Integrating Depth-Based and Deep Learning Techniques for Real-Time Video Matting without Green Screens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Virtual Production
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Video Matting
2.3. Depth-Based Video Matting
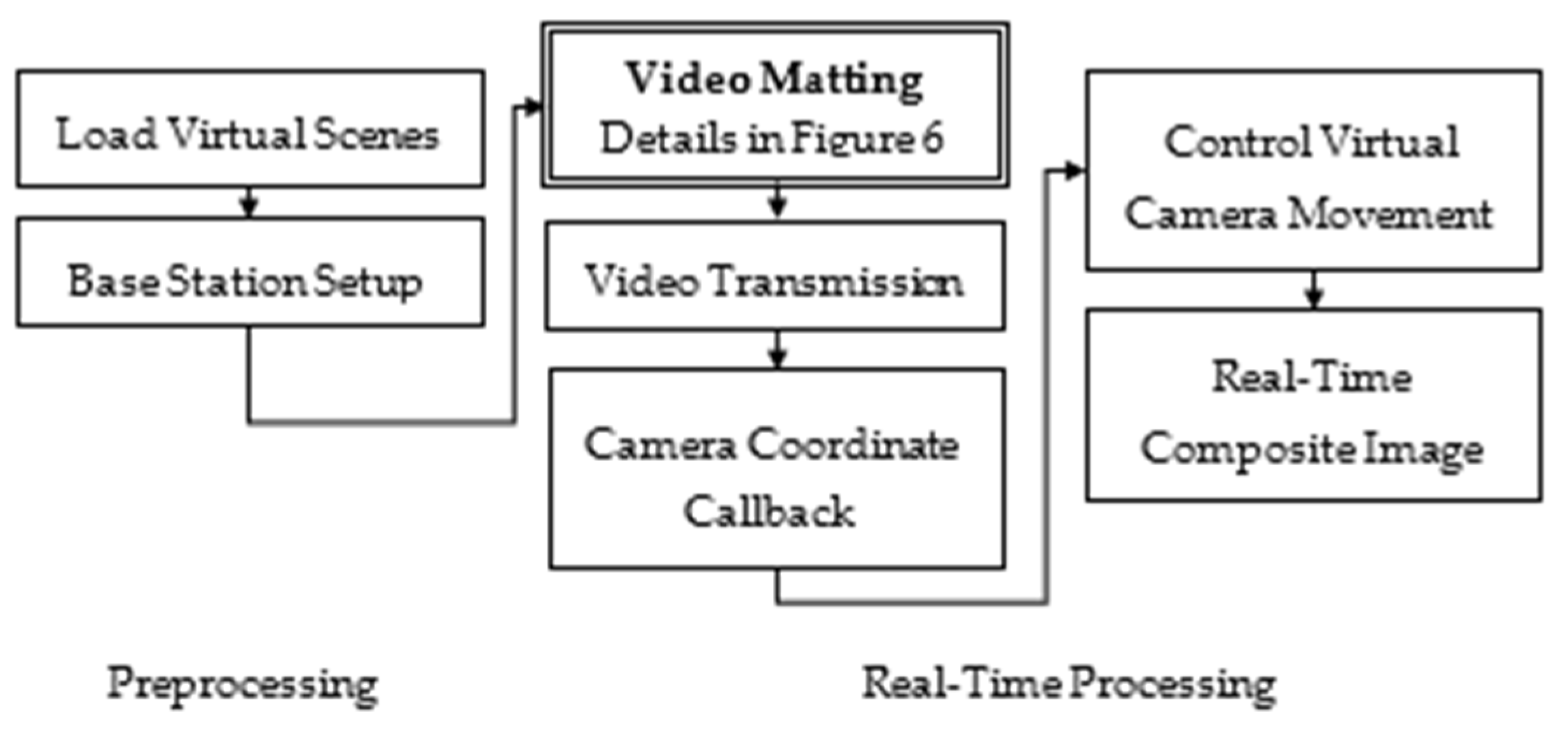
3. Methods
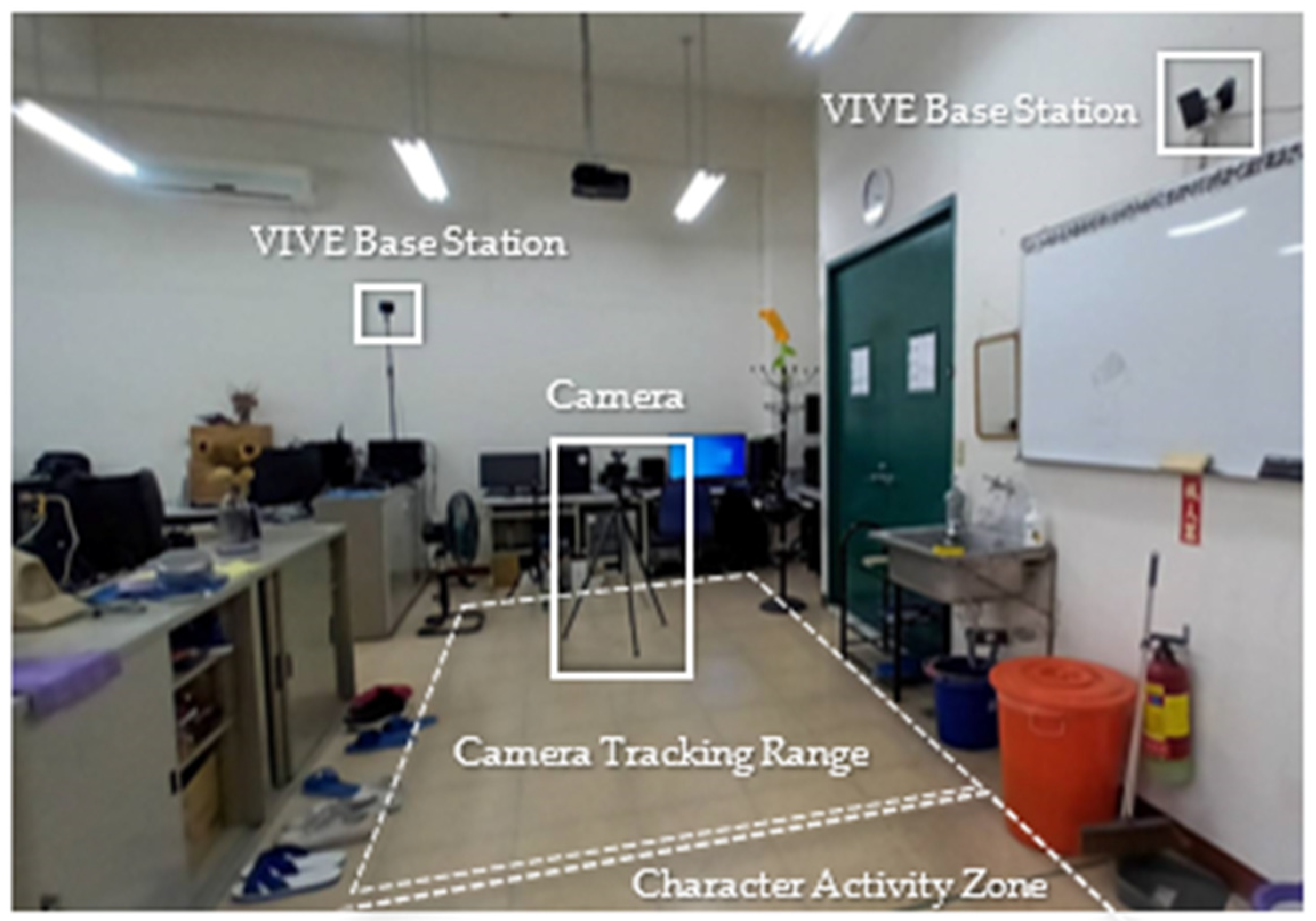
3.1. Preprocessing and Setup
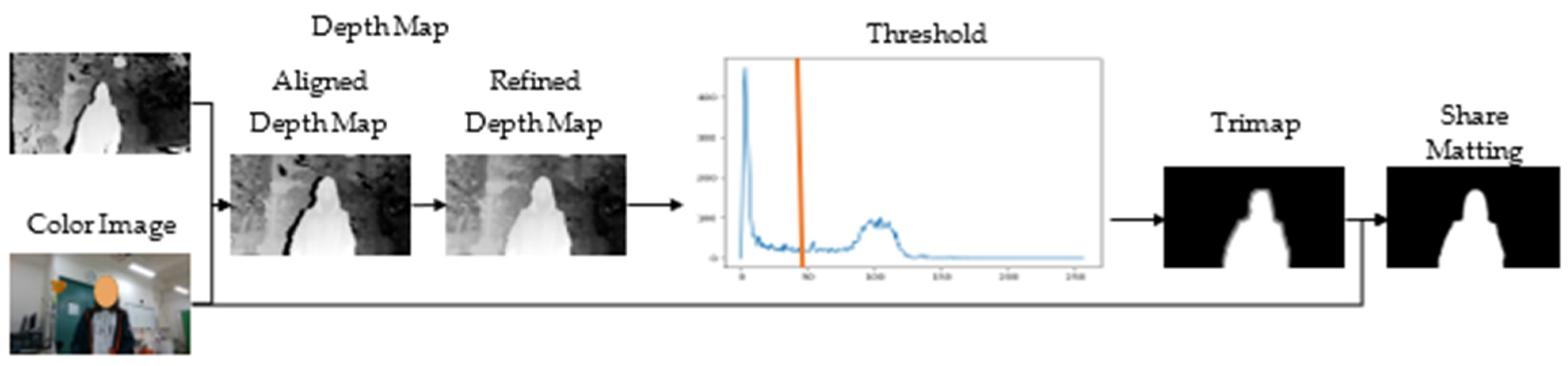
3.2. Principle of Video Matting
- represents the composite image color of pixel i;
- represents the alpha value (opacity) of pixel i, ranging from 0 (fully transparent) to 1 (fully opaque);
- represents the foreground color of pixel i;
- represents the background color of pixel i.
3.3. Deep Learning-Based Video Matting Module
3.4. Depth-Based Video Matting Module
3.5. Boundary-Selective Fusion (BSF)
- Boundary Intersection: Morphological erosion and dilation are applied and then subtracted to obtain a distinct boundary region of the alpha matte predicted by each individual matting module. The intersection of these two boundaries is considered the final boundary region;
- Maximum Union: Since the depth-based matting typically has higher spatial integrity but less accurate edges, the maximum values of the alpha mattes predicted by both methods are combined through a pixel-wise Max operation to create a union matte;
- Edge Correction: The boundary regions of the depth-based alpha matte are prone to noise and may be less reliable. Therefore, these boundary regions are replaced with the corresponding regions from the deep learning-based alpha matte, resulting in a more accurate combined alpha matte;
- Largest Connected Component Selection: Perform connected component analysis and retain only the largest connected component in the foreground. All other connected components are discarded to minimize background noise in the final alpha matte.
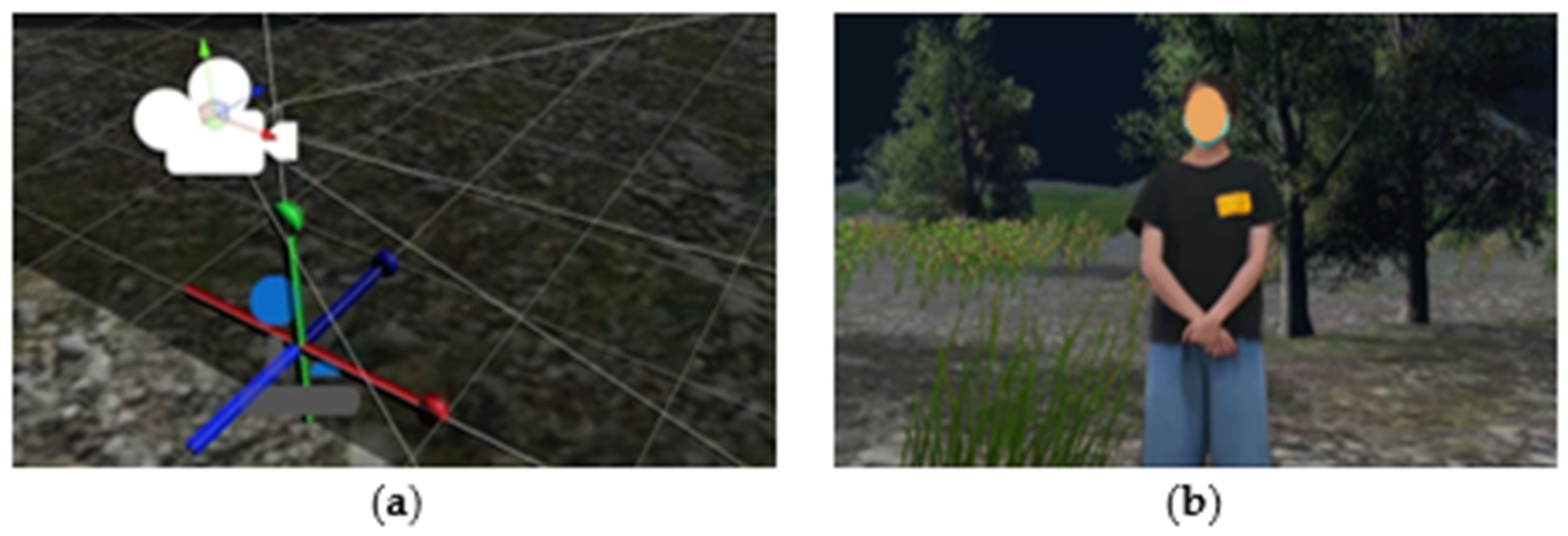
3.6. Video Transmission, Compositing, and Camera Tracking
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Speed Evaluation
4.2. Accuracy Evaluation
4.2.1. Accuracy Experiment of Human Alone
4.2.2. Accuracy Experiment of Human Holding an Object
4.3. Robustness Evaluation
4.3.1. Static and Dynamic Background Video
4.3.2. Human Holding Objects Video
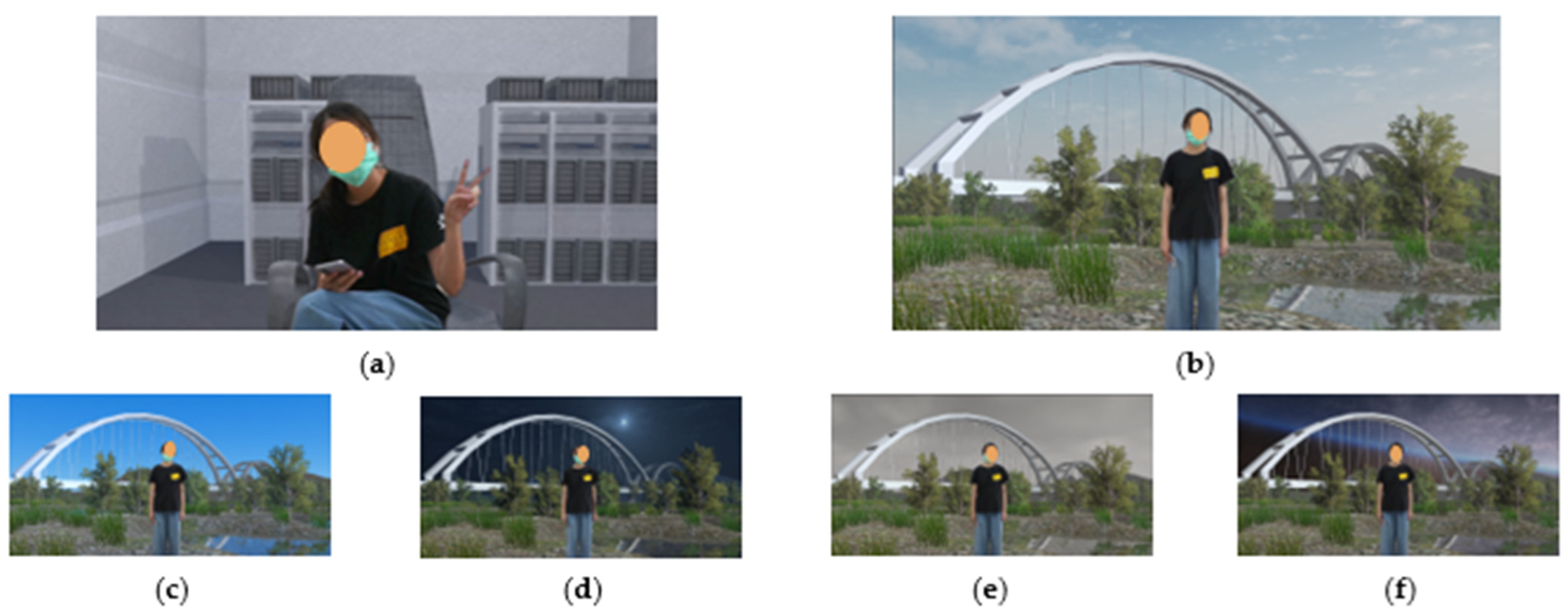
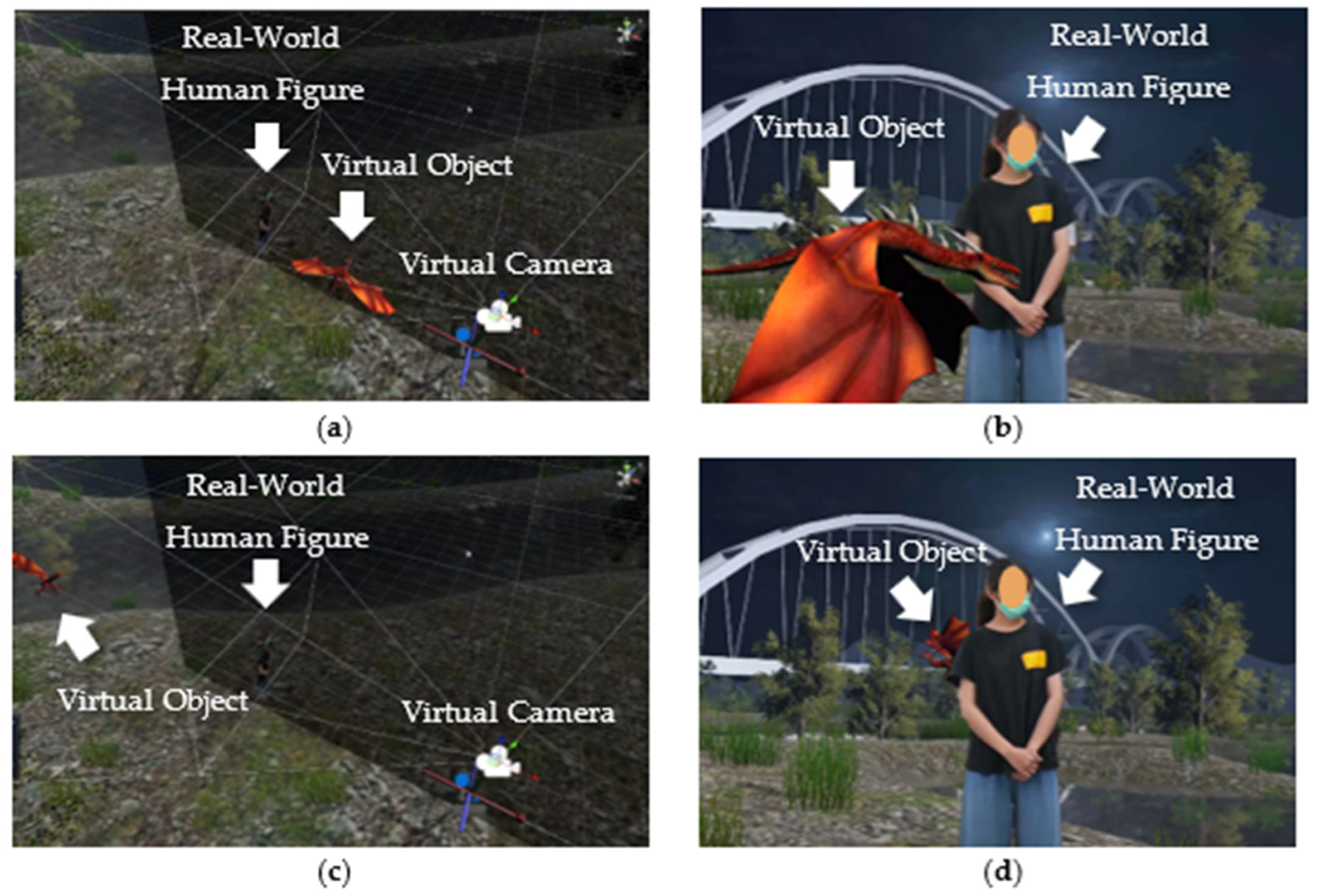
4.4. Tracking and Compositing in the Virtual Production System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swords, J.; Willment, N. The emergence of virtual production—A research agenda. Converg. Int. J. Res. New Media Technol. 2024; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gaspari, T.; Sementille, A.C.; Vielmas, D.Z.; Aguilar, I.A.; Marar, J.F. ARSTUDIO: A Virtual Studio System with Augmented Reality Features. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM SIGGRAPH International Conference on Virtual-Reality Continuum and Its Applications in Industry, Shenzhen, China, 30 November 2014; pp. 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- de Goussencourt, T.; Bertolino, P. Using the Unity® Game Engine as a Platform for Advanced Real Time Cinema Image Processing. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 4146–4149. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani, A.; Shinohara, T.; Miyaki, K. Live 6DoF Video Production with Stereo Camera. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH Asia 2019 XR, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 17 November 2019; pp. 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, I.A.; Sementille, A.C.; Sanches, S.R.R. ARStudio: A Low-Cost Virtual Studio Based on Augmented Reality for Video Production. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 33899–33920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.-C. Augmented Reality Virtual Production System. Master’s Thesis, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, 2022. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11296/gjzp5r (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Z.; Yi, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Lin, C. Rain-free and residue hand-in-hand: A progressive coupled network for real-time image deraining. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7404–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Z.; Yi, P.; Chen, C.; Han, Z.; Lu, T.; Huang, B.; Jiang, J. Decomposition makes better rain removal: An improved attention-guided deraining network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 3981–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Jiang, K.; He, J.; Lin, C.; Zhang, L. TTST: A top-k token selective transformer for remote sensing image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Z.; Yi, P.; Lu, T.; Jiang, J.; Xiong, Z. Dual-path deep fusion network for face image hallucination. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, M.; Pitié, F. F, B, Alpha Matting. [Online]. 2020. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2003.07711 (accessed on 19 February 2024).
- Lin, S.; Ryabtsev, A.; Sengupta, S.; Curless, B.; Seitz, S.; Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I. Real-Time High-Resolution Background Matting. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, K.; Yan, Q.; Lau, R.W.H. MODNet: Real-Time Trimap-Free Portrait Matting via Objective Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22 February–1 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Yang, L.; Saleemi, I.; Sengupta, S. Robust High-Resolution Video Matting with Temporal Guidance. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Goel, V.; Ohanyan, M.; Navasardyan, S.; Wei, Y.; Shi, H. VMFormer: End-to-End Video Matting with Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ohanyan, M.; Goel, V.; Navasardyan, S.; Wei, Y.; Shi, H. VideoMatt: A Simple Baseline for Accessible Real-Time Video Matting. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–22 June 2023; pp. 2177–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Zhang, M.; Lei, J.; Fu, H.; Shen, H.; Huang, Q. RGB-D Human Matting: A Real-World Benchmark Dataset and a Baseline Method. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 4041–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, C.; Oh, S.; Shrivastava, A.; Lee, J. MaGGIe: Mask guided gradual human instance matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.; Huang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xue, J. Real-time multi-person video synthesis with controllable prior-guided matting. Sensors 2024, 24, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.; Lo, W.; et al. Segment anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Virtual Event, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jain, J.; Shi, H. Matting anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Tan, B. Deep learning methods in image matting: A survey. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, S. Image Matting with Color and Depth Information. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR2012), Tsukuba, Japan, 11–15 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Wang, G.; Zhang, C. Iterative Transductive Learning for Automatic Image Segmentation and Matting with RGB-D Data. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2014, 25, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Liu, J. A Hierarchical Level Set Approach to for RGBD Image Matting. In MultiMedia Modeling; Kompatsiaris, I., Huet, B., Mezaris, V., Gurrin, C., Cheng, W.-H., Vrochidis, S., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11295, pp. 628–639. ISBN 978-3-030-05709-1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zeng, W.; Yang, B. RGBD Image Matting Using Depth Assisted Active Contours. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Audio, Language and Image Processing (ICALIP), Shanghai, China, 16–17 July 2018; pp. 385–392. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Fu, C.; Cai, J.; Cham, T. Real-Time and Temporal-Coherent Foreground Extraction with Commodity RGBD Camera. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, G.; Li, B.; Lin, W.; Cheng, Y. DART: Depth-enhanced accurate and real-time background matting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.15820. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, B. ViTMatte: Boosting image matting with pretrained plain vision transformers. Inf. Fusion 2024, 103, 102091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free Sci-Fi Office Pack|3D Sci-Fi|Unity Asset Store. Available online: https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/3d/environments/sci-fi/free-sci-fi-office-pack-195067 (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Gastal, E.S.L.; Oliveira, M.M. Shared Sampling for Real-Time Alpha Matting. Comput. Graph. Forum 2010, 29, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasbey, C.A. An Analysis of Histogram-Based Thresholding Algorithms. CVGIP Graph. Models Image Process. 1993, 55, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NDI—Removing the Limits of Video Connectivity. Available online: https://ndi.video/ (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Rhemann, C.; Rother, C.; Wang, J.; Gelautz, M.; Kohli, P.; Rott, P. A Perceptually Motivated Online Benchmark for Image Matting. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Erofeev, M.; Gitman, Y.; Vatolin, D.; Fedorov, A.; Wang, J. Perceptually Motivated Benchmark for Video Matting. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2015, Swansea, UK, 7–10 September 2015; British Machine Vision Association: Swansea, UK, 2015; pp. 99.1–99.12. [Google Scholar]








| Method | Input | Network | Dataset | Target | Automatic | Real-Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBA [11] | RGB + Trimap | One-stage CNN | Composition-1K | Anything | No | No |
| BMv2 [12] | RGB + BG | One-stage CNN + Refine | VideoMatte240K and PhotoMatte13K/85 | Human | No | Yes |
| MODNet [13] | RGB | Parallel two-stream CNN | SPD and PPM-100 | Human | Yes | Yes |
| RVM [14] | RGB | RNN | VideoMatte240K, ImageMatte, DVM, YouTubeVIS 2021, COCO and SPD | Human | Yes | Yes |
| VMFormer [15] | RGB | Transformer | ImageMatte, VideoMatte240K, BG20K and DVM | Human | Yes | Yes |
| VideoMatt [16] | RGB | CNN + Attention Mechanism | VideoMatte240, BG20K and DVM | Human | Yes | Yes |
| RGB-D Human Matting [17] | RGB-D | CNN | HDM-2K | Human | Yes | Yes |
| MaGGIe [18] | RGB | Transformer attention | Synthesized training data from several existing sources | Human | Yes | Yes |
| ControlMatting [19] | RGB | FasterNet | Adobe Image Matting, VideoMatte240K | Human | Yes | Yes |
| MAM [22] | RGB | SAM [20] + Vision Transformer [21] | Adobe Image Matting, Distinctions-646, AM2K, Human-2K, RefMatte | Anything | Yes | Yes |
| Method | Depth Source | Depth Processing | Trimap Processing | Matting Method | Automatic | Real-Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lu et al. [24] | Kinect | Region growing and bilateral filter | Variational level set based method | Bayesian matting | No | No |
| He et al. [25] | Kinect | Iteratively perform depth refinement and bi-layer classification | Iteratively perform depth refinement and bi-layer classification | Iterative transductive learning | Yes | Yes |
| Zheng et al. [26] | NJU2000 database | Directional joint bilateral filter | Hierarchical level set framework | Bayesian matting | Yes | No |
| Zhao et al. [28] | Kinect and PrimeSense 3D sensor | Shadow detection and adaptive temporal hole-filling | Adaptive background mixture with shadow detection | Closed-form temporal matting | Yes | Yes |
| DART [29] | JXNU-RGBD dataset | Bayesian manner | Bayesian inference | ViTMatte [30] | Yes | Yes |
| Ours | Intel RealSense D435i | Spatial and temporal hole-filling | Minimum method | Share matting Proposed BSF | Yes | Yes |
| Resolutions | Learning- Based (GPU+ Down-Sample 1) | Learning- Based (CPU+ Down-Sample 1) | Learning-Based (CPU) 2 | Depth-Based (CPU) | Proposed BSF 1,3 | ViT-Base 91M Parameters | MAM [22] ViT-Large 308M Parameters | ViT-Huge 636M Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 640 × 480 | 113.392 | 13.978 | 12.543 | 15.812 | 13.574 | 5.138 | 2.623 | 1.628 |
| 1280 × 720 | 102.944 | 13.502 | 4.567 | 8.185 | 5.158 | |||
| 1920 × 1080 | 82.503 | 14.704 | 1.839 | 4.221 | 2.924 |
| Error | Simple Background | Complex Background | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning-Based [14] | Depth- Based | Proposed BSF | MAM [22] | Learning-Based [14] | Depth- Based | Proposed BSF | MAM [22] | |
| MAD | 3.535 | 5.767 | 4.972 | 4.299 | 8.465 | 6.428 | 3.927 | 20.384 |
| MSE | 1.051 | 1.26 | 1.151 | 1.049 | 4.826 | 4.019 | 2.214 | 12.355 |
| Gradient | 3.466 | 3.839 | 3.697 | 3.586 | 17.15 | 16.887 | 16.467 | 15.487 |
| Conn | 3.807 | 4.419 | 3.872 | 3.778 | 35.977 | 27.99 | 16.726 | 84.188 |
| Error | Learning-Based [14] | Depth-Based | Proposed BSF | MAM [22] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAD | 4.242 | 5.164 | 4.085 | 2.364 |
| MSE | 1.937 | 2.273 | 1.768 | 0.673 |
| Gradient | 10.447 | 13.441 | 12.220 | 9.156 |
| Conn | 13.327 | 14.704 | 11.235 | 5.183 |
| Error | Learning-Based [14] | Depth-Based | Proposed BSF | MAM [22] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAD | 14.770 | 10.924 | 6.229 | 26.944 |
| MSE | 11.433 | 8.087 | 4.222 | 15.299 |
| Gradient | 11.018 | 16.095 | 11.314 | 10.463 |
| Conn | 46.647 | 34.625 | 19.163 | 75.684 |
| Original Image | Learning-Based Alpha Matte [9] | Depth-Based Alpha Matte | BSF Alpha Matte | MAM [31] Alpha Matte | Ground Truth Alpha Matte |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| MAD Error | 25.5330 | 10.8968 | 6.4486 | 5.2741 | |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| MAD Error | 22.1378 | 29.4624 | 3.2251 | 7.3851 | |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| MAD Error | 12.4419 | 8.1649 | 7.1510 | 42.5277 | |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
| MAD Error | 4.2003 | 4.1350 | 3.3013 | 33.9496 |
| Error | Static Background | Dynamic Background | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning-Based [14] | Depth- Based | Proposed BSF | MAM [22] | Learning-Based [14] | Depth- Based | Proposed BSF | MAM [22] | |
| MAD | 1.543 | 1.749 | 1.705 | 4.135 | 5.043 | 3.288 | 5.044 | 7.020 |
| dtSSD | 4.623 | 5.666 | 4.608 | 4.648 | 12.411 | 10.261 | 12.400 | 14.274 |
| Error | Learning-Based [14] | Depth-Based | Proposed BSF | MAM [22] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAD | 21.911 | 5.416 | 4.502 | 10.732 |
| dtSSD | 63.020 | 49.370 | 40.345 | 47.980 |
| Realistic Camera Movement | Move Forward | Move Backward | Move Right | Move Left | Pan Right | Pan Left |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual Camera (Unity coordinates) | 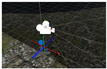 | 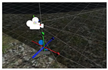 |  |  |  |  |
| Composite Image |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Realistic Camera Movement | Tilt Up | Tilt Down | Roll Right | Roll Left |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual Camera (Unity coordinates) |  |  |  |  |
| Composite Image |  |  |  |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, P.-C.; Yang, M.-T. Integrating Depth-Based and Deep Learning Techniques for Real-Time Video Matting without Green Screens. Electronics 2024, 13, 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163182
Su P-C, Yang M-T. Integrating Depth-Based and Deep Learning Techniques for Real-Time Video Matting without Green Screens. Electronics. 2024; 13(16):3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163182
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Pin-Chen, and Mau-Tsuen Yang. 2024. "Integrating Depth-Based and Deep Learning Techniques for Real-Time Video Matting without Green Screens" Electronics 13, no. 16: 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163182
APA StyleSu, P.-C., & Yang, M.-T. (2024). Integrating Depth-Based and Deep Learning Techniques for Real-Time Video Matting without Green Screens. Electronics, 13(16), 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163182






