Abstract
Multi-hop knowledge graph question answer (KGQA) is a challenging task because it requires reasoning over multiple edges of the knowledge graph (KG) to arrive at the right answer. However, KGs are often incomplete with many missing links, posing additional challenges for multi-hop KGQA. Recent research on multi-hop KGQA attempted to deal with KG sparsity with relevant external texts. In our work, we propose a multi-hop KGQA model based on relation knowledge enhancement (RKE-KGQA), which fuses both label and text relations through global attention for relation knowledge augmentation. It is well known that the relation between entities can be represented by labels in the knowledge graph or texts in the text corpus, and multi-hop KGQA needs to jump across different entities through relations. First, we assign an activation probability to each entity, then calculate a score for the enhancement relation, and then transfer the score through the activated relations and, finally, obtain the answer. We carry out extensive experiments on three datasets and demonstrate that RKE-KGQA achieves the outperformance result.
1. Introduction
Intelligent question answering plays a central role in artificial intelligence. It requires that machines understand free-form questions and infer the answers by analyzing information from a large corpus or structured knowledge base [1]. Along with the fast development of deep learning, especially pretraining technology, the state-of-the-art (SOTA) models have been shown comparatively with human performance on simple questions that only need a single hop, which just needs one relation or triple to reason the question. For simple questions whose answers can be achieved directly from the text, the pre-trained models have performed as well as humans [2]. However, multi-hop KGQA, which requires reasoning with the relations among the entities across several steps, is far from being resolved.
Recent research on multi-hop KGQA has attempted to handle KG sparsity using relevant external text. Existing models usually infer the answer by predicting the sequential relation path or embedding the KG elements to the hidden features [3]. Sun et al. [4] proposed the GraftNet model aimed at combining the text and the knowledge graph. The model can extract containing text and KG entities through an early fusion strategy, then extract answers from a question subgraph containing relevant KG facts and text sentences. Early fusion allows more flexibility in combining information from multiple sources [5]. Sun et al. [6] proposed the PullNet model, an integrated framework for retrieving information from a knowledge base or text corpus and reasoning about this heterogeneous information to find the best answer. PullNet uses an iterative process to construct a question-specific subgraph that contains information relevant to the question. In each iteration, the model constructs a heterogeneous subgraph starting from the question and the topic entities. Each iteration calculates the probability of expansion for each node based on the graph convolutional networks (GCN) and selects the k nodes that are greater than a threshold value for expansion. Then, for the selected k nodes, along with the associated documents, entities, and triples, they are updated to the constructed subgraph, the nodes are learned using GCN, and then the answers are classified. However, these GCN-based methods are usually weak in terms of interpretability because neural network models are mostly black-box, and it is difficult to evolve interpretable inference paths.
A KG is known to be helpful for the KGQA since it provides well-structured relational information and allows one to further infer indirect entities. However, it is challenging to build question answer (QA) systems that can reason over knowledge graphs based on question-answer pairs alone [7]. First, question parsing is polysemous, and it is nontrivial for the QA system to match those referred entities to the knowledge graph. Furthermore, many questions require multi-hop logic reasoning over the knowledge graph to retrieve the answers [8]. Our study is based on a large but incomplete knowledge graph and a text corpus to study the problem of multi-hop KGQA. Large knowledge graphs cannot store all the knowledge completely, so knowledge graphs are often incomplete. Generally, the corpora can store knowledge more completely but are not as structured as the knowledge graphs. Augmenting external corpus knowledge into knowledge graphs can largely compensate for the lack of knowledge graphs [9]. In addition, how to effectively fuse the external relational corpus with the structured information of the knowledge graph has been a pressing problem to be solved.
The knowledge graph consists of entities and the relations between them. The relations can be represented in two forms, as shown in Figure 1.
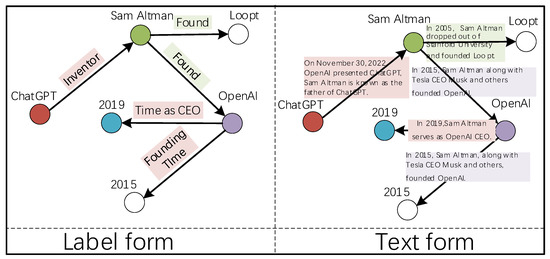
Figure 1.
Label form and text form structure diagram.
In the label form, i.e., knowledge graph, the relations are manually defined, constrained predicates. In the text form, the relations are free texts retrieved from a textual corpus. We can obtain relational text by extracting sentences that co-occur between two entities. Recent models, such as TransferNet [10], support both label and text relations in a unified framework. However, TransferNet only accomplishes the modeling of the label and textual relations separately, while not augmenting the label and text relations. We propose the RKE-KGQA model, which can jointly model the combination of knowledge base and entity-linked text and augment the graphical and textual relations through the relational tree structure to achieve complex multi-hop KGQA. The main contributions of this paper can be summarized as follows:
- We propose a tree structure to fuse relation structures in label form and text form to achieve relation knowledge enhancement.
- We propose an encoding approach that fuses global attention and soft location encoding to obtain the weight information of the relation tree structure.
- We propose a pre-trained model to solve the challenge of the model processing long text, especially for the problem of missing links, and the incorporation of text corpus can make the cross-hop semantic association between multi-hop KGQA possible.
The model is validated on three commonly used datasets and outperforms the models based on pure knowledge graph and pure text corpus and performs better than similar models.
2. Related Work
Instead of a simple single-hop QA, complex multi-hop KGQA requires multi-hop reasoning to obtain the answer. There are two main strands of existing approaches to multi-hop QA. The first is to predict the sequential relation path in a weakly supervised setting, that is, to learn the intermediate route only based on the final answer [11]. Due to the high cost of data annotation, it is impractical to show how to answer a complex question step by step. These works suffer from convergence issues due to the massive search space, which heavily hinders their performance.
Cohen et al. [12] modeled the knowledge graph as a sparse matrix, constructed the entity as a distribution on the graph, constructed the relation as a matrix, and inferenced along the relationship. The inference process is the distribution vector multiplied by the relation matrix, which is a kind of random walk on the graph.
Feng et al. [13] proposed a novel knowledge-aware approach that equips pre-trained language models with a multi-hop relational reasoning module. It performs multi-hop, multi-relational reasoning over subgraphs extracted from external knowledge graphs. The proposed reasoning module unifies path-based reasoning methods and graph neural networks to achieve better interpretability and scalability.
Zhou et al. [14] presented the interpretable reasoning network (INR). The INR model utilizes an interpretable, hop-by-hop reasoning process to answer the question. The model dynamically decides which part of the input question should be analyzed at each hop and predicts a relation corresponding to the current parsed results. Finally, it utilizes the predicted relation to update the question representation and the state of the reasoning process and then drives the next-hop reasoning.
Zhang et al. [15] presented the variational reasoning network (VRN). The VRN model learns the inference path by reinforcement learning, and its intermediate results have good interpretability. The VRN is an end-to-end variational learning algorithm that can handle the noise in question and learn multi-hop reasoning simultaneously. The VRN includes a topic entity recognition module and a KG logic reasoning module. For the topic entity recognition module, the compatibility of the entity with the problem is modeled as a probabilistic model to calculate the probability that the topic entity is mentioned in the question. For the KG logic reasoning module, the algorithm learns the reasoning rule for the question. Since there are no annotations for such a reasoning step, the QA system has to learn it from the question-answer pair.
Qiu et al. [16] presented the stepwise reasoning network (SRN). The SRN model improves the VRN by a beam search and reward shaping strategy, boosting its speed and performance. The SRN model formulates multi-relation question answering as a sequential decision problem. It performs an effective path search over the knowledge graph to obtain the answer and leverages the beam search to reduce the number of candidates significantly. Meanwhile, the potential-based reward shaping strategy can alleviate the delayed and sparse reward problem caused by weak supervision.
The second strand is to use graph neural networks. They can handle the two relation forms and achieve better performance. The EmbedKGQA model [17] uses the ComplEx model [18] to embed entities and relations in the KG into the complex vector space, obtains their combined scores, and predicts the answers by the calculation of the complex vectors. Specifically, for a natural language question , it encodes the initial embedding representation with the Roberta [19] model and then projects the vector representation into the complex embedded vector space with a feedforward neural network. The training data are the triple structure consisting of the question , its subject entity , and any entity . If is the target answer entity of , then is considered a positive sample and makes , otherwise, is considered a negative sample and makes . The embedding KGQA model uses the positive and negative samples as training data to learn the embedding vector representations of questions and entities and selects the entity with the highest score as the possible target answer.
Jin et al. [20] proposed a novel approach, namely relational chain-based embedded KGQA, which can simultaneously take advantage of the knowledge graph embedding and train with weak supervision by predicting the intermediate relational chain implied in KG to perform the multi-hop KGQA task. The module can address the incompleteness problem brought by the missing links in the incomplete knowledge graph thanks to its capability of capturing implicit KG relations.
He et al. [21] proposed an innovative teacher-student model. The main student network aims to learn how to reason out the answer to a question, while the teacher network improves the reasoning ability of the student network by learning intermediate state supervision information. The major novelty lies in the design of the teacher network, where the model utilizes both forward and backward reasoning to enhance the learning of intermediate entity distributions. By considering bidirectional inference, the teacher network can generate more reliable intermediate supervision signals, which can alleviate the issue of spurious reasoning. The authors argued that multi-hop KGQA inference algorithms that only receive feedback from the final answer can make learning unstable or ineffective and that supervised signals during learning inference are important.
Miller et al. [22] used the key-value memory to store knowledge and conduct multi-hop reasoning by iteratively reading the memory. The KVMemNN model completes the architecture through a combination of memory, input, output, response, and generalization modules. The memory module stores KG triples; the input module can preprocess external inputs, including KG triples and the preprocessing of natural language problems; the output module selects the memory in the memory module; the response module outputs the final result in the corresponding format from the memories provided by the output module; and the generalization module imports external knowledge to update the contents of the memory module.
The current mainstream approach of multi-hop KGQA is to combine structured knowledge graphs and textual knowledge to complete the task. The current mainstream approaches have early fusion and late fusion models, and the former is currently superior to the latter [10]. At the same time, multi-hop KGQA is mostly weakly supervised, and most of the current large-scale datasets are labeled final answers rather than tagged inference paths. In the existing stepwise inference paths, each triple in the text is split into independent choices to calculate the score, and then the optimal path with the highest score is found from the model, but the highest score of a single hop does not reflect the score of the whole route. Our proposed model can integrate the overall score of each link to obtain the best answer.
3. Models and Methods
Multi-hop relational reasoning takes entities as nodes and the relationships or attributes between entities as edges. The relations between entities can be in multiple forms, i.e., either in the form of structured labels, i.e., predicates or attributes, or in the form of free text. The former, i.e., structured knowledge graphs, and the latter are extracted from a large-scale text corpus based on the reproducibility of subject entities. Figure 2 shows a sample of these two forms. We call them the labeled form and text form from left to right, respectively, and we propose a hybrid form that uses knowledge enhancement relation as a relation between entities for multi-hop link inference.
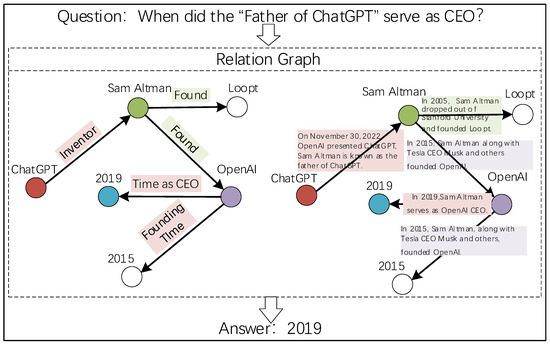
Figure 2.
Multi-hop reasoning relation diagram. The relation has label form and text form.
We propose a multi-hop KGQA model based on relation knowledge enhancement. The model divides into a knowledge aggregation layer, an encoding layer, a text interaction layer, and a multi-hop reasoning layer. Its model structure diagram is shown in Figure 3. Firstly, we obtain the subject entity of the question, retrieve the related entity triples from the knowledge graph, and send them to the knowledge aggregation layer, which uses a tree structure to concatenate the triples on the relational text to enhance the relation; the coding layer uses soft-location coding to encode the knowledge of the aggregated relation tree structure and the text enhanced by relation knowledge through global attention for feature extraction. The hidden layer features of relation knowledge enhancement are obtained and interacted with the hidden layer of the question. Then a relation probability score is obtained by combining the feature vector with the Sigmoid function. In the multi-hop reasoning layer, the distribution of the entity scores in each hop is dotted with the probability distribution of each relation edge to obtain the score distribution of the relevant entity in the next hop. Finally, we obtain the answer to the question after several iterative hops.
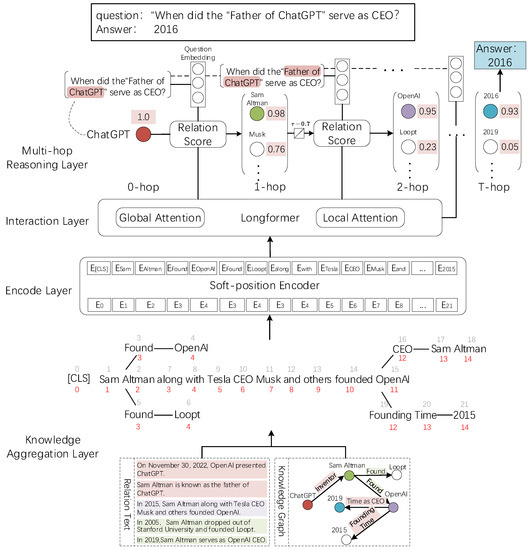
Figure 3.
RKE-KGQA model structure diagram. The diagram has a knowledge aggregation layer, an encoding layer, a text interaction layer, and a multi-hop reasoning layer.
We use to represent the knowledge graph, whose entity nodes are , and the relation between the entities is . represents the number of entities, is a matrix whose elements represent the relation or attribute value between the head entity and the tail entity . can be viewed as a series of label sets, text sets, or a hybrid form of label and text. Complex multi-hop problems usually start from the subject entity and reach the answer entity by traversing the relation.
3.1. Knowledge Aggregation Layer
A relation in a knowledge graph can be represented in two forms. The labeled form has the form of constraint predicates defined between entities. The set of relation predicates between entities in the graph is . Suppose denotes the maximum number of relations between a pair of entities, then the relation can be represented as . The text form takes the form of a free text retrieved from a text corpus, and suppose denotes the length of the text corpus, then the natural language description of the relation is . represents the k-th relation word in the text relation. Our model adopts a tree-structure approach for relation knowledge aggregation, and the textual relation exists in the form of a natural language description by extracting the co-occurring sentences of a pair of entities [23]. The natural language description of the relation knowledge tree enhancement is . represents the -th character of the relation text . For the related entities in the text relationship, their related triples are spliced to the last word of the entity [24]. Instead of augmenting the knowledge of all the entities in the text of the relationship, this process selects only the subject entities appearing in the question and the associated entities in the jump. The purpose is to enhance the relevant text knowledge of the subject entities of the question because not all the contents contribute to answering the question, so the model only enhances the external knowledge of the entities appearing in the question to speed up the processing and save space. Through knowledge aggregation, the text relations transform into a tree text structure, which better reflects the existing hidden relations between the entities. The tree structure enhances the knowledge by fusing the triple knowledge and the text relations, and its tree structure is shown in Figure 4.
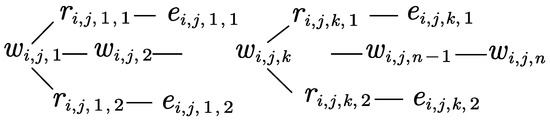
Figure 4.
Knowledge aggregation tree structure diagram.
As shown in Figure 5, the tree structure model obtains the information that Sam Altman founded OpenAI, became the CEO of OpenAI, and can even further infer the time. It is because the tree structure can obtain the hidden information or weight of a correct inference path through the global attention mechanism.

Figure 5.
Example tree structure diagram. The text relation is the relation tree trunk, Sam Altman and OpenAI are the related entity, and the triple is the relation tree branches.
3.2. Encoding Layer
After knowledge aggregation to obtain an enhanced relation tree structure, the encoding layer needs to encode the relation tree into the sequence structure required for the input of the feature extraction model while retaining its structural information. To maintain the structural information of the relation tree in the sequences, the model uses soft location encoding to preserve its structural information while using global attention to encode the extended entities.
Compared with absolute location coding and relative location coding, soft location coding uses a parallel approach to encode the location information of the tree structure. For the trunk, i.e., the relational text, the absolute position encoding approach is used for sequential encoding, while for the branches, i.e., the enhanced triple knowledge, the sequential encoding continues from its spliced word index, as shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6.
Soft position coding diagram. In the relation tree, the red number is the soft-position index, and the gray is the hard-position index.
The model retains the structure information of the tree well by converting a relation tree into an embedding representation, as shown in Figure 7. For the token embedding, each token in the sentence relation tree is converted to an embedding vector via a trainable lookup table. The tokens in the sentence relation tree require re-arrangement before the embedding operation. The tokens in the branch are inserted after the corresponding node, while subsequent tokens are moved backward. For the soft location embedding, after re-arranging, [Found] and [OpenAI] are inserted between [Altman] and [along], while the subject of [along] is [Altman]. We set the position number of [along] to 3 instead of 7, so when calculating the self-attention score in the encoder, [along] is at the next position of [Altman] by the equivalent. When calculating self-attention, we use masked self-attention so that the tokens [Found] and [Along] are unaffected, both of which have position number 3. For segment embedding, we use segmentation embedding to identify different sentences. Its final encoding is obtained by summing the token embedding, soft location embedding, and segment embedding.
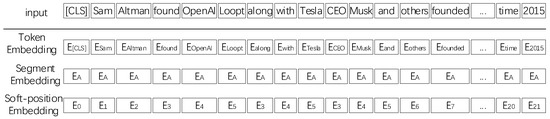
Figure 7.
Embedding representation diagram. The process of converting a relation tree into an embedding representation. For the token embedding, the tokens in the relation tree are flattened into a sequence of token embedding by their hard-position index. The soft-position index is used as position embedding along with the token embedding.
3.3. Interaction Layer
Considering that the enhanced relation tree structure has an impact on the text relations and knowledge graph relations, the model only uses global attention to extract weight information for entity words that have undergone knowledge expansion, i.e., subject entities and associated entities in multi-hop inference, and uses local window self-attention to extract weight information for other contents, which can alleviate the problem of knowledge noise. Global attention will compute the weight vector of the subject entity with all the contexts, while local attention will only compute the weight vector of the word with the contexts within its window size. The extended subject entities are set to global attention because the subject entities and associated entities are cross nodes in the textual relations and knowledge graph, i.e., the word can affect the vector of all the words and its vector will be affected by all the words, while the other contents are set to local window self-attention and can generate weight vectors without being affected by the enhanced graph knowledge as much as possible [25].
As shown in Figure 8a, the self-attention mechanism will calculate the weighted probability for all the keys , and its computation is large because it refers to the content of all the keys. In contrast, as shown in Figure 8b, the local attention mechanism with a fixed sliding window size only calculates the key within all the window sizes. It will significantly reduce the computation and memory usage from to . Therefore, to cut the memory, the model mainly uses sliding window local attention for text interaction. However, since the text can only interact with the context within its window, relying on the sliding window self-attention alone cannot guarantee that the topic entity interacts with the whole text, so we set the attention of the subject entity to be global attention. As shown in Figure 8c, the global attention is set for both the question and the knowledge extension entity, and the overall memory occupation of the model is , where is the total word length of the question and the knowledge extension entity, and is the total text length. However, because is much smaller than , the space complexity of the model can be regarded as a linear relationship, which allows the model to handle long texts with entity-text interactions. The combination of global attention and sliding window self-attention can be expressed as follows:
where , , and are weight parameters, is the hidden state of the -th attention block, denotes the dimension of the neural network, is the visible matrix. If is invisible to , the will assign the attention score to 0, which means has no effect on the hidden state of . Then, we can obtain the global attention hidden features and the local attention hidden features .
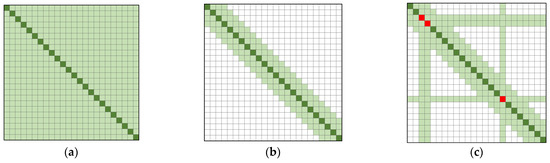
Figure 8.
Attention diagram: (a) Full attention, its computation complexity is ; (b) Local attention, its computation complexity is ; (c) Global attention, its computation complexity is .
3.4. Link Reasoning Layer
The model assigns an activation probability to each entity with an initialization probability of 1 for the topic entity and 0 for all other entities, calculates a score for the relations between the entities in each hop, passes the probability score to the corresponding tail entities of the topic entity, and then transfers the entity scores in these activated relations.
The entity scores in the hop are represented as vectors , where represents the initial scores of each entity, and only the scores of the subject entities are 1. In the hop, we obtain the hidden features of the relation containing the weight vector through the global attention module.
where is the global hidden vector weight of the relation tree learned by the global attention mechanism, is the local hidden vector weight of the relation tree learned by the local attention mechanism, and is the hidden vector weight of the relation tree. The query vectors are obtained by focusing on the question, where represents the dimension of the hidden layer.
where represents the vector representation of the question, and is the parameter of the related entity. It maps the problem vector to a specific query key . is the attention value that calculates the score based on the hidden vector , and is the weighted sum of the vector hidden vectors.
The feature vectors are mapped from the dimension to the single dimension by the MLP full connected layer, and, finally, the relation scores are obtained by the Sigmoid model.
We obtain the relation score matrix and then pass the scores of the subject entity to the tail entity along the relation link. Finally, we obtain the score matrix of the tail entity.
We can now obtain
The score of the head entity and the score of the relation are passed to the tail entity, and the answer is deduced from the entity corresponding to the link with the highest comprehensive score.
The standard set of answers is , and we construct the objective function vector . As long as it is contained in the standard set of answers, it is regarded to the correct answer.
Using the Euclidean distance between and as a loss function training objective.
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset
The statistics of the dataset are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Dataset Statistics.
MetaQA [15] is a large database of multi-hop KGQA containing 400,000 questions with up to 3 hops. It has 3 versions: Vanilla, NTM, and Audio. We chose the Vanilla version. Its KG is from the movie domain and includes 43,000 entities, 9 relation terms, and 135,000 triples. Following TransferNet [10], we constructed the free text movie information by extracting the text corpus of Wiki Movies [22], which introduces the information of movies with free text.
WebQSP [26] has a smaller scale of questions, but the scale of the KG is larger. It contains thousands of natural language questions based on Freebase [27], which has millions of entities and triples. It has either 1-hop or 2-hop questions. Following EmbedKGQA [17], we prune the knowledge base to contain only the mentioned entities.
CompWebQ [14] is an extended version of WebQSP by extending the question entities or adding constraints to the answers. CompWebQ forms patterned complex questions based on the expansion of SPARQL statements from the WebQSP dataset and then manually paraphrases the complex questions to form natural language questions. Following PullNet [6], we retrieved the subgraphs of each question using the PageRank algorithm.
4.2. Experiment Parameters
The experiment is based on the Pytorch platform. The specific experimental environment configuration is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Experimental environment configuration.
4.3. Experimental Parameter Configuration
According to the experimental process, the parameter settings in this paper are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Hyperparameter values.
We use bidirectional GRU [28] as the problem encoder and utilize a pre-trained Longformer as the relation tree structure encoder and finetune its parameters on our task. The hidden layer dimension is set to 768. The project function is a stack of a linear layer and a Tanh layer. The MLPs are implemented as simple linear layers. The loss is calculated using cross-entropy. The model is optimized using RAdam [29], which ensures both fast convergences and does not easily fall into local optimum solutions, and the convergence result is very insensitive to the initial value of the learning rate.
Due to the large number of relational paths in the relational graph, it is expensive to compute the embeddings and scores of all the routes. In the experiment, we select a subset of relations at each jump. Specifically, at the t-th hop, we choose the entities whose score is to start the inference for the next hop, where is the threshold hyperparameter. In this way, the operating range will significantly reduce. In this paper, we set the threshold to 0.7 according to the accuracy and the processing speed. The response paths with scores greater than 0.7 are highlighted, while the paths with scores less than 0.7 are ignored. The entities with high relevance in each hop are gradually activated, and the paths of the next hop are continuously updated along the paths of the entity relationships with scores greater than 0.7, resulting in an optimal solution on the overall path.
4.4. Experiment Results and Analysis
The experimental results are shown in Table 4. For 1-hop questions in MetaQA, our model achieves 97.3% accuracy, which performs similarly to the SOTA case of 1-hop questions. This is expected because the answer entity is directly connected to the topic entity. We found that the wrong error cases of 1-hop are caused by the ambiguity of the entities. The other performance on 2-hop and 3-hop questions suggests that our model can infer the correct relation from the relation knowledge enhancement with tree structure relation. WebQSP has a relatively small number of training examples but uses a large KG as background knowledge. It makes multi-hop KGQA much harder. Our model achieves 71.6% accuracy, which outperforms most of the present models, which means that it is well qualified for the large-scale knowledge base, even with a small set of training examples. ComWebQ is generated from WebQSP by extending the question entities or adding constraints to the answers to construct more complex multi-hop questions. The questions require up to four hops of reasoning on the knowledge base. We expect that single-shot retrieval of facts and text would not find efficient information to answer such questions. Our model achieves 49.2% accuracy and shows modest improvement over other approaches. We believe that relational augmentation allows semantic association across hops and performs especially well on KGs with missing relations, as augmenting relational representations by fusing external textual knowledge with global attention is effective. For example, if the KG loses the triple <Sam Altman, Creat, OpenAI> or <Sam Altman, Inventor, ChatGPT>, the model can infer the answer to the question “When did the ‘Father of ChatGPT’ serve as CEO” with the text “In 2019, Sam Altman serves as OpenAI CEO” and “On 30 November 2022, OpenAI presented ChatGPT, Sam Altman is known as the father of ChatGPT”.

Table 4.
Hit@1 results of the datasets.
Metric hit@1 is a standard assessment that measures the ratio across all validations, i.e., the entity with the highest score belongs to the correct answer. If the QA system provides a single entity and that entity is correct, then we treat the right prediction as the correct one. This evaluating indicator is popular and publicly recognized. We compare the metric with other models.
For the incomplete KG case where only 50% of the original triples are present, as shown in Table 5, our model can implicitly capture the knowledge of all the observed and unobserved around the head entities with the enhancement of the relation tree structure in global attention.

Table 5.
Hit@1 results on MetaQA of the mixed form.
To further verify that our model can alleviate the problem of knowledge graph sparseness, we conducted comparative experiments on the WebQSP dataset. As shown in Figure 9, as the KG’s started to become sparse, the RKE model did not experience significant degradation in performance as the other models. So, unlike other QA systems, even if there are few paths between the head and answer entity, our model should be able to answer some questions if there is sufficient information in the text or KG to be able to predict that path. We believe that the augmentation of textual relations alleviates the sparsity of the knowledge graph and enhances the semantics of textual expressions, which means the model can infer the relation tree.
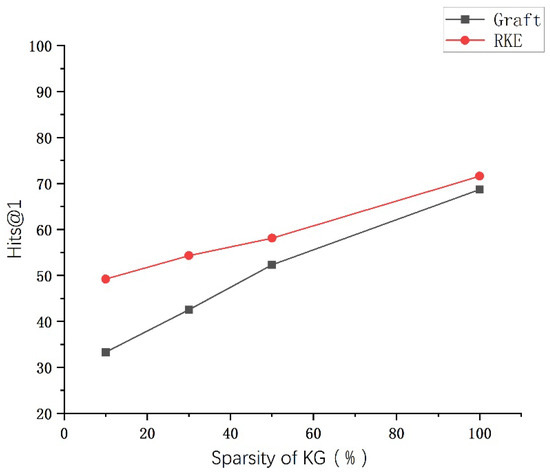
Figure 9.
Experimental comparison diagram. We chose the KGs with 10%, 20%, and 50% sparsity for comparison experiments.
To verify the influence of the global attention and threshold on the effect of the model, we designed ablation experiments. Table 6 shows the results of the ablation study. We found that global attention and threshold are significant for the model. We think global attention can fuse the hidden features of the relation and without the threshold may lead to overfitting.

Table 6.
Ablation study on MetaQA.
5. Conclusions
In the paper, we propose an effective multi-hop KGQA model based on relation knowledge enhancement. It deals with label and text relations with a tree structure and then fuses the relationship with global attention. We calculate the score of the entity and relation at each hop to obtain an optimal solution on the overall path. We show that our approach outperforms the datasets MetaQA, WebQSP, and CompWebQSP, especially for complex datasets such as WebQSP and CompWebQ. In the future, we plan to investigate the following main issues: how to support dynamic application scenarios in open domains and the rapid updating of knowledge [30] and how to introduce external knowledge, such as knowledge from web pages, to expand the knowledge coverage of the system [31].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.W. and R.H.; methodology, T.W.; software, T.W.; validation, T.W., H.W. and H.Z.; formal analysis, H.L.; investigation, H.Z.; resources, H.Z.; data curation, H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, H.L.; writing—review and editing, T.W.; visualization, T.W.; supervision, R.H.; project administration, R.H.; funding acquisition, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Youth Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 62002384 and Songshan Laboratory Major Science and Technology Project, grant number 221100210700-3.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Program of Song Shan Laboratory (included in the management of the Major Science and Technology Program of Henan Province) (221100210700-3).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Lan, Y.; He, G.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, W.X.; Wen, J.R. A Survey on Complex Knowledge Base Question Answering: Methods, Challenges and Solutions. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–27 August 2021; pp. 4483–4491. [Google Scholar]
- Petrochuk, M.; Zettlemoyer, L. Simple Questions Nearly Solved: A New Upper Bound and Baseline Approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 554–558. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y. Progress, challenges and research trends of reasoning in multi-hop knowledge graph based question answering. Big Data Res. 2021, 7, 2021026. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Dhingra, B.; Zaheer, M.; Mazaitis, K.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Cohen, W.W. Open Domain Question Answering Using Early Fusion of Knowledge Bases and Text. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 4231–4242. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, H.D.; Sheng, V.S. A Roadmap to Domain Knowledge Integration in Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Knowledge Graph, Nanjing, China, 9–11 August 2020; pp. 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Bedrax-Weiss, T.; Cohen, W.W. PullNet: Open Domain Question Answering with Iterative Retrieval on Knowledge Bases and Text; Association for Computational Linguistics: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2019; pp. 2380–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, B.; Yin, Y.; Yang, H. Explore Modeling Relation Information and Direction Information in KBQA. Neurocomputing 2022, 471, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. Translational relation embeddings for multi-hop knowledge base question answering. J. Web Semant. 2022, 74, 100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, P.; Xu, L. A knowledge inference model for question answering on an incomplete knowledge graph. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 7634–7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cao, S.; Hou, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. TransferNet: An Effective and Transparent Framework for Multi-Hop Question Answering over Relation Graph; Association for Computational Linguistics: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2021; pp. 4149–4158. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, P. A dynamic graph expansion network for multi-hop knowledge base question answering. Neurocomputing 2023, 515, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.W.; Sun, H.; Hofer, R.A.; Siegler, M. Scalable Neural Methods for Reasoning with a Symbolic Knowledge Base. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020; pp. 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, B.Y.; Wang, P.; Yan, J.; Ren, X. Scalable Multi-Hop Relational Reasoning for Knowledge-Aware Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 1295–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Huang, M.; Zhu, X. An Interpretable Reasoning Network for Multi-Relation Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–26 August 2018; pp. 2010–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, H.; Kozareva, Z.; Smola, A.; Song, L. Variational Reasoning for Question Answering with Knowledge Graph. In Proceedings of the 30th Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence (IAAI-18), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 6069–6076. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, K. Stepwise Reasoning for Multi-Relation Question Answering over Knowledge Graph with Weak Supervision. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Singapore, 3–7 February 2020; pp. 474–482. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.; Tripathi, A.; Talukdar, P. Improving Multi-Hop Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs using Knowledge Base Embeddings. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 4498–4507. [Google Scholar]
- Trouillon, T.; Welbl, J.; Riedel, S.; Gaussier, É.; Bouchard, G. Complex Embeddings for Simple Link Prediction. In Proceedings of the 33nd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 2071–2080. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Zhao, B.; Yu, H.; Tao, X.; Yin, R.; Liu, G. Improving embedded knowledge graph multi-hop question answering by introducing relational chain reasoning. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2023, 37, 255–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Lan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, W.X.; Wen, J.R. Improving Multi-Hop Knowledge Base Question Answering by Learning Intermediate Supervision Signals; The Association for Computational Linguistics: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2021; pp. 553–561. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.; Fisch, A.; Dodge, J.; Karimi, A.H.; Bordes, A.; Weston, J. Key-Value Memory Networks for Directly Reading Documents. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–4 November 2016; pp. 1400–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Ji, H.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Qian, T.; Ruan, T. Knowledge Graph and Semantic Computing: Semantic, Knowledge, and Linked Big Data. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2016, 650. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ju, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, P. K-BERT: Enabling Language Representation with Knowledge Graph. In Proceedings of the Tenth AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Hangzhou, China, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 2901–2908. [Google Scholar]
- Beltagy, I.; Peters, M.E.; Cohan, A. Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05150. [Google Scholar]
- Yih, W.T.; Richardson, M.; Meek, C.; Chang, M.W.; Suh, J. The Value of Semantic Parse Labeling for Knowledge Base Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bollacker, K.; Evans, C.; Paritosh, P.; Sturge, T.; Taylor, J. Freebase: A Collaboratively Created Graph Database for Structuring Human Knowledge. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–12 June 2008; pp. 1247–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; He, P.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Han, J. On the Variance of the Adaptive Learning Rate and Beyond. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Chen, M.; Dong, R. Multi-hop Question Answering with Knowledge Graph Embedding in a Similar Semantic Space. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Budapest, Hungary, 18–23 July 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, W.; Zuo, Z.; Qi, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, P. An improving reasoning network for complex question answering over temporal knowledge graphs. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 8195–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).