TCAD Device Modeling and Simulation Study of Organic Field Effect Transistor-Based pH Sensor with Tunable Sensitivity for Surpassing Nernst Limit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
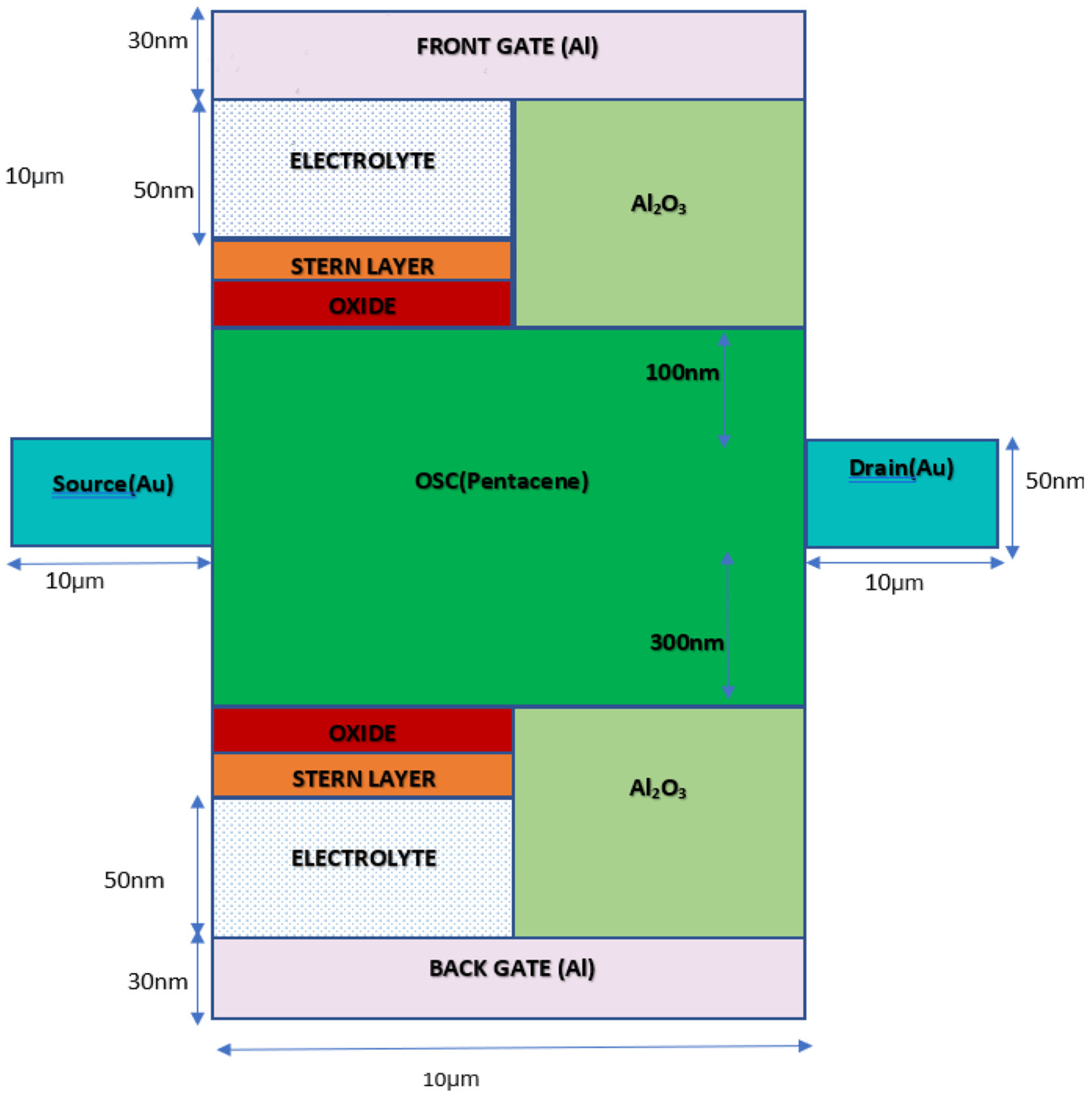
2. Simulation and Setup
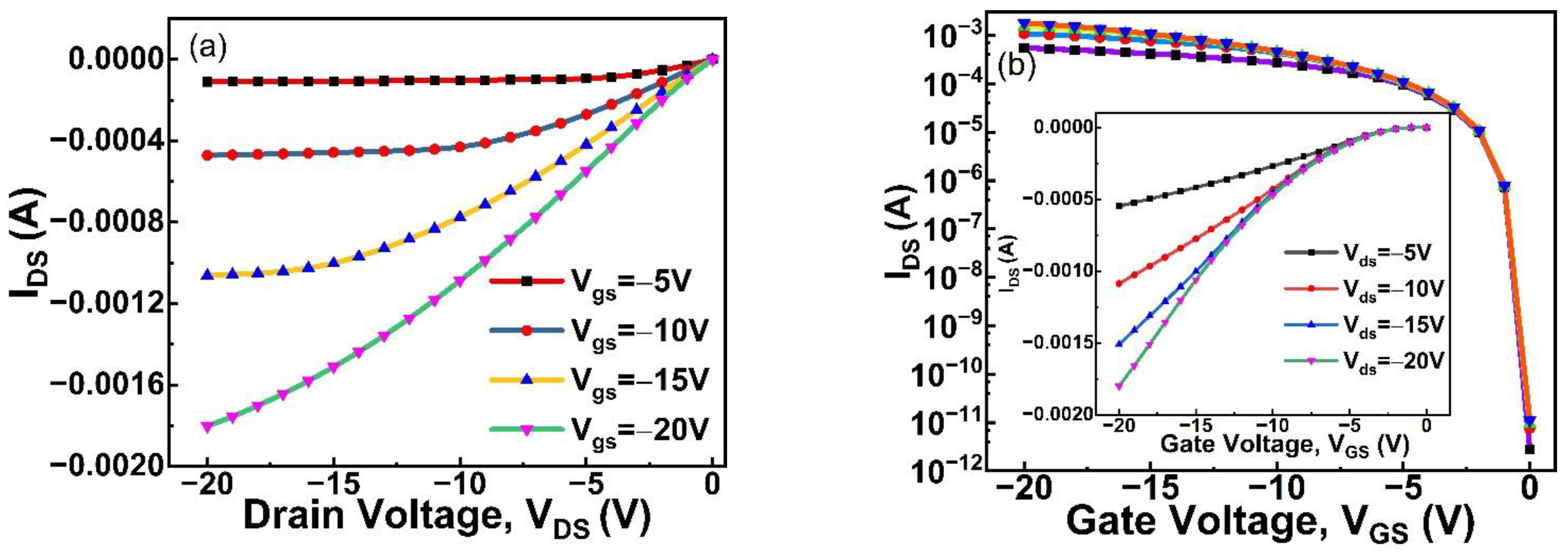
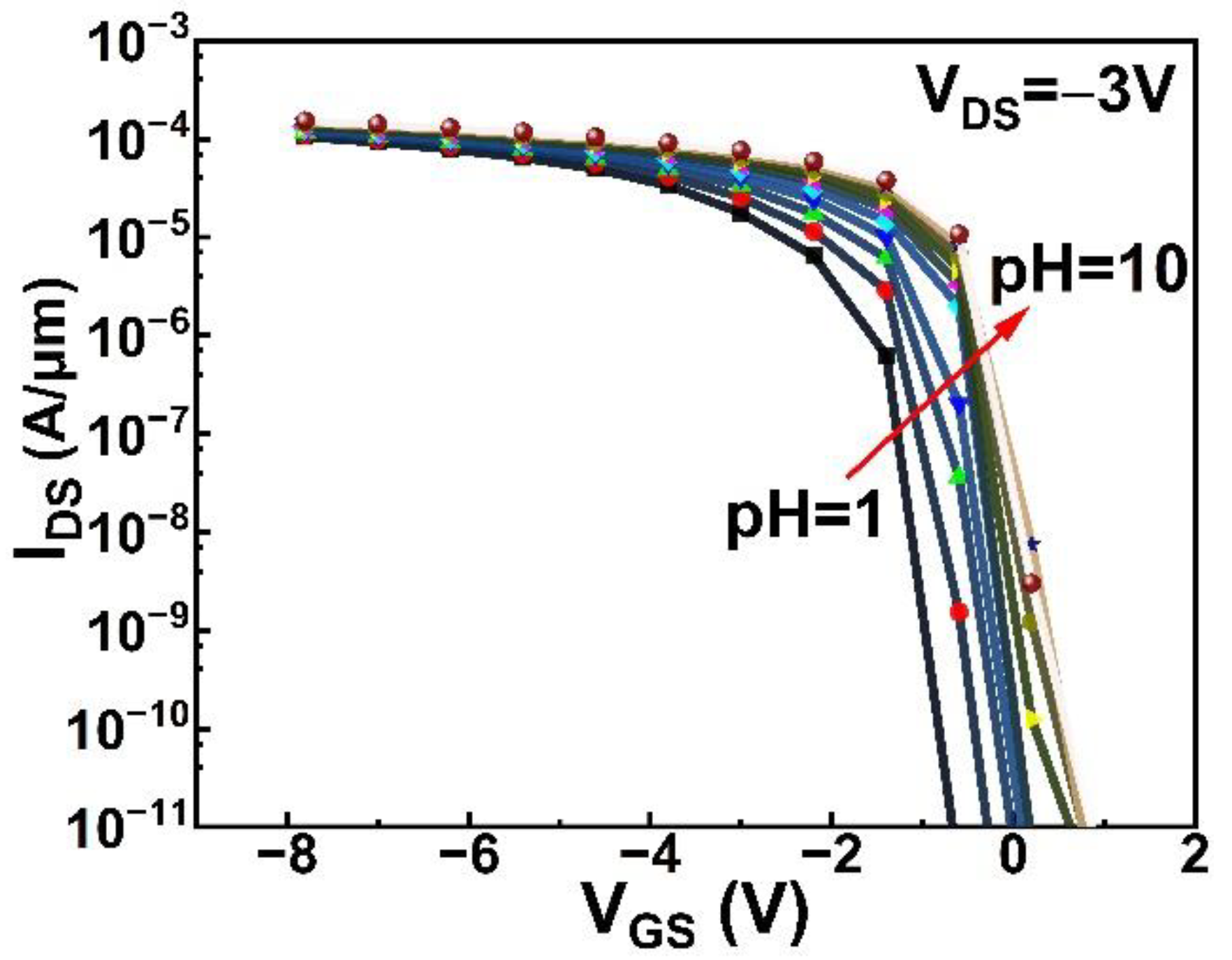
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dutta, J.C. Ion sensitive field effect transistor for applications in bioelectronic sensors: A research review. In Proceedings of the 2012 2nd National Conference on Computational Intelligence and Signal Processing (CISP), Guwahati, India, 2–3 March 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Manjakkal, L.; Szwagierczak, D.; Dahiya, R. Metal oxides based electrochemical pH sensors: Current progress and future perspectives. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 109, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, C. Design and Implementation of a pH Sensor for Micro Solution Based on Nanostructured Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor. Sensors 2020, 20, 6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakawa, H.; Louis, E.J.; MacDiarmid, A.G.; Chiang, C.K.; Heeger, A.J. Synthesis of electrically conducting organic polymers: Halogen derivatives of polyacetylene, (CH)x. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1977, 16, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Liang, G. Dual-gate pentacene organic field-effect transistors based on a nano assembled SiO2 nanoparticle thin film as the gate dielectric layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 064102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.C. Organic semiconductors. In Encyclopedia of Modern Optics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 220–231. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.K.; Joshi, A.M. Dielectric-Modulated Double Gate Bilayer Electrode Organic Thin Film Transistor-based Biosensor for Label-Free Detection: Simulation Study and Sensitivity Analysis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.15041. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, S.; Bashir, F.; Khanday, F.A. Dielectrically Modulated Label Free Metal Controlled Organic Thin Film Transistor for Biosensing Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 18318–18325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.C.; MacKenzie, J.D.; McCulloch, I.; Rivnay, J.; Salleo, A. Materials and Applications for Large Area Electronics: Solution-Based Approaches. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Lee, W.H.; Cho, K. Recent Advances in Organic Transistor Printing Processes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2302–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Someya, T. Recent Progress in the Development of Printed Thin-Film Transistors and Circuits with High-Resolution Printing Technology. Adv. Mater. 2016, 29, 1602736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundlach, D.J.; Shur, M.S.; Jackson, T.; Kanicki, J.; Martin, S.; Dodabalapur, A.; Crone, B. Electrical Behavior of Organic Transistors and Circuits. In Printed Organic and Molecular Electronics; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 347–524. [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach, D.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Jackson, T.N.; Nelson, S.F.; Schlom, D.G. Pentacene organic thin-film transistors-molecular ordering and mobility. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1997, 18, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartic, C.; Palan, B.; Campitelli, A.; Borghs, G. Monitoring pH with organic-based field-effect transistors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 83, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhu, X.; Choi, J.-W.; Ahn, C. A disposable polymer field effect transistor (FET) for pH measurement. In Proceedings of the TRANSDUCERS 03, 12th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Boston, MA, USA, 8–12 June 2003; Digest of Technical Papers (Cat. No. 03TH8664). IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1172–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Torsi, L. Novel applications of organic based thin film transistors. Microelectron. Reliab. 2000, 40, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsi, L.; Dodabalapur, A.; Sabbatini, L.; Zambonin, P. Multi-parameter gas sensors based on organic thin-film-transistors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 67, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsi, L.; Cioffi, N.; Di Franco, C.; Sabbatini, L.; Zambonin, P.; Bleve-Zacheo, T. Organic thin film transistors: From active materials to novel applications. Solid-State Electron. 2001, 45, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caboni, A.; Orgiu, E.; Barbaro, M.; Bonfiglio, A. Flexible Organic Thin-Film Transistors for pH Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, K.; Lemiti, M.; Tardy, J.; Bessueille, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Flexible pentacene ion sensitive field effect transistor with a hydrogenated silicon nitride surface treated Parylene top gate insulator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 183305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spijkman, M.-J.; Brondijk, J.J.; Geuns, T.C.T.; Smits, E.C.P.; Cramer, T.; Zerbetto, F.; Stoliar, P.; Biscarini, F.; Blom, P.W.M.; de Leeuw, D.M. Dual-Gate Organic Field-Effect Transistors as Potentiometric Sensors in Aqueous Solution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.; Seol, Y.; Lee, N.-E. Organic field-effect transistor with extended indium tin oxide gate structure for selective pH sensing. Org. Electron. 2011, 12, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chong, H.A. pH sensor using nano electrodes in organic semiconductor. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 September 2004; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 1968–1971. [Google Scholar]
- Silvaco Inc. Device Simulation Software, Version 5.2.14.R; Silvaco Inc.: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Klauk, H.; Zschieschang, U.; Halik, M. Low-voltage organic thin-film transistors with large transconductance. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 074514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.-W.; Choi, S.-J.; Ahn, J.-H.; Moon, D.-I.; Park, T.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, Y.-K. An underlap field-effect transistor for electrical detection of influenza. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 033703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Ahn, J.-H.; Choi, S.-J.; Im, M.; Kim, S.; Duarte, J.P.; Kim, C.-H.; Park, T.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, Y.-K. An underlap channel-embedded field-effect transistor for biosensor application in watery and dry environment. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2012, 11, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kymissis, I. Organic Field Effect Transistors: Theory, Fabrication and Characterization; Springer Science Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bandiziol, A.; Palestri, P.; Pittino, F.; Esseni, D.; Selmi, L. A TCAD-Based Methodology to Model the Site-Binding Charge at ISFET/Electrolyte Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 3379–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Lee, J.; Yoon, J.; Ahn, J.H.; Park, T.J.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, D.M.; Choi, S.J. TCAD-based simulation method for the electrolyte–insulator–semiconductor field-effect transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittino, F.; Palestri, P.; Scarbolo, P.; Esseni, D.; Selmi, L. Models for the use of commercial TCAD in the analysis of silicon-based integrated biosensors. Solid State Electron. 2014, 98, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, R.; Kumar, N.; Garcia, C.P.; Georgiev, V. Assessing the Effect of Scaling High-Aspect-Ratio ISFET with Physical Model Interface for Nano-Biosensing Application. Solid State Electron. 2022, 195, 108374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneshan, S.; Rasaiah, J.C.; Lynden-Bell, R.M.; Lee, S.H. Solvent structure, dynamics, and ion mobility in aqueous solutions at 25 C. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 4193–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, C.H.; Maruoka, F.; Hattori, R. Structural analysis on organic thin-film transistor with device simulation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2009, 57, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.-W.; Park, K.-M.; Song, J.-H.; Lee, C.; Hwang, D. The electrical characteristics of pentacene-based organic field-effect transistors with polymer gate insulators. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2004, 5, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minari, T.; Nemoto, T.; Isoda, S. Temperature and electric-field dependence of the mobility of a single-grain pentacene field-effect transistor. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 034506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fine, D.; Basu, D.; Dodabalapur, A. Electric-field-dependent charge transport in organic thin-film transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 054515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulos, C.D.; Malenfant, P.R. Organic thin film transistors for large area electronics. Adv. Mater. 2022, 14, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, M.; Cerdeira, A.; Puigdollers, J.; Reséndiz, L.; Pallares, J.; Marsal, L.F.; Voz, C.; Iñiguez, B. Accurate modeling and parameter extraction method for organic TFTs. Solid State Electron. 2005, 49, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, L.J.A.; Mihailetchi, V.D.; Blom, P.W.M. Bimolecular recombination in polymer/fullerene bulk heterojunction solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 052104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yates, D.E.; Levine, S.; Healy, T.W. Site-binding model of the electrical double layer at the oxide/water interface. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1: Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1974, 70, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landheer, D.; Aers, G.; McKinnon, W.R.; Deen, M.J.; Ranuarez, J.C. Model for the field effect from layers of biological macromolecules on the gates of metal-oxide-semiconductor transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 044701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, R.; Saxena, M.; Gupta, M. Analytical Model of pH sensing Characteristics of Junctionless Silicon on Insulator ISFET. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Dorvel, B.R.; Go, J.; Nair, P.R.; Elibol, O.H.; Credo, G.M.; Daniels, J.S.; Chow, E.K.C.; Su, X.; Varma, M.; et al. High-k dielectric Al2O3 nanowire and nanoplate field effect sensors for improved pH sensing. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Y.H.; Feng, P.; Zhu, L.Q.; Shi, Y.; Wan, Q. Enhancing the pH sensitivity by laterally synergic modulation in dual-gate electric-double-layer transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 073507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, S.A.; Iltesha; Ehteshamuddin, M.; Loan, S.A. Dielectrically Modulated Source-Engineered Charge-Plasma-Based Schottky-FET as a Label-Free Biosensor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfattner, R.; Foudeh, A.M.; Chen, S.; Niu, W.; Matthews, J.R.; He, M.; Bao, Z. Dual-Gate Organic Field-Effect Transistor for pH Sensors with Tunable Sensitivity. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 5, 1800381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, J.; Panda, S. Back-channel electrolyte-gated a-IGZO dual-gate thin-film transistor for enhancement of pH sensitivity over nernst limit. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, P.; Singh, R.; Chauhan, Y.S. Crossing the Nernst Limit (59 mV/pH) of Sensitivity Through Tunneling Transistor-Based Biosensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 3233–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majeed, L.; Amin, S.I.; Rasool, Z.; Bashir, I.; Kumar, N.; Anand, S. TCAD Device Modeling and Simulation Study of Organic Field Effect Transistor-Based pH Sensor with Tunable Sensitivity for Surpassing Nernst Limit. Electronics 2023, 12, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030536
Majeed L, Amin SI, Rasool Z, Bashir I, Kumar N, Anand S. TCAD Device Modeling and Simulation Study of Organic Field Effect Transistor-Based pH Sensor with Tunable Sensitivity for Surpassing Nernst Limit. Electronics. 2023; 12(3):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030536
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajeed, Lubna, Syed Intekhab Amin, Zuber Rasool, Ishrat Bashir, Naveen Kumar, and Sunny Anand. 2023. "TCAD Device Modeling and Simulation Study of Organic Field Effect Transistor-Based pH Sensor with Tunable Sensitivity for Surpassing Nernst Limit" Electronics 12, no. 3: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030536
APA StyleMajeed, L., Amin, S. I., Rasool, Z., Bashir, I., Kumar, N., & Anand, S. (2023). TCAD Device Modeling and Simulation Study of Organic Field Effect Transistor-Based pH Sensor with Tunable Sensitivity for Surpassing Nernst Limit. Electronics, 12(3), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030536










