High-Speed Tracking Controller for Stable Power Control in Discontinuous Charging Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Transient High-Speed Controller
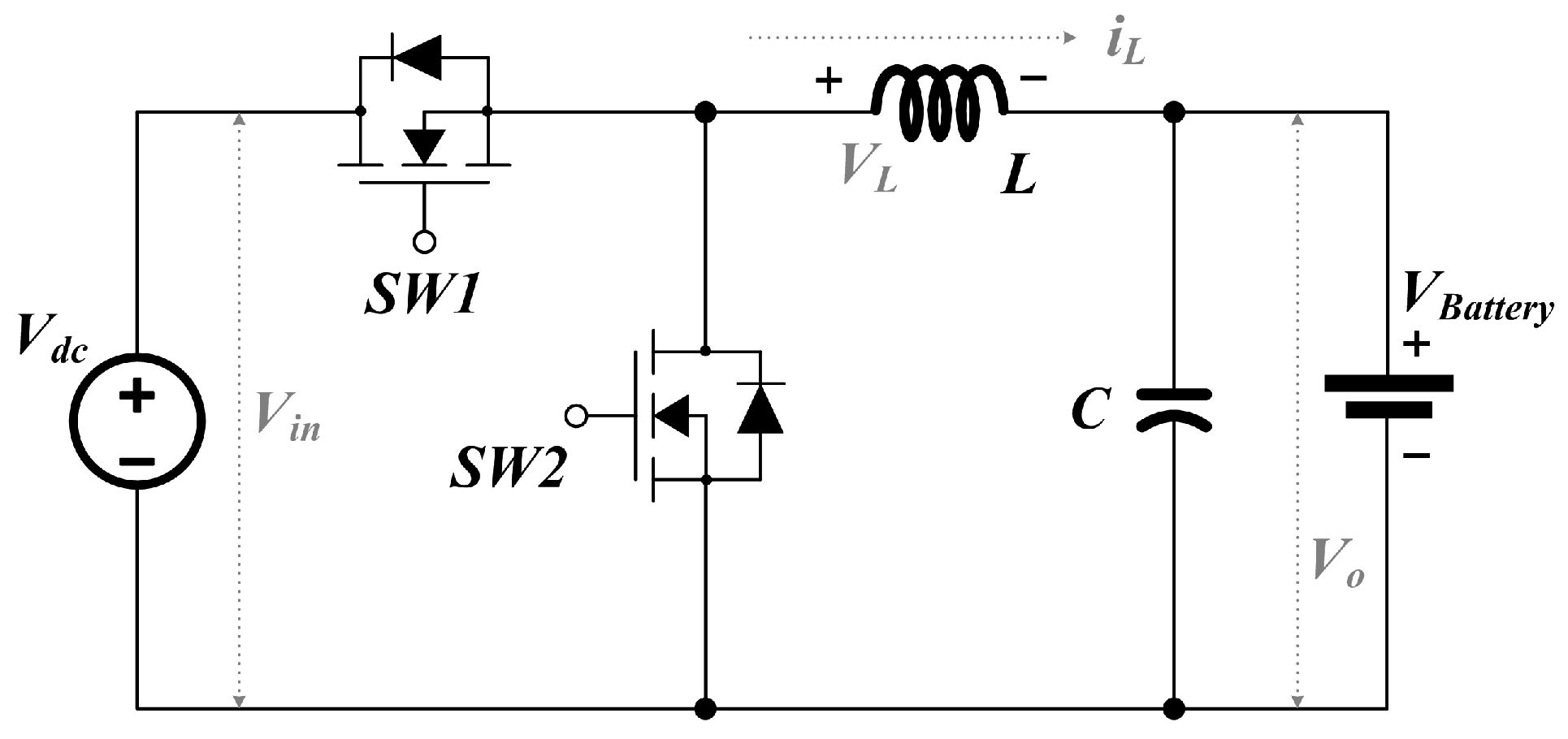
2.1. Analysis of the Synchronous Buck Converter for Charging
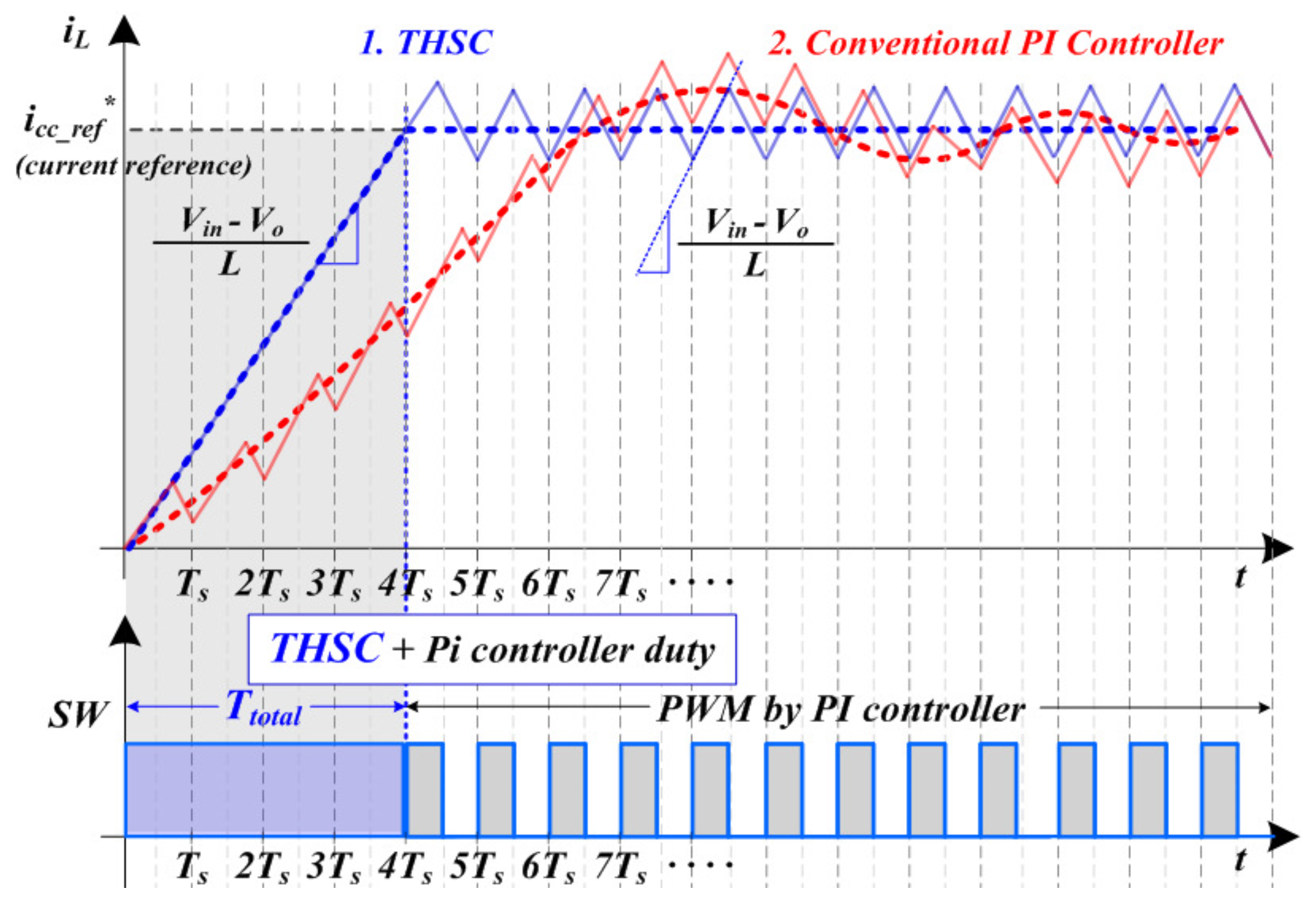
2.2. Transient High-Speed Current Controller Operation Concept
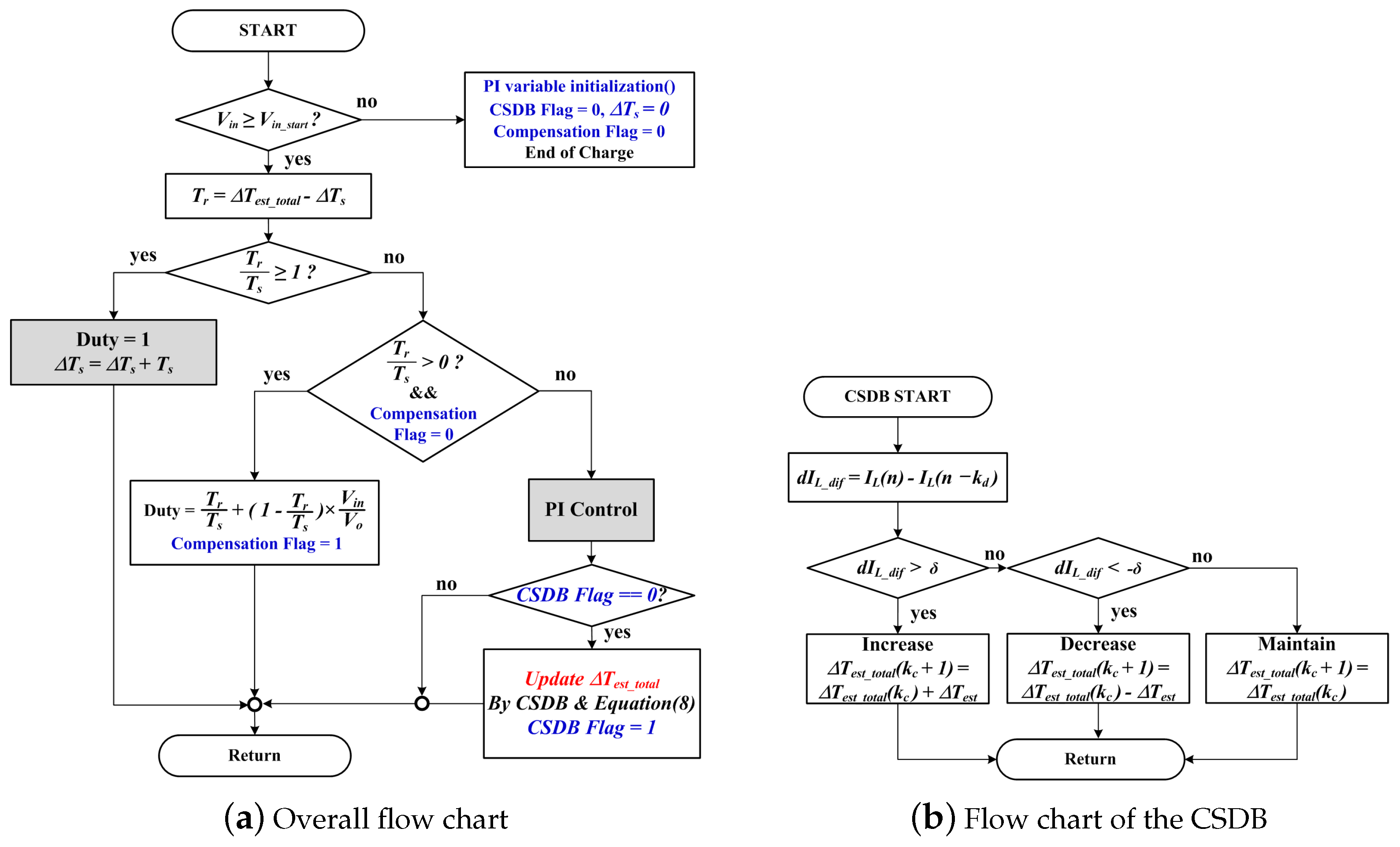
3. Proposed Control Method
Transient High-Speed Tracking Current Controller
4. Simulation and Experiment
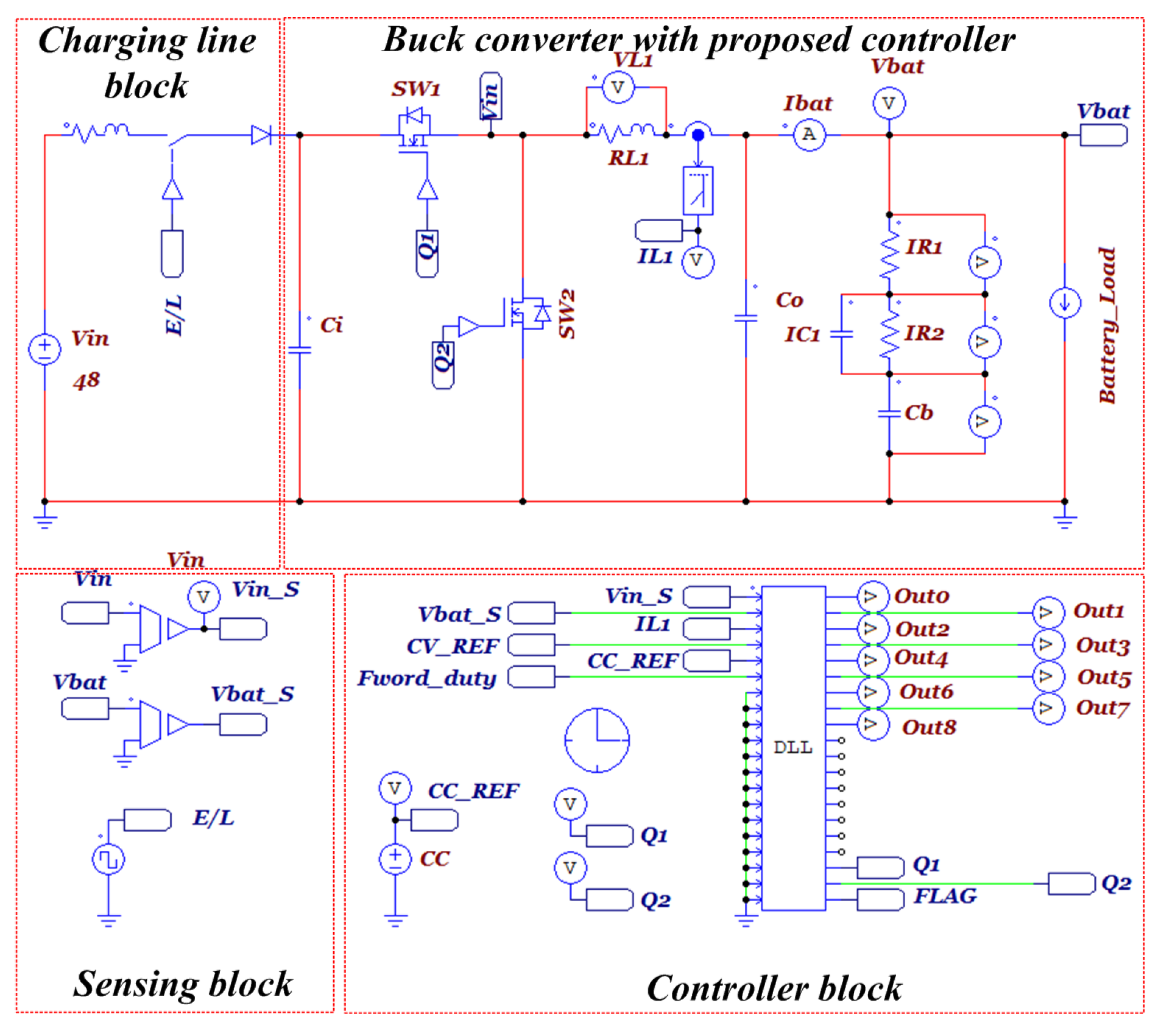
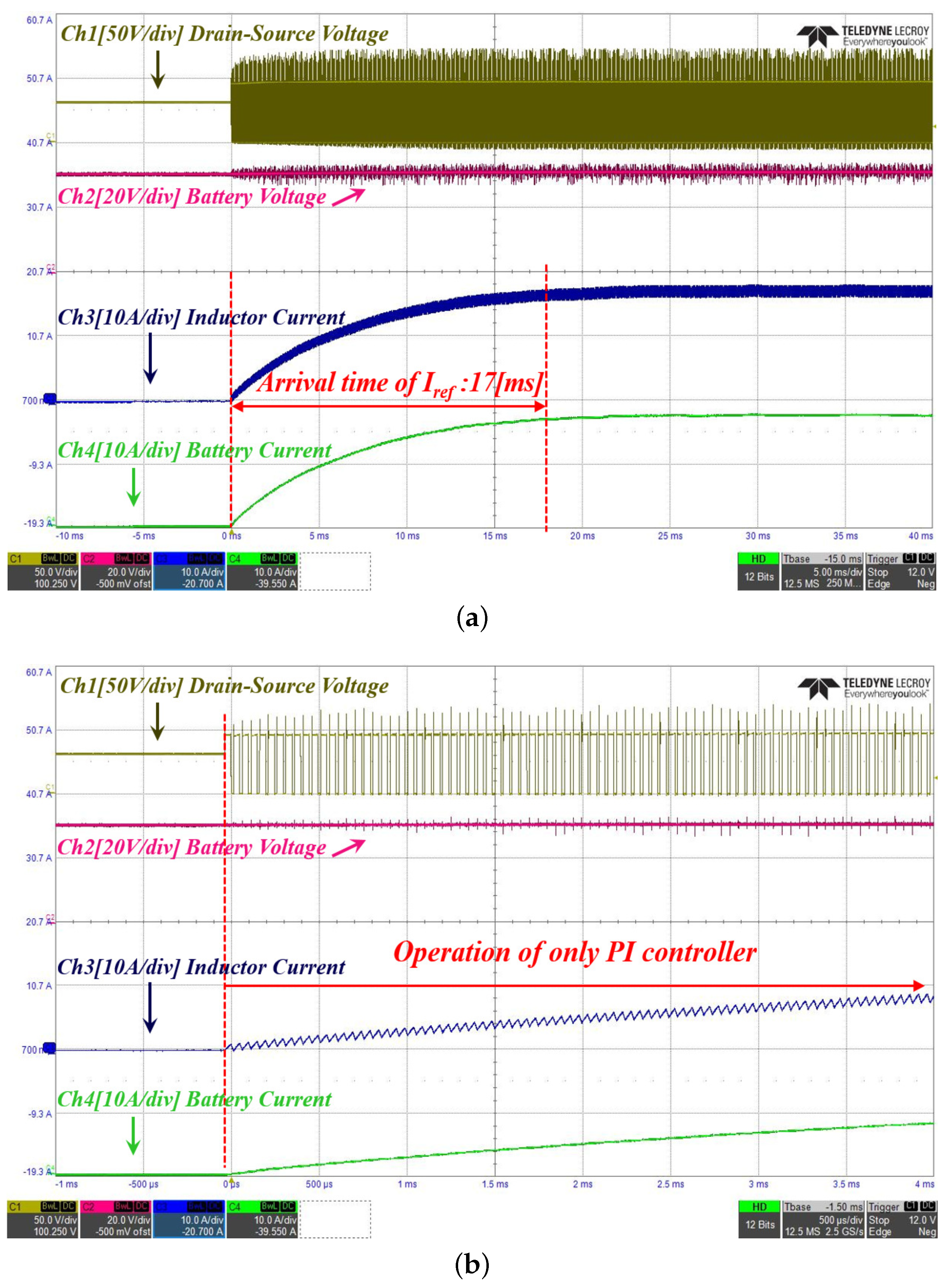
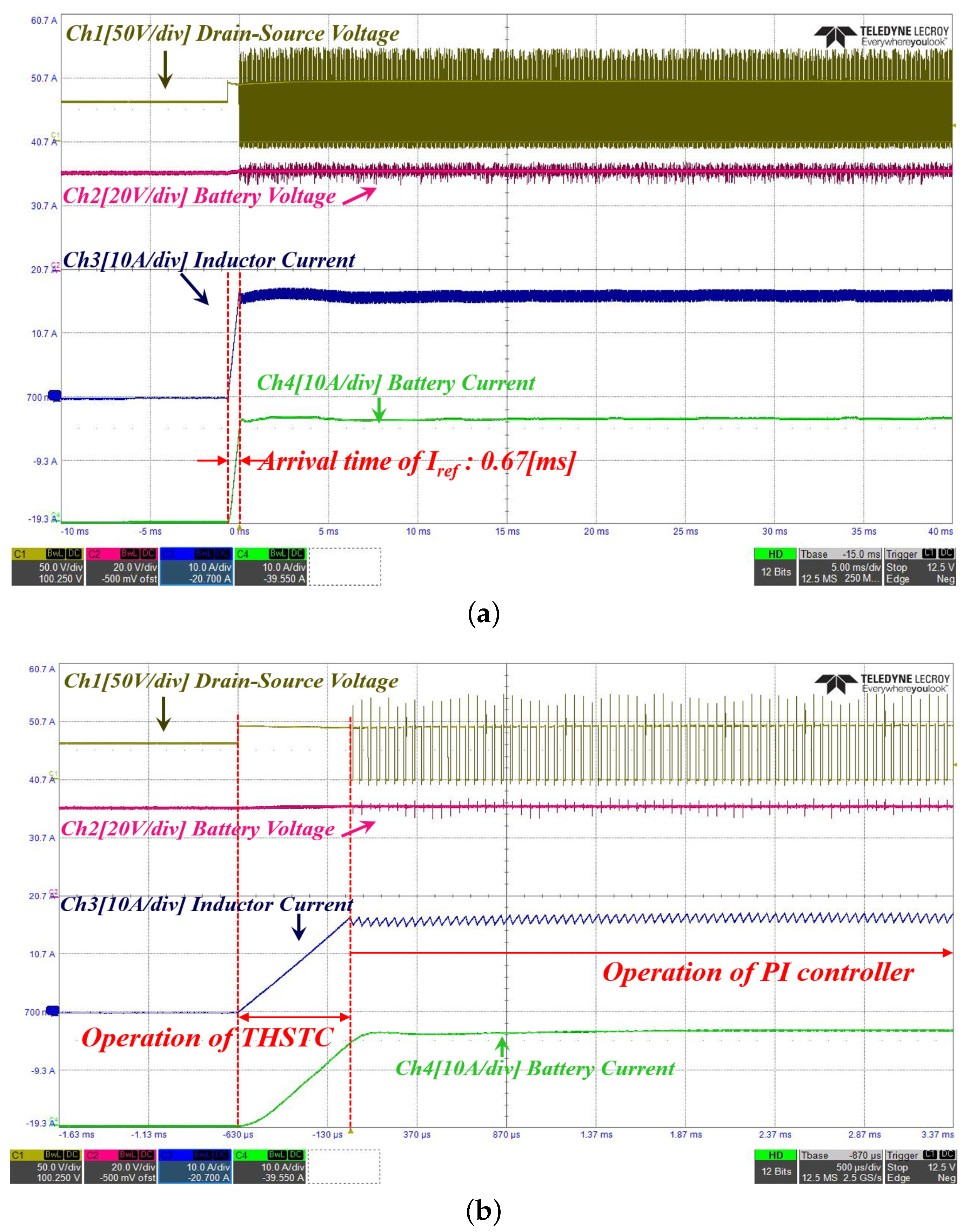
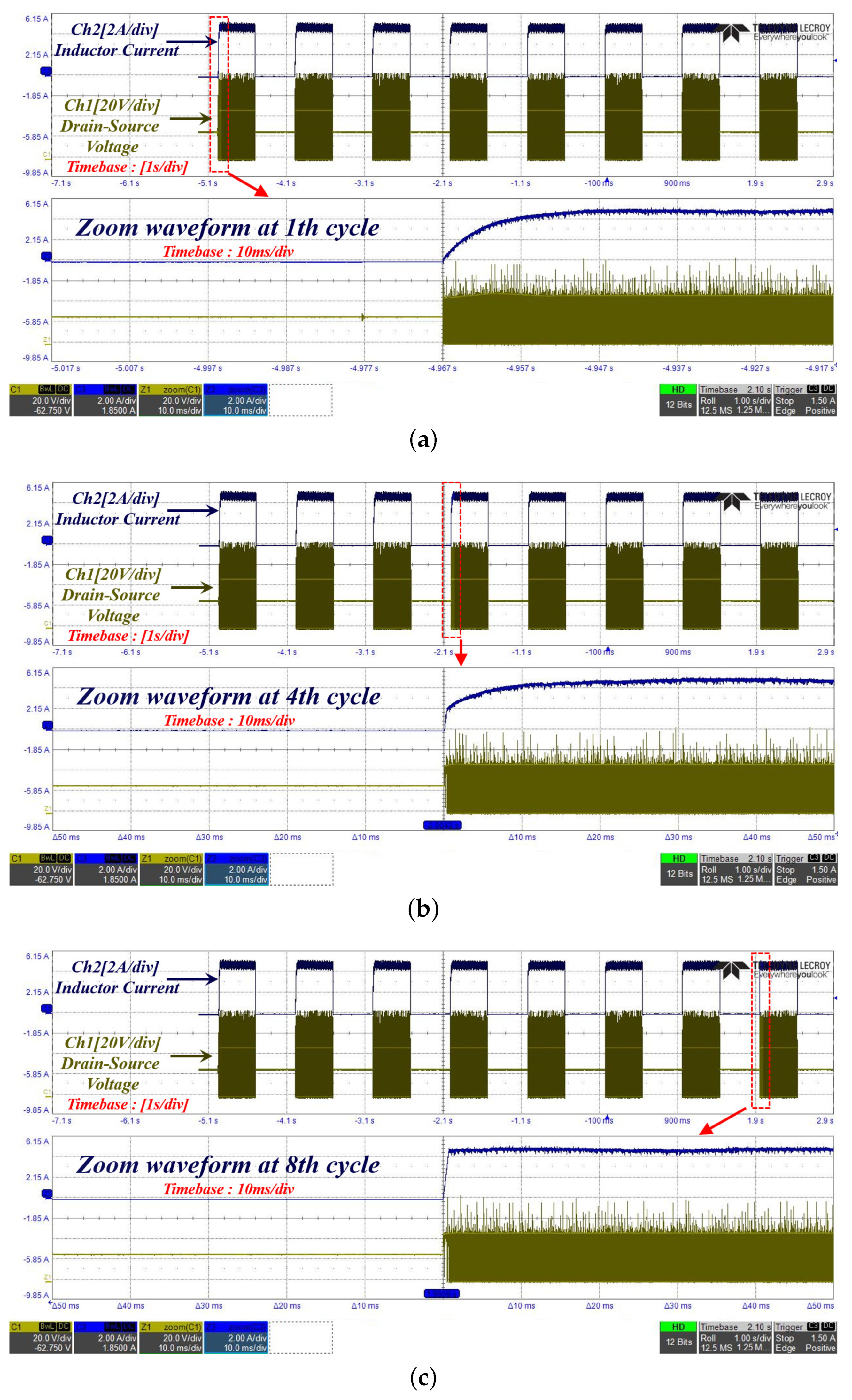
4.1. Simulation
4.2. Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| THSC | transient high-speed current controller |
| THSTC | transient high-speed tacking current controller |
| the target arrival time by calculating in THSC | |
| CSDB | current slope determination block |
| the target arrival time by CSDB in THSTC | |
| variable for increasing or decreasing | |
| the remaining operation time of the THSTC block | |
| control time (equal to sampling time) | |
| increases by every control cycle while the THSTC block is maintained | |
| the slope of the inductor current | |
| the current charging time point | |
| small positive value |
References
- Lau, K.K.L.; Chung, S.C.; Ren, C. Outdoor thermal comfort in different urban settings of sub-tropical high-density cities: An approach of adopting local climate zone (LCZ) classification. Build. Environ. 2019, 154, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Yin, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W. Examining the associations between urban built environment and noise pollution in high-density high-rise urban areas: A case study in Wuhan, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Lin, P.; Lau, S.S.Y.; Song, D. Influence of site and tower types on urban natural ventilation performance in high-rise high-density urban environment. Build. Environ. 2020, 179, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, I.L.R.; Mangera, M.; Parshotam, D.S.; Panday, A.; Pedro, J.O. Genetic algorithm based design of pid and pdf controllers for velocity tracking of a high-rise building elevator. In Proceedings of the 2018 SICE International Symposium on Control Systems (SICE ISCS), Tokyo, Japan, 9–11 March 2018; pp. 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; He, Q.; Liu, L. Variable universe fuzzy control of high-speed elevator horizontal vibration based on firefly algorithm and backpropagation fuzzy neural network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 57020–57032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Xu, P.; Yuan, H.; Ma, H.; Xue, J.; He, Z.; Li, S. Analysis of vibration monitoring data of flexible suspension lifting structure based on time-varying theory. Sensors 2020, 20, 6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kodmany, K. Elevator technology improvements: A snapshot. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 530–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, C.; Copaci, D.; Arias, J.; Moreno, L.; Blanco, D. Hoist-based shape memory alloy actuator with multiple wires for high-displacement applications. Actuators 2023, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; He, C.; Yi, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Zhang, L. Energy-based vibration modeling and solution of high-speed elevators considering the multi-direction coupling property. Energies 2020, 13, 4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Jiang, A.; Yuan, H.; Huang, G.; He, S.; Li, S. Study on theoretical model and test method of vertical vibration of elevator traction system. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8518024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, B.; Li, C.; Xu, D. Weight-transducerless control strategy based on active disturbance rejection theory for gearless elevator drives. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.H.; Hou, T.; Zhang, R.J. Dynamic analysis of high-speed traction elevator and traction car–rope time-varying system. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2019, 50, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hou, T.; Zhang, R.J.; Liu, J. Time-varying characteristics of the longitudinal vibration of a high-speed traction elevator lifting system. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 2019, 25, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghelache, G.; Nastac, S. Computational analysis of nonlinearities within dynamics of cable-based driving systems. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 227, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Swaminathan, G.; Loganathan, G.B. Design and analysis of composite belt for high rise elevators. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Quan, Z.; Li, Y.W.; Quan, L.; Hao, Y.; Ding, L. A hybrid driven elevator system with energy regeneration and safety enhancement. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 7715–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermani, M.; Shirdare, E.; Abbasi, S.; Parise, G.; Martirano, L. Elevator regenerative energy applications with ultracapacitor and battery energy storage systems in complex buildings. Energies 2021, 14, 3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, N.; Mademlis, C. Supercapacitor-based energy recovery system with improved power control and energy management for elevator applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 9389–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yang, G.; Liu, W.; Prapamonthon, P. Analysis of aerodynamic noise characteristics of high-speed train pantograph with different installation bases. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariscotti, A.; Sandrolini, L. Detection of harmonic overvoltage and resonance in AC railways using measured pantograph electrical quantities. Energies 2021, 14, 5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviraj, V.S.C.; Sen, P.C. Comparative study of proportional-integral, sliding mode, and fuzzy logic controllers for power converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1997, 33, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Sun, L.; Lee, K.Y. Disturbance rejection control of a fuel cell power plant in a grid-connected system. Control Eng. Pract. 2017, 60, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhejji, A.; Mosaad, M.I. Performance enhancement of grid-connected PV systems using adaptive reference PI controller. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, S.; Bayat, F.; Lai, C.C.; Taheri, A.; Fekih, A. Adaptive global sliding mode controller design for perturbed DC-DC buck converters. Energies 2021, 14, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Cruzado-Alba, J.; Villegas-Núñez, J.; Vite-Frías, J.A.; Carrasco Solís, J.M. Adaptive global sliding mode controller design for perturbed DC-DC buck converters. Energies 2015, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibian, S.; Jin, H. High performance predictive dead-beat digital controller for DC power supplies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2002, 17, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.; Figueroa, M.; Pérez Cruz, J.H.; Yoe Rumbo, J. Control para estabilizar y atenuar las perturbaciones en un péndulo invertido rotatorio. Rev. Mex. Física 2012, 58, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sorcia-Vázquez, F.D.J.; Garcia-Beltran, C.D.; Valencia-Palomo, G.; Brizuela-Mendoza, J.A.; Rumbo-Morales, J.Y. Decentralized robust tube-based model predictive control: Application to a four-tank-system. Rev. Mex. Ing. Química 2020, 19, 1135–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lim, S.K. High-Speed Controller to Enhance Responsiveness and Stability of Dynamic Characteristics for DC-DC Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 3996–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Hang, L. A novel interleaved parallel cascaded three-level pfc with low inductance volt-second and low common-mode noise. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 38, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, K.; Lu, L.; Wang, S.; Ouyang, M. A constant current control method with improved dynamic performance for cllc converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 1509–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, N.; Hu, J.; Mou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.W.; De Doncker, R.W. A simple DC-offset eliminating method of the series-inductance current for the dab DC–DC converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 38, 4224–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.-D.; Seok, J.; Kong, B.-S. A fast response pwm buck converter with active ramp tracking control in a load transient period. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 66, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Hwang, Y.S.; Jiang, W.M.; Lai, C.H.; Ku, J. A new improved ultra-fast-response low-transient-voltage buck converter with transient-acceleration loops and V-cubic techniques. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 3601–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanarates, C.; Zhou, Z. Design and cascade pi controller-based robust model reference adaptive control of DC-DC boost converter. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 44909–44922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zha, X.; Li, X.; Huang, M.; Sun, J. An improved equal area criterion for transient stability analysis of converter-based microgrid considering nonlinear damping effect. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 11272–11284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pei, Y.; Yang, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z. Improving light and intermediate load efficiencies of buck converters with planar nonlinear inductors and variable on time control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 27, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromauro, R.A.; Liserre, M.; Dell’Aquila, A. Study of the effects of inductor nonlinear behavior on the performance of current controllers for single-phase PV grid converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






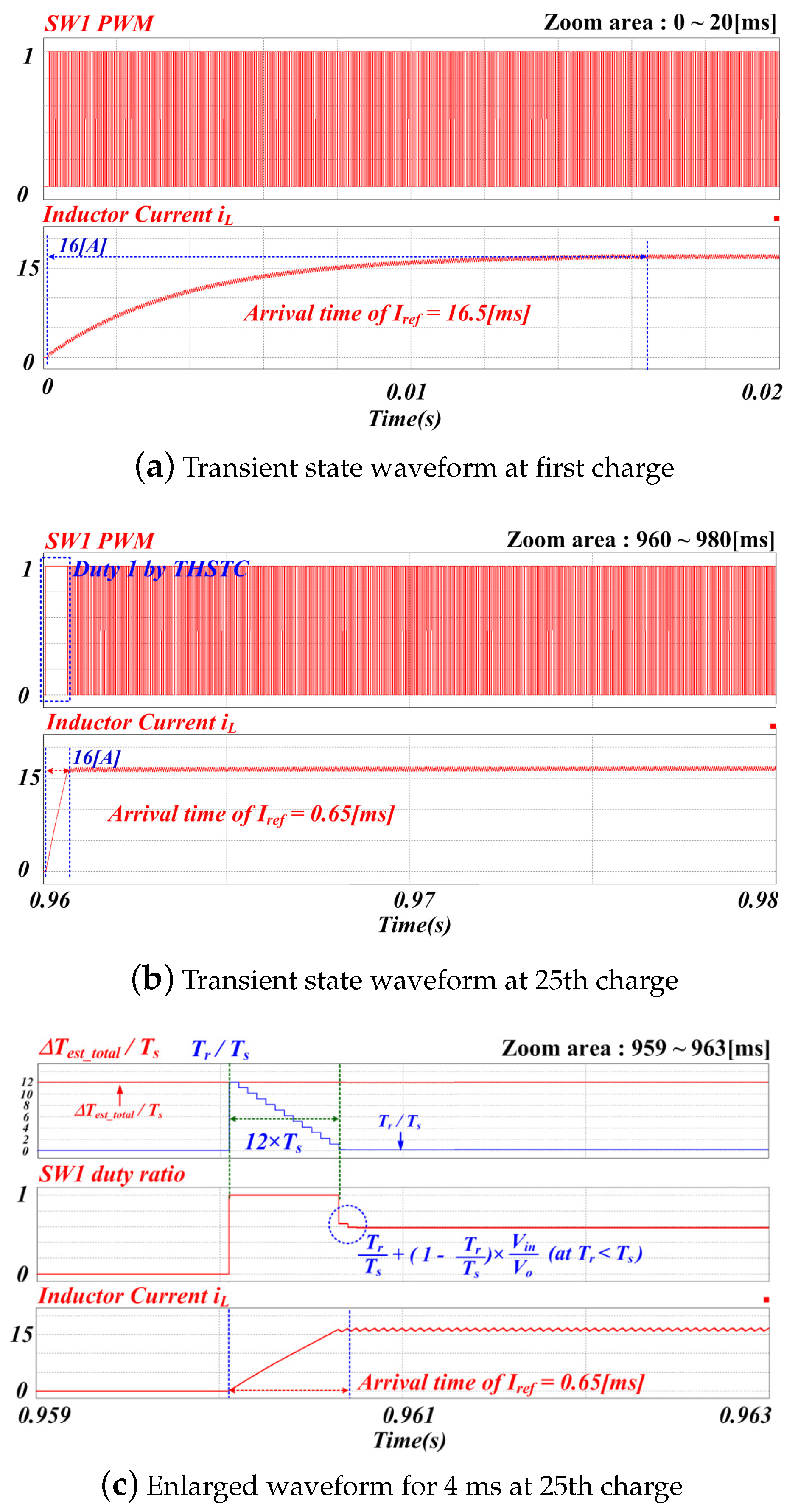
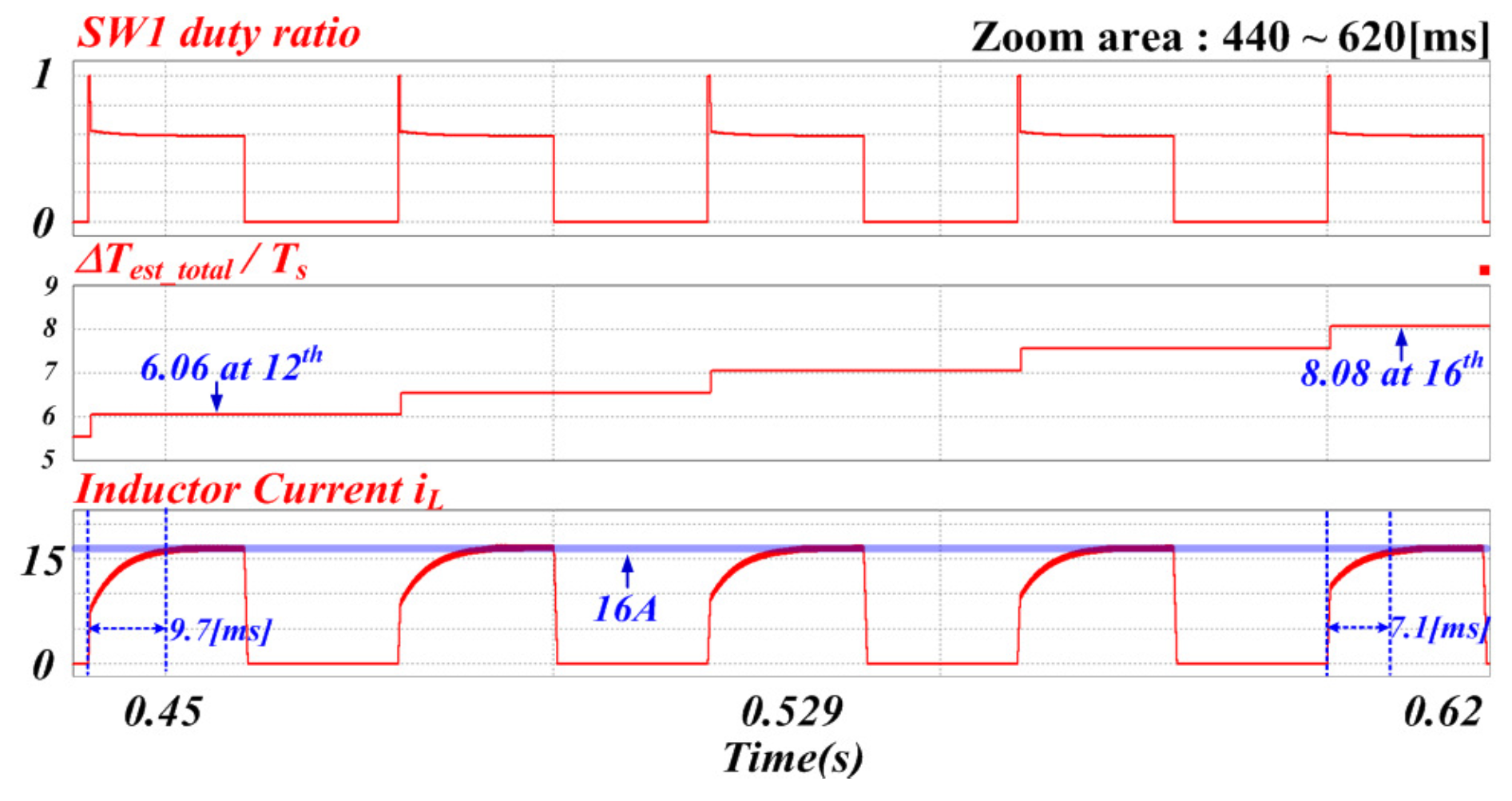
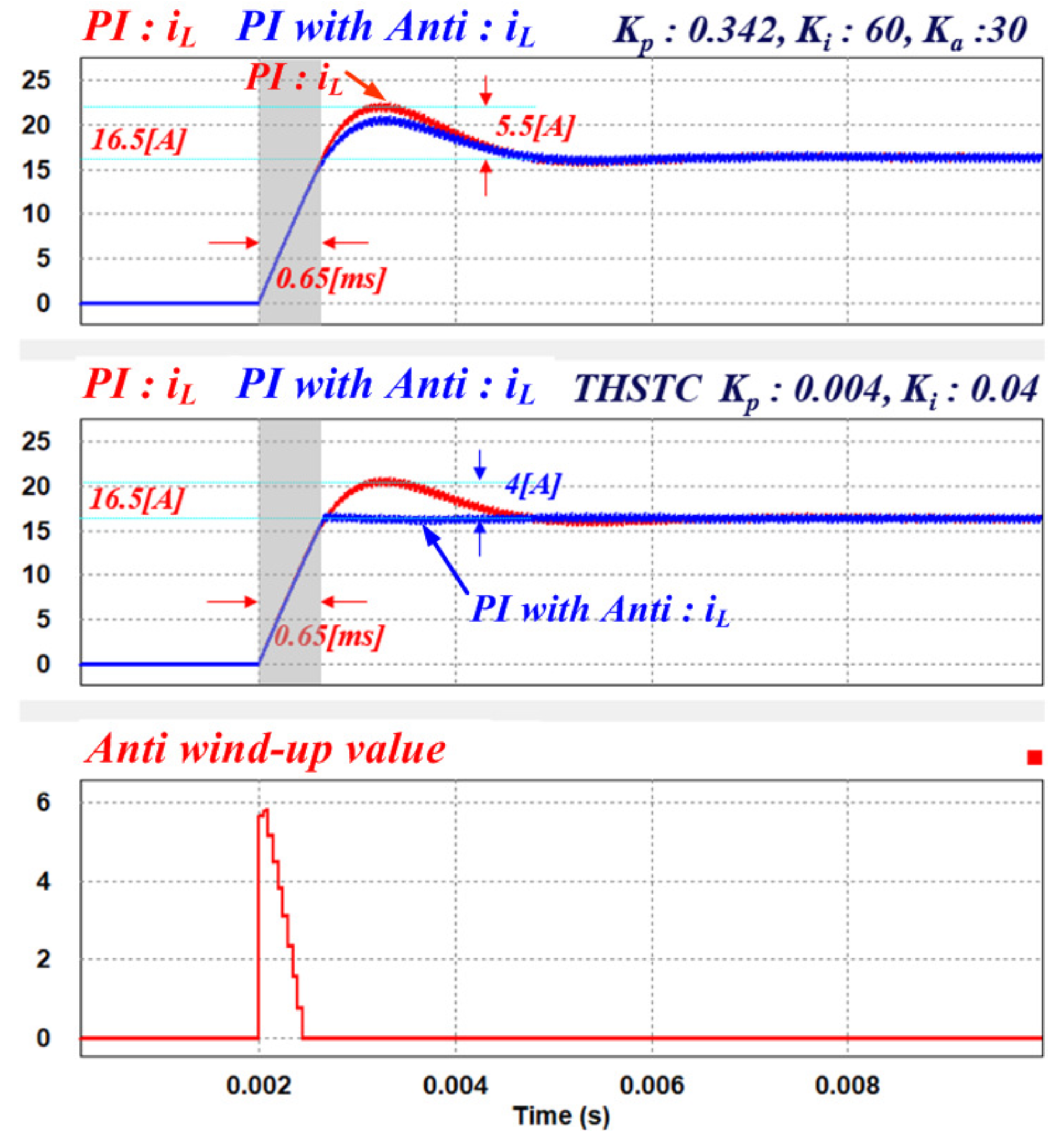

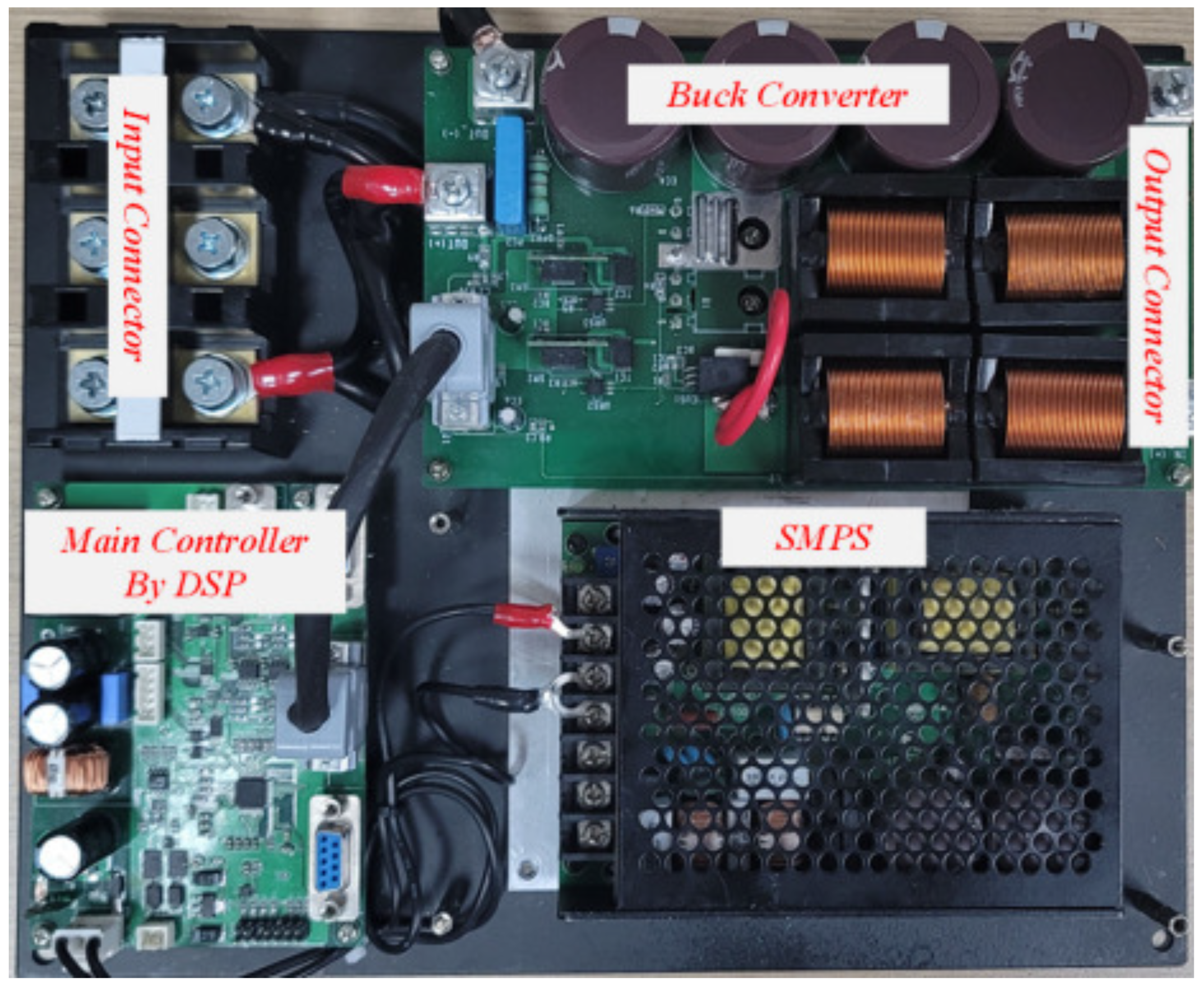
| Note | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Buck converter input voltage | 48 V | |
| Battery voltage | 28 V | |
| Current command value | 16 A | |
| Inductor’s inductance | L | 760 μH |
| Switching frequency | 20 kHz | |
| System proportional gain | 0.004 | |
| System integral gain | 0.04 | |
| Charging cycle | 20 ms |
| Note | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Buck converter input voltage | 48 V | |
| Battery voltage | 27 to 29 V | |
| Current command value | 5 to 16.5 A | |
| Inductor’s inductance | L | 760 μH |
| Switching frequency | 20 kHz | |
| System proportional gain | 0.001 | |
| System integral gain | 0.02 | |
| Charging cycle | 500 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, S.-K.; Park, J.-H.; Jun, H.-S.; Hwang, K.-B.; Hwangbo, C.; Lee, J.-H. High-Speed Tracking Controller for Stable Power Control in Discontinuous Charging Systems. Electronics 2024, 13, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13010183
Lim S-K, Park J-H, Jun H-S, Hwang K-B, Hwangbo C, Lee J-H. High-Speed Tracking Controller for Stable Power Control in Discontinuous Charging Systems. Electronics. 2024; 13(1):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13010183
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Sang-Kil, Jin-Hyun Park, Hyang-Sig Jun, Kwang-Bok Hwang, Chan Hwangbo, and Jung-Hwan Lee. 2024. "High-Speed Tracking Controller for Stable Power Control in Discontinuous Charging Systems" Electronics 13, no. 1: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13010183
APA StyleLim, S.-K., Park, J.-H., Jun, H.-S., Hwang, K.-B., Hwangbo, C., & Lee, J.-H. (2024). High-Speed Tracking Controller for Stable Power Control in Discontinuous Charging Systems. Electronics, 13(1), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13010183






