Design and Analysis of an Effective Multi-Barriers Model Based on Non-Stationary Gaussian Random Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Related Work
2.1. Geostatistical Data Regression Model
2.2. Point Pattern
2.2.1. Traditional Methods
2.2.2. Stochastic Partial Differential Equation (SPDE) Method
2.3. Integrated Nested Laplace Approximation (INLA)
3. The Basic Spatial Regression Model
4. Multi-Barriers Gaussian Random Fields
4.1. Mathematical Model
4.2. Model Comparison
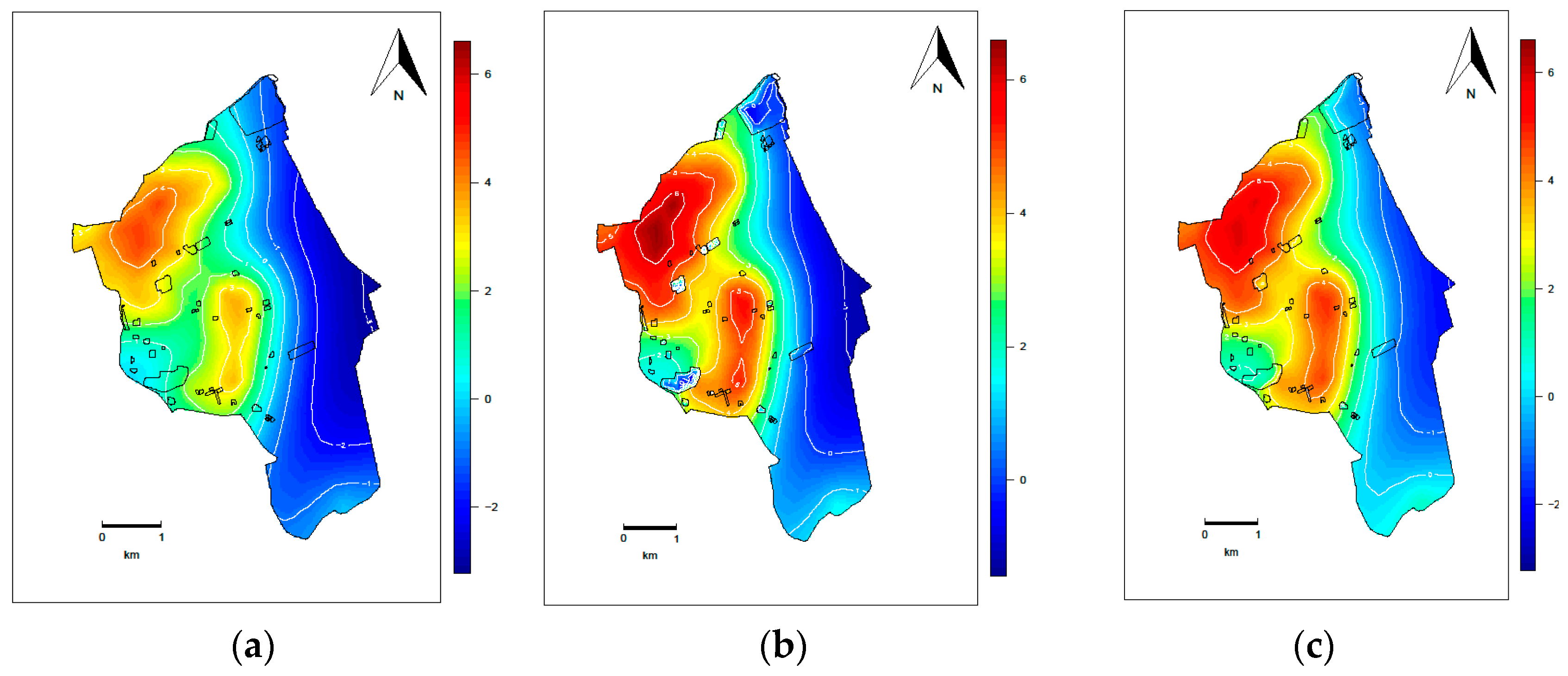
5. Experimental Analysis
5.1. Simulation Experiment of Geostatistical Data
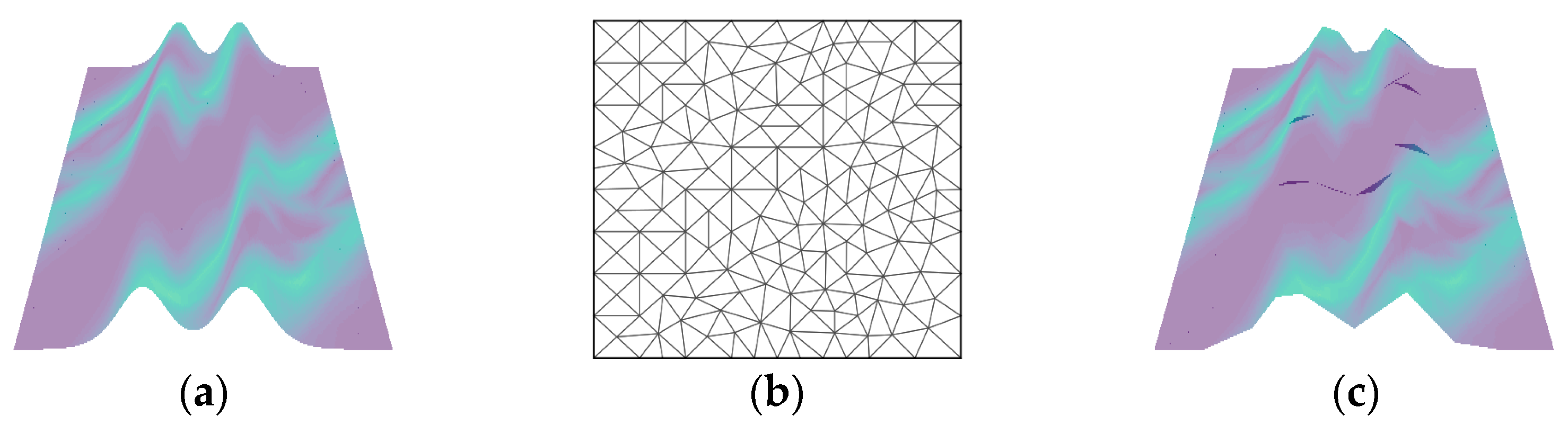
5.1.1. Data Simulation
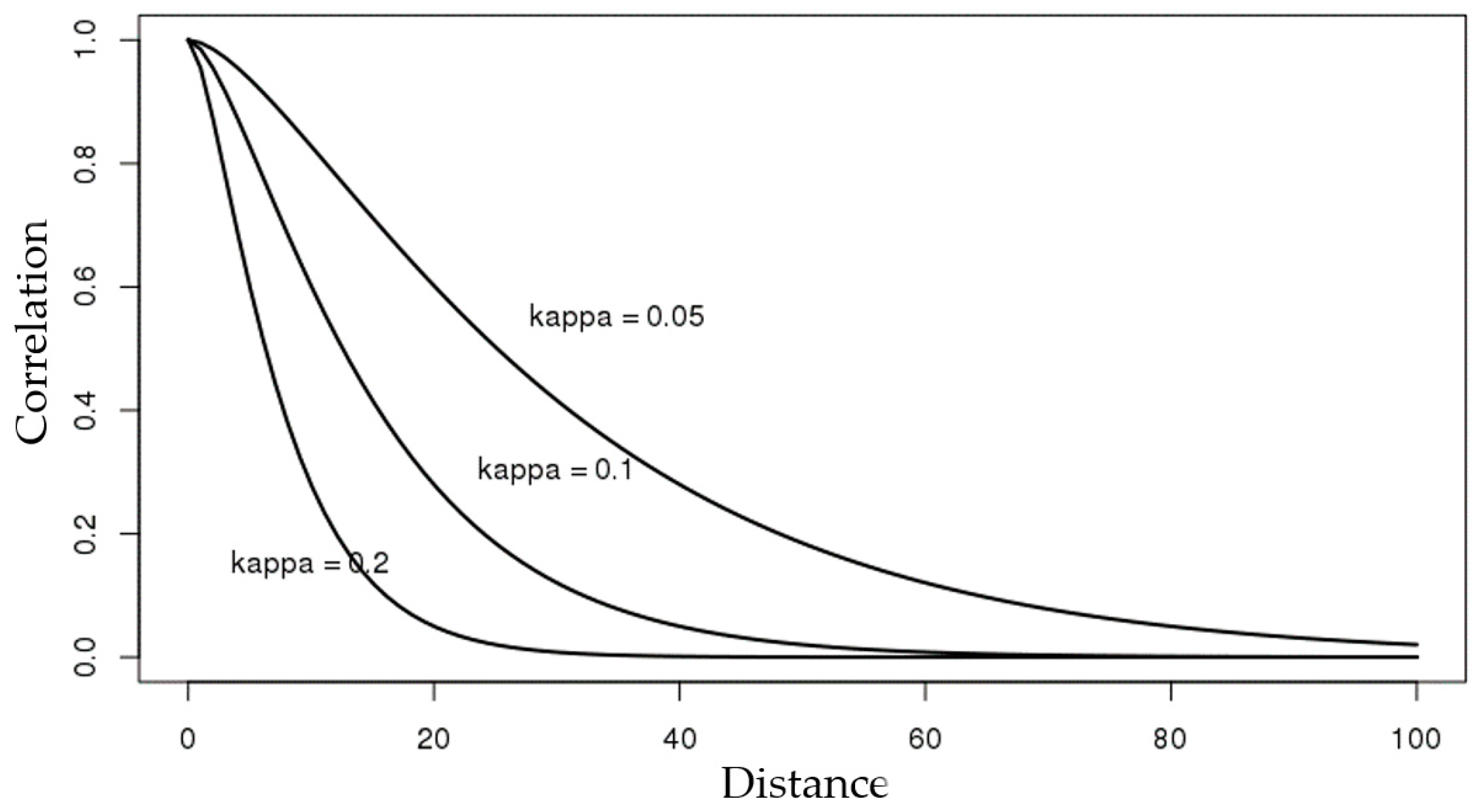
5.1.2. Parameter Analysis
5.2. Point Pattern Data
5.2.1. The Data and Area of Interest Introduction
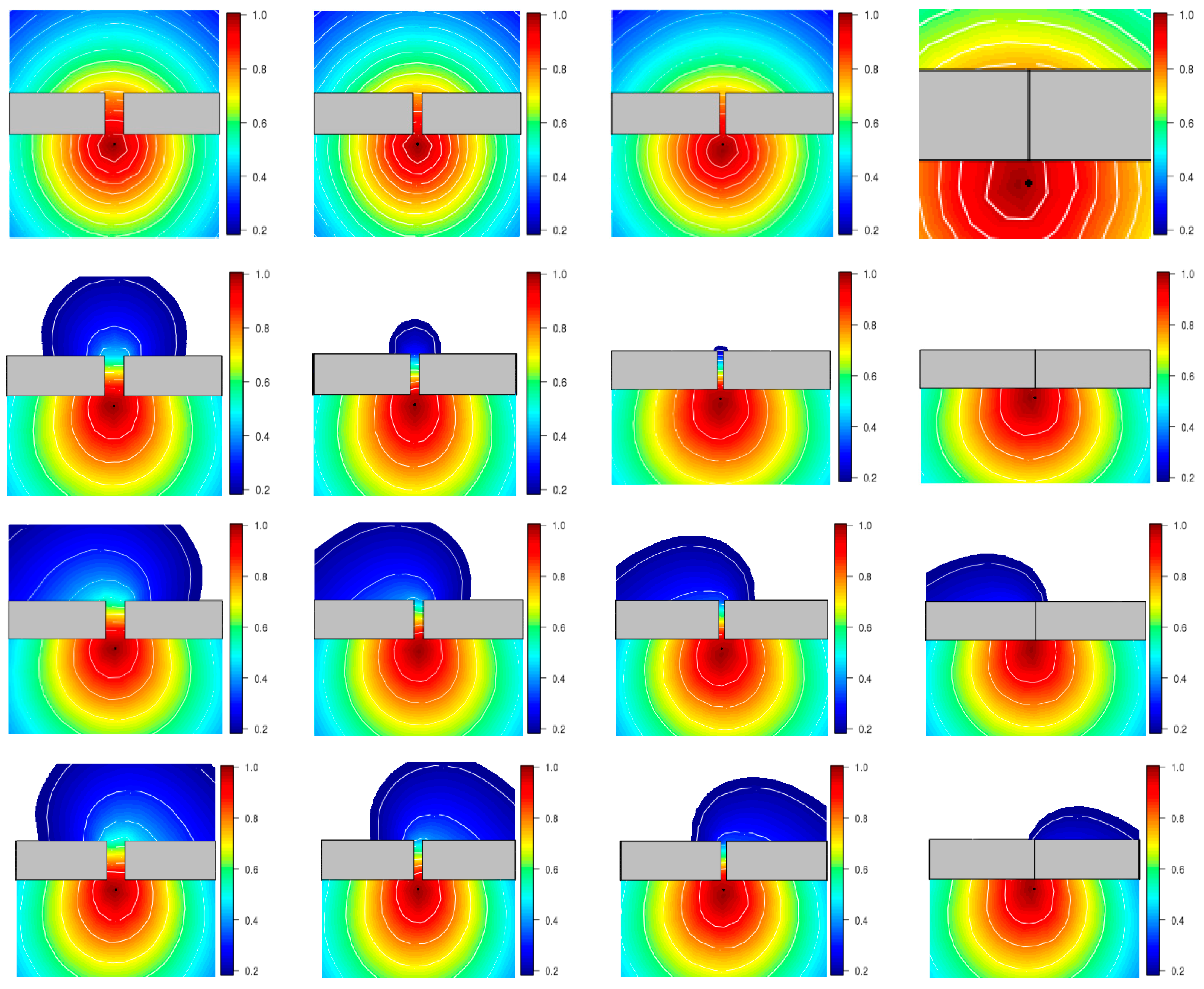
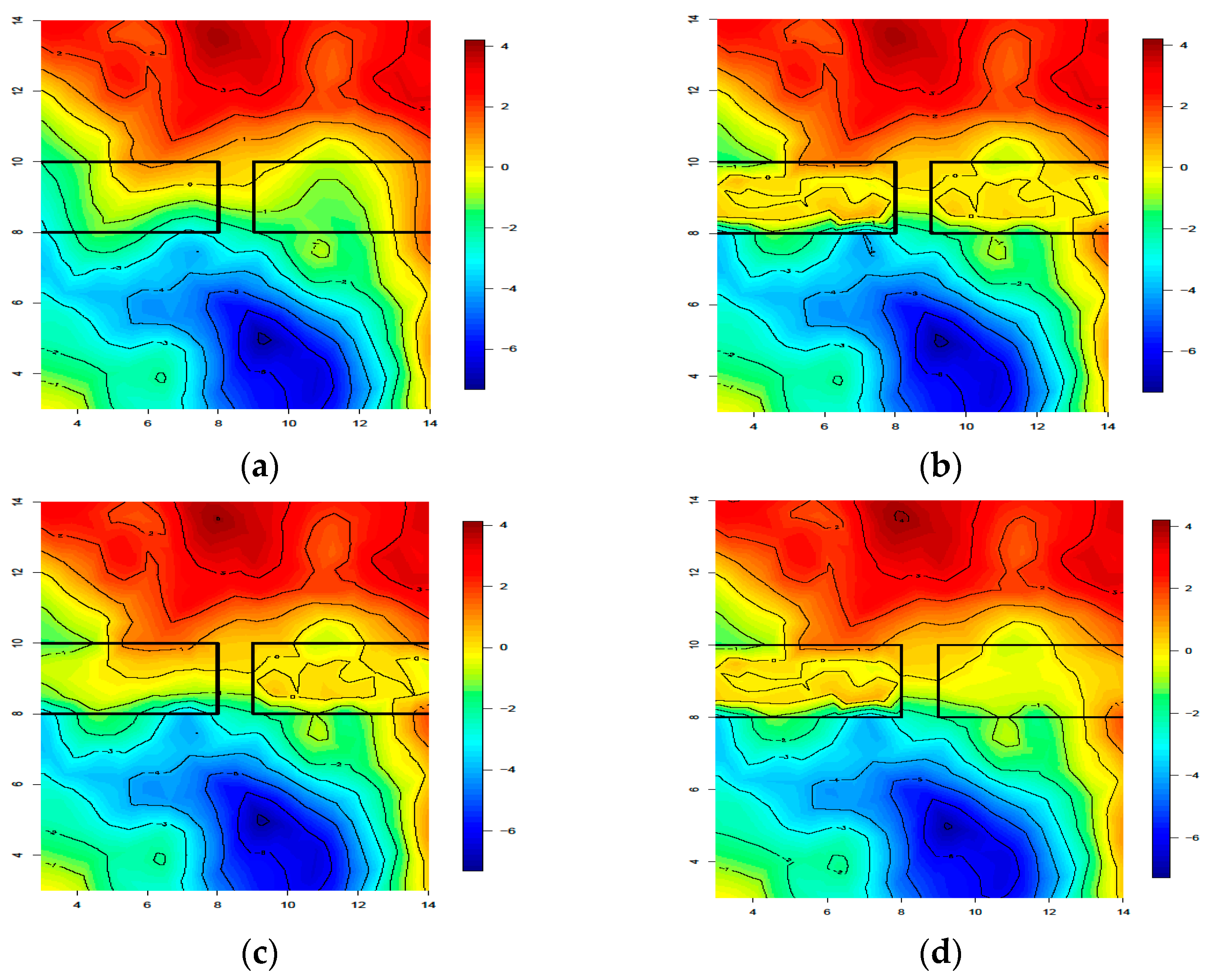
5.2.2. Parameters Analysis
6. Performance Analysis
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soso, B.; Romero, D.; Fernandez, G. Spatial analysis to identify invasion colonization strategies and management priorities in riparian ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 411, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liming, G.; Lele, Z. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Vegetation Coverage in Qinghai Lake Basin. J. Geo.-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Kimpouni, V.; De, N.J.; Massamba-Makanda, C.M. Spatial Analysis of the Woody Flora of the Djoumouna Peri-urban Forest, Brazzaville (Congo). Ecol. Evol. Biol. 2019, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuanjia, L.; Yansheng, G.; Manzhou, L.; Lin, L.; Junjie, D.; Zijian, L.; Wen, T. Spatial analysis, source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in a coal mining area in Henan, Central China. Biodeterior. Soc. 2018, 128, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Beiping, W.; Dian, Y.; Jinfeng, W.; Chengdong, X.; Junming, L.; Zhoupeng, R. Space-time Variability and Determinants of Hand, Foot and Mouth in Shandong Province: A Bayesian Spatio-temporal Modeling Approach. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2016, 18, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, A.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, N.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. VFL: A verifiable federated learning with privacy-preserving for big data in industrial IoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 3316–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri-Ardebili, M.A.; Mahdavi, G.; Abdollahi, A.; Amini, A. An RF-PCE Hybrid Surrogate Model for Sensitivity Analysis of Dams. Water 2021, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liqian, S.; Cong-cong, X.; Rui, L.; Yi, H.; Sui-heng, L.; Cheng-long, X.; Zhijie, Z. Spatial distribution characteristics of global highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 based on the spatial point pattern analysis. Chin. J. Dis. Control. Prev. 2016, 20, 555–558. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaohui, L.; Yongwei, L.; Fei, C.; Wenping, F. Selection Method for Urban Emergency Medical Institutions Considering Spatiotemporal Accessibility. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Xiang, X.; Xiong, N.; Huang, B.; Lee, H.J.; Alrifai, R.; Jiang, X.; Fang, Z. Human action monitoring for healthcare based on deep learning. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 52277–52285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakka, H.; Vanhatalo, J.; Illian, J.B.; Simpson, D.; Rue, H. Non-stationary Gaussian models with physical barriers. Spat. Stat. 2019, 29, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Møller, J.; Syversveen, A.R.; Waagepetersen, R.P. Log gaussian cox processes. Scand. Stat. Theory Appl. 1998, 25, 451–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illian, J.B.; Sørbye, S.H.; Rue, H. A toolbox for fitting complex spatial point process models using integrated nested Laplace approximation (INLA). Ann. Appl. Stat. 2012, 6, 1499–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srbye, S.H.; Illian, J.B.; Simpson, D.P. Careful prior specification avoids incautious inference for log-Gaussian Cox point processes. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 2019, 68, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardo, L.; Opitz, T.; Huser, R. Point process-based modeling of multiple debris flow landslides using INLA: An application to the 2009 Messina disaster. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk Assess 2018, 32, 2179–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, P. On stationary processes in the plane. Biometrika 1954, 41, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, F.; Rue, H.; Lindström, J. An explicit link between Gaussian fields and Gaussian Markov random fields: The stochastic partial differential equation approach. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2011, 73, 423–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rue, H.; Martino, S.; Chopin, N. Approximate Bayesian inference for latent Gaussian models by using integrated nested Laplace approximations. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2009, 71, 319–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Luo, C.; Xiong, N.; Zhang, W.; Kim, T.H. A greedy deep learning method for medical disease analysis. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 20021–20030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Stationary Gaussian Model | Nonstationary Gaussian Model (Barrier Model) | Nonstationary Gaussian Model 1 (Multi-Barriers Model) | Nonstationary Gaussian Model 2 (Multi-Barriers Model) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threshold value 1 () | - | 0.001 | 0.15 | 0.001 |
| Threshold value 2 () | - | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.15 |
| Intercept | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.24 |
| 2.76 | 2.54 | 2.55 | 2.54 | |
| 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | |
| Range | 10.13 | 9.26 | 9.28 | 9.27 |
| Range1 | 10.13 | 0.00926 | 1.392 | 0.00927 |
| Range2 | 10.13 | 0.00926 | 0.00928 | 1.39 |
| DIC | 1054.47 | 1053.09 | 1053.1 | 1053.12 |
| Stationary Gaussian Model | Nonstationary Gaussian Model (Barrier Model) | Nonstationary Gaussian Model (Multi-Barriers Model) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ) | - | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| ) | - | 0.02 | 0.1 |
| Intercept | −0.18 | −2.00 | −1.46 |
| 2.29 | 2.30 | 2.38 | |
| 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.90 | |
| Range (km) | 3.10 | 3.22 | 3.40 |
| Range1 (km) | 3.10 | 0.064 | 0.068 |
| Range2 (km) | 3.10 | 0.064 | 0.34 |
| DIC | −783.18 | −782.91 | −773.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Lin, L.; Dong, J.; Dong, Z. Design and Analysis of an Effective Multi-Barriers Model Based on Non-Stationary Gaussian Random Fields. Electronics 2023, 12, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12020345
Li Z, Liu L, Wang J, Lin L, Dong J, Dong Z. Design and Analysis of an Effective Multi-Barriers Model Based on Non-Stationary Gaussian Random Fields. Electronics. 2023; 12(2):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12020345
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhi, Lei Liu, Jiaqiang Wang, Li Lin, Jichang Dong, and Zhi Dong. 2023. "Design and Analysis of an Effective Multi-Barriers Model Based on Non-Stationary Gaussian Random Fields" Electronics 12, no. 2: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12020345
APA StyleLi, Z., Liu, L., Wang, J., Lin, L., Dong, J., & Dong, Z. (2023). Design and Analysis of an Effective Multi-Barriers Model Based on Non-Stationary Gaussian Random Fields. Electronics, 12(2), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12020345






