Abstract
The estimation of direction of arrival (DOA) is paramount in the realm of practical array signal processing systems. Nevertheless, traditional estimation methods often rely heavily on the Gaussian noise assumption, rendering them ineffective in achieving high-precision estimates in environments plagued by strong impulsive noise. To address this challenge, this paper introduces a novel DOA estimation algorithm that leverages mixed fractional lower-order correntropy (MFLOCR) in the context of Alpha-stable distributed impulsive noise. Correntropy is used as a measure of the similarity of the signals, using a Gaussian function to smooth extreme values and provide greater robustness against impulsive noise. By utilizing diverse kernel lengths to jointly regulate the kernel function, the concept of correntropy is expanded and implemented in the fractional lower-order moment (FLOM) algorithm for received signals. Subsequently, the MFLOCR is derived by adjusting the resulting form of correntropy. Finally, an enhanced DOA estimation algorithm is proposed that combines the MFLOCR operator with the MUSIC algorithm, specifically tailored for impulsive noise environments. Furthermore, a proof of boundedness is provided to validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in such noisy conditions. Simulation experiments confirmed that the proposed method outperforms existing DOA estimation methods in the context of intense impulsive noise, a low generalized signal-to-noise ratio (GSNR), and a smaller number of snapshots.
1. Introduction
Direction of arrival (DOA) estimation is a critical area in array signal processing and has wide applications in sonar, 5G communication, radar, and smart antennas [1,2,3]. However, most studies on DOA estimation have been performed assuming white Gaussian conditions of ideal additive noise. As a result, many algorithms have been developed, including super-resolution DOA estimation algorithms such as Multiple Signal Classification (MUSIC) [4,5,6] and Signal Parameter Estimation Using Rotational Invariance Techniques (ESPRIT) [7,8,9]. In practical environments, many signals and noises do not exactly follow Gaussian distributions. For example, natural lightning, switch transients in car ignitions, and accidental impacts on telephone lines can induce noise with strong impulsive characteristics [10,11,12]. The probability density functions (PDFs) of these impulsive noises decay more slowly than Gaussian distributions, resulting in thicker tails. The presence of impulsive noise can significantly degrade, or even nullify, the performances of algorithms designed under ideal noise conditions [13].
Common models used to describe impulsive noise include the Alpha-stable distribution [14], the mixed Gaussian distribution [15,16], and the Middleton Class A model [17,18]. Typically, impulsive noise has infinite variance, resulting in the absence of its second- or higher-order moments, but it does exhibit finite fractional lower-order statistics (FLOS). Therefore, several FLOS-based algorithms have been developed, such as fractional low-order moments (FLOM) [19,20], robust covariance-based (ROC) algorithms [21], and phase-controlled fractional low-order moments (PFLOM) [22]. However, when the parameters of the impulse noise are unknown, it is difficult to select the optimal settings to suppress the noise. This uncertainty limits the effectiveness of FLOS-based algorithms [23].
In recent years, correntropy has gained significant attention in robust signal processing and machine learning [24,25,26]. A higher-order statistic quantifies the two random process time structures and statistical distribution. Compared to the conventional correlation function, correntropy can extract more information, offering excellent impulsive noise suppression without requiring prior knowledge of the noise [27,28]. Zhang proposed the CRCO-MUSIC algorithm [29], which combines the MUSIC algorithm with correntropy-based correlation (CRCO). Although CRCO-MUSIC has improved the denoising performance and signal application, its accuracy still needs to be improved in cases where the signal snapshots are small and the noise is highly impulsive. The authors of [30] proposed a method using cyclic correntropy (CC) in an impulsive noise environment. The algorithm analyzes cyclic signal processing in a steady state, which has good robustness to impulsive noise.
In [31], Chen devised a correntropy-based covariance matrix (CBCM) with the MUSIC technique for source localization amidst impulsive noise. Although this method notably enhances accuracy and robustness, its real-time applicability may be hampered by considerable computational demands. In [32], Dai presented an enhanced Toeplitz approximation method incorporating a correntropy-based generalized covariance (CEGC) operator. While boasting high resolution and sidestepping array aperture loss, the method might struggle with substantial computational complexity in expansive scenarios. A bi-iterative complex fixed-point algorithm (BI-CFPA) was presented by Wang in [33] to solve the non-convex optimization issue in signal subspace estimations. This method exhibits superior efficacy across various impulsive noise conditions, especially in intense impulsive noise. Nevertheless, its optimization process complexity could be a limiting factor.
In [34], a new fractional lower-order correlation (FLOCR) algorithm was proposed, which utilizes correlation and FLOM. The algorithm outperforms other algorithms in terms of the root mean square error in highly impulsive noise environments. In [35], the authors introduced the concept of mixed correntropy to enhance the suppression of impulsive noise by mixing two Gaussian functions as kernel functions. However, when the impulsive noise intensity is high, the performance of the above DOA algorithm deteriorates due to the interference of outliers. In [36], Cai introduced an adaptive weight factor based on correntropy to suppress impulsive noise and constructed a multilayer deep neural network (DNN) framework with a real-numbered vectorized pseudo-covariance matrix as input. Despite its remarkable accuracy and resilience, this DNN-based approach can require extensive training data and computational resources.
Contributions—The invention of a novel method for DOA estimation based on mixed fractional lower-order correntropy (MFLOCR) to enhance DOA estimation in environments with impulsive noise is the primary innovation of this study. The following are the primary contributions of this study:
- Development of MFLOCR: This paper proposes a new correntropy called MFLOCR, which extends the concept of correntropy using different kernel lengths to jointly regulate the kernel function. The proposed method is based on the theory of FLOS and uses mixed correntropy with an exponential kernel instead of the traditional covariance matrix, which provides greater robustness against impulsive noise and enhances the effectiveness of the algorithm in environments with Alpha-stable distributed impulsive noise.
- MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm: An improved DOA estimation algorithm, MFLOCR-MUSIC, was developed by combining the MFLOCR operator with the traditional MUSIC algorithm. This combination is specifically tailored for improved performance in impulsive noise environments.
- Proof of Boundedness: The proof of boundedness serves to verify the efficiency and stability of the proposed MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm under impulsive noise and ensures its reliability in real applications.
- Superior Performance in Simulations: Simulation experiments showed that the proposed MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm outperforms existing DOA estimation methods in various characteristic indices. It was proven to be highly accurate and robust.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows. In Section 2, we formulate the problem, introduce signal and impulse noise models, and review existing methods based on FLOS. In Section 3, we provide an overview of correntropy and propose a new operator called MFLOCR for two independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) SαS random variables. This operator can be used to create subspace techniques when there are noise and α-stable distributed signals present. In Section 4, we present the simulation results to validate the proposed algorithm. Finally, we present conclusions in Section 5.
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Signal Model of DOA Estimation
Taking into account the impulsive noise and half-wavelength spaced uniform linear array (ULA) of M sensors that are impinged upon by K far-field narrowband sources, the fundamental observation of the mth array element at the sampling time t may be represented as follows, using the first antenna as the reference, as seen in Figure 1:
where and are the ith incident signal and the direction of arrival, respectively. is the signal wavelength, and the distance d is between two sensors, where , and is the measurement noise in the mth array element followed by the symmetric Alpha-stable (SαS) distribution.
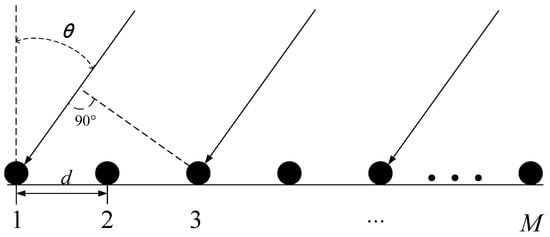
Figure 1.
The uniform line array model.
Hence, the vector of the received signals at time t is . This vector can be expressed as
where denotes the signal vector; is the array steering matrix, where is the steering vector of the kth signal source; and denotes the impulsive noise vector.
2.2. Impulsive Noise Model
The impulsive noise has a stronger tail compared to the Gaussian noise, making the probability of outliers higher, which when modeled as an SαS (symmetric Alpha-stable) distribution is defined as
where describes the characteristic exponent of the impulsive noise intensity. When , the distribution reduces to Gaussian. The symmetry parameter indicates the degree of skewness of the distribution. When , the distribution is symmetric and is called the SαS distribution. The scale parameter is similar to the variance of a regular distribution. is the positional parameter. The probability density functions of the SαS distribution for different characteristic exponents are shown in Figure 2. In this study, we simulated the impulsive noise environment using SαS distributions.
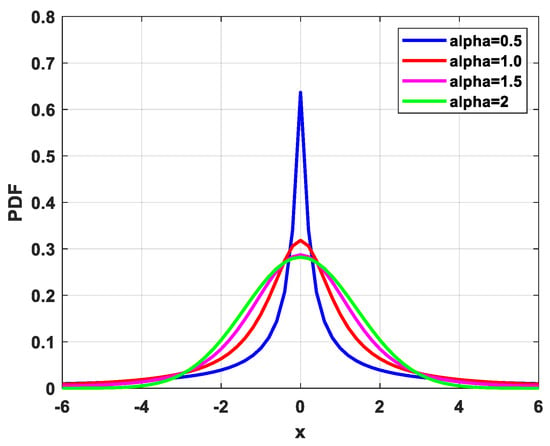
Figure 2.
The probability density functions for the SαS distribution.
2.3. Correntropy
As a novel statistical measure, correntropy is employed to quantify the spatial structure and statistical distribution of two random processes. It possesses the ability to extract richer information and mitigate the impact of outliers resulting from impulsive noise. Consequently, correntropy introduces a novel metric within the sample space. The correntropy can be expressed as
where and are the expectation and kernel functions with a width of , respectively. In practice, the prior probabilities are unknown. Therefore, the correntropy of random variables can only be estimated from a limited number of observations , which can be expressed as
where N is the number of observations, and the Gaussian kernel function is the most often utilized kernel function in correntropy. It is effective in suppressing outliers [37] and can be written as
A Taylor series expansion of (8) is further described as
where is the error variable. From the above equation, it can be known that the correntropy contains all the information of the second- and even higher-order moments.
Furthermore, the correntropy can induce a distance measure known as the correntropy-induced metric (CIM), denoted as
where . The CIM exhibits mixed-norm properties that are entirely controlled by the width of the kernel [38]. In order to estimate the DOA of the source precisely, the kernel width is varied based on the intensity of impulsive noise.
3. The Proposed MFLOCR-MUSIC Algorithm
3.1. FLOM-MUSIC Algorithm
The statistical measures of signals contain abundant information about signal characteristics. In traditional signal processing, second-order or higher-order statistical measures are often used to extract signal features. However, in an impulsive noise environment, only statistical measures less than the characteristic exponent exist for noise that follows the SαS distribution. This causes no second-order or higher-order statistical measurements of the received signals to exist, leading to degraded or even invalid DOA estimation results. In [19], a FLOM-based MUSIC estimation algorithm was proposed for DOA estimation in impulsive noise environments with an SαS distribution. The FLOM matrix is written as follows:
where X and Y are two random variables that follow the SαS distribution. The operator is defined as . The (I,j)th element of the FLOM matrix is defined as
where is the ith row of the element; if p = 2, the FLOM matrix turns into a conventional correlation. With the EVD of , we obtain
where and are the diagonal matrices that have the remaining (M − K) lesser eigenvalues and the K biggest eigenvalues of , respectively. and are the matrices composed of eigenvectors corresponding to and .
Then, the K greatest peaks of the spatial spectrum might be found in order to estimate the DOAs.
3.2. MFLOCR-MUSIC Algorithm
In order to further improve the suppression effect of the correntropy on the effect of the outliers caused by impulsive noise, a new estimator named MFLOCR-MUSIC is proposed that can be applied in SαS distributions for a wide range of .
Mixed correntropy is more effective in capturing the diverse interference scales introduced by impulsive noise, which uses two Gaussian functions with different kernel widths. The length of the kernel can influence the sensitivity of the system to transient changes in impulsive noise. A shorter kernel length may be sensitive to transient changes in impulsive noise, whereas a longer kernel length may assist in identifying long-term trends in the background signal and therefore facilitate a more effective separation of noise and signal. The utilization of kernel functions with varying kernel lengths enables a more effective differentiation of transient alterations induced by impulsive noise.
By adjusting the kernel length with different parameters, an analytical model that is more insensitive to impulsive noise can be constructed, which further improves the accuracy of DOA estimation under impulsive noise. This model can be considered a promotion of the original correlation, which contains more statistical information, defined as
The mixture factor satisfies conditions and . If , it becomes a single kernel function with an entropy of either or and is the width of the kernel. As a more flexible similarity measure, appropriate mixing coefficients can improve the performance of mixed correntropy. Given that the Gaussian kernel function performs well in reducing impulsive noise, by substituting (8) into (15), we have
It is seen that, as the kernel length increases, the higher-order moment information decays faster, resulting in the second-order statistic becoming the primary component. When , the correntropy is proportional to , which indicates that all conventional correlation information is contained in the correntropy. In contrast to conventional correntropy, mixed correntropy allows the simultaneous consideration of signal features at different time scales which improves the performance and stability of the DOA estimation and reduces the risk of overfitting.
As a result, to effectively mitigate outliers stemming from impulsive noise and enhance the DOA estimation, a novel estimator named MFLOCR was introduced. This estimator builds upon the foundation of the FLOM algorithm and is motivated by the concept of mixed correntropy mentioned above. The matrix can be defined as
where is the ith row of the element. The (I,j)th element of is denoted as
Based on the proposed algorithm’s exceptional performance, we replace the covariance matrix in MUSIC with to estimate the DOAs.
3.3. The Implementation of MFLOCR–MUSIC
In this section, the conventional subspace-based methods are extended from Gaussian-distributed noise to SαS-distributed noise environments by applying MFLOCR. We propose a new algorithm, MFLOCR-MUSIC, which combines MFLOCR with the subspace decomposition of the MUSIC algorithm. The algorithm used to estimate DOAs in an environment with impulsive noise consists of the following main steps:
Step 1. Utilizing (17) and (18), the matrix with dimensions of M × M is constructed from the data with the snapshot number N.
Step 2. Execute the eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) of the covariance to obtain the M × (M − K) dimensional noise subspace matrix :
where is the eigenvector corresponding to the M − K smaller eigenvalues.
Step 3. Compute the spatial spectrum of the MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm:
Step 4. Search for the K peaks of to estimate the DOAs of the K sources .
3.4. The Boundedness of MFLOCR
To ensure that the MFLOCR can be effectively applied to the DOA estimation problem under impulsive noise, needs to be bounded. Assuming that X and Y, which are two independent random variables with similar distributions and characteristic indices , follow the SαS distribution, the boundedness of is proved as follows:
For when the characteristic parameter satisfies , it is stated in [39] that the expectation of can be defined as
where
where is the function of Gamma. Suppose that .
In practice, the fractional low-order moment parameter satisfies and is infinitely close to −1. Since the function is monotonically decreasing and , this leads to
For , we can prove its boundedness by replacing the parameter p with 1 in the above equation:
Combining this with (24) and (25), we can obtain
The boundedness of can be proved in the same way. Based on the above, is bounded. The boundedness proof of MFLOCR above provides a theoretical basis for its application to impulsive noise DOA estimation.
4. Simulation
In this study, a comparative analysis of the proposed method against PFLOM-MUSIC [22], CRCO-MUSIC [29], and FLOCR-MUSIC [34] was conducted through numerous simulations to demonstrate the efficacy of the algorithm. Specifically, a scenario was considered where two far-field narrowband signals possessing equal power and a frequency of 1 GHz, were incident on a linear array comprising M = 8 sensors spaced at half-wavelength intervals. The noise in this scenario followed the SαS distribution. The DOAs were and . The widths of the correntropy kernel were and , and the mixing coefficients of the mixed correntropy were and . In our experiment, we set the parameter p to 1.2.
The GSNR was used in the scheme of impulsive noise, in place of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), as follows:
The following simulation was subjected to a comprehensive evaluation framework comprising 500 independent Monte Carlo trials. The performance is assessed using two key metrics: the probability of successful resolution and the RMSE. Specifically, the ratio of successfully resolved cases to the total number of Monte Carlo trials was used to calculate the probability of successful detection. The successful resolution was defined as , where in the kth Monte Carlo trial, represents the predicted DOA of the ith target. The RMSE is defined as
where L is the number of Monte Carlo trials, and K is the number of signals. The results from the simulations were acquired using a personal computer equipped with an Intel Core i5 @ 3.0 GHz CPU and MATLAB R2021b.
4.1. Effect of GSNR
The purpose of this experimental study was to investigate the algorithm performance in relation to the GSNR. The algorithm was tested from −4 dB to 8 dB to determine the effect of changing the GSNR on the method’s performance. The snapshot number was fixed at N = 200, and the characteristic exponent of was kept constant during the analysis.
As depicted in Figure 3a, the RMSE exhibits a gradual decline as the GSNR increases, indicating a significant improvement in the performance of all algorithms. Notably, when the GSNR surpasses 2 dB, the RMSEs of all algorithms fall below 0.5. However, the proposed algorithm consistently achieves a lower RMSE compared to the other algorithms, demonstrating its superior performance. Turning to Figure 3b, it is evident that with an increasing GSNR, the probability of successful resolution also rises, indicating an increase in the accuracy of these algorithms. Notably, when the GSNR reaches or exceeds 0 dB, the proposed algorithm achieves a probability of successful resolution over 0.9. This indicates that the MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm outperforms other methods and exhibits the highest accuracy.
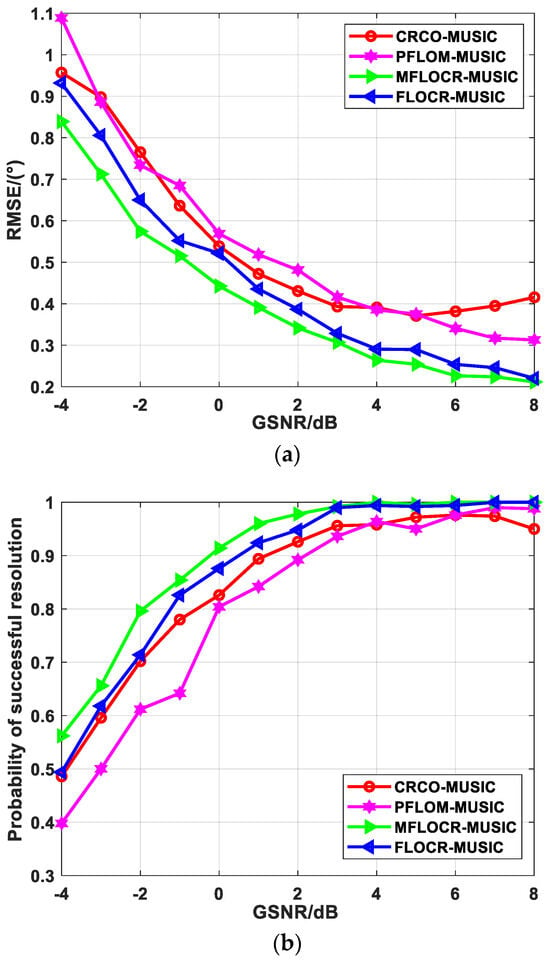
Figure 3.
Estimation performance comparison under different GSNRs: (a) RMSE; (b) probability of successful resolution.
4.2. Effect of the Number of Snapshots
The objective of this experimental investigation was to assess the influence of an increasing snapshot number, ranging from 100 to 800, on the performance of the algorithms, while maintaining a constant characteristic exponent and a GSNR = 5 dB.
As shown in Figure 4a, as the snapshot number increases, the observation matrix becomes more comprehensive, containing more useful information. This results in a continuous decline in the RMSE for all four direction estimation methods. Notably, the proposed novel method exhibits the best performance among all the simulated algorithms.
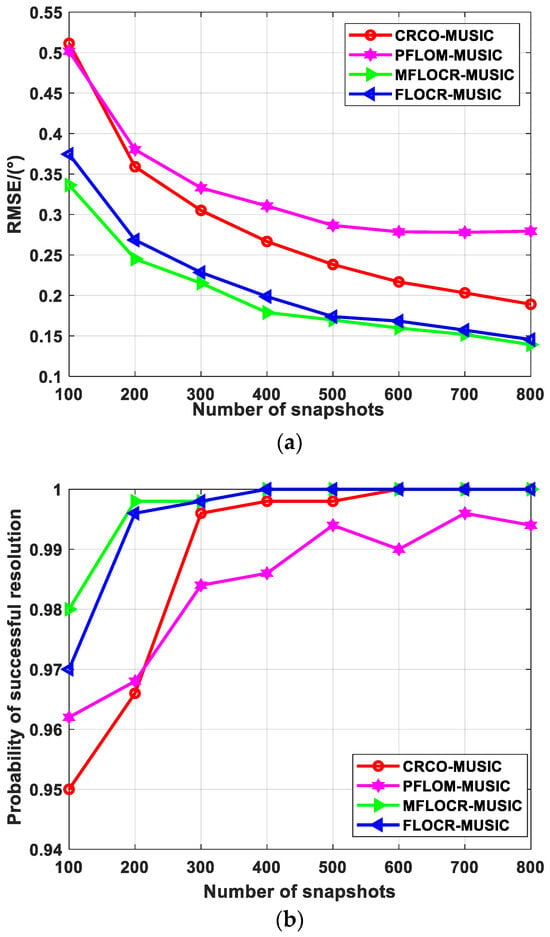
Figure 4.
Estimation performance comparison under different numbers of snapshots: (a) RMSE; (b) probability of successful resolution.
In Figure 4b, it is evident that with an increasing snapshot number, the proposed algorithm achieves significant improvements in accuracy and tends to stabilize compared to the other three algorithms. Furthermore, it is particularly effective at lower snapshot counts, underscoring the advantages of the proposed algorithm.
4.3. Characteristic Exponent
With a fixed GSNR of 5 dB and N = 200 snapshots, the aim of this series of tests was to investigate the impact of the characteristic exponent on the algorithm’s performance. As the characteristic exponent increases, the effect of impulsive noise diminishes.
Figure 5a illustrates that all algorithms perform better as the characteristic exponent increases. Notably, the RMSE of the proposed algorithm consistently remained below 0.6, and the algorithm outperformed the other three algorithms.
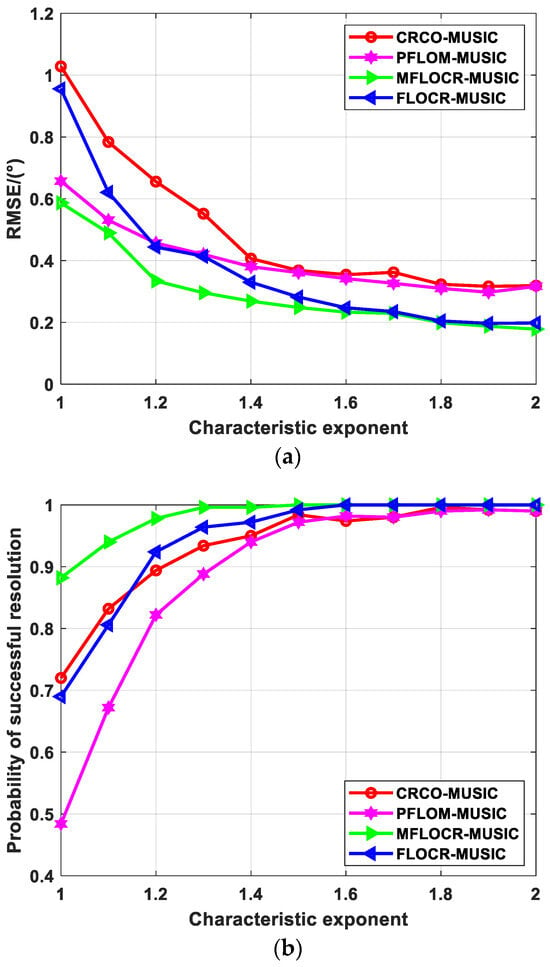
Figure 5.
Estimation performance comparison under different characteristic exponent values: (a) RMSE; (b) probability of successful resolution.
Figure 5b shows that for all algorithms, the probability of a successful resolution increases when the characteristic exponent increases. However, the proposed algorithm demonstrates superior performance in the presence of strong impulsive noise. Specifically, the accuracy of the suggested approach had already reached 0.9 when the characteristic exponent goes above a certain threshold, whereas the probability of successful resolution for the other algorithms remains below 0.6 with .
5. Conclusions
In order to overcome the performance drawbacks of conventional estimation techniques in environments with impulsive noise, this work introduced the MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm. The proposed algorithm leverages the mixed correntropy of FLOS, effectively replacing the covariance matrix in conventional approaches and providing robust suppression of impulsive noise. The MUSIC method performs exceptionally well when used for DOA estimation with the proposed correntropy. Notably, it performs exceptionally well even in situations with few snapshots and severe impulsive noise, and it does not require previous knowledge of the steady distribution noise. A thorough analysis showed that the suggested MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm works better than alternative techniques in a number of ways, achieving a high accuracy and low RMSE. The experimental results demonstrate that the MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm outperforms the other three algorithms tested. Under low GSNR conditions, the MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm achieved an RMSE improvement from 0.1 to 0.3 and an estimation accuracy improvement from 5% to 15% compared to the other algorithms. In scenarios with a low snapshot number, the MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm showed an RMSE improvement from 0.05 to 0.15 and an estimation accuracy improvement from 1% to 3%. Under conditions of intense impulsive noise, the MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm exhibited an RMSE improvement from 0.05 to 0.4 and an estimation accuracy improvement from 17% to 40% over the competing methods.
In summary, the MFLOCR-MUSIC algorithm significantly enhances the DOA estimation performance in challenging environments characterized by a low GSNR, a small snapshot number, and strong impulsive noise.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and J.H.; methodology, X.L. and J.H.; software simulation and parameter optimization, X.L. and J.H.; validation, Y.Z. and Y.T.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L. and J.H.; writing—review and editing, S.M.; supervision, X.L. X.L. and J.H. are co-first authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Xingliao Talent Program Project of Liaoning Province, grant number XLYC1907195; Songshan Laboratory Pre-Research Project, grant number YYJC062022017; National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 61801308; Liaoning Provincial Education Department Facial Project, grant number LJKMZ20220535; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 62173237; the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China, grant No. 2022-BS-216; the Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Dynamic Measurement Technology, grant number 2023-SYSJJ-04; and Aeronautical Science Foundation of China, grant number 2020Z017054001.
Data Availability Statement
The MATLAB code is available from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tang, W.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Q. Coarray interpolation for joint DOD and DOA estimation in bistatic coprime MIMO radar via decoupled atomic norm minimization. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 33, 1237–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Ghosh, J.; Kumar, P.K.; Mukhopadhyay, M. An Efficient DOA Estimation and Jammer Mitigation Method by Means of a Single Snapshot Compressive Sensing Based Sparse Coprime Array. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 123, 2737–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Pan, W.; Wang, H. Direction of Arrival Estimation Method Based on Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors for Coherent Signals in Impulsive Noise. Mathematics 2024, 12, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, M.; Zareinejad, M.; Rezaei, S.M.; Amindavar, H. DOA Estimation of Noncircular Signals Under Impulsive Noise Using a Novel Empirical Characteristic Function-Based MUSIC. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 42, 3706–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todros, K.; Hero, A.O. Robust Multiple Signal Classification via Probability Measure Transformation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 1156–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacioglu; Harmanci; Anarim; Delic. Time-of-Arrival Estimation with FLOM-MUSIC Under Impulsive Noise. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE 14th Signal Processing and Communications Applications, Antalya, Turkey, 17–19 April 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R.; Han, Y.; Sheng, W. A dual-resolution unitary ESPRIT method for DOA estimation based on sparse co-prime MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2023, 202, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, R.; Aravind Kumar, Y.V. Performance Analysis of Optimal Analog Beamforming with Modified Esprit Doa Estimation Algorithm for Mimo Noma System Over Rayleigh Fading Channel. ECS Trans. 2022, 107, 11361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Duan, Z.; Yang, Z. A Weighted Forward-Backward Spatial Smoothing DOA Estimation Algorithm Based on TLS-ESPRIT. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2021, 104, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsihrintzis, G.A.; Nikias, C.L. Performance of optimum and suboptimum receivers in the presence of impulsive noise modeled as an alpha-stable process. IEEE Trans. Commun 1995, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Tao, J.; Zakharov, Y.; Wang, B. A robust iterative receiver for single carrier underwater acoustic communications under impulsive noise. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 210, 109438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ying, W.; Yang, P.; Sun, M. Parameter estimation of underwater impulsive noise with the Class B model. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2020, 14, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikias, C.L.; Shao, M. Signal Processing with Alpha-Stable Distributions and Applications; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, H.; Champagne, B. Distributed Nonlinear System Identification in alpha-stable Noise. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rožić, N.; Banelli, P.; Begušić, D.; Radić, J. Multiple-Threshold Estimators for Impulsive Noise Suppression in Multicarrier Communications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabie, K.M.; Adebisi, B.; Tonello, A.M.; Nauryzbayev, G. For more energy-efficient dual-hop DF relaying power-line communication systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2017, 12, 2005–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaifan, K.A.; Henkel, W. accepted for publication 1 decision boundary evaluation of optimum and suboptimum detectors in class-a interference. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2017, 61, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, D. Non-Gaussian noise models in signal processing for telecommunications: New methods an results for class A and class B noise models. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1999, 45, 1129–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.H.; Mendel, J.M. A subspace-based direction finding algorithm using fractional lower order statistics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process 2001, 49, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, T. The fractional lower order moments based ESPRIT algorithm for noncircular signals in impulsive noise environments. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 96, 1673–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakalides, P.; Nikias, C.L. The robust covariation-based MUSIC (ROC-MUSIC) algorithm for bearing estimation in impulsive noise environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1996, 44, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkacemi, H.; Marcos, S. Robust subspace-based algorithms for joint angle/Doppler estimation in non-Gaussian clutter. Signal Process. 2007, 87, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Nikias, C.L. Signal processing with fractional lower order moments: Stable processes and their applications. Proc. IEEE 1993, 81, 986–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, K. Robust Regression Based on Correntropy Induced Metric. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Applications, Wuhan, China, 16–18 December 2022; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 595–603. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Cao, J.; Xue, A. Robust maximum mixture correntropy criterion-based semi-supervised ELM with variable center. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3572–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xing, L.; Zhao, H.; Du, S.; Principe, J.C. Effects of outliers on the maximum correntropy estimation: A robustness analysis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 4007–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Qu, H.; Gui, G.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, B. Maximum correntropy criterion based sparse adaptive filtering algorithms for robust channel estimation under non-Gaussian environments. J. Frankl. Inst. 2015, 352, 2708–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gao, S.; Ge, H.; Wang, W. A Variable Step Size for Maximum Correntropy Criterion Algorithm with Improved Variable Kernel Width. IEEE Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2020, 15, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, T.; Song, A.; Tang, H. A novel correntropy based DOA estimation algorithm in impulsive noise environments. Signal Process. 2014, 104, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Qiu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, L. Cyclic correntropy and its spectrum in frequency estimation in the presence of impulsive noise. Signal Process. 2016, 120, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guan, S. Correntropy-based DOA estimation algorithm under impulsive noise environments. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2020, 2020, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qiu, T.; Luan, S.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, J. An Improved Toeplitz Approximation Method for Coherent DOA Estimation in Impulsive Noise Environments. Entropy 2023, 25, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Feng, D.Z.; Chen, M.H.; Su, T.T.; Zhang, X.J. A robust direction-of-arrival estimation method for impulsive noise environments. Signal Process. 2023, 212, 109175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Qiu, T.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Li, R. Robust fractional lower order correntropy algorithm for DOA estimation in impulsive noise environments. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2021, 104, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Lu, N.; Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Qin, J. Mixture correntropy for robust learning. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 79, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Tian, Q.; Luo, Y. DOA estimation based on a deep neural network under impulsive noise. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Dogancay, K.; Yu, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Z. Robust Adaptive Filtering Algorithm Based on Maximum Correntropy Criteria for Censored Regression. Signal Process. 2019, 160, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Principe, J.C. Maximum Correntropy Estimation Is a Smoothed MAP Estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2012, 19, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.J.; So, H.C.; Huang, L. p-MUSIC: Robust directionof-arrival estimator for impulsive noise environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process 2013, 61, 4296–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).