An Efficient and High-Quality Mesh Reconstruction Method with Adaptive Visibility and Dynamic Refinement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose an improved optimization mesh-reconstruction method, and extensive experiments on BlendedMVS proved that our method can reconstruct a high-quality mesh with higher efficiency, taking only of the reconstruction time of OpenMVS [8,29] and of the reconstruction time of TDR [5] to complete the reconstruction.
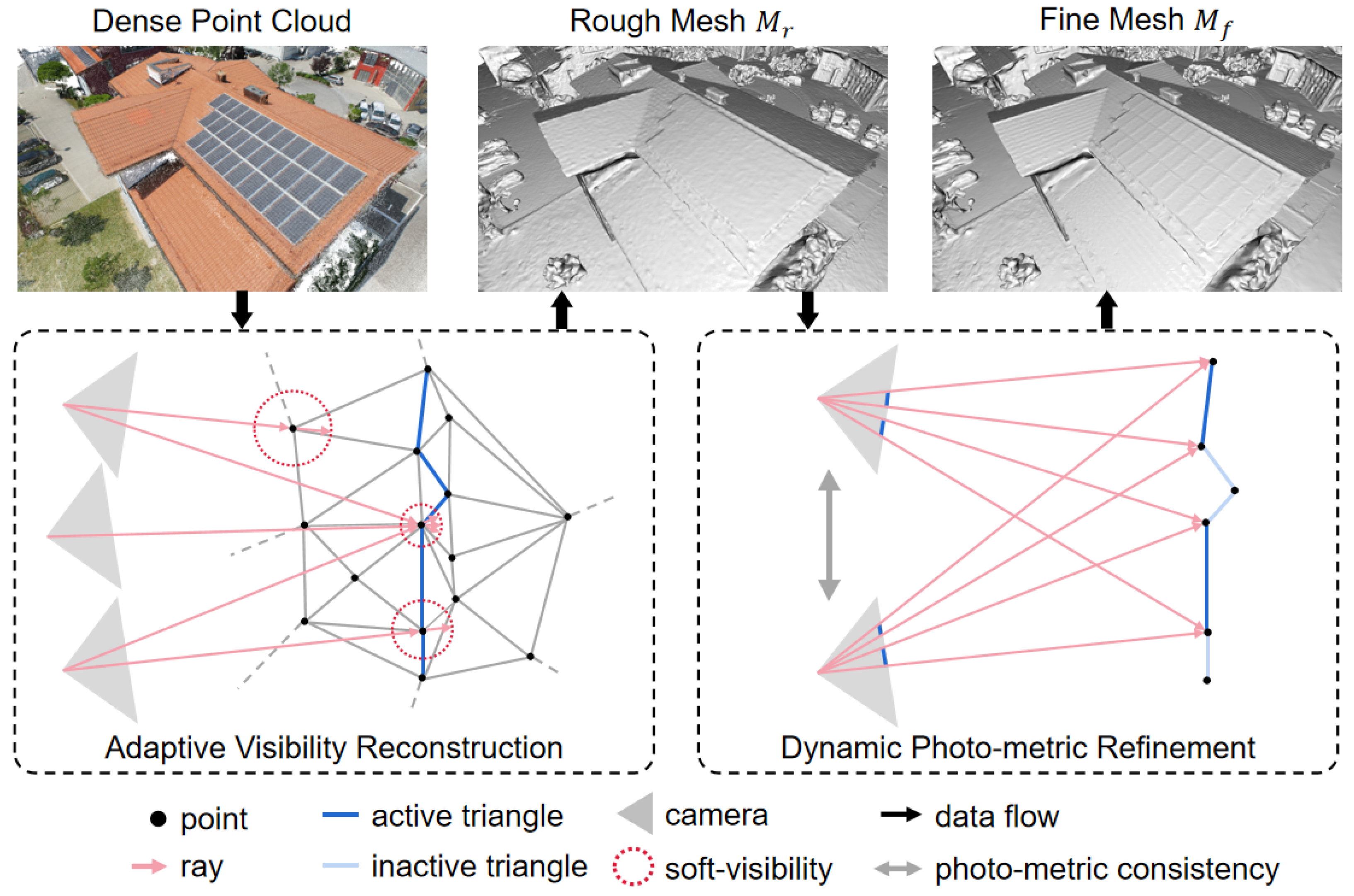
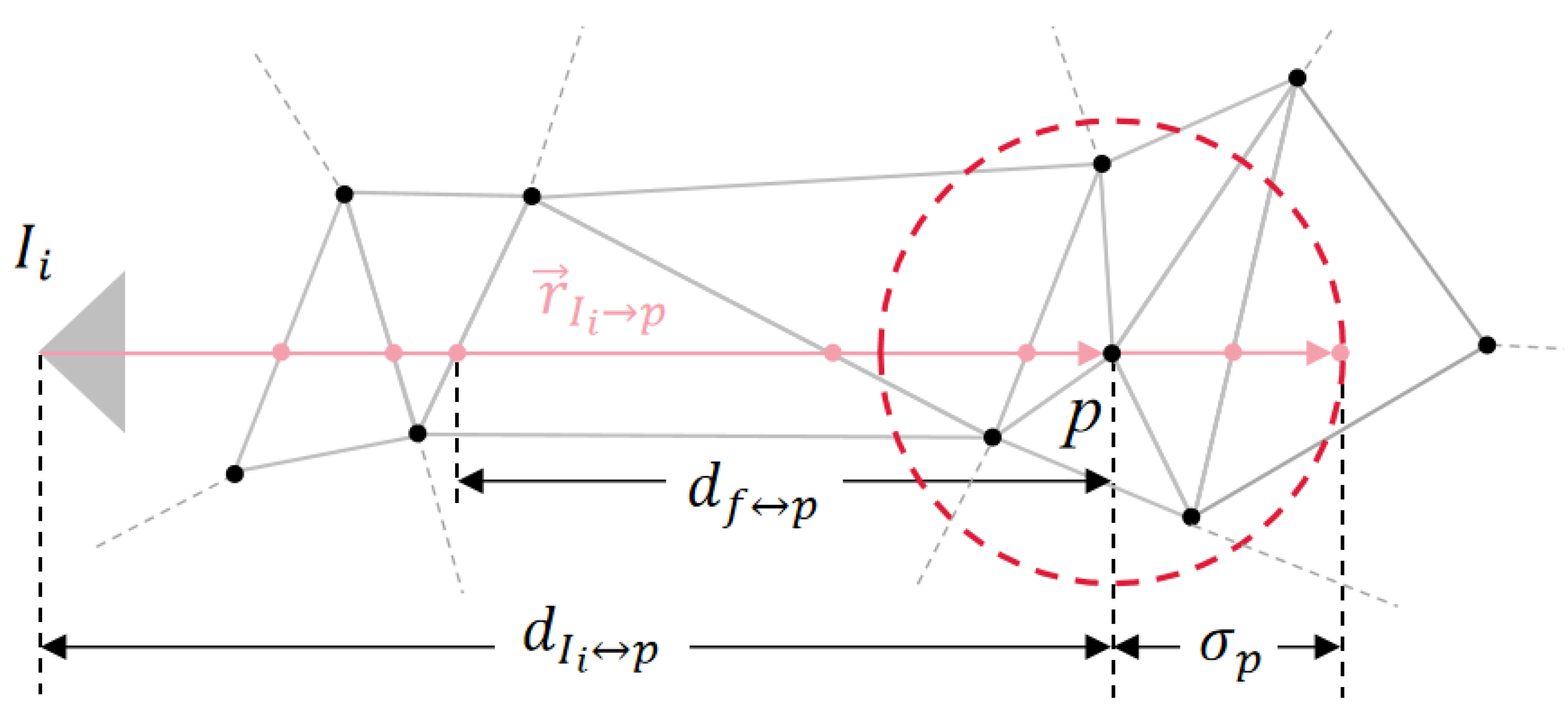
- We propose an adaptive visibility reconstruction, which analyzes the quality and importance of different points in the dense point cloud to maintain enough details and remove noise to obtain a better rough mesh.
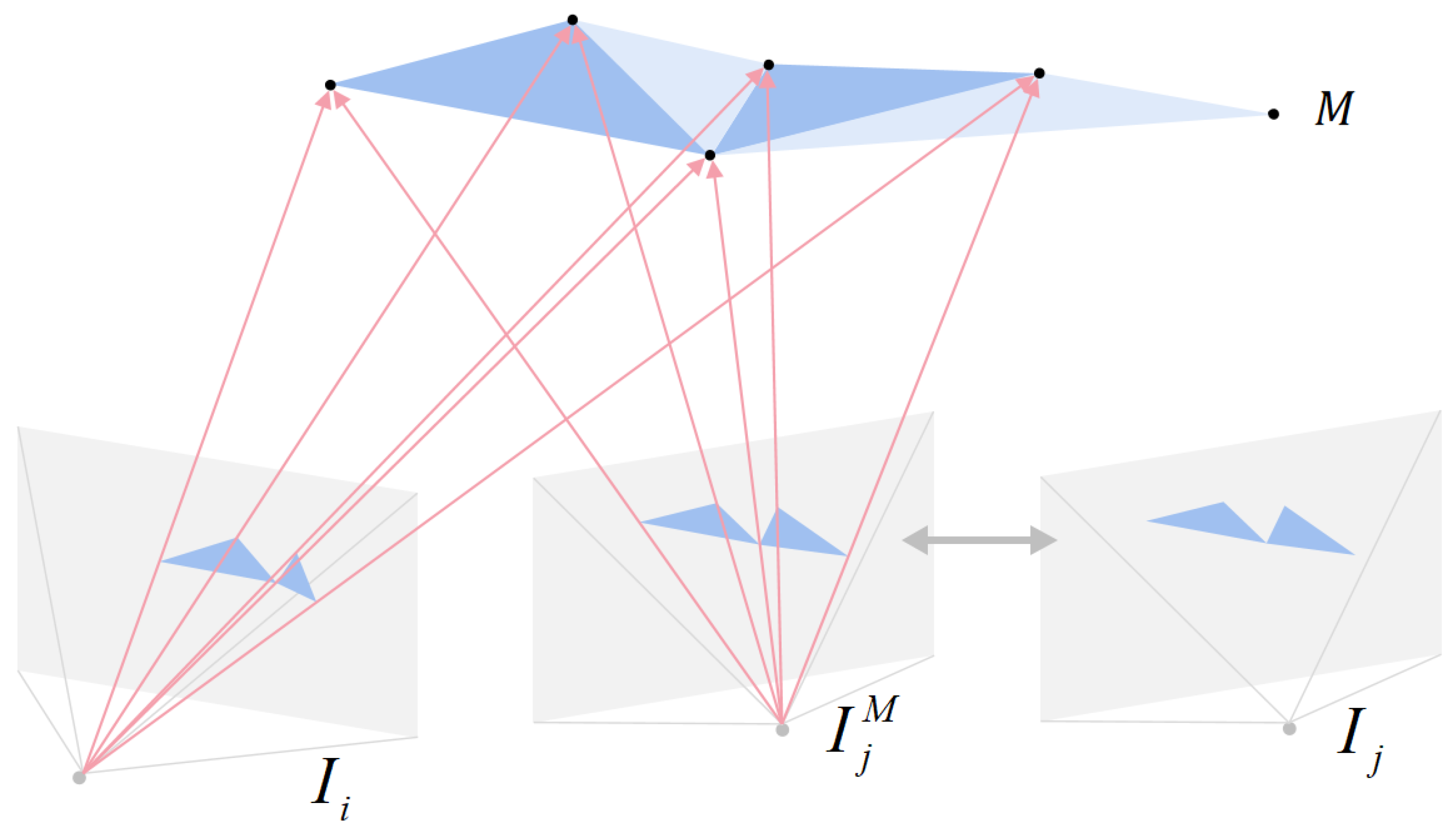
- We propose dynamic photo-metric refinement to improve the reconstruction quality and efficiency of the photo-metric refinement by utilizing the triangle gradient to adjust the learning rate and stop optimizing converged triangles dynamically.
2. Method
2.1. Adaptive Visibility Reconstruction
2.2. Dynamic Photo-Metric Refinement
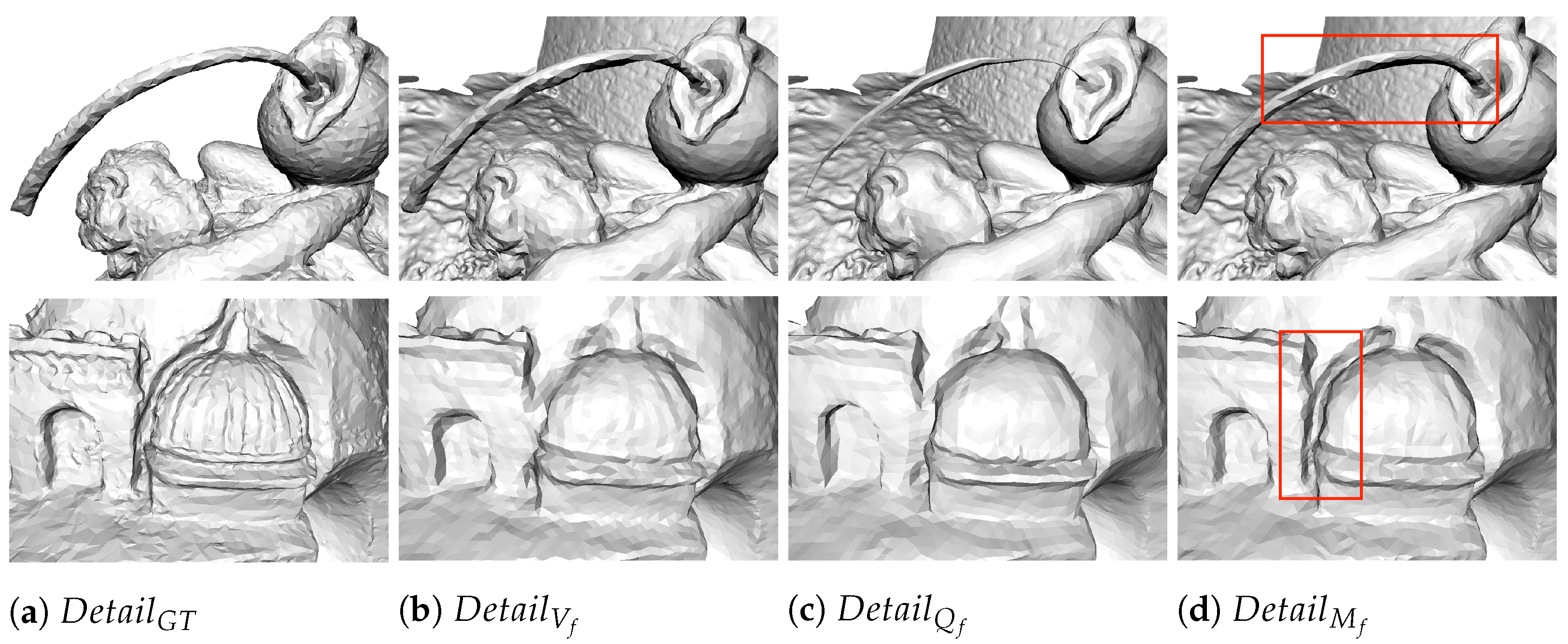
3. Experiments
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Implementation
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
3.4. Aerial Scenes
3.5. Close-Range Scenes
3.6. Real-World
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schonberger, J.L.; Frahm, J.-M. Structure-from-motion revisited. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4104–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S. Accurate multiple view 3d reconstruction using patch-based stereo for large-scale scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, D.; Qingsong, Y.; Teng, X. A GPU-PatchMatch multi-view dense matching algorithm based on parallel propagation. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2020, 49, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Sun, H.; Bao, H.; Zhang, G. DP-MVS: Detail Preserving Multi-View Surface Reconstruction of Large-Scale Scenes. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Yang, J.; Xiao, T.; Deng, F. Total Differential Photometric Mesh Refinement with Self-Adapted Mesh Denoising. Photonics 2022, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waechter, M.; Moehrle, N.; Goesele, M. Let there be color! Large-scale texturing of 3D reconstructions. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014, Proceedings of the 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Part V 13; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazhdan, M.; Chuang, M.; Rusinkiewicz, S.; Hoppe, H. Poisson surface reconstruction with envelope constraints. Comput. Graph. Forum 2020, 39, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.H.; Labatut, P.; Pons, J.P.; Keriven, R. High accuracy and visibility-consistent dense multiview stereo. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 34, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labatut, P.; Pons, J.P.; Keriven, R. Efficient multi-view reconstruction of large-scale scenes using interest points, delaunay triangulation and graph cuts. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzis, G.; Esteban, C.H.; Torr, P.H.; Cipolla, R. Multiview stereo via volumetric graph-cuts and occlusion robust photo-consistency. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 2241–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.N.; Mordohai, P.; Pollefeys, M. Multi-view stereo via graph cuts on the dual of an adaptive tetrahedral mesh. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labatut, P.; Pons, J.P.; Keriven, R. Robust and efficient surface reconstruction from range data. Comput. Graph. Forum 2009, 28, 2275–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancosek, M.; Pajdla, T. Multi-view reconstruction preserving weakly-supported surfaces. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 3121–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Jancosek, M.; Pajdla, T. Exploiting visibility information in surface reconstruction to preserve weakly supported surfaces. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 798595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, S.; Hu, Z. Detail preserved surface reconstruction from point cloud. Sensors 2019, 19, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labatut, P.; Pons, J.P.; Keriven, R. Hierarchical shape-based surface reconstruction for dense multi-view stereo. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, ICCV Workshops, Kyoto, Japan, 27 September–4 October 2009; pp. 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yao, Y.; Fang, T.; Quan, L. Reconstructing thin structures of manifold surfaces by integrating spatial curves. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2887–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, M.; Maurer, M.; Bischof, H. Efficient 3D scene abstraction using line segments. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2017, 157, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Siu, S.Y.; Fang, T.; Quan, L. Efficient multi-view surface refinement with adaptive resolution control. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Proceedings of the 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Part I 14; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Guo, B.; Peng, Z. Adaptive Fast Mesh Refinement of 3D Reconstruction Based on Image Information. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2020, 45, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Morreale, L.; Romanoni, A.; Matteucci, M. Predicting the next best view for 3d mesh refinement. In IAS 2018: Intelligent Autonomous Systems 15, Proceedings of the 15th International Conference IAS-15, Baden-Baden, Germany, 11–15 June 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Qingsong, Y.; Yingjie, Q.; Xin, C.; Fei, D. View selection strategy for photo-consistency refinement. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2020, 49, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanoni, A.; Matteucci, M. Facetwise Mesh Refinement for Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 6794–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaha, M.; Rothermel, M.; Oswald, M.R.; Sattler, T.; Richard, A.; Wegner, J.D.; Pollefeys, M.; Schindler, K. Semantically informed multiview surface refinement. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3819–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanoni, A.; Ciccone, M.; Visin, F.; Matteucci, M. Multi-view stereo with single-view semantic mesh refinement. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, D.; Xin, C.; Qingsong, Y.; Yingjie, Q. Variational refinement of mesh with line constraint for photogrammetry. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2020, 49, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanoni, A.; Matteucci, M. Mesh-based camera pairs selection and occlusion-aware masking for mesh refinement. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 125, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, L.; Fang, T.; Quan, L. Blendedmvs: A large-scale dataset for generalized multi-view stereo networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, DC, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, D. OpenMVS: Multi-View Stereo Reconstruction Library. Available online: https://cdcseacave.github.io/openMVS (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Merrell, P.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Wang, L.; Mordohai, P.; Frahm, J.M.; Yang, R.; Nistér, D.; Pollefeys, M. Real-time visibility-based fusion of depth maps. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Christoph, S. Pix4D. Available online: https://www.pix4d.com (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- CloudCompare. CloudCompare: 3D Point Cloud and Mesh Processing Software Open Source Project. Available online: https://www.cloudcompare.org (accessed on 1 October 2023).
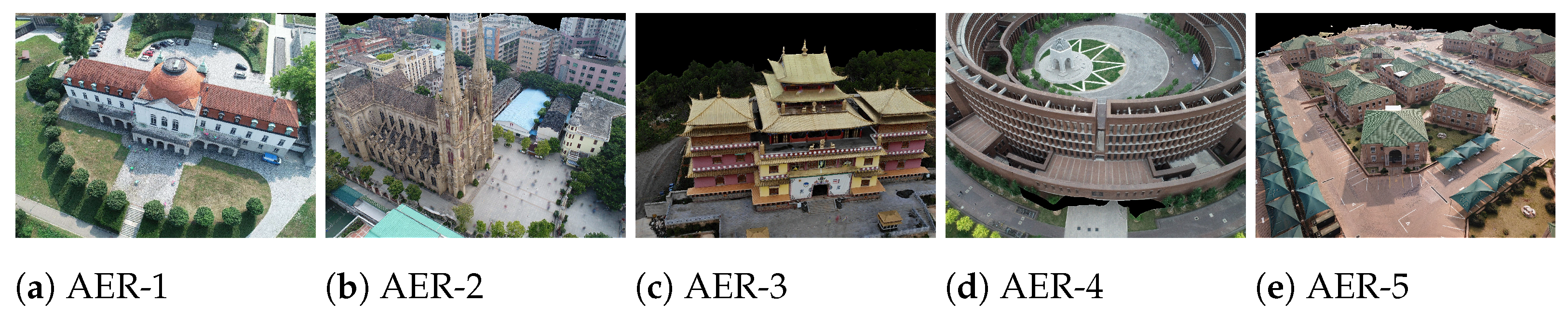









| Dataset | Number | OpenMVS [8,29] | TDBI [5] | Ours | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E() | Q() | E() | Q() | E() | Q() | Q() | ||
| AER-1 | 77 | 1708 | 0.76 | 7245 | 4.56 | 736 | 0.50 | 0.59 |
| AER-2 | 125 | 2958 | 4.65 | 13,016 | 13.67 | 1220 | 1.60 | 5.47 |
| AER-3 | 132 | 3140 | 3.62 | 8549 | 7.08 | 1189 | 1.37 | 3.71 |
| AER-4 | 149 | 3516 | 2.07 | 17,968 | 8.11 | 1457 | 1.08 | 2.47 |
| AER-5 | 186 | 6125 | 1.14 | 67,568 | 5.98 | 2106 | 1.08 | 1.97 |
| Dataset | Number | OpenMVS [8,29] | TDBI [5] | Ours | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E() | Q() | E() | Q() | E() | Q() | Q() | ||
| CLO-1 | 51 | 1073 | 8.70 | 20,680 | 17.52 | 497 | 0.65 | 10.05 |
| CLO-2 | 64 | 1172 | 0.03 | 155,636 | 6.8 | 466 | 0.57 | 1.43 |
| CLO-3 | 91 | 1820 | 0.58 | 9893 | 4.11 | 834 | 1.92 | 2.81 |
| CLO-4 | 100 | 2286 | 4.72 | 28,340 | 8.52 | 888 | 1.57 | 7.65 |
| CLO-5 | 117 | 2078 | 2.84 | 46,047 | 1.13 | 794 | 0.46 | 3.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Q.; Xiao, T.; Qu, Y.; Yang, J.; Deng, F. An Efficient and High-Quality Mesh Reconstruction Method with Adaptive Visibility and Dynamic Refinement. Electronics 2023, 12, 4716. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224716
Yan Q, Xiao T, Qu Y, Yang J, Deng F. An Efficient and High-Quality Mesh Reconstruction Method with Adaptive Visibility and Dynamic Refinement. Electronics. 2023; 12(22):4716. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224716
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Qingsong, Teng Xiao, Yingjie Qu, Junxing Yang, and Fei Deng. 2023. "An Efficient and High-Quality Mesh Reconstruction Method with Adaptive Visibility and Dynamic Refinement" Electronics 12, no. 22: 4716. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224716
APA StyleYan, Q., Xiao, T., Qu, Y., Yang, J., & Deng, F. (2023). An Efficient and High-Quality Mesh Reconstruction Method with Adaptive Visibility and Dynamic Refinement. Electronics, 12(22), 4716. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224716






