Risk-Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robot Crowd Navigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- We suggest a risk-aware deep reinforcement learning-based method for robot crowd navigation. This approach effectively addresses the freezing robot problem by enhancing the robot’s perception of a small number of humans who pose collision risks. Our experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in crowded scenario tests.
- -
- We introduce a feature encoding method based on a collision risk function. This method enables robots to anticipate humans with collision risks in a moving crowd. The collision risk function takes into account factors such as relative speed and relative position in robot–human interactions.
- -
- We propose an adaptive feature fusion model that integrates the features encoded based on the collision risk function with those encoded using learning techniques. By incorporating prior knowledge of collision risk into the learned attention, our model effectively reduces the risk of robot–human collisions in crowded scenes.
2. Related Works
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Formulation
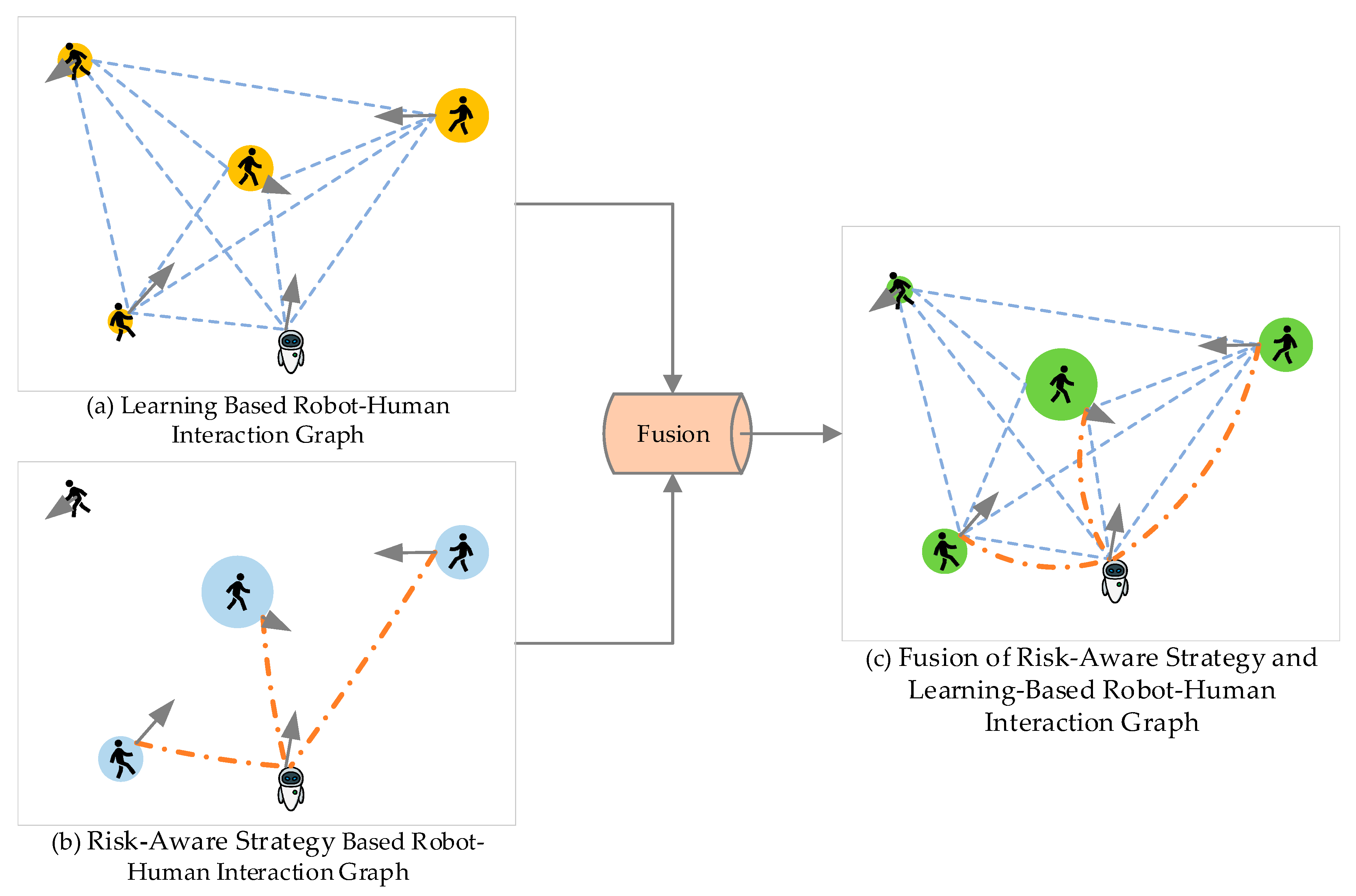
3.2. Risk-Aware Interaction Graph Representation
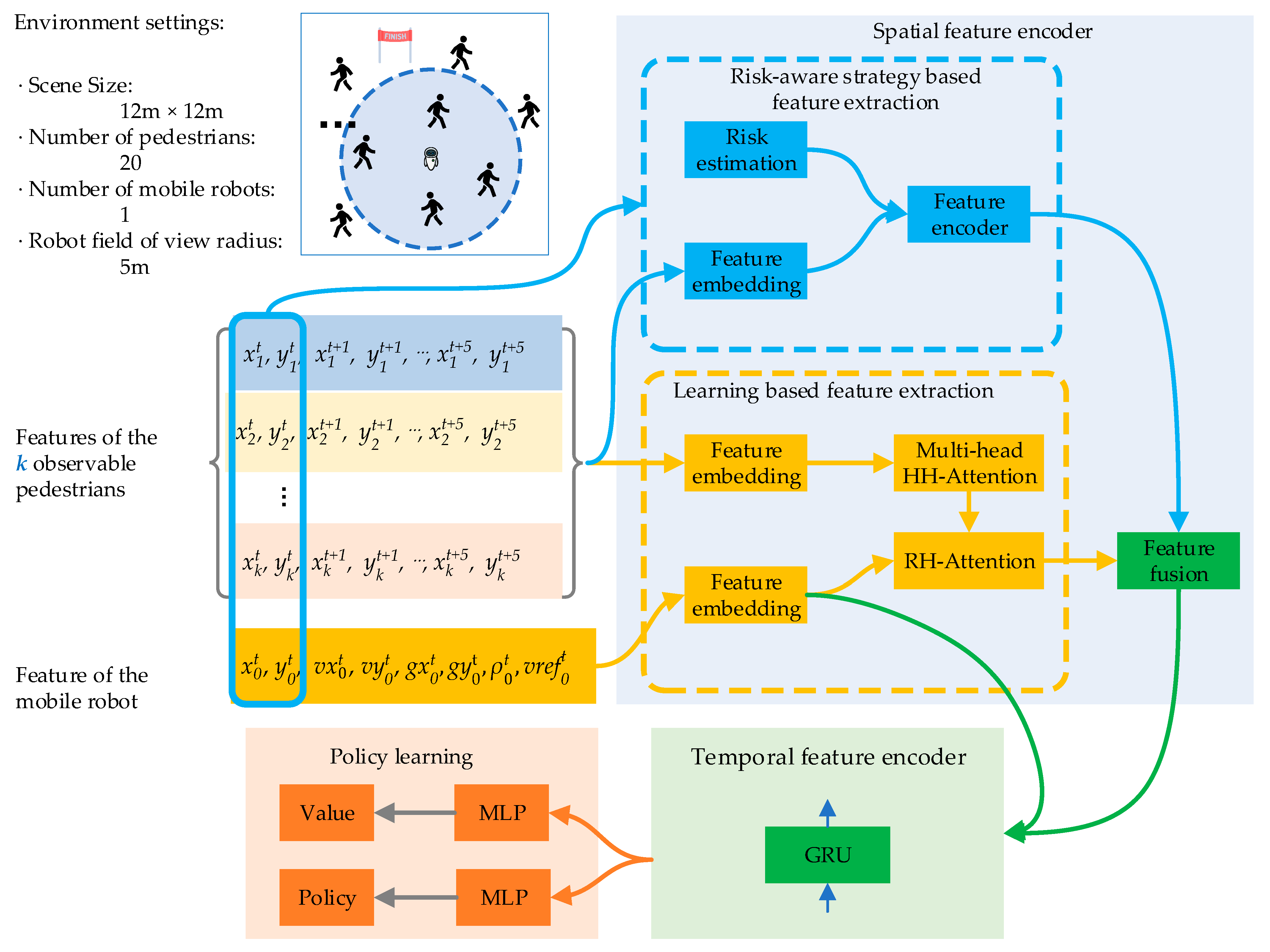
3.3. Network Architecture
3.3.1. Spatial Feature Encoder
- (a) Risk-aware strategy-based feature extraction.
- (b) Attention-based feature extraction.
- (c) Feature fusion
3.3.2. Temporal Encoder
3.3.3. Policy Learning
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Environments
4.2. Training Details for Our Proposed Method
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
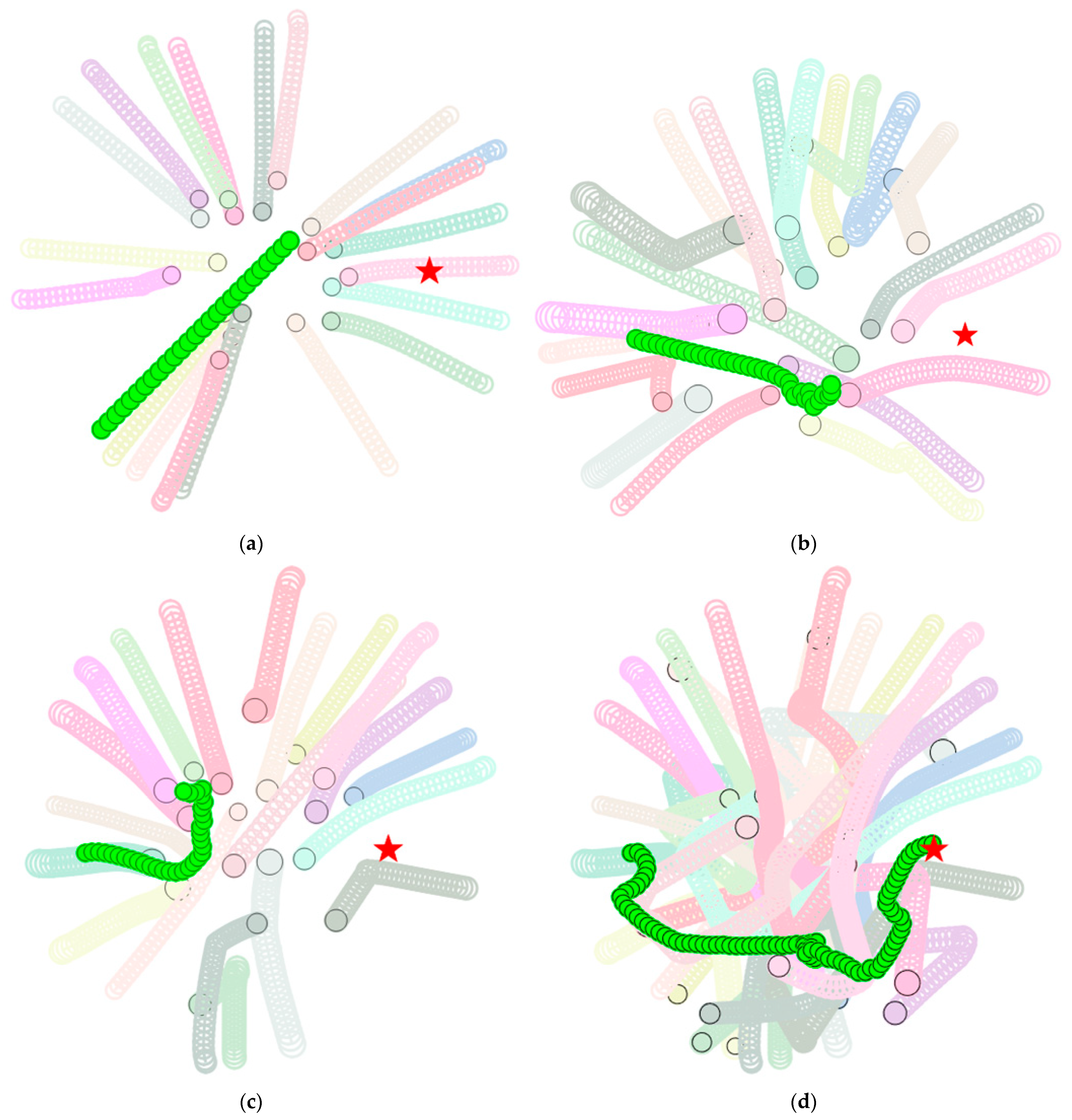
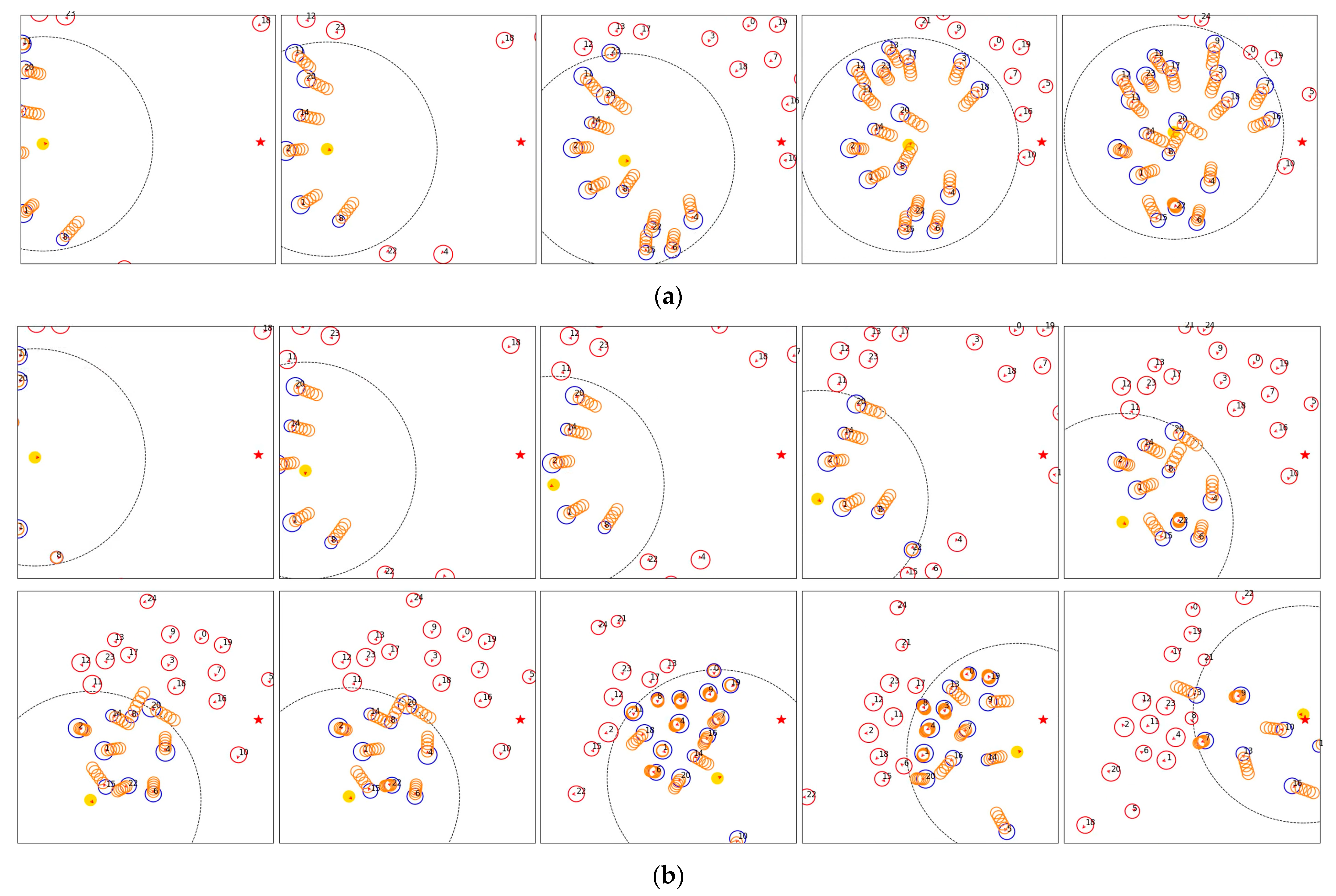
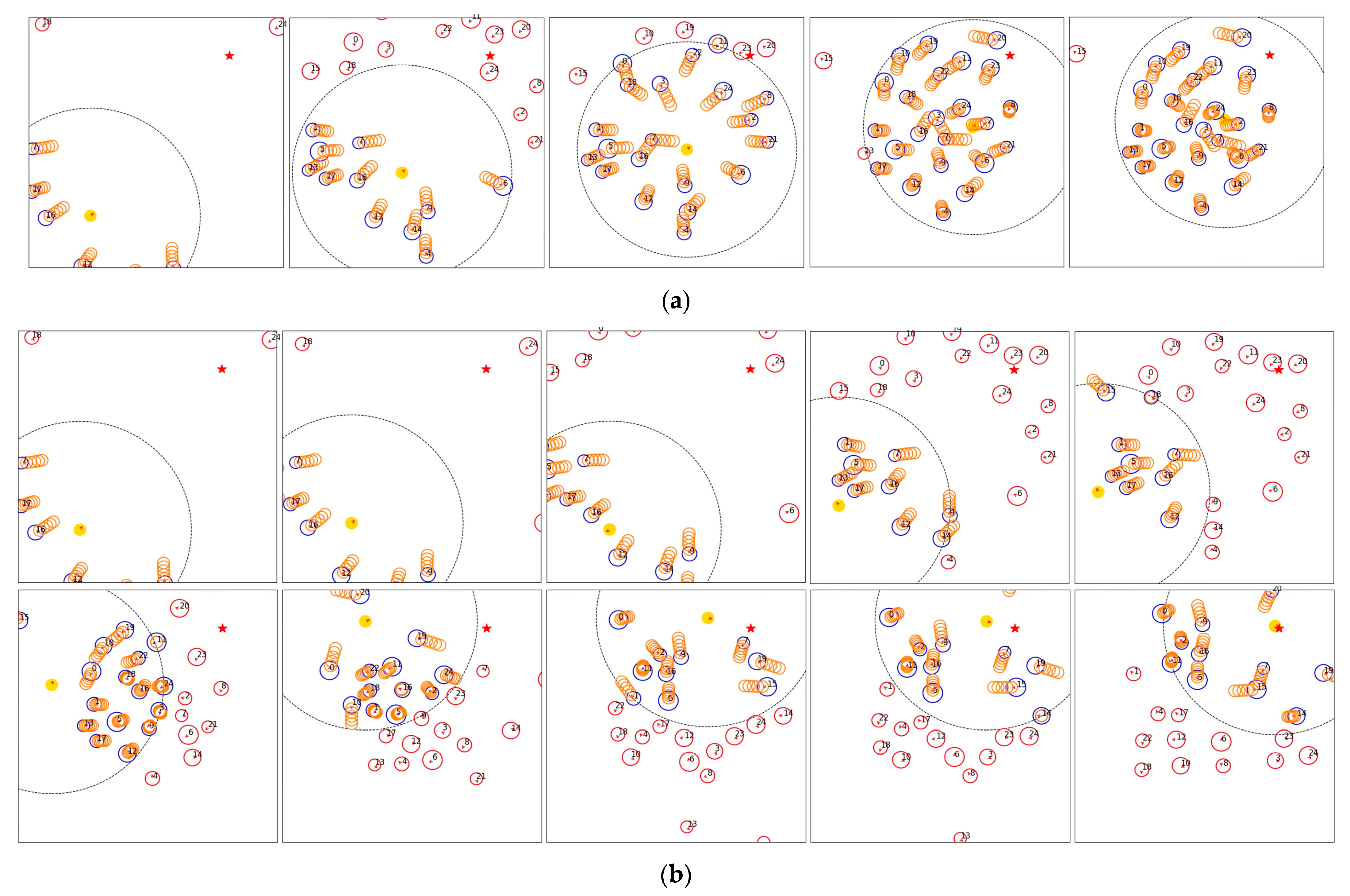
4.4. Experiment Results
4.4.1. Experiment Results for Scenarios with Low Pedestrian Density (10 Individuals)
4.4.2. Experiment Results for Scenarios with High Pedestrian Density (20 Individuals)
4.4.3. Experiment Results for 25 Pedestrian Scenarios
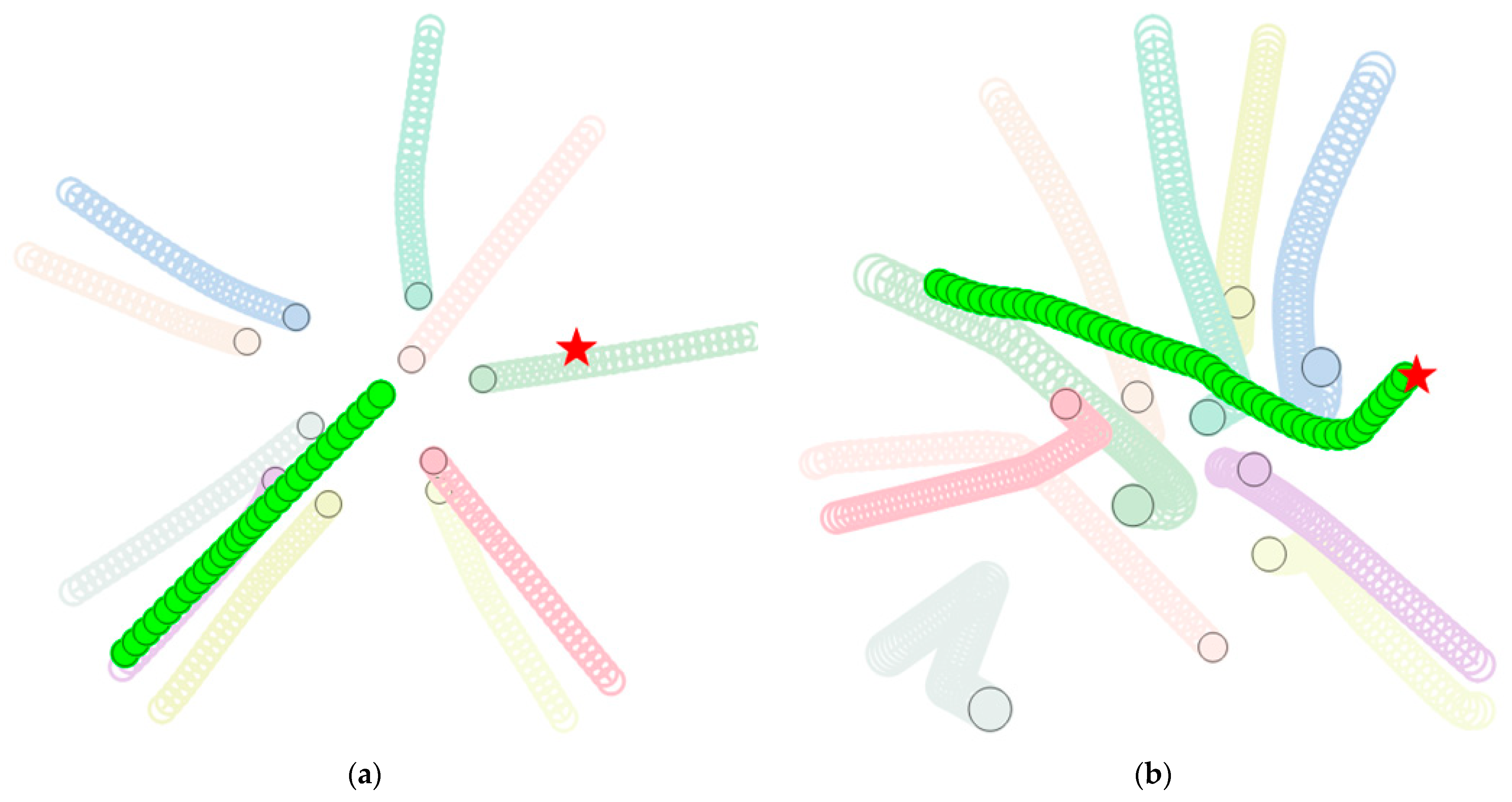
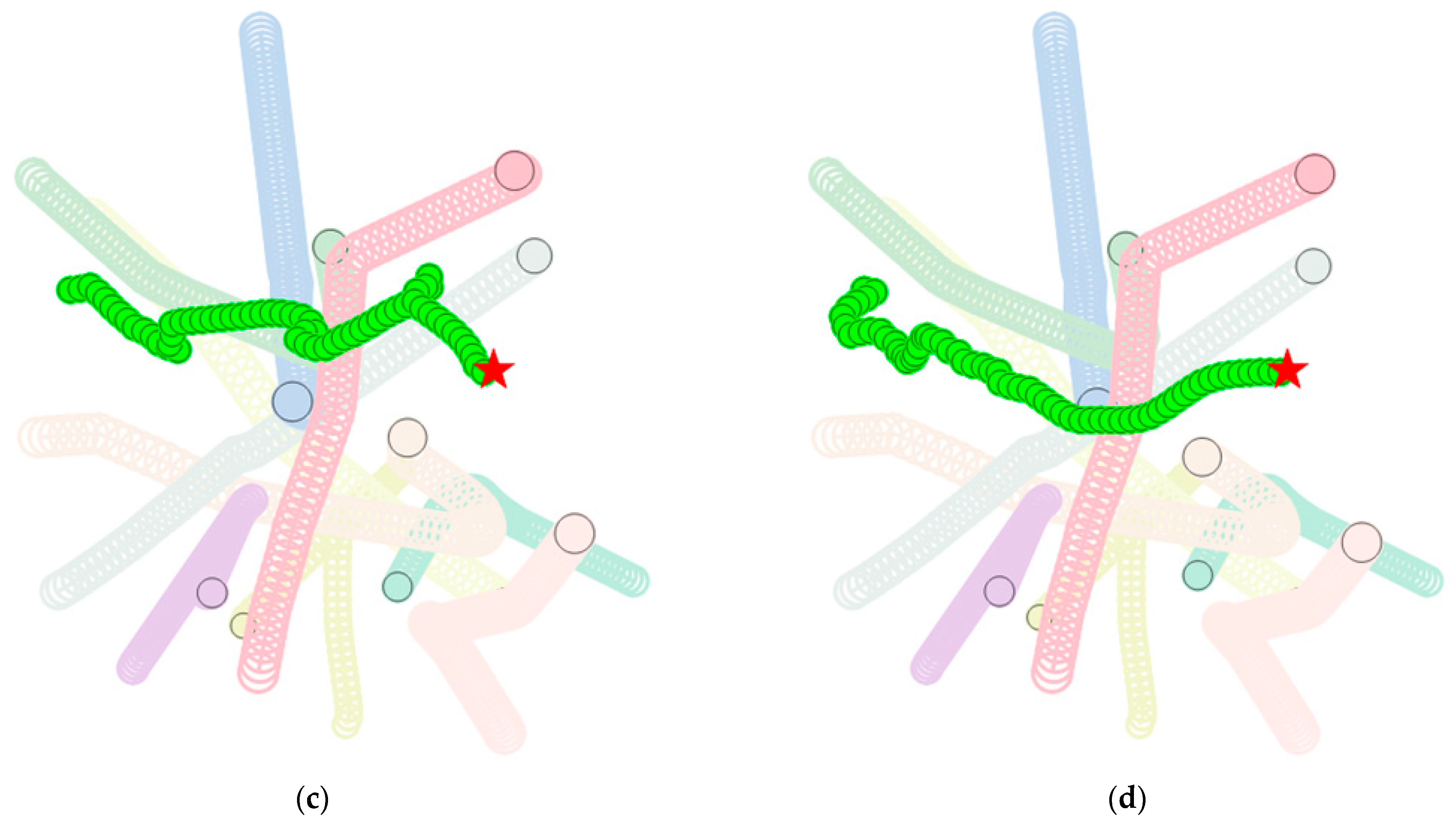
4.5. Analysis of Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brose, S.W.; Weber, D.J.; Salatin, B.A.; Grindle, G.G.; Wang, H.; Vazquez, J.J.; Cooper, R.A. The Role of Assistive Robotics in the Lives of Persons with Disability. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehab. 2010, 89, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matarić, M.J.; Scassellati, B. Socially Assistive Robotics. In Springer Handbook of Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 18, pp. 1973–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarić, M.J. Socially Assistive Robotics: Human Augmentation versus Automation. Sci. Rob. 2017, 2, eaam5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udupa, S.; Kamat, V.R.; Menassa, C.C. Shared Autonomy in Assistive Mobile Robots: A Review. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2023, 18, 827–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, B.; Warnell, G.; Stone, P. Motion Planning and Control for Mobile Robot Navigation Using Machine Learning: A Survey. Auton. Robot. 2022, 46, 569–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbing, D.; Molnár, P. Social Force Model for Pedestrian Dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 51, 4282–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Tian, J.; Hu, H.; Peng, X. Hybrid Path Planning Based on Safe A* Algorithm and Adaptive Window Approach for Mobile Robot in Large-Scale Dynamic Environment. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2020, 99, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén-Ruiz, S.; Bandera, J.P.; Hidalgo-Paniagua, A.; Bandera, A. Evolution of Socially-Aware Robot Navigation. Electronics 2023, 12, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Guo, H.; Ang, M.; Rus, D. Deep Imitation Learning for Autonomous Navigation in Dynamic Pedestrian Environments. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 4108–4115. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, M.; Chen, Y.F.; How, J.P. Collision Avoidance in Pedestrian-Rich Environments With Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 10357–10377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, R. Learning World Transition Model for Socially Aware Robot Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 9262–9268. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Nguyen, N.M.; Sakib, N.; Graves, D.; Yao, H.; Jagersand, M. Mapless Navigation among Dynamics with Social-Safety-Awareness: A Reinforcement Learning Approach from 2D Laser Scans. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 6979–6985. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, U.; Kumar, N.K.S.; Sathyamoorthy, A.J.; Manocha, D. DWA-RL: Dynamically Feasible Deep Reinforcement Learning Policy for Robot Navigation among Mobile Obstacles. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 6057–6063. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-D’Arpino, C.; Liu, C.; Goebel, P.; Martin-Martin, R.; Savarese, S. Robot Navigation in Constrained Pedestrian Environments Using Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1140–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Samsani, S.S.; Mutahira, H.; Muhammad, M.S. Memory-Based Crowd-Aware Robot Navigation Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, B.E.; Liu, M. Robot Navigation in Crowds by Graph Convolutional Networks with Attention Learned From Human Gaze. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 2754–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chang, P.; Huang, Z.; Chakraborty, N.; Hong, K.; Liang, W.; McPherson, D.L.; Geng, J.; Driggs-Campbell, K. Intention Aware Robot Crowd Navigation with Attention-Based Interaction Graph. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 12015–12021. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyamoorthy, A.J.; Patel, U.; Guan, T.; Manocha, D. Frozone: Freezing-Free, Pedestrian-Friendly Navigation in Human Crowds. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4352–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berg, J.; Guy, S.J.; Lin, M.; Manocha, D. Reciprocal N-Body Collision Avoidance. In Robotics Research; Pradalier, C., Siegwart, R., Hirzinger, G., Eds.; Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 70, pp. 3–19. ISBN 978-3-642-19456-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kamezaki, M.; Tsuburaya, Y.; Kanada, T.; Hirayama, M.; Sugano, S. Reactive, Proactive, and Inducible Proximal Crowd Robot Navigation Method Based on Inducible Social Force Model. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 3922–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, R.; Hao, Q.; Pan, J. Reinforcement Learned Distributed Multi-Robot Navigation With Reciprocal Velocity Obstacle Shaped Rewards. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 5896–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Kreiss, S.; Alahi, A. Crowd-Robot Interaction: Crowd-Aware Robot Navigation With Attention-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 6015–6022. [Google Scholar]
- Samsani, S.S.; Muhammad, M.S. Socially Compliant Robot Navigation in Crowded Environment by Human Behavior Resemblance Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 5223–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Min, B.-C. Feedback-Efficient Active Preference Learning for Socially Aware Robot Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 11336–11343. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, Y.-J.; Itkina, M.; Liu, S.; Driggs-Campbell, K. Occlusion-Aware Crowd Navigation Using People as Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 12031–12037. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Cao, C.; Pan, J. A Hierarchical Approach for Mobile Robot Exploration in Pedestrian Crowd. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Miao, Y.; Wang, H. Graph Relational Reinforcement Learning for Mobile Robot Navigation in Large-Scale Crowded Environments. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 8776–8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chang, P.; Liang, W.; Chakraborty, N.; Driggs-Campbell, K. Decentralized Structural-RNN for Robot Crowd Navigation with Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 3517–3524. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z. Crowd-Aware Mobile Robot Navigation Based on Improved Decentralized Structured RNN via Deep Reinforcement Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Fu, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Liu, W. Spatio-Temporal Transformer-Based Reinforcement Learning for Robot Crowd Navigation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.16612. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, R.; Mao, L.; Min, B.C. NaviSTAR: Socially Aware Robot Navigation with Hybrid Spatio-Temporal Graph Transformer and Preference Learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.05979. [Google Scholar]
- Shani, G.; Pineau, J.; Kaplow, R. A Survey of Point-Based POMDP Solvers. Auton. Agents Multi-Agent Syst. 2013, 27, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Liu, M.; Everett, M.; How, J.P. Decentralized Non-Communicating Multiagent Collision Avoidance with Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Marina Bay Sands, Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 285–292. [Google Scholar]


| Method | SR (%) ↑ | CR (%) ↓ | NT (s) ↓ | PL (m) ↓ | AS (m/s) ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORCA [19] | 73.0 | 27.0 | 13.56 | 17.09 | 1.26 |
| DS-RNN [28] | 86.0 | 14.0 | 15.32 | 19.05 | 1.24 |
| CrowdNav++ [17] | 95.0 | 5.0 | 12.70 | 19.10 | 1.50 |
| Ours | 98.0 | 2.0 | 13.29 | 20.15 | 1.52 |
| Method | SR (%) ↑ | CR (%) ↓ | NT (s) ↓ | PL (m) ↓ | AS (m/s) ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORCA [19] | 69.0 | 31.0 | 14.77 | 17.67 | 1.20 |
| DS-RNN [28] | 64.0 | 36.0 | 16.31 | 19.63 | 1.20 |
| CrowdNav++ [17] | 89.0 | 11.0 | 15.03 | 21.31 | 1.42 |
| Ours | 93.2 | 6.8 | 15.89 | 22.37 | 1.41 |
| Method | SR (%) ↑ | CR (%) ↓ | NT (s) ↓ | PL (m) ↓ | AS (m/s) ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CrowdNav++ [17] | 78.0 | 22.0 | 15.06 | 20.35 | 1.35 |
| Ours | 90.0 | 10.0 | 16.71 | 22.82 | 1.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Liu, M. Risk-Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robot Crowd Navigation. Electronics 2023, 12, 4744. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12234744
Sun X, Zhang Q, Wei Y, Liu M. Risk-Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robot Crowd Navigation. Electronics. 2023; 12(23):4744. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12234744
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xueying, Qiang Zhang, Yifei Wei, and Mingmin Liu. 2023. "Risk-Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robot Crowd Navigation" Electronics 12, no. 23: 4744. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12234744
APA StyleSun, X., Zhang, Q., Wei, Y., & Liu, M. (2023). Risk-Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robot Crowd Navigation. Electronics, 12(23), 4744. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12234744








