Collaborative Mixture-of-Experts Model for Multi-Domain Fake News Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel multi-domain fake-news detection framework; in particular, a mixture-of-experts model-based network based on a pre-trained representation embedding module and a collaborative module for fake-news detection.
- We propose a collaborative module that can adaptively determine the weights of the expert models to enhance or suppress their contributions to the mixture-of-experts model. This module is theoretically compatible with most mixture-of-experts models and multimodal learning methods.
- We conduct extensive experiments on the Weibo21 dataset, and the results indicate that our model framework can achieve significant improvements over the considered baseline methods.
2. Related Work
2.1. Fake-News Detection
2.2. Mixture-of-Experts Model
2.3. CLIP
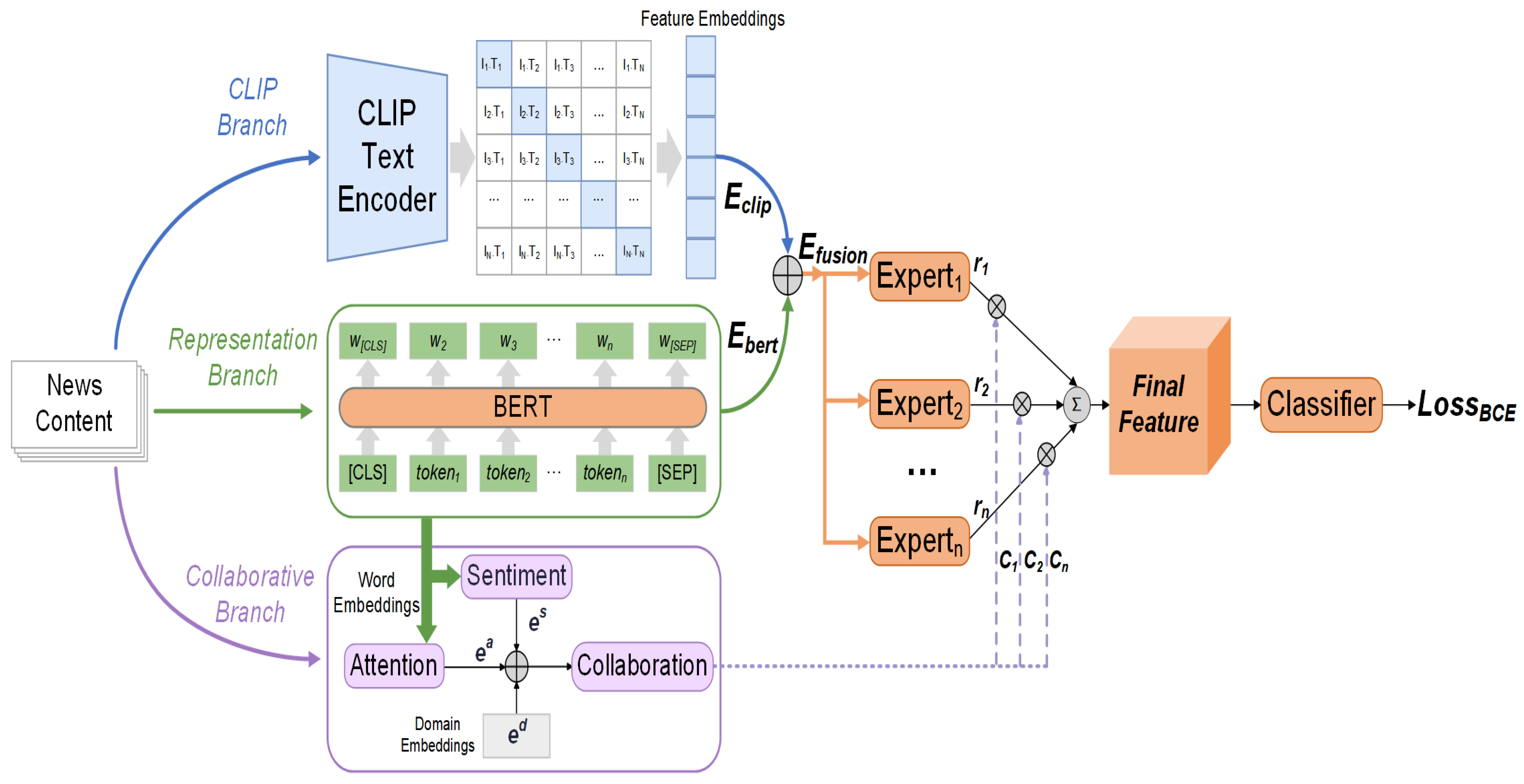
3. Approach
3.1. Content Embedding
3.2. Collaborative Branch
3.3. Mixture-of-Experts Model
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Experimental Details
4.3. Performance Comparison
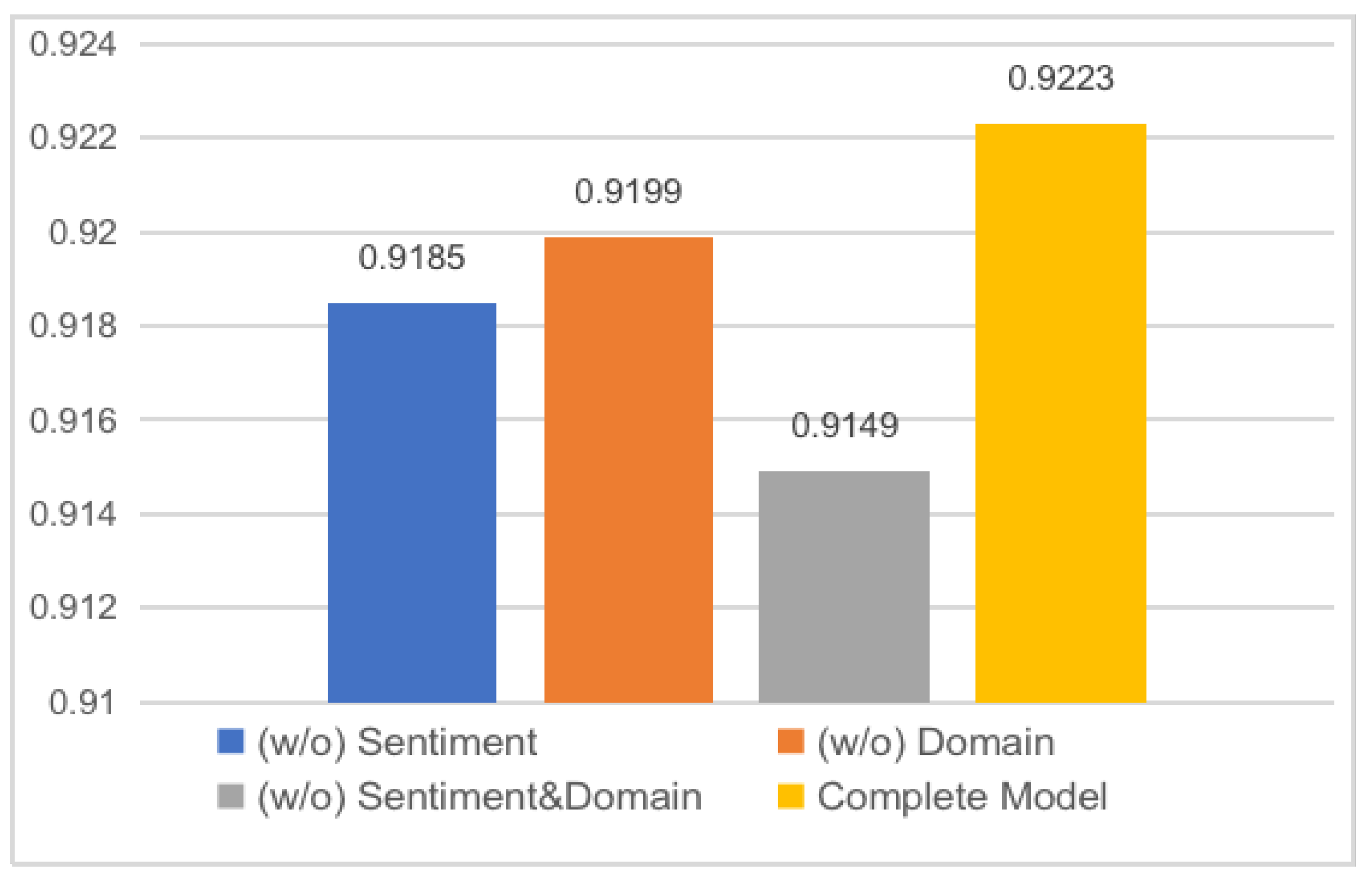
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Discussion and Future Work
- Improving the quality of original data: The accuracy of subsequent detection and analysis tasks depends on the quality of the original data. However, most original data suffers from issues such as incompleteness, sparsity, and imbalance. Therefore, one of the key challenges in future research will be to address the imbalance and poor integrity of the original data.
- Increasing the diversity of multimodal data: Social multimedia data types include various forms of media, such as social links and location information. The diversity of multimodal data can be increased further by leveraging social media attribute information such as labels, location, and time. Therefore, how to mine more external knowledge should be explored in future research.
- Integrating information from multiple platforms: Existing research has focused on a single social network, such as only using Weibo posts for fake-news detection without incorporating information provided by WeChat users. As information missing from one platform may be available on others, a thorough synthesis of information from multiple social networks can provide more comprehensive real-world social data. Therefore, the next stage could focus on cross-platform information fusion approaches, such as transfer learning, which can transfer knowledge from one social platform to another.
- Addressing redundancy and noise in social media data: The growth rate of computer hardware cannot keep pace with the increasing demand for multimedia data. The redundancy of large-scale and ultra-large-scale social media data cannot be ignored while utilizing large-scale multimedia data. To improve data quality while reducing computational efforts, a well-designed data filtering technique may be used.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takayasu, M.; Sato, K.; Sano, Y.; Yamada, K.; Miura, W.; Takayasu, H. Rumor diffusion and convergence during the 3.11 earthquake: A Twitter case study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Lamba, H.; Kumaraguru, P.; Joshi, A. Faking sandy: Characterizing and identifying fake images on twitter during hurricane sandy. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 13–17 May 2013; pp. 729–736. [Google Scholar]
- Pennycook, G.; Epstein, Z.; Mosleh, M.; Arechar, A.A.; Eckles, D.; Rand, D.G. Shifting attention to accuracy can reduce misinformation online. Nature 2021, 592, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, C.; Mendoza, M.; Poblete, B. Information credibility on twitter. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on World Wide Web, Hyderabad, India, 28 March–1 April 2011; pp. 675–684. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Cao, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J. Detection and analysis of 2016 us presidential election related rumors on twitter. In Proceedings of the Social, Cultural, and Behavioral Modeling: 10th International Conference, SBP-BRiMS 2017, Washington, DC, USA, 5–8 July 2017; Proceedings 10. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.; Cha, M.; Jung, K.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y. Prominent features of rumor propagation in online social media. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Data Mining, Dallas, TX, USA, 7–10 December 2013; pp. 1103–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Lin, D.; Cao, D. Content representation for microblog rumor detection. In Proceedings of the Advances in Computational Intelligence Systems: Contributions Presented at the 16th UK Workshop on Computational Intelligence, Lancaster, UK, 7–9 September 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Mitra, P.; Kwon, S.; Jansen, B.J.; Wong, K.F.; Cha, M. Detecting rumors from microblogs with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2016), New York, NY, USA, 6–8 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zafarani, R. Fake news: A survey of research, detection methods, and opportunities. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.00315. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, K.; Sliva, A.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Fake news detection on social media: A data mining perspective. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2017, 19, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubiaga, A.; Aker, A.; Bontcheva, K.; Liakata, M.; Procter, R. Detection and resolution of rumours in social media: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2018, 51, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, P.; Sui, J.; Lv, Q.; Tun, L.; Shang, L. Cross-modal Ambiguity Learning for Multimodal Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, Lyon, France, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khattar, D.; Goud, J.S.; Gupta, M.; Varma, V. MVAE: Multimodal Variational Autoencoder for Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, F.; Jin, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Xun, G.; Jha, K.; Su, L.; Gao, J. Eann: Event adversarial neural networks for multi-modal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 849–857. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, P.; Cao, J.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Sheng, Q.; Mi, X.; He, Q.; Lv, Y.; Guo, C.; Yu, Y. Improving Fake News Detection by Using an Entity-enhanced Framework to Fuse Diverse Multimodal Clues. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual Event, 20–24 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Li, X.; Sheng, Q.; Zhong, L.; Shu, K. Mining dual emotion for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 12–23 April 2021; pp. 3465–3476. [Google Scholar]
- Davoudi, M.; Moosavi, M.R.; Sadreddini, M.H. DSS: A hybrid deep model for fake news detection using propagation tree and stance network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 198, 116635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Kumar Sharma, D. Linguistic features based framework for automatic fake news detection. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 172, 108432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvembe, A.M.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Xu, G. Dual emotion based fake news detection: A deep attention-weight update approach. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M. Fake news detection via knowledgeable prompt learning. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 103029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Luo, L.; Karunasekera, S.; Leckie, C. Embracing domain differences in fake news: Cross-domain fake news detection using multi-modal data. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtually, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 557–565. [Google Scholar]
- Kenton, J.D.M.W.C.; Toutanova, L.K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J. Rumor detection with hierarchical social attention network. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Torino, Italy, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 943–951. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Convolutional Neural Network for Sentence Classification. Master’s Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yi, X.; Chen, J.; Hong, L.; Chi, E.H. Modeling task relationships in multi-task learning with multi-gate mixture-of-experts. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 1930–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Metzler, D.; Qin, J. Multitask mixture of sequential experts for user activity streams. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Virtual, 6–10 July 2020; pp. 3083–3091. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, Q.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. MDFEND: Multi-domain fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Gold Coast, Australia, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 3343–3347. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Yang, S.; Zhu, K.Q. False rumors detection on sina weibo by propagation structures. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 31st International Conference on Data Engineering, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 13–17 April 2015; pp. 651–662. [Google Scholar]
- Ajao, O.; Bhowmik, D.; Zargari, S. Sentiment aware fake news detection on online social networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 2507–2511. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, B.; He, L.; Bai, Y.; Qiu, X. Features of rumor spreading on wechat moments. In Proceedings of the Web Technologies and Applications: APWeb 2016 Workshops, WDMA, GAP, and SDMA, Suzhou, China, 23–25 September 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Wei, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wong, K.F. Detect rumors using time series of social context information on microblogging websites. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Melbourne, Australia, 18–23 October 2015; pp. 1751–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, E.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S. Ginger cannot cure cancer: Battling fake health news with a comprehensive data repository. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Atlanta, GA, USA, 8 June 2020; Volume 14, pp. 853–862. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. A Convolutional Approach for Misinformation Identification. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017; pp. 3901–3907. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Xu, R.; He, Y.; Wang, X. Improving sentiment analysis via sentence type classification using BiLSTM-CRF and CNN. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 72, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.P.; Kumar, A.; Rana, N.P.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Attention-based LSTM network for rumor veracity estimation of tweets. Inf. Syst. Front. 2022, 24, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Bahdanau, D.; Bengio, Y. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1259. [Google Scholar]
- Qazvinian, V.; Rosengren, E.; Radev, D.; Mei, Q. Rumor has it: Identifying misinformation in microblogs. In Proceedings of the 2011 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Edinburgh, UK, 27–31 July 2011; pp. 1589–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.R.; Counts, S.; Roseway, A.; Hoff, A.; Schwarz, J. Tweeting is believing? Understanding microblog credibility perceptions. In Proceedings of the ACM 2012 Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 February 2012; pp. 441–450. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, Y. A credibility assessment for message streams on microblogs. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on P2P, Parallel, Grid, Cloud and Internet Computing, Fukuoka, Japan, 4–6 November 2010; pp. 527–530. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.M.; Sobhani, P.; Kiritchenko, S. Stance and sentiment in tweets. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. (TOIT) 2017, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; He, W.; Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Zeng, J. Rumor identification in microblogging systems based on users’ behavior. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2015, 2, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Shu, K.; Wang, S.; Gu, R.; Wu, F.; Liu, H. Unsupervised fake news detection on social media: A generative approach. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 5644–5651. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Chen, F. Credibility evaluating method of Chinese microblog based on information fusion. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 36, 2071. [Google Scholar]
- Bazmi, P.; Asadpour, M.; Shakery, A. Multi-view co-attention network for fake news detection by modeling topic-specific user and news source credibility. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Chen, Z.; Yin, Z.Z.J.; Nie, L. Causal Inference for Leveraging Image-text Matching Bias in Multi-modal Fake News Detection. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Zhang, G.; Batra, V.; Xi, L.; Shi, L.; Liu, L. TRIMOON: Two-Round Inconsistency-based Multi-modal fusion Network for fake news detection. Inf. Fusion 2023, 93, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Si, L. Rumor detection by exploiting user credibility information, attention and multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 1173–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Wong, K.F. Detect rumor and stance jointly by neural multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the Companion Proceedings of the the Web Conference 2018, Lyon, France, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 585–593. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Cao, J.; Li, S.; Wang, D.; Zhuang, F. Generalizing to the Future: Mitigating Entity Bias in Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR ’22), New York, NY, USA, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 2120–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Du, B.; Sun, L.; Zhuang, F.; Lv, W.; Xiong, H. Multiple relational attention network for multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 1123–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, R.; Zhuang, F.; Hao, X.; Ge, K.; Zhang, X.; Lin, L.; Cao, J. Learning to expand audience via meta hybrid experts and critics for recommendation and advertising. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Singapore, 14–18 August 2021; pp. 4005–4013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhuang, F.; Wang, D. Aligning domain-specific distribution and classifier for cross-domain classification from multiple sources. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 5989–5996. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M. weibo_senti_100k and THUCNews 2022. Available online: https://ieee-dataport.org/documents/weibosenti100k-and-thucnews (accessed on 2 August 2022).
- Sina Weibo. Available online: http://www.weibo.com (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Newsverify. Available online: https://www.newsverify.com/ (accessed on 23 April 2022).
- WeiboService. Available online: http://service.account.weibo.com/ (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Vosoughi, S.; Roy, D.K.; Aral, S. The spread of true and false news online. Science 2018, 359, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachims, T. Text categorization with support vector machines: Learning with many relevant features. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning: ECML-98: 10th European Conference on Machine Learning, Chemnitz, Germany, 21–23 April 1998; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2–4 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.; Mikolov, T. Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning PMLR, Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014; pp. 1188–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, G. Google Translate http://translate.google.com. Tech. Serv. Q. 2012, 29, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 5485–5551. [Google Scholar]

| Domain | Science | Military | Education | Accidents | Politics | Health | Finance | Entertainment | Society | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real | 143 | 121 | 243 | 185 | 306 | 485 | 959 | 1000 | 1198 | 4640 |
| Fake | 93 | 222 | 248 | 591 | 546 | 515 | 362 | 440 | 1471 | 4488 |
| All | 236 | 343 | 491 | 776 | 852 | 1000 | 1321 | 1440 | 2669 | 9128 |
| Content | Domain | Fake Label |
|---|---|---|
| 【熊猫宝宝地震了也会找警察】雅安是大熊猫栖息地…警察叔叔的腿。 | Accidents | 0 |
| 今晚有三首歌是张杰以前唱过的,不同的声音…回味一下杰哥的版本吧。 | Entertainment | 0 |
| 宝宝夏天不能吹空调,吹了就会得空调病? | Health | 1 |
| 在过去,要修建一座堡垒,需要花费好几个月…里面的设施应有尽有。 | Military | 1 |
| 每天早上6点20,武昌工学院某群便炸开…发红包方式叫学生起床。 | Education | 0 |
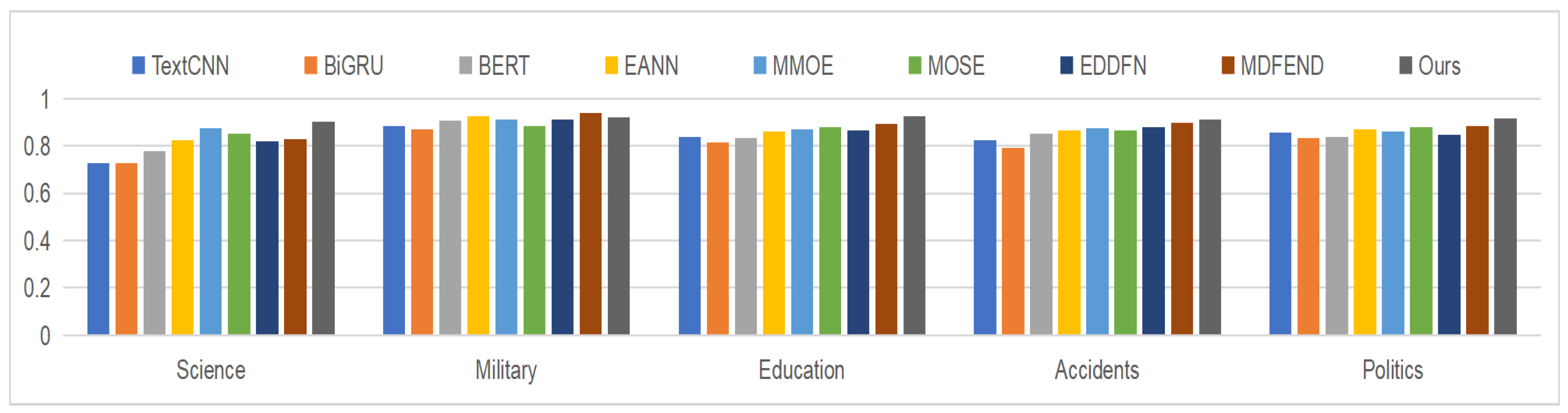
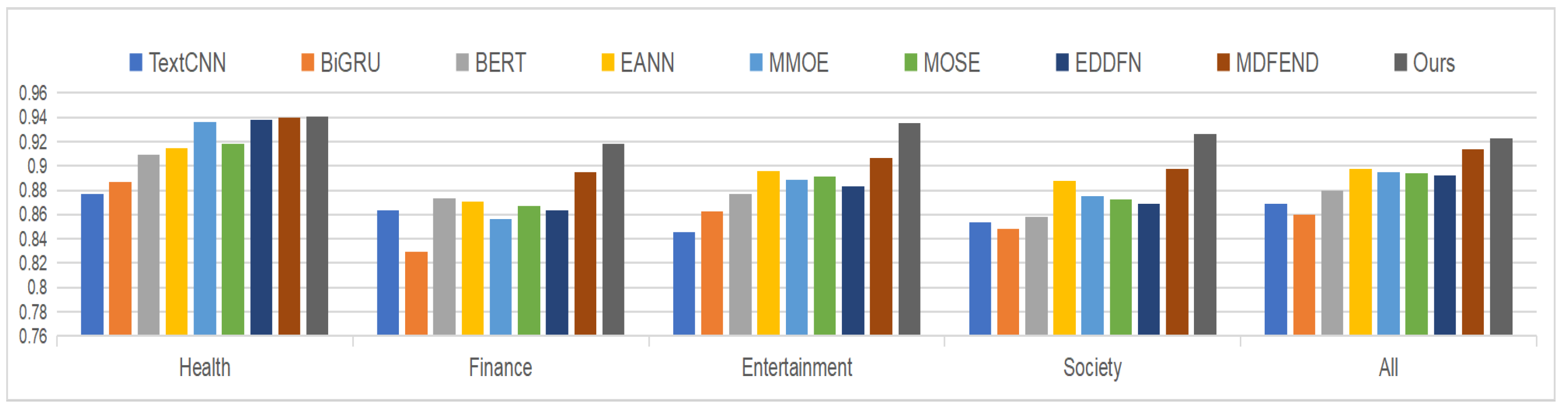
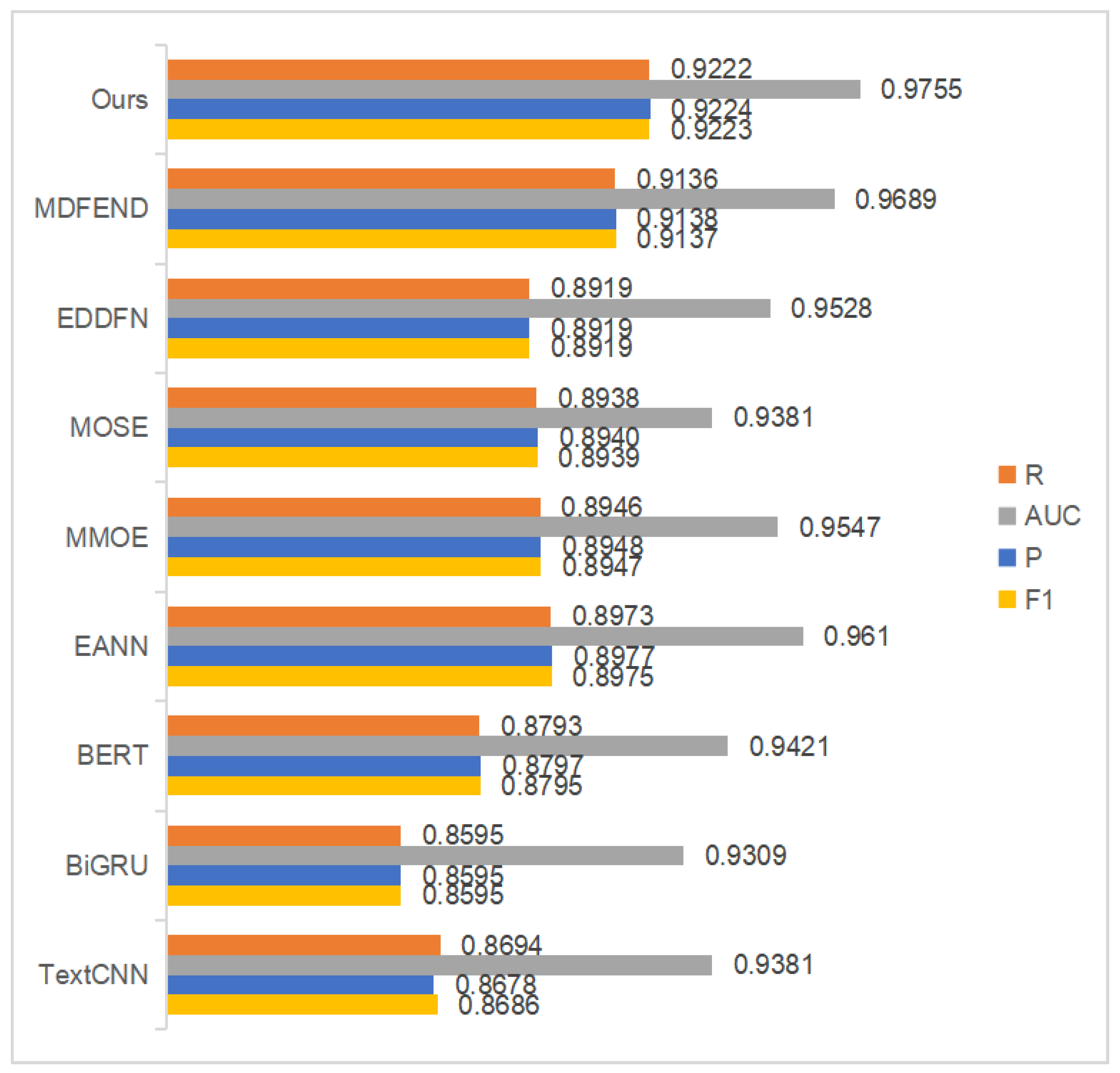
| Model | Science | Military | Education | Accidents | Politics | Health | Finance | Entertainment | Society | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TextCNN | 0.7254 | 0.8839 | 0.8362 | 0.8222 | 0.8561 | 0.8768 | 0.8638 | 0.8456 | 0.8540 | 0.8686 |
| BiGRU | 0.7269 | 0.8724 | 0.8138 | 0.7935 | 0.8356 | 0.8868 | 0.8291 | 0.8629 | 0.8485 | 0.8595 |
| BERT | 0.7777 | 0.9072 | 0.8331 | 0.8512 | 0.8366 | 0.9090 | 0.8735 | 0.8769 | 0.8577 | 0.8795 |
| EANN | 0.8225 | 0.9274 | 0.8624 | 0.8666 | 0.8705 | 0.9150 | 0.8710 | 0.8957 | 0.8877 | 0.8975 |
| MMOE | 0.8755 | 0.9112 | 0.8706 | 0.877 | 0.8620 | 0.9364 | 0.8567 | 0.8886 | 0.8750 | 0.8947 |
| MOSE | 0.8502 | 0.8858 | 0.8815 | 0.8672 | 0.8808 | 0.9179 | 0.8672 | 0.8913 | 0.8729 | 0.8939 |
| EDDFN | 0.8186 | 0.9137 | 0.8676 | 0.8786 | 0.8478 | 0.9379 | 0.8636 | 0.8832 | 0.8689 | 0.8919 |
| MDFEND | 0.8301 | 0.9389 | 0.8917 | 0.9003 | 0.8865 | 0.9400 | 0.8951 | 0.9066 | 0.8980 | 0.9137 |
| Ours | 0.9049 | 0.9204 | 0.9263 | 0.9109 | 0.9169 | 0.9407 | 0.9184 | 0.9353 | 0.9266 | 0.9223 |
| Model | Science | Military | Education | Accidents | Politics | Health | Finance | Entertainment | Society | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (w/o) CLIP | 0.8649 | 0.9015 | 0.9183 | 0.8879 | 0.9166 | 0.9247 | 0.9226 | 0.9110 | 0.9216 | 0.9077 |
| (w/o) Collaborative | 0.9032 | 0.9134 | 0.9435 | 0.8984 | 0.9167 | 0.9233 | 0.8870 | 0.9054 | 0.9264 | 0.9130 |
| (w/o) CLIP & Collaborative | 0.8365 | 0.9051 | 0.9181 | 0.8882 | 0.8935 | 0.9215 | 0.8967 | 0.9113 | 0.9074 | 0.8976 |
| Complete Model | 0.9049 | 0.9204 | 0.9263 | 0.9109 | 0.9169 | 0.9407 | 0.9184 | 0.9353 | 0.9266 | 0.9223 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, L.; Kuang, Z.; Liu, Y. Collaborative Mixture-of-Experts Model for Multi-Domain Fake News Detection. Electronics 2023, 12, 3440. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163440
Zhao J, Zhao Z, Shi L, Kuang Z, Liu Y. Collaborative Mixture-of-Experts Model for Multi-Domain Fake News Detection. Electronics. 2023; 12(16):3440. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163440
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jian, Zisong Zhao, Lijuan Shi, Zhejun Kuang, and Yazhou Liu. 2023. "Collaborative Mixture-of-Experts Model for Multi-Domain Fake News Detection" Electronics 12, no. 16: 3440. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163440
APA StyleZhao, J., Zhao, Z., Shi, L., Kuang, Z., & Liu, Y. (2023). Collaborative Mixture-of-Experts Model for Multi-Domain Fake News Detection. Electronics, 12(16), 3440. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12163440











