A Review of Deep Learning Imaging Diagnostic Methods for COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- This review provides a more comprehensive review of classification and segmentation method on CT and X-ray datasets of deep learning imaging diagnostic methods for COVID-19.
- This review provides a comprehensive summary of the available COVID-19 datasets.
- The advantages and challenges of deep learning imaging diagnostic methods for COVID-19 are given from multiple perspectives.
2. COVID-19 Datasets
2.1. Main COVID-19 Datasets
2.2. Data Enhancement Methods
3. The Methods for Supervised Learning in Diagnosis of COVID-19
3.1. The Classification Methods of COVID-19 Based on Supervised Learning
3.1.1. The Classification Methods of COVID-19 Based on VGG
3.1.2. The Classification Methods of COVID-19 Based on ResNet
3.1.3. The Classification Methods of COVID-19 Based on DenseNet
3.1.4. The Classification Methods of COVID-19 Based on Lightweight Networks
3.2. The Segmentation Methods of COVID-19 Based on Supervised Learning
3.2.1. The Segmentation Methods of COVID-19 Based on Attention Mechanism
3.2.2. The Segmentation Methods of COVID-19 Based on Multi-scale Mechanism
3.2.3. The Segmentation Methods of COVID-19 Based on Residual Connectivity Mechanism
3.2.4. The Segmentation Methods of COVID-19 Based on Dense Connectivity Mechanism
4. The Methods for Semi-Supervised Learning in Diagnosis of COVID-19
5. The Methods for Unsupervised Learning in Diagnosis of COVID-19
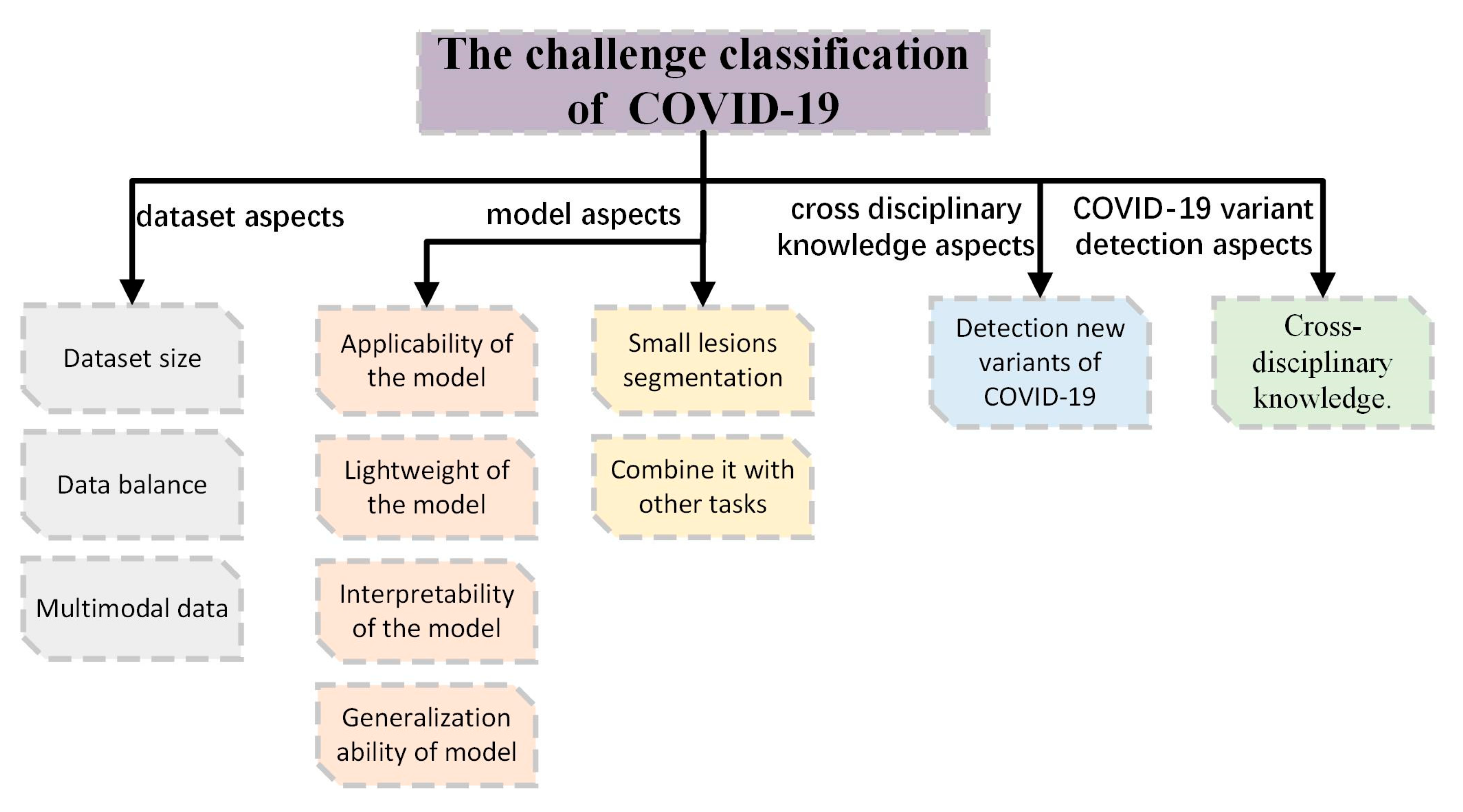
6. Challenges and Future Work
- Dataset size
- Data balance
- Multimodal data
- Aplicability of the model
- Light weight of the model
- Interpretability of the model
- Generalization ability of model
- Small lesions segmentation
- Combine it with other tasks
- Third, detection of new variants of COVID-19
- Fourth, cross disciplinary knowledge
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.A.A.; Yavuz, M.C.; Şen, M.U.; Gülşen, F.; Tutar, O.; Korkmazer, B. Comparison and ensemble of 2D and 3D approaches for COVID-19 detection in CT images. Neurocomputing 2022, 488, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
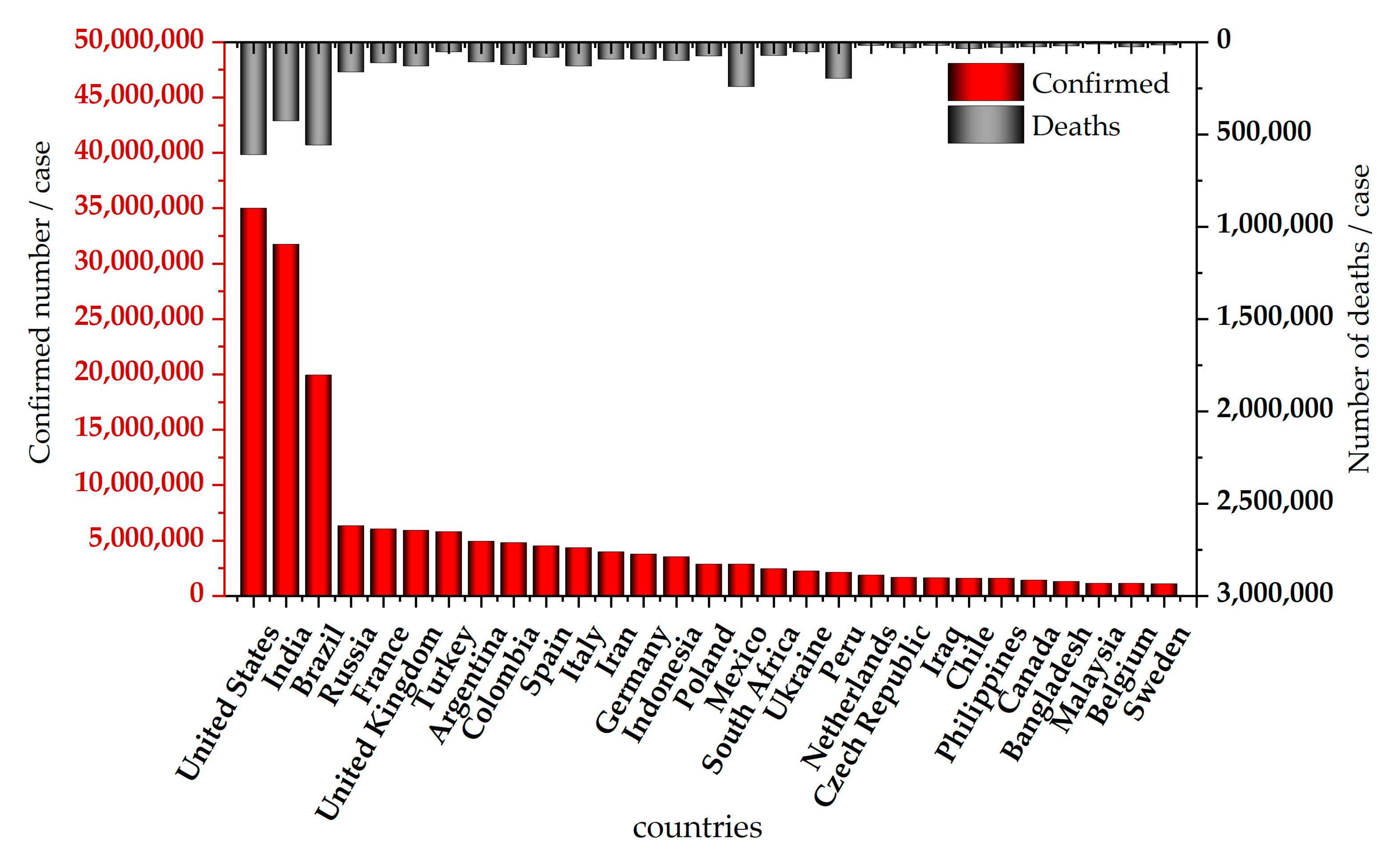
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Gourdeau, D.; Potvin, O.; Archambault, P.; Chartrand-Lefebvre, C.; Dieumegarde, L.; Forghani, R. Tracking and predicting COVID-19 radiological trajectory on chest X-rays using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Muhammad, K. A deep fuzzy model for diagnosis of COVID-19 from CT images. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2022, 122, 108883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Sun, K.; Xu, C.; Shi, X.H.; Wu, C.; Xie, T. Accurate recognition of colorectal cancer with semi-supervised deep learning on pathological images. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, D.; Huang, X.; Cui, Y.; Xia, M. SSA-Net: Spatial self-attention network for COVID-19 pneumonia infection segmentation with semi-supervised few-shot learning. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Loew, M.; Ko, H. Unsupervised domain adaptation based COVID-19 CT infection segmentation network. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 6340–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soomro, T.A.; Zheng, L.; Afifi, A.J.; Ali, A.; Yin, M.; Gao, J. Artificial intelligence (AI) for medical imaging to combat coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A detailed review with direction for future research. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, C.; Khan, M.A.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huang, B. Supervised and weakly supervised deep learning models for COVID-19 CT diagnosis: A systematic review. Comput. Meth. Prog. Bio. 2022, 218, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, N.; Elharrouss, O.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Chowdhury, M. A review of deep learning-based detection methods for COVID-19. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 143, 105233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.P.; Morrison, P.; Dao, L.; Roth, K.; Duong, T.Q.; Ghassemi, M. COVID-19 image data collection: Prospective predictions are the future. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11988. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Xie, P. Covid-ct-dataset: A ct scan dataset about COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13865. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. Covid-net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest x-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamac, M.; Ahishali, M.; Degerli, A.; Kiranyaz, S.; Chowdhury, M.E.; Gabbouj, M. Convolutional sparse support estimator-based COVID-19 recognition from X-ray images. IEEE. Trans. Neural. Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghanifar, A.; Majdabadi, M.M.; Choi, Y.; Deivalakshmi, S.; Ko, S. Covid-cxnet: Detecting COVID-19 in frontal chest x-ray images using deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 30615–30645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunair, H.; Hamza, A.B. Synthesis of COVID-19 chest X-rays using unpaired image-to-image translation. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2021, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabik, S.; Gómez-Ríos, A.; Martín-Rodríguez, J.L.; Sevillano-García, I.; Rey-Area, M.; Charte, D. COVIDGR dataset and COVID-SDNet methodology for predicting COVID-19 based on chest X-ray images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 2020, 24, 3595–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.E.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Mahbub, Z.B. Can AI help in screening viral and COVID-19 pneumonia? IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132665–132676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-QU-Ex Dataset. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/anasmohammedtahir/covidqu (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, F.; Hou, M. Automatically discriminating and localizing COVID-19 from community-acquired pneumonia on chest X-rays. Pattern Recogn. 2021, 110, 107613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signoroni, A.; Savardi, M.; Benini, S.; Adami, N.; Leonardi, R.; Gibellini, P. BS-Net: Learning COVID-19 pneumonia severity on a large chest X-ray dataset. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 71, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Tyagi, M.; Bansal, V.; Jain, V. SVD-CLAHE boosting and balanced loss function for COVID-19 detection from an imbalanced Chest X-Ray dataset. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 150, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Li, Z.; Sang, Y.; Wu, X. Clinically applicable AI system for accurate diagnosis, quantitative measurements, and prognosis of COVID-19 pneumonia using computed tomography. Cell 2020, 181, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; An, X.; Ge, C.; Yu, Z.; Chen, J. Toward data-efficient learning: A benchmark for COVID-19 CT lung and infection segmentation. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Wang, B.; Gong, D.; Luo, C.; Zhao, W.; Shen, J. COVID-19 chest CT image segmentation—A deep convolutional neural network solution. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10987. [Google Scholar]
- Morozov, S.P.; Andreychenko, A.E.; Blokhin, I.A.; Gelezhe, P.B.; Gonchar, A.P.; Nikolaev, A.E. MosMedData: Data set of 1110 chest CT scans performed during the COVID-19 epidemic. Dig. Diag. 2020, 1, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, E.; Angelov, P.; Biaso, S.; Froes, M.H.; Abe, D.K. SARS-CoV-2 CT-scan dataset: A large dataset of real patients CT scans for SARS-CoV-2 identification. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, S.; Shi, S.; Chu, X.; Tang, J.; Liu, X. Benchmarking deep learning models and automated model design for COVID-19 detection with chest CT scans. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W.; Lei, S.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, P.; Yang, Q. Open resource of clinical data from patients with pneumonia for the prediction of COVID-19 outcomes via deep learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, S.A.; Sanford, T.H.; Xu, S.; Turkbey, E.B.; Roth, H.; Xu, Z. Artificial intelligence for the detection of COVID-19 pneumonia on chest CT using multinational datasets. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Khan, A.A.; Kumar, J.; Golilarz, N.A.; Zhang, S.; Ting, Y. Blockchain-federated-learning and deep learning models for COVID-19 detection using CT imaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16301–16314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, E.; Simpson, S.; Lungren, M.P.; Hershman, M.; Roshkovan, L. Medical Imaging Data Resource Center-rsna International COVID Radiology Database Release 1a-Chest ct COVID+ (midrc-ricord-1a). Available online: https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/x/DoDTB (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Gunraj, H.; Sabri, A.; Koff, D.; Wong, A. COVID-Net CT-2: Enhanced deep neural networks for detection of COVID-19 from chest CT images through bigger, more diverse learning. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Gao, S.H.; Mei, J.; Xu, J.; Fan, D.P.; Zhang, R.G. Jcs: An explainable COVID-19 diagnosis system by joint classification and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3113–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimzadeh, M.; Attar, A.; Sakhaei, S.M. A fully automated deep learning-based network for detecting COVID-19 from a new and large lung ct scan dataset. Biomed. Signal. Process. 2021, 68, 102588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, P.; Heidarian, S.; Enshaei, N.; Naderkhani, F.; Rafiee, M.J.; Oikonomou, A. COVID-CT-MD, COVID-19 computed tomography scan dataset applicable in machine learning and deep learning. Sci. Data. 2021, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toğaçar, M.; Muzoğlu, N.; Ergen, B.; Yarman, B.S.B.; Halefoğlu, A.M. Detection of COVID-19 findings by the local interpretable model-agnostic explanations method of types-based activations extracted from CNNs. Biomed. Signal. Process. 2022, 71, 103128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.; Chin, R.K.Y. Diverse COVID-19 CT Image-to-Image Translation with Stacked Residual Dropout. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vayá, M.D.L.I.; Saborit, J.M.; Montell, J.A.; Pertusa, A.; Bustos, A.; Cazorla, M. Bimcv COVID-19+: A large annotated dataset of rx and CT images from COVID-19 patients. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.01174. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Tang, Y.; Lee, S.; Zhu, Y.; Summers, R.M.; Lu, Z. COVID-19-CT-CXR: A freely accessible and weakly labeled chest X-ray and CT image collection on COVID-19 from biomedical literature. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2020, 7, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, Q.; Lu, H.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, X. GAN review: Models and medical image fusion applications. Inform. Fusion 2023, 91, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, H.; Loew, M.; Ko, H. COVID-19 CT image synthesis with a conditional generative adversarial network. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 2020, 25, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Goyal, M.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Al-Turjman, F.; Pinheiro, P.R. Covidgan: Data augmentation using auxiliary classifier gan for improved COVID-19 detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 91916–91923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Tang, S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y. Deep learning for COVID-19 chest CT (computed tomography) image analysis: A lesson from lung cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotech. 2021, 19, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshooi, A.H.; Amirkhani, A. A novel data augmentation based on Gabor filter and convolutional deep learning for improving the classification of COVID-19 chest X-Ray images. Biomed. Signal. Process. 2022, 72, 103326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loey, M.; Manogaran, G.; Khalifa, N.E.M. A deep transfer learning model with classical data augmentation and CGAN to detect COVID-19 from chest CT radiography digital images. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.M.; Elshennawy, N.M.; Sarhan, A.M. Deep-chest: Multi-classification deep learning model for diagnosing COVID-19, pneumonia, and lung cancer chest diseases. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elazab, A.; Abd Elfattah, M.; Zhang, Y. Novel multi-site graph convolutional network with supervision mechanism for COVID-19 diagnosis from X-ray radiographs. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2022, 114, 108041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, V.V.; Proutski, A.; Karpovsky, A.; Kirpich, A.; Litmanovich, D.; Nefaridze, D. Indirect supervision applied to COVID-19 and pneumonia classification. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2022, 28, 100835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, T.; Choudhary, P. FocusCovid: Automated COVID-19 detection using deep learning with chest X-ray images. Evol. Syst. 2021, 13, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Tian, S.; Yu, L.; Gao, C.; Kang, X.; Ma, X. ResGANet: Residual group attention network for medical image classification and segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 76, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lu, S.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, Y.D. ResGNet-C: A graph convolutional neural network for detection of COVID-19. Neurocomputing 2021, 452, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bao, Y.; Wen, Y.; Lu, H.; Luo, H.; Xiang, Y. Prior-attention residual learning for more discriminative COVID-19 screening in CT images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2572–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbo, F.J.P. Diagnosing COVID-19 chest x-rays with a lightweight truncated DenseNet with partial layer freezing and feature fusion. Biomed. Signal. Process. 2021, 68, 102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, G.; Oh, Y.; Seo, J.B.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, J.H. Vision transformer using low-level chest X-ray feature corpus for COVID-19 diagnosis and severity quantification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.07235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ning, J.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, L. A depthwise separable dense convolutional network with convolution block attention module for COVID-19 diagnosis on CT scans. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 137, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, M.; Dhavale, S.V.; Ingole, J. Corona-Nidaan: Lightweight deep convolutional neural network for chest X-Ray based COVID-19 infection detection. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 3026–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Santosh, K.C.; Pal, U. Truncated inception net: COVID-19 outbreak screening using chest X-rays. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owais, M.; Yoon, H.S.; Mahmood, T.; Haider, A.; Sultan, H.; Park, K.R. Light-weighted ensemble network with multilevel activation visualization for robust diagnosis of COVID19 pneumonia from large-scale chest radiographic database. App. Soft Comput. 2021, 108, 107490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, B.; Nair, M.S. Computer-aided detection of COVID-19 from CT scans using an ensemble of CNNs and KSVM classifier. Signal Image Video Process. 2022, 16, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25 June–2 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 16–21 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Ye, X.; Lu, H.; Zheng, X.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y. Dense Convolutional Network and Its Application in Medical Image Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2384830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Chang, X.; Lu, H.; Ye, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X. Pooling Operations in Deep Learning: From “Invariable” to “Variable”. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 4067581. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Dong, B.; Wang, S.; Cui, H.; Fan, D.P.; Ma, J.; Chen, G. COVID-19 lung infection segmentation with a novel two-stage cross-domain transfer learning framework. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 74, 102205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Menaka, R.; Hariharan, M.; Won, D. Contour-enhanced attention CNN for CT-based COVID-19 segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 2022, 125, 108538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, P.; Song, F.; Fan, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y. D2A U-net: Automatic segmentation of COVID-19 CT slices based on dual attention and hybrid dilated convolution. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Huang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Wang, T.; Song, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z. DUDA-Net: A double U-shaped dilated attention network for automatic infection area segmentation in COVID-19 lung CT images. Int. J. Comput. Ass. Rad. 2021, 16, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitrungrotsakul, T.; Chen, Q.; Wu, H.; Iwamoto, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhu, W. Attention-RefNet: Interactive Attention Refinement Network for Infected Area Segmentation of COVID-19. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 2021, 25, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, F.; Jiang, T.; Yang, D.; Xu, T. MSD-Net: Multi-scale discriminative network for COVID-19 lung infection segmentation on CT. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 185786–185795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, G.R.; Lu, T. MPS-net: Multi-point supervised network for CT image segmentation of COVID-19. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 47144–47153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Chowdhury, R.S.; Das, R.; Maulik, U. Dense Dilated Deep Multiscale Supervised U-Network for biomedical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 143, 105274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Wang, B.; Gong, D.; Luo, C.; Zhao, W.; Shen, J. COVID-19 chest CT image segmentation network by multi-scale fusion and enhancement operations. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2021, 7, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Shen, L.; Guan, Q.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ruan, S. Deep co-supervision and attention fusion strategy for automatic COVID-19 lung infection segmentation on CT images. Pattern Recogn. 2022, 124, 108452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Canu, S.; Ruan, S. Automatic COVID-19 CT segmentation using U-Net integrated spatial and channel attention mechanism. Int. J. Imag. Syst. Tech. 2021, 31, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Yan, F.; Xie, C. Automatic Segmentation of COVID-19 CT Images Using Improved MultiResUNet. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Automation Congress, Shanghai, China, 6–8 November 2020; pp. 1614–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Y. Residual attention u-net for automated multi-class segmentation of COVID-19 chest CT images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05645. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xie, X.; Liu, J. SCOAT-Net: A novel network for segmenting COVID-19 lung opacification from CT images. Pattern Recog. 2021, 119, 108109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.N.J.; Zhu, H.; Khan, A.; Zhuang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Mahesh, V.G.; Karthik, G. ADID-UNET—A segmentation model for COVID-19 infection from lung CT scans. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e349. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Dong, L.; Dou, Q.; Lin, F.; Zhang, K.; Feng, Z. Self-Ensembling Co-Training Framework for Semi-Supervised COVID-19 CT Segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 2021, 25, 4140–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Heng, P.A. Dual-consistency semi-supervised learning with uncertainty quantification for COVID-19 lesion segmentation from CT images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Sringer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Abdel-Basset, M.; Hawash, H. RCTE: A reliable and consistent temporal-ensembling framework for semi-supervised segmentation of COVID-19 lesions. Inf. Sci. 2021, 578, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Chang, V.; Hawash, H.; Chakrabortty, R.K.; Ryan, M. FSS-2019-nCov: A deep learning architecture for semi-supervised few-shot segmentation of COVID-19 infection. Knowl. Based Syst. 2021, 212, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Zhu, H.; Guo, W.; Xu, G.; Zou, G. Deep semi-supervised learning with contrastive learning and partial label propagation for image data. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 245, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Zhou, T.; Ji, G.P.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, G.; Fu, H. Inf-net: Automatic COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from CT images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2626–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Hoque, M.A.; Khan, M.A.I.; Ahmed, S. COVID-19 Detection Using Feature Extraction and Semi-Supervised Learning from Chest X-ray Images. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Region 10 Symposium, Jeju, Korea, 23–25 August 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, R.F.; Escorcia-Gutierrez, J.; Gamarra, M.; Gupta, D.; Castillo, O.; Kumar, S. Unsupervised deep learning based variational autoencoder model for COVID-19 diagnosis and classification. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2021, 151, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, N.; Hossain, M.A.F.; Ali, M.; Sukanya, M.I.; Mahmud, T.; Fattah, S.A. AutoCovNet: Unsupervised feature learning using autoencoder and feature merging for detection of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 1685–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpiniti, M.; Ahrabi, S.S.; Baccarelli, E.; Piazzo, L.; Momenzadeh, A. A novel unsupervised approach based on the hidden features of Deep Denoising Autoencoders for COVID-19 disease detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 192, 116366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morís, D.I.; de Moura, J.; Novo, J.; Ortega, M. Cycle generative adversarial network approaches to produce novel portable chest X-rays images for COVID-19 diagnosis. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–12 June 2021; pp. 1060–1064. [Google Scholar]
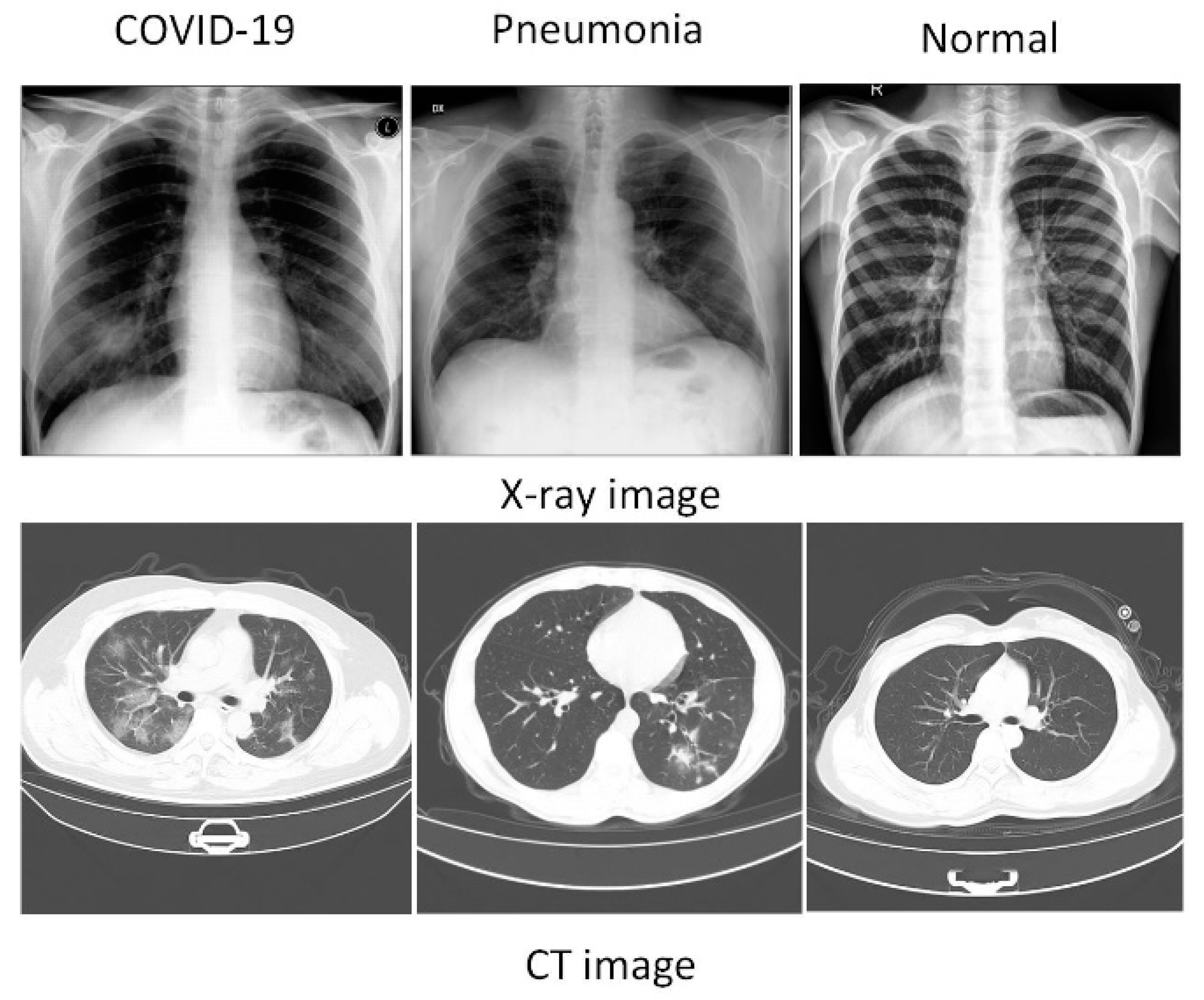



| Datasets Name | Image Modal | Sample Size | Country | Date | Data Format | Online URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-chestxray [11] | X-ray | 434 (NCP: 434) | Canada | 2,2020 | JPEG PNG JPG | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset |
| QaTa-Cov19 [14] | X-ray | 6286 (BP: 2760, VP: 1485, Normal: 1579, NCP: 462) | Italy Spain China | 5,2020 | / | / |
| COVID-CXNet [15] | X-ray | 452 (NCP: 452) | Canada | 6,2020 | JPG PNG | https://github.com/armiro/COVID-CXNet |
| Synthetic COVID-19 CXR [16] | X-ray | 21,295 (NCP: 21,295) | / | 10,2020 | JPG | https://github.com/hasibzunair/synthetic-covid-cxr-dataset |
| COVIDGR [17] | X-ray | 852 (Normal: 426, NCP: 426) | Spain | 11,2020 | JPG | https://github.com/ari-dasci/OD-covidgr |
| COVID-19 radiography database [18] | X-ray | 15,153 (NCP: 3616, VP: 1345, Normal: 10,192) | India | 3,2021 | PNG | https://www.kaggle.com/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database |
| COVID-QU-Ex [19] | X-ray | 13,119 (NCP: 11,956, Pneumonia: 1163) | / | 3,2021 | PNG | https://www.kaggle.com/anasmohammedtahir/covidqu |
| COVID19-DB [20] | X-ray | 1559 (NCP: 225, Normal: 1334) | China | 8,2022 | JPG | / |
| BrixIA COVID-19 [21] | X-ray | 4703 (NCP: 4703) | Italy | 8,2020 | DICOM | https://github.com/BrixIA/Brixia-score-COVID-19 |
| COVIDx-CXR [13] | X-ray | 30,000 (patient: 16,400, X-ray: 30,000) | Canada | 11,2021 | PNG | https://github.com/lindawangg/COVID-Net |
| Balanced Augmented COVID CXR Dataset [22] | X-ray | 30,233 (NCP: 8769, LO: 7662, Normal: 8192, VP: 5410) | India | 11,2022 | PNG | https://www.kaggle.com/tr1gg3rtrash/balanced-augmented-covid-cxr-dataset |
| COVID-CT [12] | CT | 812 (NCP: 349, N-NCP: 463) | China | 3,2020 | PNG JPG | https://github.com/UCSD-AI4H/COVID-CT |
| CC-CCII [23] | CT | 617,775 (NCP, CP, Normal) | China | 4,2020 | JPG PNG | http://ncov-ai.big.ac.cn/download |
| COVID-CT-Seg [24] | CT | 20 (NCP: 20) | China | 4,2020 | DICOM | https://gitee.com/junma11/COVID-19-CT-Seg-Benchmark |
| Yan [25] | CT | 165,667 (patient: 861, CT: 165,667) | China | 4,2020 | / | / |
| MosMedData [26] | CT | 20,685 (patient: 1521, CT: 19,685) | Russia | 4,2020 | NIFIT | https://mosmed.ai/datasets/covid19_1110/ |
| SARS-CoV-2 CT-scan [27] | CT | 2482 (NCP: 1252, N-NCP: 1230) | Brazil | 5,2020 | PNG | https://www.kaggle.com/plameneduardo/sarscov2-ctscan-dataset |
| HKBU _HPML_COVID-19 [28] | CT | 340,190 (NCP: 131,517, CP: 135,038, Normal 73,635) | China | 6,2020 | PNG | https://github.com/HKBU-HPML/HKBU_HPML_COVID-19 |
| HUST-19 [29] | CT | 19,685 (patient: 1521, CT: 19,685) | China | 8,2020 | DICOM JPEG | http://ictcf.biocuckoo.cn/HUST-19.php |
| TCIA [30] | CT | 2724 (patient: 2617, CT: 2724) | China Japan Italy | 8,2020 | / | / |
| CC-19 [31] | CT | 34,006 | China | 12,2020 | JPG | https://github.com/abdkhanstd/COVID-19 |
| MIDRC-RICORD-1a [32] | CT | 31,856 (NCP: 28,395, N-NCP: 5611) | USA | 12.2020 | DICOM | https://doi.org/10.7937/VTW4-X588 |
| COVIDx-CT [13] | CT | 104,009 (Normal: 8066, NCP: 358, Pneumonia 5538) | China | 9,2020 | PNG | https://github.com/lindawangg/COVID-Net |
| COVID-Net CT-2 [33] | CT | 200,000 | / | 1,2021 | CKPT | https://github.com/haydengunraj/COVIDNet-CT/blob/master/docs/models.md |
| COVIDx CT-2A [13] | CT | 194,922 (CT: 194,922) | China Iran AustraliaEngland | 1,2021 | JPG | https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/hgunraj/covidxct |
| COVIDx CT-2B [13] | CT | 201,103 (CT: 201,103) | China Iran AustraliaEngland | 1,2021 | JPG | https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/hgunraj/covidxct |
| COVID-CS [34] | CT | 145,167 (NCP: 69,626, N-NCP: 75,541) | China | 2,2021 | JPG | https://github.com/yuhuan-wu/JCS |
| COVID-CT-Set [35] | CT | 63,849 (NCP: 15,589, Normal: 48,260) | Iran | 3,2021 | TIFF | https://github.com/mr7495/COVID-CTset |
| COVID-CT-MD [36] | CT | 308 (NCP: 160, CP: 69, Normal: 79) | Iran | 4,2021 | DICOM | https://github.com/ShahinSHH/COVID-CT-MD |
| Cov-Pne-Bac [37] | CT | 1566 (NCP: 631, VP: 417, CP: 518) | Turkey | 1,2022 | JPG | / |
| Large-scale Synthetic COVID-19 CT Dataset [38] | CT | 376,000 | / | 9,2022 | JPG | https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/lee123456789/largescale-synthetic-covid19-ct-dataset |
| BIMCV-COVID19+ [39] | X-ray CT | 23,527 (X-ray18 840, CT: 6687) | Spain | 6,2020 | / | https://github.com/BIMCV-CSUSP/BIMCV-COVID-19 |
| COVID-19-CT-CXR [40] | X-ray CT | 1590 (CT: 1327, CXR 263) | USA | 11,2020 | / | https://github.com/ncbi-nlp/COVID-19-CT-CXR |
| Network Name | Modal | Sample Size | Results (%) | Open Source (Y/N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG19 [47] | X-ray CT | COVID-19: 4320 Pneumonia: 5856 Normal: 20,000 Lung cancer: 3500 | Acc = 98.05 Recall = 98.05 Auc = 99.66 F1 = 98.24 | Y |
| VGG [48] | X-ray | COVID-19: 5656 Normal: 5656 | Acc = 96.41 Sen = 96.60 Spe = 96.20 Auc = 97.70 | N |
| VGG-16 [49] | X-ray | COVID-19: 816 Pneumonia: 867 Normal: 948 | Acc = 90.00 F1 = 90.00 | N |
| Resnet [37] | CT | COVID-19: 631 VP: 417 BP: 518 | Acc = 99.62 | N |
| FocusCovid [50] | X-ray | / | Acc = 99.40 | |
| ResGANet [51] | CT | COVID-19: 349 Normal: 397 | Acc = 80.00 F1 = 81.00 Auc = 82.00 | N |
| ResGNet-C [52] | CT | COVID-19: 148 Normal: 148 | Acc = 96.62 Sen = 97.33 Spe = 95.91 | N |
| 3D-ResNet [53] | CT | COVID-19: 1315 Pneumonia: 2406 Normal: 936 | Auc = 97.30 | N |
| DenseNet-Tiny [54] | X-ray | COVID-19: 1281 Pneumonia: 4657 Normal: 3270 | Acc = 97.99 Pre = 98.38 Recall = 98.15 F1 = 98.26 | Y |
| DenseNet [55] | X-ray | COVID-19: 2431 Pneumonia: 1468 Normal: 13,649 | Auc = 94.9 Sen = 90.2 Acc = 80.2 | N |
| AM-SdenseNet [56] | CT X-ray | COVID-19:828 Normal:1000 | Acc = 99.18 | Y |
| Corona-Nidnna [57] | X-ray | COVID-19: 245 Pneumonia: 5551 Normal: 8066 | Acc = 95.00 Recall = 94.00 | Y |
| InceptionV3 [58] | X-ray | COVID-19: 162 Pneumonia: 4280 | Acc = 99.96 | N |
| IST-CovNet [1] | CT | COVID-19: 92,905 Pneumonia: 67,712 Normal: 40,030 | Acc = 93.69 | N |
| ML-CAM [59] | X-ray CT | COVID-19: 3254 Normal: 2217 | Acc = 94.72 | N |
| CNN + CFS [60] | CT | COVID-19: 349 Normal: 397 | Acc = 91.60 Sen = 71.70 Pre = 90.40 F1 = 91.00 | N |
| Mechanism | Network Name | Sample Size | Results (%) | Open Source (Y/N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attention mechanism | nCoVSegNet [67] | Slices: 244,537 | Dice = 66.80 ESN = 70.70 SPE = 99.75 PPV = 69.77 | Y |
| Attention mechanism | CAD CNN [68] | Slices: 393 | Dice = 85.43 Recall = 88.10 | N |
| Attention mechanism | D2A U-Net [69] | Slices: 3949 | Dice = 72.98 Recall = 70.71 | N |
| Attention mechanism | DUDA-Net [70] | Slices: 557 | Dice = 87.06 Iou = 77.09 Acc = 99.06 Sen = 90.85 | Y |
| Attention mechanism | RefNet [71] | Slices: 230 | Dice = 91.37 Sen = 91.54 | N |
| Multi-scale mechanism | MSD-Net [72] | Slices: 4780 | Sen = 90.85 Spe = 99.59 | N |
| Multi-scale mechanism | MPS-Net [73] | Slices: 300 | Dice = 83.25 Sen = 84.06 Spe = 99.88 Iou = 74.20 | N |
| Multi-scale mechanism | [74] | Slices: 3929 | Dice = 83.25 Iou = 74.20 | Y |
| Multi-scale mechanism | COVID-SegNet [75] | Slices: 165,667 | Sen = 84.06 Spe = 99.88 | N |
| Multi-scale mechanism | JSC [34] | Slices: 2885 | Dice = 78.50 | Y |
| Residual connectivity mechanism | ResUnet [76] | Slices: 5349 | Dice = 85.19 Sen = 84.66 Prec = 84.22 | Y |
| Residual connectivity mechanism | Backbone + Res_dil + Attention [77] | Slices: 473 | Dice = 83.1 | N |
| Residual connectivity mechanism | MultiResUNet [78] | Slices: 3520 | Dice = 74.28 | N |
| Residual connectivity mechanism | Literature [79] | Slices: 100 | Dsc = 94 Acc = 89 Pre = 95 | N |
| Dense connectivity mechanism | SCOAT-Net [80] | Slices: 17 | DSC = 88.99 SEN = 87.85 PPV = 90.28 | N |
| Dense connectivity mechanism | ADID-UNET [81] | Slices: 1318 | Dice = 80.31 Pre = 84.76 Spe = 99.66 Auc = 95.51 | Y |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, T.; Liu, F.; Lu, H.; Peng, C.; Ye, X. A Review of Deep Learning Imaging Diagnostic Methods for COVID-19. Electronics 2023, 12, 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051167
Zhou T, Liu F, Lu H, Peng C, Ye X. A Review of Deep Learning Imaging Diagnostic Methods for COVID-19. Electronics. 2023; 12(5):1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051167
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Tao, Fengzhen Liu, Huiling Lu, Caiyue Peng, and Xinyu Ye. 2023. "A Review of Deep Learning Imaging Diagnostic Methods for COVID-19" Electronics 12, no. 5: 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051167
APA StyleZhou, T., Liu, F., Lu, H., Peng, C., & Ye, X. (2023). A Review of Deep Learning Imaging Diagnostic Methods for COVID-19. Electronics, 12(5), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051167






