LA-Net: An End-to-End Category-Level Object Attitude Estimation Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and an Attention Mechanism
Abstract
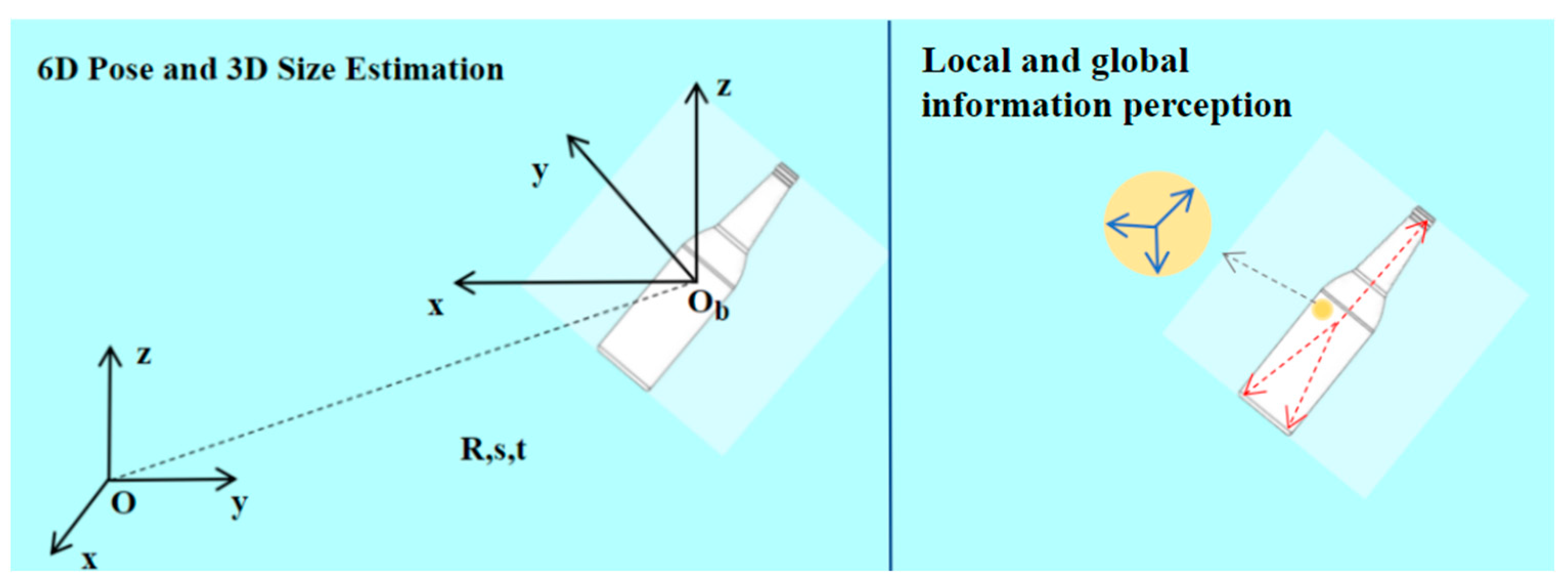
1. Introduction
- We have extended the network architecture of the 3DGCN and proposed a new framework called LA-Net. Building upon the structure of the 3DGCN, LA-Net integrates an additional parallel linear branch designed to extract and fuse features from different hierarchical levels within the network. This enhancement significantly boosts the network’s expressive power, improving its capability to recognize complex patterns.
- We introduce the PSA (Pyramid Split Attention) attention mechanism and the Max-Pooling layer, which can perceive the local and global geometric information of the point cloud. It is especially advantageous in dealing with objects with complex shapes while also being robust against noise.
- Our experimental results show that LA-Net can effectively improve object pose accuracy. Compared with the baseline method (HS-Pose), LA-Net can more effectively ascertain object poses from objects with complex shapes.
2. Related Works
3. Methods
3.1. Background of 3DGCN
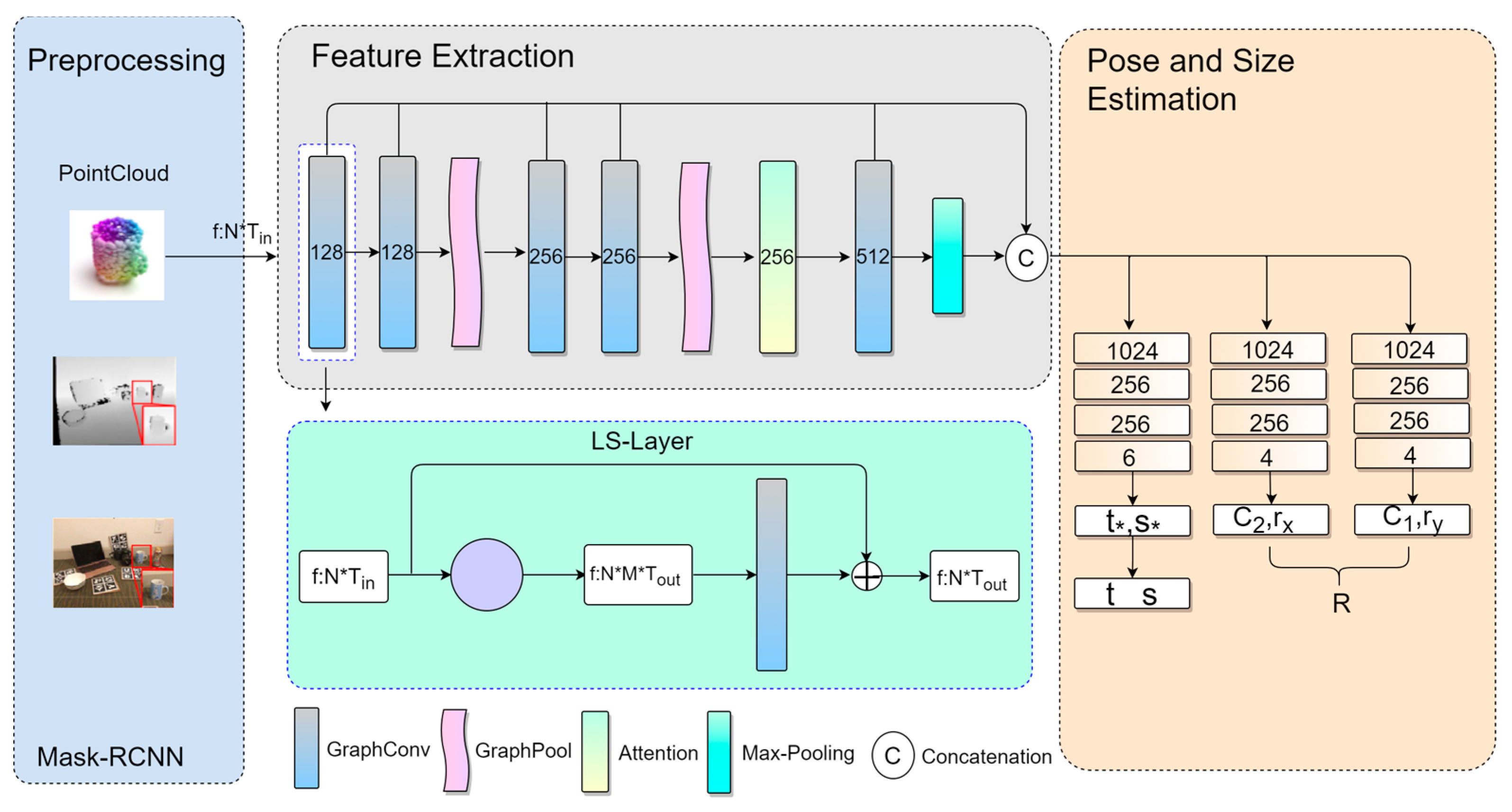
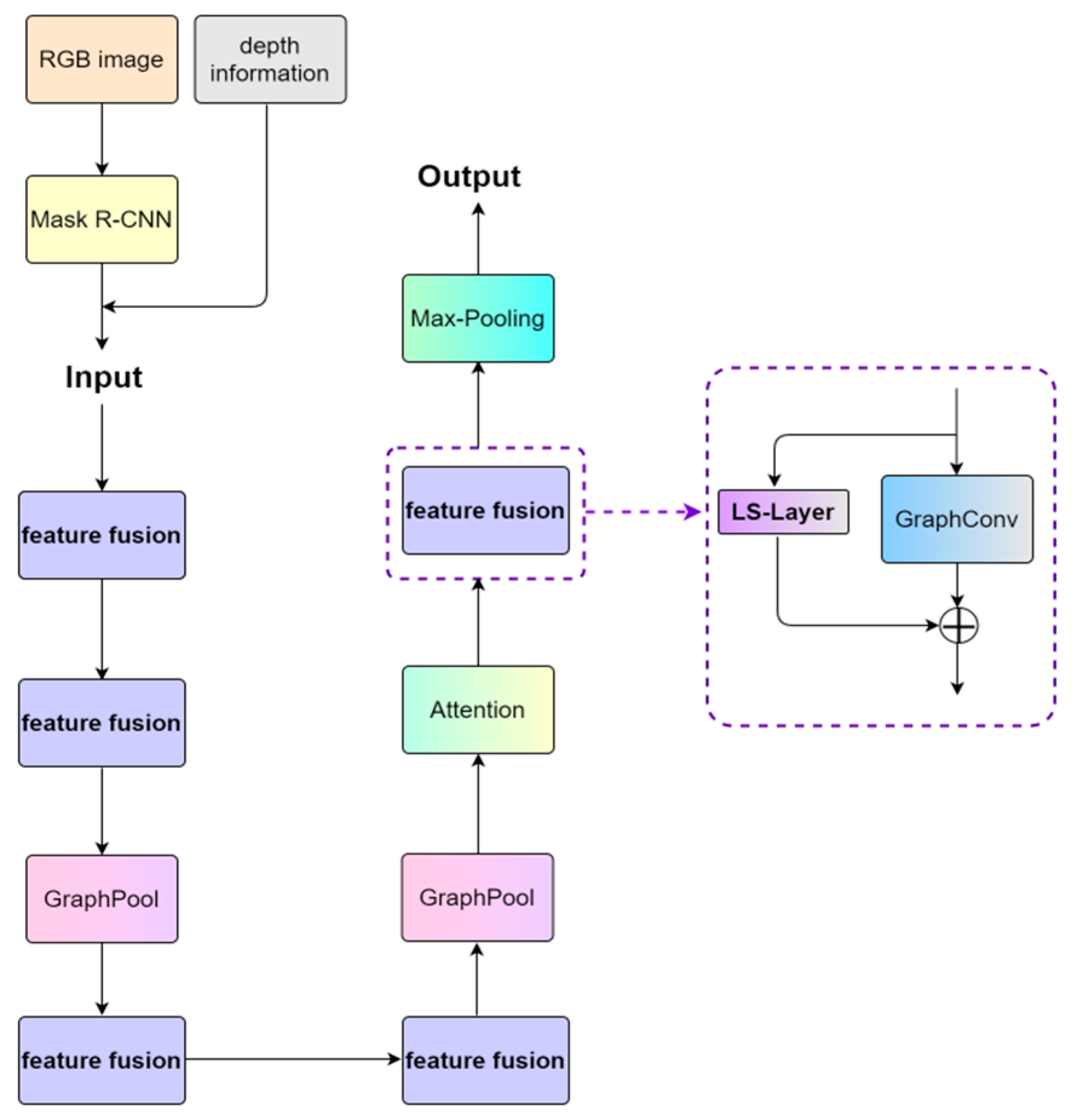
3.2. Overall Framework
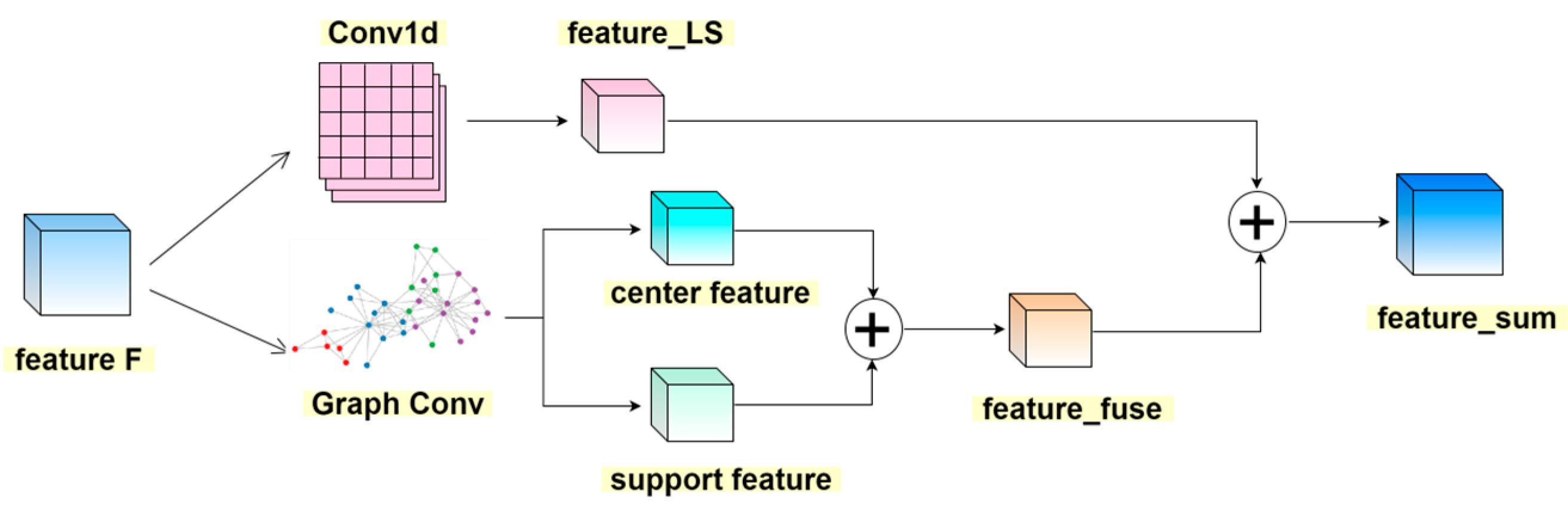
3.3. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (LS-Layer)
3.4. Pyramid Split Attention
3.5. Selection of Network Parameters
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Environment and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Ablation Study
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kothari, N.; Gupta, M.; Vachhani, L.; Arya, H. Pose estimation for an autonomous vehicle using monocular vision. In Proceedings of the 2017 Indian Control Conference (ICC), Guwahati, India, 4–6 January 2017; pp. 424–431. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Rambach, J.; Minaskan, N.; Lesur, P.; Pugani, A.; Stricker, D. Deep multi-state object pose estimation for augmented reality assembly. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct), Beijing, China, 10–18 October 2019; pp. 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Dang, L.M.; Nguyen, T.N.; Han, D.; Lee, A.; Jang, I.; Moon, H. A deep learning-based hybrid framework for object detection and recognition in autonomous driving. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 194228–194239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remus, A.; D’Avella, S.; Di Felice, F.; Tripicchio, P.; Arizzano, C.A. i2c-net: Using instance-level neural networks for monocular category-level 6D pose estimation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, C.; Garcia-Hernando, G.; Sock, J.; Kim, T.-K. Instance-and category-level 6d object pose estimation. In RGB-D Image Analysis and Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 243–265. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, S. Point-set anchors for object detection, instance segmentation and pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part X 16;. Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 527–544. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Jia, K.; Li, Y. Dualposenet: Category-level 6d object pose and size estimation using dual pose network with refined learning of pose consistency. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3560–3569. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Ang, M.H.; Lee, G.H. Shape prior deformation for categorical 6d object pose and size estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XXI 16. Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 530–546. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Song, J.; Huang, Q. Hybridpose: 6d object pose estimation under hybrid representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Manhardt, F.; Tombari, F.; Ji, X. Gdr-net: Geometry-guided direct regression network for monocular 6d object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 16611–16621. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D.; Heikkilä, J.; Rahtu, E. Ove6d: Object viewpoint encoding for depth-based 6d object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6803–6813. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Tian, W.; Xiong, L.; Li, H. Epro-pnp: Generalized end-to-end probabilistic perspective-n-points for monocular object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2781–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Sridhar, S.; Huang, J.; Valentin, J.; Song, S.; Guibas, L.J. Normalized object coordinate space for category-level 6d object pose and size estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 5–20 June 2019; pp. 2642–2651. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.; Huang, Z.; Gu, N.; Wang, G. MSSPA-GC: Multi-Scale Shape Prior Adaptation with 3D Graph Convolutions for Category-Level Object Pose Estimation. Neural Netw. 2023, 166, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, P.; Armagan, A.; Kim, T.K. Accurate 6d object pose estimation by pose conditioned mesh reconstruction. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 4147–4151. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.H.; Huang, S.Y.; Wang, Y.C.F. Convolution in the cloud: Learning deformable kernels in 3d graph convolution networks for point cloud analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1800–1809. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Dong, H. Generative category-level object pose estimation via diffusion models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Irshad, M.Z.; Zakharov, S.; Ambrus, R.; Kollar, T.; Kira, Z.; Gaidon, A. Shapo: Implicit representations for multi-object shape, appearance, and pose optimization. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 275–292. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D.; Heikkilä, J.; Rahtu, E. Sc6d: Symmetry-agnostic and correspondence-free 6d object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Prague, Czech Republic, 12–15 September 2022; pp. 536–546. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.N.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Salzmann, M.; Lepetit, V. Templates for 3d object pose estimation revisited: Generalization to new objects and robustness to occlusions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6771–6780. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, G.; Cheng, S.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Su, Y.; Tan, J. Zero-Shot 3D Pose Estimation of Unseen Object by Two-step RGB-D Fusion. Neurocomputing 2024, 597, 128041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jia, X.; Chang, H.J.; Zheng, Y.; Su, Y.; Tan, J. Fs-net: Fast shape-based network for category-level 6d object pose estimation with decoupled rotation mechanism. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 1581–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Di, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lou, Z.; Manhardt, F.; Ji, X.; Navab, N.; Tombari, F. Gpv-pose: Category-level object pose estimation via geometry-guided point-wise voting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6781–6791. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Dasgupta, E.; Chen, H.; Leonardis, A.; Zhang, W.; Chang, H. Hs-pose: Hybrid scope feature extraction for category-level object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17163–17173. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Liu, Z.; Cheang, C.; Fu, Y.; Guo, G.; Xue, X. Sar-net: Shape alignment and recovery network for category-level 6d object pose and size estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6707–6717. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Di, Y.; Manhardt, F.; Tombari, F.; Ji, X. Ssp-pose: Symmetry-aware shape prior deformation for direct category-level object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 7452–7459. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zu, K.; Lu, J.; Zou, Y.; Meng, D. EPSANet: An efficient pyramid squeeze attention block on convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Macao, China, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 1161–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, K. Vi-net: Boosting category-level 6d object pose estimation via learning decoupled rotations on the spherical representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 14001–14011. [Google Scholar]
- Pitteri, G.; Ramamonjisoa, M.; Ilic, S.; Lepetit, V. On object symmetries and 6d pose estimation from images. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 16–19 September 2019; pp. 614–622. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay, J.; To, T.; Sundaralingam, B.; Xiang, Y.; Fox, D.; Birchfield, S. Deep object pose estimation for semantic robotic grasping of household objects. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.10790. [Google Scholar]
- Targ, S.; Almeida, D.; Lyman, K. Resnet in resnet: Generalizing residual architectures. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.08029. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Z.; Tong, X.; Zhu, J.H.; Gao, R. Ghost-YOLOX: A lightweight and efficient implementation of object detection model. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 4552–4558. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J.; Nie, Z.; Yu, J.; Xie, F.; Song, R. (Eds.) Intelligent Robotics and Applications: 14th International Conference, ICIRA 2021, Yantai, China, 22–25 October 2021, Proceedings, Part III; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Di, Y.; Lou, Z.; Manhardt, F.; Tombari, F.; Ji, X. Rbp-pose: Residual bounding box projection for category-level pose estimation. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 655–672. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; He, P.; Chen, P.; Lin, X.; Gao, J.; Han, J. On the variance of the adaptive learning rate and beyond. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.03265. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, H.; Huang, J.; Hua, X.; Zhang, L. Gradient centralization: A new optimization technique for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part I 16. Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 635–652. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Lucas, J.; Ba, J.; Hinton, G. Lookahead optimizer: K steps forward, 1 step back. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar]


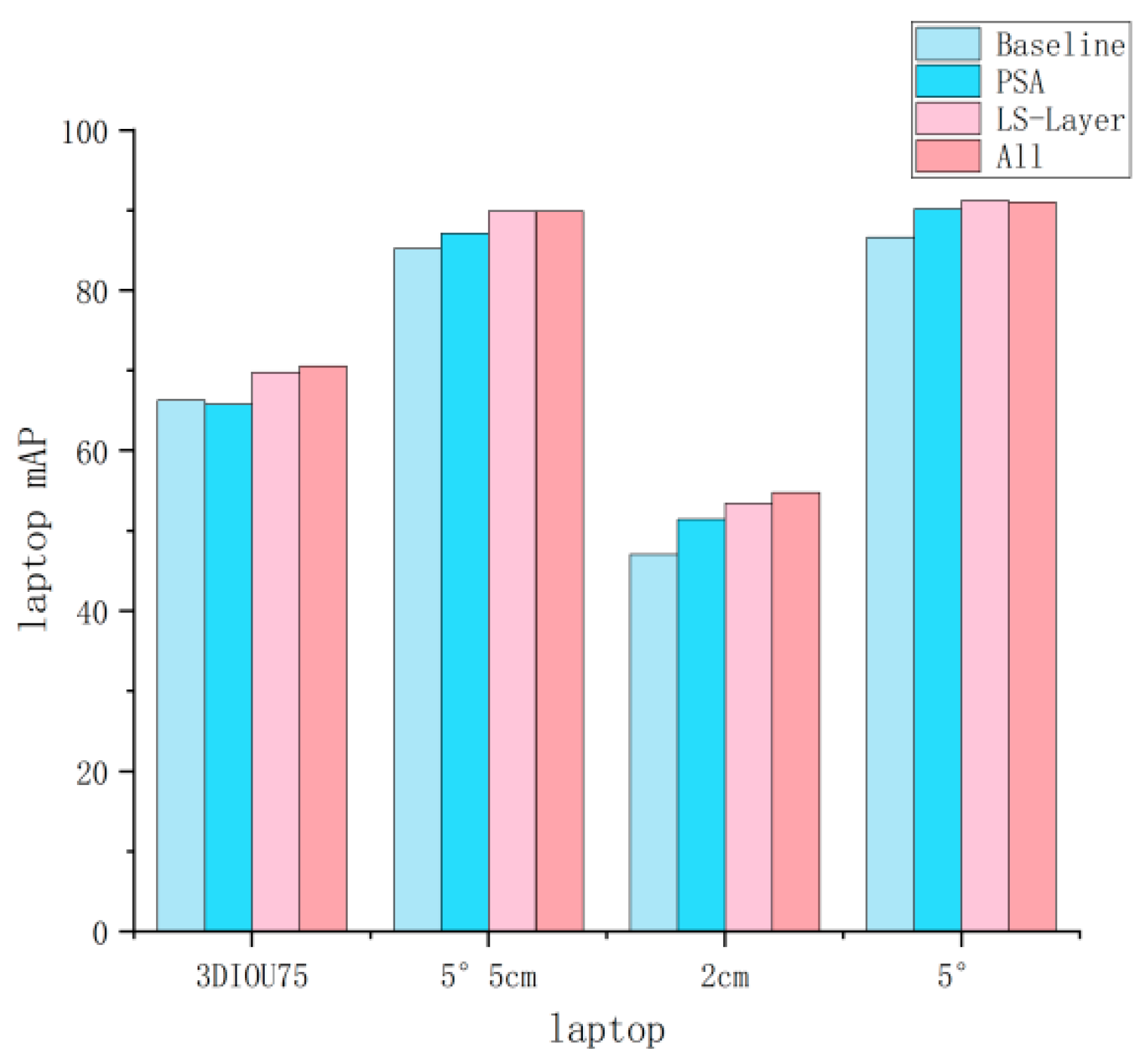

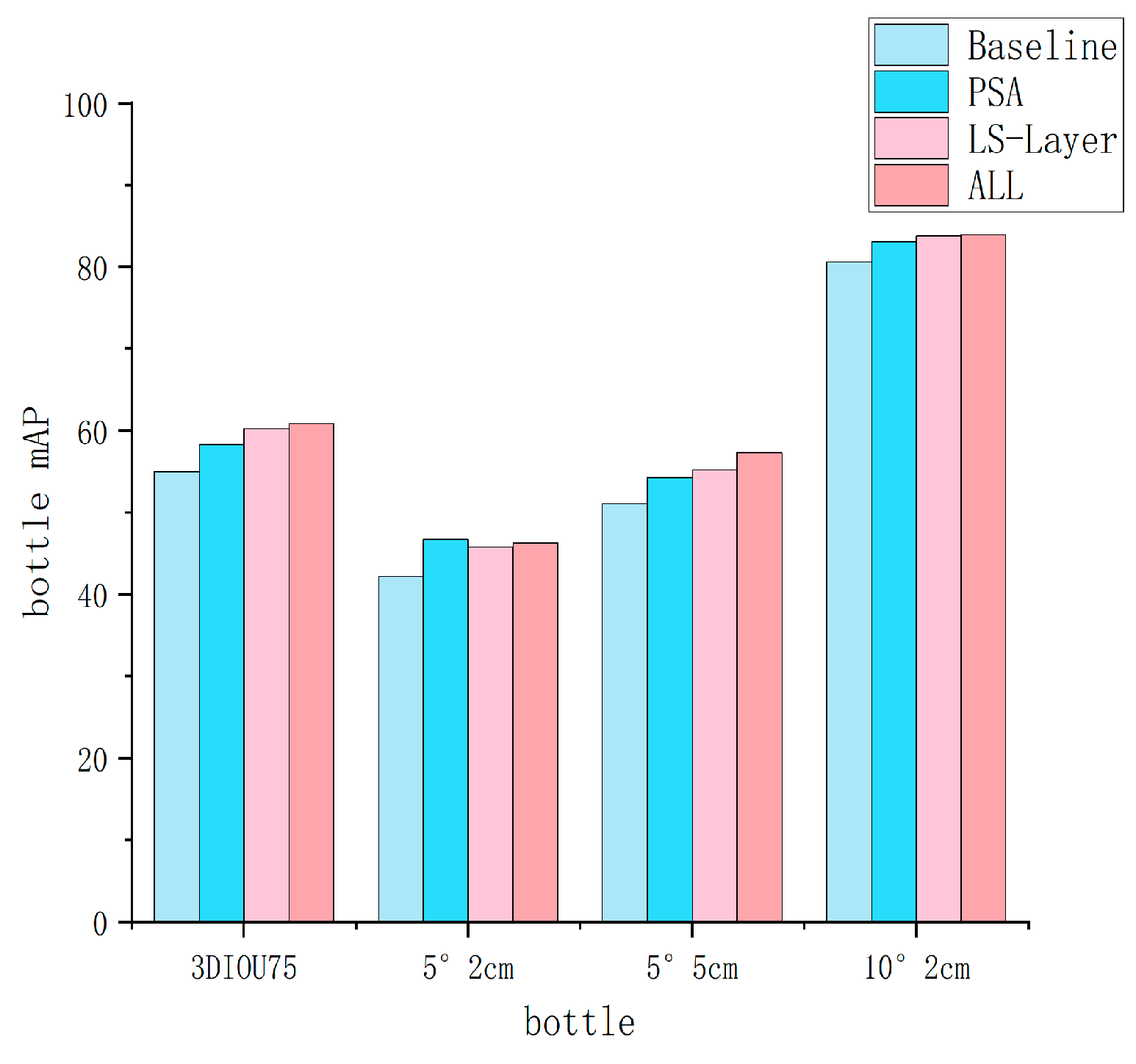
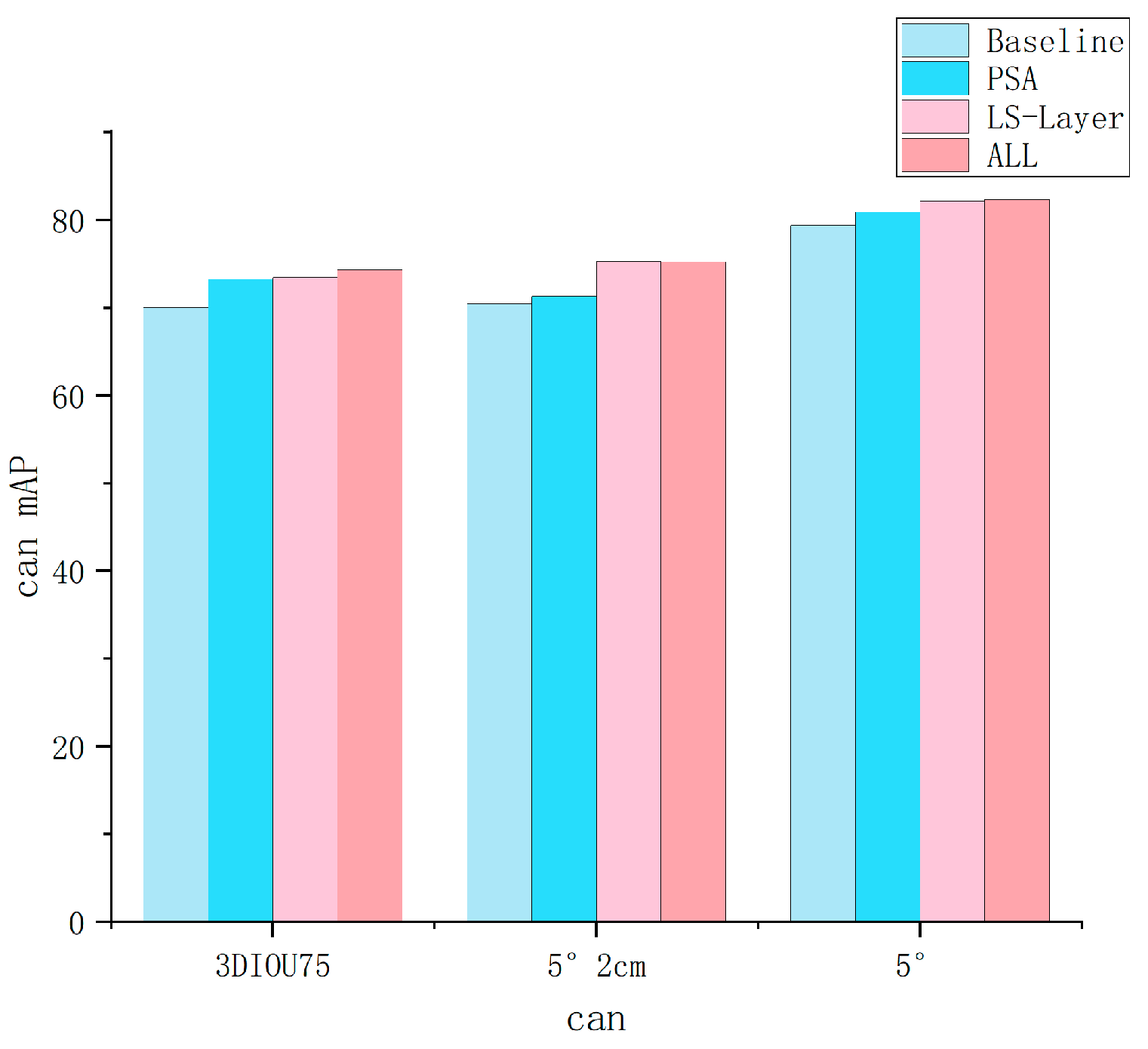

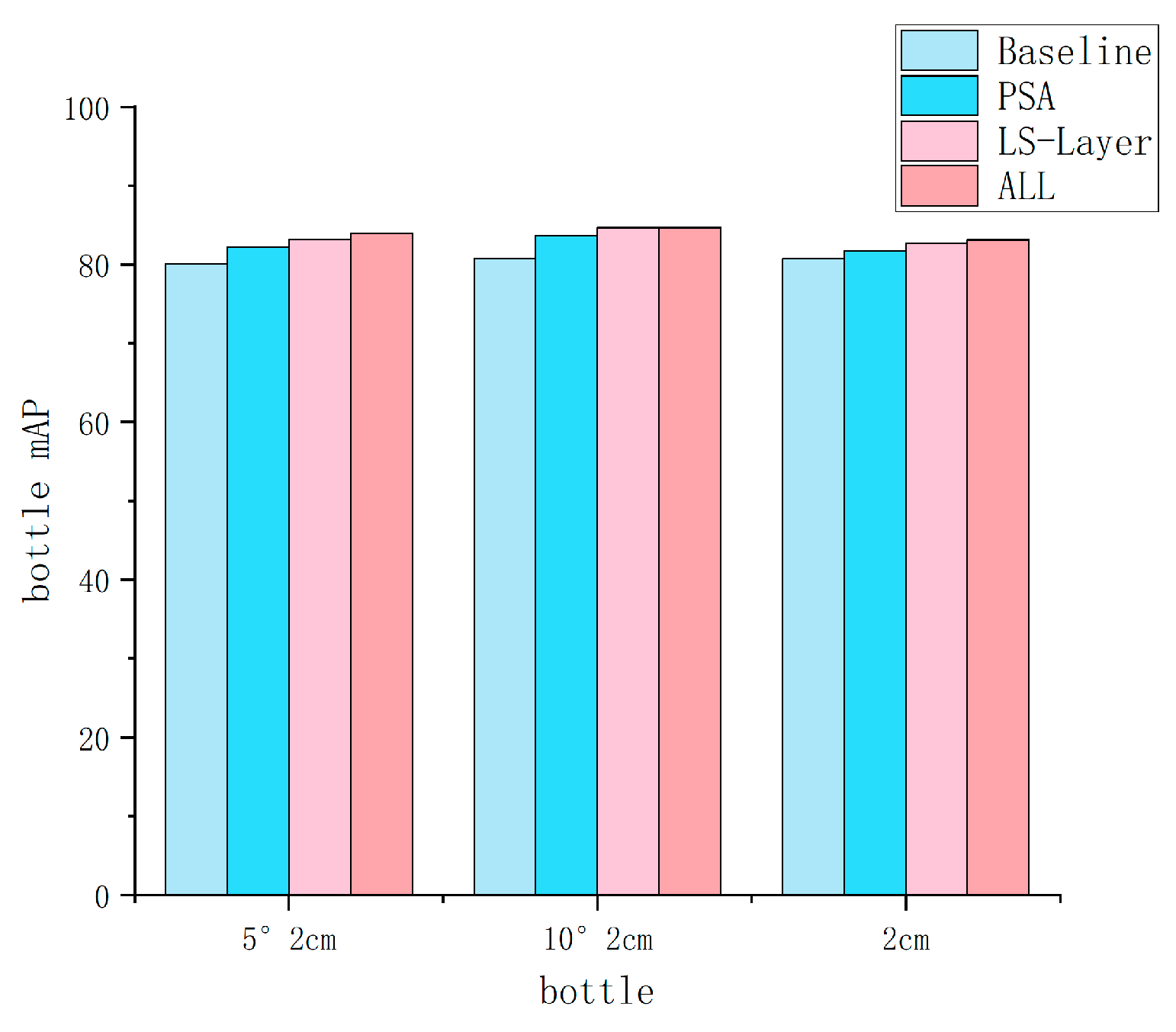
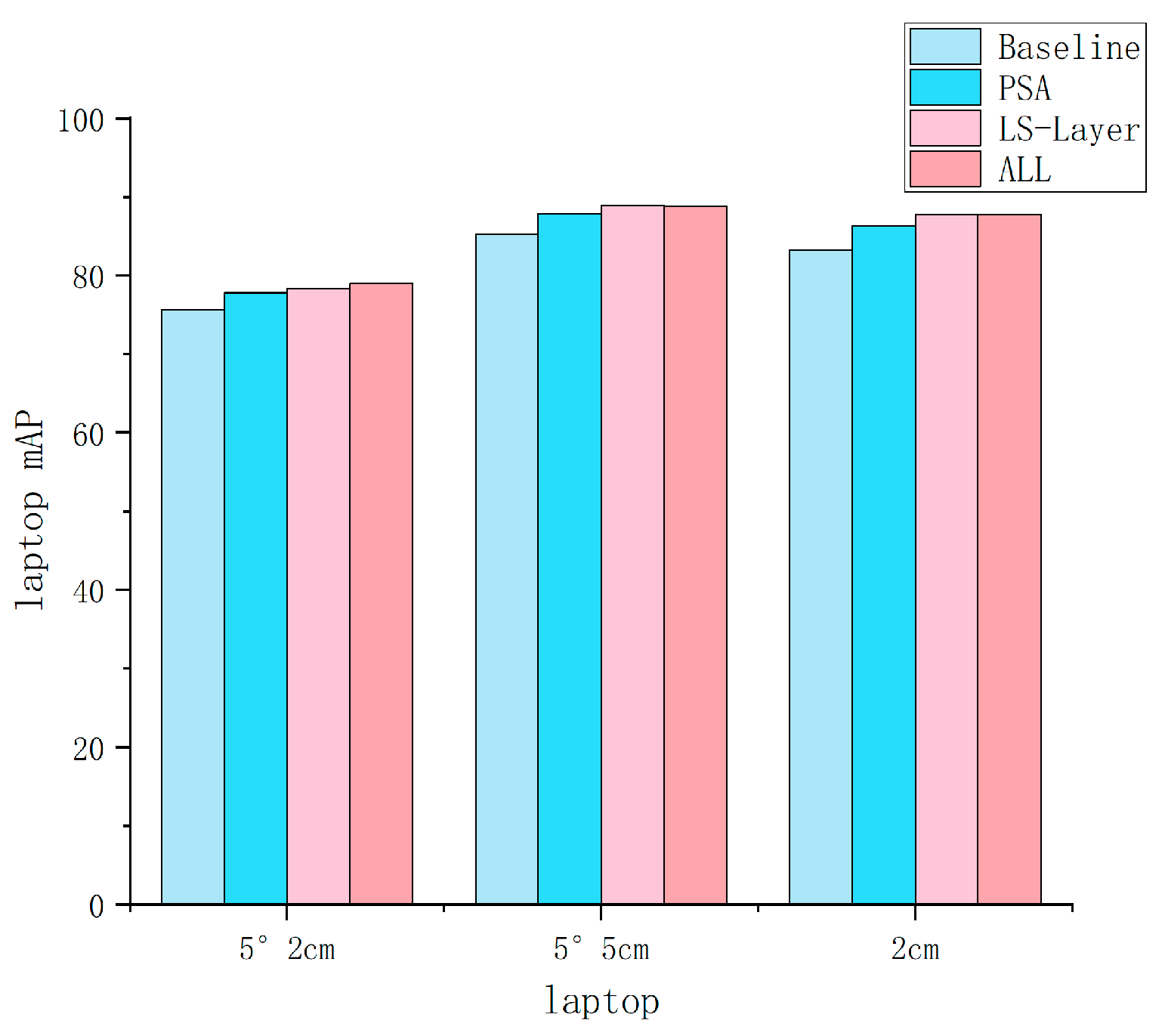

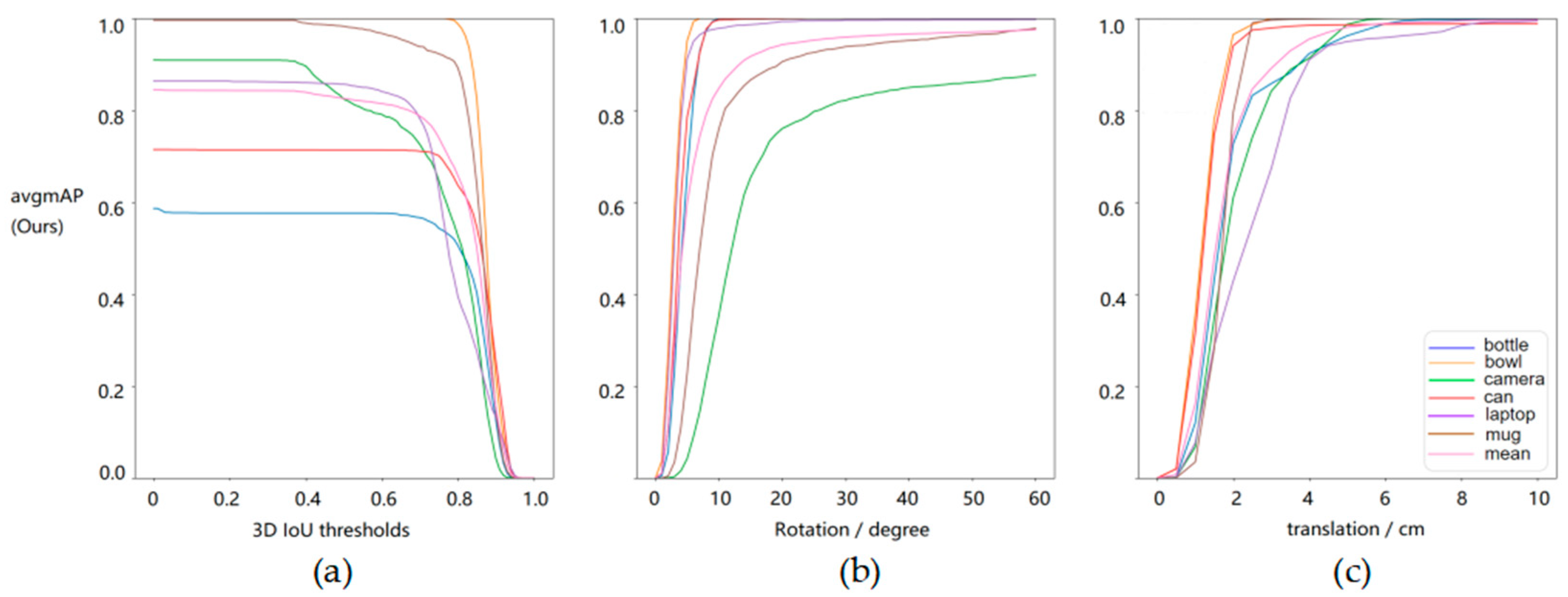
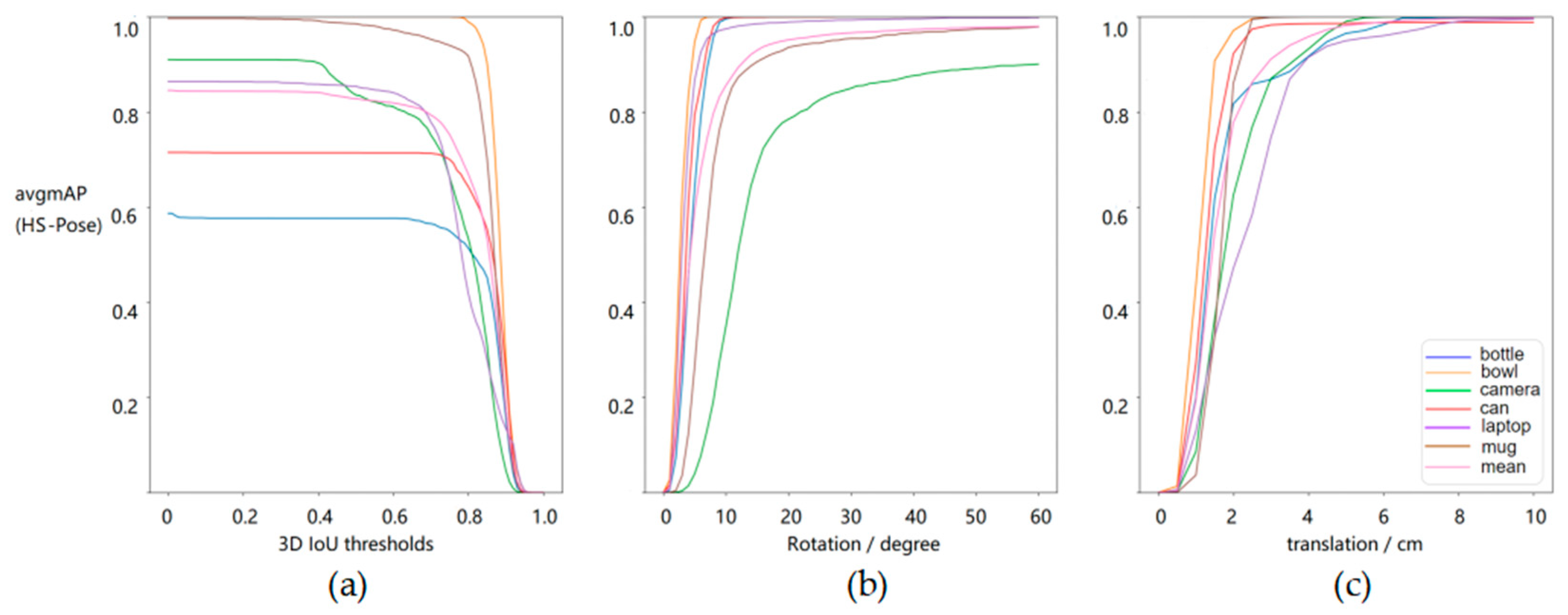
| Row | Method | IoU25 | IoU50 | IoU75 | 5°2 cm | 5°5 cm | 10°2 cm | 10°5 cm | 2 cm | 5° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | HS − Pose [24] | 84.2 | 82.1 | 74.7 | 46.5 | 55.2 | 68.6 | 82.7 | 78.2 | 58.2 |
| B0 | A0 + PSA | 84.3 | 82.5 | 76.9 | 47.9 | 57.5 | 70.9 | 85.5 | 79.5 | 61.2 |
| C0 | A0 + LS − Layer | 84.3 | 83.2 | 78.4 | 49.3 | 58.7 | 71.6 | 86.3 | 80.5 | 62.4 |
| D0 | A0 + PSA + LS-Layer + Max-Pooling | 84.5 | 83.6 | 79.1 | 49.5 | 59.8 | 71.9 | 87.0 | 79.5 | 62.6 |
| Method | IoU25 | IoU50 | IoU75 | 5°2 cm | 5°5 cm | 10°2 cm | 10°5 cm | 10°10 cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DaulPoseNet [7] | - | 79.8 | 62.2 | 29.3 | 35.9 | 50.0 | 66.8 | - |
| FS-Net [22] | 84.0 | 81.1 | 63.5 | 19.9 | 33.9 | - | 69.1 | 71.0 |
| GPV-Pose [23] | 84.1 | 83.0 | 64.4 | 32.0 | 42.9 | 55.0 | 73.3 | 74.6 |
| HS-Pose [24] | 84.2 | 82.1 | 74.7 | 46.5 | 55.2 | 68.6 | 82.7 | 83.7 |
| SAR-Net [25] | - | 79.3 | 62.4 | 31.6 | 42.3 | 50.3 | 68.3 | - |
| SSP-Pose [26] | 84.0 | 82.3 | 66.3 | 34.7 | 44.6 | - | 77.8 | 79.7 |
| SPD [8] | 83.4 | 77.3 | 53.2 | 19.3 | 21.4 | 43.2 | 54.1 | - |
| RBP-Net [35] | - | - | 67.8 | 38.2 | 48.1 | 63.1 | 79.2 | - |
| Ours | 84.5 | 83.6 | 79.1 | 49.5 | 59.8 | 71.9 | 87.0 | 88.0 |
| Method | IoU50 | IoU75 | 5°2 cm | 5°5 cm | 10°2 cm | 10°5 cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DaulPoseNet [7] | 92.4 | 86.4 | 64.7 | 70.7 | 77.2 | 84.7 |
| GPV-Pose [23] | 93.4 | 88.3 | 72.1 | 79.1 | - | 89.0 |
| HS-Pose [24] | 93.3 | 89.4 | 73.3 | 80.5 | 80.4 | 89.4 |
| SAR-Net [25] | 86.8 | 79.0 | 66.7 | 70.9 | 75.3 | 80.3 |
| SSP-Pose [26] | - | 86.8 | 64.7 | 75.5 | - | 87.4 |
| SPD [8] | 93.2 | 83.1 | 54.3 | 59.0 | 73.3 | 81.5 |
| RBP-Pose [35] | 93.1 | 89.0 | 73.5 | 79.6 | 82.1 | 89.5 |
| Ours | 95.2 | 92.9 | 76.3 | 82.6 | 83.5 | 91.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Guo, C.; Ma, Q.; Song, W. LA-Net: An End-to-End Category-Level Object Attitude Estimation Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and an Attention Mechanism. Electronics 2024, 13, 2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142809
Wang J, Liu G, Guo C, Ma Q, Song W. LA-Net: An End-to-End Category-Level Object Attitude Estimation Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and an Attention Mechanism. Electronics. 2024; 13(14):2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142809
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing, Guohan Liu, Cheng Guo, Qianglong Ma, and Wanying Song. 2024. "LA-Net: An End-to-End Category-Level Object Attitude Estimation Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and an Attention Mechanism" Electronics 13, no. 14: 2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142809
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, G., Guo, C., Ma, Q., & Song, W. (2024). LA-Net: An End-to-End Category-Level Object Attitude Estimation Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and an Attention Mechanism. Electronics, 13(14), 2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142809






