression:
where is additive Gaussian white noise at time t, denotes the time-varying wireless channel impulse response with time delay , refers to the mathematical convolution operator, and signifies the modulation scheme, which converts digital data into analog signal format. The modulator maps the transmission symbol to a specific modulated signal. Specifically, the modulator converts the transmission symbol into a form suitable for transmission based on the selected modulation scheme . refers to the transmission symbol in the communication system, which is the analog signal or complex baseband digital signal obtained after the modulation of digital information, defined as follows:
Without considering noise, the baseband complex envelope of the received signal can be expressed as Equation (2), where represents the amplitude of the signal, is the carrier frequency offset, represents the carrier phase shift introduced by propagation delay, is the phase jitter, represents one of the complex symbols obtained from the modulation type, is the normalization timing offset between the transmitter and the signal receiver, and is the main purpose of the transmission pulse shape modulation classifier. The main objective of the modulation classifier is to identify the modulation scheme adopted by a given received signal without relying on prior information. Specifically, its task is to infer the probability distribution of the modulation type behind it according to the received signal .
The received continuous time signal , after amplification, down-conversion, and low-pass filtering processing, is ultimately converted into a discrete time digital signal with a sampling rate of which represents the sampling of the signal at the discrete time point . Mathematically, this can be expressed as follows:
where = 1/ refers to the sampling interval, and is the fixed sampling rate.
where is the in-phase component (real part) of the nth sample in the discrete time domain sequence. is the quadrature component (imaginary part) of the nth sample in the discrete time domain sequence. is an imaginary unit.
3. Proposed Model
This section introduces CTRNet for AMR tasks, which is a framework designed with a self-attention mechanism. The attention mechanism enables the network to focus on the correlation between each element when processing input sequences. Transformer is adept at dealing with long-distance dependencies, capturing global information effectively. The CNN excels at extracting features from local windows, exhibiting strong inductive bias ability to capture local patterns and structures in signals. This capability enables CTRNet to effectively capture long-distance dependencies, integrating global information effectively without the need for additional overlay layers and extracting features from it. This section begins with an overview of the framework, followed by detailed explanations including the data preprocessing stage, the embedding module, and the encoder, and concludes with a description of the data processing flow.
Based on the architecture of the CTRNet model, as illustrated in Figure 1, it can be broadly divided into two parts: the data preprocessing and the CTRNet. CTRNet primarily consists of three components: the linear projection layer, the Transformer encoding layers, and the multi-layer perception heads.
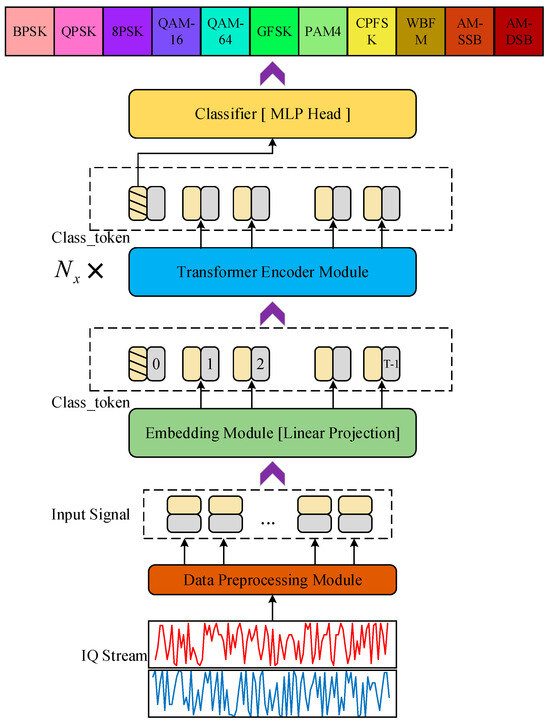
Figure 1.
Overall network architecture of the CTRNet method.
The signal modulation recognition process based on the CTRNet model can be summarized as follows: Initially, the input IQ signals undergo initialization and standardized preprocessing to ensure that the data input into the model are appropriately transformed into sequential signals. Subsequently, they are embedded into the linear sequence of the linear projection layer; these preprocessed IQ data perform a linear transformation to extract discriminative features. Prior to inputting the linear sequence into the Transformer encoder, the position embeddings are added to help the model understand positional information within the sequence. These position embeddings, typically learnable, enhance the model’s ability to perceive sequence order by adding unique encodings to each position in the input sequence. The Transformer encoders are employed to capture long-distance dependencies within the sequence. Comprising multiple Transformer blocks, each block includes self-attention mechanisms and feedforward neural networks. These blocks facilitate the transformation of the input sequence into higher-level feature representations, which are further processed in the MLP heads. The MLP heads constitute the final section responsible for classification decisions. They receive the output from the Transformer encoder as input and employ several fully connected layers and dropout layers for the classification task. These layers enable the learning of the ultimate signal modulation classification results from the high-level features extracted by the Transformer encoder. The entire process utilizes the capabilities of the CTRNet model to process sequential data efficiently, thereby achieving the effective classification of IQ signals. Each component plays a crucial role in processing and feature extraction, ensuring the accurate differentiation of various signal modulation patterns.
3.1. Preprocessing Stage of IQ Data
IQ signals undergo preprocessing to transform them into a sequence suitable for use within the network architecture. This architecture requires embedded forms as its input, whereas the original IQ data consist of paired samples, namely in-phase and quadrature data. To effectively input IQ signals into the network, the long IQ signal sequence is segmented into multiple equally sized shorter sequences. These short sequences serve as one of the inputs to the network, ensuring that each sequence is of equal length and contains complete signal information. Details of this pretreatment step are illustrated in Figure 2.
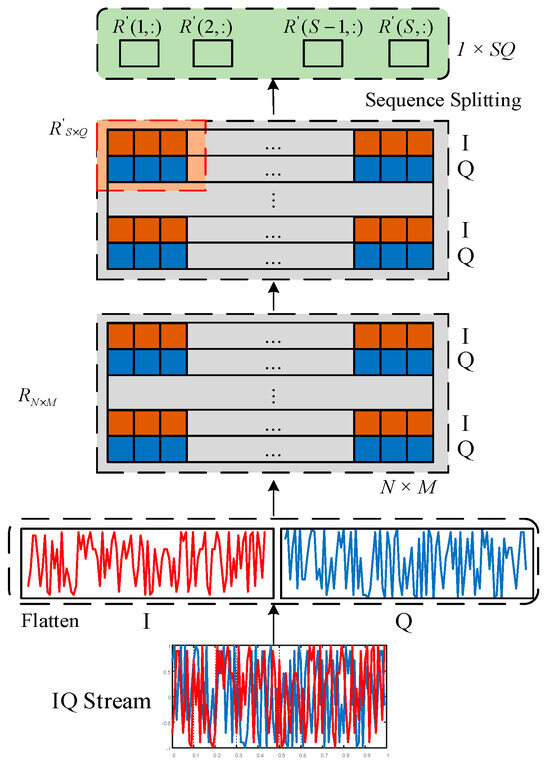
Figure 2.
Data preprocessing flow for IQ signals.
The specific steps are as follows:
Step 1: Combine the and sequences of signal into a vector ,
where denotes the length of the original signal data.
Step 2: Transform vector into matrix by sequentially filling the row vector into a matrix R with the size of , where .
Step 3: Divide the matrix into matrices of size , where is the number of blocks into which is divided, and the corresponding dimension is (, ).
The number of blocks in the row direction, , indicates that the rows are divided into blocks; the number of blocks in the column direction, , indicates that the column is divided into blocks.
Step 4: After partitioning into blocks, reorder the matrix in row-major order into a sequence of length , which contains all the elements of the whole matrix .
Step 5: Pass the concatenated sequence as the input to the network for its subsequent processing or operations.
3.2. Embedding Module
The purpose of the embedding module is to convert the input signal into multiple frames through framing operation. As shown in Figure 3, each frame consists of in-phase and quadrature components, and the vector of each frame is vertically concatenated from these components. These vectors are then horizontally connected to form the input feature . This frame-by-frame embedding method is simple and parameter-efficient, while also performing well, where represents the number of frames, and and are the frame size and sliding step size, respectively.
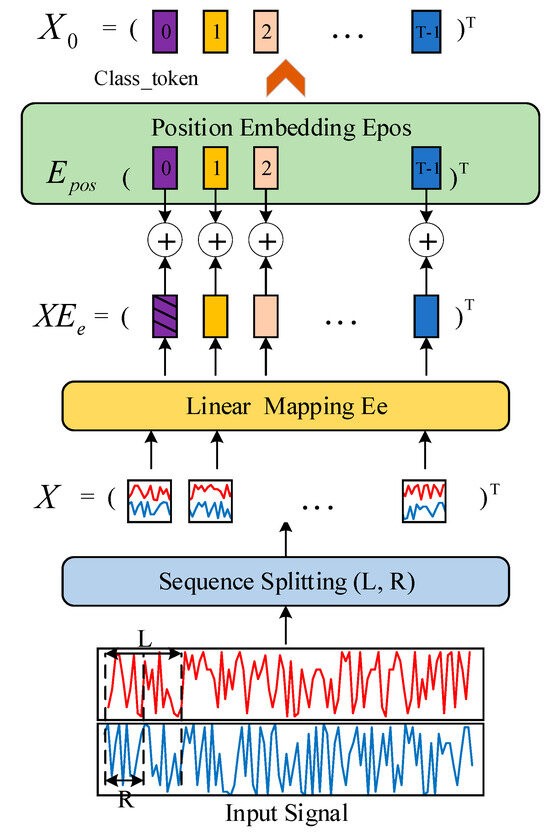
Figure 3.
Schematic of the frame-by-frame embedding module.
The input feature is first transformed into a token sequence using a linear token embedding projection , where . Subsequently, a class token is connected along the first dimension. The class token is initially randomly initialized and updated during the training process. It is then combined with the learnable position encoding matrix for position embedding. The resulting output serves as the input to the Transformer layer.
The input feature sequence is expressed as the input of the th Transformer layer. These operations eliminate CNN or RNN layers, allowing the analysis of global features without local constraints.
Specifically, for a particular position and dimension, the value of the trigonometric signal function is uniquely determined. Utilizing Fourier transform to transform the frequency domain into the time domain, corresponding to an impulse signal, the location is also unique, so each position has a unique value for each dimension, thus introducing temporal information. The position encoding algorithm is based on the above principle, specifically manifested as follows:
where refers to the position of the signal in the input sequence, represents the dimension of position encoding, and and represent even and odd dimensions, respectively.
As the length of the input feature decreases, that is, , the computational complexity of the Transformer block significantly reduces. This is due to the fact that the computational cost of the Transformer’s attention mechanism decreases when dealing with shorter input sequences. This method avoids the locality that may be introduced in the traditional CNN or RNN modules. Simultaneously, by reducing the length of the input features, it lowers the computational complexity, thereby improving the model’s performance and efficiency [59,60].
3.3. Architecture of Transformer Encoder
The Transformer-based encoder adopts a modular architecture, as shown in Figure 4, which allows each layer to work independently. Communication between layers is facilitated through an attention mechanism, providing flexibility in adjusting the size and complexity of the model. In this setup, each module has a input layer, which accepts the component of the signal data as input. These components are divided into blocks with the size of , with each block undergoing linear embedding after the addition of positional information embeddings.
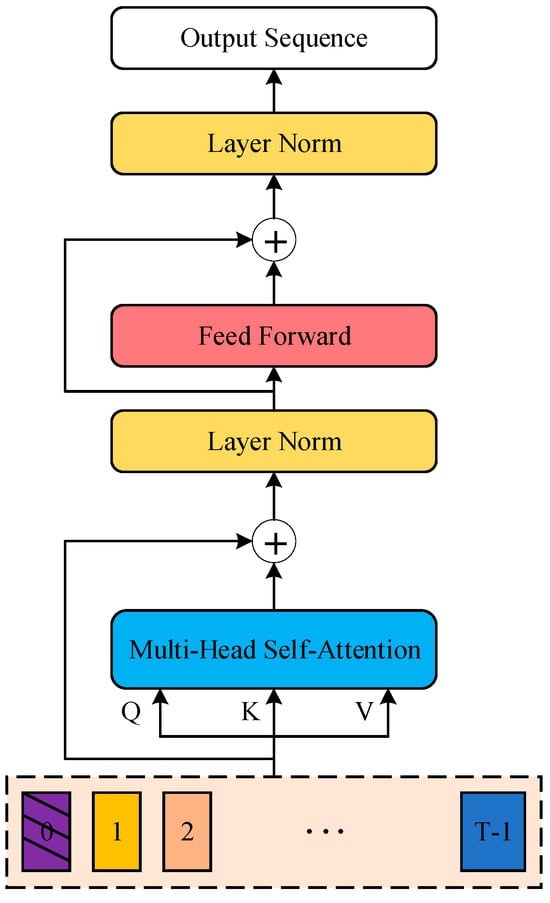
Figure 4.
Architecture of the Transformer encoder.
3.3.1. Multi-Head Self-Attention (MHSA)
The multi-head self-attention mechanism was put forward by the Google team and is widely applied in Transformer language models [50], capable of independent use in both encoding and decoding processes.
Compared with the traditional attention mechanisms, it pays more attention to the long-distance dependencies within the input sequence. The computation of the output of the self-attention mechanism is as follows:
Firstly, from the same input matrix of a data source, queries , keys , and values are derived through linear transformations using weight matrices (, , ). The process is as follows: , , . The dimensions of are , where is the sequence length and is the dimensionality of each vector, as depicted in Figure 5.
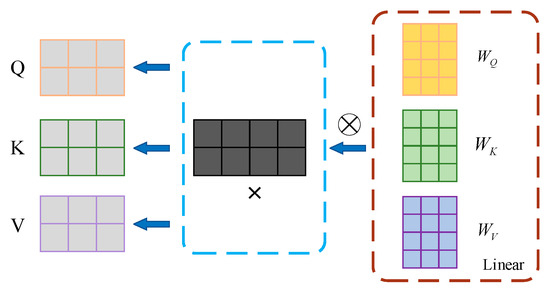
Figure 5.
Generation process of query, key, and value.
Secondly, attention scores are computed by performing dot products between each and pair. To control the range of attention scores, the dot product results are scaled using , where is a scaling factor mitigating gradient vanishing issues brought by softmax.
Subsequently, the softmax function is then applied to normalize and obtain weights corresponding to each key. These weights are then multiplied with their respective values , followed by weighted summation to derive the value at each position in the output sequence.
Finally, due to the Transformer employing multiple independent parallel attention heads (typically heads), each head utilizes separate weight matrices to perform the aforementioned attention computation, as illustrated in Figure 6. The outputs from each head are concatenated together and undergo a final linear transformation for the ultimate output. The final output sequence integrates various information from the input data, where each position’s value depends not only on individual input positions but also incorporates contributions from global information obtained through the attention mechanism. Mathematical expressions for the output of MHSA are given in Equations (15) and (16).
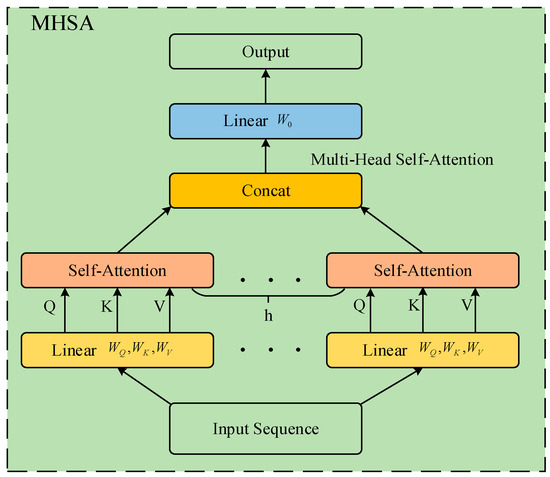
Figure 6.
Diagram of multi-head self-attention (MHSA).
The feature vectors of the input sequence are mapped to multiple query, key, and value matrices. Each head independently computes self-attention, generating attention weights and weighted features. The weighted features from all heads are concatenated and subjected to a linear transformation to produce the final output. Figure 6 illustrates how the outputs from different heads are integrated into the final multi-head self-attention result. Different attention heads can focus on and capture various parts or types of relationships within the sequence, thereby providing richer contextual information. The multi-head attention mechanism enables parallel computation across multiple attention heads, enhancing the efficiency of the model.
3.3.2. Feedforward Neural Network
The feedforward neural network is used to independently and uniformly analyze each token. It consists of two fully connected layers structured as an MLP (Multi-Layer Perceptron), with one layer utilizing the ReLU activation function and the other without activation, and its definition is as shown in Equation (17).
In this paper, the feedforward neural network described above has been enhanced by replacing the traditional MLP activation function with a Bilinear layer, which optimizes and reduces the number of parameters while improving the model performance. See Figure 7 for details.
where denotes the element-by-element product.
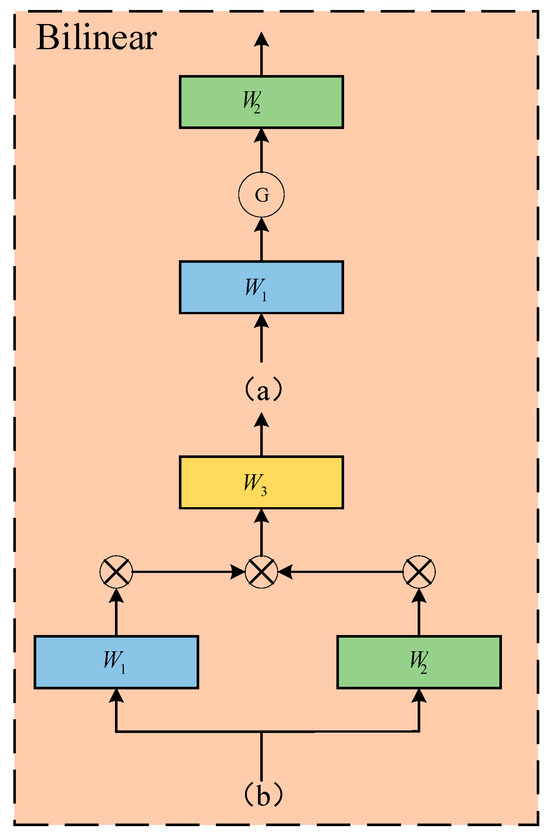
Figure 7.
Design of FFN: (a) the MLP layer; (b) the Bilinear layer.
This indicates that the design of the Bilinear layer can more effectively handle feature representations, thereby enhancing the quality and efficiency of tasks. This method demonstrates improved performance in processing FFN blocks, particularly when compared to traditional MLPs.
3.3.3. Encoder Data Processing Flow
Step 1: Input data are fed into the MHSA mechanism for processing, which assigns scores to each element to determine their relative importance, resulting in the generation of new data.
Step 2: The Add operation is performed to establish residual connections; the new data generated within the MHSA mechanism are added to the original input data to ensure that the data processed through attention yield better results than the original data input directly.
Step 3: Layer normalization is conducted to stabilize the data.
Step 4: A two-layer feedforward neural network maps the data processed through attention back to their original shape and size, ensuring consistency in the data dimensions before entering the next encoder after multiple folding encoder operations.
Step 5: The encoder stack, composed of encoder layers, outputs a finely calculated and reconstructed vector representation that captures the complex relationships between individual elements and other elements in the input sequence.
Through these steps, the model ensures the effective transmission and processing of information across multiple encoder layers while preparing for subsequent tasks.
4. Performance Evaluation
In this section, we assess the performance of the proposed system through a series of comprehensive experiments. These experiments include comparing the performance of the encoder before and after improvements, parameter analysis, and benchmarking the classification performance of the standard architecture against other baseline methods. The training dataset ratio used in the experiments is 0.8, with the Adam optimizer and an initial learning rate of 0.001. Classification cross-entropy is employed as the loss function. All the training and predictions for these experiments were implemented in TensorFlow, utilizing two GeForce GTX 2070 GPUs for accelerated computation.
4.1. Experimental Dataset and Implementation Details
Experiments were conducted using the RadioML2016.10A dataset widely used in the AMR research field [51,52]. This dataset comprises 11 kinds of modulation types, including analog modulations such as AM-DSB, AM-SSB, and WBFM, which use continuous speech signals as data sources, mainly composed of original speech with some off-time, and digital modulations including BPSK, QPSK, 8PSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, GFSK, PAM4, and CPFSK using ASCII-format Shakespeare collections. Each frame consists of 128 IQ samples. The dataset is composed of modulation-type label–SNR combinations, generating a total of 220,000 frames. The signal-to-noise ratio ranges from −20:2:18 dB with a step size of 2 dB. The sampling rate is set at 200 kHz, with a maximum sampling rate offset of 50 Hz, a standard deviation of 0.01 Hz, a maximum carrier frequency offset of 500 Hz, a standard deviation of 0.01 Hz, and eight sinusoidal wave numbers used in frequency-selective fading. The channel transmission environment includes AWGN noise, the selective fading of AWGN, Rice distribution and Rayleigh distribution, central frequency offset (CFO), and sampling rate offset (SRO).
4.2. Performance Comparison of Encoder before and after Improvement
Using a standard architecture as the base model, one version utilizes the original encoder, while the other employs an improved encoder. Figure 8 illustrates the data for each epoch during the training process. Specifically, the figure displays the average accuracy on the validation set when using the improved encoder compared to the original encoder.
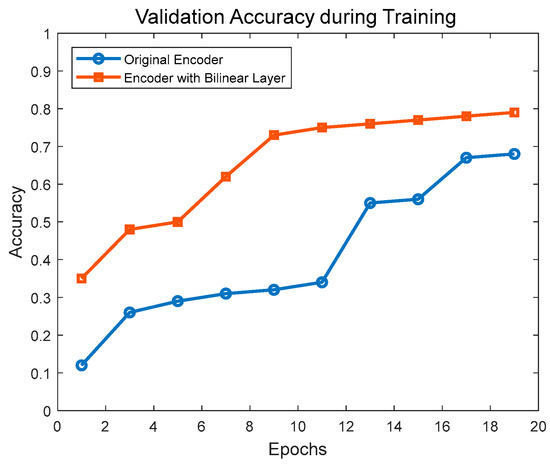
Figure 8.
Accuracy curves of improved encoder vs. original encoder.
According to the results shown in Figure 8, the encoder with the Bilinear layer performs better on the training set in each epoch, with its average classification accuracy curve consistently above that of the original encoder. This indicates that the Bilinear encoder is able to learn features and patterns from the data more effectively. It demonstrates faster improvement starting from the fifth epoch and reaches the classification accuracy level of the original encoder by the eighth epoch. This suggests that the Bilinear encoder has a faster convergence rate, enabling more efficient learning of information from the training data and demonstrating superior performance.
Figure 9 illustrates that under different SNR levels, the curve of the improved encoder with the Bilinear layer consistently remains at the top of the graph, maintaining or even enhancing the model’s modulation recognition accuracy compared to the original encoder. The Bilinear layer is typically used to enhance the model’s feature extraction capabilities in classification tasks, thereby improving the overall performance of the model. By incorporating the improvement in the Bilinear layer, significant enhancements in modulation recognition accuracy of the encoder can be achieved under various SNR conditions. This improvement is of great significance for enhancing the robustness and accuracy of the model in noisy environments.
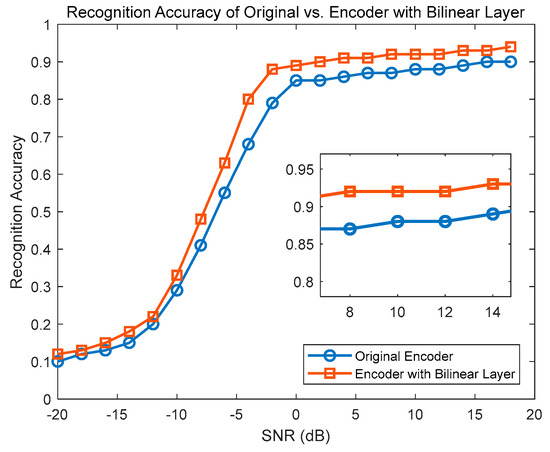
Figure 9.
Relationship between recognition accuracy of two different encoders and SNR.
4.3. Parameter Analysis
In the context of the CTRNet model for classification tasks, its performance is influenced by various parameter settings. Fine-tuning these parameters is one of the key steps in enhancing the model performance. The following are the main parameters affecting the classification performance of the CTRNet model and their effects:
(1) Sliding-window size and step length: The sliding-window size in the CTRNet model includes the frame size (L) and the sliding step (R), specifying the granularity of relationship modeling along the temporal dimension. It determines the length and overlapping of subsequences extracted from the original sequence. Larger window sizes and step lengths result in less overlap and longer subsequences, potentially capturing more global features but also risking the loss of some local features. Conversely, smaller window sizes and step lengths will capture local features more frequently, which may lead to overfitting or the loss of overall contextual information. Among them, the fixed parameters include 16 attention heads, 512 dimensions of hidden layers, a batch size of 32, and 50 training epochs. The test parameters are sliding-window sizes of 8 and 16 and step lengths of 4, 6, and 8.
In Figure 10, the combination of a sliding-window size and step length of 16*8 achieves the highest recognition accuracy, aiding the model in effectively capturing the discriminative features used for classification. This indicates that larger window sizes can help the model capture a wider range of information from the input data, while larger step lengths can accelerate the model’s movement and processing speed on the data. This contributes to the model’s comprehensive understanding and differentiation of features within the input data.
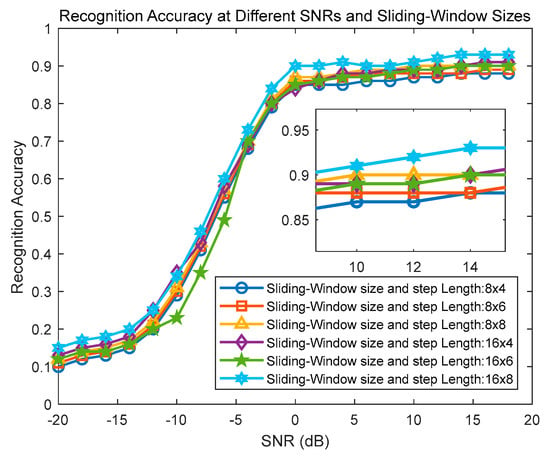
Figure 10.
Recognition accuracy curve for different combinations of sliding-window sizes and step lengths.
(2) Number of attention heads: In the self-attention mechanism, the number of attention heads specifies how many attention heads learn relationships simultaneously. Among them, the fixed parameters include a sliding-window size of 16, a step length of 8, 512 dimensions of hidden layers, a batch size of 32, and 50 training epochs. The test parameters are 4, 8, 16, and 32 attention heads.
In Figure 11, when the number of attention heads is 16 (H = 16), a good balance can be achieved, enabling the model to capture the crucial information and patterns within the input sequences without overfitting the training data, resulting in optimal recognition performance. A smaller number of attention heads (H = 4) may limit the model’s expressive and learning capabilities, leading to poor performance in handling complex sequences and capturing long-distance dependencies. On the other hand, a larger number of attention heads (H = 32) can provide more linear spatial representation and enhanced relationship capturing ability, yet often at the cost of increased computational complexity and potential overfitting, especially with insufficient training data or inadequate regularization.
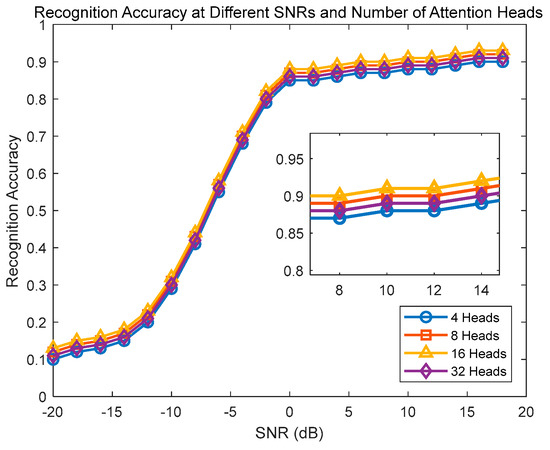
Figure 11.
Impact of number of attention heads on recognition performance of CTRNet model.
The attention span in CTRNet is akin to the receptive field size in CNNs, where a larger attention span enhances feature extraction capability. This suggests that larger attention spans assist the model in capturing more extensive contextual information and global structures within sequences, thereby improving its feature extraction and representation capabilities.
(3) Batch size: Batch size refers to the number of samples used in each update of the model parameters. The fixed parameters in the experiment include a sliding-window size of 16, a step length of 8, 16 attention heads, 512 dimensions of hidden layers, and 50 training epochs. The test parameters are batch sizes of 16, 32, and 64.
When the batch size is 16, it facilitates more frequent updates of model parameters because each batch generates a gradient update. This helps the model converge to a better solution faster, especially during the early stages of training. Larger batch sizes (such as 32) typically result in more stable gradient estimates due to the averaging of gradients over more samples. This helps to reduce the gradient variance, leading to a smoother training process. However, when the batch size becomes too large (e.g., 64 or larger), it may introduce a number of issues during training. These issues include inaccurate gradient estimates, particularly problematic for smaller datasets, which can make it difficult for the model to converge to the optimal solution. Additionally, excessively large batch sizes can increase memory requirements, thereby reducing training efficiency. Therefore, from Figure 12, it can be observed that the optimal batch size in the experiment is 32, where the model achieves the best recognition performance.
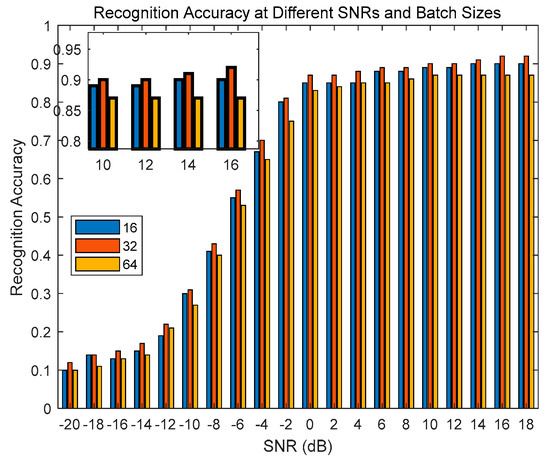
Figure 12.
Recognition performance under different batch sizes.
4.4. Comparison Experiments with Baseline Models
Several typical deep learning models were selected as baselines, including a CNN, DenseNet, CLDNN, LSTM, and ResNet. These models were modified and improved upon to adapt to the requirements of the AMR task.
Figure 13 illustrates the comparison of signal modulation recognition accuracy among various models under different SNR conditions. The proposed CTRNet model demonstrates significant advantages starting at −10 dB SNR, surpassing other algorithms in recognition accuracy. This indicates its strong adaptability to noisy environments, with an average recognition accuracy of 64.3% and reaching up to 93.98% under specific conditions, showcasing robustness and stable performance across various noise levels. In contrast, the CNN-based models exhibit poorer performance at lower SNRs, showing a performance decline of nearly 13% compared to the proposed model.
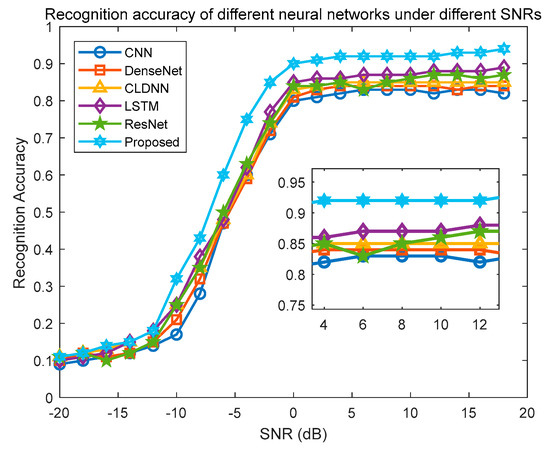
Figure 13.
Comparison of recognition accuracy of different neural network models under different SNRs.
The DenseNet-based models also show relatively lower performance, trailing by approximately 10% in terms of SNR performance compared to the proposed model. This suggests that the CTRNet-based model excels in extracting more robust features. Regarding the CLDNN and ResNet models, the proposed model shows performance improvements of around 9% and 5%, respectively, under low- and high-SNR conditions. This indicates superior recognition performance of the proposed model under various noise conditions. The LSTM-based models achieve an average recognition accuracy of 58.05%, peaking at 87.68%, which is better than the previous baseline models, especially in high-SNR environments, but still falls short of the proposed model. The ResNet, as a common baseline model, performs well in high-noise environments but achieves a slightly lower average recognition accuracy (59.55%) compared to the CTRNet. Even under optimal conditions, the ResNet’s highest recognition accuracy (89.85%) is surpassed by the CTRNet’s 94%, highlighting the CTRNet’s advantage under extreme conditions. The proposed CTRNet algorithm significantly enhances the recognition accuracy compared to other mainstream algorithms, particularly demonstrating high efficiency and accuracy in complex electromagnetic environments and low-SNR conditions.
The performance of the CTRNet algorithm under various SNR conditions is crucial, particularly analyzed through confusion matrices and recognition accuracy graphs. The confusion matrix illustrates how well the CTRNet algorithm classifies different modulation types across various SNR levels. Each row represents the true modulation type, while each column represents the predicted modulation type by the model. The confusion matrix not only showcases the model’s accuracy in each category but also reveals the difficulty of classifying specific modulation types under different SNR conditions, which provides vital information for assessing and improving the model performance. For instance, frequent misclassifications of certain modulation types as others under the condition of a low SNR may indicate poorer algorithm performance in low-SNR environments, necessitating further optimization or special handling for low-SNR conditions. As the SNR increases, the diagonal of the confusion matrix becomes sharper, indicating an improved recognition accuracy of the model under high-SNR conditions. This signifies that the model more accurately classifies signals into their true modulation types when the SNR is high.
Figure 14 illustrates the confusion matrix under different SNR conditions, reflecting the performance variation in the CTRNet algorithm in recognizing different modulation types. At higher SNR levels (Figure 14d,e), the diagonal of the confusion matrix becomes clearer, indicating the improved recognition accuracy of the algorithm across various modulation types with an increasing SNR. Nevertheless, there remains a certain difficulty in distinguishing between the AM-DSB (Amplitude Modulation–Double Sideband) and WBFM (Wideband Frequency Modulation) categories. This could be due to silent periods present during the generation of the dataset, blurring the differences in their signal features. At a 0 dB SNR, the confusion matrix shows more confusion and misclassifications. There is some degree of confusion between QAM16 and QAM64, as QAM16 is a subset of the QAM64 constellation diagram, making their signal sometimes features similar. Under less-than-ideal channel conditions, this similarity becomes more pronounced, making it harder for the model to accurately distinguish their modulation features. At lower SNR levels (Figure 14a,b), the confusion matrix may display significant confusion, leading to a notable decrease in accuracy, as the classifier struggles to find sufficient features in signals close to the noise level to differentiate between modulation types.
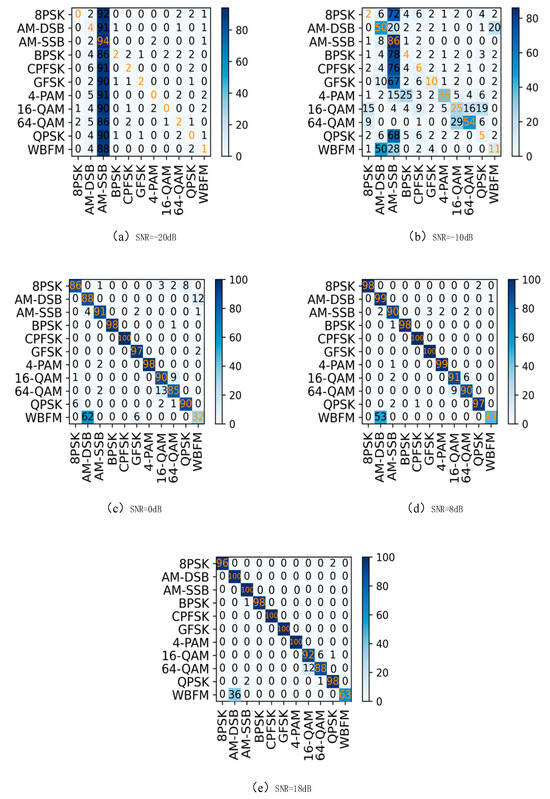
Figure 14.
Confusion matrix of CTRNet: (a) SNR = −20 dB; (b) SNR = −10 dB; (c) SNR = 0 dB; (d) SNR = 8 dB; (e) SNR = 18 dB.
In Table 1, the numerical results of various metrics are summarized to more rigorously evaluate the performance of different models [33,36,56].

Table 1.
Comparison of accuracy parameters (%) for different models.
The overall accuracy (OA) refers to the proportion of correctly classified samples by the classifier. A higher OA indicates a better overall classification capability of the model. This method achieves the highest recognition accuracy and predicts quality consistently under the same SNR.
The average accuracy (AA) is the average of the recognition accuracies for each modulation type. A higher AA indicates that the model performs well in classifying various modulation types, demonstrating the superior performance of the proposed method in terms of AA measurement. The AA can be calculated as shown in Equation (19):
where , with being the number of sample classes in the dataset, denotes true positives (predicted positive), denotes true negatives (predicted negative), denotes false positives (predicted positive), and denotes false negatives (predicted negative).
Precision refers to the proportion of samples classified as a certain class that actually belong to that class. Recall denotes the proportion of samples belonging to a certain class that are correctly classified as that class. The high precision and recall indicate good performance of the model in terms of accuracy and coverage. The precision and recall can be calculated as shown in Equations (20) and (21):
In terms of precision, both the LSTM model and the proposed model perform slightly better, achieving an accuracy of 0.72, whereas the other models (CNN, DenseNet, CLDNN, ResNet) have an accuracy of 0.70, slightly lower than the former two. Regarding recall, the proposed model is slightly higher than the other models, reaching 0.67, while the recall rates of other models range from 0.61 to 0.65. This suggests that the proposed model can better capture the distribution of the target class in the data.
The F1-score is a metric that comprehensively considers both precision and recall, calculated as their harmonic mean. It provides a single measurement standard when the precision and recall are imbalanced, as shown in Equation (22):
The proposed model achieved the highest F1-score at 0.68, demonstrating slightly superior performance compared to other models (LSTM has an F1-score of 0.66, while the other models have an F1-score of 0.65 or lower). This indicates that the proposed model is more accurate in correctly predicting positive cases.
In summary, the proposed model performs relatively well across the accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score metrics, though it performs similarly to the LSTM model in some aspects. The CNN model shows slight deficiencies in recall, while DenseNet, CLDNN, and ResNet exhibit comparable and stable overall performance.
To validate the superior computational speed of our proposed model, we compared it with several benchmark deep learning models. The experiments were conducted under the same hardware environment, and Table 2 records the time consumption of each model during both training and inference processes.

Table 2.
Comparison of training time and total number of parameters for various deep models.
The results indicate that our model significantly outperforms other benchmark models in training time. Specifically, the training time of the proposed model is 6 s, whereas other models require considerably longer training times. In comparison, our model is 72.7% faster than the CNN, 70% faster than DenseNet, 64.7% faster than CLDNN, and 25% faster than LSTM. Although our model has fewer parameters than the CNN, its computational efficiency is markedly improved, demonstrating excellent performance in terms of computational resources. This makes our model particularly suitable for deployment in resource-constrained environments.
These results highlight that despite having fewer parameters, our model achieves a significant reduction in training time, showcasing its advantages in computational speed. These features make our model highly valuable in practical applications, especially for tasks that require rapid training and inference.
Figure 15 illustrates the recognition accuracy of CTRNet across various modulation types and different SNR levels. These curves depict how CTRNet’s ability to recognize different modulation types varies with SNR conditions. Typically, the recognition accuracy should improve with increasing SNR, but there may be performance degradations or fluctuations within certain SNR ranges, which is due to increased noise making signal recognition challenging. This variability might also reflect the algorithm’s stability under varying signal strengths. Notably, under high-SNR conditions, WBFM and AM-DSB exhibit relatively low recognition accuracy and are prone to mutual confusion. This could stem from similar features in their generated data or specific challenges posed by noise conditions. The recognition accuracy of digital modulation types (such as QAM, PSK, etc.) improves with increasing SNR. This is because a higher SNR provides clearer signal features, making it easier for the algorithm to distinguish between different modulation types. Different modulation types may present varying levels of complexities and challenges in recognition. For instance, the distinction between QAM16 and QAM64 may decrease when the SNR decreases, because noise under lower-SNR conditions may cause confusion and the misclassification of constellation points.
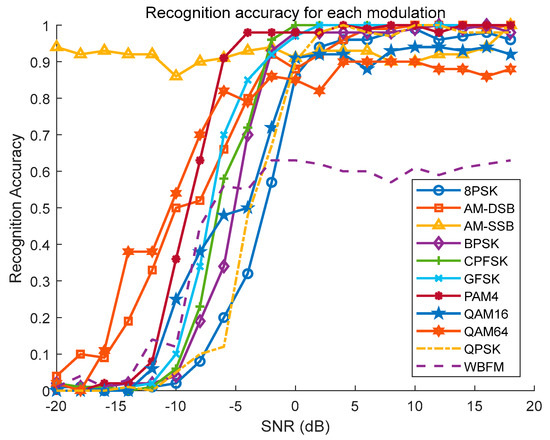
Figure 15.
Relationship between recognition accuracy of different modulation types and SNR.
4.5. Comparison Using Different Datasets
Here, we describe the comparison results of network performance using the same CTRNet standard model trained on different datasets (RML2016.10A and RML2016.10B datasets). Both datasets are commonly used for evaluating the performance of wireless signal modulation recognition systems. The distinction between RML2016.10A and RML2016.10B lies in the latter having 2000 signal samples per SNR, making it larger in scale. It is evident that the network trained on the RML2016.10B dataset outperforms the one trained on the RML2016.10A dataset. This suggests that for the Transformer architecture networks, a larger-scale dataset like RML2016.10B can provide better training outcomes and higher recognition accuracy. This is typically because more data enable the network to learn more extensive and complex features, thereby enhancing performance.
In Figure 16, the recognition accuracy values shown are based on the average of multiple modulated signals, rather than using only one modulated signal. Figure 16 also demonstrates the comparison of average recognition accuracy under different SNR conditions. For the Transformer-based network architecture, increasing the dataset size has a notably positive impact on performance. The RML2016.10B dataset offers richer and more diverse training samples compared to RML2016.10A, thus resulting in better recognition accuracy. Under high-SNR conditions, the performance of the two datasets may be relatively similar because of a clearer distinction between the signal and noise. In the case of a low SNR, some minor differences may be observed, particularly in recognition rates of complex modulation schemes, where the boundary between the signal and noise becomes blurred.
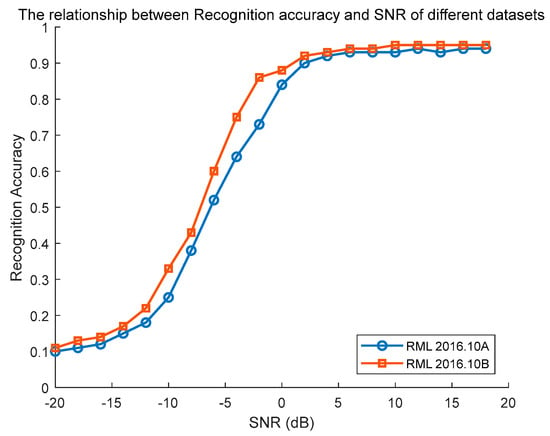
Figure 16.
Relationship between average recognition accuracy and SNR for different datasets.
4.6. Data Classification Visualization Analysis
Figure 17 presents t-SNE visualizations of fully connected layer features. It illustrates that in multipath fading channels, classification errors typically arise within different modulation orders of the same mode. Samples of the same category are closely clustered, indicating successful grouping by the model and thus good classification performance. Conversely, samples from distinct categories exhibit significant separation, further demonstrating effective classification. However, some overlap between different categories suggests occasional difficulty in distinguishing them. Notably, the method shows limitations in distinguishing WBFM, suggesting potential for optimization. Isolated points in the visualization might signify anomalies or noise, impacting classifier performance; addressing these outliers could enhance model effectiveness. In summary, closely clustered and well-separated categories indicate strong classification performance, while overlap or outliers may necessitate model refinement.
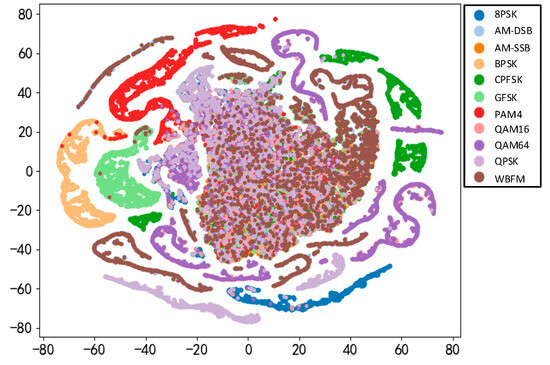
Figure 17.
Visualization of fully connected layer features.
5. Conclusions
This paper introduces a new efficient AMR method based on CTRNet, focusing on innovative preprocessing stages, improved embedding modules, and optimized feedforward neural networks to improve AMR performance. Specifically, the IQ signals undergo a preprocessing stage where they are transformed into signal sequences. The long IQ signal sequences are segmented into multiple equal-length short sequences, ensuring that each sequence is of equal length and contains complete signal information. The embedding module aims to transform input signals into multiple frames using a fixed-size and -step-length sliding-window operation. These frames consist of in-phase and quadrature components, which are horizontally concatenated to form input features. This frame-by-frame embedding method is simple, parameter-efficient, and performs well. The design of this module helps to enhance the model’s ability to capture features, thereby improving the recognition accuracy. The introduction of the Bilinear structure optimizes the feedforward neural network (FFN) of the Transformer. Compared to traditional Transformer structures, this design aims to enhance performance while reducing model size. Experimental studies investigate the impact of different parameter settings on the performance of the CTRNet model to determine the optimal configuration. This systematic parameter optimization effectively improves the model performance. The proposed model outperforms other deep learning models in terms of the recognition accuracy and runtime speed. This makes the new model particularly suitable for real-time communication applications.
However, when implementing automatic modulation recognition under neural network architectures, further control measures and multi-objective optimization are also crucial considerations. The dynamic adjustment of algorithm parameters allows real-time tuning based on network traffic, signal strength, and noise levels, thereby enhancing the recognition accuracy and stability. Additionally, incorporating online learning mechanisms enables the system to continuously adapt to new data. Moreover, fault detection and recovery mechanisms are important; timely adjustments or strategy switches can be made when a decline in recognition accuracy is detected. This will be the focus of our future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z., A.Y. and Y.S.; methodology—origin drawing, W.Z. and K.X.; software, W.Z. and K.X.; validation, W.Z. and K.X.; formal analysis, A.Y. and Y.S.; investigation, W.Z.; data curation, W.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, W.Z.; writing—review and editing, W.Z., K.X. and Y.S.; visualization, W.Z.; supervision, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
This dataset was downloaded from https://www.deepsig.ai/datasets, accessed on 2 November 2021.The name of the dataset is RadioML.2016.10A.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Peng, S.; Sun, S.; Yao, Y.-D. A survey of modulation classification using deep learning: Signal representation and data preprocessing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 7020–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.-C.; Chen, K.-C.; Li, G.Y.; Mahonen, P. Cognitive radio networking and communications: An overview. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 3386–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Qi, P.; Chen, S.; Yang, X. Fusion methods for CNN-based automatic modulation classification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 66496–66504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, O.; Abdi, A.; Bar-Ness, Y.; Su, W. Survey of automatic modulation classification techniques: Classical approaches and new trends. IET Commun. 2007, 1, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, F.; Dobre, O.A.; Popescu, D.C. On the likelihood-based approach to modulation classification. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 2009, 8, 5884–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugg, K.M.; Long, C.S.; Polydoros, A. Combined likelihood power estimation and multiple hypothesis modulation classification. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the Twenty-Ninth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 30 October–1 November 1995; Volume 2, pp. 1137–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Nandi, A.K.; Azzouz, E.E. Algorithms for automatic modulation recognition of communication signals. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1997, 46, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, E.; Nandi, A.K. Procedure for automatic recognition of analogue and digital modulations. IEE Proc. Commun. 1996, 143, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Mendel, J.M. Maximum-likelihood classification for digital amplitude-phase modulations. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2000, 48, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Yao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, P. Automatic modulation classification of overlapped sources using multiple cumulants. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 66, 6089–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Pei, Y.; Huang, Y.D.; Liang, Y.C. Modulation-constrained clustering approach to blind modulation classification for MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Polydoros, A. Digital modulation classification: The BPSK versus QPSK case. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 88, 21st Century Military Communications-What’s Possible? Conference Record. Military Communications Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–26 October 1988; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Polydoros, A.; Kim, K. On the detection and classification of quadrature digital modulations in broad-band noise. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1990, 38, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.D.; Ting, S.K.; Nandi, A.K. Na¨ıve Bayes classification of adaptive broadband wireless modulation schemes with higher order cumulants. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems, Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 15–17 December 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- DeSimio, M.P.; Prescott, G.E. Adaptive generation of decision functions for classification of digitally modulated signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1988 National Aerospace and Electronics Conference, Dayton, OH, USA, 23–27 May 1988; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 1010–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.-C.; Saquib, M.; Yun, Z. Novel automatic modulation classification using cumulant features for communications via multipath channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2008, 7, 3098–3105. [Google Scholar]
- Lopatka, J.; Pedzisz, M. Automatic modulation classification using statistical moments and a fuzzy classifier. In Proceedings of the WCC 2000-ICSP 2000. 2000 5th International Conference on Signal Processing Proceedings. 16th World Computer Congress 2000, Beijing, China, 21–25 August 2000; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 3, pp. 1500–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Swami, A.; Sadler, B.M. Hierarchical digital modulation classification using cumulants. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2000, 48, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.W.; Zhu, Z.; Nandi, A.K. Automatic modulation classification using combination of genetic programming and KNN. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 2742–2750. [Google Scholar]
- Dobre, O.A.; Bar-Ness, Y.; Su, W. Higher-order cyclic cumulants for high order modulation classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference, 2003. MILCOM 2003, Boston, MA, USA, 13–16 October 2003; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Orlic, V.D.; Dukic, M.L. Automatic modulation classification algorithm using higher-order cumulants under real-world channel conditions. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2009, 13, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsue, S.-Z.; Soliman, S.S. Automatic modulation recognition of digitally modulated signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference, ‘Bridging the Gap. Interoperability, Survivability, Security’, Boston, MA, USA, 15–18 October 1989; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 645–649. [Google Scholar]
- Fontes, A.I.; Pasa, L.A.; de Sousa, V.A., Jr.; Abinader, F.M., Jr.; Costa, J.A.; Silveira, L.F. Automatic modulation classification using information theoretic similarity measures. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 3–6 September 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Azzouz, E.E.; Nandi, A.K. Automatic identification of digital modulation types. Signal Process. 1995, 47, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Eldemerdash, Y.A.; Dobre, O.A.; Zhang, S.; Li, C. Modulation classification using received signal’s amplitude distribution for coherent receivers. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2017, 29, 1872–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Hu, S.; Yu, C.; Zhu, P.; Peng, X.; Ouyang, J. Deep learning in digital modulation recognition using high order cumulants. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 63760–63766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, S.; Li, Z. Automatic modulation classification based on deep residual networks with multimodal information. IEEE Trans. Cognit. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Corgan, J.; Clancy, T.C. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks, Aberdeen, UK, 2–5 September 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Roy, T.; Clancy, T.C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.J.; West, N. Radio machine learning dataset generation with gnu radio. In Proceedings of the GNU Radio Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 12–16 September 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, T. Toward convolutional neural networks on pulse repetition interval modulation recognition. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 2286–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Wei, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M. ACSE networks and autocorrelation features for PRI modulation recognition. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 1729–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-W.; Park, C.H. A unified method for deinterleaving and PRI modulation recognition of radar pulses based on deep neural networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 89360–89375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Meert, W.; Giustiniano, D.; Lenders, V.; Pollin, S. Deep learning models for wireless signal classification with distributed low-cost spectrum sensors. IEEE Trans. Cognit. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X. Automatic modulation classification using recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 13–16 December 2017; pp. 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.-M.; Philip, S.Y. Classification, denoising, and deinterleaving of pulse streams with recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 55, 1624–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Z. Attention-based radar PRI modulation recognition with recurrent neural networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 57426–57436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Liu, W. Radar emitter classification with attention-based multi-RNNs. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 2000–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J. Work modes recognition and boundary identification of MFR pulse sequences with a hierarchical seq2seq LSTM. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2020, 14, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Luo, C.; Parr, G.; Luo, Y. A spatiotemporal multi-channel learning framework for automatic modulation recognition. IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 1629–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z. Deep learning-based modulation recognition with multi-cue fusion. IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 1757–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Wang, C.; Gan, C.; Xiang, Y. Automatic modulation classification using CNN-LSTM based dual-stream structure. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 13521–13531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunhao, S.; Hua, X.; Lei, J.; Zisen, Q. ConvLSTMAE: A spatiotemporal parallel autoencoders for automatic modulation classification. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, N.E.; O’Shea, T. Deep architectures for modulation recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN), Baltimore, MD, USA, 6–9 March 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, K.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Y. Sequential Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks for Fast Automatic Modulation Classification. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 27182–27188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Qu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Liang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X. Self-attention bi-lstm networks for radar signal modulation recognition. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 5160–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Recurrent models of visual attention. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2014, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–11 December 2014; NeurIPS: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; NeurIPS: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Automatic modulation classification based on improved R-transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), Harbin City, China, 28 June–1 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi-Rad, S.; Jain, S. MCformer: A transformer based deep neural network for automatic modulation classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Madrid, Spain, 7–11 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.; Keskar, N.S.; Socher, R. Weighted transformer network for machine translation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.02132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yao, L.; Chen, L.; Lin, B.; Cai, D.; He, X.; Liu, W. CrossFormer: A versatile vision transformer hinging on cross-scale attention. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.00154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jiao, L.; Li, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Yang, S. Evolutionary dual-stream transformer. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2015, 25, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Gan, F.; Cao, X.; Liu, W. Signal modulation classification based on the transformer network. IEEE Trans. Cognit. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, B.; Liu, C.; Xiong, W.; Li, S. Abandon locality:Frame-wise embedding aided transformer for automatic modulation recognition. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Fan, X.; Liu, H. Robust and efficient modulation recognition with pyramid signal transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 1868–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X.; Jiang, Z.J.; Huang, Q.S.; Cao, W.C.; Li, J.L. Lightweight Speaker Verification Using Transformation Module with Feature Partition and Fusion. IEEE-ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Ning, C.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Sangmanee, C.; Cui, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, W. An Automatic Internal Wave Recognition Algorithm Based on CNN Applicable to an Ocean Data Buoy System. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).