Deep-Autoencoder-Based Radar Source Recognition: Addressing Large-Scale Imbalanced Data and Edge Computing Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Radar Radiation Identification Models
2.2. Neural Network on Edge Devices
3. Empirical Feature Selection
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Feature Encoding Design
3.3. Normalization for Continuous Feature Values
4. RIR-DA Model
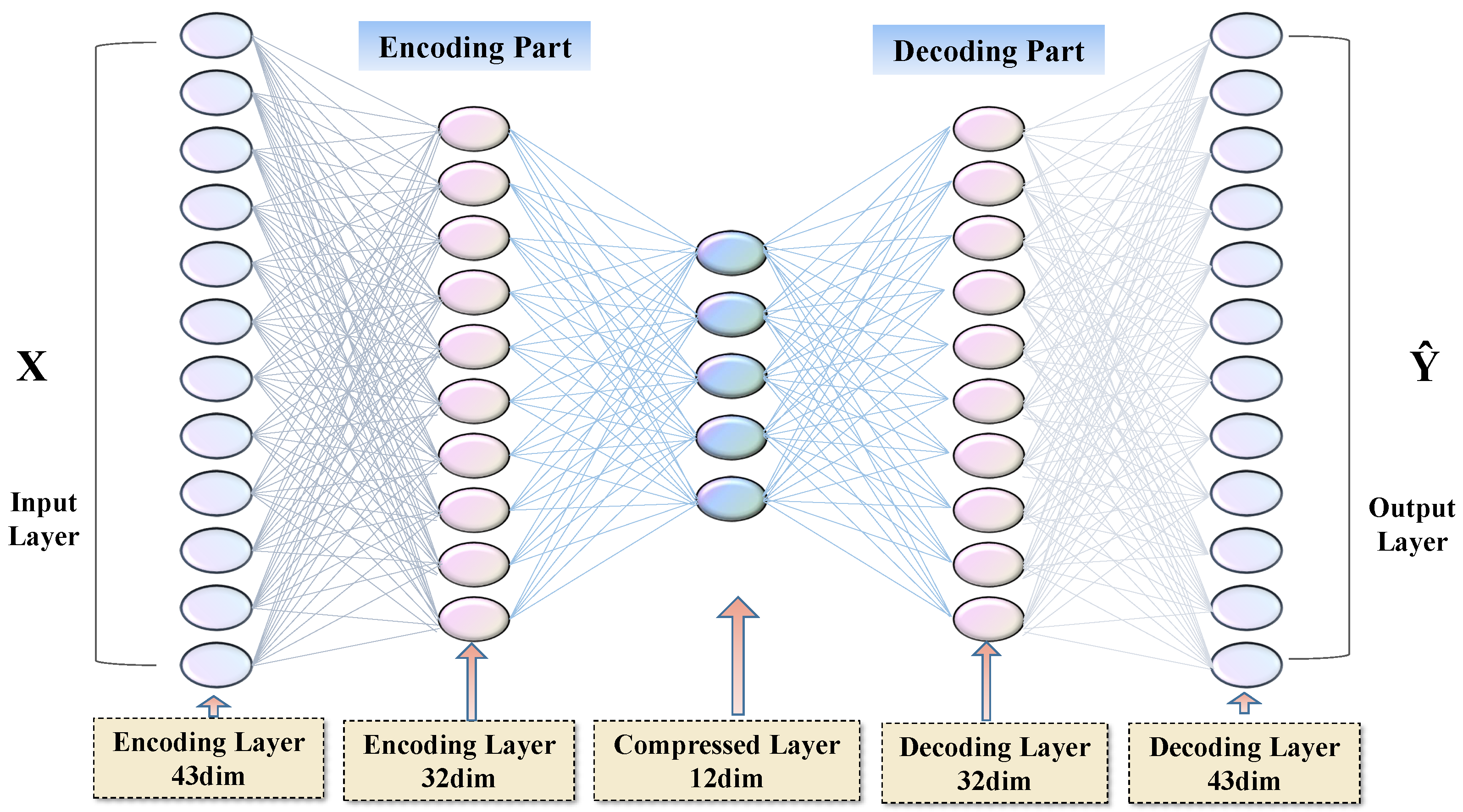
4.1. Deep Autoencoder Model
4.2. RIR-DA Model Architecture
4.3. Model Loss Function Optimization
5. Model Hardware Acceleration Solution
5.1. NXP T4240 Microprocessor
5.2. Hardware Adaptation of RIR-DA Model Architecture
5.3. Evaluation of Hardware Acceleration Performance
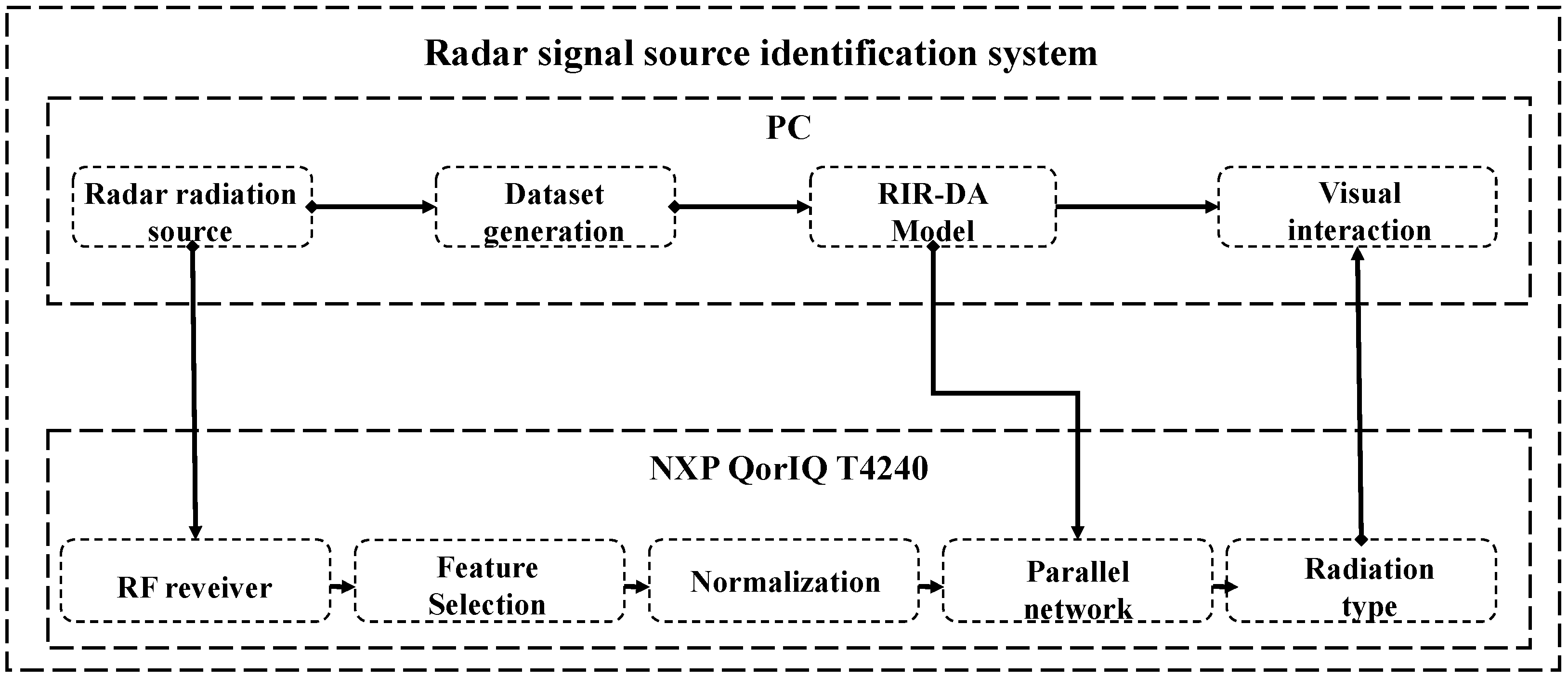
5.4. Intelligent Identification System
6. Experimental Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butt, F.A.; Jalil, M. An overview of electronic warfare in radar systems. In Proceedings of the 2013 The International Conference on Technological Advances in Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (TAEECE), Konya, Turkey, 9–11 May 2013; pp. 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Gu, L.; Zhu, L. Identification and parameter estimation algorithm of radar signal subtle features. Phys. Commun. 2020, 42, 101140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedare, T.; Shah, V.K.; Jakubisin, D.J.; Reed, J.H. Interference suppression using deep learning: Current approaches and open challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 66238–66266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debauche, O.; Mahmoudi, S.; Mahmoudi, S.A.; Manneback, P.; Bindelle, J.; Lebeau, F. Edge computing and artificial intelligence for real-time poultry monitoring. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 175, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binetti, M.S.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. The use of weather radar data: Possibilities, challenges and advanced applications. Earth 2022, 3, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shen, W. Radar target characterization and deep learning in radar automatic target recognition: A review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, D.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lou, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D. Radar emitter signal recognition based on MSST and HOG feature extraction. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2022, 49, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P. Research on radar signal recognition based on automatic machine learning. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, D. Deep-learning for radar: A survey. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 141800–141818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, H. Modulation recognition of radar signals based on adaptive singular value reconstruction and deep residual learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Liu, A.; Yu, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhu, H. Radar HRRP target recognition model based on a stacked CNN–Bi-RNN with attention mechanism. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Bai, X. End-to-end radar HRRP target recognition based on integrated denoising and recognition network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Tian, L.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, H. Region-factorized recurrent attentional network with deep clustering for radar HRRP target recognition. Signal Process. 2021, 183, 108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Electronic radar signal recognition based on wavelet transform and convolution neural network. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 3559–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, Y.H. Radar target classification considering unknown classes using deep convolutional neural network ensemble. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2021, 15, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, C.; Jin, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, D. Detection of sea-surface target of coastal defense radar based on Stacked Autoencoder (SAE) algorithm. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2022, 16, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. A Prior-Knowledge-Guided Neural Network Based on Supervised Contrastive Learning for Radar HRRP Recognition. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 2854–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X. Generative adversarial networks with Gramian angular field for handling imbalanced data in specific emitter identification. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 2929–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W. SMOTE-based Category Imbalance for Radar Radiation Source Sorting and Identification. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Information Technology, Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (ICIBA), Chongqing, China, 6–8 November 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X. Edge AI: On-demand accelerating deep neural network inference via edge computing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 19, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.H.; Pasha, M.A.; Masud, S. Advancements in microprocessor architecture for ubiquitous AI—An overview on history, evolution, and upcoming challenges in AI implementation. Micromachines 2021, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwack, J.; Tramm, J.; Bertoni, C.; Ghadar, Y.; Homerding, B.; Rangel, E.; Knight, C.; Parker, S. Evaluation of performance portability of applications and mini-apps across amd, intel and nvidia gpus. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Workshop on Performance, Portability and Productivity in HPC (P3HPC), St. Louis, MO, USA, 14 November 2021; pp. 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrolaza, J.P.; Obermaisser, R.; Abella, J.; Cazorla, F.J.; Grüttner, K.; Agirre, I.; Ahmadian, H.; Allende, I. Multi-core devices for safety-critical systems: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2020, 53, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Li, P.; Gao, Y.; Si, J.; Al-Dhahir, N. Efficient FPGA Implementation of Convolutional Neural Networks and Long Short-Term Memory for Radar Emitter Signal Recognition. Sensors 2024, 24, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.; Jung, Y.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y. FPGA implementation of an efficient FFT processor for FMCW radar signal processing. Sensors 2021, 21, 6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tang, C.; Vishwakarma, S.; Woodbridge, K.; Chetty, K. Design of high-speed software defined radar with GPU accelerator. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2022, 16, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifai, S.; Vincent, P.; Muller, X.; Glorot, X.; Bengio, Y. Contractive auto-encoders: Explicit invariance during feature extraction. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Bellevue, WA, USA, 28 June–2 July 2011; pp. 833–840. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, A.; Mohri, M.; Zhong, Y. Cross-entropy loss functions: Theoretical analysis and applications. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 23803–23828. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
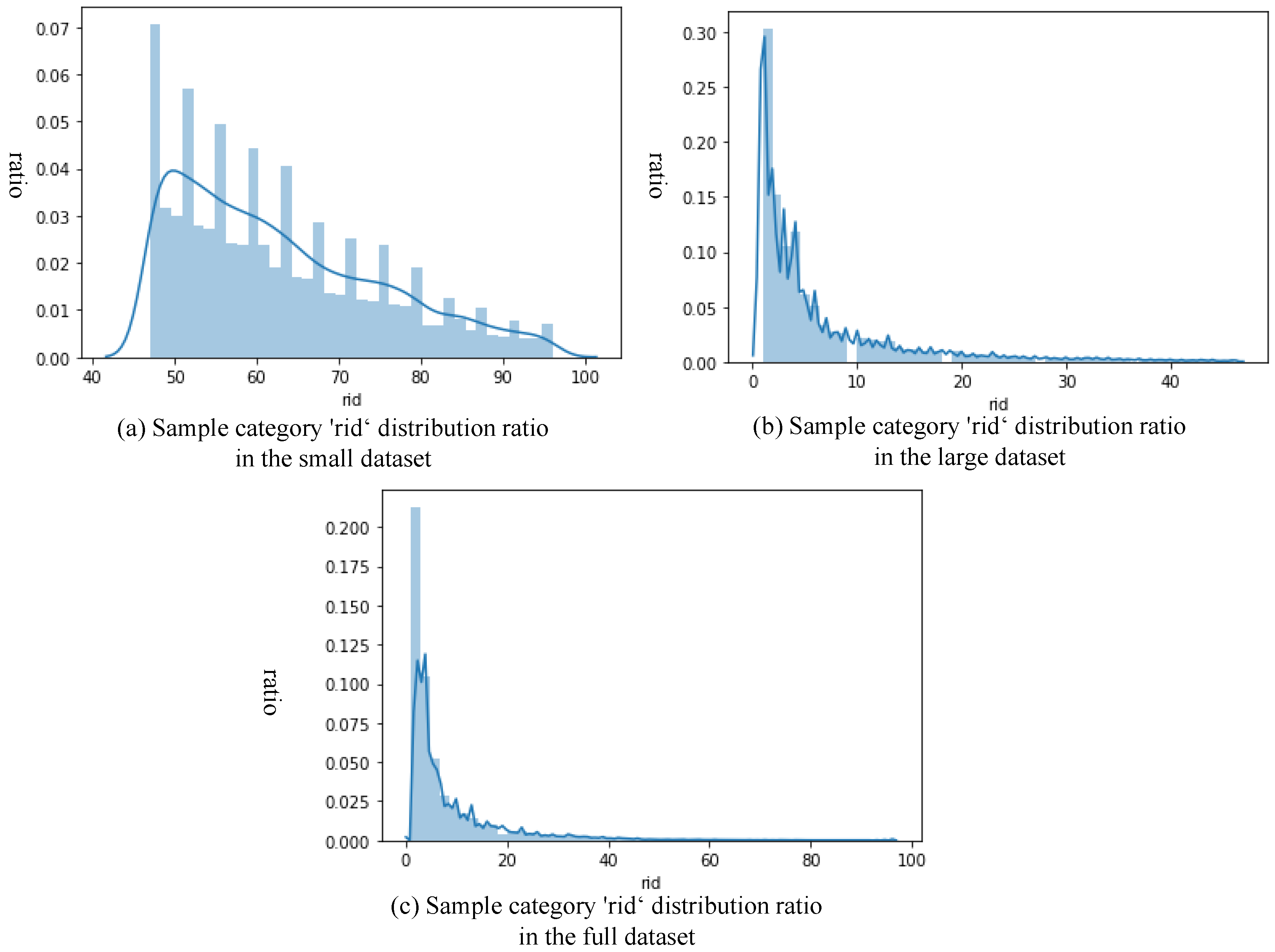



| Test Set Type | Sample Count | Time | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Sample Dataset | 249,367 | 5.29 s | 95.6% |
| Large Sample Dataset | 246,010 | 5.07 s | 96.0% |
| Small Sample Dataset | 3358 | 0.09 s | 83.9% |
| Model | Accuracy (Full Sample) | Radar Signal Number | Dataset Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | ≥90% | 11 | |
| Adaboost | ≥93% | 20 | |
| NN | ≥91% | 20 | |
| U-CNN | ≥95% | 67 | |
| RIR-DA | ≥95% | 96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Fang, J. Deep-Autoencoder-Based Radar Source Recognition: Addressing Large-Scale Imbalanced Data and Edge Computing Constraints. Electronics 2024, 13, 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13152891
Liu Y, Li X, Fang J. Deep-Autoencoder-Based Radar Source Recognition: Addressing Large-Scale Imbalanced Data and Edge Computing Constraints. Electronics. 2024; 13(15):2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13152891
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuehua, Xiaoyu Li, and Jifei Fang. 2024. "Deep-Autoencoder-Based Radar Source Recognition: Addressing Large-Scale Imbalanced Data and Edge Computing Constraints" Electronics 13, no. 15: 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13152891
APA StyleLiu, Y., Li, X., & Fang, J. (2024). Deep-Autoencoder-Based Radar Source Recognition: Addressing Large-Scale Imbalanced Data and Edge Computing Constraints. Electronics, 13(15), 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13152891






